Characteristics of radionuclides in sediments collected from the Beibu Gulf and influence factors
-
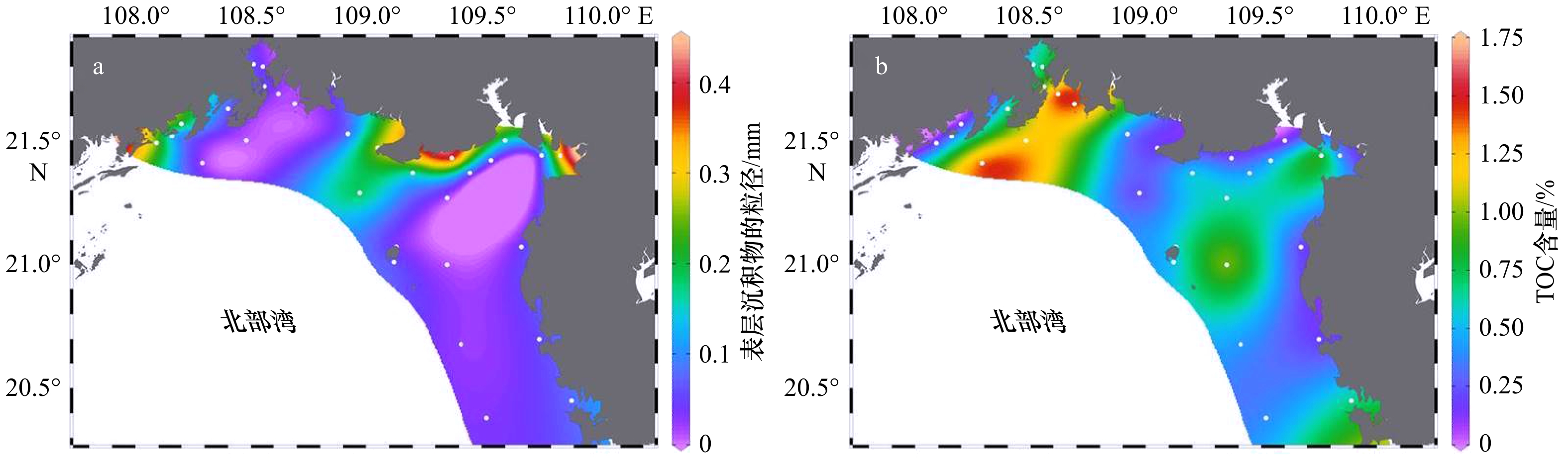
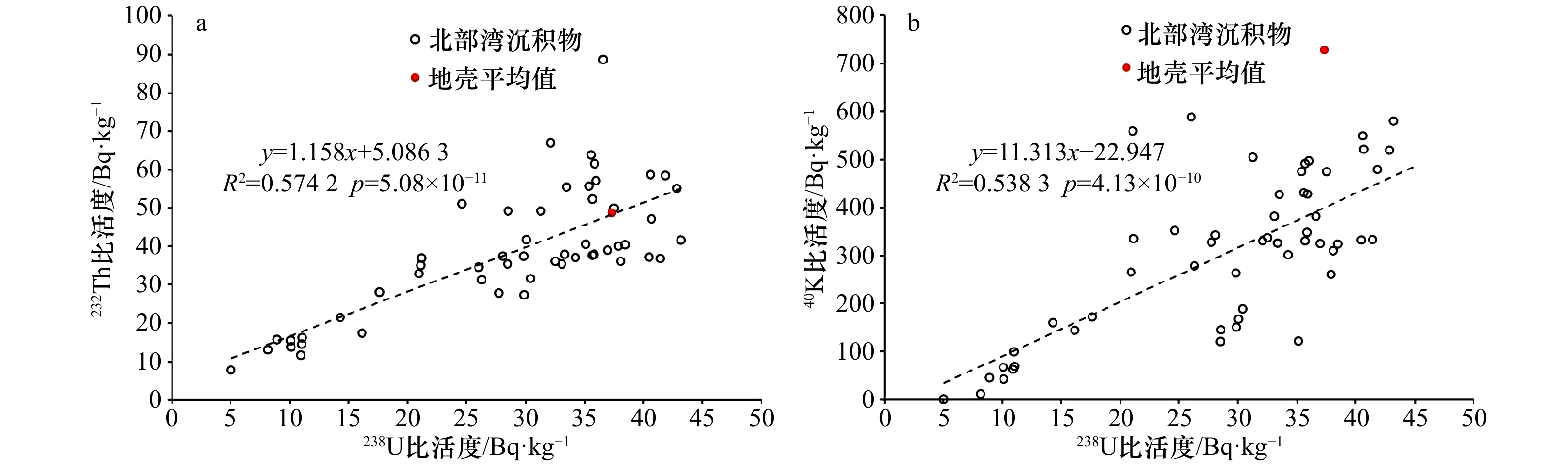
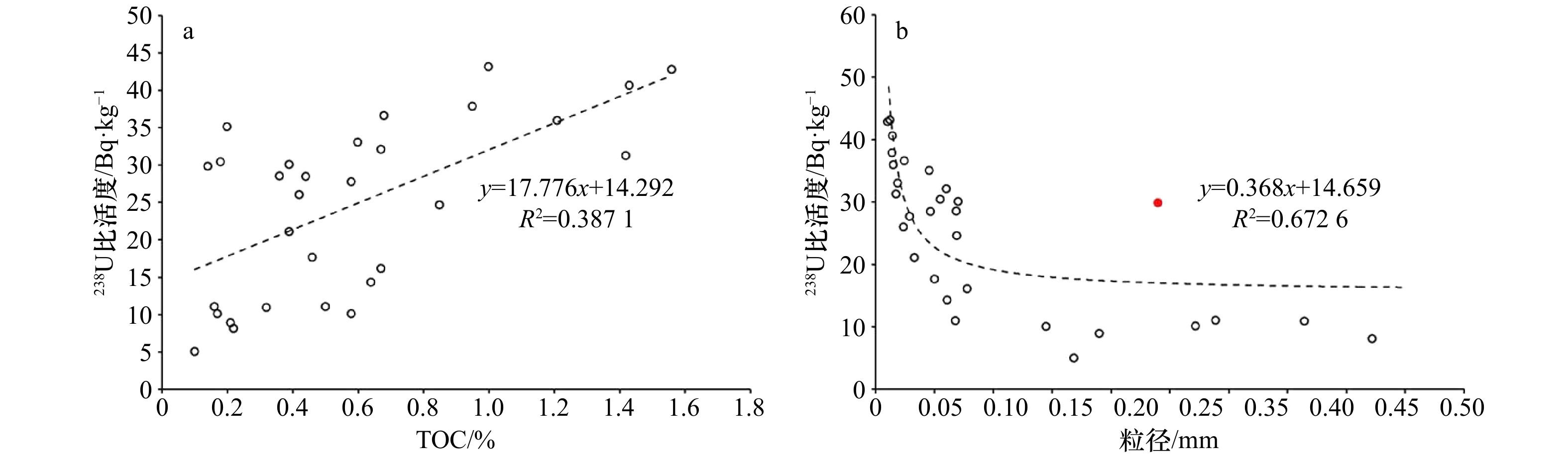
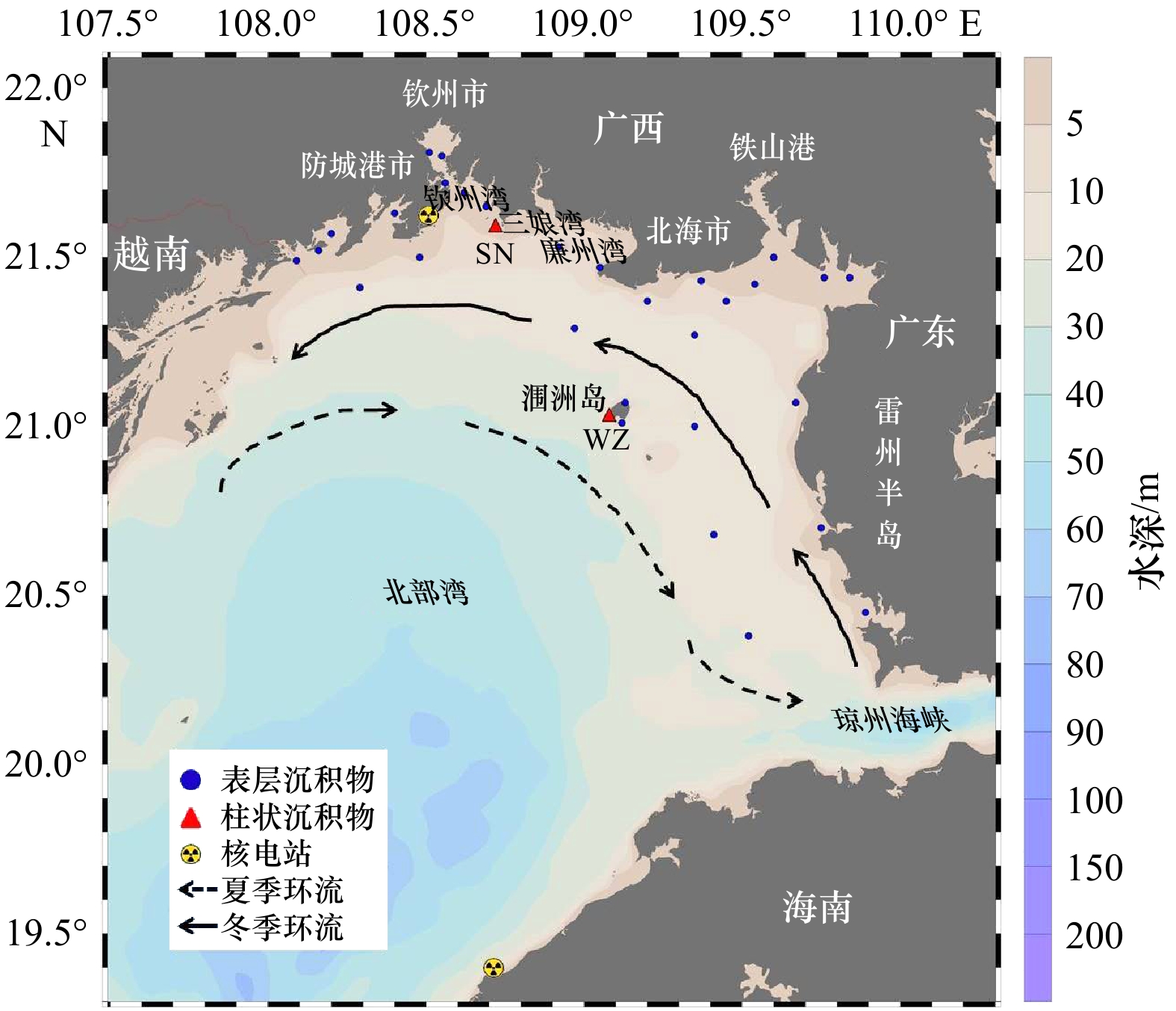
摘要: 北部湾是我国大西南地区重要的海上通道,也是我国重要的渔场之一。本研究利用高纯锗γ谱仪系统分析北部湾表层和柱状沉积物中4种最主要的天然放射性核素(238U、226Ra、228Ra、40K)含量和分布特征。结果显示,北部湾沉积物中放射性核素含量低于我国大部分海域的结果,高于珊瑚礁区的极低放射性水平的结果。北部湾沉积物中4种核素都存在“蝴蝶”状空间分布特征,该特征主要源于沉积物粒径的非线性调控,且与沉积物总有机碳浓度存在正相关。此外,利用Mn和210Pb所指示的氧化还原状态和物理/生物扰动过程也可以对柱状沉积物中氧化还原敏感型核素(比如,238U)分布产生一定的影响。本文从232Th/238U、40K/238U、226Ra/238U活度比值角度,发现北部湾沉积物具有典型的陆源沉积物特征,且显著不同于南海珊瑚礁区中生源沉积物特征。本研究有利于掌握滨海核电发展背景下的北部湾海洋环境中放射性核素水平,揭示核素的“蝴蝶”状分布特征和控制因素,探索基于放射性核素的地球化学新指标在海洋沉积过程中的应用。Abstract: The Beibu Gulf is not only a key sea passage in the southwestern China but also one of important fishing grounds in the South China Sea (SCS). In this study, naturally occurring radionuclides (238U, 226Ra, 228Ra, and 40K) in surface sediments and sediment cores of the Beibu Gulf were comprehensively analyzed using high purity germanium (HPGe) γ spectrometry. Our results indicated that radioactivity level of sediments in the Beibu Gulf was lower than that in most of China's seas and was higher than the extremely low radioactivity level of sediments in coral reefs. All nuclides in surface sediments of the Beibu Gulf had a spatial distribution of “butterfly pattern”, attributing to the non-linear regulation of sediment grain size and positive role of total organic carbon in sediment. Additionally, redox state and physical/biological disturbance derived from the proxies of Mn and 210Pb could also affect vertical distribution of redox-sensitive nuclide (eg, 238U) in sediment cores. On the basis of the 232Th/238U, 40K/238U, and 226Ra/238U activity ratio, we found that sediments of the Beibu Gulf had terrigenous characteristics, which were significantly different from biogenic sediments in coral reefs. Our study provided radioactivity level in the Beibu Gulf under the background of the rapid development of nuclear power plant, revealed the "butterfly pattern" of radionuclides and their influence factors, and explored the feasibility of novel geochemical proxies based on radionuclides in marine sedimentation.
-
Key words:
- radionuclide /
- nuclear power plant /
- redox-sensitive element /
- geochemical proxy /
- sedimentation
-
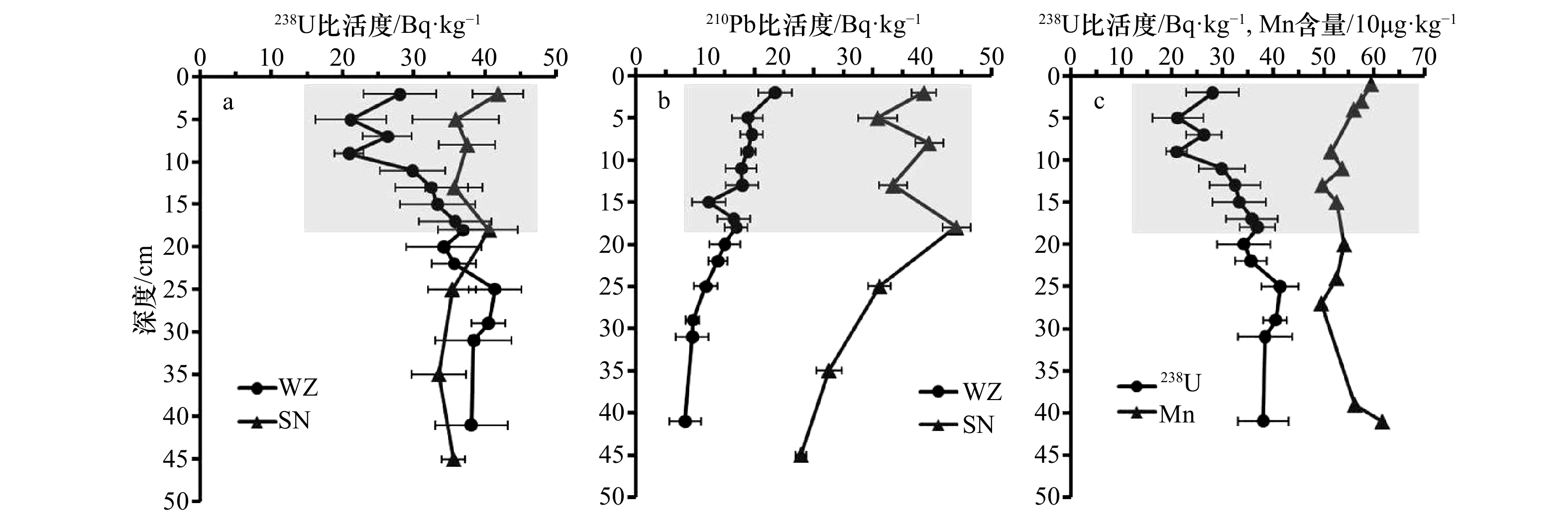
图 3 涠洲岛(WZ)与三娘湾(SN)沉积物柱状样中放射性核素238U(a)、226Ra(b)、228Ra(c)、40K(d)比活度剖面图
图中虚线和点线分别代表涠洲岛和三娘湾的柱样中核素比活度平均值
Fig. 3 Vertical profiles of specific activities of 238U(a), 226Ra(b), 228Ra(c), and 40K(d) in sediment cores from the stations of WZ and SN
The average value was indicated by the dashed line and dotted line for WZ and SN, respectively
表 1 不同海域的表层沉积物中238U、226Ra、228Ra、40K含量(单位:Bq/kg)
Tab. 1 Activities of 238U、226Ra、228Ra、40K in surface sediments from distinct sea regions (unit: Bq/kg)
地区 238U 226Ra 228Ra 40K 参考文献 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 范围 平均值 大连湾 26.4~47.0 34.9 11.2~25.3 19.3 — — 669~807 746 [24] 莱州湾 — 54.4±11.7 — 28.6±4.30 — 57.9±9.70 — 542±21.0 [25] 胶州湾 32.4~56.2 39.2±8.80 20.6~44.1 26.5±3.30 35.7~53.3 40.3±4.80 607~732 688±58.0 [26] 长江口 14.1~62.3 32.8±10.6 13.7~52.3 24.3±7.4 26.1~71.9 40.9±9.4 392~898 628±135 [27] 厦门海域 11.5~65.1 40.2 27.5~40 32.4 49.9~94.3 69.3 510~1096 692 [28] 大亚湾 36.6~64.1 49.2±3.9 15.6~29.7 20.9±0.7 40.3~52.7 47.2±1.9 360~482 432±19 [29] 黄茅海—广海湾 66.5~98.8 77.4 32.0~48.7 36.6 49.7~64.8 58.1 505~644 571 [30] 阳江海域 75.2~102.0 82.4±5.2 32.6~38.6 35.5±2.0 40.9~70.6 57.1±3.1 580~660 621±29 [31] 白龙半岛 12.0~87.0 48.3±20.2 10.3~51.8 32.4±9.40 13.2~72.9 46.1±13.4 69.6~514 355±125 [32] 南海东北部 21.2~59.0 35.4±3.0 25.9~32.4 27.7±1.3 22.6~65.2 44.9±5.9 273~686 538±52 [34] 海南岛东部 6.0~33.2 21.7±6.4 12.6~25.5 19.0±1.0 — — — — [33] 南沙海域 19.9~70.2 — 14.1~147 — 11.0~80.0 — 155~868 — [35] 中国土壤 7.30~449 38.5±21.1 2.80~533 37.6±23.4 10.3~1844 54.6±51.3 ND~1548 584±183 [36] 南海珊瑚礁 22.1~38.2 29.0±5.09 1.47~9.39 3.34±2.51 0.51~14.4 5.08±4.91 2.15~154 24.4±49.1 [20] 北部湾 5.07~43.2 24.7±11.6 4.33~42.2 22.2±10.7 7.76~88.8 34.4±18.7 0.16~588 253±192 本文 注:"—"代表没有数据。 表 2 不同海域表层沉积物的辐射环境质量评价
Tab. 2 Assessment of environmental radiation quality for sediments from other sea regions
-
[1] 高劲松, 陈波, 侍茂崇. 北部湾夏季环流结构及生成机制[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(1): 99−112.Gao Jinsong, Chen Bo, Shi Maochong. Summer circulation structure and formation mechanism in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 45(1): 99−112. [2] Liu Xinming, Lin Wuhui. Natural radioactivity in the beach sand and soil along the coastline of Guangxi Province, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135: 446−450. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.07.057 [3] 乔延龙, 林昭进. 北部湾地形、底质特征与渔场分布的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2007(S1): 232−238.Qiao Yanlong, Lin Zhaojin. The relationship between the main features of landform, the distritubiton of bottom sediment and fishery distribution[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2007(S1): 232−238. [4] 林武辉, 陈立奇, 何建华, 等. 日本福岛核事故后的海洋放射性监测进展[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(1): 269−276.Lin Wuhui, Chen Liqi, He Jianhua, et al. Review on monitoring marine radioactivity since the Fukushima Nuclear Accident[J]. China Environmental Science, 2015, 35(1): 269−276. [5] Liu Yongxue, Sun Chao, Sun Jiaqi, et al. Satellite data lift the veil on offshore platforms in the South China Sea[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 33623. doi: 10.1038/srep33623 [6] Gäfvert T, Færevik I, Rudjord A L. Assessment of the discharge of NORM to the North Sea from produced water by the Norwegian oil and gas industry[J]. Radioactivity in the Environment, 2006, 8: 193−205. doi: 10.1016/S1569-4860(05)08013-7 [7] 林武辉, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 海洋沉积过程的铀系放射性核素示踪技术: 物源识别、沉积、再悬浮[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020: In Press. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018092001Lin Wuhui, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Uranium-series radionuclides as tools for tracking marine sedimentary processes: source identification, sedimentation rate, and sediment resuspension[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020: In Press. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2018092001 [8] 林武辉, 陈立奇, 余雯, 等. 海洋生物辐射剂量评价方法及应用[C]//福建省海洋学会2014年学术年会暨福建省科协第十四届学术年会分会场论文集. 平潭: 福建省海洋学会, 2014: 326−334.Lin Wuhui, Chen Liqi, Yu Wen, et al. The methodology and application of radiation dose assessment for non human species in marine environment[C]//2014 Annual Conference of Fujian Ocean Society. Pingtan: Fujian Marine Society, 2014: 326−334. [9] Batlle J V I, Aoyama M, Bradshaw C, et al. Marine radioecology after the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident: are we better positioned to understand the impact of radionuclides in marine ecosystems?[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 618: 80−92. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.005 [10] 肖晓, 石要红, 冯秀丽, 等. 北部湾表层沉积物粒度分布规律及沉积动力分区[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(5): 83−89.Xiao Xiao, Shi Yaohong, Feng Xiuli, et al. Surface sediment characteristics and dynamics in Beibu Gulf[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(5): 83−89. [11] 徐志伟, 汪亚平, 李炎, 等. 多元统计及物源分析支持的北部湾东部海域沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋学报, 2010, 32(3): 67−78.Xu Zhiwei, Wang Yaping, Li Yan, et al. Sediment transport patterns in the eastern Beibu Gulf based on grain-size multivariate statistics and provenance analysis[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2010, 32(3): 67−78. [12] Gan Huayang, Lin Jinqin, Liang Kai, et al. Selected trace metals (As, Cd and Hg) distribution and contamination in the coastal wetland sediment of the northern Beibu Gulf, South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 66(1/2): 252−258. [13] 陈亮, 李团结, 杨文丰, 等. 南海北部近海沉积物重金属分布及来源[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(3): 464−470.Chen Liang, Li Tuanjie, Yang Wenfeng, et al. Distribution and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments, Northern South China Sea[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(3): 464−470. [14] 窦衍光, 李军, 李炎. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(2): 147−157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.02.006Dou Yanguang, Li Jun, Li Yan. Rare earth element compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in the eastern Beibu Gulf[J]. Geochimica, 2012, 41(2): 147−157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.02.006 [15] Pan Changgui, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the riverine and coastal water of the Beibu Gulf, South China: spatiotemporal distribution and source identification[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 660: 297−305. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.019 [16] Zhang Ruiling, Pei Jiying, Zhang Ruijie, et al. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in mariculture farms, estuaries and the coast of the Beibu Gulf, China: bioconcentration and diet safety of seafood[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2018, 154: 27−35. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.02.006 [17] 童国榜, 陈亮, 龙江平, 等. 北部湾东部表层孢粉沉积特征及其沉积动力环境[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57(8): 902−911.Tong Guobang, Chen Liang, Long Jiangping, et al. Surface pollen distribution patterns in Beibu Gulf and corresponding sediment dynamics environment[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(8): 902−911. [18] 侍茂崇. 北部湾环流研究述评[J]. 广西科学, 2014, 21(4): 313−324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.001Shi Maochong. Study comments on circulation in Beibu Gulf[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2014, 21(4): 313−324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2014.04.001 [19] 林武辉, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 珊瑚礁区沉积物的极低放射性水平特征与成因[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(21): 2173−2183.Lin Wuhui, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Extremely low radioactivity in marine sediment of coral reefs and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(21): 2173−2183. [20] Lin Wuhui, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Radioactive level of coral reefs in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 142: 43−53. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.030 [21] 林武辉, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 罕见的地表低辐射水平区域: 珊瑚礁区[J]. 辐射防护, 2018, 38(4): 287−292.Lin Wuhui, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Unusual low radiation area on the surface of the earth: coral reefs[J]. Radiation Protection, 2018, 38(4): 287−292. [22] 胡昊, 许冬, 龙江平, 等. 北部湾海底沉积物稀土元素与影响因子关系的BP神经网络定量分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34(1): 18−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.01.003Hu Hao, Xu Dong, Long Jiangping, et al. Quantitative analysis of BP neural network on the relationships between ΣREE content and impact factors in Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2016, 34(1): 18−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.01.003 [23] 何映雪, 林峰, 陈敏, 等. 春季北部湾北部海域颗粒有机物的碳、氮同位素组成[J]. 厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 53(2): 246−251.He Yingxue, Lin Feng, Chen Min, et al. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic composition of particulate organic matter in the Northern Beibu Gulf in spring[J]. Journal of University:Natural Science, 2014, 53(2): 246−251. [24] 杜金秋, 关道明, 姚子伟, 等. 大连近海沉积物中放射性核素分布及环境指示[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(5): 1889−1895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.036Du Jinqiu, Guan Daoming, Yao Ziwei, et al. Distribution and environmental significances of radionuclides in sediments of Dalian coastal area[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(5): 1889−1895. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.036 [25] 王启栋, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等. 昌邑滨海湿地沉积物的放射性核素水平与环境指示意义[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(8): 3026−3033.Wang Qidong, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang, et al. Distribution and environmental significances of radionuclides in the sediment of the Changyi Coastal Wetland[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(8): 3026−3033. [26] 贾成霞, 刘广山, 徐茂泉, 等. 胶州湾表层沉积物放射性核素含量与矿物组成[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2003, 34(5): 490−498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.004Jia Chengxia, Liu Guangshan, Xu Maoquan, et al. Radionuclides and minerals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2003, 34(5): 490−498. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2003.05.004 [27] Wang Jinlong, Du Jinzhou, Bi Qianqian. Natural radioactivity assessment of surface sediments in the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 114(1): 602−608. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.09.040 [28] 陈锦芳, 刘广山, 黄奕普. 厦门潮间带表层沉积物天然放射系不平衡研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 2005, 24(3): 274−282.Chen Jinfang, Liu Guangshan, Huang Yipu. Disequilibrium of natural decay series in sediments of intertidal mudflats of Xiamen[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2005, 24(3): 274−282. [29] Zhou Peng, Li Dongmei, Li Haitao, et al. Distribution of radionuclides in a marine sediment core off the waterspout of the nuclear power plants in Daya Bay, northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2015, 145: 102−112. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.03.018 [30] 赵峰, 吴梅桂, 周鹏, 等. 黄茅海—广海湾及其邻近海域表层沉积物中γ放射性核素含量水平[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2015, 34(4): 77−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011Zhao Feng, Wu Meigui, Zhou Peng, et al. Radionuclides in surface sediments from the Huangmaohai Estuary-Guanghai Bay and its adjacent sea area of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(4): 77−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.04.011 [31] 吴梅桂, 周鹏, 赵峰, 等. 阳江核电站附近海域表层沉积物中γ放射性核素含量水平[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(1): 43−47.Wu Meigui, Zhou Peng, Zhao Feng, et al. The concentration of γ radionuclides in surface marine sediments from Yangjiang nuclear power plant and its adjacent sea area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(1): 43−47. [32] 毛远意, 林静, 黄德坤, 等. 北部湾白龙半岛邻近海域沉积物中放射性核素含量水平[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2018, 37(2): 194−202. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.006Mao Yuanyi, Lin Jing, Huang Dekun, et al. Radionuclides in the surface sediments along the coast of Bailong Peninsula in Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2018, 37(2): 194−202. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2018.02.006 [33] Huang Dekun, Du Jinzhou, Deng Bing, et al. Distribution patterns of particle-reactive radionuclides in sediments off eastern Hainan Island, China: implications for source and transport pathways[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 57: 10−17. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.04.019 [34] 刘广山, 黄奕普, 陈敏, 等. 南海东北部表层沉积物天然放射性核素与137Cs[J]. 海洋学报, 2001, 23(6): 76−84.Liu Guangshan, Huang Yipu, Chen Min, et al. Specific activity and distribution of natural radionuclides and 137Cs in surface sediments of the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2001, 23(6): 76−84. [35] 刘广山, 黄奕普, 陈敏, 等. 南沙海区表层沉积物放射性核素分布特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2001, 25(8): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2001.08.001Liu Guangshan, Huang Yipu, Chen Min, et al. Distribution features of radionuclides in surface sediments of Nansha Sea Areas[J]. Marine Sciences, 2001, 25(8): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2001.08.001 [36] Wang Zuoyuan. Natural radiation environment in China[J]. International Congress Series, 2002, 1225: 39−46. doi: 10.1016/S0531-5131(01)00548-9 [37] 杨守业. 一沙一世界——藏于海底的地球环境变迁史[J]. 自然杂志, 2017, 39(5): 313−319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.05.001Yang Shouye. To see a world in a grain of sand: environment changes recorded in global seafloor[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2017, 39(5): 313−319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2017.05.001 [38] Cukrov N, Mlakar M, Cuculić V, et al. Origin and transport of 238U and 226Ra in riverine, estuarine and marine sediments of the Krka River, Croatia[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2009, 100(6): 497−504. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2009.03.012 [39] Adams J A S, Weaver C E. Thorium-to-uranium ratios as indicators of sedimentary processes: example of concept of geochemical facies[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1958, 42(2): 387−430. [40] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523−1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3 [41] Ramos D P S, Morgan L E, Lloyd N S, et al. Reverse weathering in marine sediments and the geochemical cycle of potassium in seawater: insights from the K isotopic composition (41K/39K) of deep-sea pore-fluids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2018, 236: 99−120. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.02.035 [42] 刘韶, 吴良基, 秦佩玲. 铀系法在南海深海沉积物沉积速度研究中的应用[J]. 热带海洋, 1983, 2(3): 244−247.Liu Shao, Wu Liangji, Qin Peiling. Application of the uranium series method to the study on the depositional rate of deep-sea sediments in south China Sea[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1983, 2(3): 244−247. [43] 赵一阳. 中国渤海沉积物中铀的地球化学[J]. 地球化学, 1980(1): 101−105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1980.01.014Zhao Yiyang. Geochemistry of uranium in sediments of Bohai Gulf, China[J]. Geochimica, 1980(1): 101−105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1980.01.014 [44] 刘季花, 梁宏锋, 姚德, 等. 东太平洋沉积物U的地球化学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(1): 59−67.Liu Jihua, Liang Hongfeng, Yao De, et al. Geochemistry of uranium in deep sea sediments from East Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1996, 16(1): 59−67. [45] Lee S H, Povinec P P, Chisholm J R M, et al. Distribution of natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in northwest Mediterranean coastal sediments[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2017, 172: 145−159. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.03.018 [46] Rosenthal Y, Boyle E A, Labeyrie L, et al. Glacial enrichments of authigenic Cd and U in subantarctic sediments: a climatic control on the elements' oceanic budget?[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 1995, 10(3): 395−413. [47] Dunk R M, Mills R A, Jenkins W J. A reevaluation of the oceanic uranium budget for the Holocene[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 190(1/4): 45−67. [48] Morford J L, Emerson S. The geochemistry of redox sensitive trace metals in sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(11/12): 1735−1750. [49] Al-Qasmi H, Law G T W, Fifield L K, et al. Deposition of artificial radionuclides in sediments of Loch Etive, Scotland[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2018, 187: 45−52. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.02.001 [50] 林武辉, 莫敏婷, 宁秋云, 等. 广西防城港核电周边红树林沉积物是否存在放射性核素富集特征?[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020: In Press. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190091Lin Wuhui, Mo Minting, Ning Qiuyun, et al. Do the enrichment of radionuclides occur in the mangrove systems nearby the Fangchenggang Nuclear Power Plant in Guangxi province?[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020: In Press. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190091 [51] Papadopoulos A. 226Ra/238U and 228Th/228Ra disequilibrium as weathering indices in beach sand sediments associated with granitoids from Cyclades. Greece[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2019, 100: 223−233. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.002 -




 下载:
下载: