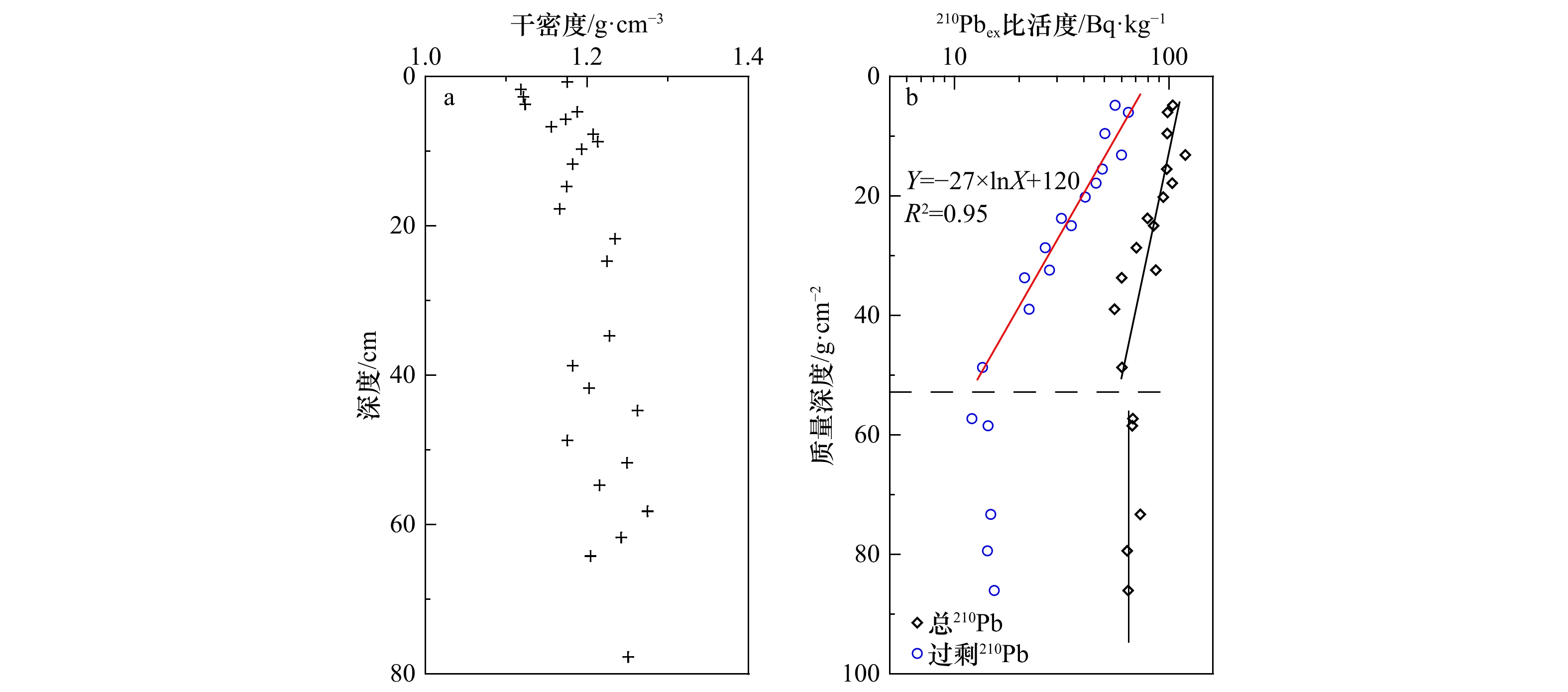
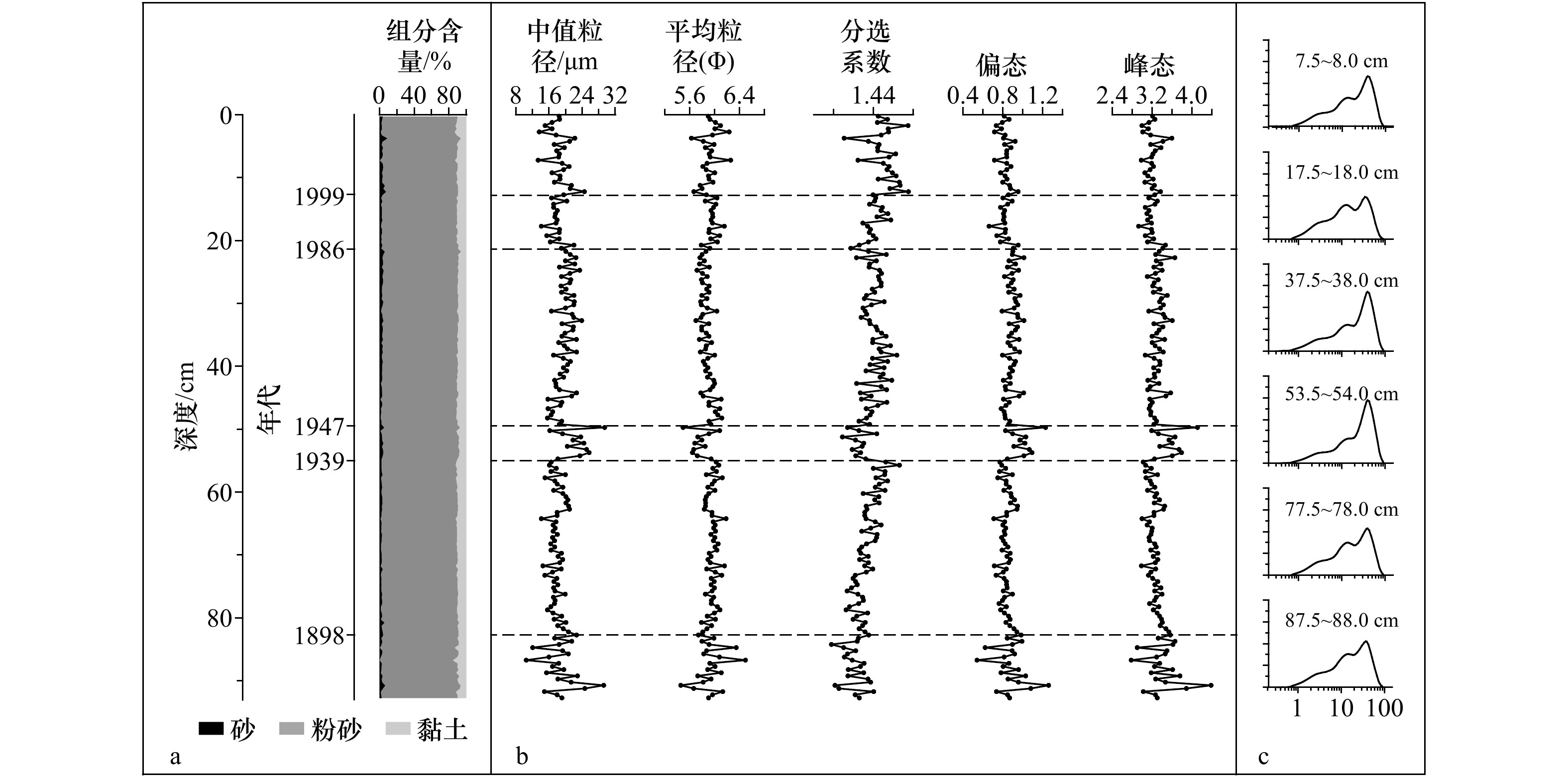
Impacts of channel shifts and interannual sediment load reducing of the Yellow River on the grain size characteristics of sediments in the Shandong mud wedge over the past 100 years
-
摘要: 对山东半岛泥质楔柱状样进行沉积物粒度分析,并在210Pb测年基础上结合黄河年输沙量、悬浮泥沙粒径、河口位置及沿岸流强弱替代指标等数据研究近百年来黄河改道及输沙量变化对远端沉积区沉积特征的影响。研究结果显示,研究区沉积物粒度的变化是黄河入海泥沙特征和沿岸流等水动力作用共同影响的结果。1884–1939年及1947–1999年,研究区沉积物粒度特征的变化主要受到沿岸流强弱的影响;1939–1947年及1999–2012年,受1938–1947年花园口决堤以及20世纪90年代末以来黄河年输沙量持续偏低致使源区泥沙不足的影响,沉积物粒度相对粗化,与沿岸流强度的相关性减弱。与黄河入海泥沙近端沉积区不同,研究区粒度特征对黄河尾闾改道事件不敏感,且对花园口决堤及年输沙量低于临界值的响应有一定程度的延迟,这与该区沉积物经历了再悬浮过程及中间复杂的物质混合有关。黄河改道及输沙量变化仍然是远端沉积区沉积特征演化不可忽视的因素。Abstract: In this study, sediment grain size of a core retrieved from Shandong mud wedge has been tested. On the basis of 210Pb dating, the impacts of channel shifts and changes of annual sediment load of the Yellow River on the sedimentary characteristics of the remote depositional zone over the past 100 years have been studied by analyzing the temporal changes of grain size in the core, Yellow River's annual sediment load, particle size of suspended sediment in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, Yellow River estuary location, and replacement index of coastal current intensity. The results show that grain size of sediments in the study area is affected by characteristics of sediments input of the Yellow River and strength of coastal hydrodynamics. During the period 1884−1939 AD and 1947−1999 AD, the variation of grain-size characteristics in the area was mainly affected by strength of the coastal current. During the period 1939−1947 AD and 1999−2012 AD, sediments in this area were obviously coarsened, and their correlation with the coastal current intensity weakened. Such a coarsening trend of sediment is likely attributed to the insufficient sediment input of the Yellow River, because the Yellow River was cut down at the Huayuankou during 1938−1947 AD and the annual sediment load of the Yellow River was continuous lowering since the end of the 1990s. Different from proximal depositional zone, grain-size characteristics of this remote offshore depositional area was not sensitive to the channel shifts in the lower reaches of the Yellow River. A certain delay also existed in the response of sediment grain size to the reduction of annual sediment load. The reason was that sediment in this area was subjected to resuspension and complex material mixing. Channel shifts of the Yellow River and change of sediment load were still factors that could not be ignored for evolution of sedimentary characteristics of remote depositional zone.
-
Key words:
- grain size /
- end-members modelling /
- the Shandong mud wedge /
- Yellow River /
- sediment load /
- channel shifts
-
图 4 端元数量限定因素及分离结果
a. 端元间相关系数及拟合角度偏移;b. EM1、EM2及对26.0~26.5 cm层位粒度频率分布曲线的拟合
Fig. 4 Limiting factors to number of end members and decomposition results
a. Correlation coefficient among different end-members and angles offset between fitting and real value; b. EM1, EM2 and fitting value for grain-size at 26.0−26.5 cm
图 5 EM1与LZ2017-2、BHB15-8孔粒度频率分布曲线
LZ2017-2孔位于黄河水下三角洲,坐标:37°27′43″N,119°14′53″E;BHB15-8孔位于渤海湾,坐标:38°32′54″N,118°33′00″E,数据未发表
Fig. 5 Grain-size frequency distribution curve of EM1 and the LZ2017-2, BHB15-8 cores
Core LZ2017-2 is located in the Yellow River Underwater Delta with latitude and longitude of 37 27′43″N and 119 14′53″E; Core BHB15-8 is located in the Bohai Bay with latitude and longitude of 38°32′54″N and 118°33′00″E,the data are not published
图 6 SY17-2孔沉积物粒度指标与东亚冬季风指数、黄河年输沙量、黄河悬浮泥沙中值粒径对比
黄河年输沙量数据引自国家科技基础条件平台−国家地球系统科学数据共享平台(http://www.geodata.cn)、黄河流域水文数据及中国河流泥沙公报;黄河悬浮泥沙中值粒径数据引自文献[60];东亚冬季风指数引自文献[61-62]
Fig. 6 Interannual variation of grain size indicators of the Core SY17-2, East Asian winter monsoon index, sediment load of the Yellow River and middle size of suspended sediment in the lower reaches of the Yellow River
Sediment load of the Yellow River data are based on National Earth System Science Data Center (http://www.geodata.cn), hydrological data of Yellow River and China River Sediment Bulletin; middle size of suspended sediment data are cited from reference [60]; East Asian winter monsoon index is cited from reference [61-62]
表 1 SY17-2孔沉积物粒度参数统计结果
Tab. 1 Statistical results of grain-size parameters of the Core SY17-2
组分含量/% 中值粒径/μm 平均粒径/μm 分选系数 偏态 峰态 黏土 粉砂 砂 最大值 15.78 88.95 8.99 31.66 24.10 1.51 1.40 4.79 最小值 6.24 83.15 0.20 10.49 11.09 1.34 0.54 2.78 平均值 10.31 86.85 2.84 18.98 16.67 1.43 0.86 3.30 标准偏差 1.21 0.84 1.14 2.85 1.63 0.03 0.10 0.23 变异系数 0.12 0.01 0.40 0.15 0.10 0.02 0.11 0.07 表 2 端元相对含量及平均粒径统计结果
Tab. 2 Statistical results of end-members abundance and mean size
统计特征值 EM1 EM2 最大值/% 94.31 55.05 最小值/% 44.95 5.69 平均值/% 70.49 29.51 标准偏差 6.09 6.09 变异系数 0.09 0.21 端元平均粒级/μm 12.67 39.83 -
[1] Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: the importance of small mountainous rivers[J]. Journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5): 525−544. doi: 10.1086/629606 [2] Milliman J D, Qin Y S, Ren M E, et al. Man's influence on the erosion and transport of sediment by Asian rivers: the Yellow River (Huanghe) example[J]. Journal of Geology, 1987, 95(6): 751−762. doi: 10.1086/629175 [3] Syvitski J P M, Vörösmarty C J, Kettner A J, et al. Impact of humans on the flux of terrestrial sediment to the global coastal ocean[J]. Science, 2005, 308(5720): 376−380. doi: 10.1126/science.1109454 [4] Syvitski J P M, Milliman J D. Geology, geography, and humans battle for dominance over the delivery of fluvial sediment to the coastal ocean[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2007, 115(1): 1−19. doi: 10.1086/509246 [5] Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng, Saito Y, et al. Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe (Yellow River) sediment load (1950−2005): impacts of climate change and human activities[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2007, 57(3/4): 331−354. [6] Jiao Juying, Wang Zhijie, Zhao Guangju, et al. Changes in sediment discharge in a sediment-rich region of the Yellow River from 1955 to 2010: implications for further soil erosion control[J]. Journal of Arid Land, 2014, 6(5): 540−549. doi: 10.1007/s40333-014-0006-8 [7] Xue Chunting. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(3/4): 321−330. [8] 庞家珍, 司书亨. 黄河河口演变-Ⅰ. 近代历史变迁[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1979, 10(2): 136−141.Pang Jiazhen, Si Shuheng. The estuary changes of Huanghe River-Ⅰ. Changes in modern time[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1979, 10(2): 136−141. [9] Saito Y, Wei Helong, Zhou Yongqing, et al. Delta progradation and chenier formation in the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(4): 489−497. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00080-2 [10] Qiao Shuqing, Shi Xuefa, Saito Y, et al. Sedimentary records of natural and artificial Huanghe (Yellow River) channel shifts during the Holocene in the southern Bohai Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2011, 31(13): 1336−1342. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.05.007 [11] Hu Limin, Guo Zhigang, Shi Xuefa, et al. Temporal trends of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in the Bohai Sea, China: evidence from the sedimentary record[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(10): 1181−1193. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.08.009 [12] Wu Xiao, Bi Naishuang, Kanai Y, et al. Sedimentary records off the modern Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and their response to deltaic river channel shifts over the last 200 years[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 108: 68−80. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.04.028 [13] Syvitski J P M. Deltas at risk[J]. Sustainability Science, 2008, 3(1): 23−32. doi: 10.1007/s11625-008-0043-3 [14] Syvitski J P M, Kettner A J, Overeem I, et al. Sinking deltas due to human activities[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2(10): 681−686. doi: 10.1038/ngeo629 [15] Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng, Li Guangxue, et al. Wave climate modeling on the abandoned Huanghe (Yellow River) delta lobe and related deltaic erosion[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2006, 224: 906−918. doi: 10.2112/03-0081.1 [16] Chu Z X, Sun X G, Zhai S K, et al. Changing pattern of accretion/erosion of the modern Yellow River (Huanghe) subaerial delta, China: based on remote sensing images[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 227(1/2): 13−30. [17] Lee S H, Shinn Y J, Lee K E, et al. Depositional development of an isolated mound and adjacent area in the southern Yellow Sea during the last postglacial sea-level rise[J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 265(1/2): 19−30. [18] Nan Qingyun, Li Tiegang, Chen Jinxia, et al. Holocene paleoenvironment changes in the northern Yellow Sea: evidence from alkenone-derived sea surface temperature[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 483: 83−93. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.01.031 [19] Yang Shouye, Youn J S. Geochemical compositions and provenance discrimination of the central south Yellow Sea sediments[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 243(1/4): 229−241. [20] Mei Xi, Li Rihui, Zhang Xunhua, et al. Evolution of the Yellow Sea warm current and the Yellow Sea cold water mass since the middle Pleistocene[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016, 442: 48−60. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.018 [21] Yang Z S, Liu J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 240(1/4): 169−176. [22] 沈星, 褚忠信, 王玥铭, 等. 北黄海西部与南黄海中部泥质区岩芯敏感粒级及其环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(1): 124−133.Shen Xing, Chu Zhongxin, Wang Yueming, et al. Sensitive grain size and its environmental significance of modern mud patches in southern and northern parts of the Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(1): 124−133. [23] 秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉, 等. 黄海地质[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989.Qin Yunshan, Zhao Yiyang, Chen Lirong, et al. Geology of the Yellow Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989. [24] Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean: A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011. [25] 刘爱菊, 尹逊福, 卢铭. 黄海潮汐特征(Ⅰ)[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1983, 1(2): 1−7.Liu Aiju, Yin Xunfu, Lu Ming. The tide characteristics of the Huanghai Sea[Ⅰ][J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1983, 1(2): 1−7. [26] 刘爱菊, 尹逊福, 卢铭. 黄海潮汐特征(Ⅱ)[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1984, 2(2): 24−27.Liu Aiju, Yin Xunfu, Lu Ming. The tide characteristics of the Huanghai Sea(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas, 1984, 2(2): 24−27. [27] 张志欣. 中国近海沿岸流及毗邻流系的观测与分析研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Zhang Zhixin. Observation and analysis of the coastal current and its adjacent current system in the China offshore waters[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [28] 孙俊川. 黄海冬季环流的数值模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2015.Sun Junchuan. Numerical study on the circulation in the Yellow Sea in winter[D]. Beijing: The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [29] Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S. The Shandong mud wedge and post-glacial sediment accumulation in the Yellow Sea[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2001, 21(4): 212−218. doi: 10.1007/s00367-001-0083-5 [30] Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao Shu, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2004, 209(1/4): 45−67. [31] Liu Jian, Saito Y, Wang Hong, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 236(3/4): 165−187. [32] McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation[M]//Tucker M E. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1988. [33] Goldberg E D. Geochronology with Pb-210[C]. Radioactive Dating. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1963: 121-131. [34] Crozaz G, Picciotto E, De Breuck W. Antarctic snow chronology with 210Pb[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(12): 2597−2604. doi: 10.1029/JZ069i012p02597 [35] Koide M, Soutar A, Goldberg E D. Marine geochronology with 210Pb[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1972, 14(3): 442−446. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(72)90146-X [36] 薛春汀, 刘健, 孔祥淮. 1128−1855年黄河下游河道变迁及其对中国东部海域的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(5): 25−36.Xue Chunting, Liu jian, Kong Xianghuai. Channel shifting of lower Yellow River in 1128−1855 AD and its influence to the sedimentation in Bohai, Yellow and East China Seas[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(5): 25−36. [37] Middleton G V. Hydraulic interpretation of sand size distributions[J]. Journal of Geology, 1976, 84(4): 405−426. doi: 10.1086/628208 [38] Ashley G M. Interpretation of polymodal sediments[J]. Journal of Geology, 1978, 86(4): 411−421. doi: 10.1086/649710 [39] 安福元, 马海州, 樊启顺, 等. 粒度在沉积物物源判别中的运用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2012, 20(1): 49−56.An Fuyuan, Ma Haizhou, Fan Qishun, et al. The application of grain size analysis in sediments provenance discriminance[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2012, 20(1): 49−56. [40] Weltje G J. End-member modeling of compositional data: numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem[J]. Mathematical Geology, 1997, 29(4): 503−549. doi: 10.1007/BF02775085 [41] Paterson G A, Heslop D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(12): 4494−4506. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006070 [42] 范德江, 杨作升, 郭志刚. 中国陆架210Pb测年应用现状与思考[J]. 地球科学进展, 2000, 15(3): 297−302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011Fan Dejiang, Yang Zuosheng, Guo Zhigang. Review of 210Pb dating in the continental shelf of China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2000, 15(3): 297−302. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2000.03.011 [43] 李凤业, 袁巍, Demaster D J, 等. 南海、南黄海、渤海210Pb垂直分布模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1991, 11(3): 35−43.Li Fengye, Yuan Wei, Demaster D J, et al. Profile model of 210Pb in the South China Sea, South Huanghai Sea and Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1991, 11(3): 35−43. [44] 李国刚, 胡邦琦, 李军, 等. 山东半岛沿岸海域表层沉积物的常量元素及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(3): 45−54.Li Guogang, Hu Bangqi, Li Jun, et al. Geochemistry of major elements in the surface sediments of the offshore area of Shandong Peninsula and its geological implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(3): 45−54. [45] 张晓波, 张勇, 孔祥淮, 等. 山东半岛南部近岸海域表层沉积物稀土元素的物源指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(3): 57−66.Zhang Xiaobo, Zhang Yong, Kong Xianghuai, et al. Rare earth elements analysis for provenance study of surface sediments off south Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(3): 57−66. [46] Liu Jian, Saito Y, Kong Xianghuai, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediment as indicators of post-glacial environmental changes off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2009, 29(7): 846−855. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.01.002 [47] Qiao Lulu, Zhong Yi, Wang Nan, et al. Seasonal transportation and deposition of the suspended sediments in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea and the related mechanisms[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2016, 66(5): 751−766. doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0950-2 [48] Bi Naishuang, Yang Zuosheng, Wang Houjie, et al. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present Huanghe (Yellow River) subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 352−362. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.06.005 [49] Yang Zuosheng, Ji Youjun, Bi Naishuang, et al. Sediment transport off the Huanghe (Yellow River) delta and in the adjacent Bohai Sea in winter and seasonal comparison[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 173−181. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2010.06.005 [50] Wang Houjie, Wang Aimei, Bi Naishuang, et al. Seasonal distribution of suspended sediment in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 17−32. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.006 [51] Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39−51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.08.001 [52] 任寒寒, 范德江, 张喜林, 等. 黄河入海口变迁的沉积记录: 来自粒度和210Pb的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(4): 21−29.Ren Hanhan, Fan Dejiang, Zhang Xilin, et al. Sedimentary records of the Yellow River mouth migration: evidence from grain-size and 210Pb[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(4): 21−29. [53] 黄学智. 基于FVCOM的黄渤海潮汐潮流的数值模拟[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2016.Huang Xuezhi. Numerical simulation of tide and tidal current in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea based on the FVCOM[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2016. [54] 张凯南. 北黄海冷水团对悬浮体物质组成和沉积环境的影响机制[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2018.Zhang Kainan. The influence of the North Yellow Sea cold water mass on the properties of suspended particulate matter and sedimentary environment[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018. [55] 王勇智, 乔璐璐, 杨作升, 等. 近岸强海流切变锋作用下悬浮沉积物的输送和沉积——以山东半岛东端外海为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(3): 486−496.Wang Zhiyong, Qiao Lulu, Yang Zuosheng, et al. Suspended sediment transport and deposition due to strong regional shear current front: an example from the shelf waters off eastern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(3): 486−496. [56] 藏政晨, 王厚杰, 薛佐, 等. 黄海近岸锋面的时空变化及其对沉积物输运和沉积的影响[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2015, 31(7): 1−10.Zang Zhengchen, Wang Houjie, Xue Zuo, et al. Temporal and spatial variability of nearshore fronts in the Yellow Sea and its influence on sediment transport and deposition[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2015, 31(7): 1−10. [57] Qiao Shuqing, Yang Zuosheng, Liu Jingpu, et al. Records of late-Holocene East Asian winter monsoon in the East China Sea: key grain-size component of quartz versus bulk sediments[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 230(1/2): 106−114. [58] Hu Bangqi, Yang Zuosheng, Zhao Meixun, et al. Grain size records reveal variability of the East Asian Winter Monsoon since the Middle Holocene in the Central Yellow Sea mud area, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(10): 1656−1668. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4447-7 [59] Zhou Xin, Yang Wenqing, Xiang Rong, et al. Re-examining the potential of using sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength[J]. Quaternary International, 2014, 333: 173−178. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2013.12.013 [60] 孙维婷, 穆兴民, 赵广举, 等. 黄河干流悬移质泥沙粒径构成变化分析[J]. 人民黄河, 2015, 37(5): 4−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2015.05.002Sun Weiting, Mu Xingmin, Zhao Guangju, et al. Analysis of grainsize composition of suspended sediment of the Yellow River[J]. Yellow River, 2015, 37(5): 4−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2015.05.002 [61] 施能, 鲁建军, 朱乾根. 东亚冬、夏季风百年强度指数及其气候变化[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 1996, 19(2): 168−177.Shi Neng, Lu Jianjun, Zhu Qiangen. East Asian Winter/Summer Monsoon intensity indices with their climatic change in 1873−1989[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 1996, 19(2): 168−177. [62] 邵鹏程, 李栋梁. 东亚冬季风指数的分类和比较[J]. 气象科学, 2012, 32(2): 226−235. doi: 10.3969/2012jms.0018Shao Pengcheng, Li Dongliang. Classification and comparison of East Asian Winter Monsoon indices[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2012, 32(2): 226−235. doi: 10.3969/2012jms.0018 [63] Bi Naishuang, Wang Houjie, Yang Zuosheng. Recent changes in the erosion-accretion patterns of the active Huanghe (Yellow River) delta lobe caused by human activities[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2014, 90: 70−78. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2014.02.014 [64] 刘淑平. 黄河三角洲冲淤时空变化特征及发展趋势预测[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2007.Liu Shuping. Study on spacial-temporal evolution of erosion/deposition of Yellow River delta and trend forecast[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2007. [65] Cui Buli, Li Xiaoyan. Coastline change of the Yellow River estuary and its response to the sediment and runoff (1976-2005)[J]. Geomorphology, 2011, 127(1/2): 32−40. -





 下载:
下载: