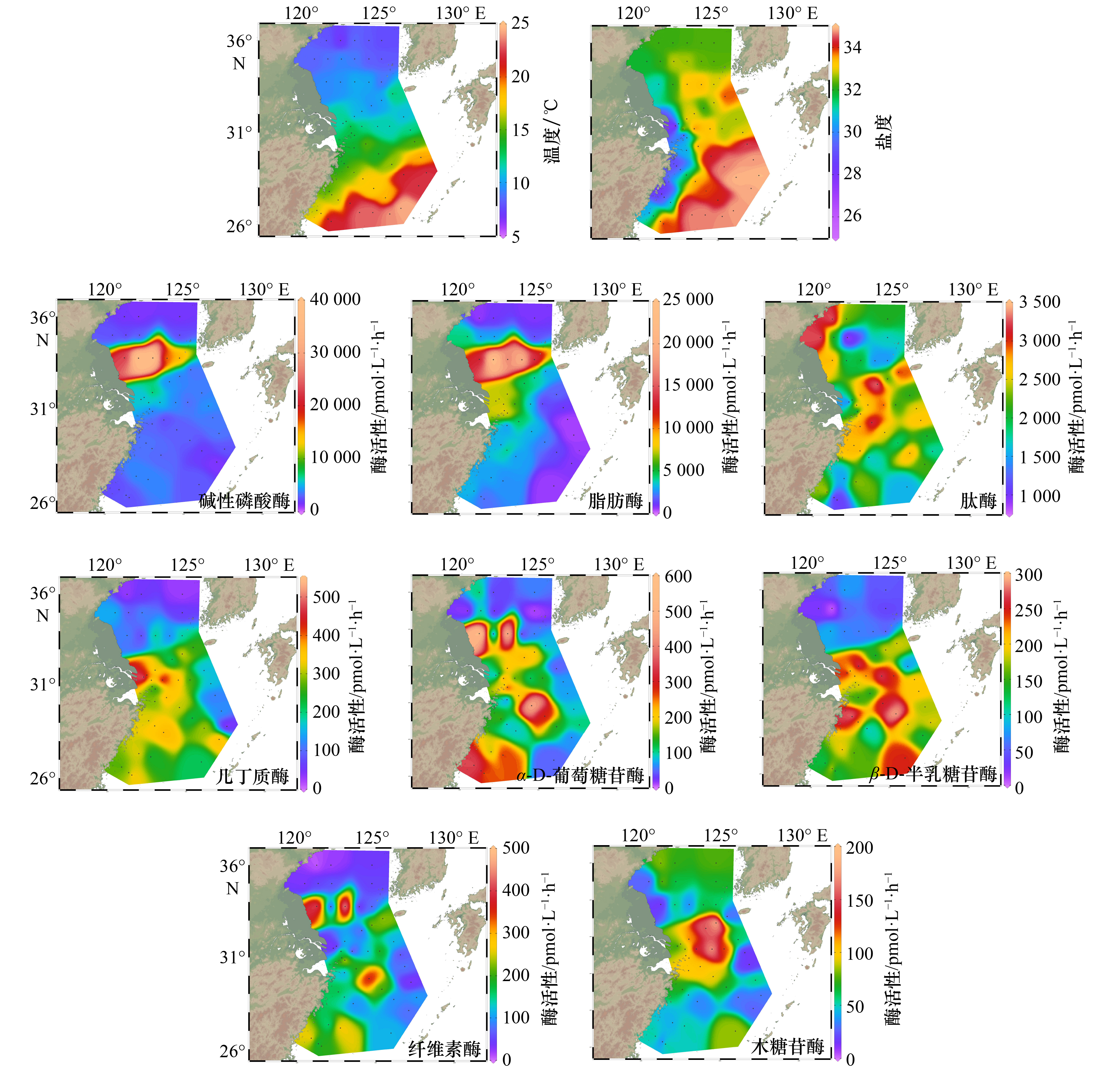
Horizontal distribution of extracellular enzyme activities in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea in spring
-
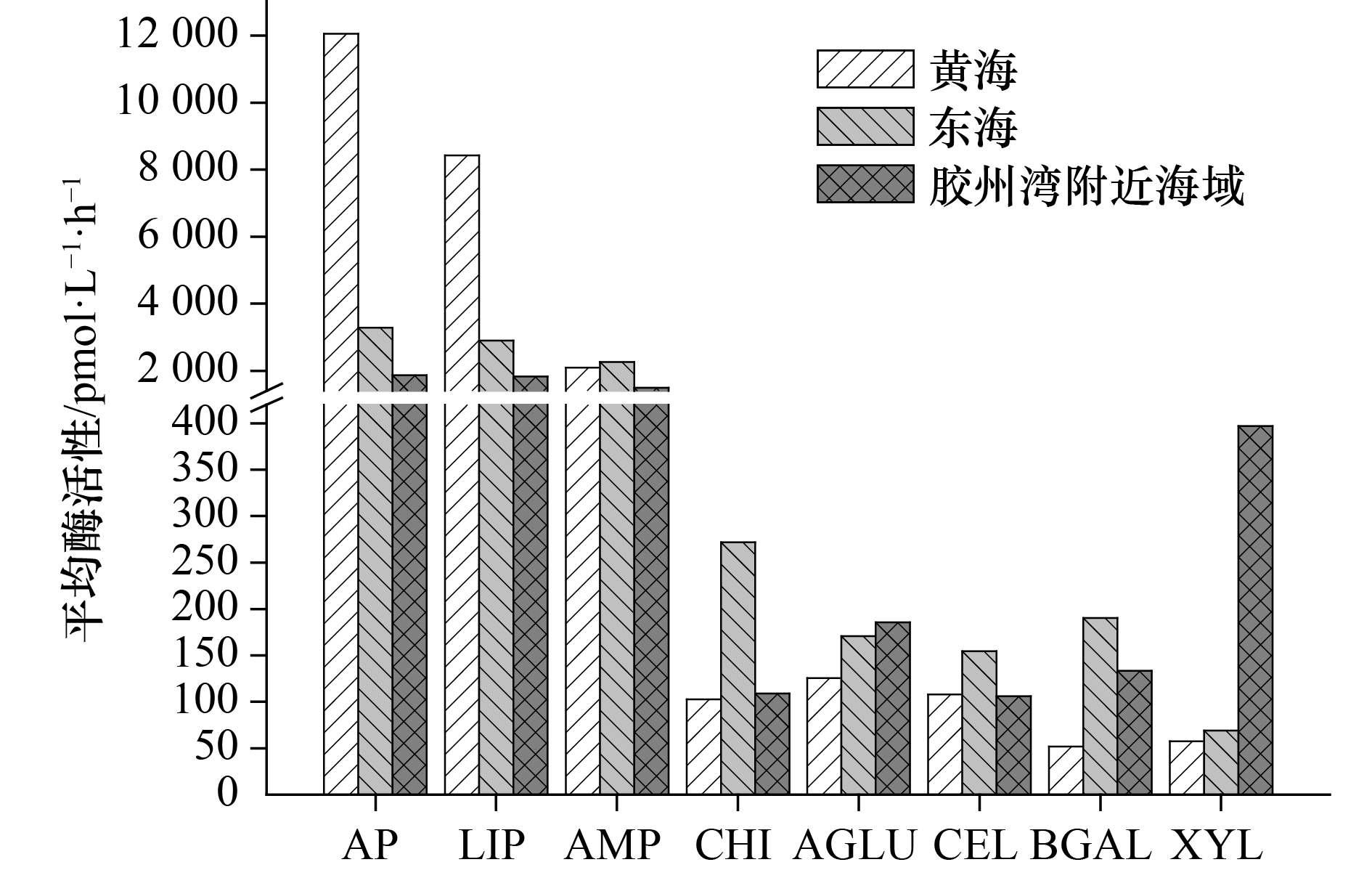
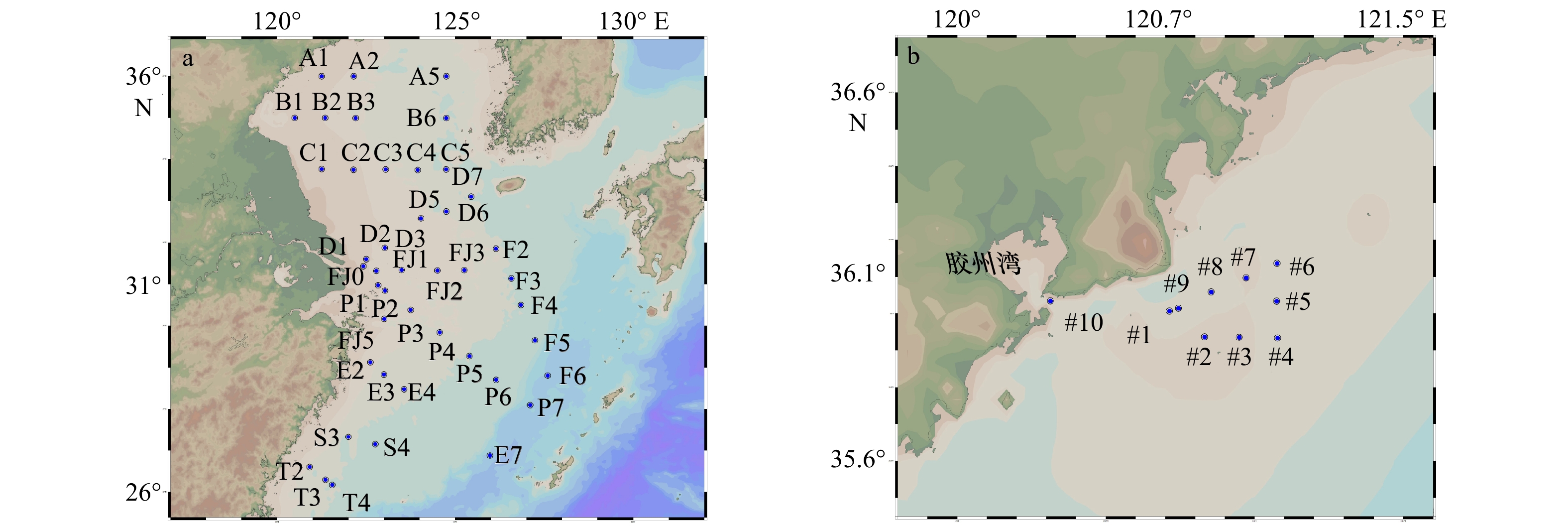
摘要: 海水胞外酶活性可以指示有机物的分布特征以及微生物的营养状况。我们测定了2017年3月25日至4月15日黄海和东海44个大面站以及2018年4月28日至29日胶州湾湾口附近海域10个站位表层海水中的8种胞外酶活性并研究了其分布特征。2017年春季黄、东海表层海水中碱性磷酸酶和脂肪酶活性较高,高值区出现在苏北沿岸和南黄海中部,碱性磷酸酶与磷酸盐浓度之间呈正相关。其余6种酶(肽酶、几丁质酶、纤维素酶、α-D-葡萄糖苷酶、β-D-半乳糖苷酶、木糖苷酶)活性高值区出现在长江口以东的外海,东海的β-D-半乳糖苷酶、木糖苷酶平均酶活性显著高于黄海。8种酶活性平均值排列顺序由大到小为:碱性磷酸酶、脂肪酶、肽酶、几丁质酶、α-D-葡萄糖苷酶、β-D-半乳糖苷酶、纤维素酶、木糖苷酶,其中α-D-葡萄糖苷酶和β-D-半乳糖苷酶的活性基本一致。2018年春季胶州湾附近海域海水中碱性磷酸酶、脂肪酶、木糖苷酶活性分布为近岸高于远岸,几丁质酶活性为近岸低于远岸。8种酶活性平均值排列顺序由大到小为:碱性磷酸酶、脂肪酶、肽酶、木糖苷酶、α-D-葡萄糖苷酶、β-D-半乳糖苷酶、几丁质酶、纤维素酶,其中几丁质酶和纤维素酶的活性基本一致。黄海的碱性磷酸酶和脂肪酶平均酶活性均显著高于东海和胶州湾附近海域。糖类水解酶(几丁质酶、纤维素酶、α-D-葡萄糖苷酶、β-D-半乳糖苷酶、木糖苷酶)平均酶活性在黄海最低。本文的结果对于理解中国近海海水有机碳的分布、浮游植物及异养细菌对有机碳的降解具有重要意义。Abstract: The extracellular enzyme activity of seawater can indicate the distribution characteristics of organic and the nutritional status of microorganisms. Activities of eight extracellular enzymes, including alkaline phosphatase, lipase, leucine aminopeptidase, chitinase, cellulose, xylosidase, α-D-glucosidase and β-D-galactosidase, were measured in the surface seawaters collected from 44 stations of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea from March 25 to April 15, 2017 and from 10 stations of the Jiaozhou Bay nearby waters from April 28 to 29, 2018. In the spring of 2017, the high-value areas of alkaline phosphatase and lipase appeared in the northern coast of Jiangsu and the middle of the Yellow Sea, alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphate concentration were positively correlated. High activity areas of the other six enzymes (leucine aminopeptidase, chitinase, cellulose, xylosidase, α-D-glucosidase and β-D-galactosidase) appeared in the open sea outside the east of the Changjiang River Estuary. The average activities of β-D-galactosidase and xylosidase were significantly higher in the East China Sea than in the Yellow Sea. The decreasing order of average enzyme activities of the eight enzymes was as follows: alkaline phosphatase, lipase, leucine aminopeptidase, chitinase, α-D-glucosidase, β-D-galactosidase, cellulose, xylosidase, the values of α-D-glucosidase and β-D-galactosidase are proximate. The activities of alkaline phosphates, lipase and xylosidase in the Jiaozhou Bay nearby waters in spring 2018 decreased from nearshore to far shore. The decreasing order of the average enzyme activity of the eight enzymes was as follows: alkaline phosphatase, lipase, leucine aminopeptidase, xylosidase, α-D-glucosidase, β-D-galactosidase, cellulose, chitinase, the values of cellulose and chitinase are proximate. The alkaline phosphatase and lipase activities in the Yellow Sea were significantly higher than those in the East China Sea and Jiaozhou Bay. The average enzymatic activities of polysaccharide hydrolases (chitinase, cellulose, α-D-glucosidase, β-D-galactosidase and xylosidase) were the lowest in the Yellow Sea compared with those in the East China Sea and Jiaozhou Bay nearby waters. Our results are beneficial to understand the degradation of organic carbon by plankton and heterotrophic bacteria and the distribution of marine organic carbon in the coastal water of China.
-
Key words:
- extracellular enzyme activity /
- alkaline phosphatase /
- leucine aminopeptidase /
- lipase
-
表 1 2017年春季黄、东海表层海水温度、盐度和胞外酶活性的变化范围及平均值
Tab. 1 Variation and average of temperatures, salinities and eight extracellular enzyme activities in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea during spring 2017
温度/℃ 盐度 酶活性/pmol·L−1·h−1 AP LIP AMP CHI AGLU BGAL CEL XYL 变化范围 6.91~24.47 25.81~34.94 1 313~38 530 424~23 473 850~3 355 29~547 9~558 2~290 10~456 14~185 平均值 14.00 32.59 5 891±8 186 4 760±5 268 2 241±729 235±131 155±184 155±97 136±113 71±50 注:±表示标准偏差。 表 2 2018年春季胶州湾附近海域表层海水温度、盐度和胞外酶活性的变化范围及平均值
Tab. 2 Variation and average of temperatures, salinities and eight extracellular enzyme activities in the Jiaozhou Bay nearby waters during spring 2018
温度/℃ 盐度 酶活性/pmol·L−1·h−1 AP LIP AMP XYL AGLU BGAL CHI CEL 变化范围 9.41~11.29 31.92~32.33 0~4 621 473~4 442 792~2 050 14~1 142 18~346 12~423 0~366 0~386 平均值 10.55 32.15 1 865±1 332 1 821±1 124 1 499±417 397±304 186±112 133±116 109±126 106±156 注:±表示标准偏差。 表 3 2017年春季黄、东海和2018年春季胶州湾附近海域8种胞外酶活性之间的相关性分析
Tab. 3 Correlation analysis between eight extracellular enzyme activities of the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea during spring 2017 and the Jiaozhou Bay nearby waters during spring 2018
AP LIP AMP CHI AGLU BGAL CEL XYL 黄、东海 AP 1 LIP 0.883** 1 AMP −0.110 −0.115 1 CHI −0.191 −0.045 0.001 1 AGLU 0.292 0.199 0.165 0.165 1 BGAL −0.280 −0.250 0.112 0.606** 0.195 1 CEL 0.314* 0.190 0.152 0.157 0.862** 0.180 1 XYL −0.161 −0.018 0.236 0.289 0.024 0.270 −0.033 1 胶州湾附近海域 AP 1 LIP 0.369 1 AMP −0.441 0.313 1 CHI −0.306 −0.418 −0.207 1 AGLU −0.606 0.093 0.546 0.322 1 BGAL −0.122 −0.396 0.043 0.461 0.271 1 CEL 0.116 0.611 0.394 −0.528 0.049 −0.344 1 XYL 0.817** 0.314 −0.208 −0.429 −0.524 0.028 0.241 1 注:**表示p<0.01;*表示p<0.05。 表 4 温度、盐度及Chl a与8种胞外酶活性的相关性分析
Tab. 4 Relationship between temperature, salinity, Chl a and eight extracellular enzyme activities
胞外酶 黄、东海 胶州湾附近海域 温度 盐度 Chl a 温度 盐度 AP −0.283 −0.069 −0.165 0.511 −0.488 LIP −0.360* −0.214 −0.135 0.146 −0.851** AMP −0.204 0.103 0.032 −0.561 −0.042 CHI 0.326* −0.193 −0.018 0.063 0.500 AGLU 0.136 0.070 −0.038 −0.203 −0.014 BGAL 0.412** 0.011 −0.033 −0.315 0.376 CEL 0.159 0.072 −0.012 −0.476 −0.598 XYL −0.291 −0.106 0.082 0.180 −0.477 注: **表示p<0.01;*表示p<0.05。 -
[1] Thurman E M. Organic geochemistry of natural waters[M]//Organic Geochemistry of Natural Waters. Dordrecht: Springer, 1985: 425−440. [2] Azam F, Fenchel T, Field J G, et al. The ecological role of water-column microbes in the sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1983, 10(3): 257−263. [3] Hagström Å, Azam F, Andersson A, et al. Microbial loop in an oligotrophic pelagic marine ecosystem: possible roles of cyanobacteria and nanoflagellates in the organic fluxes[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1988, 49(1/2): 171−178. [4] Chróst R J, Münster U, Rai H, et al. Photosynthetic production and exoenzymatic degradation of organic matter in the euphotic zone of a eutrophic lake[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1989, 11(2): 223−242. doi: 10.1093/plankt/11.2.223 [5] Vetter Y A, Deming J W. Extracellular enzyme activity in the Arctic Northeast Water Polynya[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1994, 114(1/2): 23−34. [6] Chróst R J. Microbial ectoenzymes in aquatic environments[M]//Overbeck J, Chróst R J. Aquatic Microbial Ecology. New York: Springer, 1990: 47-78. [7] Garde K, Gustavson K. The impact of UV-B radiation on alkaline phosphatase activity in phosphorus-depleted marine ecosystems[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 1999, 238(1): 93−105. doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(99)00005-2 [8] 洪华生, 戴民汉, 郑效成. 海水中碱性磷酸酶活力的测定及其在磷的循环中的作用初探[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1992, 23(4): 415−420.Hong Huasheng, Dai Minhan, Zheng Xiaocheng. Measurement of alkaline phosphatase activity in sea water substrates and investigation on the role of alkaline phosphatase in the cycling of phosphorus[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1992, 23(4): 415−420. [9] Duhamel S, Dyhrman S T, Karl D M. Alkaline phosphatase activity and regulation in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2010, 55(3): 1414−1425. doi: 10.4319/lo.2010.55.3.1414 [10] Biche S U, Das A, Mascarenhas-Pereira M B L, et al. Alkaline phosphatase: an appraisal of its critical role in C-limited deep-sea sediments of central Indian Basin[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 2017, 34(3): 274−288. doi: 10.1080/01490451.2016.1190804 [11] 姜经梅, 赵慧, 沈铭能, 等. 长江口潮滩表层沉积物中碱性磷酸酶活性及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31(10): 2233−2239.Jiang Jingmei, Zhao Hui, Shen Mingneng, et al. Distribution and impact factor of alkaline phosphatase activity in the intertidal surface sediments of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31(10): 2233−2239. [12] 周易勇, 李建秋, 陈旭东, 等. 东湖溶解态磷酸酶的活性、动力学特征及其空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 1997, 18(5): 37−40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1997.05.010Zhou Yiyong, Li Jianqiu, Chen Xudong, et al. Activity, kinetics and spatial variation of dissolved alkaline phosphatase in lake Donghu[J]. Environmental Science, 1997, 18(5): 37−40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1997.05.010 [13] 宋春雷, 曹秀云, 李建秋, 等. 湖泊磷酸酶与微生物活性对内源磷负荷的贡献及其与富营养化的关系[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2006, 49(S2): 102−113.Song Chunlei, Cao Xiuyun, Li Jianqiu, et al. Contributions of phosphatase and microbial activity to internal phosphorus loading and their relation to lake eutrophication[J]. Science in China Series D, 2006, 49(S2): 102−113. [14] Ivančić I, Fuks D, Radić T, et al. Phytoplankton and bacterial alkaline phosphatase activity in the northern Adriatic Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2010, 69(2): 85−94. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.08.004 [15] Duhamel S, Björkman K M, van Wambeke F, et al. Characterization of alkaline phosphatase activity in the North and South Pacific Subtropical Gyres: implications for phosphorus cycling[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2011, 56(4): 1244−1254. doi: 10.4319/lo.2011.56.4.1244 [16] Hashimoto S, Fujiwara K, Fuwa K. Relationship between alkaline phosphatase activity and orthophosphate in the present Tokyo Bay[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part A: Environmental Science and Engineering, 1985, 20(7): 781−809. doi: 10.1080/10934528509375258 [17] Koike I, Nagata T. High potential activity of extracellular alkaline phosphatase in deep waters of the central Pacific[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 1997, 44(9/10): 2283−2294. [18] 黄邦钦, 洪华生, 薛雄志. 厦门西海域水体中碱性磷酸酶活力分布及其影响因子分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2000, 22(1): 62−68.Huang Bangqin, Hong Huasheng, Xue Xiongzhi. Distribution and controlling factors of alkaline phosphatase activity in western Xiamen waters[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2000, 22(1): 62−68. [19] Arrieta J M, Herndl G J. Changes in bacterial β-glucosidase diversity during a coastal phytoplankton bloom[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2002, 47(2): 594−599. doi: 10.4319/lo.2002.47.2.0594 [20] Brown S E, Goulder R. Extracellular-enzyme activity in trout-farm effluents and a recipient river[J]. Aquaculture Research, 1996, 27(12): 895−901. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.1996.tb01249.x [21] Caruso G. Leucine aminopeptidase, β-glucosidase and alkaline phosphatase activity rates and their significance in nutrient cycles in some coastal mediterranean sites[J]. Marine Drugs, 2010, 8(4): 916−940. doi: 10.3390/md8040916 [22] 郑天凌, 王斐, 徐美珠, 等. 台湾海峡水域的β-葡萄糖苷酶活性[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2001, 7(2): 175−182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2001.02.017Zheng Tianling, Wang Fei, Xu Meizhu, et al. β-glucosidase activity in the Taiwan Strait[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2001, 7(2): 175−182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687X.2001.02.017 [23] 宋福行. 胶州湾海水中胞外酶活性的动态变化及其调控因素的初步研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2001.Song Fuxing. Preliminary study on the extracellular enzymatic activity and the affecting factors in the Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2001. [24] 赵丽军, 田继远, 于娟, 等. 2013年秋末黄渤海海水中胞外酶活性水平和垂直变化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(7): 2171−2181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.043Zhao Lijun, Tian Jiyuan, Yu Juan, et al. Horizontal and vertical variations of activities of extracellular enzymes in the seawater of the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea in late autumn, 2013[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(7): 2171−2181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.07.043 [25] Hoppe H G. Use of fluorogenic model substrates for Extracellular Enzyme Activity (EEA) measurement of bacteria[M]//Kemp P F, Sherr B F, Sherr E B, et al. Current Methods in Aquatic Microbial Ecology. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1993: 423−431. [26] Hoppe H G. Significance of exoenzymatic activities in the ecology of brackish water: measurements by means of methylumbelliferyl-substrates[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1983, 11: 299−308. doi: 10.3354/meps011299 [27] Parsons T R, Maita Y, Lalli C M. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1984: 23−58. [28] Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M. Methods of Seawater Analysis[M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 1999: 159−228. [29] Holmes R M, Aminot A, Kérouel R, et al. A simple and precise method for measuring ammonium in marine and freshwater ecosystems[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1999, 56(10): 1801−1808. doi: 10.1139/f99-128 [30] 周易勇, 付永清. 水体磷酸酶: 来源、特征及其生态学意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 1999, 11(3): 274−282. doi: 10.18307/1999.0313Zhou Yiyong, Fu Yongqing. Phosphatases in natural water: origin, characteristics and ecological significance[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1999, 11(3): 274−282. doi: 10.18307/1999.0313 [31] Huang Bangqin, Huang Shiyu, Weng Yan, et al. Effect of dissolved phosphorus on alkaline phosphatase activity in marine microalgae[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2000, 19(2): 29−35. [32] Perry M J. Alkaline phosphatase activity in subtropical Central North Pacific waters using a sensitive fluorometric method[J]. Marine Biology, 1972, 15(2): 113−119. doi: 10.1007/BF00353639 [33] Taga N, Kobori H. Phosphatase activity in Eutrophic Tokyo Bay[J]. Marine Biology, 1978, 49(3): 223−228. doi: 10.1007/BF00391134 [34] Jones J G. Studies on freshwater bacteria: association with algae and alkaline phosphatase activity[J]. Journal of Ecology, 1972, 60(1): 59−75. doi: 10.2307/2258040 [35] Jones J G. Studies on freshwater micro-organisms: phosphatase activity in lakes of differing degrees of eutrophication[J]. Journal of Ecology, 1972, 60(3): 777−791. doi: 10.2307/2258564 [36] 王保栋, 王桂云, 郑昌洙, 等. 南黄海营养盐的平面分布及横向输运[J]. 海洋学报, 1999, 21(6): 124−129.Wang Baodong, Wang Guiyun, Zheng Changzhu, et al. Horizontal distributions and transportation of nutrients in the southern Huanghai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1999, 21(6): 124−129. [37] Li Hongmei, Zhang Chuansong, Han Xiurong, et al. Changes in concentrations of oxygen, dissolved nitrogen, phosphate, and silicate in the southern Yellow Sea, 1980−2012: sources and seaward gradients[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 44−55. [38] Chróst R J. Environmental control of the synthesis and activity of aquatic microbial ectoenzymes[M]//Chróst R J. Microbial Enzymes in Aquatic Environments. New York: Springer, 1991: 29−59. [39] Kalwasińska A, Brzezinska M S. Extracellular enzymatic activities in subsurface water of eutrophic Lake Chełmżyńskie, Poland[J]. Journal of Freshwater Ecology, 2013, 28(4): 517−527. doi: 10.1080/02705060.2013.793220 [40] 谷体华, 王丹, 林丽贞, 等. 台湾海峡南部上升流区亮氨酸氨肽酶活性的初步研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2008, 32(12): 42−46.Gu Tihua, Wang Dan, Lin Lizhen, et al. Preliminary study on Leucine aminopeptidase activity in the upwelling region of the Southern Taiwan Straits[J]. Marine Sciences, 2008, 32(12): 42−46. [41] Williams C J, Jochem F J. Ectoenzyme kinetics in Florida Bay: implications for bacterial carbon source and nutrient status[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2006, 569: 113−127. doi: 10.1007/s10750-006-0126-z [42] Mudryk Z J, Skórczewski P. Extracellular enzyme activity at the air-water interface of an estuarine lake[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 59(1): 59−67. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2003.08.001 [43] Chróst R J. Characterization and significance of β-glucosidase activity in lake water[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1989, 34(4): 660−672. doi: 10.4319/lo.1989.34.4.0660 [44] Rulík M, Spáčil R. Extracellular enzyme activity within hyporheic sediments of a small lowland stream[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2004, 36(10): 1653−1662. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.005 [45] 胡春, 陈岩, 杨桂朋, 等. 2017年春季黄东海碳水化合物的分布特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(6): 848−855. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190605Hu Chun, Chen Yan, Yang Guipeng, et al. Study on the distribution of dissolved carbohydrates in the South Yellow Sea and the East China Sea during spring[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(6): 848−855. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190605 [46] Tholosan O, Lamy F, Garcin J, et al. Biphasic extracellular proteolytic enzyme activity in benthic water and sediment in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 1999, 65(4): 1619−1626. doi: 10.1128/AEM.65.4.1619-1626.1999 [47] Unanue M, Ayo B, Agis M, et al. Ectoenzymatic activity and uptake of monomers in marine bacterioplankton described by a biphasic kinetic model[J]. Microbial Ecology, 1999, 37(1): 36−48. doi: 10.1007/s002489900128 -




 下载:
下载: