Pollution characteristics of micro plastics and heavy metals in the intertidal zone sandy sediments of the offshore area of Qinhuangdao
-
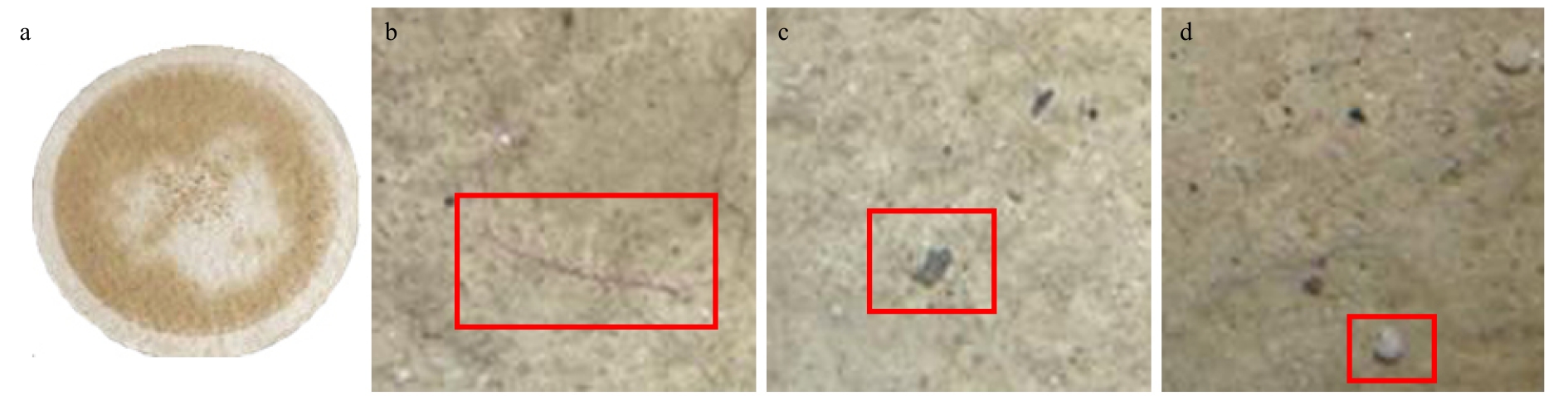
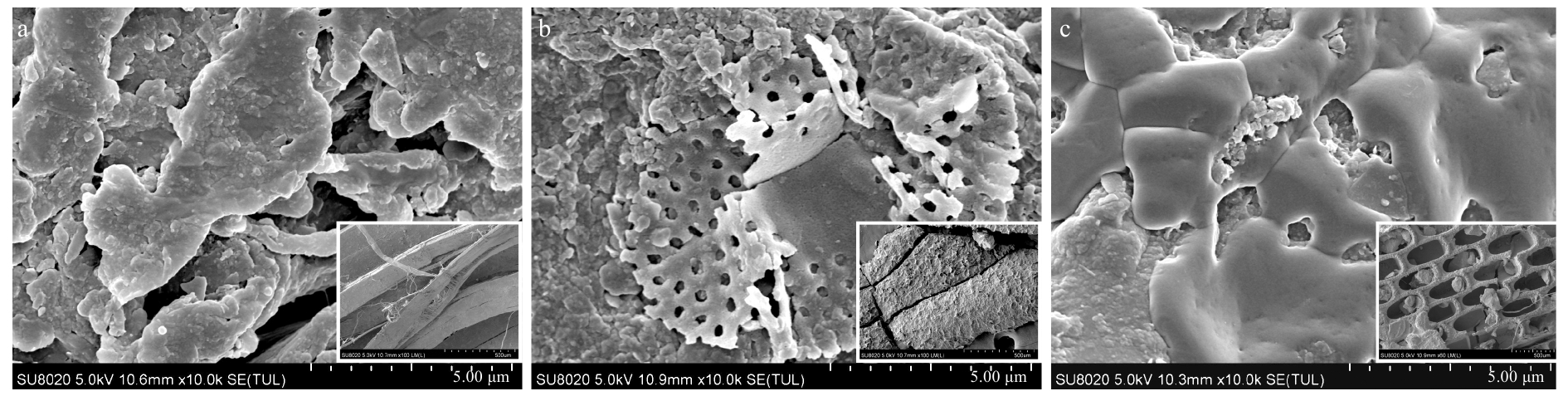
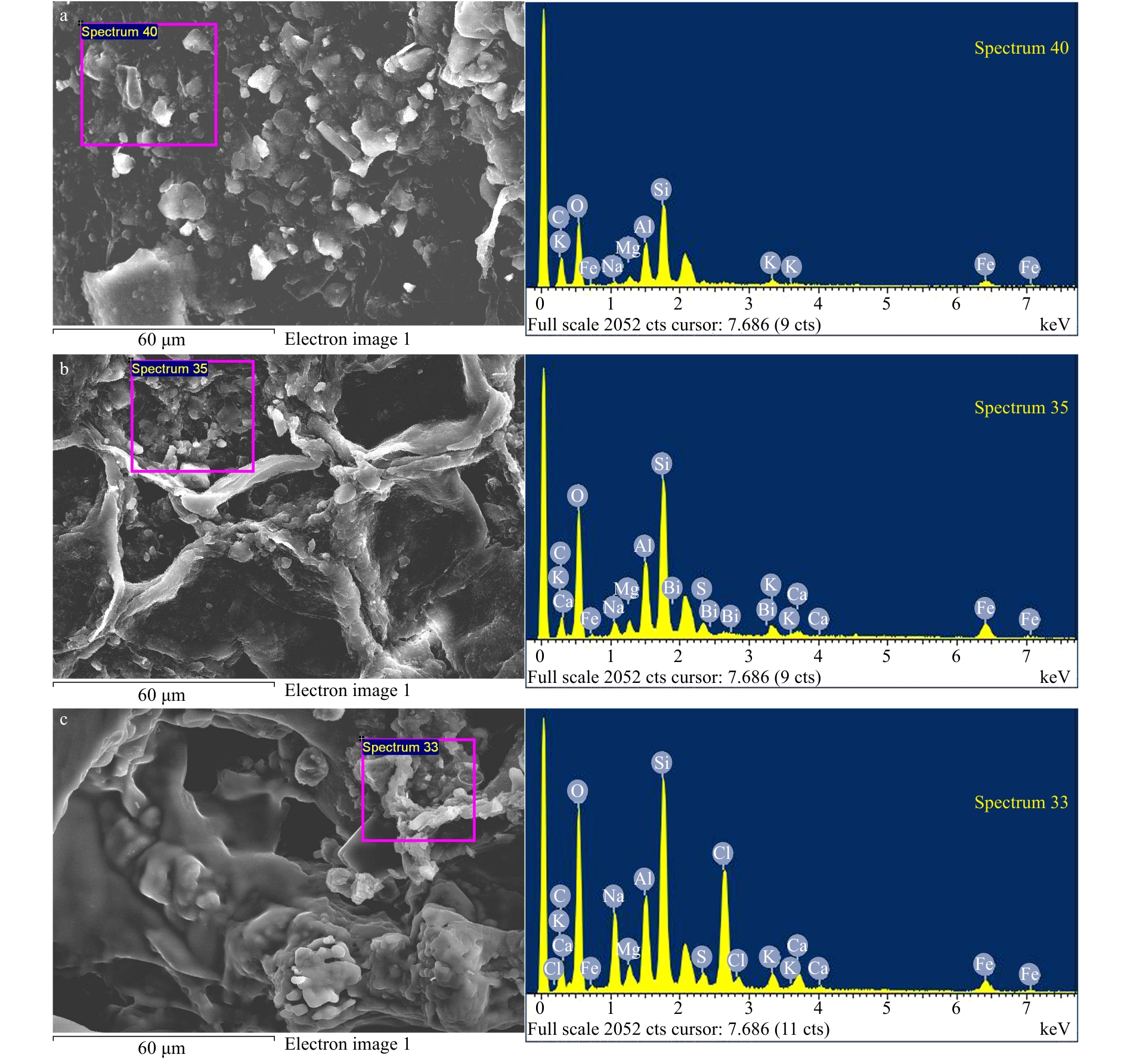
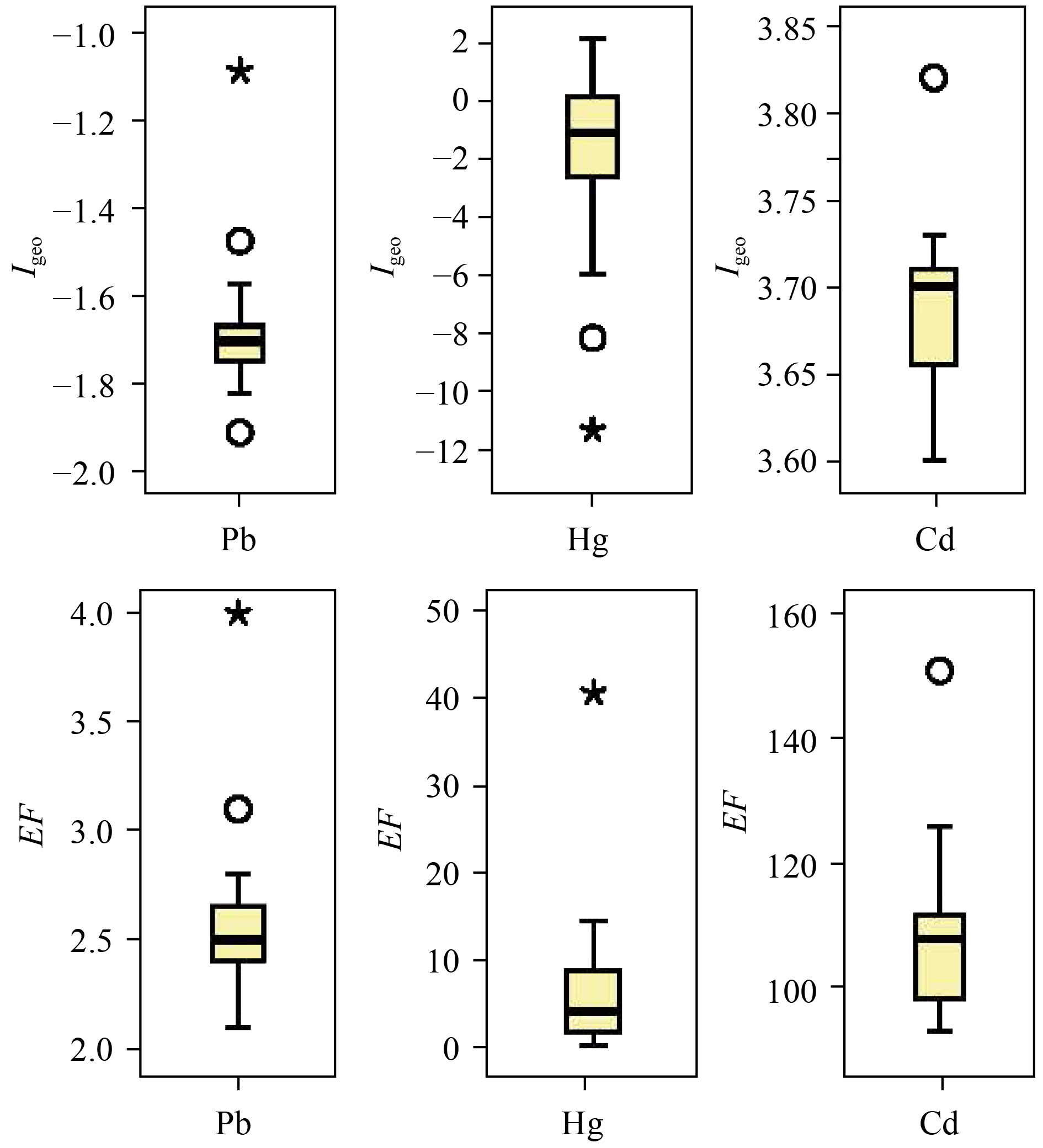
摘要: 基于密度分离原理,利用饱和NaCl溶液对秦皇岛近岸海域潮间带砂质沉积物中的微塑料进行了浮选和分离提取,采用显微红外光谱方法分析附着在滤膜上的微塑料颗粒形貌和材质。结合扫描电子显微镜−能谱仪(Scanning Electron Microscopy Energy Dispersive Spectrometer,SEM-EDS)对微塑料样品进行微观形貌观察及微区成分的分析。并采用地累积指数(Geo Accumulation Indexes,Igeo)和富集系数(Enrichment Factors,EF)分析砂质沉积物中重金属Hg、Cd和Pb污染水平和富集特点。分析砂质沉积物中烧失量(Loss on Ignition,LOI)、总有机碳(Total Organic Carbon,TOC)、总氮(Total Nitrogen,TN)以及碳氮的稳定同位素组成(δ13C和δ15N),探讨有机质的可能来源。结果表明:秦皇岛近岸海域潮间带砂质沉积物中有纤维类、发泡类、薄膜类3种微塑料,以纤维类的微塑料为主。微塑料表层富集有Si、Al、Mg、Fe和Ca等元素。沉积物中Hg和Cd富集水平较高,Pb富集水平较低。沉积物TOC和TN含量较低,LOI为TOC的1.6倍,δ13C、δ15N和TOC/TN的数值范围均显示有机质以海洋浮游植物藻类等海源为主。Abstract: Micro plastics in sandy sediments collected from the intertidal zone of the offshore area of Qinhuangdao were floated by saturated NaCl solution and filtrated with membrane filter. Micro plastic particles were observed using microscope and infrared spectroscopy to discuss the origin and morphology. The surface morphology of micro plastics particles was characterized by scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS) to analyze surface morphology and elements. The geo accumulation indexes (Igeo) and enrichment factors (EF) were used to study the pollution level and enrichment of heavy metals (Hg, Cd and Pb) in sandy sediments. Total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN) and loss on ignition (LOI) and stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen (δ13C and δ15N) in sandy sediments were determined in order to analyze the source characteristics. The results indicated that there were three types of micro plastics: fiber, foam and film. Fiber was in the majority of micro plastics. Micro plastic particles were enriched with Si, Al, Mg, Fe and Ca in the surface. Hg and Cd were seriously enriched, and Pb was not enriched in the sandy sediments. The concentrations of TOC and TN were low; TOC/TN ratio and stable isotopic composition of C and N (δ13C and δ15N) indicated that TOC originated from marine plankton algae.
-
Key words:
- Qinhuangdao /
- intertidal zone /
- micro plastics /
- heavy metals /
- nutrients
-
表 1 标准物质中各元素含量及回收率
Tab. 1 Concentrations and recoveries of elements in certified reference material
元素 标准值/mg∙kg−1 测定值/mg∙kg−1 回收率/% Al 15 036±1 006 17 271±850 114.9 Hg 0.28±0.03 0.30±0.02 107.1 Cd 1.12±0.08 1.02±0.06 91.1 Pb 25.0±2.0 24.5±1.4 90.8 TOC 6 200±800 5 400±1 000 87.1 TN 720±90 650±120 90.2 表 2 秦皇岛近岸海域潮间带砂质沉积物重金属及营养盐含量
Tab. 2 Concentrations of heavy metals and nutrients of the sediments in the coastal intertidal zone of Qinhuangdao
含量 偏度 峰度 沉积物环境背景值 生物效应 Al/% 0.61±0.02(1) −0.2 −0.6 − − Hg/mg∙kg−1 0.11±0.06 −0.5 −1.0 0.05 ERL: 0.15;ERM: 0.71 Cd/mg∙kg−1 2.69±0.02 3.8 14.8 0.14 ERL: 1.2;ERM: 9.6 Pb/mg∙kg−1 7.78±0.30 2.7 8.6 16.6 ERL: 46.7;ERM: 218 LOI/% 1.06±0.02 0.3 −0.5 − − TOC/% 0.68±0.12 1.4 4.8 − − TN/% 0.11±0.01 5.5 30.0 − − TOC/TN 6.53±1.20 −0.8 7.9 − − δ13C/‰ −20.23±0.32 3.7 14.9 − − δ15N/‰ 4.16±0.79 −0.7 0.3 − − 注:(1)表示均值±1倍标准差;−表示无数据;ERL表示效应区间低值;ERM效应区间中值。 -
[1] Zhang Hua. Transport of microplastics in coastal seas[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2017, 199: 74−86. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.09.032 [2] 刘启明, 梁海涛, 锡桂莉, 等. 厦门湾海滩微塑料污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(3): 1217−1221.Liu Qiming, Liang Haitao, Xi Guili, et al. Microplastic pollution of the beaches in Xiamen Bay, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(3): 1217−1221. [3] Yu Xubiao, Ladewig S, Bao Shaowu, et al. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics at selected coastal sites along the southeastern United States[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 613−614: 298−305. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.100 [4] Auta H S, Emenike C U, Fauziah S H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions[J]. Environment International, 2017, 102: 165−176. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.02.013 [5] Bour A, Haarr A, Keiter S, et al. Environmentally relevant microplastic exposure affects sediment-dwelling bivalves[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 236: 652−660. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.006 [6] Green D S, Boots B, O'connor N E, et al. Microplastics affect the ecological functioning of an important biogenic habitat[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(1): 68−77. [7] Hitchcock J N, Mitrovic S M. Microplastic pollution in estuaries across a gradient of human impact[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 247: 457−466. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.069 [8] Ashton K, Holmes L, Turner A. Association of metals with plastic production pellets in the marine environment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2010, 60(11): 2050−2055. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.014 [9] Sun Conghui, Wei Qi, Ma Lixia, et al. Trace metal pollution and carbon and nitrogen isotope tracing through the Yongdingxin River estuary in Bohai Bay, Northern China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 115(1/2): 451−458. [10] Chen Yueqin, Song Qiuyang, Pan Ling, et al. Trace metals, organic carbon and nutrients in the Beidagang Wetland Nature Reserve, northern China[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(10): e0204812. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204812 [11] Sutherland R A. Loss-on-ignition estimates of organic matter and relationships to organic carbon in fluvial bed sediments[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1998, 389(1/3): 153−167. doi: 10.1023/A:1003570219018 [12] Imhof H K, Schmid J, Niessner R, et al. A novel, highly efficient method for the separation and quantification of plastic particles in sediments of aquatic environments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2012, 10(7): 524−537. doi: 10.4319/lom.2012.10.524 [13] Zhu Xia. Optimization of elutriation device for filtration of microplastic particles from sediment[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 92(1/2): 69−72. [14] 方志青, 陈秋禹, 尹德良, 等. 三峡库区支流河口沉积物重金属分布特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2607−2614.Fang Zhiqing, Chen Qiuyu, Yin Deliang, et al. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of the estuary of the tributaries in the Three Gorges Reservoir, SW China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2607−2614. [15] 王宁, 刘清伟, 职音, 等. 中国城市污泥中汞含量的时空分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(5): 2296−2305.Wang Ning, Liu Qingwei, Zhi Yin, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of mercury in municipal sewage sludge in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(5): 2296−2305. [16] 蓝小龙, 宁增平, 肖青相, 等. 广西龙江沉积物重金属污染现状及生物有效性[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(2): 748−757.Lan Xiaolong, Ning Zengping, Xiao Qingxiang, et al. Spatial distribution, sources and bioavailability of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Longjiang River, Southern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(2): 748−757. [17] Sutherland R A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii[J]. Environmental Geology, 2000, 39(6): 611−627. [18] 朱晓桐, 衣俊, 强丽媛, 等. 长江口潮滩表层沉积物中微塑料的分布及沉降特点[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(5): 2067−2074.Zhu Xiaotong, Yi Jun, Qiang Liyuan, et al. Distribution and settlement of microplastics in the surface sediment of Yangtze Estuary[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(5): 2067−2074. [19] Kwon B G, Koizumi K, Chung S Y, et al. Global styrene oligomers monitoring as new chemical contamination from polystyrene plastic marine pollution[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 359−367. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.039 [20] 简敏菲, 周隆胤, 余厚平, 等. 鄱阳湖−饶河入湖段湿地底泥中微塑料的分离及其表面形貌特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(2): 579−586.Jian Minfei, Zhou Longyin, Yu Houping, et al. Separation and microscopic study of microplastics from the sediments of the wetland in the estuary of Raohe River of Poyang Lake[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(2): 579−586. [21] 周隆胤, 简敏菲, 余厚平, 等. 乐安河−鄱阳湖段底泥微塑料的分布特征及其来源[J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(5): 1222−1232. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803010115Zhou Longyin, Jian Minfei, Yu Houping, et al. Distribution of microplastics and its source in the sediments of the Le’an River in Poyang Lake[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(5): 1222−1232. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803010115 [22] 张雷, 秦延文, 郑丙辉, 等. 环渤海典型海域潮间带沉积物中重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(8): 1676−1684.Zhang Lei, Qin Yanwen, Zheng Binghui, et al. Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sediments from typical areas in the Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(8): 1676−1684. [23] 郑舜琴, 张淑美. 渤海湾沉积物中的汞[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1985, 16(2): 121−126.Zheng Shunqin, Zhang Shumei. Mercury in sediments of Bohai Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1985, 16(2): 121−126. [24] 秦延文, 孟伟, 郑丙辉, 等. 渤海湾天津段潮间带沉积物柱状样重金属污染特征[J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(2): 268−273. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.02.014Qin Yanwen, Meng Wei, Zheng Binghui, et al. Contaminative features of heavy metals for tidal sediment cores in Tianjin Bohai Bay[J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(2): 268−273. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.02.014 [25] 吴光红, 朱兆洲, 刘二保, 等. 天津城市排污河道沉积物中重金属含量及分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(2): 413−420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.02.024Wu Guanghong, Zhu Zhaozhou, Liu Erbao, et al. Concentrations and distribution of heavy metals in urban sewage discharge channel of Tianjin[J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(2): 413−420. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.02.024 [26] Long E R, Field L J, MacDonald D D. Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1998, 17(4): 714−727. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620170428 [27] 刘东艳, 申旭红, 王玉珏, 等. 烟台四十里湾表层沉积物有机质来源及环境意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(5): 205−212.Liu Dongyan, Shen Xuhong, Wang Yujue, et al. Tracking the sources of organic matter in the surface sediments of Sishili Bay, Northern Yellow Sea and the environmental implication[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(5): 205−212. [28] 石勇, 刘志帅, 高建华, 等. 鸭绿江河口西岸潮滩沉积物有机质对流域变化的响应[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(1): 115−124.Shi Yong, Liu Zhishuai, Gao Jianhua, et al. Variation of sediment organic matter in western tidal flat of Yalu River Estuary and its respond to basin changes[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(1): 115−124. [29] 于海燕, 俞志明, 宋秀贤, 等. 长江口海域悬浮颗粒有机物的稳定氮同位素季节分布与关键生物地球化学过程[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(2): 16−22.Yu Haiyan, Yu Zhiming, Song Xiuxian, et al. Seasonal distribution of the isotopic composition of suspended particulate nitrogen in the Changjiang River estuary and its biogeochemistry implications[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(2): 16−22. [30] 刘敏, 侯立军, 许世远, 等. 长江口潮滩有机质来源的C、N稳定同位素示踪[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(6): 918−926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.06.015Liu Min, Hou Lijun, Xu Shiyuan, et al. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes as tracers to source organic matter in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59(6): 918−926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.06.015 -




 下载:
下载: