Population structure and spatial distribution of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
-
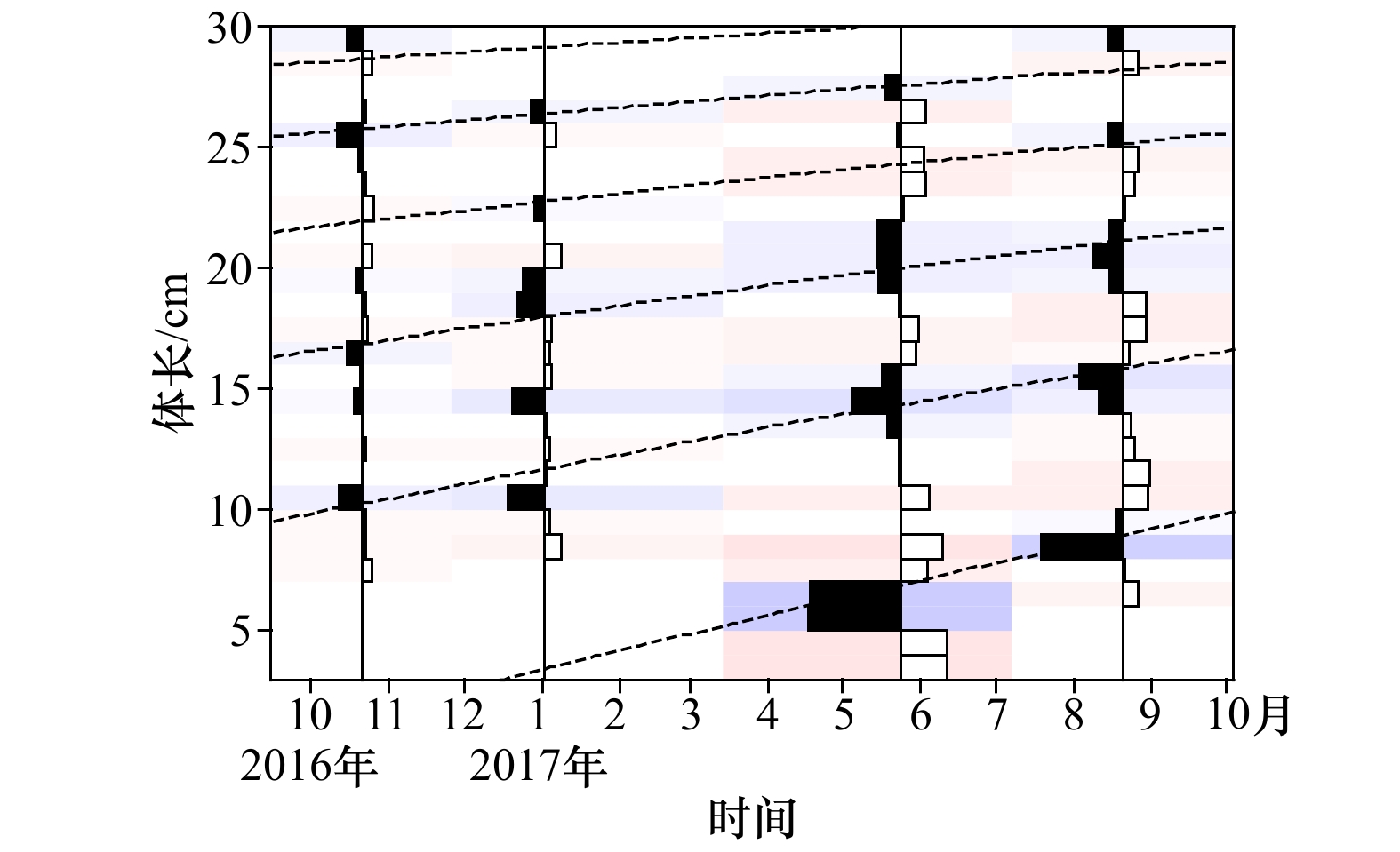
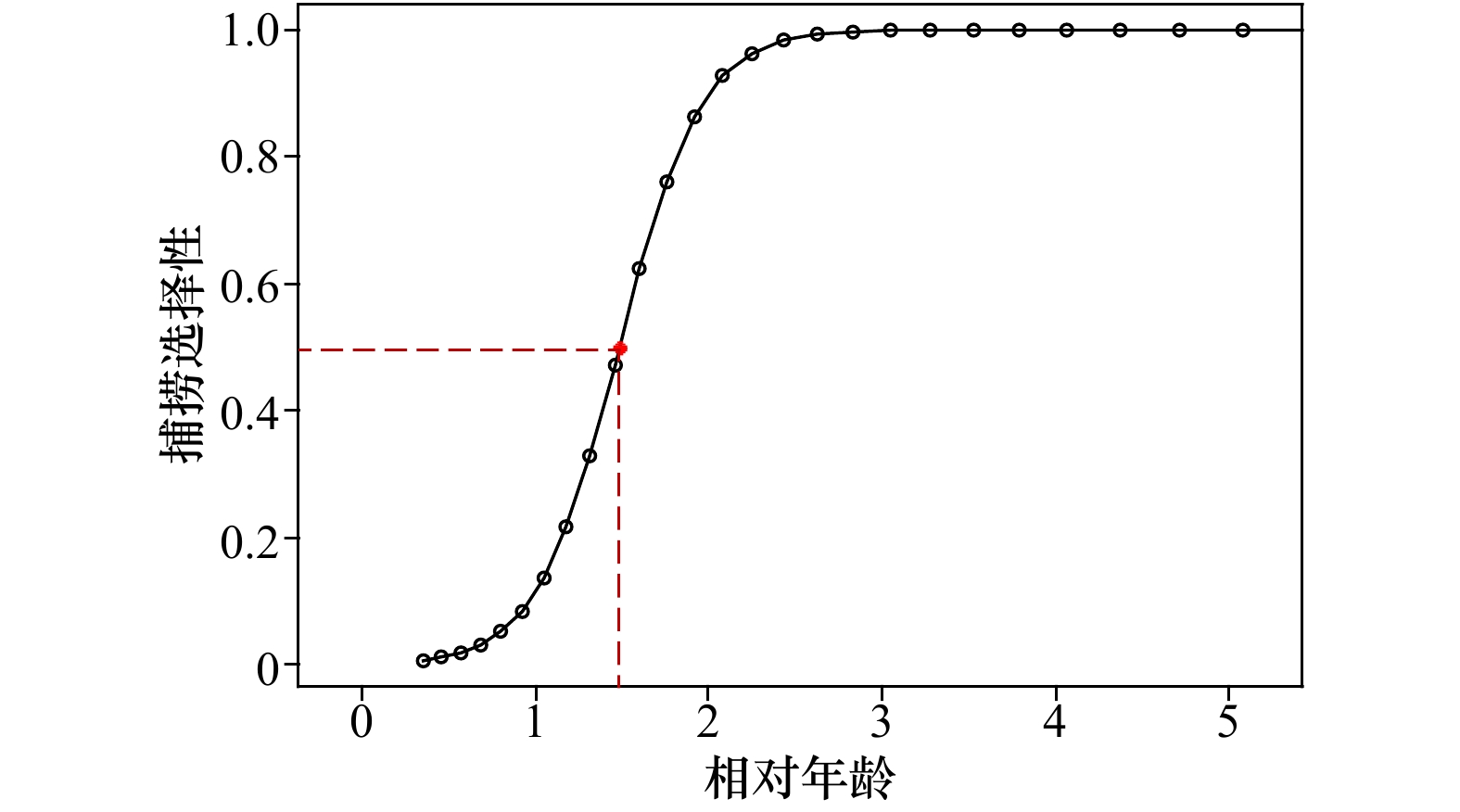
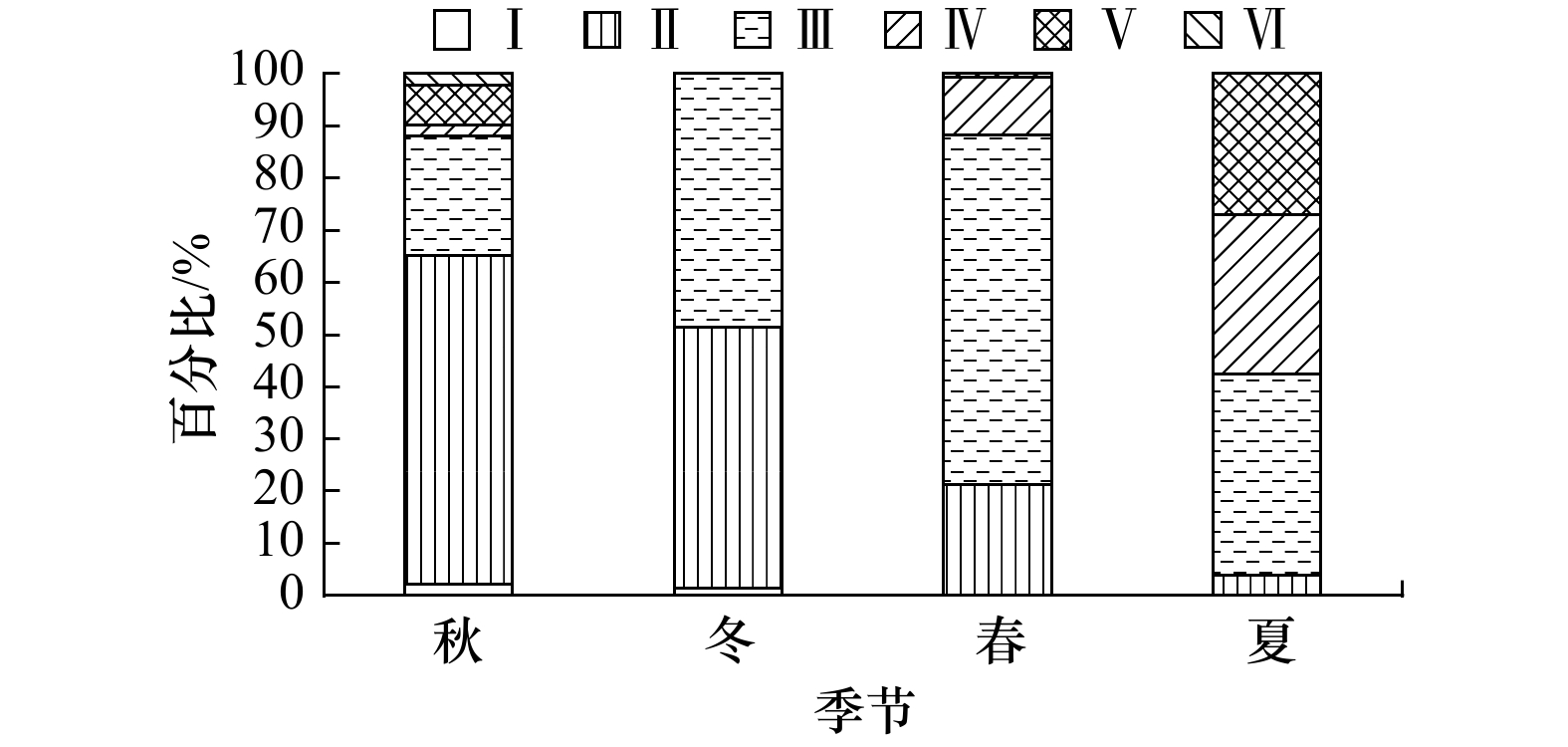
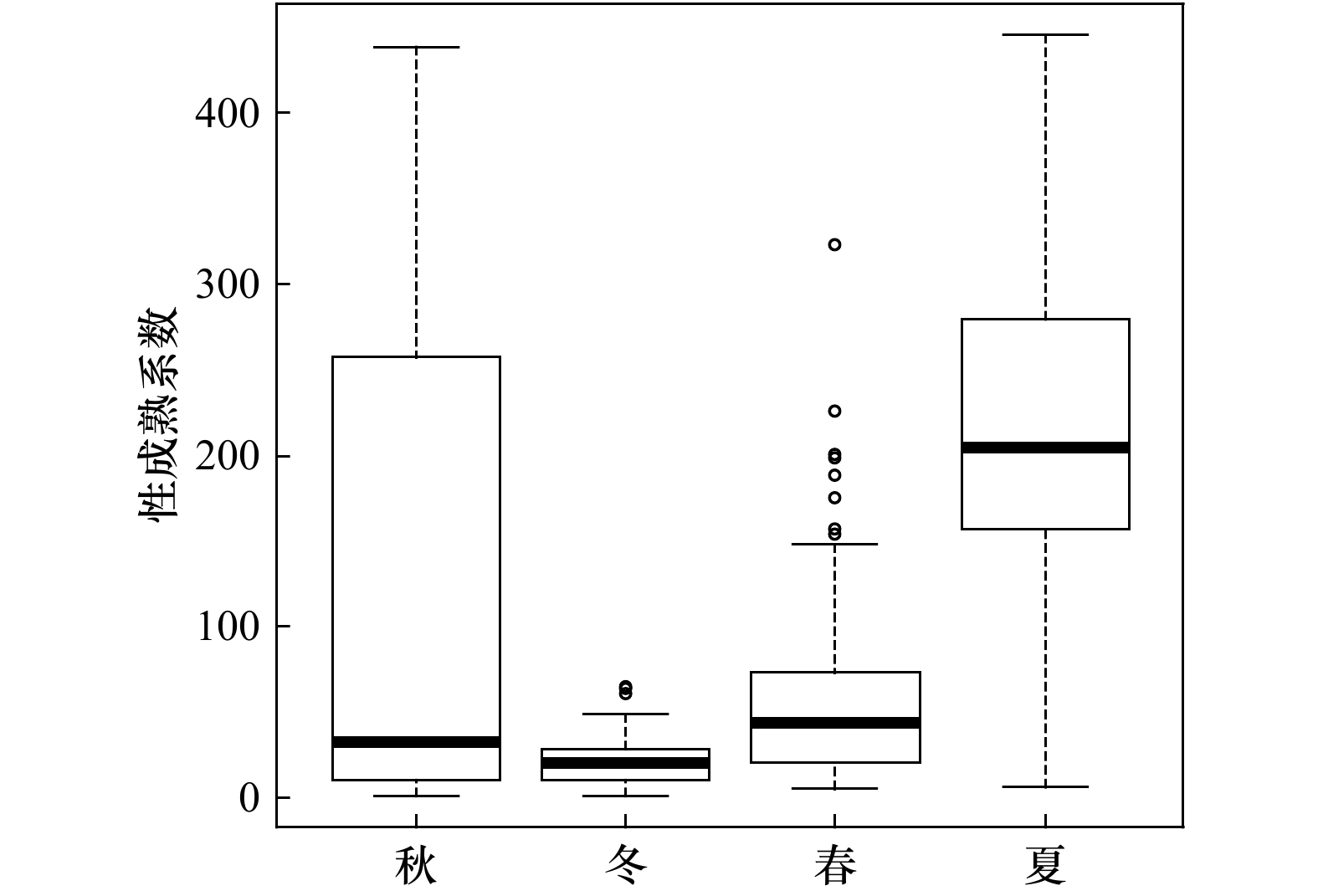
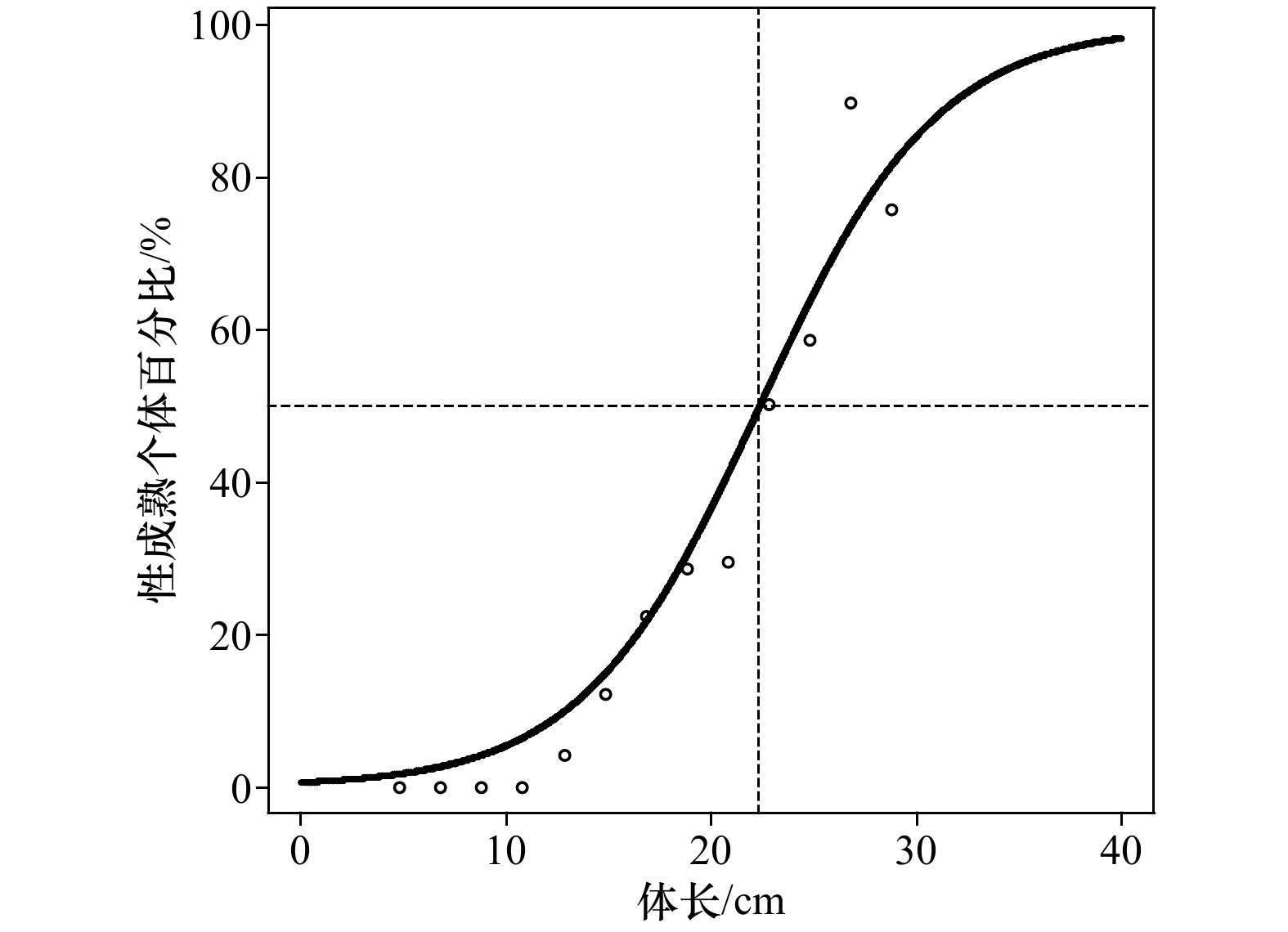
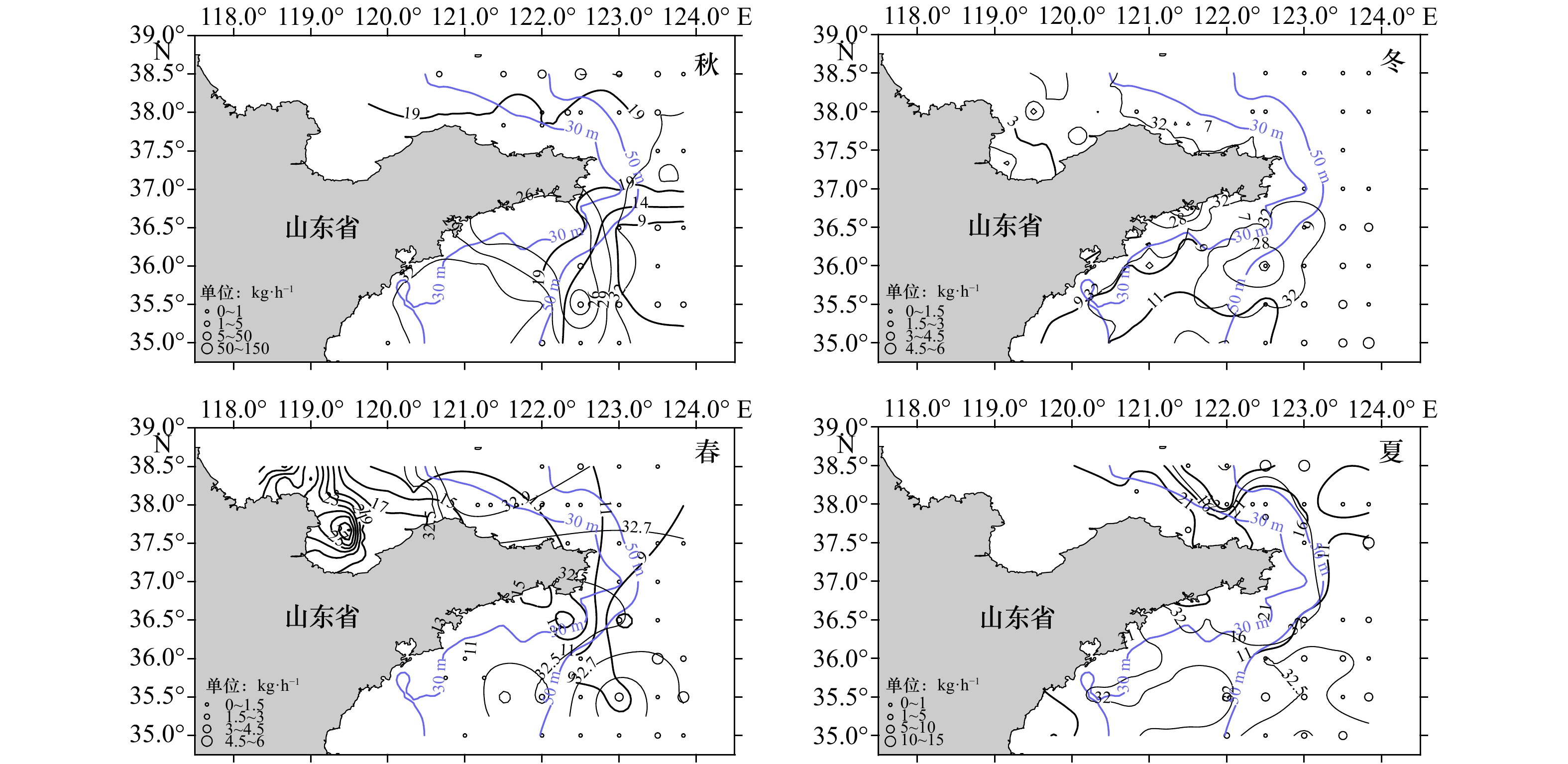
摘要: 根据秋(2016年10月)、冬(2017年1月)、春(2017年5月)和夏(2017年8月)4个季节在山东近海的底拖网调查数据,对高眼鲽(Cleisthenes herzensteini)种群结构和资源分布的季节差异进行研究。结果表明,高眼鲽的平均体长在秋、冬季较大,而平均体质量则在夏、秋季较大。当体长大于15 cm时,体质量呈现较大的季节变化,体质量增长率在夏季最大。采用von Bertalanffy生长方程表示其生长特性,生长参数L∞为37.85 cm、K为0.28、t0为−0.57。通过Pauly经验公式求得高眼鲽的自然死亡系数为0.54。体长转换的渔获曲线求得总死亡系数为1.69,进而求得现阶段的捕捞死亡系数为1.15,开发率高达68.05%,并求得开捕年龄为1.48龄,开捕体长为12.68 cm。年龄组成为1~5龄,其中1龄与2龄个体分别占总数的45.15%与40.23%。各季节中,只有夏季样品的雌雄性比与1∶1差异显著(p<0.05),且雌性的数量显著多于雄性。50%性成熟体长为22.35 cm,性成熟比例和平均性成熟系数最高的季节出现在夏季。高眼鲽主要分布在底层水温为6.45~19.06℃、底层盐度为31.82~33.10和50 m等深线以深的海域,其平均渔获量在秋季远多于其他季节,在冬季陡然下降,随后缓慢上升。山东近海高眼鲽显现出体长分布狭窄、饵料条件恶化、产卵期延迟和过度捕捞等现象,休渔期前后资源量变化剧烈。Abstract: Based on the survey data from the bottom-trawl surveys in Shandong coastal waters in autumn (October 2016), winter (January 2017), spring (May 2017) and summer (August 2017), the seasonal variations of population structure and spatial distribution of Cleisthenes herzensteini were studied. The results showed that the average length of C. herzensteini was larger in autumn and winter, while the average mass was larger in summer and autumn. When the length is more than 15 cm, the seasonal variation of mass is larger, and the growth rate of mass is the biggest in summer. The ages of C. herzensteini ranged from 1 to 5 years old, in which individuals of 1 and 2 years old accounted for 45.15% and 40.23% of the population, respectively. The parameters of the von Bertalanffy growth equation, L∞, K and t0, were 37.85 cm, 0.28 and −0.57, respectively. The Pauly empirical formula evaluated the natural mortality to be 0.54. The total mortality, the fishing mortality, the exploitation ratio, the age of first capture and the length of first capture were 1.69, 1.15, 68.05%, 1.48 years old and 12.68 cm, respectively. In each season, only the ratio of male to female in summer was significantly different from that in 1:1 (p<0.05), and the number of females was significantly higher than that of males. 50% of the length of sexual maturity is 22.35 cm. The highest ratio of sexual maturity and the highest average coefficient of sexual maturity occur in summer. C. herzensteini mainly distributes in areas with bottom water temperature of 6.45−19.06℃, bottom salinity of 31.82−33.10 and depth of more than 50 m. Its average catch in autumn is much more than that in other seasons, which declines sharply in winter and then rises slowly. The C. herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters showed some phenomena, such as narrow length distribution, deterioration of food supply, delayed spawning period and over-exploited stock. The resources changed dramatically before and after the forbidden fishing period.
-
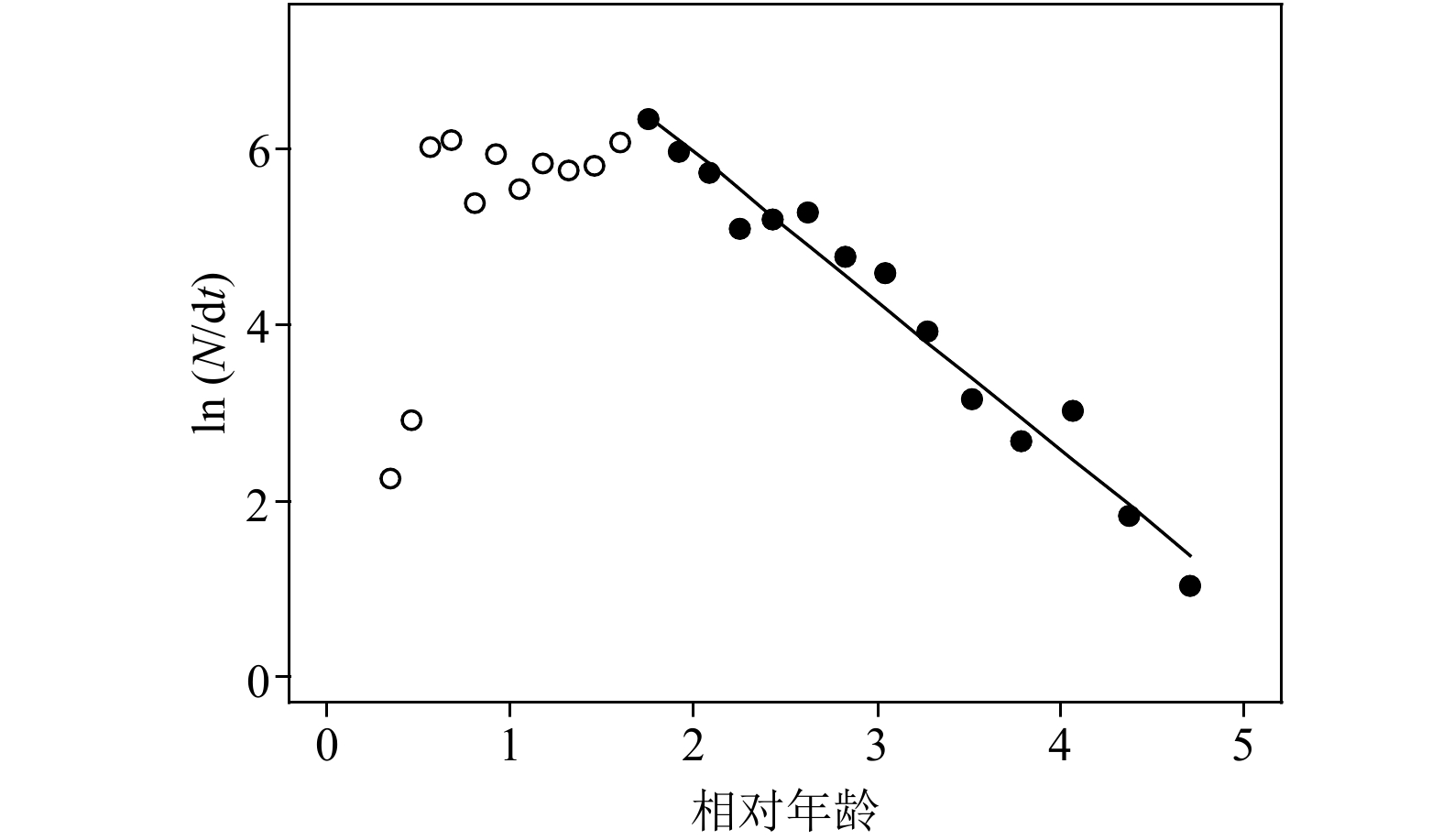
图 5 山东近海高眼鲽体长转化的渔获曲线
N为各体长组的尾数占总样品尾数的百分比,t为相应体长组由下限生长到上限所需要的时间
Fig. 5 The length-converted catch curve of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
N represents the percentage of the number of each length group in the total number of samples, t represents the time needed for the corresponding length group to grow from the lower limit to the upper limit
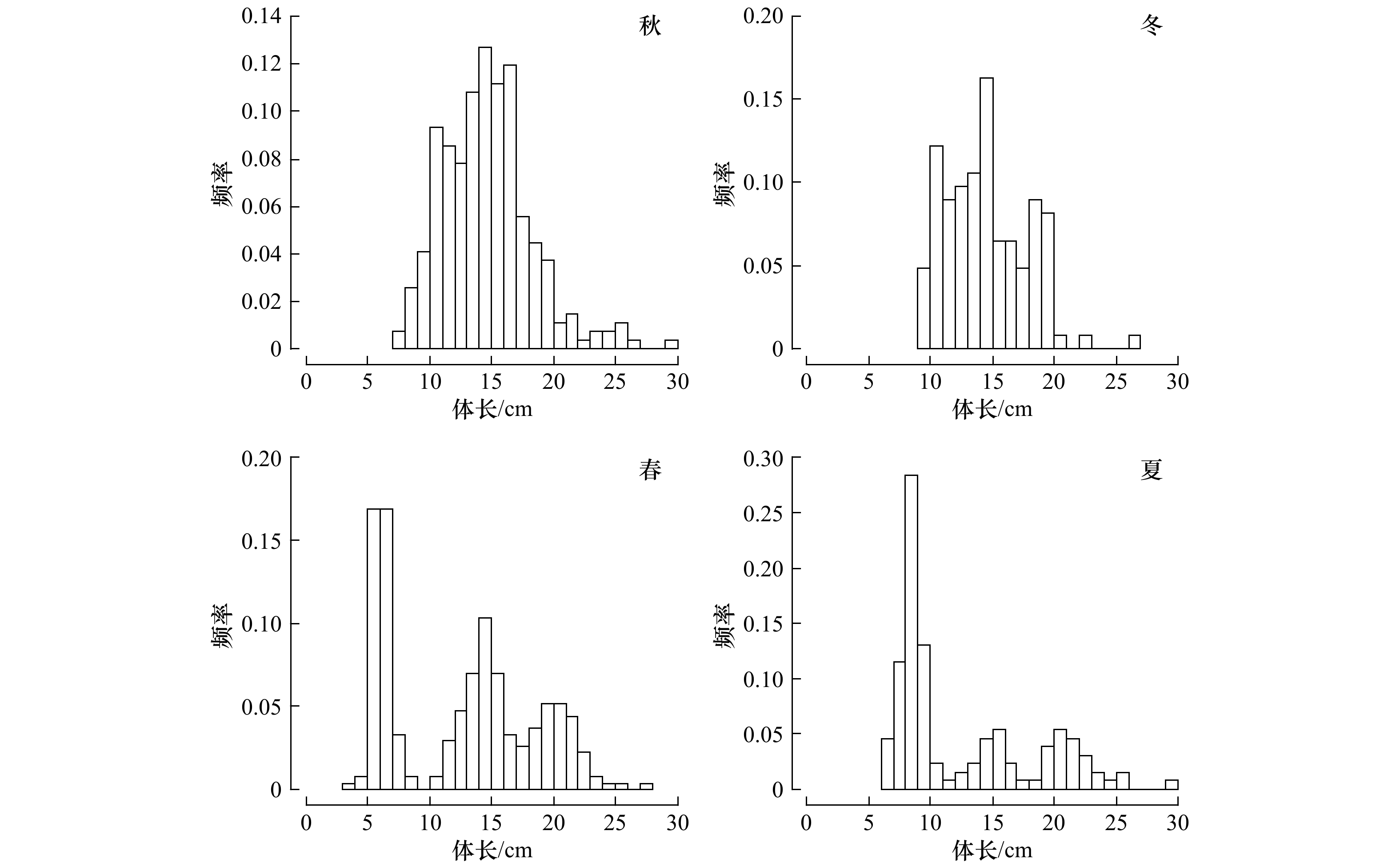
表 1 山东近海高眼鲽体长和体质量组成的季节变化
Tab. 1 Seasonal variations in length and mass of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
季节 样品量/尾 体长/cm 体质量/g 范围 优势组 平均值±标准差 范围 优势组 平均值±标准差 秋 268 7.5~29.5 10~18(76.49%) 14.74±3.64 3.87~440.73 0~50(65.67%) 51.22±55.72 冬 123 9.0~26.5 10~16(63.41%) 14.53±3.26 8.03~359.11 5~65(76.42%) 45.71±41.50 春 272 3.8~27.1 6~16(54.78%) 12.57±5.84 0.96~267.15 0~60(73.53%) 44.00±50.78 夏 130 6.6~29.6 6~10(56.92%) 12.56±5.64 2.46~487.50 0~70(75.38%) 52.66±80.95 表 2 山东近海高眼鲽体长−体质量关系参数
Tab. 2 Parameters of length-mass relationships for Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
季节 a b R2 秋 8.125×10−3 3.156 0.870 冬 4.276×10−3 3.389 0.969 春 9.244×10−3 3.119 0.990 夏 3.564×10−3 3.492 0.976 表 3 山东近海高眼鲽性比的季节变化
Tab. 3 Seasonal variations in sex ratios (♀:♂) of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
季节 综合 体长组/cm <10 10~15 15~20 >20 秋 0.54∶1 ♀(1) 0.04∶1* 1.3∶1 1.25∶1 冬 1.13∶1 — 0.52∶1 2∶1 1∶1 春 1.89∶1 — 1.05∶1 1.2∶1 ♀(38) 夏 12∶1* — 5∶1 5.5∶1 ♀(21) 注:*表示存在显著差异(p<0.05);“—”表示无数据;♀和♂分别表示全为雌性和雄性,括号内为尾数。 表 4 山东近海高眼鲽平均渔获量、贡献率和出现频率的季节变化
Tab. 4 Mean catch, the percentage in the total catch by mass and the occurrence frequency of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters.
季节 平均渔获量/kg·h−1 贡献率 出现频率 秋 7.57 1.61% 16.38% 冬 1.12 0.96% 15.82% 春 1.17 0.86% 20.90% 夏 2.78 0.61% 17.51% 表 5 山东近海高眼鲽相对资源密度及其温盐分布的季节变化
Tab. 5 Seasonal variations in the relative stock density, temperature and salinity of the distribution area of Cleisthenes herzensteini in Shandong coastal waters
季节 资源密度范围/kg·h−1 底层水温/℃ 底层盐度 范围 主要范围 范围 主要范围 秋 0.007~140.352 7.06~19.76 18.56~19.06(87.74%) 19.77~33.26 31.92~32.07(68.23%) 冬 0.005~5.784 6.84~11.32 9.34~10.84(75.09%) 22.66~32.96 32.11~32.96(95.24%) 春 0.024~5.483 6.45~18.61 6.45~9.45(99.47%) 31.09~33.10 32.43~33.10(99.47%) 夏 0.032~13.985 6.55~24.21 8.05~12.55(97.09%) 31.22~33.10 31.82~32.42(77.49%) -
[1] 万瑞景, 姜言伟. 黄海硬骨鱼类鱼卵、仔稚鱼及其生态调查研究[J]. 海洋水产研究, 1998, 19(1): 60−73.Wan Ruijing, Jiang Yanwei. Studies on the ecology of eggs and larvae of osteichthyes in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 1998, 19(1): 60−73. [2] 李思忠, 王惠民. 中国动物志: 硬骨鱼纲·鲽形目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995: 225-229.Li Sizhong, Wang Huimin. Fauna Sinica: Osteichthyes Pleuronectiformes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995: 225−229. [3] 姜卫民, 韦晟, 孙建明. 黄海高眼鲽食性及摄食季节变化的研究[J]. 海洋水产研究, 1989(10): 9−15.Jiang Weimin, Wei Sheng, Sun Jianming. Feeding habits and seasonal variation of diet of Cleithenes herzensteini (Schmidt)[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 1989(10): 9−15. [4] 刘静, 陈咏霞, 马琳. 黄渤海鱼类图志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015.Liu Jing, Chen Yongxia, Ma Lin. Fishes of the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. [5] Shan Xiujuan, Jin Xianshi, Zhou Zhipeng, et al. Stock dynamics of Cleisthenes herzensteini in the central and southern Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(5): 244−252. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2012.07.010 [6] Jin Xianshi, Xu Binduo, Tang Qisheng. Fish assemblage structure in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea during autumn and spring[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 2003, 62(5): 1194−1205. doi: 10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00116.x [7] 张波. 黄海中部高眼鲽的摄食及随体长的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2007, 18(8): 1849−1854.Zhang Bo. Diet composition and ontogenetic variation in feeding habits of Cleithenes herzensteini in central Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2007, 18(8): 1849−1854. [8] 窦硕增, 杨纪明, 陈大刚. 渤海石鲽、星鲽、高眼鲽及焦氏舌鳎的食性[J]. 水产学报, 1992, 16(2): 162−166.Dou Shuozeng, Yang Jiming, Chen Dagang. Food habits of stone flounder, spotted flounder, high-eyed flounder and red tongue sole in the Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1992, 16(2): 162−166. [9] 姜言伟. 高眼蝶(Cleisthenes herzensteini Schmidt)的早期发育[J]. 海洋水产研究, 1980(1): 105−113.Jiang Yanwei. The early life history of plaice, Cleisthenes herzensteini (Schmidt)[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 1980(1): 105−113. [10] 滕广亮, 单秀娟, 金显仕, 等. 黄海高眼鲽卵巢发育特征及卵径分布[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(1): 12−20.Teng Guangliang, Shan Xiujuan, Jin Xianshi, et al. A study on the ovary-development characters and oocyte size-distribution of Cleisthenes herzensteini in the Yellow Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(1): 12−20. [11] Xiao Yongshuang, Zhang Yan, Yanagimoto T, et al. Population genetic structure of the point-head flounder, Cleisthenes herzensteini, in the northwestern Pacific[J]. Genetica, 2011, 139(2): 187−198. doi: 10.1007/s10709-010-9536-y [12] Wang Yajun, Jiang Jiajun, Wang Xubo, et al. Isolation and characterization of twenty novel microsatellite markers of pointhead flounder (Cleisthenes herzensteini)[J]. Conservation Genetics Resources, 2013, 5(1): 137−139. doi: 10.1007/s12686-012-9752-0 [13] 侯英民. 山东海情[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2010.Hou Yingmin. Sea Conditions in Shandong Province[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2010. [14] 陈大刚. 黄渤海渔业生态学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991.Chen Dagang. Fishery Ecology in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1991. [15] 吕振波. 山东近海经济生物资源调查与评价[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2010.Lü Zhenbo. Investigation and Evaluation of Economic and Biological Resources in Shandong Coastal Waters[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2010. [16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763.6-2007, 海洋调查规范 第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. GB/T 12763.6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [17] Keys A B. The weight-length relation in fishes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1928, 14(12): 922−925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.14.12.922 [18] Froese R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: History, meta-analysis and recommendations[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2006, 22(4): 241−253. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00805.x [19] Von Bertalanffy L. A quantitative theory of organic growth (inquiries on growth laws. II)[J]. Human Biology, 1938, 10(2): 181−213. [20] Pauly D, David N. ELEFAN I, a BASIC program for the objective extraction of growth parameters from length-frequency data[J]. Meeresforschung, 1981, 28(4): 205−211. [21] Pauly D. Gill size and temperature as governing factors in fish growth: a generalization of von Bertalanffy’ s growth formula[R]//Berichte aus dem Institut für Meereskunde an der Christian-Albrechts-Universität No. 63. Kiel: Kiel University, 1979: 121−123. [22] 陈大刚. 渔业资源生物学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1997.Chen Dagang. Fishery Resources Biology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1997. [23] Pauly D. Length-converted catch curves and the seasonal growth of fishes[J]. Fishbyte, 1990, 8(3): 33−38. [24] Pauly D. On the interrelationships between natural mortality, growth parameters, and mean environmental temperature in 175 fish stocks[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 1980, 39(2): 175−192. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/39.2.175 [25] 何宝全, 李辉权. 珠江河口棘头梅童鱼的资源评估[J]. 水产学报, 1988, 12(2): 124−134.He Baoquan, Li Huiquan. Stock assessment of Collichthys lucidus in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1988, 12(2): 124−134. [26] 杜荣骞. 生物统计学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2003.Du Rongqian. Biostatistics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2003. [27] 黄海水产研究所. 海洋水产资源调查手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1981: 38-39.Yellow Sea Fishery Research Institute. Investigation Handbook of Marine Fisheries Resources Survey[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific and Technical Press, 1981: 38-39. [28] Lysack W. 1979 Lake Winnipeg fish stock assessment program[R]. Winnipeg: Manitoba Department of Natural Resources, 1980. [29] Г. В. 尼科里斯基. 鱼类种群变动理论[M]. 黄宗强, 译. 北京: 农业出版社, 1982: 156-229.Никольский Г В. Theory of Fish Population Dynamics[M]. Huang Zongqiang, trans. Beijing: Agriculture Press, 1982: 156−229. [30] Chen Dagang, Liu Changan, Dou Shuozeng. The biology of flatfish (Pleuronectinae) in the coastal waters of China[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1992, 29(1/3): 25−33. [31] 郭学武, 张波, 孙耀, 等. 真鲷幼鱼的摄食与生态转换效率—一种现场研究方法在室内的应用[J]. 海洋水产研究, 1999, 20(2): 26−31.Guo Xuewu, Zhang Bo, Sun Yao, et al. The consumption and ecological conversion efficiency of age-0 red sea bream (Pagrosomus major), the lab application of an in situ approach[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 1999, 20(2): 26−31. [32] 李忠炉, 金显仕, 单秀娟, 等. 小黄鱼体长-体质量关系和肥满度的年际变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(3): 602−610.Li Zhonglu, Jin Xianshi, Shan Xiujuan, et al. Inter-annual changes on body weight-length relationship and relative fatness of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis)[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(3): 602−610. [33] 张波, 唐启升. 渤、黄、东海高营养层次重要生物资源种类的营养级研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2004, 22(4): 393−404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.001Zhang Bo, Tang Qisheng. Study on trophic level of important resources species at high trophic levels in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2004, 22(4): 393−404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2004.04.001 [34] Froese R, Pauly D. FishBase. World Wide Web electronic publication[EB/OL].[2017-10-15]. http://www.fishbase.org/search.php. [35] Ricker W E. Methods for Assessment of Fish Production in Fresh Waters[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Press, 1968: 93-123. [36] 董婧, 王冲, 唐明芝, 等. 黄海区玉筋鱼体长和体重的关系[J]. 水产科学, 2004, 23(10): 9−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2004.10.003Dong Jing, Wang Chong, Tang Mingzhi, et al. Relationship between body length and body weight of Pacific sand lance in the Yellow Sea[J]. Fisheries Science, 2004, 23(10): 9−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2004.10.003 [37] Stergiou K I, Moutopoulos D K. A review of length-weight relationships of fishes from Greek marine waters[J]. Naga, 2001, 24(1/2): 23−39. [38] 沈国英, 黄凌风, 郭丰, 等. 海洋生态学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 69-70.Shen Guoying, Huang Lingfeng, Guo Feng, et al. Marine Ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 69−70. [39] 孔啸兰, 江艳娥, 龚玉艳, 等. 南海中北部尾明角灯鱼渔业生物学特性的初步研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2016, 12(4): 117−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.04.015Kong Xiaolan, Jiang Yan'e, Gong Yuyan, et al. A preliminary study on fishery biology of Ceratoscopelus warmingii in the central and northern South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2016, 12(4): 117−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.04.015 [40] Dou Shuozeng. Life history cycles of flatfish species in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1995, 34(1/3): 195−210. [41] 王娇, 张崇良, 薛莹, 等. 黄河口鱼类群落分类学多样性的研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(4): 86−95.Wang Jiao, Zhang Chongliang, Xue Ying, et al. Taxonomic diversity of fish community in the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(4): 86−95. [42] 王娇, 张崇良, 薛莹, 等. 黄河口及其邻近水域鱼类生态类群组成及其季节变化[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(4): 41−51.Wang Jiao, Zhang Chongliang, Xue Ying, et al. Composition of ecological groups and their seasonal changes of fish in Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(4): 41−51. [43] 程家骅, 林龙山, 凌建忠, 等. 东海区小黄鱼伏季休渔效果及其资源合理利用探讨[J]. 中国水产科学, 2004, 11(6): 554−560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2004.06.012Cheng Jiahua, Lin Longshan, Ling Jianzhong, et al. Effects of summer close season and rational utilization on redlip croaker (Larimichthys polyactis Bleeker) resource in the East China Sea Region[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2004, 11(6): 554−560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2004.06.012 -




 下载:
下载: