Analysis on the community characteristics and potential ecological risk of jellyfish in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde, Fujian Province
-
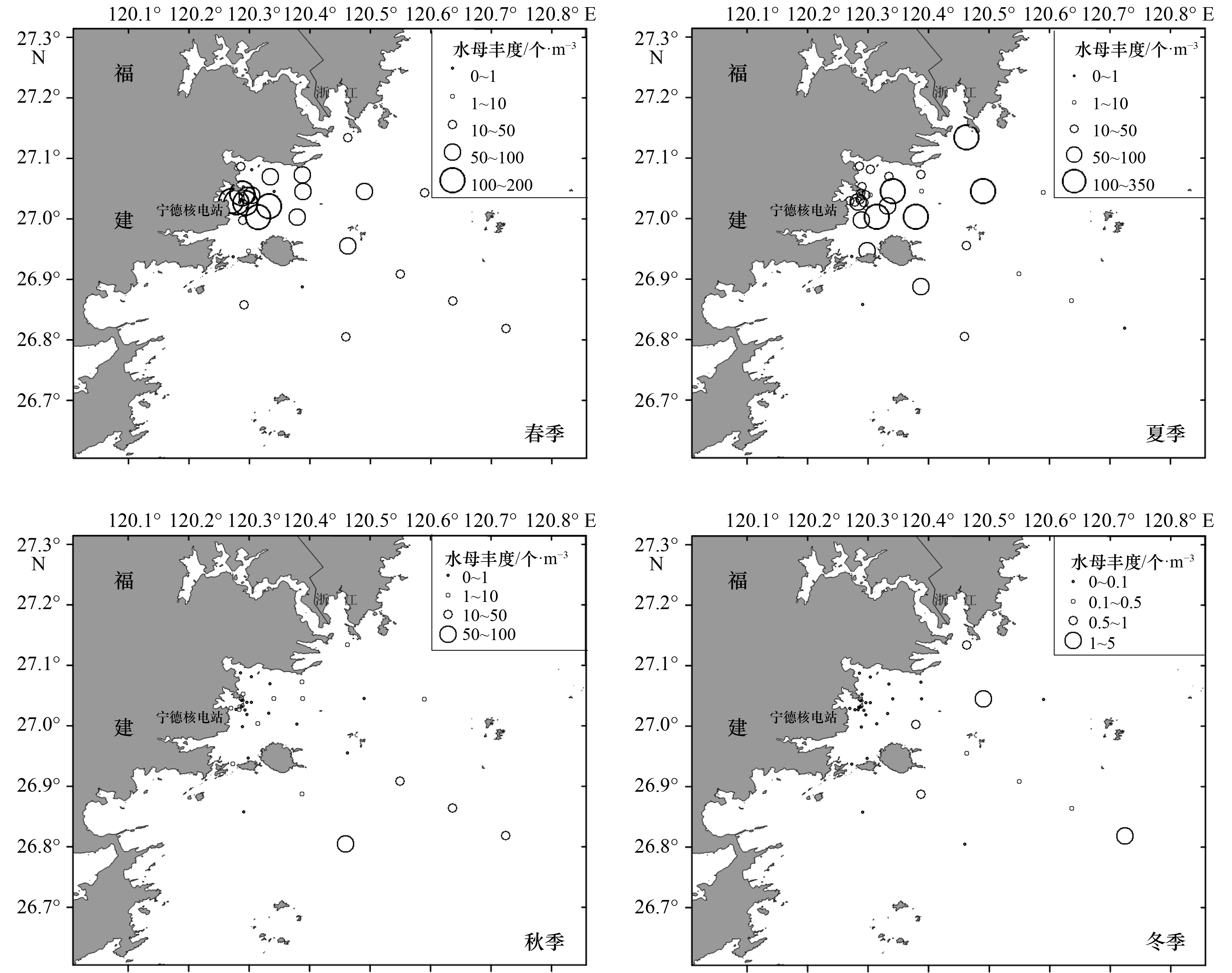
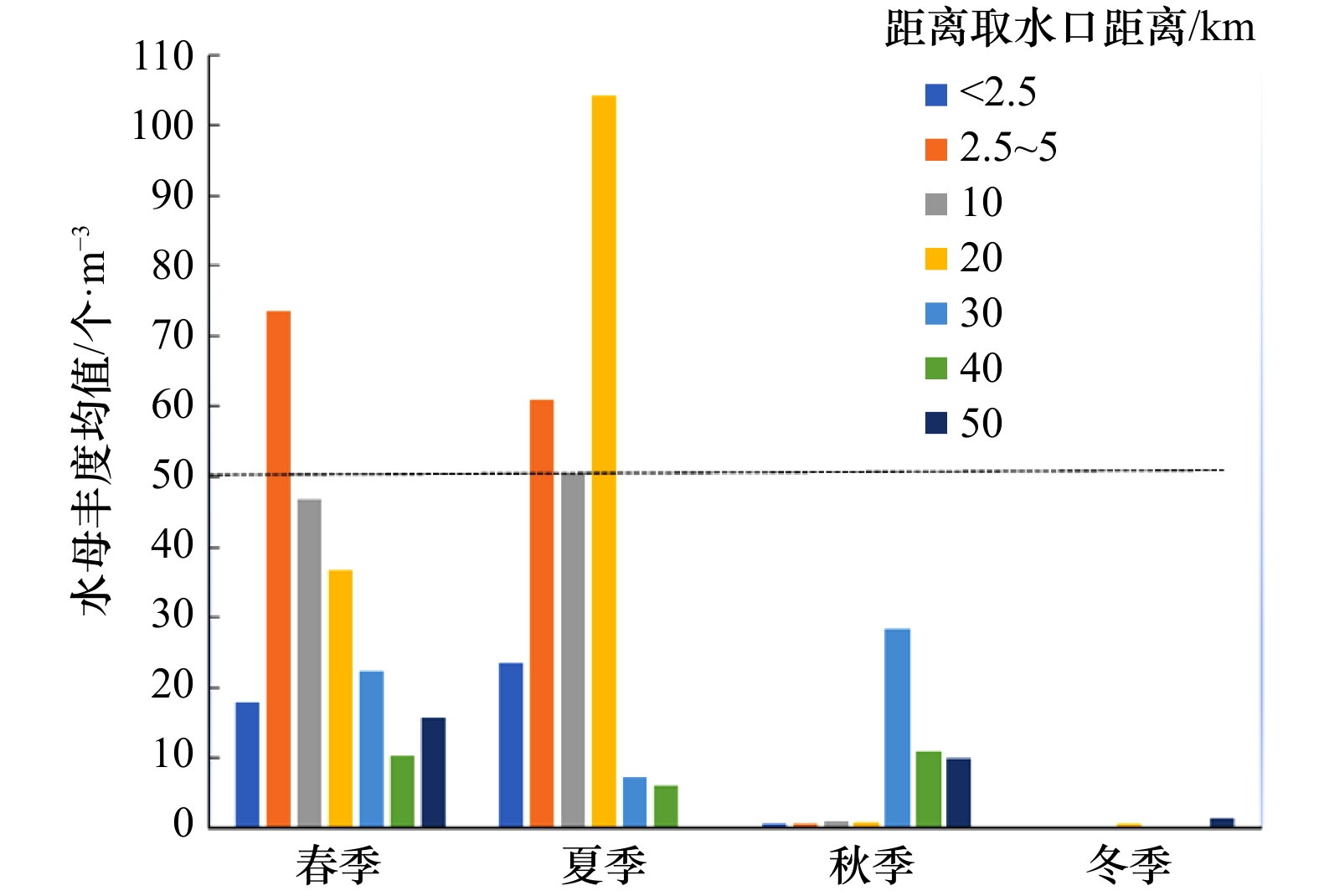
摘要: 根据2018年1月(冬季)、4月(春季)、7月(夏季)和11月(秋季)在宁德晴川湾海域浮游动物调查的4个航次数据,分析该海域水母群落结构和季节变化特征,讨论了水母对宁德晴川湾核电站安全生产潜在的风险。结果表明:宁德晴川湾海域水母类种类组成、丰度分布和优势种演替均存在季节变化,春、夏、秋、冬该海域水母种数分别为7种、16种、9种和3种,丰度均值分别为(45.48±8.24)个/m3、(50.26±12.13)个/m3、(3.68±1.91)个/m3和(0.18±0.07)个/m3,首要优势种分别为印度感棒水母(Laodicea indica)、球型侧腕水母(Pleurobrachia globosa)、双生水母(Diphyes chamissonis)和耳状囊水母(Euphysa aurata),优势种类组成季节演替明显。春季和夏季水母的丰度与浮游动物的总丰度呈极显著相关,在夏季其数量与浮游动物中的桡足类数量呈显著相关(p<0.05,R=0.363),秋季和冬季水母群落的丰度主要受盐度的影响。秋、冬季该海域盐度、温度均较低,水母的丰度也较低。根据宁德晴川湾核电站附近海域水母分布特征,以水母丰度50 个/m3为风险阈值考虑,夏季为潜在高风险季节,需重点关注距核电站冷源取水口5~20 km海域;其次是春季,重点关注距取水口2.5~5 km海域;秋季和冬季基本不会因水母而引起核电站冷源安全事故发生。Abstract: Based on the data from the zooplankton survey in the waters around the Ningde nuclear power plant in January (winter), April (spring), July (summer) and November (autumn) 2018, the structure and seasonal changes of jellyfish communities in the area were analyzed. The potential risks of jellyfish to the safe production of nuclear power in Ningde were discussed. The results showed that there were seasonal changes in the species composition, abundance distribution and dominant species succession of jellyfish in the Ningde nuclear power plant area. The numbers of jellyfish species in the spring, summer, autumn and winter were 7, 16, 9 and 3, respectively. The mean abundances were (45.48±8.24) ind./m3, (50.26±12.13) ind./m3, (3.68±1.91) ind./m3, and (0.18±0.07) ind./m3, respectively. The main dominant species were Laodicea indica, Pleurobrachia globosa, Diphyes chamissonis and Euphysa aurata. The seasonal succession of dominant species was obvious. The correlation analysis between the change of jellyfish abundance and environmental factors showed that the abundance of jellyfish in spring and summer was significantly related to the total abundance of zooplankton, and its number was significantly related to the number of copepods in zooplankton in summer(p<0.05, R=0.363). The abundance of jellyfish communities in autumn and winter was mainly affected by salinity. The salinity of the sea area was relatively low in autumn and winter, and the temperature is also low, so the abundance of jellyfish was also low. According to the distribution characteristics of jellyfish in Ningde, the jellyfish abundance of 50 ind./m3 was considered as the risk threshold value, and summer was the potentially high-risk season for ecological disasters. It was necessary to focus on the 5−20 km away from the intake area in summer; followed by the spring, the focus was on the 2.5−5 km away from the intake area; in autumn and winter, the safety of nuclear power sources was basically not caused by jellyfish.
-
Key words:
- jellyfish /
- zooplankton /
- community characteristics /
- ecological risk /
- Qingchuan Bay of Ningde
-
表 1 宁德晴川湾海域调查站位基本信息
Tab. 1 Basic information of survey stations in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde
站号 纬度 经度 距取水口距离/km 1 27°02′37″N 120°17′23″E <2.5(取水口附近) 2 27°02′32″N 120°17′19″E <2.5(取水口附近) 3 27°02′32″N 120°17′10″E <2.5(取水口附近) 4 27°02′27″N 120°17′11″E <2.5(取水口附近) 5 27°02′21″N 120°16′58″E <2.5(取水口附近) 6 27°02′23″N 120°17′04″E <2.5(取水口附近) 7 27°03′09″N 120°17′23″E 2.5 8 27°02′37″N 120°17′36″E 2.5 9 27°02′21″N 120°17′03″E 2.5 10 27°01′53″N 120°16′29″E 2.5 11 27°02′19″N 120°16′03″E 2.5 12 27°02′19″N 120°18′12″E 2.5 13 27°01′39″N 120°17′31″E 2.5 14 27°01′04″N 120°17′47″E 2.5 15 27°05′23″N 120°17′16″E 5 16 27°05′11″N 120°18′53″E 5 17 27°04′09″N 120°20′05″E 5 18 27°02′43″N 120°20′24″E 5 19 27°01′14″N 120°19′57″E 5 20 27°00′11″N 120°18′50″E 5 21 26°59′52″N 120°17′17″E 5 22 26°56′12″N 120°16′23″E 10 23 26°56′52″N 120°18′33″E 10 24 27°00′10″N 120°22′44″E 10 25 27°02′41″N 120°23′18″E 10 26 27°04′23″N 120°23′15″E 10 27 27°08′04″N 120°27′44″E 20 28 27°02′41″N 120°29′23″E 20 29 26°57′16″N 120°27′44″E 20 30 26°53′15″N 120°23′15″E 20 31 26°51′50″N 120°17′13″E 20 32 26°48′35″N 120°26′09″E 40 33 26°54′32″N 120°32′59″E 40 34 27°02′37″N 120°35′24″E 40 35 26°51′50″N 120°38′09″E 50 表 2 宁德晴川湾海域不同季节水母种类组成名录
Tab. 2 Species composition of jellyfish in different seasons in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde
序号 类别 中文名 拉丁名 冬季 春季 夏季 秋季 1 水螅水母 多管水母属 Aequorea sp. + + 2 水螅水母 半口壮丽水母 Aglaura hemistoma + + + + 3 水螅水母 和平水母属 Eirene sp. + 4 水螅水母 耳状囊水母 Euphysa aurata + 5 水螅水母 束手水母属 Gossea sp. + 6 水螅水母 印度感棒水母 Laodicea indica + 7 水螅水母 厦门隔膜水母 Leuckartiara hoepplii + 8 水螅水母 四叶小舌水母 Liriope tetraphylla + + 9 水螅水母 薮枝螅水母属 Obelia sp. + 10 水螅水母 钩手水母属 Scolionema sp. + 11 水螅水母 似钩手水母 Scolionema suvaense + 12 水螅水母 两手筐水母 Solmundella bitentaculata + + 13 管水母 华丽盛装水母 Agalma elegans + 14 管水母 双生水母 Diphyes chamissonis + + + 15 管水母 拟细浅室水母 Lensia subtiloides + + + 16 管水母 五角水母 Muggiaea atlantica + + + 17 管水母 双小水母 Nanomia bijuga + 18 钵水母 灯塔水母 Turritopsis nutricula + 19 栉水母 刺胞栉水母 Euchlora rubra + + 20 栉水母 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa + + + 备注:+表示检出,空白表示未检出。 表 3 不同季节水母优势种的优势度、平均丰度和出现频率统计
Tab. 3 Dominances, average abundance and frequency of the dominant jellyfish species in different seasons
季节 优势种 优势度(Y) 平均丰度/个·m−3 出现频率/% 春季 印度感棒水母 0.15 18.65 37.1 双生水母 0.08 11.02 34.3 球型侧腕水母 0.07 12.74 25.7 夏季 球型侧腕水母 0.60 42.12 71.4 薮枝螅水母 0.04 4.78 37.1 双生水母 0.03 2.50 62.9 秋季 双生水母 0.07 2.69 20.0 球型侧腕水母 0.03 0.45 51.4 冬季 耳状囊水母 0.08 0.14 20.0 表 4 宁德晴川湾海域不同季节水母丰度与环境因子相关性分析
Tab. 4 Correlation between jellyfish abundance and environmental factors in different seasons in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde
因子
季节浮游动物丰度 浮游动物湿重生物量 桡足类丰度 水温 盐度 pH 春季 0.477** 0.269 0.247 0.032 −0.131 −0.091 夏季 0.620** 0.078 0.363* 0.029 −0.158 −0.157 秋季 0.243 0.331 −0.019 0.078 0.494** 0.096 冬季 −0.173 −0.025 −0.183 0.298 0.460** 0.307 注:**表示在p=0.01(双尾)水平上相关;*表示在p=0.05(双尾)水平相关。 -
[1] 高尚武, 洪惠馨, 张士美. 中国动物志 无脊椎动物 第二十七卷 刺胞动物门 水螅虫纲 管水母亚纲 钵水母纲[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.Gao Shangwu, Hong Huixin, Zhang Shimei. Fauna Sinica, Invertebrata, Vol. Twenty-seven[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. [2] 张芳, 孙松, 李超伦. 海洋水母类生态学研究进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(2): 121−130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.001Zhang Fang, Sun Song, Li Chaolun. Advances in the study of marine jellyfish ecology[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(2): 121−130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.001 [3] 丁峰元, 程家骅. 东海区沙海蜇的动态分布[J]. 中国水产科学, 2007, 14(1): 83−89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2007.01.012Ding Fengyuan, Chen Jiahua. Dynamic distribution of Stomolophus meleagris in the East China Sea Region[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2007, 14(1): 83−89. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2007.01.012 [4] 李聪. 我国水母灾害研究现状与展望[J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(2): 156−162.Li Cong. Review on the current situation and perspective of Chinese jellyfish disasters' research[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2018, 40(2): 156−162. [5] Purcell J E, Uye S I, Lo W T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: a review[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 350: 153−174. doi: 10.3354/meps07093 [6] 韩瑞, 纪平, 赵懿珺, 等. 滨海核电厂取水堵塞事件调研及分析[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 44(S1): 75−80.Han Rui, Ji Ping, Zhao Yijun, et al. Investigation and analysis of water intake blockage in offshore nuclear power plant[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2018, 44(S1): 75−80. [7] 张芳, 李超伦, 孙松, 等. 水母灾害的形成机理、监测预测及防控技术研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6): 1187−1195. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171000258Zhang Fang, Li Chaolun, Sun Song, et al. Progress on studying jellyfish bloom, and the monitoring and control[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1187−1195. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171000258 [8] 左涛, 王俊, 吴强, 等. 2015年5月黄海及东海北部大型水母分布及生物量估算[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(1): 195−204.Zuo Tao, Wang Jun, Wu Qiang, et al. Spatial distribution and biomass of large jellyfish in the Yellow Sea and northern part of the East China Sea in May 2015[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2016, 47(1): 195−204. [9] 孟亚辉, 胡立生, 李建文, 等. 提升核电冷源安全性的海生物监测技术研究[J]. 电力安全技术, 2019, 21(3): 33−39.Meng Yahui, Hu Lisheng, Li Jianwen, et al. Research on marine biological monitoring technology to improve the cold source safety of nuclear power plant[J]. Electric Safety Technology, 2019, 21(3): 33−39. [10] 季轩梁, 刘桂梅, 高姗. 水母暴发因素及模型研究的现状和展望[J]. 海洋预报, 2013, 30(5): 84−91. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2013.05.013Ji Xuanliang, Liu Guimei, Gao Shan. Review on current situation and perspective of jellyfish outbreak and its modeling study[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2013, 30(5): 84−91. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2013.05.013 [11] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763. 6-2007, 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 12763. 6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [12] 孙儒泳. 动物生态学原理[M]. 2版. 北京: 北京师范大学出版社, 1992: 356−357.Sun Ruyong. Principles of Animal Ecology[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Beijing Normal University Publishing House, 1992: 356−357. [13] 杨关铭, 何德华, 王春生, 等. 台湾以北海域浮游桡足类生物海洋学特征的研究 Ⅱ. 群落特征[J]. 海洋学报, 1999, 21(6): 72−80.Yang Guanming, He Dehua, Wang Chunsheng, et al. Study on the biological oceanography characteristics of planktoniccopepods in the waters north of Taiwan Island Ⅱ. Community characteristics[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1999, 21(6): 72−80. [14] 连光山, 林玉辉, 蔡秉及, 等. 大亚湾浮游动物群落的特征[G]//国家海洋局第三海洋研究所. 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999: 180−186.Lian Guangshan, Lin Yuhui, Cai Bingji, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community in Daya Bay[G]//Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration. Collections of Papers on Marine Ecology in the Daya Bay (Ⅱ). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1999: 180−186. [15] 於凡, 许波涛, 李勇, 等. 海生物暴发对核电厂冷源系统的影响分析及对策探讨[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 44(2): 61−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2018.02.013Yu Fan, Xu Botao, Li Yong, et al. Analysis of the impact of marine biological outbreaks on the cold source system of nuclear power plants and discussion on countermeasures[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2018, 44(2): 61−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2018.02.013 [16] 唐娅菲. 滨海核电运行安全典型致灾生物研究——以宁德核电为例[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018.Tang Yafei. Study on typical disaster-causing organisms of coastal nuclear power operation safety: taking Ningde nuclear power as an example[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018. [17] 张朝文, 关春江, 徐鹏, 等. 辽东湾东部海域核电冷源取水区的风险生物分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(1): 41−45. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190107Zhang Chaowen, Guan Chunjiang, Xu Peng, et al. Analysis on risk organisms for the cold source water of nuclear power plantin the eastern waters of Liaodong Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(1): 41−45. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190107 [18] 周永东, 刘子藩, 薄治礼, 等. 东、黄海大型水母及其调查监测[J]. 水产科技情报, 2004, 31(5): 224−227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1994.2004.05.018Zhou Yongdong, Liu Zipan, Bo Zhili, et al. Large jellyfish in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea and its investigation and monitor[J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 2004, 31(5): 224−227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1994.2004.05.018 [19] 程家骅, 丁峰元, 李圣法, 等. 东海区大型水母数量分布特征及其与温盐度的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2005, 25(3): 440−445. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.03.009Cheng Jiahua, Ding Fengyuan, Li Shengfa, et al. A study on the quantity distribution of macro-jellyfish and its relationship to seawater temperature and salinity in the East China Sea Region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2005, 25(3): 440−445. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.03.009 [20] 曲长凤, 宋金明, 李宁. 水母旺发的诱因及对海洋环境的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(12): 3701−3712.Qu Changfeng, Song Jinming, Li Ning. Causes of jellyfish blooms and their influence on marine environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(12): 3701−3712. [21] 孙松, 于志刚, 李超伦, 等. 黄、东海水母暴发机理及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 401−405. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203001001Sun Song, Yu Zhigang, Li Chaolun, et al. Progress in the jellyfish bloom research in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 401−405. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203001001 [22] Brinckmann-Voss A. Seasonality of hydroids (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria) from an intertidal pool and adjacent subtidal habitats at Race Rocks, off Vancouver Island, Canada[J]. Scientia Marina, 1996, 66(1): 89−97. [23] Thibault-Botha D, Lutjeharms J R E, Gibbons M J. Siphonophore assemblages along the east coast of South Africa; mesoscale distribution and temporal variations[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2004, 26(9): 1115−1128. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbh104 [24] 孙松. 对黄、东海水母暴发机理的新认知[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 406−410. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203002002Sun Song. New perception of jellyfish bloom in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 406−410. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203002002 [25] 徐兆礼, 高倩, 陈佳杰, 等. 东海栉水母对温度和盐度生态适应的Yield-Density模型[J]. 生态学杂志, 2008, 27(1): 68−72.Xu Zhaoli, Gao Qian, Chen Jiajie, et al. Yield-density model on adaptation of ctenophora to water temperature and salinity in East China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2008, 27(1): 68−72. [26] 张金标. 我国东南近岸海域球型侧腕水母的分布和丰度[J]. 海洋学报, 1983, 5(S1): 840−846.Zhang Jinbiao. Distribution and abundance of Pleurobrachia globosa in the coastal waters of China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1983, 5(S1): 840−846. -





 下载:
下载: