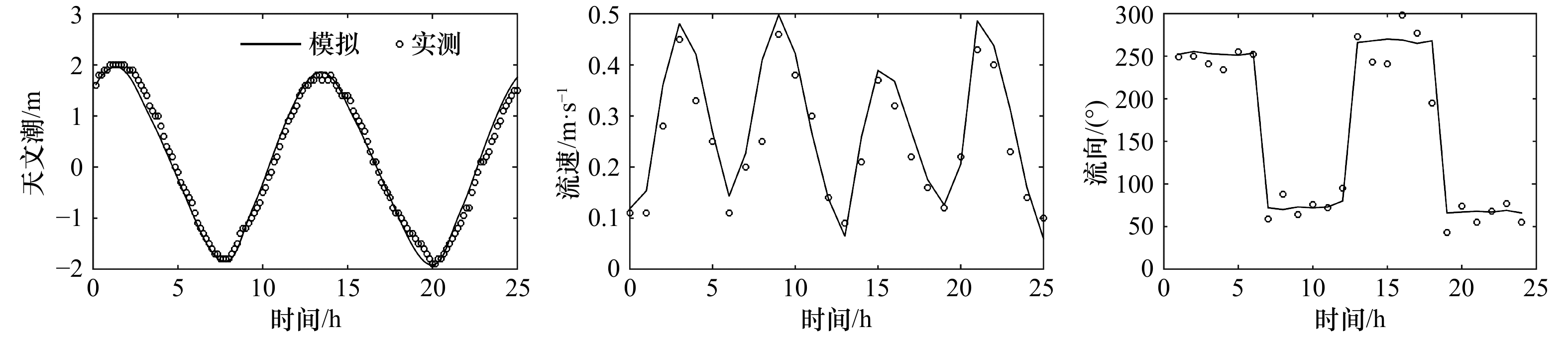
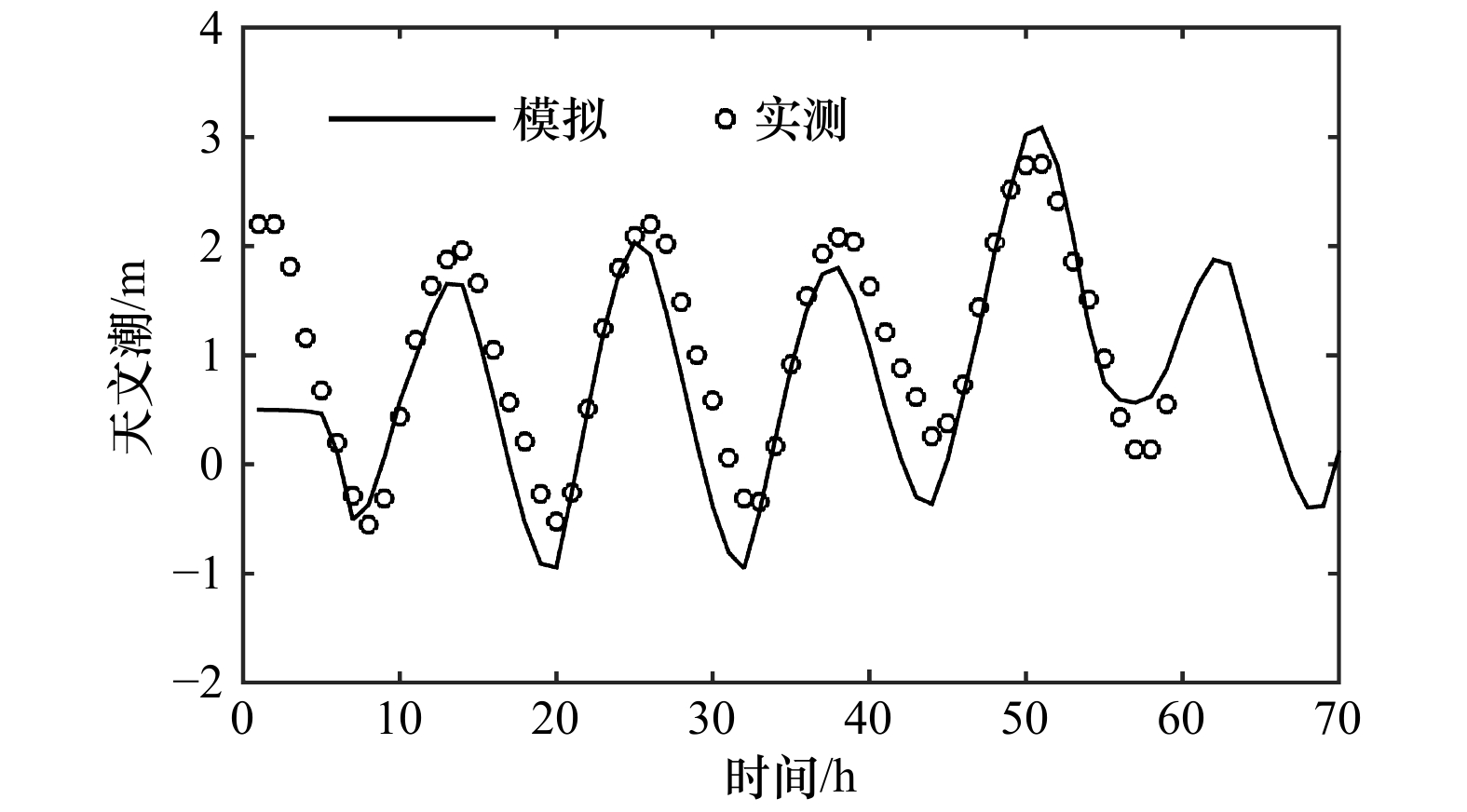
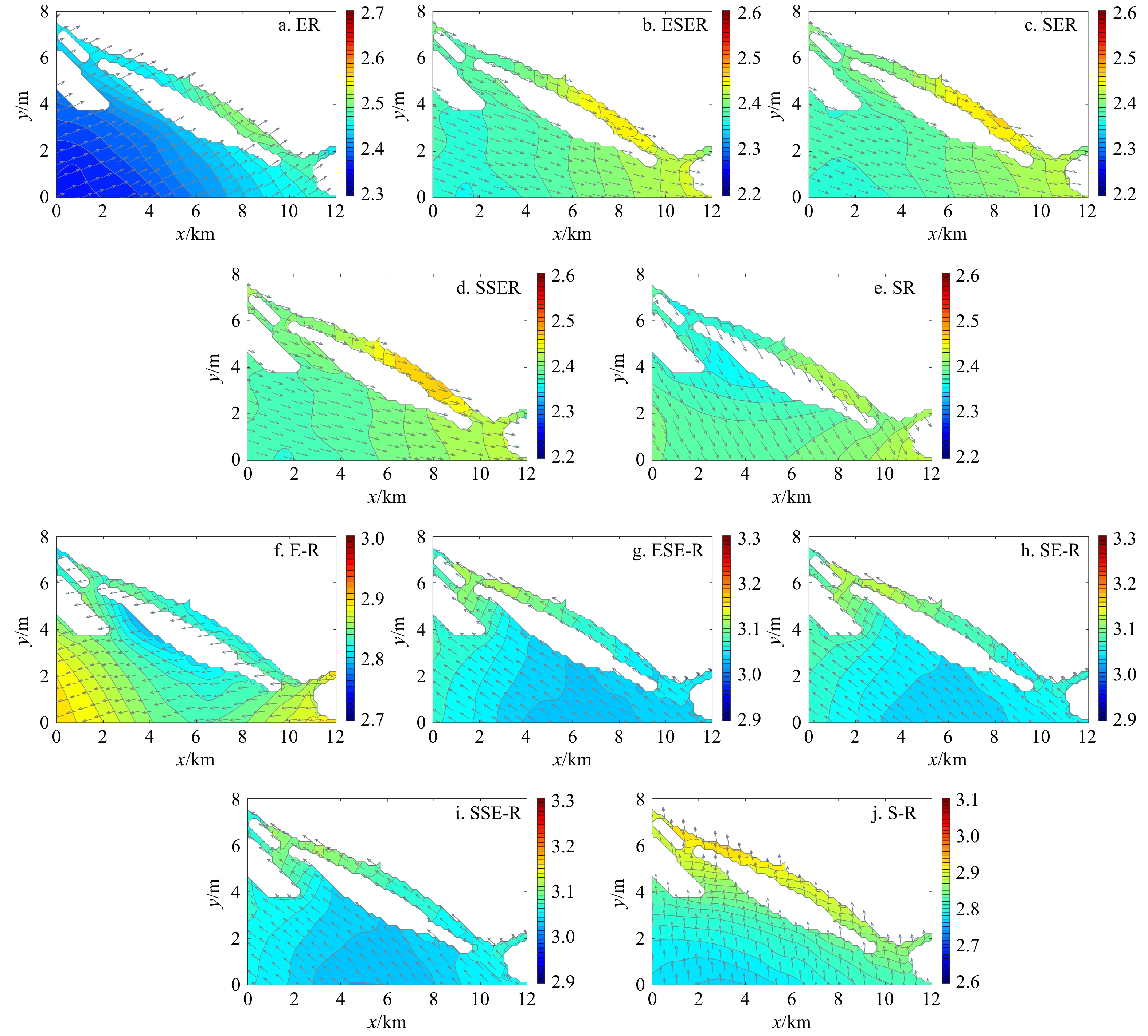
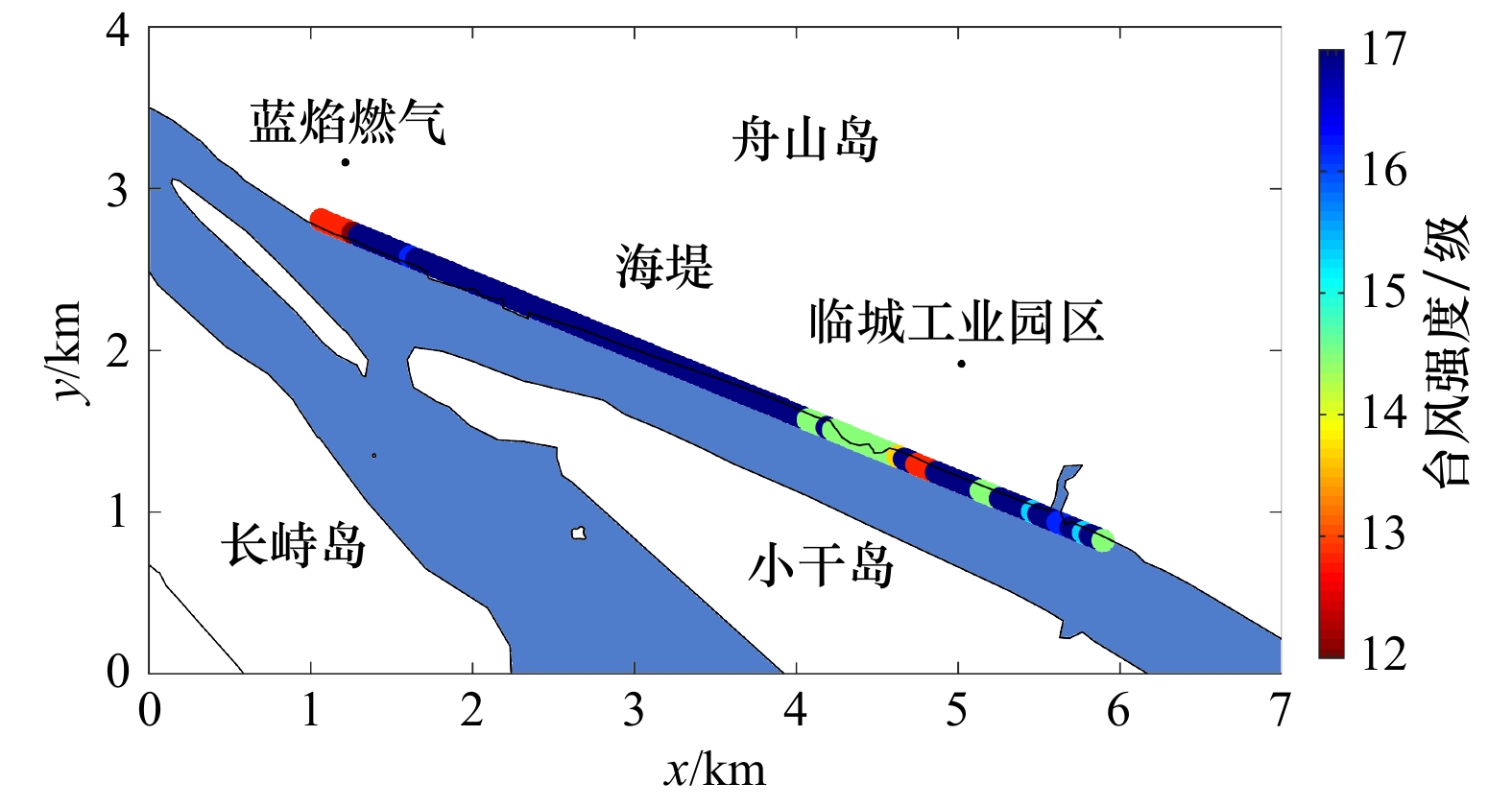
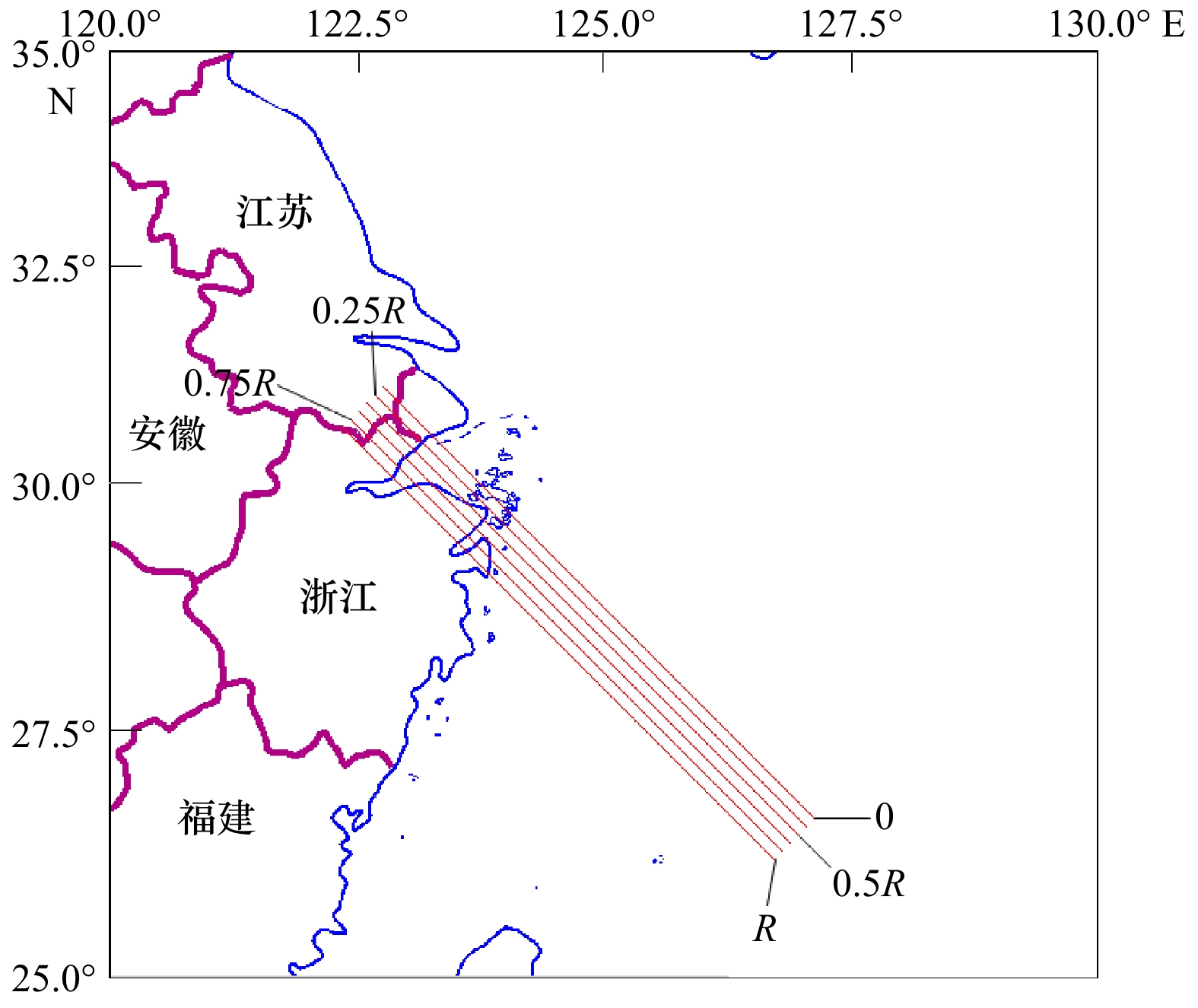
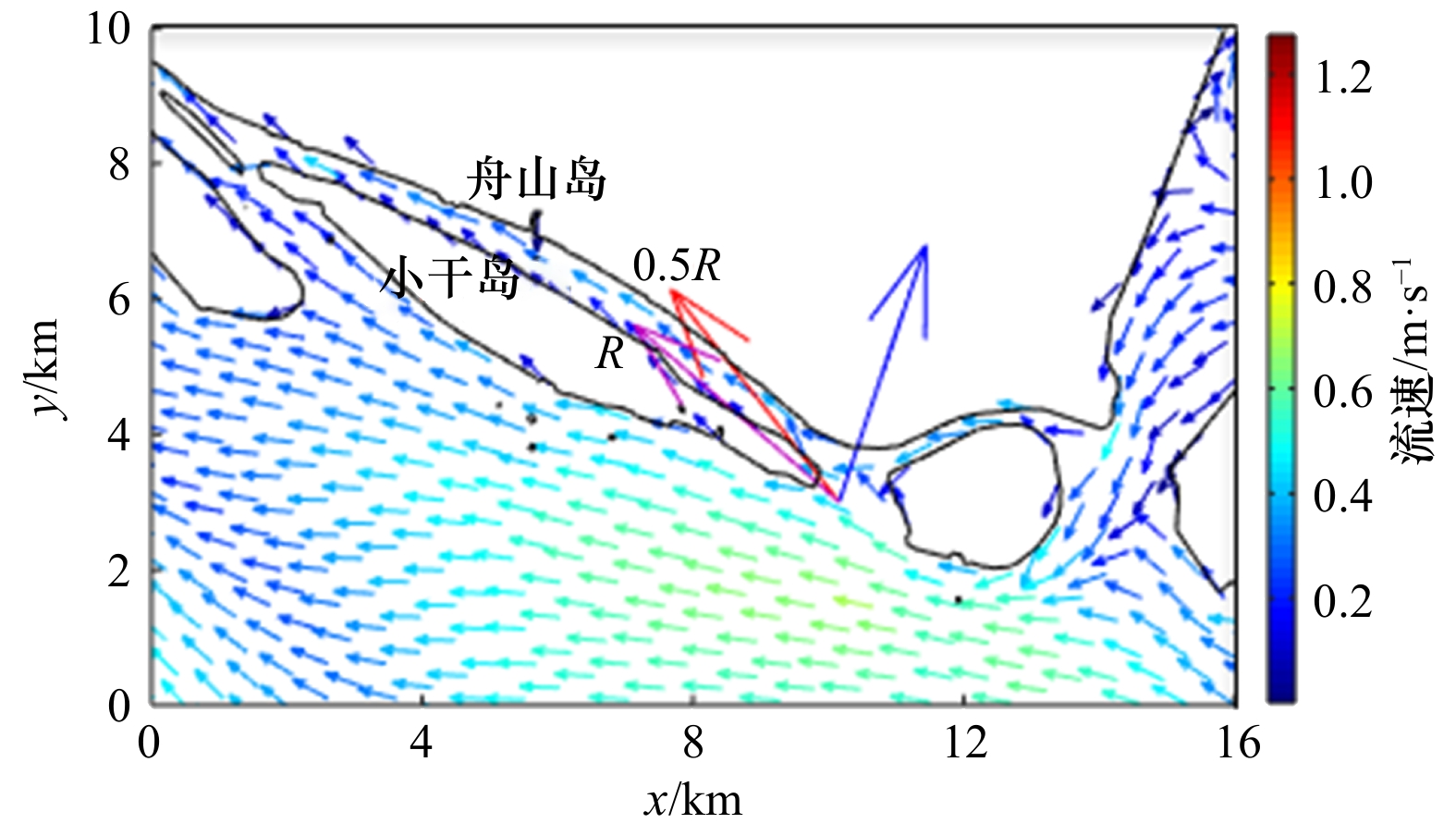
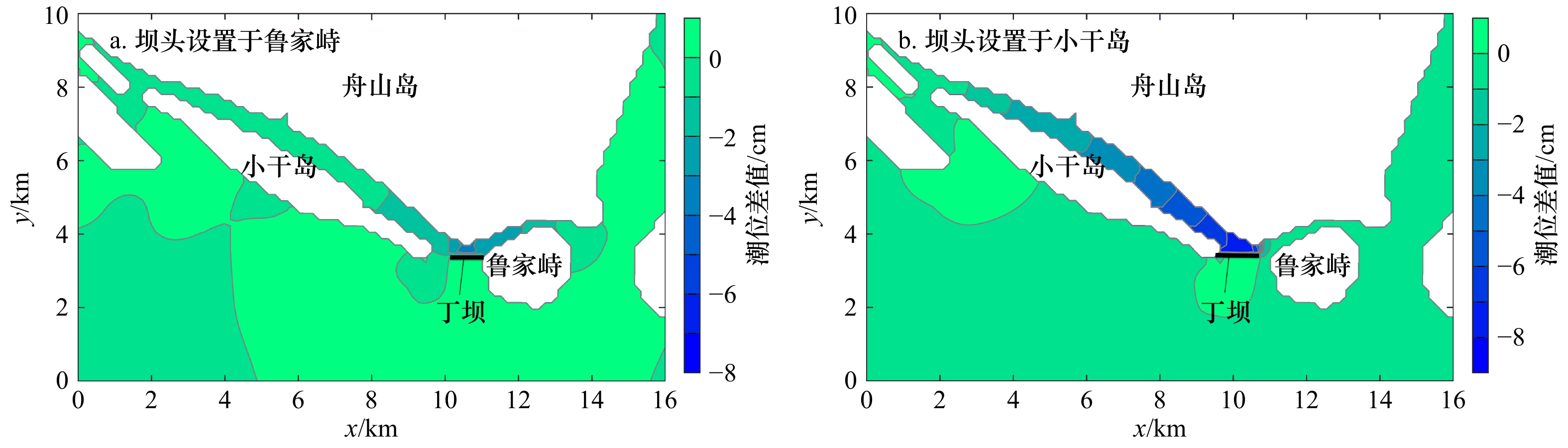
| [1] |
Sebastian A, Proft J, Dietrich J C, et al. Characterizing hurricane storm surge behavior in Galveston Bay using the SWAN + ADCIRC model[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2014, 88: 171−181. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2014.03.002
|
| [2] |
Dietrich, J C, Zijlema M, Westerink J J, et al. Modeling hurricane waves and storm surge using integrally-coupled, scalable computations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2011, 58(1): 45−65. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.08.001
|
| [3] |
Xie Dongmei, Zou Qingping, Cannon J W. Application of SWAN+ADCIRC to tide-surge and wave simulation in Gulf of Maine during Patriot’s Day storm[J]. Water Science and Engineering, 2016, 9(1): 33−41. doi: 10.1016/j.wse.2016.02.003
|
| [4] |
Rego J L, Li Chunyan. Nonlinear terms in storm surge predictions: effect of tide and shelf geometry with case study from Hurricane Rita[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115(C6): C06020.
|
| [5] |
Zhou Jifu, Liu Jinlong. Estimation of extreme hydrodynamic environments of Puti Island wind farm in Bohai Sea[J]. Procedia IUTAM, 2017, 25: 74−81. doi: 10.1016/j.piutam.2017.09.012
|
| [6] |
Xie Lian, Liu Huiqing, Peng Machuan. The effect of wave-current interactions on the storm surge and inundation in Charleston Harbor during Hurricane Hugo 1989[J]. Ocean Modelling, 2008, 20(3): 252−269. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2007.10.001
|
| [7] |
孙志林, 纪汗青, 方诗标, 等. 台风过境方位对洞头渔港增水的影响[J]. 水力发电学报, 2018, 37(1): 70−78. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20180108Sun Zhilin, Ji Hanqing, Fang Shibiao, et al. Influence of typhoon moving directions on storm surges at Dongtou fishing port[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 70−78. doi: 10.11660/slfdxb.20180108
|
| [8] |
匡翠萍, 宋竑霖, 顾杰, 等. 黄骅港风生流及紊动的三维特性[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 51(1): 38−45, 67.Kuang Cuiping, Song Honglin, Gu Jie, et al. Three-dimensional characteristics of wind-induced current and turbulence at Huanghua Harbor[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2017, 51(1): 38−45, 67.
|
| [9] |
Luijendijk A P, Ranasinghe R, de Schipper M A, et al. The initial morphological response of the sand engine: a process-based modelling study[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2017, 119: 1−14. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2016.09.005
|
| [10] |
Hope M E, Westerink J J, Kennedy A B, et al. Hindcast and validation of Hurricane Ike (2008) waves, forerunner, and storm surge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(9): 4424−4460. doi: 10.1002/jgrc.20314
|
| [11] |
Kennedy A B, Gravois U, Zachry B C, et al. Origin of the Hurricane Ike forerunner surge[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38(8): L08608.
|
| [12] |
Liu Xing, Jiang Wensheng, Yang Bo, et al. Numerical study on factors influencing typhoon-induced storm surge distribution in Zhanjiang Harbor[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 215: 39−51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.09.019
|
| [13] |
Wang Yuxing, Duan Yihong, Guo Zhixing, et al. Deterministic-probabilistic approach for probable maximum typhoon-induced storm surge evaluation over Wenchang in the South China Sea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2018, 214: 161−172. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2018.09.025
|
| [14] |
Wang Yanping, Mao Xinyan, Jiang Wensheng. Long-term hazard analysis of destructive storm surges using the ADCIRC- SWAN model: a case study of Bohai Sea, China[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation & Geoinformation, 2018, 73: 52−62.
|
| [15] |
Luo Yao, Shi Hui, Wang Dongxiao. Multivariate analysis of extreme storm surges in a semi-enclosed bay[J]. Ocean Science Discussions, 2017, 14(2): 1−18.
|
| [16] |
刘永玲, 冯建龙, 江文胜, 等. 热带气旋资料长度对风暴潮危险性评估结果的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3): 60−70.Liu Yongling, Feng Jianlong, Jiang Wensheng, et al. Effects of a tropical cyclone data sets length on the result of risk assessment of storm surge[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(3): 60−70.
|
| [17] |
孙志林, 黄森军, 焦建格, 等. 河口区径流对台风暴潮影响研究[J]. 天津大学学报: 自然科学与工程技术版, 2017, 50(5): 519−526.Sun Zhilin, Huang Senjun, Jiao Jiange, et al. Effect of runoff on typhoon storm surge in estuaries[J]. Journal of Tianjin University: Science and Technology, 2017, 50(5): 519−526.
|
| [18] |
Sun Zhilin, Huang Senjun, Jiao Jiange, et al. Effects of cluster land reclamation projects on storm surge in Jiaojiang Estuary, China[J]. Water Science and Engineering, 2017, 10(1): 59−69. doi: 10.1016/j.wse.2017.03.003
|
| [19] |
Lyddon C, Brown J M, Leonardi N, et al. Uncertainty in estuarine extreme water level predictions due to surge-tide interaction[J]. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(10): e0206200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206200
|
| [20] |
刘睿哲, 朱庆勇, 倪培桐. 珠江河口地区风暴潮增水过程数值模拟[J]. 广东水利水电, 2018(4): 6−10. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2018.04.002Liu Ruizhe, Zhu Qingyong, Ni Peitong. Numerical simulation of storm surge process in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Guangdong Water Resources & Hydropower, 2018(4): 6−10. doi: 10.11905/j.issn.1008-0112.2018.04.002
|
| [21] |
Lyddon C, Brown J M, Leonardi N, et al. Flood hazard assessment for a hyper-tidal estuary as a function of tide-surge-morphology interaction[J]. Estuaries & Coasts, 2018, 41(6): 1565−1586.
|
| [22] |
Deltares. Delft3D FLOW User Manual[M]. The Netherlands: Deltares, 2014.
|
| [23] |
Deltares. Delft3D TIDE User Manual[M]. The Netherlands: Deltares, 2014.
|
| [24] |
王喜年. 风暴潮预报知识讲座第五讲: 风暴潮预报技术(2)[J]. 海洋预报, 2002, 19(2): 64−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.02.010Wang Xinian. The lecture of storm surge forecast fifth: the storm surge forecasting technology (2)[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2002, 19(2): 64−70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.02.010
|
| [25] |
王喜年. 风暴潮讲座第三讲: 风暴潮数值模式计算中气压场和风场的处理[J]. 海洋预报, 1986, 3(4): 56−64. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.1986.04.008Wang Xinian. The lecture of storm surge forecast third: treatment of pressure field and wind field in storm surge numerical model calculation[J]. Marine Forecasts, 1986, 3(4): 56−64. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.1986.04.008
|





 下载:
下载: