Topographic evolution and driving factors of the Chongming Eastern Beach and its adjacent areas in the Changjiang River Estuary
-
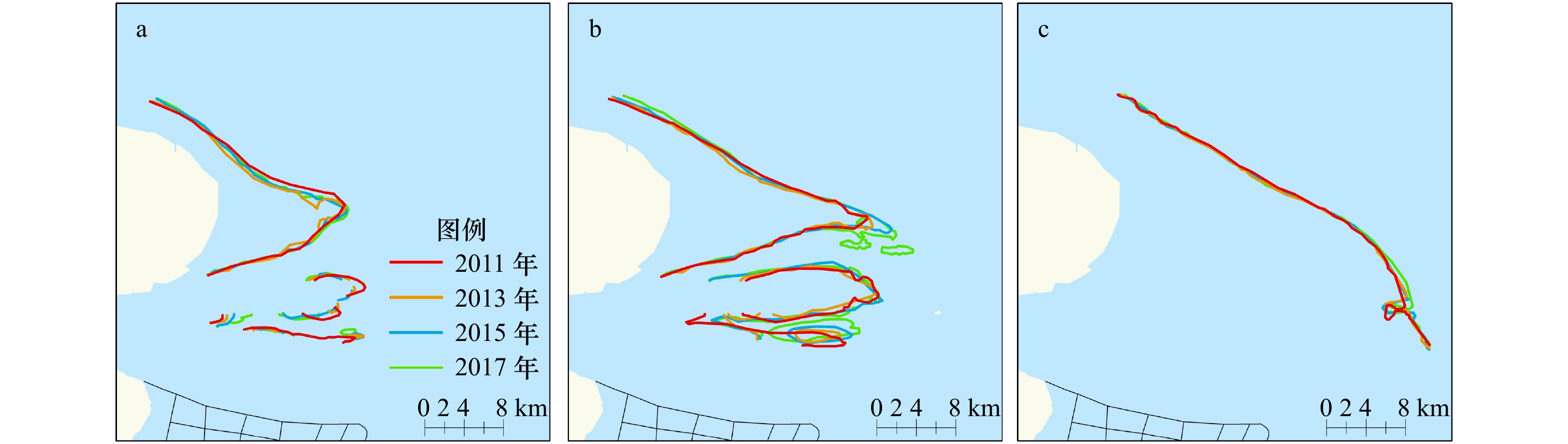
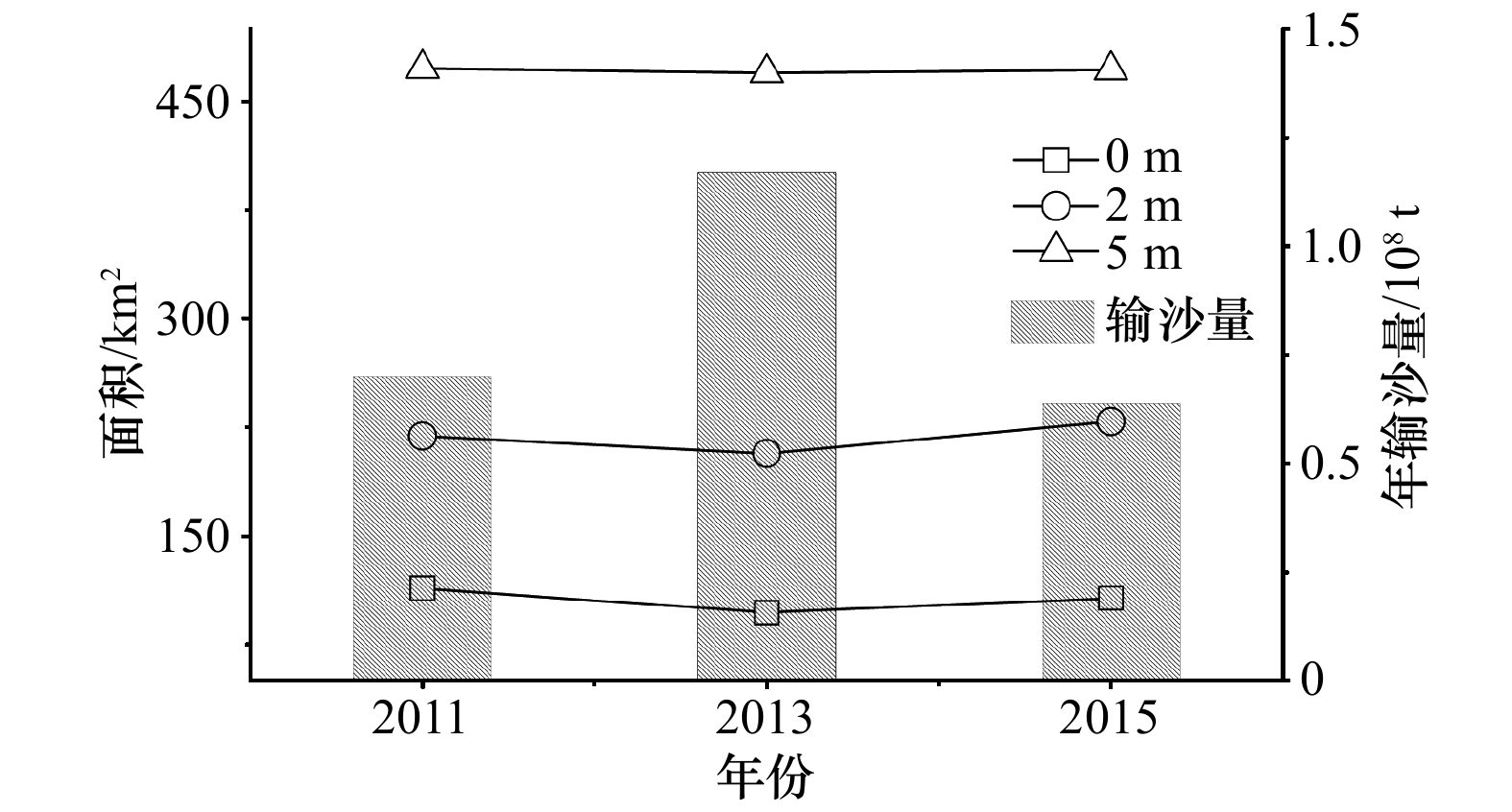
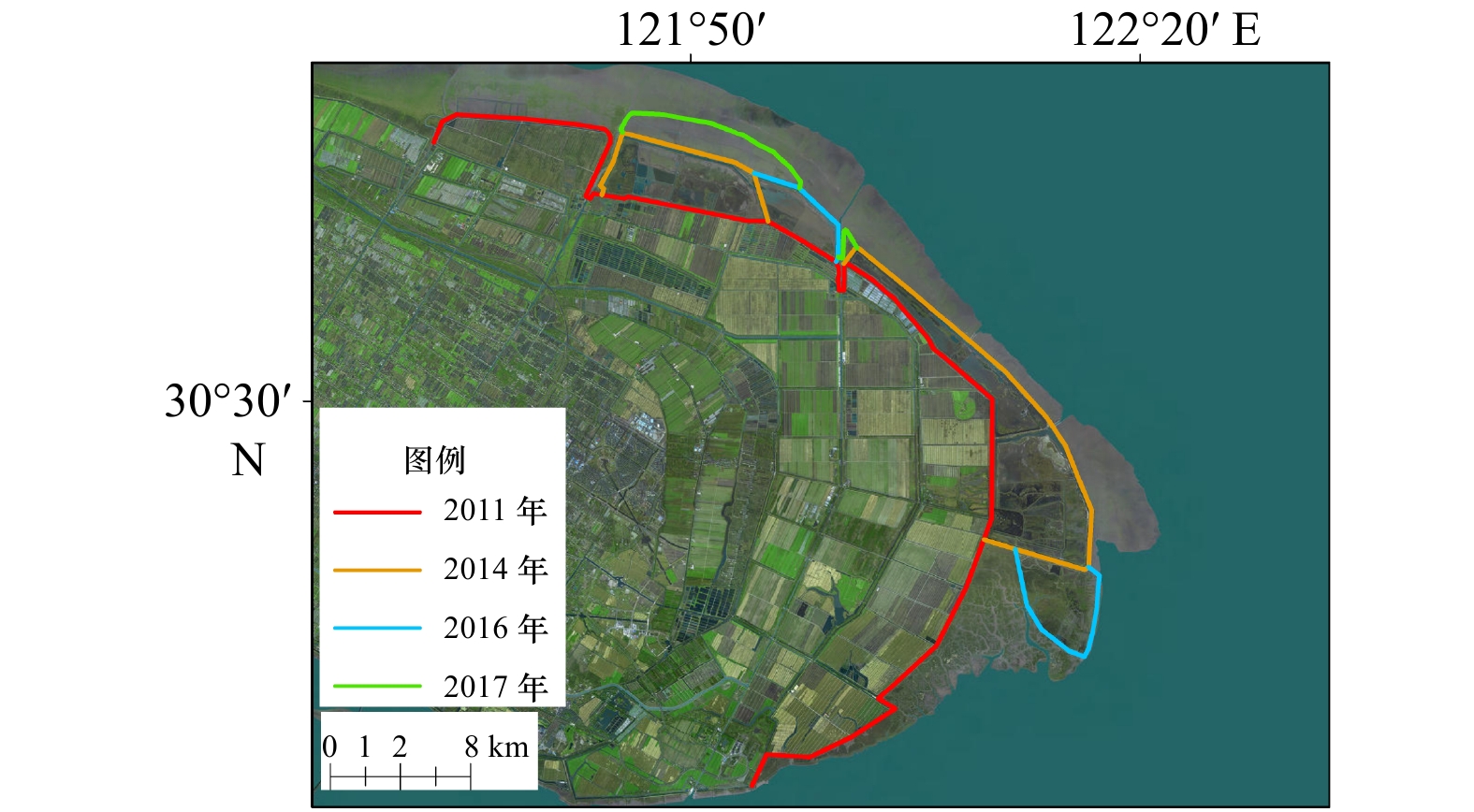
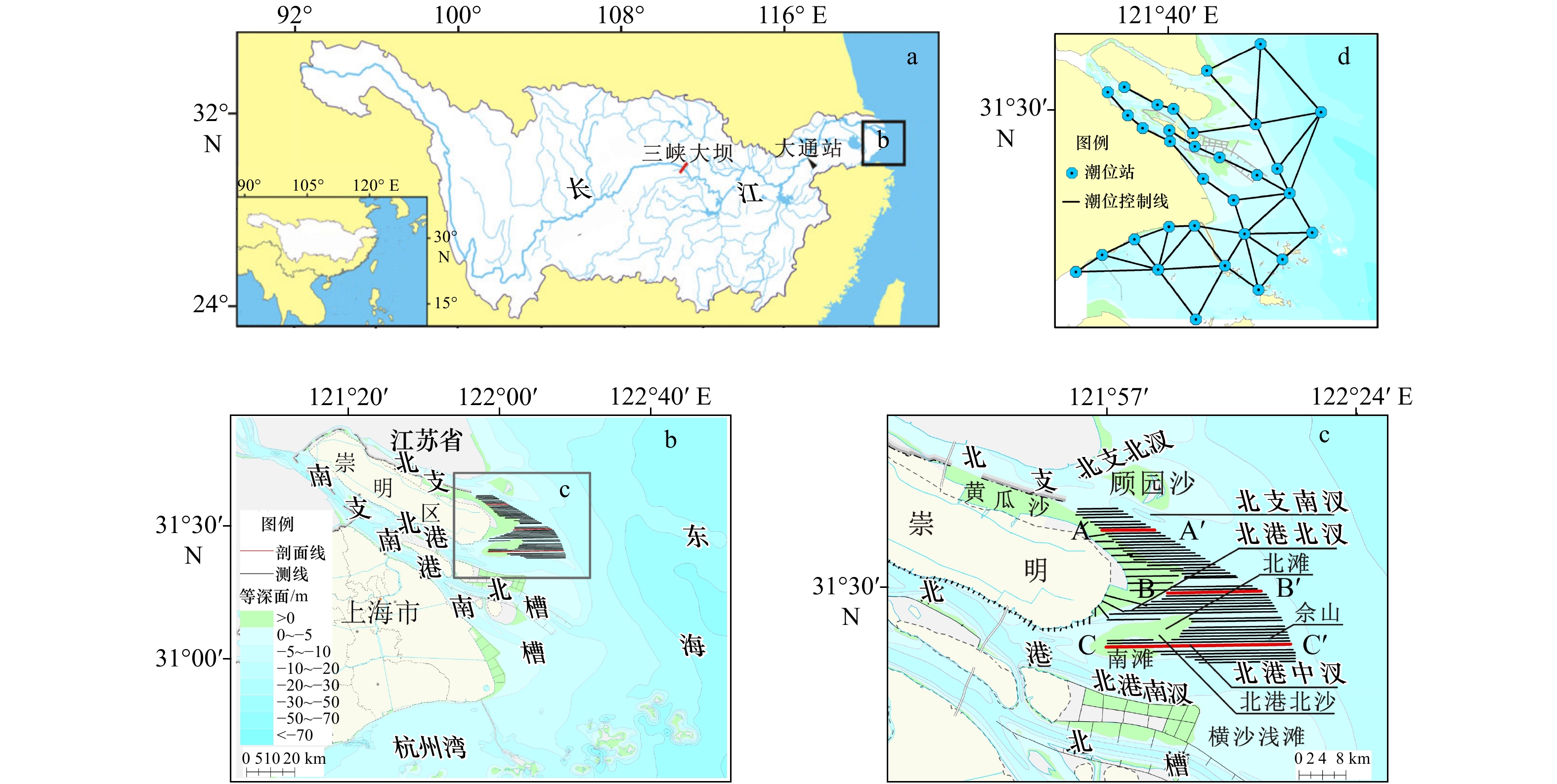
摘要: 河口大型滩涂演化关系到航运通畅、生态保护以及近岸工程的安全性,是地貌学和工程界关注的热点。利用单波束测深系统对长江口崇明东滩进行高精度监测,并结合近年来周围环境因素分析其冲淤格局。结果表明:(1) 2011−2017年间崇明东滩和北港北沙基本以淤积为主,北港北汊河槽中央局部形成−2 m心滩,−5 m等深线包络面积基本稳定,整体呈“长高不长大”的格局;(2)海洋来沙是其淤积的主要物源,汊道涨落潮时空分异而形成的两大环流是塑造此地形的主要原因;崇明东滩和北港北沙的淤积直接挤压北港北汊的发展,沙体淤积可能会引起未来两大沙体的并靠;(3)崇明东滩、北支南沿的滩涂整治工程是促进北支萎缩和崇明东滩淤积的重要因素,另外横沙通道落潮分流增加,青草沙围水工程改变了北港河槽的曲率,也有利于北港北沙的淤积。Abstract: The evolution of large tidal flat in estuaries is related to smooth navigation, ecological protection and safety of offshore engineering. It is also a hot topic in geomorphology and engineering. A single beam bathymetric system was used to monitor the Chongming Eastern Beach in the Changjiang River Estuary. The scouring and silting pattern was analyzed based on the environmental factors in recent years. The results are as follows: (1) Chongming Eastern Beach and the north inlet of the North Channel are mainly deposited in 2011−2017 years, and the northern sand terrain of the North Channel is greater than that of the Chongming Eastern Beach, and the central part of the North Branch of the North Channel is −2 m deep in the central area, which is a silt up situation, and the envelope area of the −5 m contour in the study area is basically stable, and the whole pattern is "long height and no growth". (2) Marine sediment is the main source of silting, and the main circulation of the two large circulation formed by the time and space of the rising and falling of the three branches in the study area is the main reason. (3) The reclamation project in the south of the Chongming Eastern Beach and the North Branch is the main factor causing the North Branch atrophy and the silt of the Chongming Eastern Beach, and the ebb tidal diversion of the cross sand channel. As a result, the curvature of the North Channel is a key factor leading to the deposition of North Sand in the North Channel. The siltation of the two beaches directly squeezed the development of the North Branch of the North Channel, which was the main cause of its transition from the tidal trough to the ebb trough, and the siltation situation in the North Branch of the North Channel may cause the next two large sand bodies.
-
Key words:
- Chongming Eastern Beach /
- branch /
- reclamation /
- erosion and deposition
-
表 1 北港北汊道断面参数
Tab. 1 Cross-sectional parameters of North Branch of North Harbour
时间 位置 U/m·s−1 f/s−1 B/m 平均水深/m 最大水深/m β Sc 宽深比 Keh 2011年 断面b 1.06 7.56×10−5 2 724.33 3.64 4.67 7.7×10−4 8 14.34 0.99 断面c 0.88 7.56×10−5 4 368.86 2.47 2.78 7.7×10−4 8 26.76 1.95 2013年 断面b 1.17 7.56×10−5 2 335.37 3.78 4.73 7.7×10−4 8 12.78 0.91 断面c 0.82 7.56×10−5 4 518.74 2.47 2.73 7.7×10−4 8 27.22 1.88 2015年 断面b 1.13 7.56×10−5 2 251.97 4.18 5.06 7.7×10−4 8 11.35 0.76 断面c 1.01 7.56×10−5 3 741.73 2.29 2.48 7.7×10−4 8 26.71 2.07 2017年 断面b 1.15 7.56×10−5 2 167.11 3.81 5.41 7.7×10−4 8 12.22 0.82 断面c 1.08 7.56×10−5 3 885.163 2.32 2.58 7.7×10−4 8 26.87 2.26 -
[1] Williams T P, Bubb J M, Lester J N. Metal accumulation within salt marsh environments: a review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1994, 28(5): 277−290. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)90152-X [2] Grosholz E. Ecological and evolutionary consequences of coastal invasions[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2002, 17(1): 22−27. [3] 欧维新, 杨桂山, 李恒鹏, 等. 苏北盐城海岸带景观格局时空变化及驱动力分析[J]. 地理科学, 2004, 24(5): 610−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.05.016Ou Weixin, Yang Guishan, Li Hengpeng, et al. Spatio-temporal variation and driving forces of landscape patterns in the coastal zone of Yancheng, Jiangsu[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2004, 24(5): 610−615. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.05.016 [4] 汪亚平, 潘少明, Wang H V, et al. 长江口水沙入海通量的观测与分析[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(1): 35−46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.01.004Wang Yaping, Pan Shaoming, Wang H V, et al. Measurements and analysis of water discharges and suspended sediment fluxes in Changjiang estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(1): 35−46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.01.004 [5] 刘红, 何青, 王元叶, 等. 长江口表层沉积物粒度时空分布特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2007, 25(3): 445−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.017Liu Hong, He Qing, Wang Yuanye, et al. Temporal and spatial characteristics of surface sediment grain-size distribution in Changjiang estuary[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25(3): 445−455. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2007.03.017 [6] Yang S L, Milliman J D, Xu K H, et al. Downstream sedimentary and geomorphic impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 138: 469−486. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.07.006 [7] Dai Zhijun, Liu J T, Wei Wen, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 4: 6600. doi: 10.1038/srep06600 [8] 蒋杰, 何青, 朱磊, 等. 长江口浑浊带核心区北槽水动力特征研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(1): 11−20.Jiang Jie, He Qing, Zhu Lei, et al. Analysis of hydrodynamic features of the North Passage in the turbidity maximum, Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(1): 11−20. [9] 黎兵, 严学新, 何中发, 等. 长江口水下地形演变对三峡水库蓄水的响应[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(18): 1735−1744. doi: 10.1360/N972014-01074Li Bing, Yan Xuexin, He Zhongfa, et al. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on the bathymetric evolution of the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(18): 1735−1744. doi: 10.1360/N972014-01074 [10] 陈勇, 王寒梅, 史玉金, 等. 1958–2015年长江口水下三角洲地形演变特征及趋势[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(3): 314−321.Chen Yong, Wang Hanmei, Shi Yujin, et al. Characteristics and trends of morphological evolution of the Yangtze subaqueous delta during 1958–2015[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(3): 314−321. [11] 陈勇, 何中发, 黎兵, 等. 长江河口拦门沙河段滩涂演化特征及驱动机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(9): 95−105.Chen Yong, He Zhongfa, Li Bing, et al. Evolution of tidal flat in the bar area of the Yangtze Estuary and their driving factors[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(9): 95−105. [12] 茅志昌, 虞志英, 徐海根. 上海潮滩研究[M]. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 2014.Mao Zhichang, Yu Zhiying, Xu Haigen. Study of Tidal Flats in Shanghai[M]. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press, 2014. [13] 郭兴杰, 王寒梅, 史玉金, 等. 近年来横沙东滩围垦区前沿地形演化规律及驱动因素分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(11): 142−149.Guo Xingjie, Wang Hanmei, Shi Yujin, et al. Analysis of the evolution process and the driving factors in the coast of the reclamation area of East Hengsha shoal during recent years[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(11): 142−149. [14] 路兵, 蒋雪中. 滩涂围垦对崇明东滩演化影响的遥感研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2013, 17(2): 342−349.Lu Bing, Jiang Xuezhong. Reclamation impacts on the evolution of the tidal flat at Chongming Eastern Beach in Changjiang estuary[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 17(2): 342−349. [15] 郑宗生, 周云轩, 田波, 等. 基于数字海图及遥感的近60年崇明东滩湿地演变分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2013, 25(1): 130−136. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2013.01.23Zheng Zongsheng, Zhou Yunxuan, Tian Bo, et al. Evolution analysis of East Chongming Shoal wetland in recent 60 years based on digital nautical chart and remote sensing[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2013, 25(1): 130−136. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2013.01.23 [16] 阮俊杰, 黄沈发, 王卿, 等. 基于遥感信息的二十年来上海市滩涂湿地时空动态分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2010, 19(S2): 94−100.Ruan Junjie, Huang Shenfa, Wang Qing, et al. Twenty-year dynamics of tidal marshes in Shanghai based on remote sensing data[J]. Resources and Environment of the Yangtze River Basin, 2010, 19(S2): 94−100. [17] 高宇, 赵斌. 人类围垦活动对上海崇明东滩滩涂发育的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2006, 22(8): 475−479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.08.117Gao Yu, Zhao Bin. The effect of reclamation on mud flat development in Chongming Island, Shanghai[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2006, 22(8): 475−479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2006.08.117 [18] 丁文慧, 姜俊彦, 李秀珍, 等. 崇明东滩南部盐沼植被空间分布及影响因素分析[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(7): 704−716. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0067Ding Wenhui, Jiang Junyan, Li Xiuzhen, et al. Spatial distribution of species and influencing factors across salt marsh in southern East Chongming Shoal[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(7): 704−716. doi: 10.17521/cjpe.2015.0067 [19] 任璘婧, 李秀珍, 杨世伦, 等. 崇明东滩盐沼植被变化对滩涂湿地促淤消浪功能的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(12): 3350−3358.Ren Linjing, Li Xiuzhen, Yang Shilun, et al. The impact of salt marsh change on sediment accumulation and wave attenuation at the East Chongming Island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(12): 3350−3358. [20] 曹浩冰, 葛振鸣, 祝振昌, 等. 崇明东滩盐沼植被扩散格局及其形成机制[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(14): 3944−3952.Cao Haobing, Ge Zhenming, Zhu Zhenchang, et al. The expansion pattern of saltmarshes at East Chongming Shoal and its underlying mechanism[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(14): 3944−3952. [21] 李雅娟, 杨世伦, 侯立军, 等. 崇明东滩表层沉积物重金属空间分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(7): 2368−2375.Li Yajuan, Yang Shilun, Hou Lijun, et al. Spatial distribution and contamination evaluation of heavy metals in the intertidal surface sediments of eastern Chongming[J]. Environmental Science, 2012, 33(7): 2368−2375. [22] Dyer K R, Huntley D A. The origin, classification and modelling of sand banks and ridges[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1999, 19(10): 1285−1330. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(99)00028-X [23] Ludwick J C. Tidal currents, sediment transport, and sand banks in Chesapeake bay entrance, Virginia[M]//Geology & Engineering. New York: Academic Press, 1975: 365-380. [24] Dai Z J, Fagherazzi S, Mei X F, et al. Linking the infilling of the North Branch in the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary to anthropogenic activities from 1958 to 2013[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 379: 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.05.006 [25] 莫若瑜, 郭兴杰, 杨忠勇. 长江口北港重大工程对河势演变的影响[J]. 水运工程, 2015(12): 98−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2015.12.018Mo Ruoyu, Guo Xingjie, Yang Zhongyong. Effect of large-scale hydraulic projects on river regime evolution in north channel of Yangtze estuary[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2015(12): 98−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2015.12.018 [26] Cheng Peng, Wang Aijun, Jia Jianjun. Analytical study of lateral-circulation-induced exchange flow in tidally dominated well-mixed estuaries[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 140: 1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.03.013 [27] Zhong Yaozhao, Li Yan, Wu Xiongbin, et al. Morphodynamics of a tidal ridge system in the southwestern Yellow Sea: HF radar study[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 206: 27−37. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.08.025 [28] 郑树伟, 程和琴, 石盛玉, 等. 长江大通至徐六泾水下地形演变的人为驱动效应[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 61(7): 940−950. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9169-4Zheng Shuwei, Cheng Heqin, Shi Shengyu, et al. Impact of anthropogenic drivers on subaqueous topographical change in the Datong to Xuliujing reach of the Yangtze River[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(7): 940−950. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9169-4 [29] 郭兴杰, 程和琴, 计娜, 等. 长江口横沙通道演变对北槽深水航道上段回淤的影响[J]. 泥沙研究, 2015(3): 21−26.Guo Xingjie, Cheng Heqin, Ji Na, et al. Study on the influences of fluvial processes of Hengsha Watercourse to deep water channel[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2015(3): 21−26. -




 下载:
下载: