Investigation into the spatial and temporal tide-river dynamics and the underlying controlled factors along the tidal reach of the Changjiang River
-
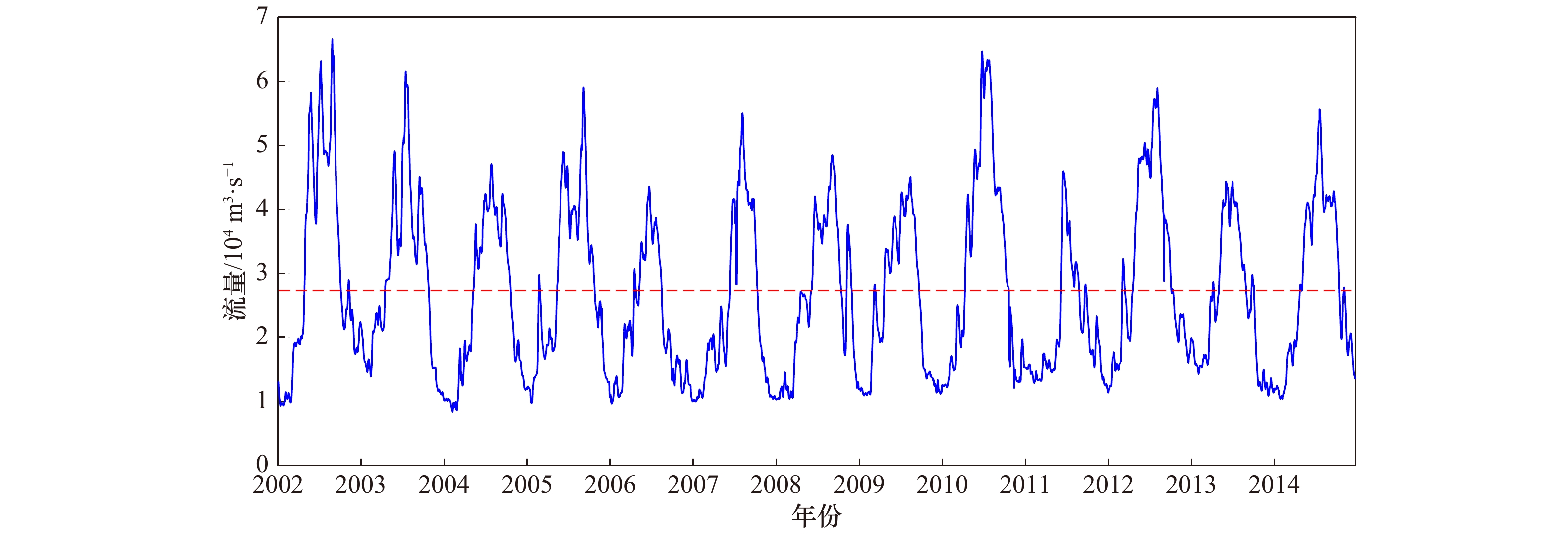
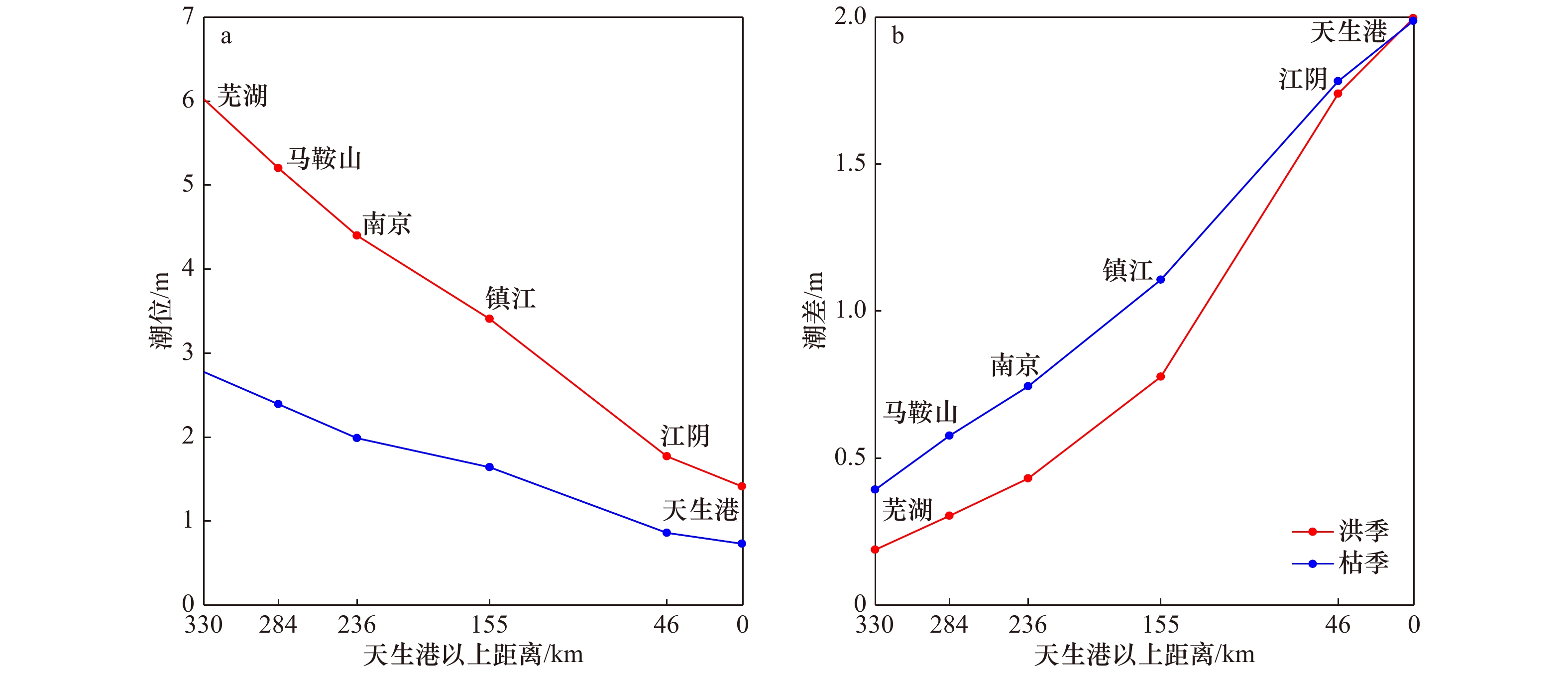
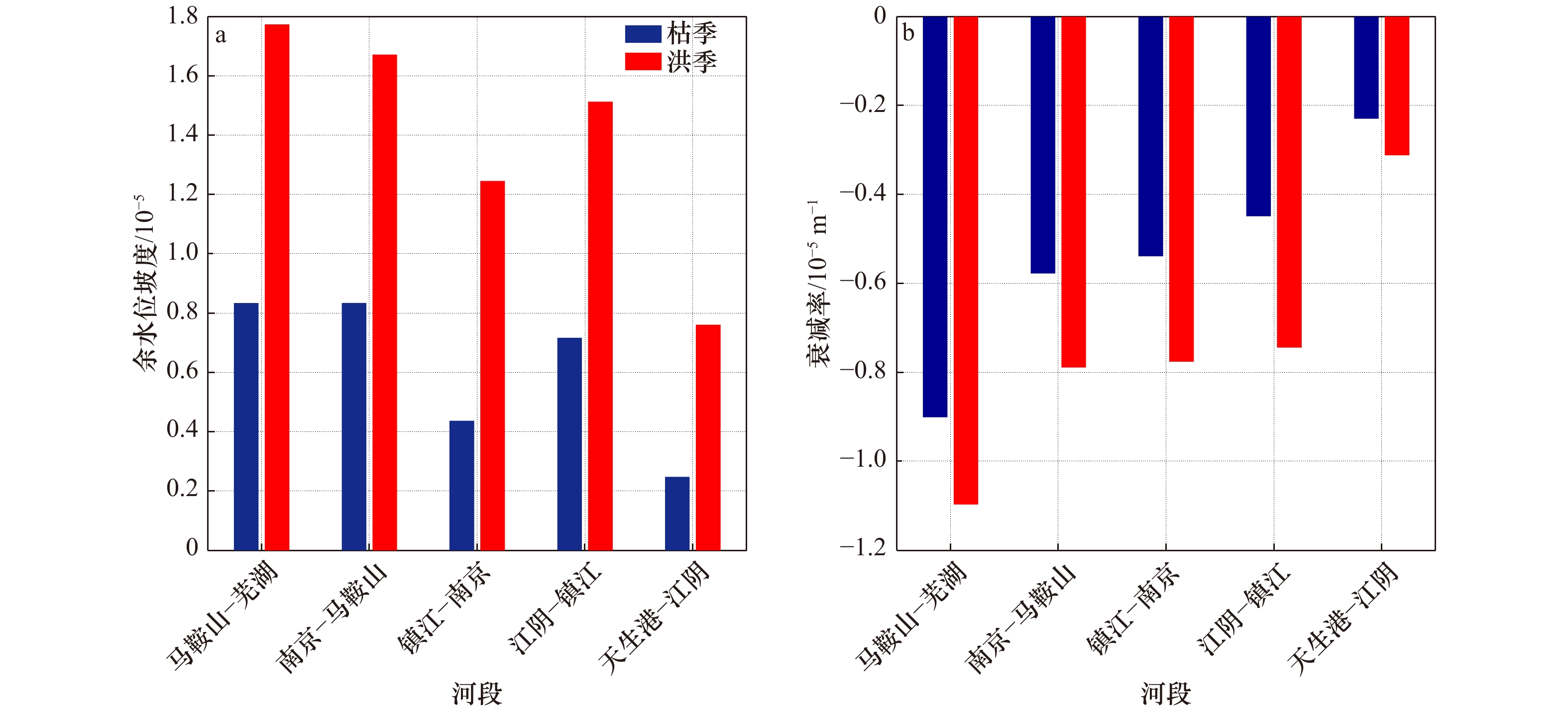
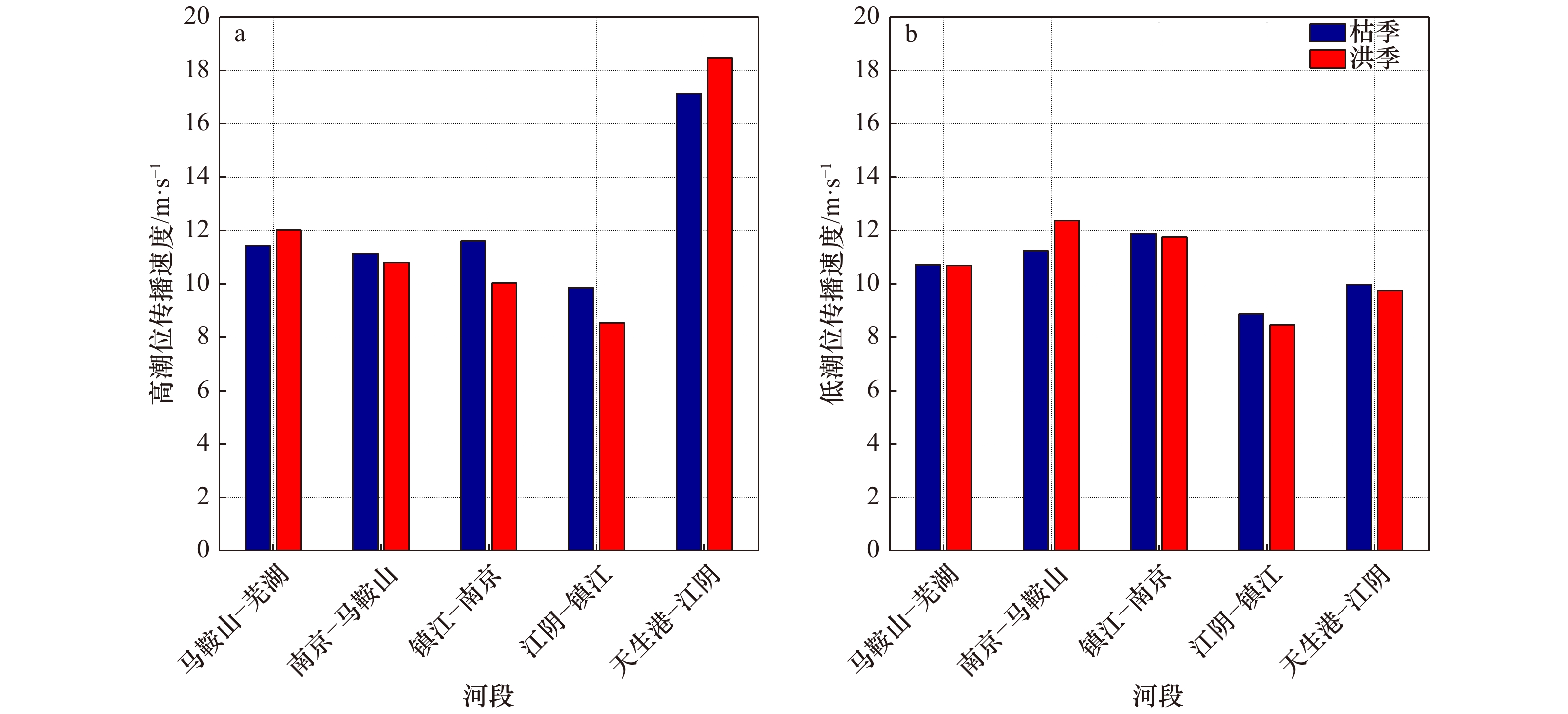
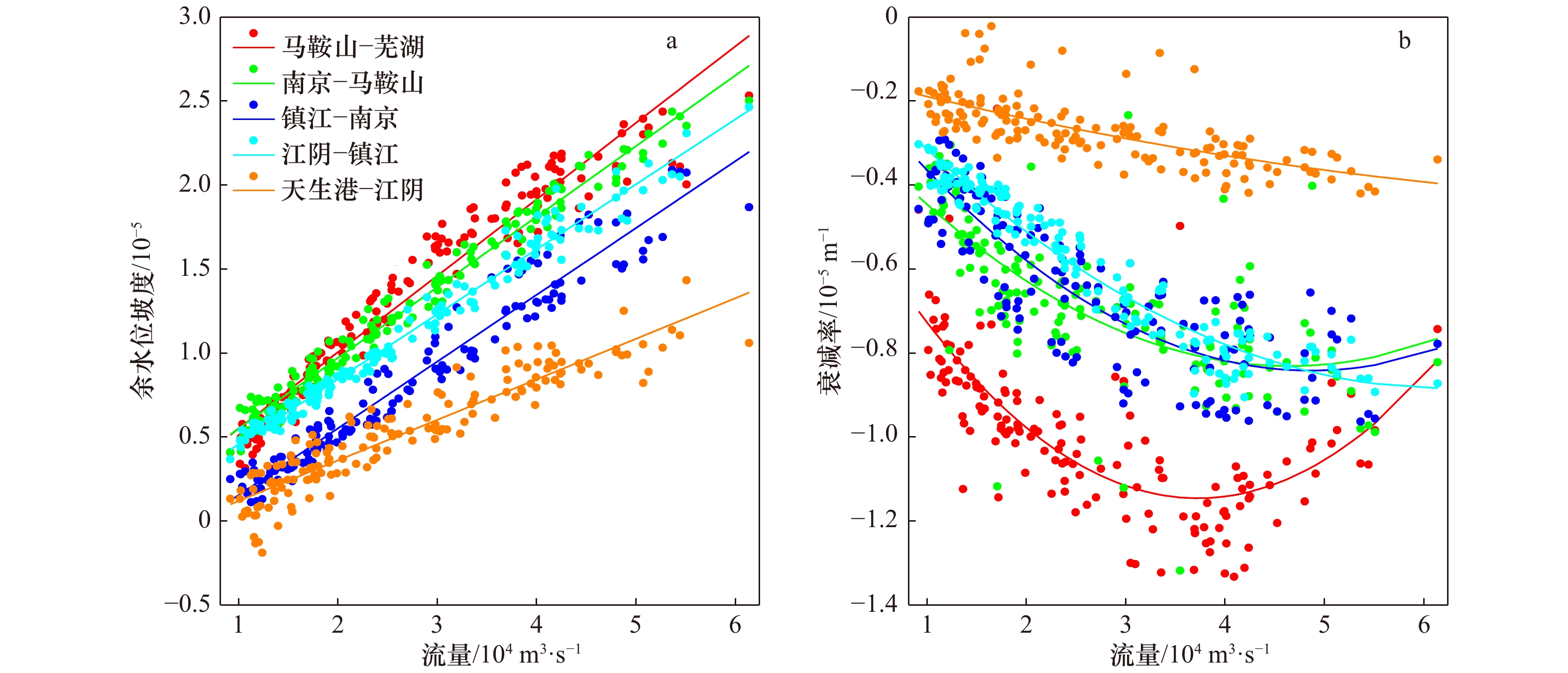
摘要: 径潮相互作用是感潮河段水动力变化的典型特征,受其影响潮波传播具有明显的洪枯季及沿程变化。本文基于长江感潮河段天生港、江阴、镇江、南京、马鞍山及芜湖6个潮位站2002−2014年连续高低潮位资料及大通站月均流量数据,统计分析长江感潮河段潮波振幅衰减率、潮波传播速度及余水位坡度等传播特征值的洪枯季及沿程变化特征,并探讨这些潮波传播特征的变化规律及其主要影响因素。结果表明,潮波传播特征的洪枯季差异自上游至下游逐渐减小,其分界点位于天生港与江阴之间(其中,天生港和江阴站的多年平均洪枯季潮差差值约为0.01 m和−0.04 m);径流动力对潮波衰减的影响主要位于江阴以上河段,江阴以下河段主要受潮汐动力控制;径流驱动下余水位坡度引起的余水位及水深增加,导致潮波传播的有效摩擦减小,当流量超过某个阈值时潮波振幅衰减反而减弱,特别是上游马鞍山-芜湖段最为明显,统计结果表明该河段流量阈值约为33 000 m3/s。本文分析结果作为前人研究的重要补充,可为长江河口感潮河段径潮相互作用机制研究及河口治理等提供基础参考。Abstract: As tidal waves propagate into the estuary, they are featured by significant longitudinal variation in seasonal scale due to the nonlinear interactions between tide and river discharge. In this study, the variations of tide-river dynamics in terms of tidal damping rate, wave celerity and residual water level slope were explored based on long-term time series of tidal water levels from 2002 to 2014 along the tidal reach of the Changjiang River (including the Tianshenggang, Jiangyin, Zhenjiang, Nanjing, Maanshan and Wuhu stations) in together with the monthly averaged river discharge observed at Datong hydrological stations. Subsequently, the underlying controlled factors that influence the tidal wave propagation were discussed. It was shown that the seasonal difference in tide-river dynamics was gradually reduced in the seaward direction. We identified a transitional zone located between the Tianshenggang and Jiangyin stations, where the seasonal differences in tidal range are 0.01 m and −0.04 m, respectively. Generally, upstream from Jiangyin Station the dynamics character was river-dominated, while in the lower reaches it was mainly controlled by the tidal forcing. In addition, we show that there exists a threshold in river discharge in the upper reaches of the tidal reach of the Changjiang River due to the increase of residual water level and hence water depth caused by the residual water level slope. This phenomenon was particularly true in the upstream reach between Maanshan to Wuhu stations, where the threshold of river discharge was approximately 33 000 m3/s. The results obtained from this study can enhance our understanding of tide-river interaction, and will, hopefully, provide guidelines for water resources management in the tidal reach of the Changjiang River.
-
Key words:
- Changjiang River Estuary /
- tidal river /
- river discharge /
- tidal damping /
- residual water level
-
图 6 余水位坡度(a−e)、潮波振幅衰减率(f−j)及潮波传播速度(k−o)与河段下游站点潮波振幅的关系
Fig. 6 The relationship between residual water level slope (a−e), tidal amplitude damping rate (f−j), tidal wave celerity (k−o) and tidal wave amplitude at the downstream station for different reaches along the tidal reach of the Changjiang River
表 1 大通站流量特征值和沿程主要潮位站潮波特征值
Tab. 1 Characteristic values of discharge at Datong Station and characteristic values of tide wave at different tidal gauging stations
站点 特征值 最大值 最小值 中位数 标准差 洪季均值 枯季均值 大通 流量/m3·s−1 66 600 8 380 23 400 13 237 36 825 16 848 芜湖 潮位/m 9.04 1.16 3.97 2.01 6.02 2.77 潮差/m 0.63 0.10 0.27 0.14 0.19 0.39 马鞍山 潮位/m 7.91 0.91 3.38 1.74 5.24 2.39 潮差/m 0.90 0.15 0.41 0.19 0.29 0.56 南京 潮位/m 6.78 0.64 2.81 1.49 4.44 1.99 潮差/m 1.05 0.24 0.58 0.22 0.42 0.72 镇江 潮位/m 5.37 0.25 2.30 1.08 3.42 1.63 潮差/m 1.36 0.52 0.96 0.22 0.76 1.10 江阴 潮位/m 3.29 −0.41 1.24 0.54 1.78 0.85 潮差/m 2.05 1.49 1.76 0.11 1.72 1.76 天生港 潮位/m 2.98 −0.67 1.17 0.40 1.41 0.73 潮差/m 2.33 1.76 1.99 0.11 2.00 1.99 表 2 长江不同感潮河段潮波传播特征值之间的线性相关系数
Tab. 2 Linear correlation coefficient of tidal wave propagation in different tidal reaches of the Changjiang River
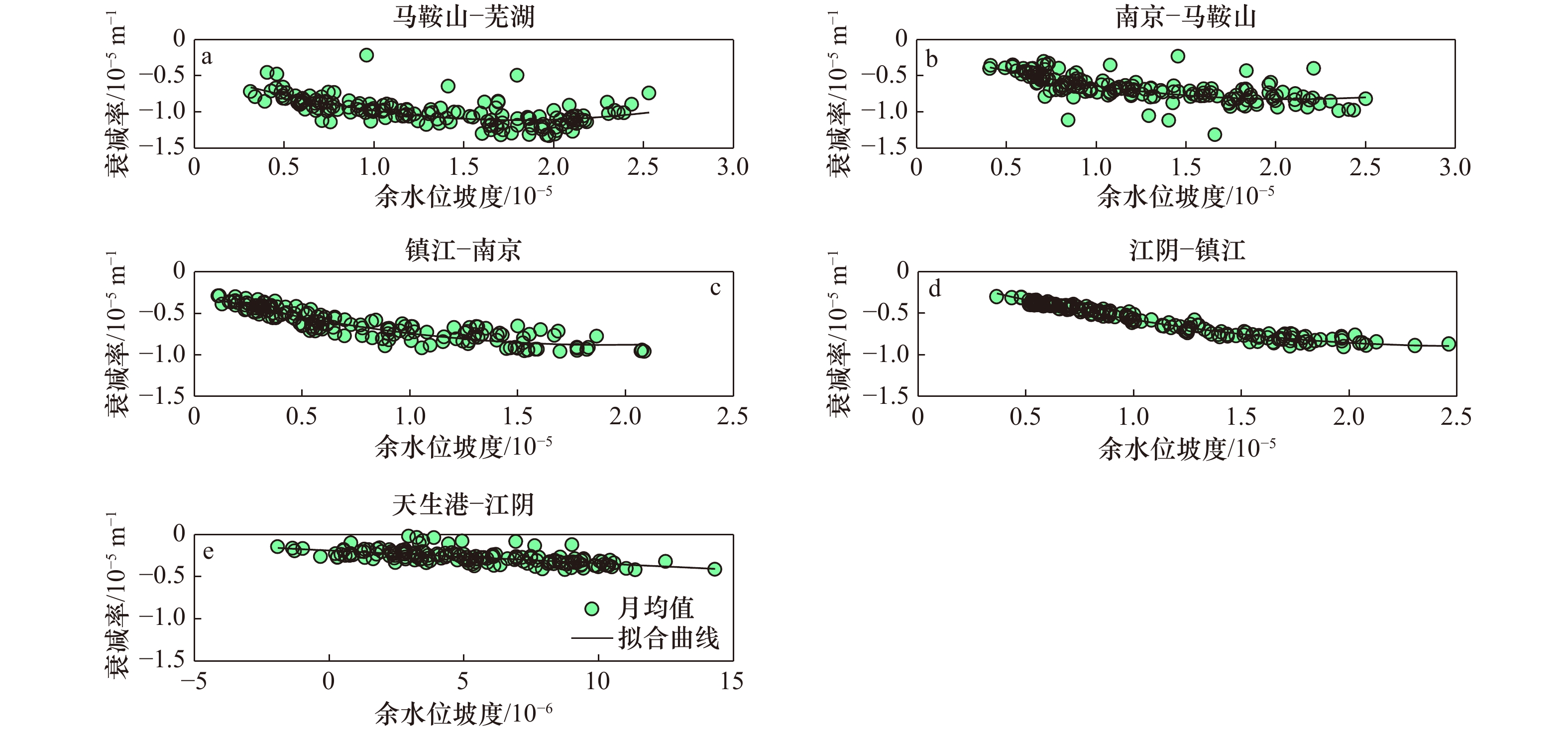
相关系数 马鞍山−芜湖 南京−马鞍山 镇江−南京 江阴−镇江 天生港−江阴 流量−余水位坡度 0.94 0.98 0.95 0.98 0.89 流量−衰减率 0.51 0.54 0.75 0.95 0.49 余水位坡度−衰减率 0.44 0.54 0.84 0.97 0.41 δH−c2 0.31 0.12 0.42 0.64 0.11 -
[1] 韩曾萃, 尤爱菊, 徐有成, 等. 强潮河口环境和生态需水及其计算方法[J]. 水利学报, 2006, 37(4): 395−402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2006.04.003Han Zengcui, You Aiju, Xu Youcheng, et al. Calculation methods of environmental and ecological water demand for macro-tidal estuary[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 37(4): 395−402. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2006.04.003 [2] 陆永军, 李浩麟, 王红川, 等. 强潮河口拦门沙航道回淤及治理措施[J]. 水利学报, 2005, 36(12): 1450−1456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2005.12.009Lu Yongjun, Li Haolin, Wang Hongchuan, et al. Back silting and regulation of waterway with sand bar in strong tidal estuary[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 36(12): 1450−1456. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2005.12.009 [3] 白玉川, 张彬, 张胤祺, 等. 波浪挟沙能力及航道骤淤机理的研究[J]. 水利学报, 2007, 38(6): 646−653. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.06.002Bai Yuchuan, Zhang Bin, Zhang Yinqi, et al. Sediment-carrying capacity of wave and mechanism of sudden silting in navigation channel[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2007, 38(6): 646−653. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2007.06.002 [4] Buschman F A, Hoitink A J F, van der Vegt M, et al. Subtidal water level variation controlled by river flow and tides[J]. Water Resources Research, 2009, 45(10): W10420. [5] Godin G, Martínez A. Numerical experiments to investigate the effects of quadratic friction on the propagation of tides in a channel[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1994, 14(7/8): 723−748. [6] LeBlond P H. Forced fortnightly tides in shallow rivers[J]. Atmosphere-Ocean, 1979, 17(3): 253−264. doi: 10.1080/07055900.1979.9649064 [7] Savenije H H G. Salinity and Tides in Alluvial Estuaries[M]. 2nd ed. Delft, the Netherlands: Delft University of Technology Water Resources Section, 2012. [8] Sassi M G, Hoitink A J F. River flow controls on tides and tide-mean water level profiles in a tidal freshwater river[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(9): 4139−4151. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20297 [9] Horrevoets A C, Savenije H H G, Schuurman J N, et al. The influence of river discharge on tidal damping in alluvial estuaries[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2004, 294(4): 213−228. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.02.012 [10] 欧素英, 杨清书. 珠江三角洲网河区径流潮流相互作用分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(1): 125−131.Ou Suying, Yang Qingshu. Interaction of fluctuating river flow with a barotropic tide in river network of the Zhujiang Delta[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(1): 125−131. [11] 倪培桐, 韦惺, 吴超羽, 等. 珠江河口潮能通量与耗散[J]. 海洋工程, 2011, 29(3): 67−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2011.03.009Ni Peitong, Wei Xing, Wu Chaoyu, et al. Tidal energy flux and dissipation in the Pearl River estuary[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2011, 29(3): 67−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2011.03.009 [12] Jay D A, Leffler K, Diefenderfer H L, et al. Tidal-fluvial and estuarine processes in the Lower Columbia River: I. along-channel water level variations, Pacific Ocean to Bonneville Dam[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2015, 38(2): 415−433. doi: 10.1007/s12237-014-9819-0 [13] 路川藤, 陈志昌, 罗小峰. 长江感潮河段二维潮流数值模拟[J]. 水运工程, 2012(8): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.08.003Lu Chuanteng, Chen Zhichang, Luo Xiaofeng. Two-dimensional tidal mathematical model in tidal river of Yangtze River[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2012(8): 11−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2012.08.003 [14] 路川藤, 罗小峰, 陈志昌. 长江潮流界对径流、潮差变化的响应研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 49(2): 201−205.Lu Chuanteng, Luo Xiaofeng, Chen Zhichang. Study of current limit causing by runoff and tidal range in Yangtze River[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2016, 49(2): 201−205. [15] 路川藤, 陈志昌, 罗小峰. 长江口北槽潮波传播变化特征研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2015, 32(8): 9−14.Lu Chuanteng, Chen Zhichang, Luo Xiaofeng. Variation characteristics of tidal wave propagation in the north channel of Yangtze estuary[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2015, 32(8): 9−14. [16] 张智伟, 蒋陈娟, 李闪闪. 长江近口段水动力特征对来水变异的响应[J]. 海洋学研究, 2017, 35(1): 25−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.01.003Zhang Zhiwei, Jiang Chenjuan, Li Shanshan. Response of hydrodynamics in tidal reach of the Yangtze River to variation in runoff[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2017, 35(1): 25−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2017.01.003 [17] Kuang Cuiping, Chen Wei, Gu Jie, et al. River discharge contribution to sea-level rise in the Yangtze River Estuary, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 134: 63−75. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2017.01.004 [18] Cai Huayang, Savenije H H G, Jiang Chenjuan, et al. Analytical approach for determining the mean water level profile in an estuary with substantial fresh water discharge[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2016, 20(3): 1177−1195. doi: 10.5194/hess-20-1177-2016 [19] 沈焕庭, 潘定安. 长江河口潮流特性及其对河槽演变的影响[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 1979(1): 131−144.Shen Huanting, Pan Dingan. The characteristics of tidal current an its effects on channel changes of the Yangtze estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 1979(1): 131−144. [20] 谷国传, 胡方西. 长江径流与长江河口海平面关系[M]//陈吉余, 沈焕庭, 恽才兴. 长江河口动力过程和地貌演变. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1988: 198-204.Gu Guochuan, Hu Fangxi. Relationship Between sea level rise and river discharge in the Changjiang River[M]//Chen Jiyu, Shen Huanting, Yun Caixing. Hydrodynamics Processes and Morphological Evolution in the Changjiang Estuary. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technlogy Press, 1988: 198−204. [21] 李国芳, 谭亚, 张秀菊. 感潮河段上游流量对潮位预报的影响[J]. 河海大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 34(2): 144−147.Li Guofang, Tan Ya, Zhang Xiuju. Influence of upstream discharge in tidal level prediction for tidal reaches[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2006, 34(2): 144−147. [22] 王文才, 李一平, 杜薇, 等. 长江感潮河段潮汐变化特征[J]. 水资源保护, 2017, 33(6): 121−124. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.06.19Wang Wencai, Li Yiping, Du Wei, et al. Tidal variation features of tidal reach of Changjiang River[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2017, 33(6): 121−124. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2017.06.19 [23] 刘新成, 沈焕庭, 杨清书. 长江河口段潮差变化研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 1999(2): 89−94.Liu Xincheng, Shen Huanting, Yang Qingshu. Analysis of tidal range in Changjang estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 1999(2): 89−94. [24] 吴玲莉, 张玮. 长江下游感潮河段极值水位的周期分析[J]. 水运工程, 2009(4): 134−139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2009.04.029Wu Lingli, Zhang Wei. Analysis of the periodicity of yearly extreme water level in the tidal reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2009(4): 134−139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2009.04.029 [25] 杨正东, 朱建荣, 王彪, 等. 长江河口潮位站潮汐特征分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012(5): 111−119.Yang Zhengdong, Zhu Jianrong, Wang Biao, et al. Analysis of tidal characteristics of the tide gauges in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 2012(5): 111−119. [26] Guo Leicheng, van der Wegen M, Jay D A, et al. River-tide dynamics: exploration of nonstationary and nonlinear tidal behavior in the Yangtze River estuary[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(5): 3499−3521. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010491 [27] 郭磊城, 朱春燕, 何青, 等. 长江河口潮波时空特征再分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2017, 36(6): 652−661. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.06.007Guo Leicheng, Zhu Chunyan, He Qing, et al. Examination of tidal wave properties in the Yangtze River estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2017, 36(6): 652−661. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2017.06.007 [28] 宋永港, 朱建荣, 吴辉. 长江河口北支潮位与潮差的时空变化和机理[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2011(6): 10−19.Song Yonggang, Zhu Jianrong, Wu Hui. Spatial and temporal variations and mechanism of the tidal level and range in the North Branch of the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University: Natural Science, 2011(6): 10−19. [29] Lu Sheng, Tong Chaofeng, Lee D Y, et al. Propagation of tidal waves up in Yangtze Estuary during the dry season[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(9): 6445−6473. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010414 [30] Savenije H H G, Veling E J M. Relation between tidal damping and wave celerity in estuaries[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C4): C04007. -





 下载:
下载: