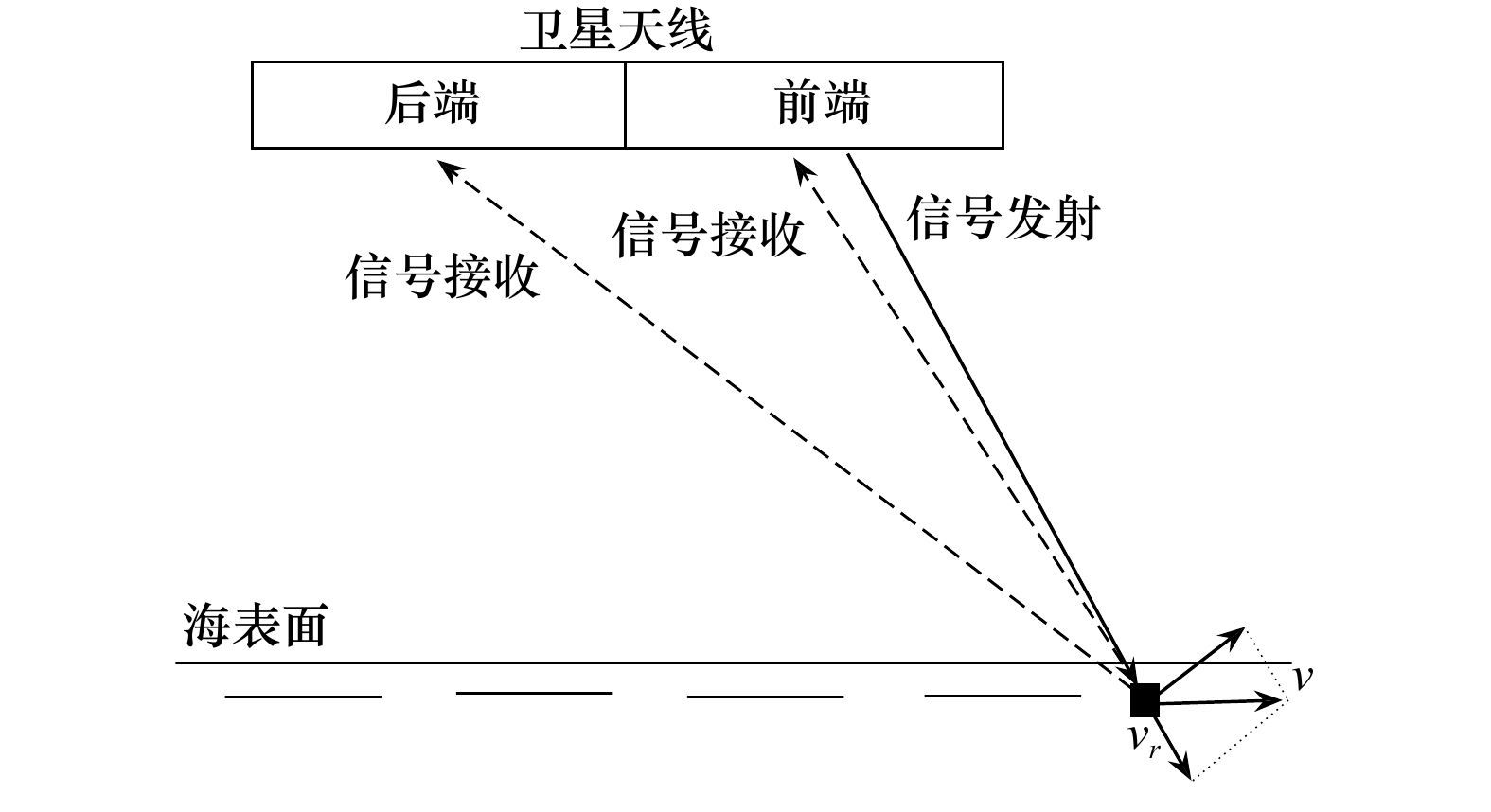
Exploratory research on the retrieval of internal wave parameters and sea surface current velocity based on TerraSAR-X satellite data
-
摘要: 本文利用TerraSAR-X(TSX)卫星于2010年4月22日在南海东沙岛附近海域获取的数据进行海洋内孤立波动力要素和海表流速信息的提取研究。基于TSX数据的后向散射强度信息,利用经验模态分解法得到内孤立波半波宽度,再利用两层模型法和参数化法计算得到内孤立波振幅和相速度。反演结果显示,利用参数化方法得到的振幅(约21~39 m)和两层模型法得到的相速度(约1.07 m/s)与历史实测资料较为一致。进而利用TSX的顺轨干涉数据获取研究海域内的多普勒速度,再分别采用M4S模型法和直接分离法处理,进而提取海表流速。结果显示,两种方法得到的海表流速的全场平均值较为一致,均为1.10 m/s左右。M4S模型法对流速最大值的改变量较大而直接分离法对流速最小值的改变量较大。M4S模型对内孤立波波峰线区域海表流速的修正大于无内孤立波的海域。最后,基于KdV方程计算得到内孤立波引起的表面流的流速约为0.28 m/s,对反演出的海表流速贡献占比23%。Abstract: In this paper, we conducted a study on deriving internal wave parameters and sea surface current velocity in the vicinity of Dongsha Island from spaceborne SAR data of TerraSAR-X (TSX), acquired on April 22, 2010. Based on the intensity data of the TSX scene, characteristic half width of the internal wave was obtained through the empirical mode decomposition method. Then amplitude and phase speed of the internal solitary wave were calculated using the two-layer model method and the parameterization method, respectively. The results suggested that the amplitude (approximately 21–39 m) acquired by the parameterization method and the phase speed (approximately 1.06 m/s) obtained by the two-layer model method were consistent with the historical measurements. Furthermore, the Doppler velocity in the research area was calculated using along-track interferometry data of the TSX scene. The M4S model and the direct-separation method were used to extract the sea surface current velocity. The mean sea surface current field of the study area obtained by the two methods were consistent, which were both of approximately 1.10 m/s. The M4S model led to more adjustments to maximum of the surface velocity whereas more adjustments to the minimum values were found in the direct-separation method. Moreover, it was found that the adjustment of surface current retrieval using the M4S model were more in the region of wave crest of the internal waves. Finally, based on the KdV equation, the velocity of internal-wave-induced surface flow is about 0.28 m/s, which contributes 23% to the retrieved sea surface current velocity.
-
图 2 TSX卫星在东沙岛附近获取的快视图(2010年4月22日22:13 UTC)(a),对应该快视图的雷达后向散射强度(b),降噪处理后对应快视图的相位差(c)
海域大小约30 km(距离向)×110 km(方位向),图a中右下部所示明亮区域为东沙岛和东沙环礁;图b中5个断面用于内波参数提取的计算;图c用于后续海表流场的反演
Fig. 2 Quicklook of the TSX scene acquired over Dongsha Island at 22:13 UTC on April 22, 2010 (a); the corresponding radar backscatter intensity of the TSX scene (b); the derived phase difference from the ATI data of the TSX scene (c)
Sea area size is 30 km (range direction)×110 km (azimuth direction), the bright areas are Dongsha Island and Dongsha Atoll in a; the 5 transects in b are used to extract parameters of the internal wave; c is further used to retrieve the sea surface current
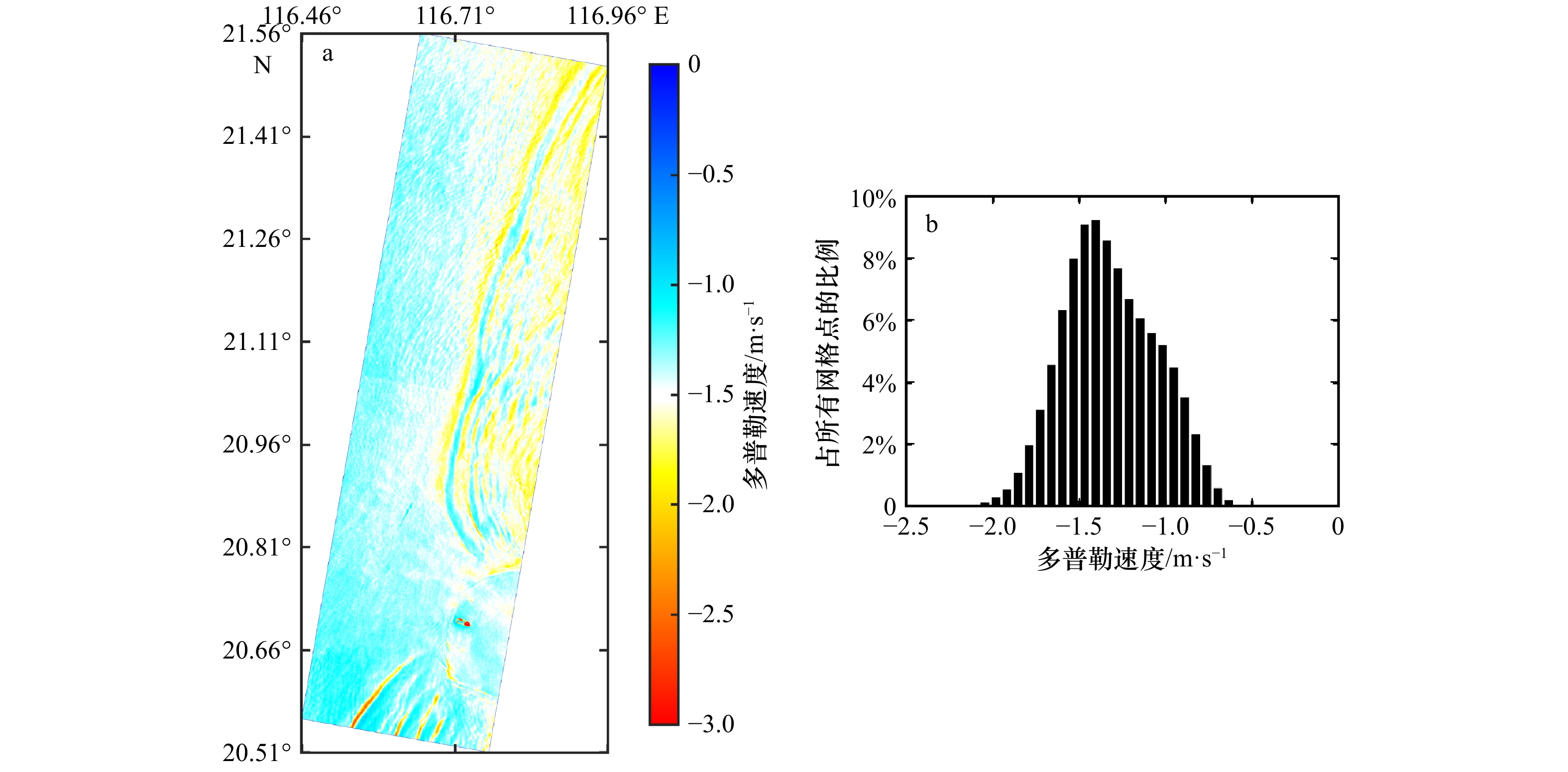
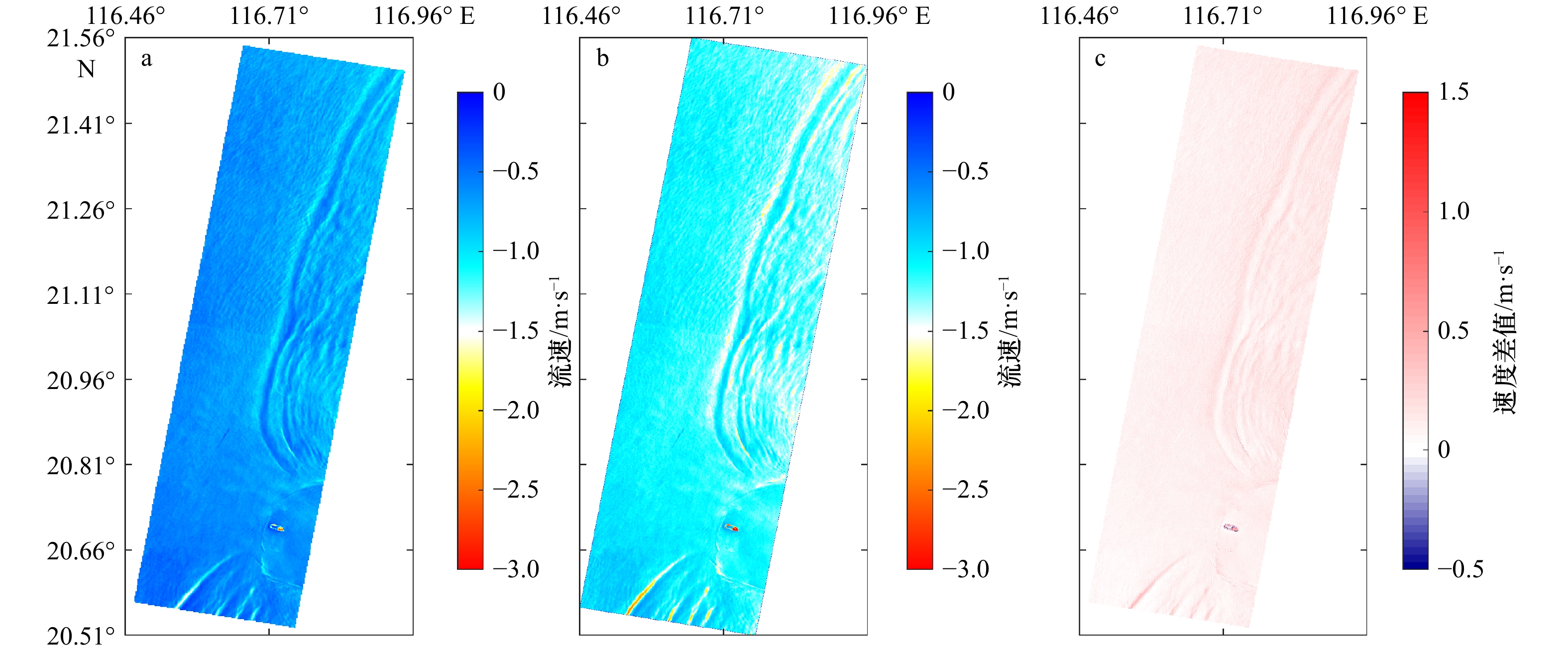
图 7 M4S模型法得到的海表流速结果(雷达视向)(a),直接分离法得到的海表流速结果(雷达视向)(b),两者的差值(c)
Fig. 7 Sea surface current speed (component in the line of sight) retrieved using the M4S model (a), sea surface current speed (component in the line of sight) derived using the separation method (b); differences between the two retrievals (c)
表 1 TSX获取的SAR图像的基本信息
Tab. 1 Technical specification of the TerraSAR-X ATI data
产品级别 工作模式 极化方式 天线接收模式 空间分辨率 单视斜距复
影像条带成像 HH DRA 约2 m 表 2 不同模态的归一化方差
Tab. 2 Normalized variance of the 8 intrinsic modes
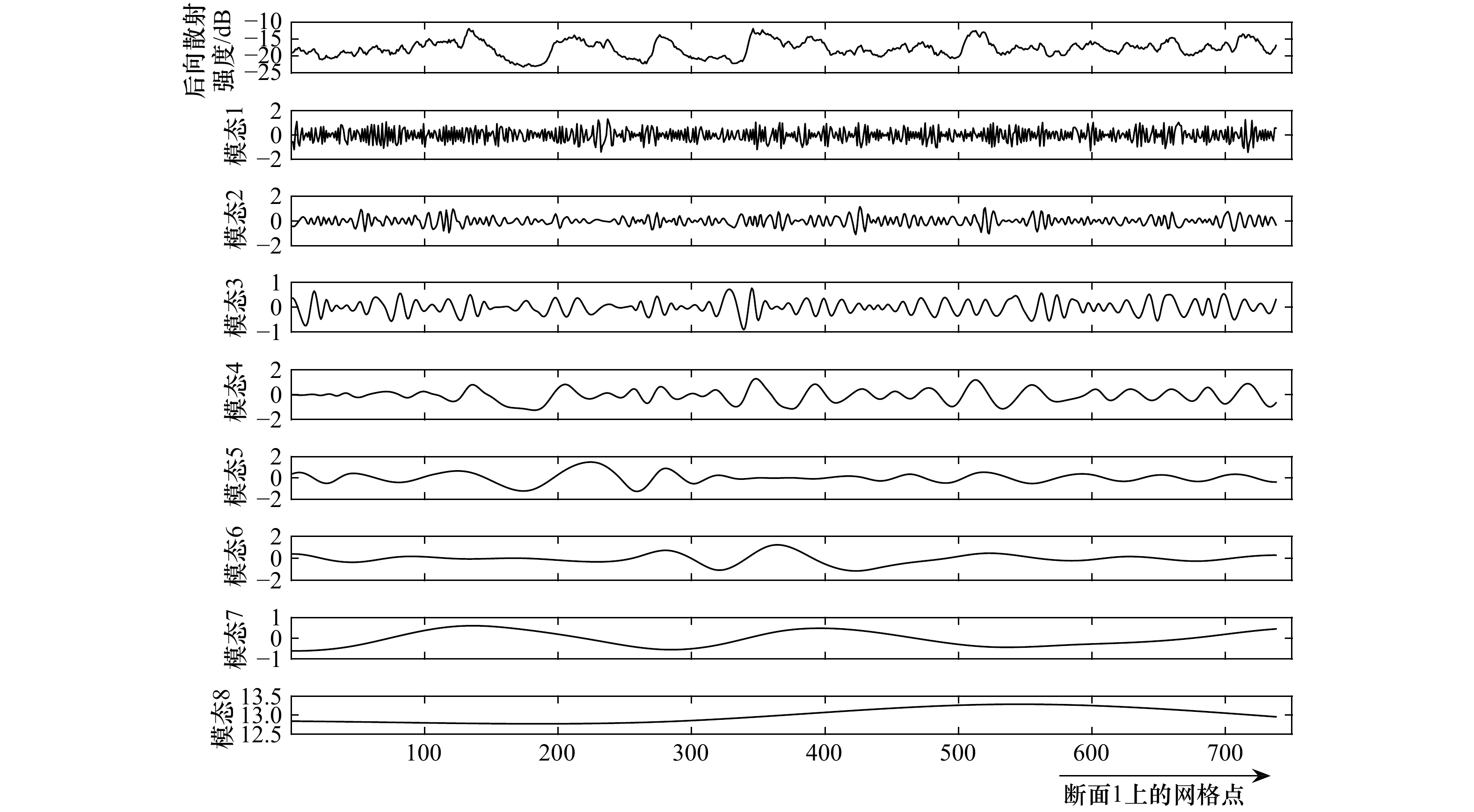
模态 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 归一化方差 0.058 0.142 0.103 0.286 0.161 0.109 0.052 0.089 表 3 图2b中各断面内孤立波特征半宽度
Tab. 3 Characteristic half width of internal solitary wave in each transect in Fig.2b
断面 1 2 3 4 5 特征半宽度/m 749.8 663.3 687.3 713.6 709.3 表 4 利用两层模型法和参数化方法提取得到的图2b中5个断面内孤立波的振幅和相速度
Tab. 4 Amplitude and phase speed of internal solitary waves in the 5 transects marked in Fig. 2b, obtained using the two-layer-model and the parameterization method
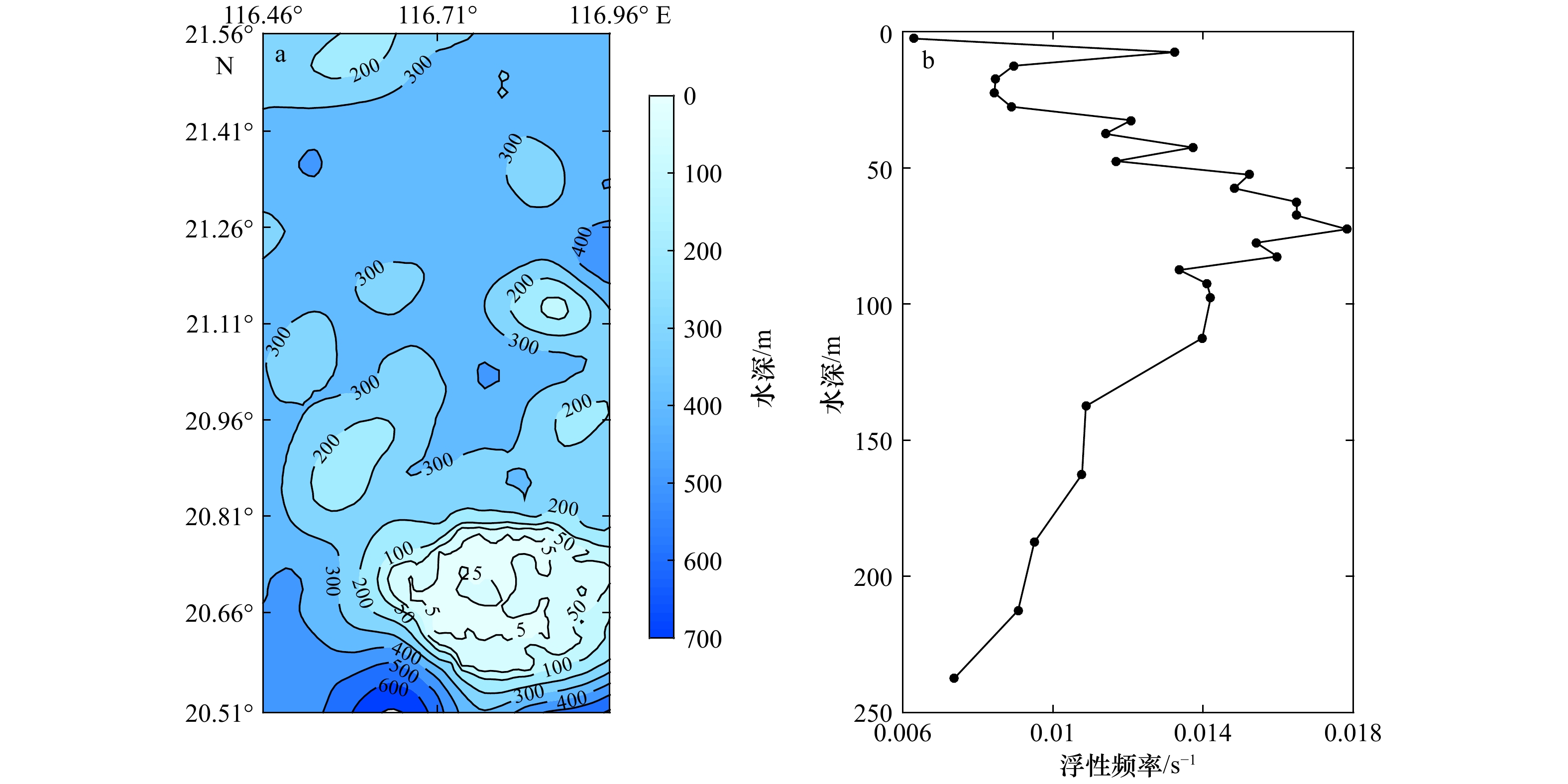
断面 两层模型法 参数化法 振幅/m 相速度/m·s–1 振幅/m 1 6.72 1.07 38.69 2 4.83 1.06 21.45 3 4.97 1.08 27.33 4 4.84 1.10 29.70 5 5.27 1.11 32.25 表 5 利用M4S模型法和直接分离法得到的速度及原多普勒速度对比
Tab. 5 Comparison of the velocities obtained by the M4S model method and direct-separation method and the Doppler velocity
原多普勒速度 M4S模型法 直接分离法 流速最大值/m·s–1 2.71 1.83 2.30 相对变化比率 –32.33% –15.12% 流速最小值/m·s–1 0.48 0.43 0.19 相对变化比率 –11.71% –61.27% 流速平均值/m·s–1 1.39 1.10 1.11 相对变化比率 –20.81% –19.96% -
[1] Zhang Z, Fringer O B, Ramp S R. Three-dimensional, nonhydrostatic numerical simulation of nonlinear internal wave generation and propagation in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C5): C05022. [2] Guo C, Chen X. A review of internal solitary wave dynamics in the northern South China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2014, 121: 7−23. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.04.002 [3] Alford M H, Peacock T, MacKinnon J A, et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7550): 65−69. doi: 10.1038/nature14399 [4] Liu A K, Chang Y S, Hsu M K, et al. Evolution of nonlinear internal waves in the East and South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C4): 7995−8008. doi: 10.1029/97JC01918 [5] 杨劲松, 周长宝, 黄韦艮, 等. 合成孔径雷达图像内波参数提取方法研究[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2000, 15(1): 6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.01.002Yang Jinsong, Zhou Changbao, Huang Weigen, et al. Study on extracting internal wave parameter of SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2000, 15(1): 6−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2000.01.002 [6] Zheng Quanan, Yuan Yeli, Klemas V, et al. Theoretical expression for an ocean internal soliton synthetic aperture radar image and determination of the soliton characteristic half width[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2001, 106(C12): 31415−31423. doi: 10.1029/2000JC000726 [7] 申辉. 海洋内波的遥感与数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2005.Shen Hui. Remote sensing and numerical modeling of oceanic internal waves[D]. Beijing: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005. [8] 甘锡林, 黄韦艮, 杨劲松, 等. 基于希尔伯特-黄变换的合成孔径雷达内波参数提取新方法[J]. 遥感学报, 2007, 11(1): 39−47. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20070106Gan Xilin, Huang Weigen, Yang Jinsong, et al. A new method to extract internal wave parameters from SAR imagery with Hilbert-Huang Transform[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2007, 11(1): 39−47. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20070106 [9] Li Xiaofeng, Clemente-Colón P, Friedman K S. Estimating oceanic mixed-layer depth from internal wave evolution observed from Radarsat-1 SAR[J]. Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest, 2000, 21(1): 130−135. [10] Apel J R, Gonzalez F I. Nonlinear features of internal waves off Baja California as observed from the SEASAT imaging radar[J]. Jounal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1983, 88(C7): 4459−4466. doi: 10.1029/JC088iC07p04459 [11] 曾侃. 从卫星合成孔径雷达海表图像研究海洋内波的三个问题[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2002.Zeng Kan. Three aspects of studying oceanic internal waves by space-borne synthetic aperture radar images[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2002. [12] 甘锡林, 黄韦艮, 杨劲松, 等. 利用多源遥感卫星数据研究南海内波的时空分布特征[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2007, 22(2): 242−245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.02.024Gan Xilin, Huang Weigen, Yang Jinsong, et al. The study of spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of internal waves in the South China Sea from multi-satellite data[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2007, 22(2): 242−245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0323.2007.02.024 [13] Xue Jingshuang, Graber H C, Lund B, et al. Amplitudes estimation of large internal solitary waves in the mid-Atlantic bight using synthetic aperture radar and marine X-band radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3250−3258. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2221467 [14] 王晶, 郭凯, 孙美玲, 等. 3层模型的内波传播方程与参数反演[J]. 遥感学报, 2015, 19(2): 188−194.Wang Jin, Guo Kai, Sun Meiling, et al. Nonlinear Schrödinger equation and parametric inversion of internal wave propagation using three-layer model[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(2): 188−194. [15] Korteweg D J, de Vries G. XLI On the change of form of long waves advancing in a rectangular canal, and on a new type of long stationary waves[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 1895, 39(240): 422−443. [16] 李立, 许金电, 靖春生, 等. 南海海面高度、动力地形和环流的周年变化—TOPEX/Poseidon卫星测高应用研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2003, 46(2): 127−138.Li Li, Xu Jindian, Jing Chunsheng, et al. Annual variation of sea surface height, dynamic topography and circulation in the South China Sea: a TOPEX/Poseidon satellite altimetry study[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2003, 46(2): 127−138. [17] Fernández-Prieto D, Sabia R. Remote Sensing Advances for Earth System Science[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013. [18] Madsen K S, Høyer J L, Tscherning C C. Near-coastal satellite altimetry: sea surface height variability in the North Sea--Baltic Sea area[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(14): L14601. doi: 10.1029/2007GL029965 [19] 林珲, 范开国, 申辉, 等. 星载SAR海洋内波遥感研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(3): 1081−1091. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.049Lin Hui, Fan Kaiguo, Shen Hui, et al. Review on remote sensing of oceanic internal wave by space-borne SAR[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(3): 1081−1091. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.03.049 [20] Goldstein R M, Zebker H A. Interferometric radar measurement of ocean surface currents[J]. Nature, 1987, 328(6132): 707−709. doi: 10.1038/328707a0 [21] Goldstein R M, Zebker H A, Barnett T P. Remote sensing of ocean currents[J]. Science, 1989, 246(4935): 1282−1285. doi: 10.1126/science.246.4935.1282 [22] Romeiser R, Thompson D R. Numerical study on the along-track interferometric radar imaging mechanism of oceanic surface currents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(1): 446−458. doi: 10.1109/36.823940 [23] 甘锡林, 黄韦艮, 杨劲松, 等. 基于M4S模型的合成孔径雷达海洋内波参数反演新方法[C]//中国海洋湖沼学会第九次全国会员代表大会暨学术研讨会论文摘要汇编. 青岛: 中国海洋湖沼学会, 2007.Gan Xilin, Huang Weigen, Yang Jinsong, et al. A new method for retrieving internal wave parameters from synthetic aperture radar based on M4S model[C]//Compilation of Abstracts of Ninth National Congress and Academic Seminar. Qingdao: Chinese Society for Oceanology and Limnology, 2007. [24] 任永政. 从卫星TerraSAR-X图像反演海面风场和海表流场方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Ren Yongzheng. Study on retrieval algorithms of sea surface wind fields and sea surface current fields from TerraSAR-X images[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. [25] 范开国, 黄韦艮, 甘锡林, 等. SAR海洋内波表层流反演方法探讨[J]. 遥感学报, 2010, 14(1): 122−130.Fan Kaiguo, Huang Weigen, Gan Xilin, et al. Retrieving internal wave surface currents from SAR image[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 14(1): 122−130. [26] Romeiser R, Suchandt S, Runge H, et al. First analysis of TerraSAR-X along-track inSAR-derived current fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 820−829. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2030885 [27] Romeiser R, Runge H, Suchandt S, et al. Quality assessment of surface current fields from TerraSAR-X and TanDEM-X along-track interferometry and Doppler centroid analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2759−2772. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2265659 [28] Romeiser R, Graber H C. Advanced remote sensing of internal waves by spaceborne along-track inSAR-a demonstration with TerraSAR-X[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6735−6751. [29] Alpers W, Hennings I. A theory of the imaging mechanism of underwater bottom topography by real and synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1984, 89(C6): 10529−10546. doi: 10.1029/JC089iC06p10529 [30] Mittermayer J, Alberga V, Buckreuss S, et al. TerraSAR-X: predicted performance[C]//Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites VI. International Society for Optics and Photonics. Crete, Greece: SPIE, 2003, 4881: 244-256. [31] Moller D, Frasier S J, Porter D L, et al. Radar-derived interferometric surface currents and their relationship to subsurface current structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C6): 12839−12852. doi: 10.1029/98JC00781 [32] Shemer L, Marom M, Markman D. Estimates of currents in the nearshore ocean region using interferometric synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1993, 98(C4): 7001−7010. doi: 10.1029/92JC02962 [33] Graber H C, Thompson D R, Carande R E. Ocean surface features and currents measured with synthetic aperture radar interferometry and HF radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1996, 101(C11): 25813−25832. doi: 10.1029/96JC02241 [34] Kim D J, Moon W M, Moller D, et al. Measurements of ocean surface waves and currents using L-and C-band along-track interferometric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(12): 2821−2832. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817210 [35] Breit H, Fritz T, Balss U, et al. TerraSAR-X SAR processing and products[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 727−740. [36] Gabele M, Brautigam B, Schulze D, et al. Fore and aft channel reconstruction in the TerraSAR-X dual receive antenna mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 795−806. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2032920 [37] Alpers W. Theory of radar imaging of internal waves[J]. Nature, 1985, 314(6008): 245−247. doi: 10.1038/314245a0 [38] Jia T, Liang J J, Li X M, et al. SAR Observation and numerical simulation of internal solitary wave refraction and reconnection behind the Dongsha Atoll[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(1): 74−89. doi: 10.1002/2017JC013389 [39] Orr M H, Mignerey P C. Nonlinear internal waves in the South China Sea: observation of the conversion of depression internal waves to elevation internal waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(C3): 3064. doi: 10.1029/2001JC001163 [40] Zeng Kan, He Mingxia. A simple boundary process technique for empirical mode decomposition[C]//International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Anchorage, AK, USA: IEEE, 2004, 6: 4258-4261. [41] 杨劲松, 黄韦艮, 周成虎, 等. 利用SAR图像计算内波深度和振幅的可行性研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2003, 15(1): 29−32, 42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070X.2003.01.009Yang Jinsong, Huang Weigen, Zhou Chenghu, et al. The feasibility of applying SAR imagery to the estimation of wave depth and amplitude[J]. Remote Sensing for Land and Resources, 2003, 15(1): 29−32, 42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070X.2003.01.009 [42] Holloway P E, Pelinovsky E, Talipova T. A generalized Korteweg-de Vries model of internal tide transformation in the coastal zone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1999, 104(C8): 18333−18350. doi: 10.1029/1999JC900144 [43] Ramp S R, Tang T Y, Duda T F, et al. Internal solitons in the northeastern South China Sea. Part I: sources and deep water propagation[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2004, 29(4): 1157−1181. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2004.840839 [44] 李海艳. 利用合成孔径雷达研究海洋内波[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004.Li Haiyan. Studying ocean internal waves with SAR[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004. -




 下载:
下载: