Macrobenthic community and its relationship with environmental factors in the Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang Province, China
-
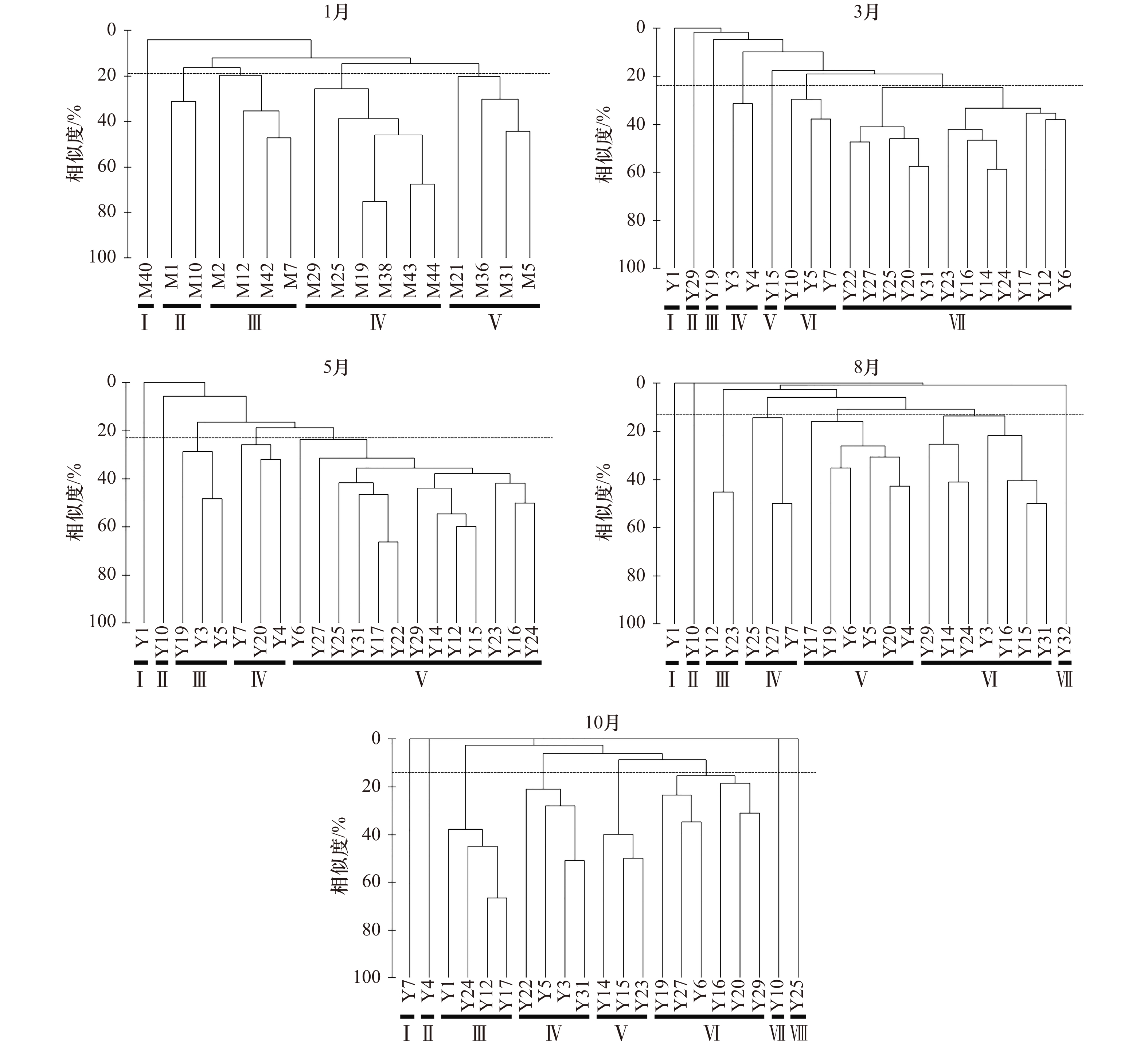
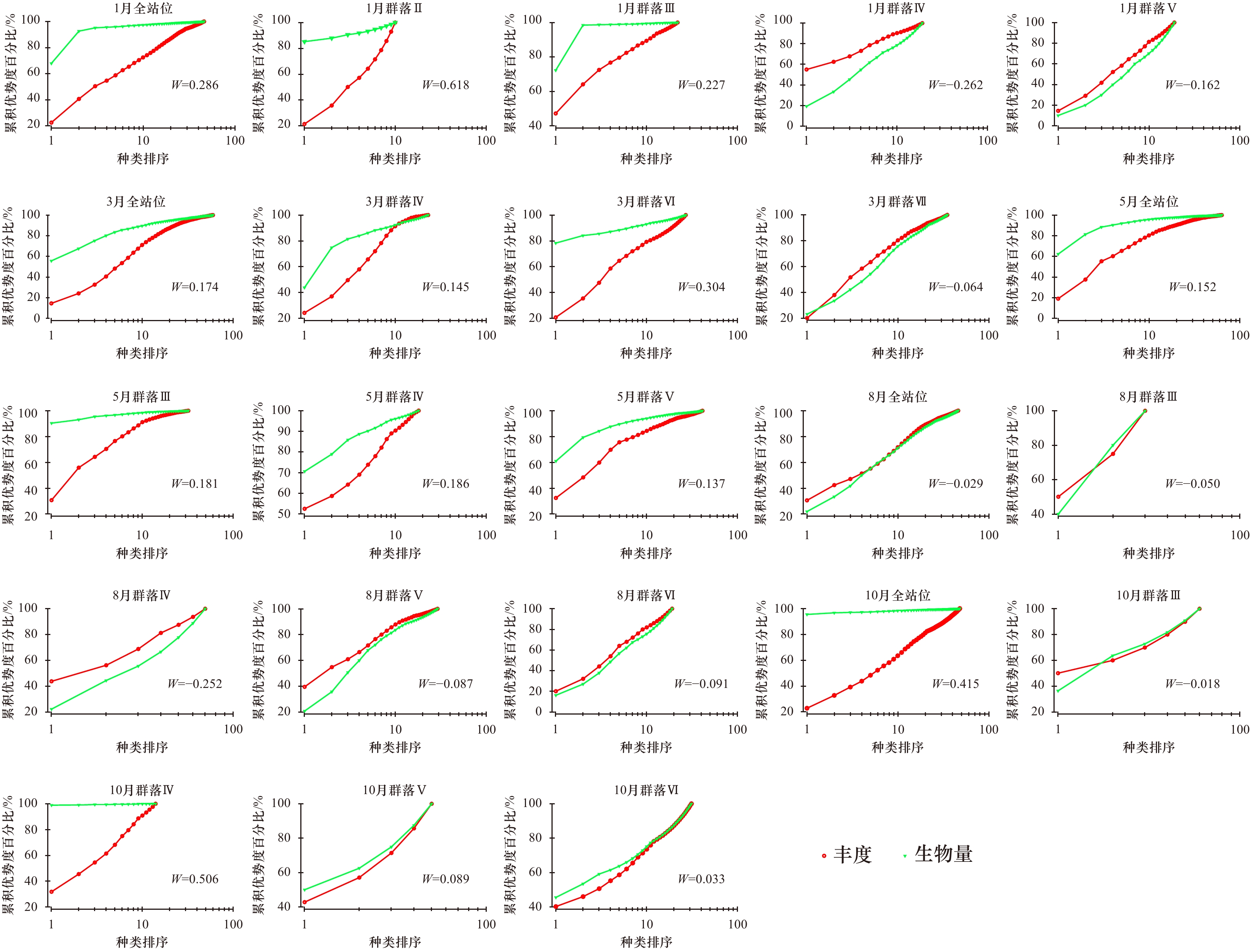
摘要: 为了解和掌握乐清湾大型底栖动物群落及其与环境因子的相关性,于2015年1月、3月、5月、8月和10月开展了5个航次的大型底栖动物和环境因子的调查。结果表明,1月、3月和5月3个月份的群落结构和空间分布均较为接近,优势群落的主要特征种为薄云母蛤和不倒翁虫;8月和10月的优势群落不明显,主要群落特征种有不倒翁虫、双形拟单指虫、寡鳃齿吻沙蚕、小头虫、中蚓虫属一种等。丰度/生物量曲线(ABC曲线)分析表明5月的群落结构较稳定,1月、3月、8月和10月均处于不同程度的扰动状态,其中8月的受扰动程度最大。BVSTEP分析表明亚硝酸盐是乐清湾大型底栖动物群落各月份差异的主要环境驱动因子,盐度和氨氮分别是影响乐清湾3月和5月大型底栖动物群落结构的主要环境因子。典范对应分析(CCA)表明水温对乐清湾大型底栖群落特征种时空分布影响最大,其次是盐度、溶解氧、含氮营养盐和pH等。通过CCA排序图发现大部分群落特征种分布在含氮营养盐较低的水域,表明高浓度的含氮营养盐已经对乐清湾的大型底栖动物产生了负面影响。
-
关键词:
- 乐清湾 /
- 大型底栖动物群落 /
- 环境因子 /
- 丰度/生物量曲线 /
- 典范对应分析(CCA)
Abstract: To evaluate the relationship between macrobenthic communities and environmental factors in the Yueqing Bay, five surveys were conducted in this study in January, March, May, August and October 2015. We found that both community structure and spatial distribution were similar in January, March and May, with Yoldia similis and Sternaspis sculata as the characteristic species. The dominant communities were not obvious in neither August nor October, the characteristic species of the main community were S. sculata, Nephtys oligobranchia, Capitella capitata, and Mediomastus sp. With the aid of abundance/biomass curve (ABC curve) analysis, we found that the communities were the most stable in May, and the most vulnerable in August. Results of BVSTEP analysis showed that nitrite was the dominant environmental factor for monthly difference of macrobenthic communities in the Yueqing Bay. In addition, salinity and ammonia nitrogen were the key environmental factors affecting the macrobenthic community structure in March and May, respectively. Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) further showed that water temperature had the greatest influence on the spatial and temporal distribution of characteristic species of macrobenthic communities in the Yueqing Bay, followed by salinity, dissolved oxygen, nitrogen nutrients and pH, etc. The CCA biplot also showed that the majority of the community species were distributed in the waters with low nitrogen nutrients, indicating that high concentrations of nitrogen nutrients had a negative impact on the distribution of macrobenthos in the Yueqing Bay. -
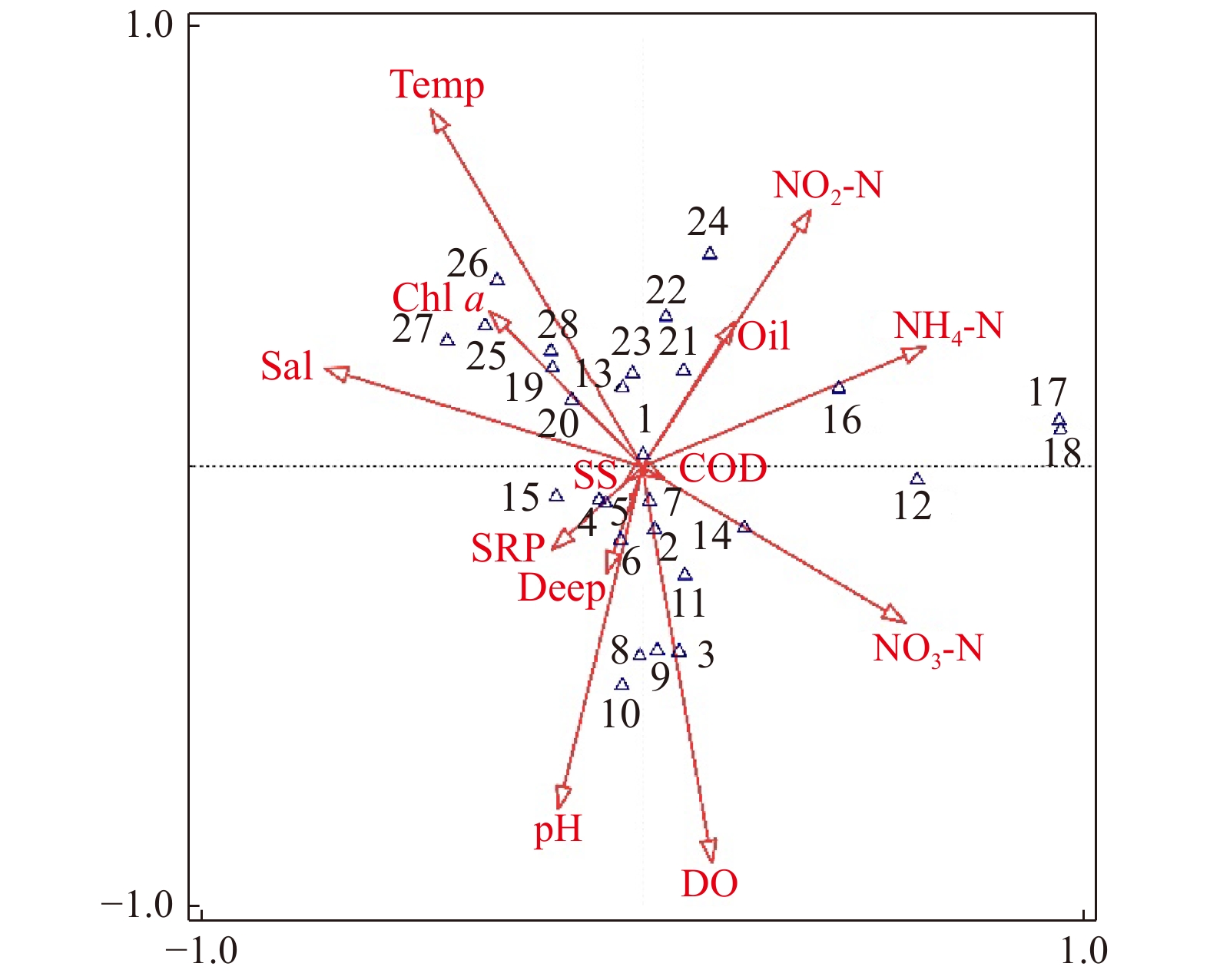
图 5 乐清湾大型底栖动物群落特征种与环境因子的CCA二维排序图
图中序号为各月份的群落特征种,1:寡鳃齿吻沙蚕;2:索沙蚕属一种;3:后指虫;4:多丝独毛虫;5:不倒翁虫;6:薄云母蛤;7:中蚓虫属一种;8:沙钩虾属一种;9:日本细莱毛虫;10:蛇尾幼体;11:钩虾一种;12:腺袋才女虫;13:钩毛虫属一种;14:叶须虫属一种;15:背毛背蚓虫;16:光滑河篮蛤;17:冠奇异稚齿虫;18:全刺沙蚕属一种;19:双形拟单指虫;20:似蛰虫;21:米列虫;22:异蚓虫;23:小头虫;24:中华后指虫;25:异毛虫一种;26:双唇索沙蚕;27:纽虫一种;28:长吻沙蚕
Fig. 5 CCA biplot of macrobenthic community characteristic species and environmental factors in the Yueqing Bay
Community characteristic species names of each month, 1: Nephtys oligobranchia; 2: Lumbrineris sp.; 3: Laonice cirrata; 4: Tharyx multifilis; 5: Sternaspis sculata; 6:Yoldia similis; 7: Mediomastus sp.; 8: Byblis sp.; 9: Levinsenia gracilis japonica; 10: Ophiuroidea; 11: Gammaridae; 12: Polydora triglanda; 13: Sigambra sp.; 14: Phyllodoce sp.; 15: Notomastus cf.aberans; 16: Potamocorbula laevis; 17: Paraprionospio cristata; 18: Nectoneanthes sp.; 19: Cossurella dimorpha; 20: Amaeana trilobata; 21: Melinna aberrans; 22: Heteromastus filiforms; 23: Capitella capitata; 24: Laonice sinica; 25: Paraonidae; 26: Lumbrineris cruzensis; 27: Nemertea; 28: Glycera chirori
表 1 乐清湾海域环境参数(平均值±标准差)的月份变化
Tab. 1 Monthly change of environmental parameters (mean±standard deviation) in the Yueqing Bay
调查时间 1月 3月 5月 8月 10月 水深/m 8.0±4.7 9.9±6.1 8.1±4.0 8.4±5.3 9.4±5.6 水温/℃ 10.8±0.6 10.7±0.6 19.6±1.3 29.2±1.3 23.4±0.5 pH 8.12±0.06 8.01±0.04 7.94±0.08 7.97±0.05 8.04±0.03 盐度 25.654±0.799 25.728±1.722 27.155±0.612 28.980±1.982 25.218±0.623 溶解氧/mg·L−1 9.19±0.15 8.94±0.59 7.16±045 6.12±0.40 6.93±0.18 化学耗氧量/mg·L−1 1.30±0.37 1.62±0.56 1.38±0.82 1.02±0.55 1.44±0.79 悬浮物/mg·L−1 222.3±106.4 459.4±247.4 353.8±334.4 291.4±293.4 262.8±156.8 叶绿素a/μg·L−1 1.2±0.3 1.1±0.3 1.2±0.4 2.5±1.1 1.3±04 磷酸盐/mg·L−1 0.046 5±0.003 1 0.043 4±0.003 0 0.039 9±0.005 3 0.041 5±0.008 7 0.055 0±0.007 4 亚硝酸盐−氮/mg·L−1 0.005 8±0.002 8 0.008 7±0.006 5 0.014 1±0.013 7 0.011 2±0.017 0 0.013 0±0.009 9 硝酸盐−氮/mg·L−1 0.588 0±0.049 4 0.610 7±0.088 8 0.590 0±0.044 7 0.339 7±0.091 0 0.554 1±0.042 3 氨−氮/mg·L−1 0.045 8±0.014 6 0.060 0±0.041 0 0.053 1±0.027 4 0.050 4±0.029 5 0.043 6±0.011 1 油类/mg·L−1 0.014±0.006 0.025±0.021 0.025±0.021 0.028±0.028 0.038±0.030 砂/% − − − 4.40±11.65 − 粉砂/% − − − 67.23±8.54 − 黏土/% − − − 28.37±5.28 − 注:“−”表示无数据。 表 2 乐清湾大型底栖动物群落结构与环境因子的BVSTEP相关性分析
Tab. 2 BVSTEP analysis of community structure and environmental factors of macrobenthos in the Yueqing Bay
时间 多因子组合 相关系数 显著性水平 单因子 相关系数 年度 亚硝酸盐、磷酸盐、叶绿素a、氨氮、水温 0.340 0.01 亚硝酸盐 0.228 1月 盐度、油类、亚硝酸盐、磷酸盐、pH、悬浮物 0.432 0.06 盐度 0.294 3月 盐度、水温、硝酸盐、氨氮 0.488 0.02 盐度 0.435 5月 氨氮、磷酸盐、pH、溶解氧 0.605 0.01 氨氮 0.461 8月 磷酸盐、亚硝酸盐、粉砂、化学耗氧量、悬浮物、氨氮 0.43 0.38 磷酸盐 0.182 10月 氨氮、溶解氧 0.111 0.90 氨氮 0.103 表 3 乐清湾大型底栖动物群落结构特征种与环境因子之间CCA分析结果
Tab. 3 CCA results of structural characteristics and environmental factors of macrobenthic community in the Yueqing Bay
排序轴 1 2 3 4 特征值 0.426 0.315 0.252 0.209 特征种和环境因子相关性 0.885 0.810 0.706 0.705 特征种−环境变量累积百分数/% 23.37 40.66 54.47 65.95 表 4 环境因子的解释率和显著性检验结果
Tab. 4 Interpretation rate of environmental factors and significance test results
环境因子 解释率/% F值 P值 水温 4.7 4.2 0.002 盐度 4.4 3.9 0.002 溶解氧 4.2 3.7 0.002 硝酸盐−氮(NO3-N) 3.9 3.4 0.002 亚硝酸盐−氮(NO2-N) 3.8 3.4 0.002 pH 3.7 3.3 0.002 氨氮(NH4-N) 3.4 2.9 0.016 叶绿素a 2.5 2.2 0.018 磷酸盐(SRP) 2.5 2.2 0.006 化学需氧量(COD) 2.4 2.1 0.010 油类 2 1.7 0.038 悬浮物(SS) 1.7 1.4 0.106 水深 1.1 1.0 0.522 -
[1] Dauer D M. Biological criteria, environmental health and estuarine macrobenthic community structure[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1993, 26(5): 249−257. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(93)90063-P [2] 闫丽娜, 叶深, 李德伟, 等. 乐清湾口海域春、秋季鱼类种类组成和数量分布[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2013, 44(4): 1062−1067.Yan Lina, Ye Shen, Li Dewei, et al. Species composition and quantitative distribution of fishes in spring and autumn in the Yueqing Bay mouth[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2013, 44(4): 1062−1067. [3] 郭远明, 钟志, 李佩佩, 等. 2011年7月乐清湾水产生物大规模死亡原因调查[J]. 现代农业科技, 2013(11): 284−286, 289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2013.11.182Guo Yuanming, Zhou Zhi, Li Peipei, et al. Investigation on massive mortality cause of hydrobiont in Yueqing Bay in July, 2011[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2013(11): 284−286, 289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2013.11.182 [4] 胡颢琰, 唐静亮, 李秋里, 等. 浙江省近岸海域底栖生物生态研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2006, 24(3): 76−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2006.03.008Hu Haoyan, Tang Jingliang, Li Qiuli, et al. Studies on benthic ecology in Zhejiang coastal waters[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2006, 24(3): 76−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2006.03.008 [5] 贾海波, 胡颢琰, 唐静亮, 等. 浙江南部近岸海域大型底栖生物生态[J]. 台湾海峡, 2011, 30(4): 577−582.Jia Haibo, Hu Haoyan, Tang Jingliang, et al. Ecology of macrobenthos in the south of Zhejiang coastal waters[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2011, 30(4): 577−582. [6] 廖一波, 寿鹿, 曾江宁, 等. 浙江西门岛海洋特别保护区大型底栖动物功能群特征及其与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1): 3−10.Liao Yibo, Shou Lu, Zeng Jiangning, et al. Functional groups of marine macrobenthos in relation to environmental factors around the Ximen Island national marine special reserve, Zhejiang[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(1): 3−10. [7] 戴泽蘅. 浙江省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988: 162−165.Office of the Leading Group for Comprehensive Investigation of Coastal Zone and Coastal Resources in Zhejiang Province. Comprehensive Survey of Coastal Zone and Coastal Resources in Zhejiang Province[M]. Beijing:China Ocean Press, 1988: 162−165. [8] 杨俊毅, 高爱根, 宁修仁, 等. 乐清湾大型底栖生物群落特征及其对水产养殖的响应[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(1): 34−41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.01.004Yang Junyi, Gao Aigen, Ning Xiuren, et al. Characteristics on macrofauna and the responses on aquiculture in Yueqing Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(1): 34−41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.01.004 [9] 王航俊, 邹清, 刘亚林, 等. 乐清湾大型底栖动物种类和数量组成特征及变化[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(6): 78−87. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170703001Wang Hangjun, Zhou Qing, Liu Yalin, et al. The characteristics and changes of the species and quantity of macrobenthos in Yueqing Bay[J]. Marine Science, 2018, 42(6): 78−87. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170703001 [10] Clarke K R, Ainsworth M. A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1993, 92: 205−219. doi: 10.3354/meps092205 [11] 曲方圆, 于子山, 隋吉星, 等. 丰度生物量比较法应用局限性[J]. 海洋科学, 2009, 33(6): 118−121.Qu Fangyuan, Yu Zishan, Sui Jixing, et al. The limitations of abundance biomass comparison method[J]. Marine Science, 2009, 33(6): 118−121. [12] 贾胜华, 曾江宁, 廖一波, 等. 洞头列岛及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落结构的研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34(2): 83−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.02.011Jia Shenghua, Zeng Jiangning, Liao Yibo, et al. Research on macrozoobenthic community structure in Dongtou Islands and adjacent sea area[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2016, 34(2): 83−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2016.02.011 [13] 廖一波, 曾江宁, 寿鹿, 等. 象山港人工鱼礁投放对大型底栖动物群落结构的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2014, 45(3): 487−495. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20130500044Liao Yibo, Zeng Jiangning, Shou Lu, et al. Impact of artificial reef on macrobenthic community structure in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2014, 45(3): 487−495. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20130500044 [14] 王全超, 李宝泉. 烟台近海大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2013, 44(6): 1667−1680. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20130300003Wang Quanchao, Li Baoquan. Community structure of macrobenthos in coastal water off Yantai, East China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2013, 44(6): 1667−1680. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20130300003 [15] 董鹏, 张海波, 叶仙森, 等. 象山港中部海域大型底栖动物群落组成及多样性特征[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2015, 24(3): 430−440.Dong Peng, Zhang Haibo, Ye Xiansen, et al. Community structure and biodiversity characteristics of macrobenthos in the middle of Xiangshan Bay[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2015, 24(3): 430−440. [16] 寿鹿, 曾江宁, 廖一波, 等. 杭州湾大型底栖动物季节分布及环境相关性分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(6): 151−159.Shou Lu, Zeng Jiangning, Liao Yibo, et al. Seasonal distribution of macrozoobenthos in relation to environmental factors in Hangzhou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(6): 151−159. [17] 符芳菲, 李纯厚, 徐姗楠. 胶州湾冬季大型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的相关性[J]. 中国水产科学, 2018, 25(1): 159−168.Fu Fangfei, Li Chunhou, Xu Shannan. Analysis of the characteristics of the macrobenthic community of Jiaozhou Bay in winter[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2018, 25(1): 159−168. [18] 吴斌, 宋金明, 李学刚. 黄河口大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与环境因子的耦合分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(4): 62−72.Wu Bin, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang. Characteristics of benthic macroinvertebrate community structure and its coupling relationships with environment factors in Huanghe estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(4): 62−72. [19] 徐勇, 隋吉星, 李新正, 等. 南黄海大型底栖动物群落划分及变化[J]. 广西科学, 2016, 23(4): 339−345.Xu Yong, Sui Jixing, Li Xinzheng, et al. Variations of macrofaunal community classification in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 2016, 23(4): 339−345. [20] 彭松耀, 李新正, 徐勇, 等. 十年间黄海大型底栖动物优势种的变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(3): 536−542.Peng Songyao, Li Xinzheng, Xu Yong, et al. Variation of macrobenthos in Yellow Sea in past 10 years[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(3): 536−542. [21] 杨东, 周政权, 张建设, 等. 烟台牟平海洋牧场夏季大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(5): 134−143.Yang Dong, Zhou Zhengquan, Zhang Jianshe, et al. Characteristics of macrobenthic communities at the Muping marine ranch of Yantai in summer[J]. Marine Science, 2017, 41(5): 134−143. [22] Shou L, Zeng J N, Liao Y B, et al. Temporal and spatial variability of benthic macrofauna communities in the Yangtze River estuary and adjacent area[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 2013, 16(1): 31−39. [23] 刘录三, 郑丙辉, 李宝泉, 等. 长江口大型底栖动物群落的演变过程及原因探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(3): 134−145.Liu Lusan, Zheng Binghui, Li Baoquan, et al. Long-term trends of macrobenthos in Changjiang Estuary, China in relation to environmental changes[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(3): 134−145. [24] Warwick R M. A new method for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities[J]. Marine Biology, 1986, 92(4): 557−562. doi: 10.1007/BF00392515 [25] 李荣冠, 江锦祥. 应用丰度生物量比较法监测海洋污染对底栖生物群落的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 1992, 14(1): 108−114.Li Rongguan, Jiang Jinxiang. Monitoring the affection of marine pollution on macrobenthos community using the abundance/biomass comparison[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1992, 14(1): 108−114. [26] 孙新新, 黄一彬. 温州市50余年四季降水特征及其变化趋势分析[J]. 浙江水利科技, 2015(3): 30−33.Sun Xinxin, Huang Yibin. Analysis of precipitation characteristics and its changing trend in the four seasons of Wenzhou[J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics, 2015(3): 30−33. [27] Peng S Y, Li X Z, Wang H F, et al. Macrobenthic community structure and species composition in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea in jellyfish bloom[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014, 32(3): 576−594. doi: 10.1007/s00343-014-3068-8 [28] 周然, 覃雪波, 彭士涛, 等. 渤海湾大型底栖动物调查及与环境因子的相关性[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 64(1): 50−58.Zhou Ran, Qin Xuebo, Peng Shitao, et al. Macroinvertebrate investigation and their relation to environmental factors in Bohai Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 64(1): 50−58. [29] Glockzin M, Zettler M L. Spatial macrozoobenthic distribution patterns in relation to major environmental factors—A case study from the Pomeranian Bay (southern Baltic Sea)[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2008, 59(3): 144−161. doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2008.01.002 [30] 李宝泉, 李新正, 于海燕, 等. 胶州湾底栖软体动物与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2005, 36(3): 193−198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.03.001Li Baoquan, Li Xinzheng, Yu Haiyan, et al. Macrobenthic Mollusca fauna and its relations to environmental factors in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2005, 36(3): 193−198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2005.03.001 [31] Jayaraj K A, Jayalakshmi K V, Saraladevi K. Influence of environmental properties on macrobenthos in the northwest Indian shelf[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2007, 127(1/3): 459−475. [32] 刘晓收, 赵瑞, 华尔, 等. 莱州湾夏季大型底栖动物群落结构特征及其与历史资料的比较[J]. 海洋通报, 2014, 33(3): 283−292. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.03.006Liu Xiaoshou, Zhao Rui, Hua Er, et al. Macrofaunal community structure in the Laizhou Bay in summer and the comparison with historical data[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2014, 33(3): 283−292. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2014.03.006 [33] Carvalho S, Moura A, Gaspar M B, et al. Spatial and inter-annual variability of the macrobenthic communities within a coastal lagoon (Óbidos lagoon) and its relationship with environmental parameters[J]. Acta Oecologica, 2005, 27(3): 143−159. doi: 10.1016/j.actao.2004.11.004 [34] 徐勇, 线薇微, 李文龙. 2012年春季和秋季长江口无脊椎动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2014, 44(7): 82−90.Xu Yong, Xian Weiwei, Li Wenlong. Invertebrate community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters in spring and autumn, 2012[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(7): 82−90. [35] 彭松耀, 赖子尼, 蒋万祥, 等. 珠江口大型底栖动物的群落结构及影响因子研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2010, 34(6): 1179−1189.Peng Songyao, Lai Zini, Jiang Wanxiang, et al. Study on community structure of macrozoobenthos and impact factors in Pearl River estuary[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2010, 34(6): 1179−1189. [36] 刘坤, 林和山, 何雪宝, 等. 厦门近岸海域大型底栖动物摄食功能群及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(12): 95−105.Liu Kun, Lin Heshan, He Xuebao, et al. Functional feeding groups of macrozoobenthos and their relationships to environmental factors in Xiamen coastal waters[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(12): 95−105. [37] Elser J J, O’Brien W J, Dobberfuhl D R, et al. The evolution of ecosystem processes: growth rate and elemental stoichiometry of a key herbivore in temperate and arctic habitats[J]. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 2000, 13(5): 845−853. doi: 10.1046/j.1420-9101.2000.00215.x [38] 苏强. 生长速率假说及其在浮游动物营养动力学中的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(11): 1204−1210.Su Qiang. Growth rate hypothesis research progresses: Implications for zooplankton[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(11): 1204−1210. [39] 陈雷, 徐兆礼, 陈胜, 等. 2007年乐清湾富营养化空间特征及其成因分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2010, 19(1): 91−97.Chen Lei, Xu Zhaoli, Chen Sheng, et al. Causal analysis and distribution of eutrophication index in the Yueqing Bay in spring summer of 2007[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2010, 19(1): 91−97. [40] 刘迅, 王莉, 顾晓英, 等. 浙江檀头山岛周围海域夏、秋季大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(3): 553−567.Liu Xun, Wang Li, Gu Xiaoying, et al. Characteristics of the community structure of macrobenthos around Zhejiang Tantoushan Island waters in summer and autumn[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(3): 553−567. [41] Dippner J W, Ikauniece A. Long-term zoobenthos variability in the Gulf of Riga in relation to climate variability[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2001, 30(3/4): 155−164. -





 下载:
下载: