Numerical simulations and statistical analysis of surf on the generalized topography of the Nansha Islands
-
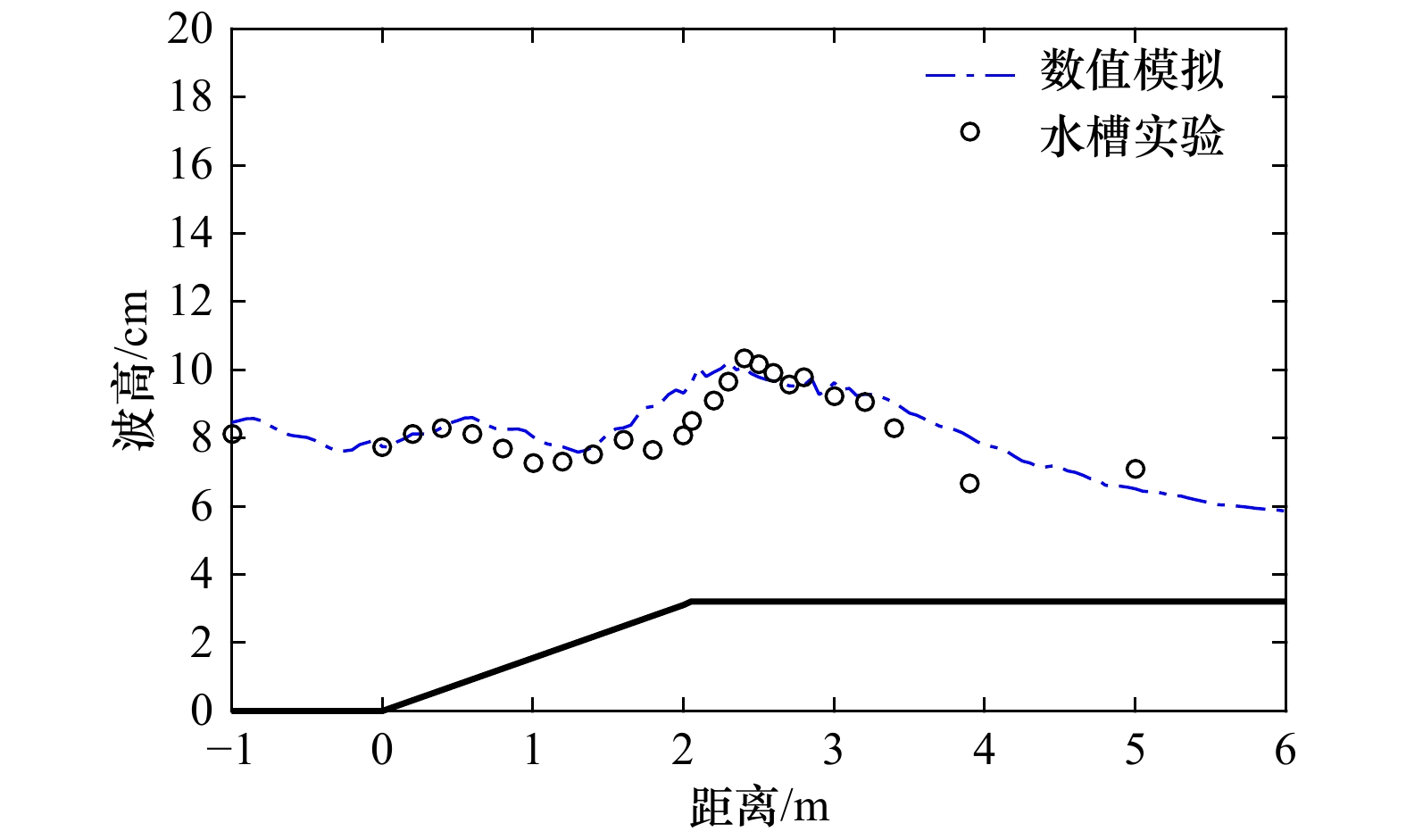
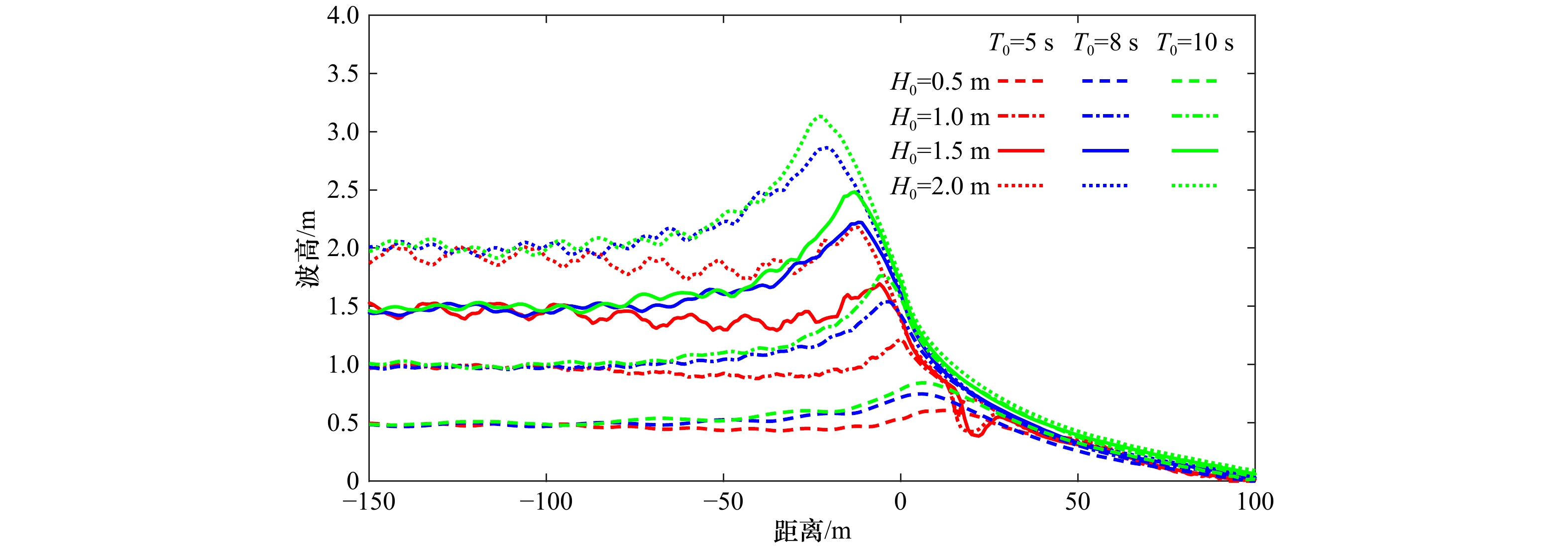
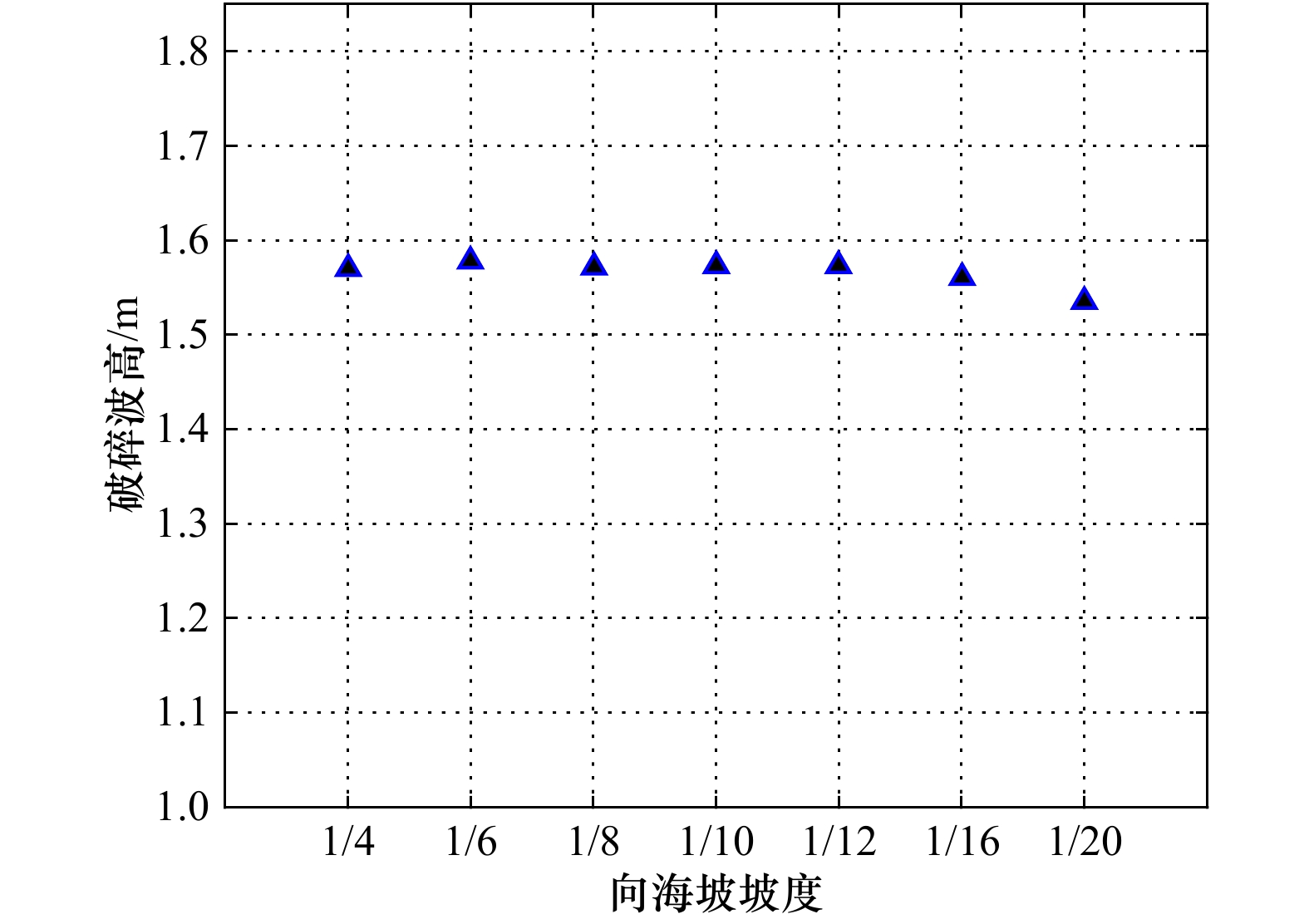
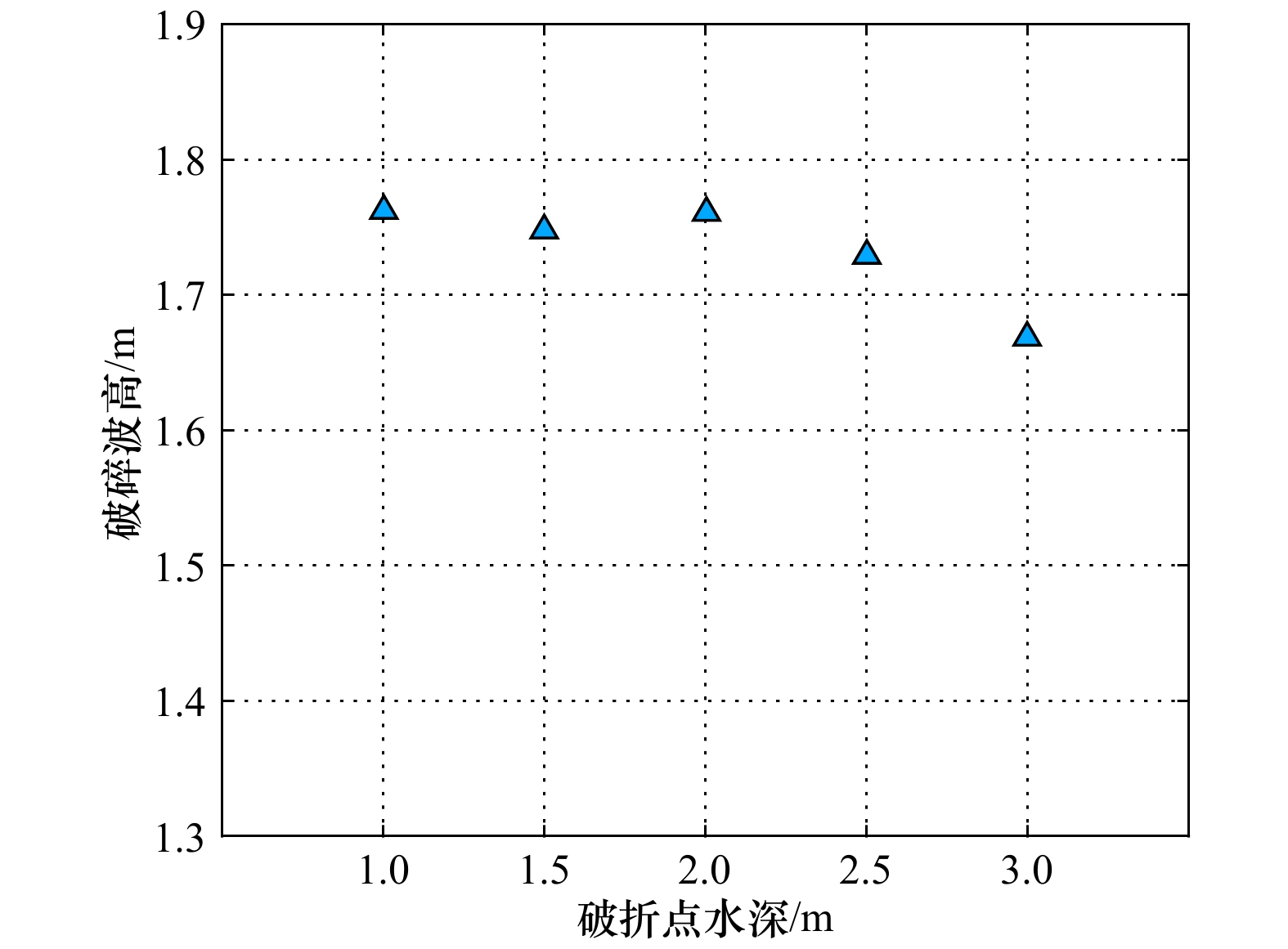
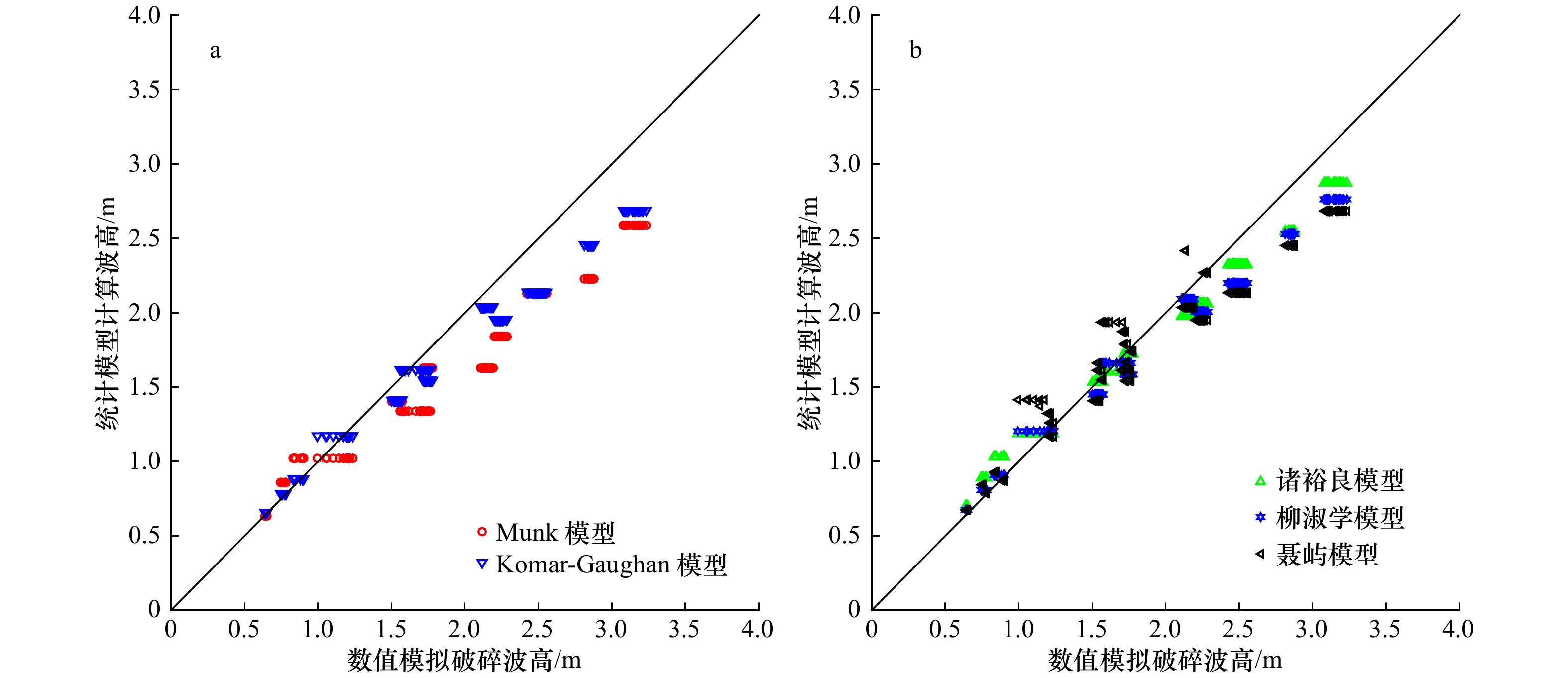
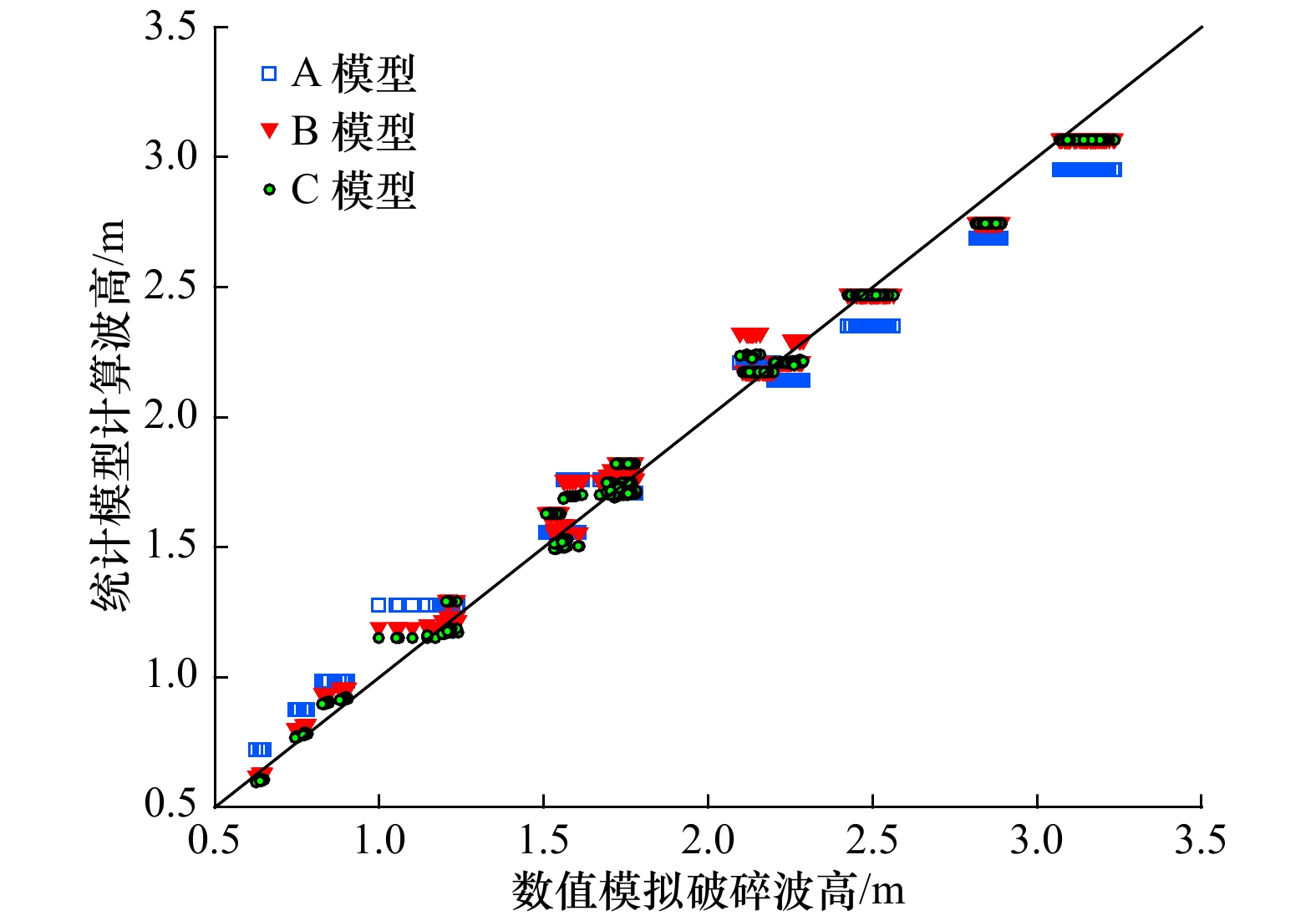
摘要: 南沙群岛珊瑚岛礁众多,大多数岛礁具有向海坡陡峭、外礁坪比较平缓的特征。将南沙群岛岛礁的迎浪向地形概化为陡坡和缓坡组成的双斜坡,采用FUNWAVE-TVD模式数值模拟概化地形上的波浪,根据模拟的破碎波高分析其拍岸浪特征。对拍岸浪数值模拟结果进行比较分析,向海坡的坡度对拍岸浪影响不大,外礁坪上拍岸浪高随地形坡度增大而略有增大;向海坡和外礁坪交界位置(即坡折点)水深对拍岸浪有比较明显的影响,拍岸浪高随坡折点水深增大而减小;拍岸浪高随入射波高和波周期增大而增大。利用大量的拍岸浪数值模拟数据对国内外5种统计模型进行检验,并且基于拍岸浪数值模拟数据建立了3种南沙群岛岛礁拍岸浪统计模型,计算结果显示这些模型适用性较好。
-
关键词:
- 南沙群岛岛礁 /
- 概化地形 /
- 拍岸浪 /
- FUNWAVE-TVD /
- 统计模型
Abstract: There are hundreds of islands and reefs in Nansha Islands. Most of them are characterized by steep seaward slope and gentle outer reef flat. The wave-facing topography of reefs were generalized to a pair of slopes. FUNWAVE-TVD was adopted to simulate shoaling and breaking. Breaking wave heights simulated by the model were analyzed. The slope of seaward slopes has little influence on surf. The breaking wave height on the outer reef flat only increases slightly as the slope increases. The water depth at the turning of the seaward slope and the out reef flat (i.e. the turning point of the slope) has relatively obvious influence on the surf. The breaking wave height decreases with the increasing of water depth at the turning point. The breaker height will also increase with the increasing of incident wave height and wave period. Five statistical models of breaking wave heights compared with the simulating results. Three types of new statistical models are also established based on the simulating result. The results of error calculation show that these models have good applicability.-
Key words:
- reefs of Nansha Islands /
- generalized topography /
- surf /
- FUNWAVE-TVD /
- statistical model
-
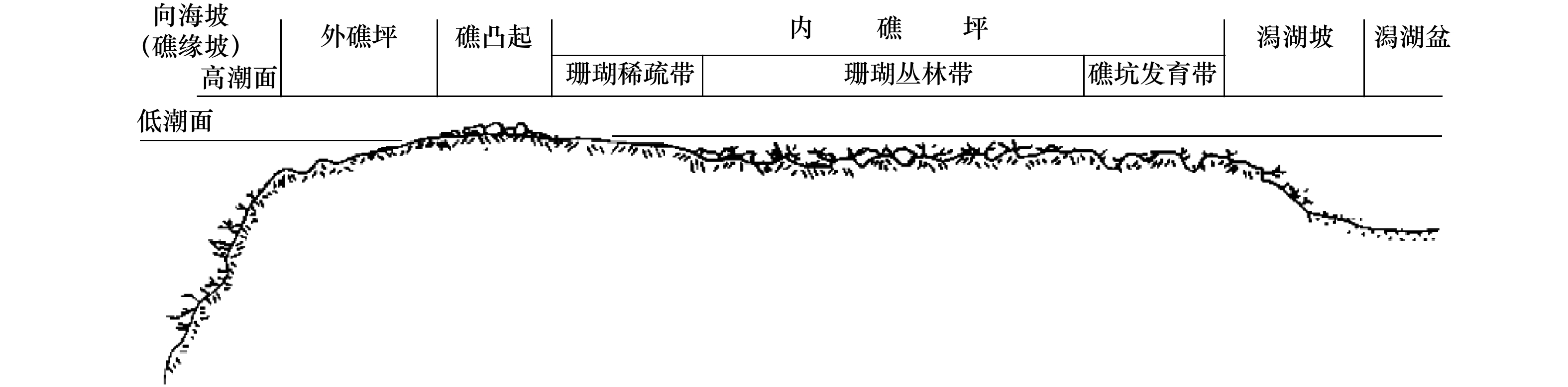
图 1 南沙群岛珊瑚礁体类型[16]
Fig. 1 Types of the coral reefs of the Nansha Islands
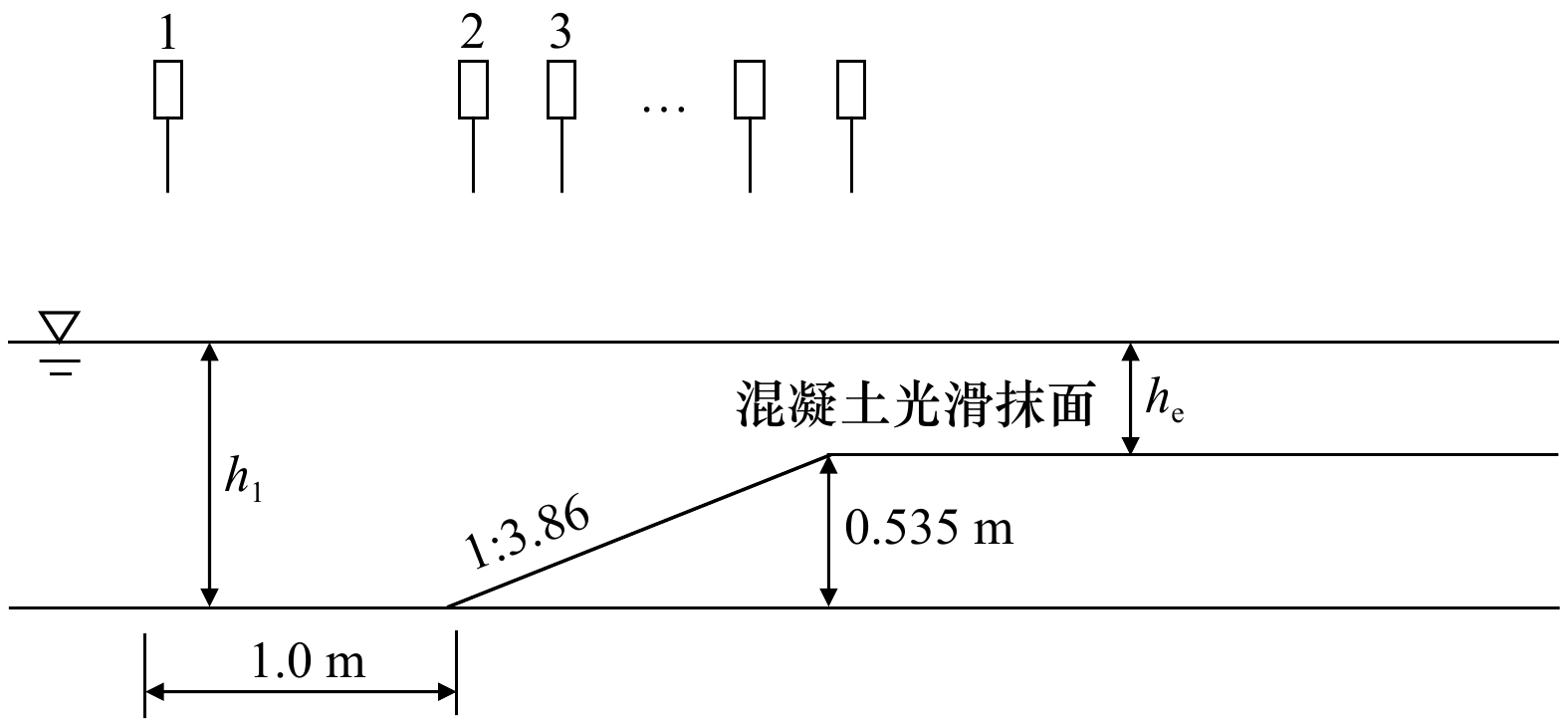
表 1 720个波浪数值模拟算例的参数设置
Tab. 1 The 720 cases of wave numerical simulations
外礁坪坡度s2 坡折点水深hr/m 入射波周期T0/s 入射波高H0/m 1∶30 1∶40 1∶50 1∶60 1.0 0.5 1∶70 1.5 5 1.0 1∶80 2.0 8 1.5 1∶100 2.5 10 2.0 1∶150 3.0 1∶300 1∶500 1∶700 1∶1 000 -
[1] 中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛及其邻近海区综合调查研究报告(一)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 1−5.The Multidisciplinary Oceanographic Expedition Team of Academia Sinaca to Nansha Islands. Comprehensive Investigation Report on Nansha Islands and Adjacent Sea Areas(1)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 1−5. [2] Lee T T, Black K P. The energy spectra of surf waves on a coral reef[C]//Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Coastal Engineering. Hamburg, Germany: American Society of Civil Engineers, 1978: 588−608. [3] Young I R. Wave transformation over coral reefs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1989, 94(C7): 9779−9789. doi: 10.1029/JC094iC07p09779 [4] Hardy T A, Young I R. Field study of wave attenuation on an offshore coral reef[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1996, 101(C6): 14311−14326. doi: 10.1029/96JC00202 [5] Lowe R J, Falter J L, Bandet M D, et al. Spectral wave dissipation over a barrier reef[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C4): C04001. [6] Seelig W N. Laboratory study of reef-lagoon system hydraulics[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1983, 109(4): 380−391. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1983)109:4(380) [7] Gourlay M R, Colleter G. Wave-generated flow on coral reefs-an analysis for two-dimensional horizontal reef-tops with steep faces[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2005, 52(4): 353−387. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2004.11.007 [8] 梅弢, 高峰. 波浪在珊瑚礁坪上传播的水槽试验研究[J]. 水道港口, 2013, 34(1): 13−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2013.01.003Mei Tao, Gao Feng. Flume experiment research on law of wave propagation in reef flat[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2013, 34(1): 13−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8443.2013.01.003 [9] Yao Yu, Huang Zhenhua, Monismith S G, et al. Characteristics of monochromatic waves breaking over fringing reefs[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2013, 29(1): 94−104. [10] 姚宇, 杜睿超, 袁万成, 等. 珊瑚岸礁破碎带附近波浪演化实验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(12): 66−73.Yao Yu, Du Ruichao, Yuan Wancheng, et al. Experimental study of wave transformation around the surf zone over fringing reefs[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2015, 37(12): 66−73. [11] 姚宇, 唐政江, 杜睿超, 等. 珊瑚礁破碎带附近波浪演化和波生流实验研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(2): 12−19. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160313001Yao Yu, Tang Zhengjiang, Du Ruichao, et al. Experimental study of wave transformation and wave-driven current around the surf zone over coral reefs[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(2): 12−19. doi: 10.11759/hykx20160313001 [12] 刘宁. 波浪在岛礁地形上传播特性的试验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2014.Liu Ning. Experimental research on wave propagation characteristics under reef terrain[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2014. [13] 聂屿, 朱首贤, 李训强, 等. 基于波浪水槽实验建立陡坡-礁盘地形的拍岸浪统计计算模型[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2018, 36(3): 374−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.03.004Nie Yu, Zhu Shouxian, Li Xunqiang, et al. A statistical model for surf shoaling and breaking on reefs with steep bathymetry based on flume experiments[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2018, 36(3): 374−383. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2018.03.004 [14] 刘清君, 孙天霆, 王登婷. 岛礁陡坡地形上波浪破碎试验研究[J]. 水运工程, 2018(12): 42−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2018.12.009Liu Qingjun, Sun Tianting, Wang Dengting. Experimental research on wave breaking on steep reef terrain[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 2018(12): 42−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-4972.2018.12.009 [15] 诸裕良, 宗刘俊, 赵红军, 等. 复合坡度珊瑚礁地形上波浪破碎的试验研究[J]. 水科学进展, 2018, 29(5): 717−727.Zhu Yuliang, Zong Liujun, Zhao Hongjun, et al. Experimental study of waves breaking over coral reef topography of a composite slope[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2018, 29(5): 717−727. [16] 赵焕庭. 南沙群岛自然地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996: 42−60, 53−56.Zhao Huanting. Physical Geography of Nansha Islands[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 42−60, 53−56. [17] 陈欣树, 宋朝景, 赵焕庭. 南沙群岛部分珊瑚礁浅水地形[G]//中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛及其邻近海区地质地球物理及岛礁研究论文集(二). 北京: 科学出版社, 1994: 59−68.Chen Xinshu, Song Chaojing, Zhao Huanting. Shallow water topography of some coral reefs in Nansha Islands[G]//Nansha Comprehensive Investigation Team of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Papers on Geophysics and Reef Research in Nansha Islands and Adjacent Sea Areas (2). Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 59−68. [18] 谢以萱. 南沙群岛海区地形基本特征[G]//中国科学院南沙综合科学考察队. 南沙群岛及其邻近海区地球物理及岛礁研究论文集(一). 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991: 1−11.Xie Yixuan. Basic terrain characteristics of Nansha Islands sea area[G]//Nansha Comprehensive Investigation Team of Chinese Academy of Sciences. Papers on Geophysics and Reef Research in Nansha Islands and Adjacent Sea Areas(1). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1991: 1−11. [19] Wei Ge, Kirby J T, Grilli S T, et al. A fully nonlinear Boussinesq model for surface waves. Part 1. Highly nonlinear unsteady waves[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1995, 294: 71−92. doi: 10.1017/S0022112095002813 [20] Kirby J T. Boussinesq models and their application to coastal processes across a wide range of scales[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 2016, 142(6): 03116005. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)WW.1943-5460.0000350 [21] Munk W H. The solitary wave theory and its application to surf problems[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1949, 51(3): 376−424. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1949.tb27281.x [22] Komar P D, Gaughan M K. Airy wave theory and breaker height prediction[C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Coastal Engineering. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada: American Society of Civil Engineers, 1972: 405−418. [23] 柳淑学, 刘宁, 李金宣, 等. 波浪在珊瑚礁地形上破碎特性试验研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2015, 33(2): 42−49.Liu Shuxue, Liu Ning, Li Jinxuan, et al. Experimental researches on wave propagation characteristics on reefs terrain[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2015, 33(2): 42−49. -





 下载:
下载: