Tidal and seasonal asymmetry of suspended sediment concentration in branched channels of the Changjiang River Estuary
-
摘要: 入海河口由于径流的存在以及河口地貌形态的影响,存在涨、落潮水动力、悬沙以及盐度分布等不对称现象,同时这一不对称现象还存在显著的区域性和季节性差异。根据2013年7月和2014年1月洪、枯季长江口定点准同步水文泥沙调查结果,发现长江口分汊型河槽悬沙浓度在时间上存在洪枯季、大小潮不对称特征,在空间上存在东西向沿程分布、南北向横向分布以及垂向上表底层分布不对称特征。河势演变形成南、北支河口涨、落潮悬沙浓度不对称分布的整体格局;洪、枯季变化影响河口涨、落潮悬沙分布的再分配过程;大潮涨、落潮过程对悬沙分布不对称影响显著大于小潮;季节性风浪作用影响河口最大浑浊带涨、落潮悬沙不对称南北差异;底部高含沙浓度对口门段涨、落潮悬沙不对称性贡献显著。Abstract: Due to the influence of runoff and estuarine morphology, asymmetrical phenomena of hydrodynamics, suspended sediment concentration (SSC) and salinity occurs between the flooding and ebbing stage in the estuary. Such a phenomena also shows significant regional and seasonal differences. Based on hydrological survey in July 2013 and January 2014 in the Changjiang River Estuary, it is found that suspended sediment concentration in the branched channels of the Changjiang River Estuary has asymmetric characteristics, which varies with flood and dry season as well as spring and neap tide. In terms of spatial variability, there exists along channel difference, inter-channel difference as well as water colume difference. The evolution of the estuary controlls the overall SSC difference between the North Branch and South Branch. The flood and dry seasons affect the redistribution process of SSC in the estuary. Spring tides has a stronger impact on SSC asymmetry than that of neap tides. Theseasonal wave condition affect the SSC asymmetric distribution in the turbidity maximum zone of the estuary along the north-south direction. The high sediment concentration near the bottom contributes significantly to the SSC asymmetry between flooding and ebbing stages at the river mouth.
-
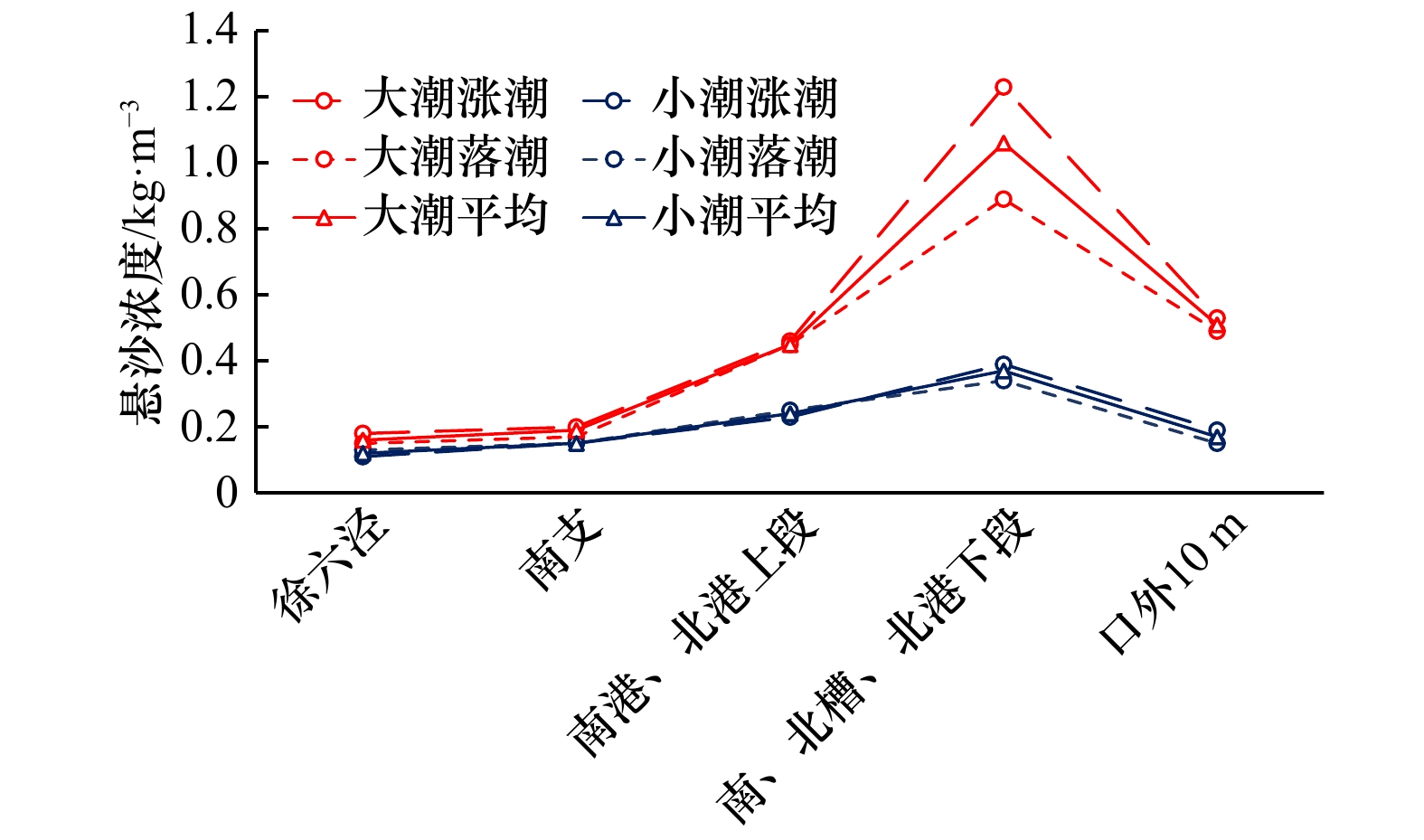
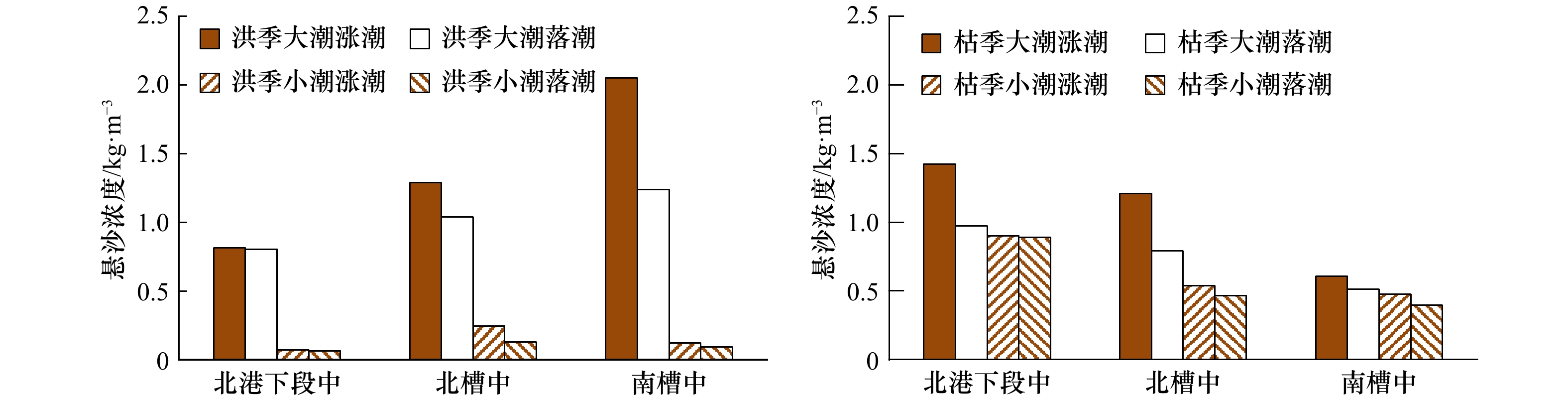
表 1 长江河口典型河槽悬沙浓度分布(单位:kg/m3)
Tab. 1 Suspended sediment concentration in the typical channels of Changjiang River Estuary(unit: kg/m3)
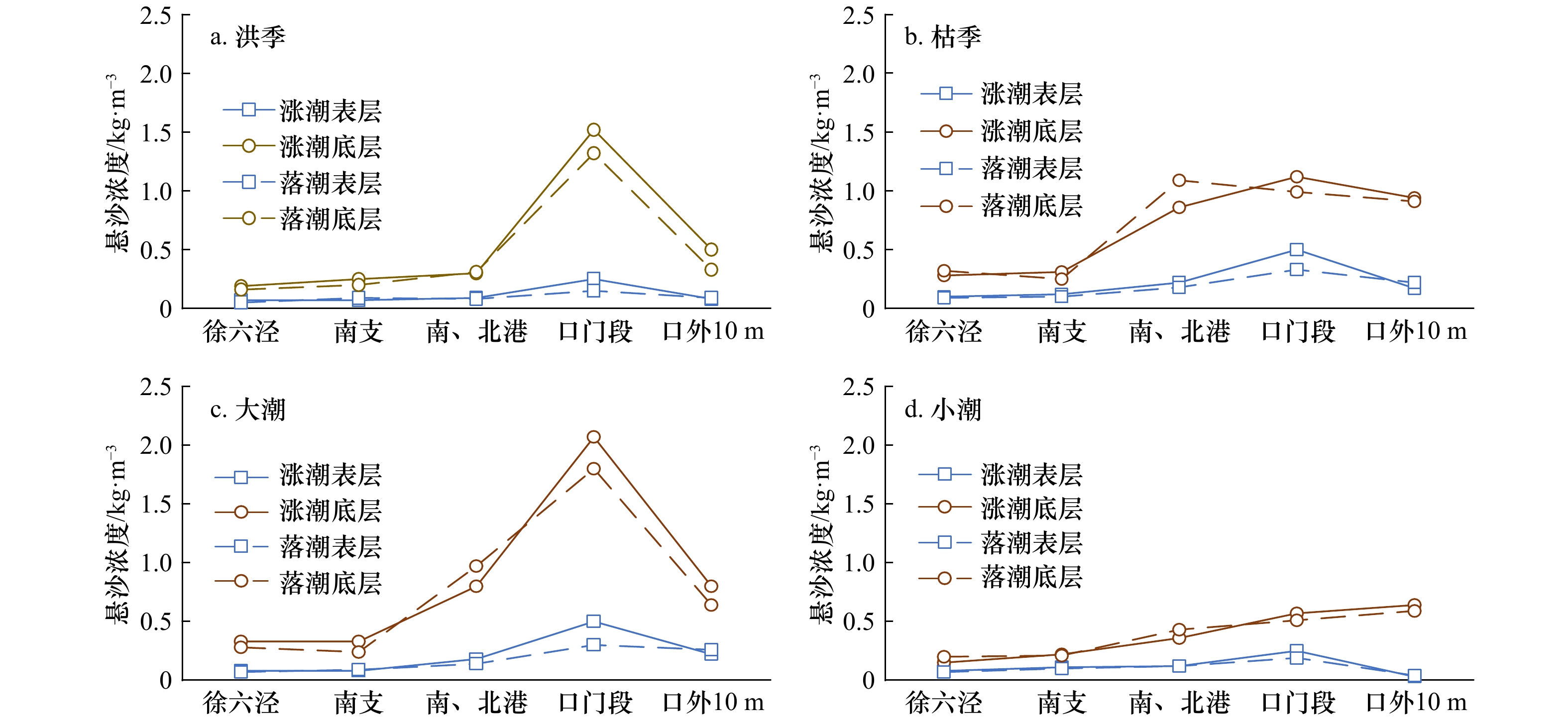
徐六泾 北支中段 北支下段 南支 南港和北港上段 南、北槽和北港下段 口外10 m线 洪季 0.10 1.29 0.62 0.15 0.19 0.65 0.22 枯季 0.18 1.17 0.41 0.19 0.51 0.76 0.47 大潮 0.16 1.56 0.89 0.18 0.45 1.05 0.51 小潮 0.12 0.90 0.14 0.15 0.24 0.36 0.18 平均 0.14 1.23 0.51 0.17 0.35 0.71 0.34 表 2 长江口南、北支河口涨、落潮含沙量分布(单位:kg/m3)
Tab. 2 Distribution of suspended sediment concentration between flood and ebb in the south and north branches of the Changjiang River Estuary (unit: kg/m3)
洪季
涨潮枯季
涨潮涨潮
平均洪季
落潮枯季
落潮落潮
平均平均 徐六泾 0.11 0.18 0.14 0.10 0.18 0.14 0.14 北支河口 1.08 0.82 0.95 0.85 0.77 0.81 0.88 南支河口 0.47 0.63 0.55 0.37 0.54 0.45 0.50 口外10 m 0.24 0.49 0.36 0.19 0.45 0.32 0.34 表 3 长江口洪、枯季涨、落潮盐度分布
Tab. 3 Distribution of salinity between flood and ebb of flood and dry seasons of the Changjiang River Estuary
徐六泾 南支上段 南港、
北港上段南槽、北槽、
北港下段口外
10 m线洪季涨潮 0.2 0.2 0.2 6.6 25.6 洪季落潮 0.2 0.2 0.2 9.1 25.3 洪季平均 0.2 0.2 0.2 7.9 25.4 枯季涨潮 0.2 0.9 0.6 12.9 25.3 枯季落潮 0.2 0.9 0.8 15.1 25.5 枯季平均 0.2 0.9 0.7 14.0 25.4 表 4 长江口典型河槽潮差分布(单位:m)
Tab. 4 Distribution of tidal range in the typical channels of the Changjiang River Estuary (unit: m)
徐六泾 南支上段 南港、
北港上段南槽、北槽、
北港下段口外
10 m线洪季大潮 2.88 3.33 3.36 3.49 3.85 枯季大潮 2.55 2.93 3.24 2.96 3.60 大潮平均 2.71 3.13 3.30 3.23 3.73 洪季小潮 2.28 2.13 1.19 1.41 1.88 枯季小潮 2.05 2.20 2.16 2.21 1.88 小潮平均 2.17 2.16 1.67 1.81 1.88 -
[1] Huang Haosheng, Chen Changsheng, Blanton J O, et al. A numerical study of tidal asymmetry in Okatee Creek, South Carolina[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2008, 78(1): 190−202. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2007.11.027 [2] 王彪, 朱建荣, 李路. 长江河口涨落潮不对称性动力成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(3): 19−27.Wang Biao, Zhu Jianrong, Li Lu. A study on the dynamics of the asymmetry between flood and ebb in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2011, 33(3): 19−27. [3] 李谊纯, 董德信, 陈波. 河口往复流中潮流不对称与推移质输沙的关系[J]. 海洋科学, 2015, 39(6): 99−103. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130410007Li Yichun, Dong Dexin, Chen Bo. A study on the relationship between tidal asymmetry and bed-load transport in estuarine rectilinear current[J]. Marine Sciences, 2015, 39(6): 99−103. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130410007 [4] Li Zhanhai, Wang Yaping, Cheng Peng, et al. Flood-ebb asymmetry in current velocity and suspended sediment transport in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(10): 37−47. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0923-9 [5] 张钊. 长江口南槽悬沙输运涨落潮不对称研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017.Zhang Zhao. Flood-ebb asymmetry in suspended sediment transport in the South Passage of the Changjiang Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2017. [6] 沈焕庭, 潘定安. 长江河口潮流特性及其对河槽演变的影响[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 1979(1): 131−144.Shen Huanting, Pan Ding’an. The characteristics of tidal current and its effects on the channel changes of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 1979(1): 131−144. [7] 杜家笔, 裴艳东, 高建华, 等. 弱动力浅海中的悬沙输运机制: 以天津港附近海域为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(1): 136−144.Du Jiabi, Pei Yandong, Gao Jianhua, et al. The suspended sediment transport associated with low flow patterns in shallow waters: a case study from the Tianjin subtidal area[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(1): 136−144. [8] 沈逸, 何青, 张迨, 等. 长江口浑浊带北槽悬沙输运研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(1): 16−23.Shen Yi, He Qing, Zhang Dai, et al. Study on transport of suspended sediment in the Turbidity Maximum Zone in the North Passage of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(1): 16−23. [9] 陈沈良, 谷国传, 张国安. 长江口南汇近岸水域悬沙沉降速度估算[J]. 泥沙研究, 2003(6): 45−51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.008Chen Shenliang, Gu Guochuan, Zhang Guo'an. Settling velocity of suspended sediment in the Nanhui nearshore waters of Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2003(6): 45−51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.008 [10] 杨云平, 李义天, 王冬, 等. 长江口悬沙有效沉速时空变化规律[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2012(5): 24−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2012.05.005Yang Yunping, Li Yitian, Wang Dong, et al. Space-time variation in effective settling velocity of suspended sediment in Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2012(5): 24−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2012.05.005 [11] 陈沈良, 张国安, 杨世伦, 等. 长江口水域悬沙浓度时空变化与泥沙再悬浮[J]. 地理学报, 2004, 59(2): 260−266. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.02.012Chen Shenliang, Zhang Guo'an, Yang Shilun, et al. Temporal and spatial changes of suspended sediment concentration and resuspension in the Yangtze River Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2004, 59(2): 260−266. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2004.02.012 [12] 时钟, 朱文蔚, 周洪强. 长江口北槽口外细颗粒悬沙沉降速度[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2000, 34(1): 18−22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2000.01.005Shi Zhong, Zhu Wenwei, Zhou Hongqiang. Settling velocity of fine suspended sediment in the Changjiang estuary[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2000, 34(1): 18−22. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-2467.2000.01.005 [13] 沈焕庭, 张超, 茅志昌. 长江入河口区水沙通量变化规律[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2000, 31(3): 288−294. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.03.009Shen Huanting, Zhang Chao, Mao Zhichang. Patterns of variations in the water and sediment fluxes from the Changjiang River to the estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2000, 31(3): 288−294. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2000.03.009 [14] 张国安, 虞志英, 何青, 等. 长江口深水航道治理一期工程前后泥沙运动特性初步分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 2003(6): 31−38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.006Zhang Guo'an, Yu Zhiying, He Qing, et al. Primary analysis on sediment motion before & after 1st phase engineering of the deep waterways in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2003(6): 31−38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2003.06.006 [15] 左书华, 李九发, 万新宁, 等. 长江河口悬沙浓度变化特征分析[J]. 泥沙研究, 2006(3): 68−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.03.012Zuo Shuhua, Li Jiufa, Wan Xinning, et al. Characteristics of temporal and spatial variation of suspended sediment concentration in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2006(3): 68−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2006.03.012 [16] 陆叶峰, 杨世伦, 刘建华, 等. 长江口悬沙浓度时空变化研究——以2012年和2013年洪季为例[J]. 人民长江, 2015, 46(5): 19−25.Lu Yefeng, Yang Shilun, Liu Jianhua, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of suspended sediment concentration (SSC) in Yangtze Estuary: A case study on flood seasons of 2012 and 2013[J]. Yangtze River, 2015, 46(5): 19−25. [17] 何超, 丁平兴, 孔亚珍. 长江口及其邻近海域洪季悬沙分布特征分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2008(2): 15−21.He Chao, Ding Pingxing, Kong Yazhen. Analysis of temporal and spatial variation characteristics of suspended sediment concentration of the Yangtze estuary and adjacent sea areas in flood seasons[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2008(2): 15−21. [18] 张迨, 何青, 沈健, 等. 长江口浑浊带水沙特性研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2015(4): 31−37.Zhang Dai, He Qing, Shen Jian, et al. Study on flow and sediment transport of the turbidity zone in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2015(4): 31−37. [19] 戴志军, 朱文武, 李为华, 等. 近期长江口北槽河道浮泥变化及影响因素研究[J]. 泥沙研究, 2015(1): 49−54, 74.Dai Zhijun, Zhu Wenwu, Li Weihua, et al. Research on recent changes of fluid mud and its impacted factors in the north passage of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2015(1): 49−54, 74. [20] 时钟, 陈伟民. 长江口北槽最大浑浊带泥沙过程[J]. 泥沙研究, 2000(1): 28−39. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2000.01.005Shi Zhong, Chen Weimin. Fine sediment transport in turbidity maximum at the north passage of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2000(1): 28−39. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0468-155X.2000.01.005 [21] 杨世伦, 谢文辉, 朱骏, 等. 大河口潮滩地貌动力过程的研究——以长江口为例[J]. 地理学与国土研究, 2001, 17(3): 44−48.Yang Shilun, Xie Wenhui, Zhu Jun, et al. A study of intertidal flat morphodynamics of a large river mouth: Yangtze River mouth[J]. Geography and Territorial Research, 2001, 17(3): 44−48. [22] 张文祥, 杨世伦, 李鹏, 等. 基于OBS-3A、ADP-XR崇明东滩悬沙变化及动力过程研究[G]//2006年华东六省一市地学科技论坛论文集. 南昌: 中国地质学会, 江西省地质学会, 2006: 260-268.Zhang Wenxiang, Yang Shilun, Li Peng, et al. Measurement of variation in SSC and dynamic process using OBS-3A and ADP-XR in eastern chongming tidal flat[G]//Regional Science and Technology Forum of Six Provinces and One City in East China. Nanchang: Geological Society of China, Geological Society of Jiangxi Province, 2006: 260−268. [23] 王飞, 李九发, 李占海, 等. 长江口南槽河道水沙特性及河床沙再悬浮研究[J]. 人民长江, 2014, 45(13): 9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2014.13.005Wang Fei, Li Jiufa, Li Zhanhai, et al. Research on flow and sediment characteristics and bed sediment re-suspension in South Passage of Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Yangtze River, 2014, 45(13): 9−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2014.13.005 [24] 陈景东, 汪亚平, 史本伟, 等. 长江口北港口门海域悬沙输运机制分析[J]. 海洋工程, 2014, 32(3): 45−54.Chen Jingdong, Wang Yaping, Shi Benwei, et al. Mechanisms on the suspended sediment transport in the mouth of North Channel of Yangtze River estuary[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2014, 32(3): 45−54. [25] Yang Z, Wang H, Saito Y, et al. Dam impacts on the Changjiang (Yangtze) River sediment discharge to the sea: The past 55 years and after the Three Gorges Dam[J]. Water Resources Research, 2006, 42(4): W04407. [26] Yang S L, Zhang J, Xu X J. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on downstream delivery of sediment and its environmental implications, Yangtze River[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(10): L10401. [27] 高抒. 长江三角洲对流域输沙变化的响应: 进展与问题[J]. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25(3): 233−241.Gao Shu. Changjiang delta sedimentation in response to catchment discharge changes: progress and problems[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2010, 25(3): 233−241. [28] 韩乃斌, 卢中一. 长江口北支演变及治理的探讨[J]. 人民长江, 1984(3): 40−45.Han Naibin, Lu Zhongyi. Discussion on the evolution and control of the North Branch of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Yangtze River, 1984(3): 40−45. -





 下载:
下载: