Oxidative stress and energy utilization responses of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum) to environmental hypoxia stress
-
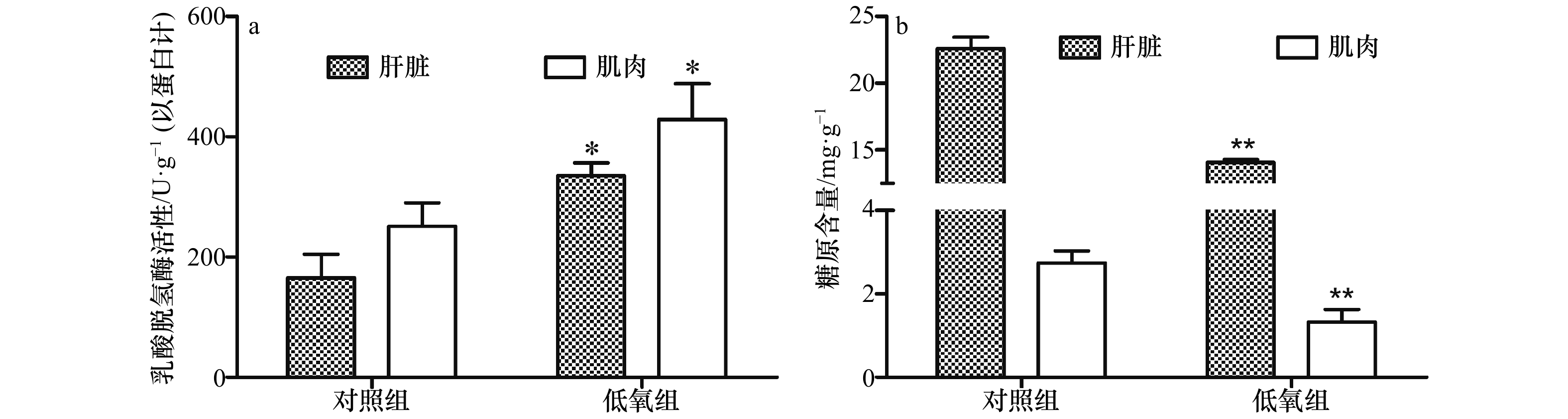
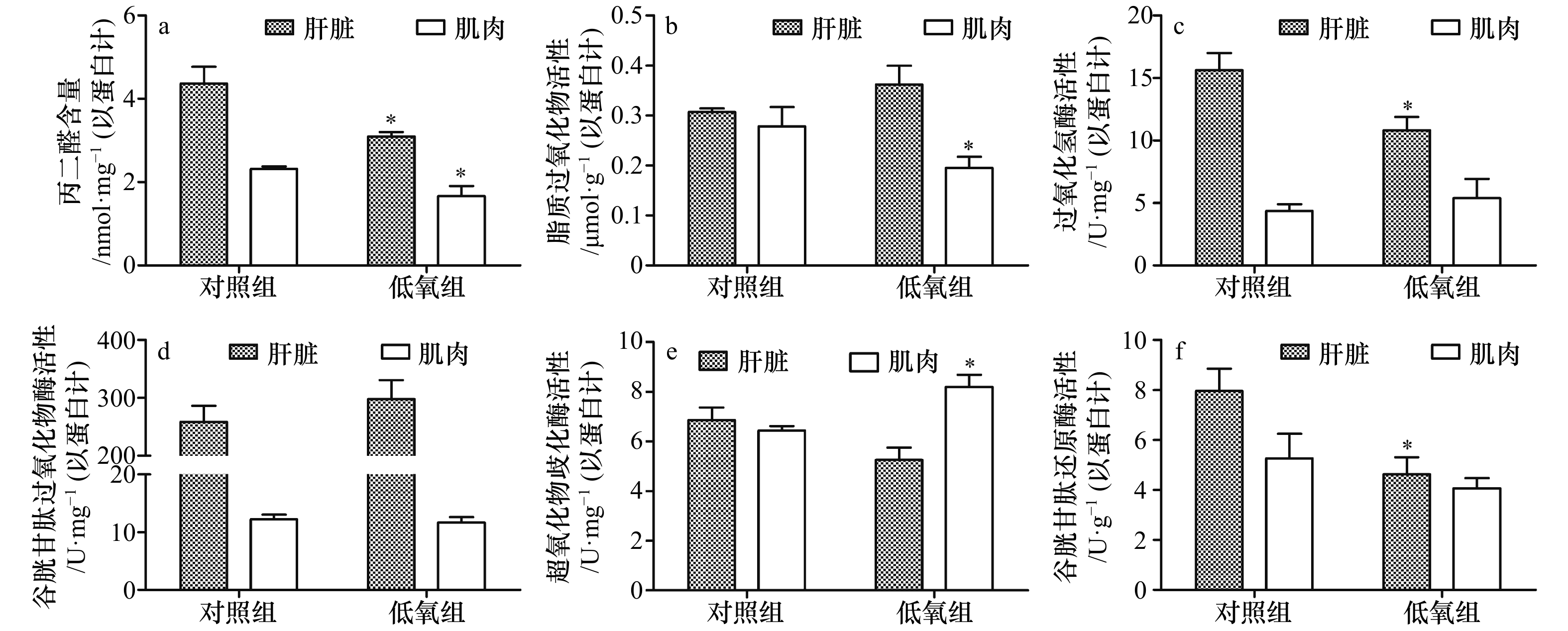
摘要: 本文探究环境低氧对军曹鱼(Rachycentron canadum)氧化应激和能量利用指标的影响,为军曹鱼的健康养殖提供参考依据。通过设置低氧胁迫–恢复实验,将军曹鱼幼鱼(平均体质量(220.67±20.73)g)在低氧((2.64±0.25)mg/L)胁迫3 h及复氧((6.34±0.15)mg/L)8 h、24 h和48 h后,测定其肝脏和肌肉组织的氧化应激与能量利用指标。结果显示,低氧胁迫后,肝脏中丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)和谷胱甘肽还原酶(Glutathione Reductase,GR)活力均显著低于对照组(p<0.05),乳酸脱氢酶(Lactate Dehydrogenase,LDH)活性显著高于对照组(p <0.05);肌肉中MDA和脂质过氧化物(Lipid Peroxidase,LPO)活性均显著低于对照组(p<0.05),超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase,SOD)和LDH活性均显著高于对照组(p<0.05);肌糖原和肝糖原含量极显著低于对照组(p<0.01)。复氧过程中,肝脏和肌肉中MDA、LPO、SOD、CAT、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(Glutathione Peroxidase,GPx)和GR含量均出现不同程度的升高;肝糖原在复氧24 h后显著高于对照组(p<0.05),复氧48 h后显著低于对照组(p<0.05);肌糖原在复氧8 h、24 h和48 h后均显著低于对照组(p<0.05)。研究表明,低氧胁迫能够对军曹鱼幼鱼机体造成一定的氧化损伤,肝脏和肌肉组织的酶活力和能量供应发生变化;低氧胁迫后的再复氧环境,对机体造成更为强烈的氧化损伤,可通过自身生理调节逐渐恢复到正常水平。Abstract: This study investigated the oxidative stress and energy utilization responses of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum) to environmental hypoxia stress, and provided reference for the healthy cultivation of cobia. Through the hypoxia stress-reoxygenation test, the oxidative stress and energy utilization indexes of liver and muscle tissues were measured after hypoxia ((2.64±0.25)mg/L) stress for 3 h and reoxygenation ((6.34±0.15)mg/L) stress for 8 h, 24 h and 48 h. The results showed that after hypoxia stress, the activity of malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase (CAT) and glutathione reductase (GR) in the liver were significantly lower than that in the control group (p<0.05), and the activity of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was significantly higher than that in the control group (p<0.05). MDA and lipid peroxidase (LPO) activities in muscle were significantly lower than those in control group (p<0.05), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and LDH activities were significantly higher than those in control group (p<0.05). The contents of muscle glycogen and liver glycogen were significantly lower than those of control group (p<0.01). During reoxygenation, the contents of MDA, LPO, SOD, CAT, glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and GR in liver and muscle all increased differentially. Liver glycogen content was significantly higher than that of the control group 24 h after reoxygenation (p<0.05), and significantly lower than that of the control group 48 h after reoxygenation (p<0.05). Muscle glycogen content was significantly lower than that of control group after reoxygenation for 8 h, 24 h and 48 h (p<0.05). In conclusion, hypoxia stress can cause some oxidative damage to the body of cobia, and the enzyme activity and energy supply of liver and muscle tissues change. The reoxygenation environment after hypoxia stress causes more severe oxidative damage to the body, which can be gradually restored to the normal level through physiological regulation.
-
Key words:
- Rachycentron canadum /
- hypoxia stress /
- oxidative stress /
- energy utilization
-
表 1 复氧过程对军曹鱼幼鱼肝脏和肌肉氧化应激指标的影响
Tab. 1 Effects of reoxygenation on oxidative stress indicator of liver and muscle of juvenile cobia
氧化应激指标 复氧时间/h 肝脏 肌肉 丙二醛/nmol·mg−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 4.36±0.41a 2.31±0.06a 8 h 4.37±0.57a 3.49±0.16b 24 h 8.24±0.27c 4.95±0.58c 48 h 6.46±0.25b 2.52±0.11a 脂质过氧化物/μmol·g−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 0.31±0.01a 0.28±0.04a 8 h 1.19±0.27b 2.07±0.31c 24 h 1.96±0.65bc 1.71±0.18bc 48 h 2.29±0.26c 1.40±0.14b 过氧化氢酶/U·mg−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 15.64±1.36a 4.38±0.54a 8 h 26.58±4.02b 7.83±2.38ab 24 h 38.45±3.65c 9.08±2.02b 48 h 27.51±1.25b 6.83±3.18ab 谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶/U·mg−1 (以蛋白计) 对照组 258.50±27.57a 12.21±0.81a 8 h 352.38±16.26b 25.99±2.10c 24 h 429.41±23.61c 24.23±1.07bc 48 h 424.53±21.03c 21.73±1.82b 超氧化物歧化酶/U·mg−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 6.86±1.76a 6.44±0.17a 8 h 9.23±1.56ab 11.02±1.28b 24 h 11.63±1.58b 12.57±1.83b 48 h 9.62±2.27ab 12.64±1.44b 谷胱甘肽还原酶/U·g−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 7.96±0.89a 5.27±0.98a 8 h 48.91±22.04b 38.73±15.49b 24 h 42.96±1.50b 40.07±16.66b 48 h 43.42±12.63b 22.58±9.64ab 注:同一列中不同字母上标的数值互相之间差异显著(p<0.05)。 表 2 复氧过程对军曹鱼幼鱼肝脏和肌肉能量利用指标的影响
Tab. 2 Effects of reoxygenation on energy utilization indicator of liver and muscle of juvenile cobia
能量利用指标 复氧时间/h 肝脏 肌肉 乳酸脱氢酶/U·g−1
(以蛋白计)对照组 165.37±39.61ab 251.12±39.10a 8 h 193.32±2.58b 320.55±101.18a 24 h 149.39±18.28ab 331.92±38.58a 48 h 140.87±11.27a 372.32±67.30a 糖原/mg·g−1 对照组 22.57±0.89b 2.74±0.03b 8 h 19.82±1.10ab 1.82±0.48a 24 h 33.28±1.73c 1.90±0.42a 48 h 18.81±1.94a 1.55±0.18a 注:同一列中不同字母上标的数值互相之间差异显著(p<0.05)。 -
[1] 张国松. 瓦氏黄颡鱼(Pelteobagrus vachelli)应对低氧胁迫的分子机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2017.Zhang Guosong. Study on the molecular mechanism of Pelteobagrus vachelli in response to hypoxia stress[D]. Nanjing : Nanjing Normal University, 2017. [2] Wu R S S. Hypoxia: from molecular responses to ecosystem responses[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 45(1−12): 35−45. [3] Buentello J A, Gatlin Ⅲ D M, Neill W H. Effects of water temperature and dissolved oxygen on daily feed consumption, feed utilization and growth of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus)[J]. Aquaculture, 2000, 182(3/4): 339−352. [4] 李洁. 限制溶解氧供应对褐牙鲆幼鱼生长的影响及其机制的实验研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2011.Li Jie. Effects of restricted the supply of dissolved oxygen on the growth of juvenile brown flounder, (Paralichthys olivaceus) and the mechanism[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2011. [5] Lai Kengpo, Li J W, Tse A C K, et al. Hypoxia alters steroidogenesis in female marine medaka through miRNAs regulation[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2016, 172: 1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.12.012 [6] 穆景利, 靳非, 赵化德, 等. 水体低氧的早期暴露对青鳉(Oryzias latipes)后期的生长、性别比和繁殖能力的影响[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(2): 137−146. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160508002Mu Jingli, Jin Fei, Zhao Huade, et al. Early-life exposure to hypoxia altered growth, sex ratio, and reproduction in medaka (Oryzias latipes)[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(2): 137−146. doi: 10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20160508002 [7] Diaz R J. Overview of hypoxia around the world[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2001, 30(2): 275−281. doi: 10.2134/jeq2001.302275x [8] Dybas C L. Dead zones spreading in world oceans[J]. BioScience, 2005, 55(7): 552−557. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2005)055[0552:DZSIWO]2.0.CO;2 [9] 常志成, 温海深, 张美昭, 等. 溶解氧水平对花鲈幼鱼氧化应激与能量利用的影响及生理机制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(7): 20−28.Chang Zhicheng, Wen Haishen, Zhang Meizhao, et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen levels on oxidative stress response and energy utilization of juvenile Chinese sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) and associate physiological mechanisms[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(7): 20−28. [10] 王永红, 张建设, 曾霖. β-葡聚糖对低氧胁迫下大黄鱼幼鱼的保护作用及其机理[J]. 水产学报, 2018, 42(6): 828−837.Wang Yonghong, Zhang Jianshe, Zeng Lin. β-glucan decreases intensity of hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) and its corresponding mechanisms[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2018, 42(6): 828−837. [11] 张晓梅, 王春琳, 李来国, 等. 耗氧率及溶氧胁迫对长蛸体内酶活力的影响[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2010, 3(2): 72−79.Zhang Xiaomei, Wang Chunlin, Li Laiguo, et al. Oxygen consumption rate and effect of hypoxia stress on enzyme activity of Octopus variabilis[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2010, 3(2): 72−79. [12] 陈刚, 张健东, 吴灶和. 军曹鱼幼鱼耗氧率与窒息点的研究[J]. 水产养殖, 2005, 26(1): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2005.01.001Chen Gang, Zhang Jiandong, Wu Zaohe. Study on the oxygen consumption rate and the asphyxianted point of Rachycentron canadum[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 2005, 26(1): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2005.01.001 [13] 陈强, 刘泓宇, 谭北平, 等. 饲料胆固醇对军曹鱼幼鱼生长、血液生化指标及脂代谢的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 35−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2016.01.007Chen Qiang, Liu Hongyu, Tan Beiping, et al. Effects of dietary cholesterol level on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters and lipid metabolism of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2016, 36(1): 35−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2016.01.007 [14] 熊向英, 黄国强, 彭银辉, 等. 低氧胁迫对鲻幼鱼生长、能量代谢和氧化应激的影响[J]. 水产学报, 2016, 40(1): 73−82.Xiong Xiangying, Huang Guoqiang, Peng Yinhui, et al. Effect of hypoxia on growth performance, energy metabolism and oxidative stress of Mugil cephalus[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2016, 40(1): 73−82. [15] 王健伟. 低氧对鳊鱼幼鱼临界游泳和匀加速游泳能力的影响及其生化机制[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2015.Wang Jianwei. The effects of hypoxia on critical swimming and constant accelerate swimming performance and biochemical mechanism in juvenile Parabramis pekinensis[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2015. [16] 黄建盛, 陆枝, 陈刚, 等. 急性低氧胁迫对军曹鱼大规格幼鱼血液生化指标的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(6): 76−84.Huang Jiansheng, Lu Zhi, Chen Gang, et al. Acute hypoxia stress on blood biochemical indexes of large-sized juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(6): 76−84. [17] Lushchak V I. Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2011, 101(1): 13−30. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.10.006 [18] Victor V M, Esplugues J V, Hernandez-Mijares A, et al. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis: a potential therapy with mitochondria-targeted antioxidants[J]. Infectious Disorders - Drug Targets, 2009, 9(4): 376−389. doi: 10.2174/187152609788922519 [19] Ortuño J, Esteban M A, Meseguer J. Lack of effect of combining different stressors on innate immune responses of seabream (Sparus aurata L.)[J]. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 2002, 84(1/2): 17−27. [20] Lushchak V I, Bagnyukova T V, Lushchak O V, et al. Hypoxia and recovery perturb free radical processes and antioxidant potential in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues[J]. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 2005, 37(6): 1319−1330. [21] Sampaio F G, de Lima Boijink C, Oba E T, et al. Antioxidant defenses and biochemical changes in pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus) in response to single and combined copper and hypoxia exposure[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology, 2008, 147(1): 43−51. [22] Lushchak V I, Bagnyukova T V. Hypoxia induces oxidative stress in tissues of a goby, the rotan Perccottus glenii[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2007, 148(4): 390−397. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2007.07.007 [23] 张志伟. 鲢低氧应激相关基因的克隆与表达分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2011.Zhang Zhiwei. Molecular cloning and differential expression patterns of hypoxic stress related genes in silver carp[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2011. [24] 何伟, 曹振东, 付世建. 温度和低氧对白鲢乳酸与糖水平的影响[J]. 重庆师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 30(5): 27−31.He Wei, Cao Zhendong, Fu Shijian. Effects of temperature and hypoxia on lactate and carbohydrate level in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix)[J]. Journal of Chongqing Normal University: Natural Science, 2013, 30(5): 27−31. [25] 揭小华, 彭雄, 黄波, 等. 乳酸脱氢酶编码基因在肿瘤中表达及其转录调控机制的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤, 2015, 35(11): 1271−1277.Jie Xiaohua, Peng Xiong, Huang Bo, et al. Progress in research on expression and transcriptional regulation of lactate dehydrogenase coding genes in cancer[J]. Tumor, 2015, 35(11): 1271−1277. [26] Vagner M, Lefrançois C, Ferrari R S, et al. The effect of acute hypoxia on swimming stamina at optimal swimming speed in flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus[J]. Marine Biology, 2008, 155(2): 183−190. doi: 10.1007/s00227-008-1016-x [27] 区又君, 陈世喜, 王鹏飞, 等. 低氧环境下卵形鲳鲹的氧化应激响应与生理代谢相关指标的研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(3): 120−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.03.016Ou Youjun, Chen Shixi, Wang Pengfei, et al. Study on oxidative stress response and physiological metabolism related indices of Trachinotus ovatus under hypoxia stress[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2017, 13(3): 120−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.03.016 [28] Chew S F, Ip Y K. Biochemical adaptations of the mudskipper Boleophthalmus boddaerti to a lack of oxygen[J]. Marine Biology, 1992, 112(4): 567−571. doi: 10.1007/BF00346174 [29] 彭银辉, 黄国强, 李洁, 等. 溶氧水平对梭鱼幼鱼能量代谢与氧化应激的影响[J]. 广西科学, 2013, 20(4): 294−298.Peng Yinhui, Huang Guoqiang, Li Jie, et al. Energy metabolism and oxidative stress of juvenile Liza haematocheila as dissolved oxygen decline[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2013, 20(4): 294−298. [30] Sharpe R L, Milligan C L. Lactate efflux from sarcolemmal vesicles isolated from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss white muscle is via simple diffusion[J]. Journal of Experimental Biology, 2003, 206(3): 543−549. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00126 -




 下载:
下载: