Application of long term and short term memory neural network in prediction of chlorophyll a concentration
-
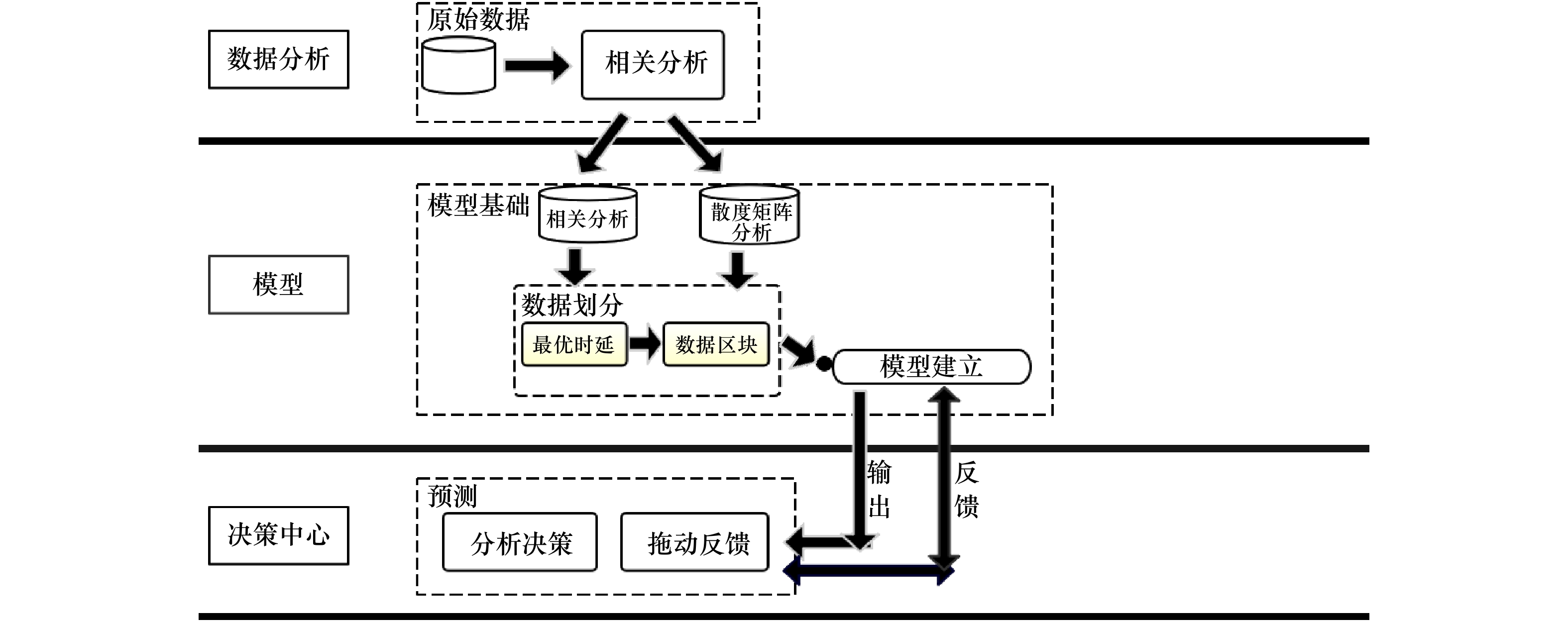
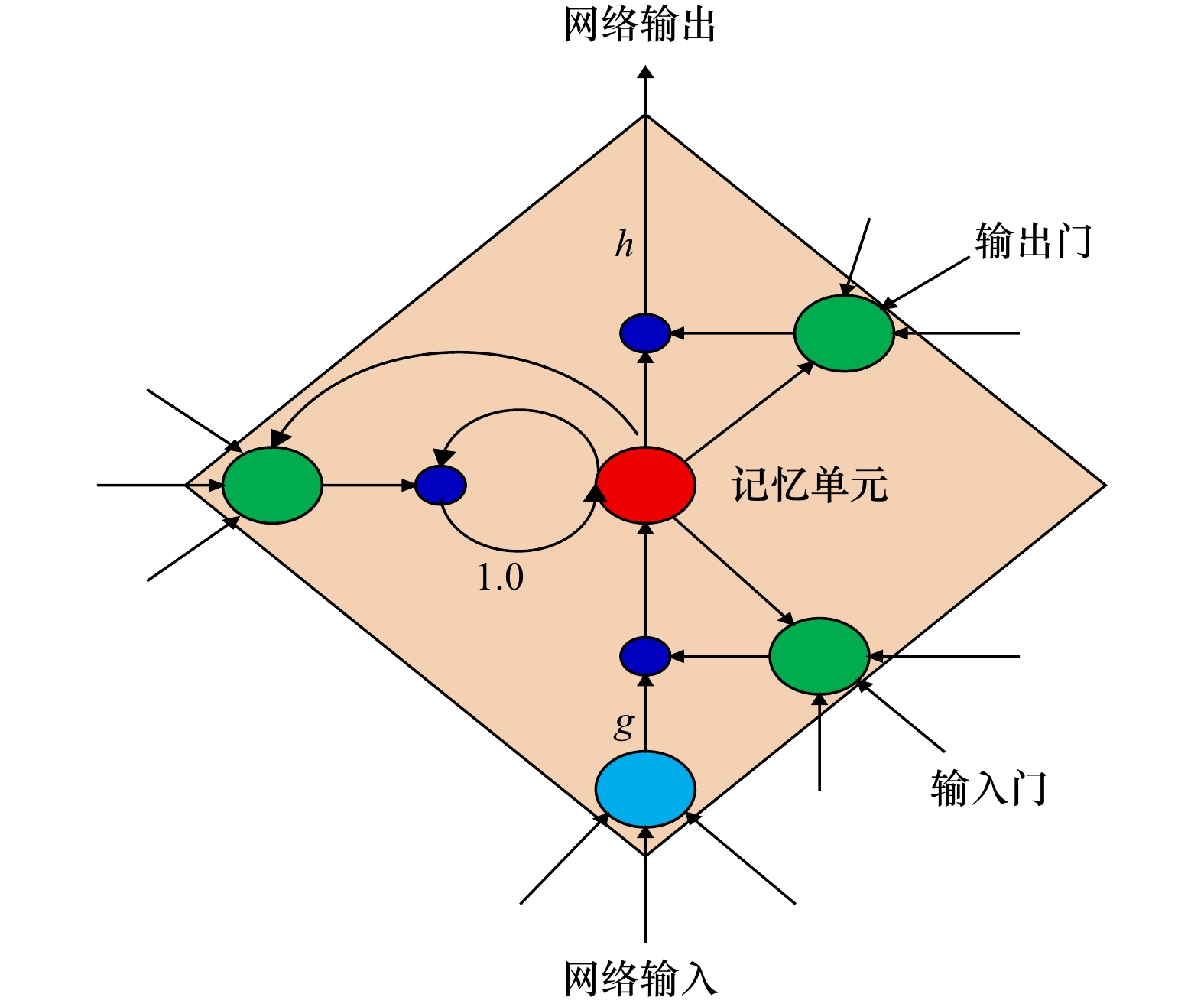
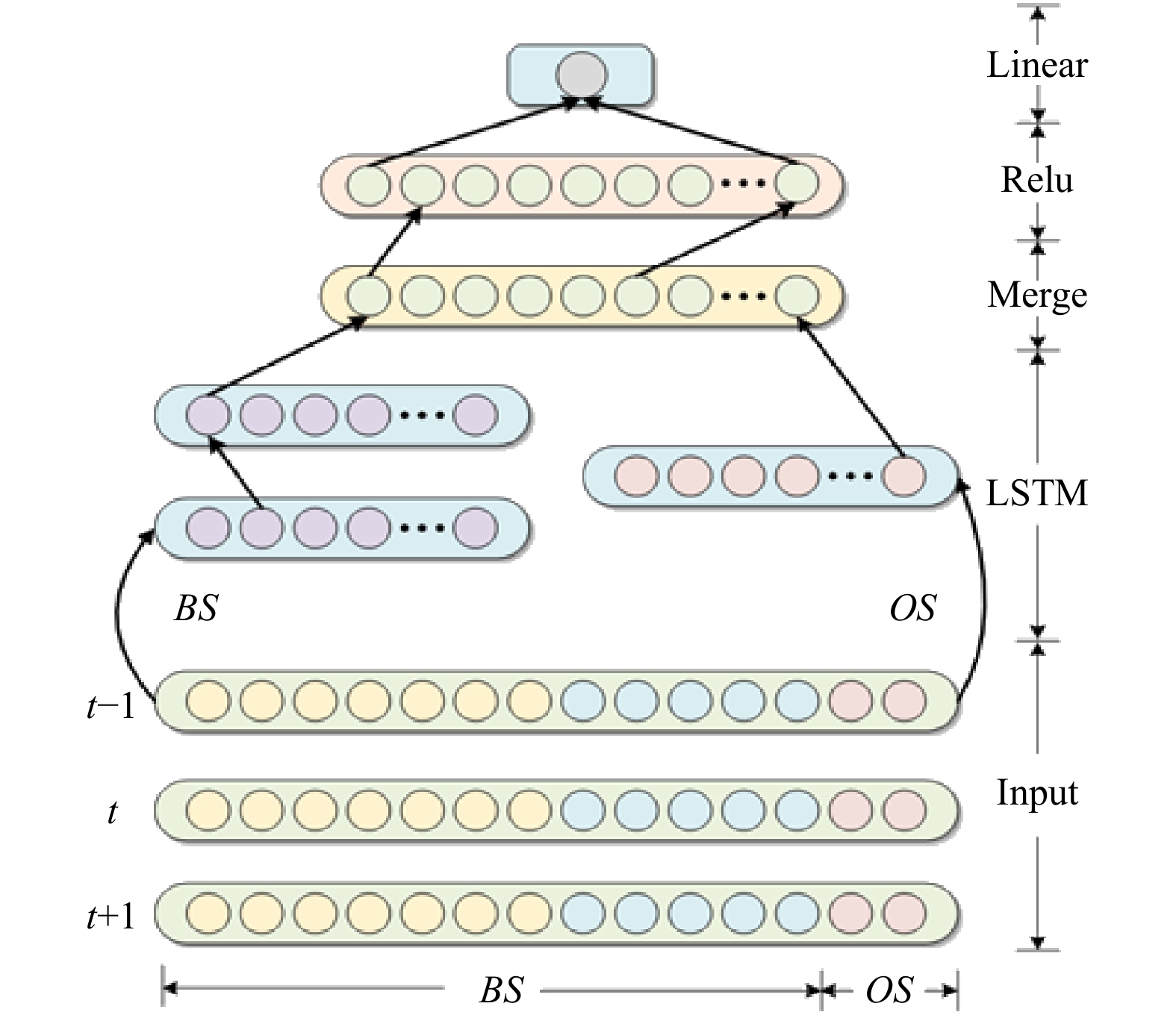
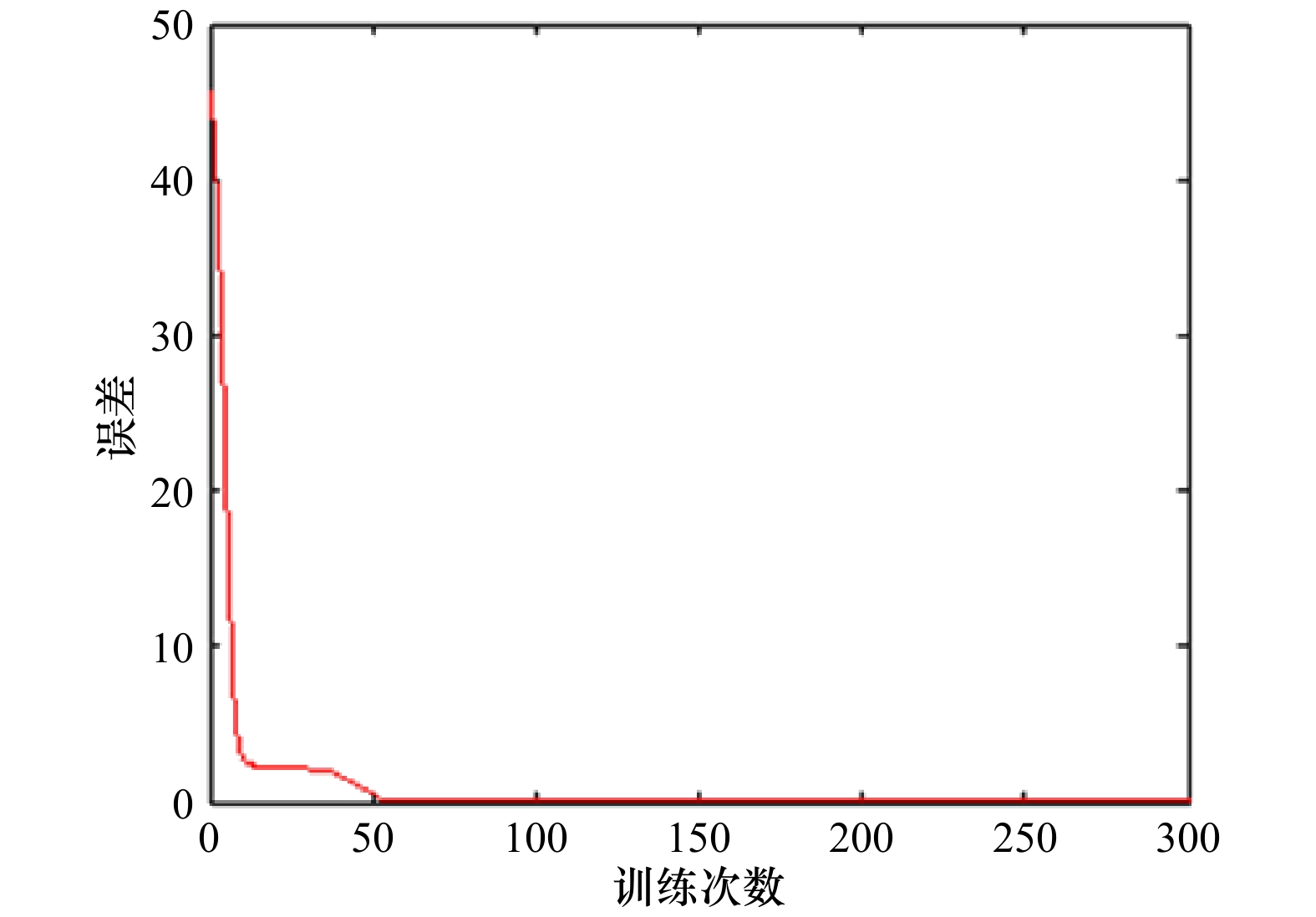
摘要: 针对传统人工神经网络对叶绿素a浓度预测存在训练速度慢、收敛精度低、易陷入局部最优,尤其是无法灵活的利用任意长度的历史信息对叶绿素a浓度进行预测等问题,本文根据海洋各要素与叶绿素a浓度之间的长短期依赖程度,对叶绿素a浓度与各要素间的关系进行界定,分别将各要素与叶绿素a浓度之间的长期依赖关系与短期依赖关系分割开来,并且在长短期记忆(Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM)神经网络模型的基础上构建融合的LSTM预测模型,模型中的长期依赖关系与短期依赖关系分别使用不同的神经元,最终在模型的最上层进行长短期融合。本文选取三都澳站位的连续监测资料作为实验数据,实验结果表明本文构建的模型不仅具有训练误差下降快的优点,与其他3种经典的神经网络模型相比,预测精度也有显著提高。
-
关键词:
- 叶绿素a /
- 融合的LSTM预测模型 /
- 多要素 /
- 神经网络
Abstract: Prediction of chlorophyll a concentration in traditional artificial network methods has some disadvantages, such as slower training speed, lower convergence precision, and easy to fall into local optimum situation. In particular, it is not possible to flexibly use historical information of any length to predict chlorophyll a concentration. To solve these problems, this paper defines the relationship between chlorophyll a concentration and various elements, depending on the long-term and short-term dependence between elements and the concentration of chlorophyll a. In this way, the long-term dependence between each element and the chlorophyll a concentration is separated from the short-term dependence. Then, based on the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), a merged LSTM prediction model was proposed. In this model, short and long term dependencies were presented respectively by different neurons and finally merged at the top of the model. The experimental data involves the continuous monitoring data of the station of Sandu Ao. The main result includes that the model has the advantage of fast reduction of training error, but also has significantly higher prediction accuracy compared with other three classical neural network models.-
Key words:
- chlorophyll a /
- Merged-LSTM /
- multi-factors /
- neural network
-
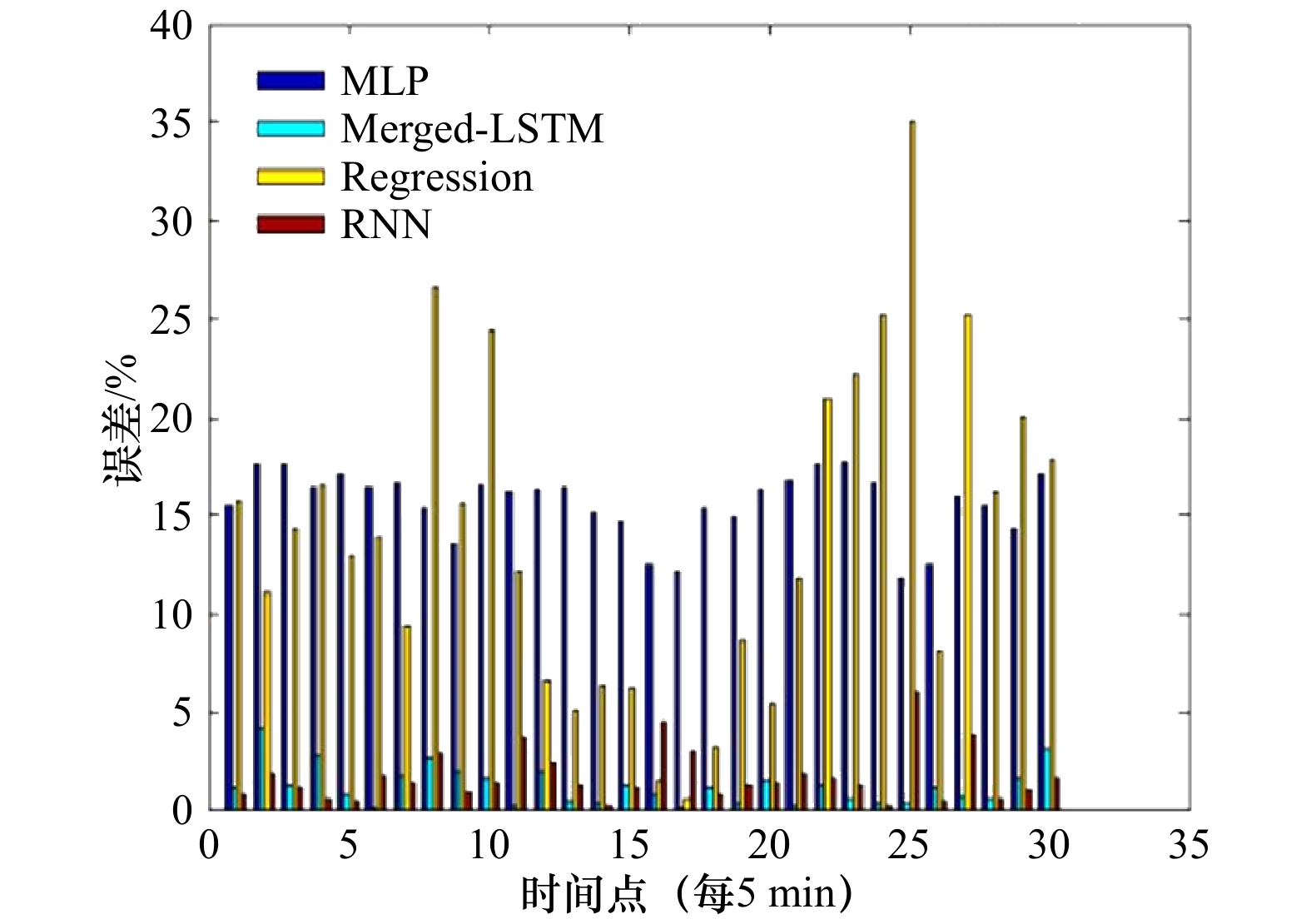
图 8 实际叶绿素a浓度值和预测叶绿素a浓度值
actual为真实值,Merged-LSTM为本文所提出的模型,RNN为递归神经网络,MLP为多层感知器,Regression为回归方法
Fig. 8 Actual and predicted chlorophyll a concentration
actual represents the true value, Merged-LSTM is the proposed model, RNN is recursive neural network, MLP is multilayer perceptron, Regression is the regression method
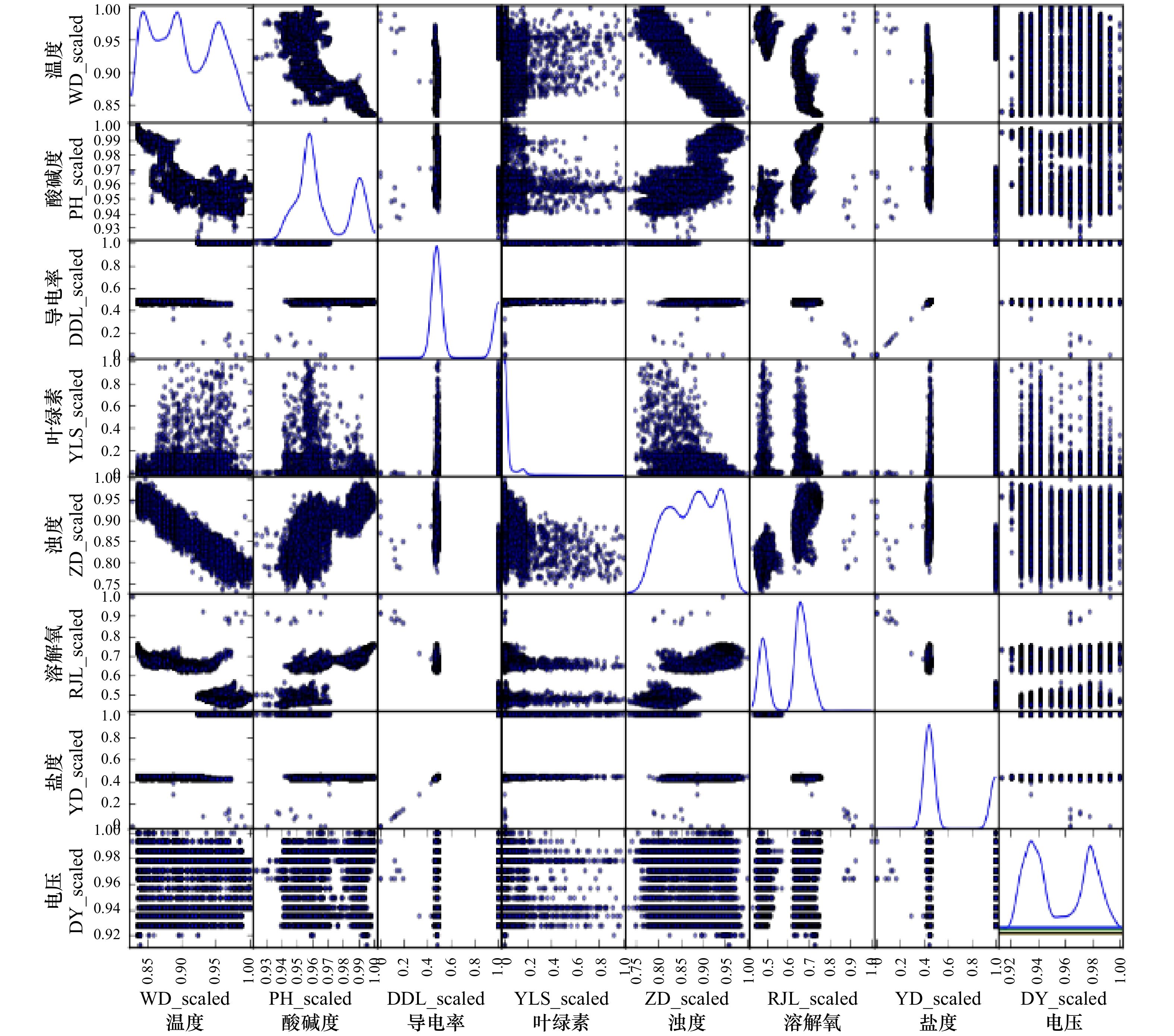
表 1 不同时延下相关系数
Tab. 1 Correlation coefficient under different time delays
1 2 3 4 5 6 温度(WD) −0.31 −0.23 −0.27 −0.25 −0.24 −0.22 PH值 −0.42 −0.42 −0.35 −0.39 −0.32 −0.39 电导率(DDL) −0.38 −0.38 −0.38 −0.38 −0.38 −0.38 浊度(ZD) 0.48 0.43 0.44 0.43 0.43 0.43 溶解氧(RJY) −0.29 −0.22 −0.22 −0.22 −0.22 −0.23 盐度(YD) 0.54 0.56 0.46 0.58 0.51 0.54 电压(DY) −0.13 −0.13 −0.13 −0.13 −0.12 −0.12 -
[1] 史锐, 张红, 岳荣, 等. 基于小波理论的干旱区内陆湖泊叶绿素a的TM影像遥感反演[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(3): 1043−1053.Shi Rui, Zhang Hong, Yue Rong, et al. A wavelet theory based remote sensing inversion of chlorophyll a concentrations for inland lakes in arid areas using TM image data[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(3): 1043−1053. [2] 罗建美, 霍永伟, 韩晓庆. 基于HJ卫星的近岸Ⅱ类水体叶绿素a浓度定量遥感反演研究——以滦河口北部海域为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(4): 117−129.Luo Jianmei, Huo Yongwei, Han Xiaoqing. Inversion of chlorophyll a concentration in offshore Ⅱ. waters using HJ satellite data--Example in the north of the Luanhe Delta[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(4): 117−129. [3] 盛琳, 陈静, 刘锐, 等. 一种水质分析方法: 基于GOCI影像的东平湖叶绿素a浓度估算[J]. 环境保护, 2017, 45(10): 60−63.Sheng Lin, Chen Jing, Liu Rui, et al. A method of water quality analysis: chlorophyll a concentration estimation of Dongping Lake based on GOCI image[J]. Environmental Protection, 2017, 45(10): 60−63. [4] Vollenweider R A. Scientific fundamentals of the eutrophication of lakes and flowing waters, with particular reference to nitrogen and phosphorus as factors in eutrophication[R]. Paris, France: OECD, 1968. [5] Jørgensen S E, Mejer H, Friis M. Examination of a lake model[J]. Ecological Modelling, 1978, 4(2/3): 253−278. [6] 毛江美, 陈新军, 余景. 基于神经网络的南太平洋长鳍金枪鱼渔场预报[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(10): 34−43.Mao Jiangmei, Chen Xinjun, Yu Jing. Forecasting fishing ground of Thunnus alalunga based on BP neural network in the South Pacific Ocean[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(10): 34−43. [7] 赵玉芹, 汪西莉, 蒋赛. 渭河水质遥感反演的人工神经网络模型研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2009, 24(1): 63−67. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2009.1.63Zhao Yuqin, Wang Xili, Jiang Sai. Study on neural network model for Weihe River water quality retrieving using remote-sensing image[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2009, 24(1): 63−67. doi: 10.11873/j.issn.1004-0323.2009.1.63 [8] 卢志娟, 朱玲, 裴洪平, 等. 基于小波分析与BP神经网络的西湖叶绿素a浓度预测模型[J]. 生态学报, 2008, 28(10): 4965−4973. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.10.042Lu Zhijuan, Zhu Ling, Pei Hongping, et al. The model of chlorophyll a concentration forecast in the West Lake based on wavelet analysis and BP neural networks[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, 28(10): 4965−4973. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.10.042 [9] 周露洪, 谷孝鸿, 曾庆飞, 等. 利用BP神经网络短期预测太湖不同湖区叶绿素a浓度[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2012, 33(4): 1−6.Zhou Luhong, Gu Xiaohong, Zeng Qingfei, et al. Applications of back propagation neural network for short-term prediction of chlorophyll a concentration in different regions of Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2012, 33(4): 1−6. [10] 杨柳, 韩瑜, 汪祖茂, 等. 基于BP神经网络的温榆河水质参数反演模型研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2013, 24(6): 25−28. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2013.06.006Yang Liu, Han Yu, Wang Zumao, et al. Study on retrieval model of water quality parameter in Wenyu River based on BP neural network[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2013, 24(6): 25−28. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2013.06.006 [11] 仝玉华, 周洪亮, 黄浙丰, 等. 一种自优化RBF神经网络的叶绿素a浓度时序预测模型[J]. 生态学报, 2011, 31(22): 6788−6795.Tong Yuhua, Zhou Hongliang, Huang Zhefeng, et al. Time series prediction of the concentration of chlorophyll a based on RBF neural network with parameters self-optimizing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2011, 31(22): 6788−6795. [12] Dekker A G, Brando V E, Anstee J M, et al. Imaging Spectrometry of Water[M]//van der Meer F D, de Jong S M. Imaging Spectrometry: Basic Principles and Prospective Applications. Dordrecht: Springer, 2002: 307-359. [13] 柴永强, 邵峰晶, 孙仁诚, 等. 基于决策树的MODIS影像赤潮智能检测技术[J]. 青岛大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 25(2): 47−52.Chai Yongqiang, Shao Fengjing, Sun Rencheng, et al. The intelligent detection technology of redtide from modis imagery based on decision tree[J]. Journal of Qingdao University: Natural Science Edition, 2012, 25(2): 47−52. [14] 李修竹, 苏荣国, 张传松, 等. 基于支持向量机的长江口及其邻近海域叶绿素a浓度预测模型[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(1): 69−76.Li Xiuzhu, Su Rongguo, Zhang Chuansong, et al. A Chl a prediction model based on support vector machine in Yangtze River estuaries and its Adjacent sea areas[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(1): 69−76. [15] 钟令枢. 基于ARIMA-LSTM的架空线状态数据挖掘[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016.Zhong Lingshu. Overhead line status data mining based on ARIMA-LSTM[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016. [16] Gers F A, Schmidhuber J, Cummins F. Learning to forget: continual prediction with LSTM[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Edinburgh, UK: IET, 1999. [17] Graves A. Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. [18] Shi Xingjian, Chen Zhourong, Wang Hao, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. [19] Yang Yuting, Dong Junyu, Sun Xin, et al. A CFCC-LSTM model for sea surface temperature prediction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 207−211. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2780843 [20] Greff K, Srivastava R K, Koutnik J, et al. LSTM: a search space odyssey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(10): 2222−2232. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582924 [21] Ma Xuezhe, Hovy E. End-to-end Sequence Labeling via Bi-directional LSTM-CNNs-CRF[M]. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. [22] Ordóñez J F, Roggen D. Deep convolutional and LSTM recurrent neural networks for multimodal wearable activity recognition[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(1): 115. doi: 10.3390/s16010115 [23] Gers F A, Eck D, Schmidhuber J. Applying LSTM to time series predictable through time-window approaches[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Vienna, Austria: Springer, 2001: 669−676. -




 下载:
下载: