Late Quaternary cyclic variations of ice sheet and paleoproductivity in the Amundsen Sea sector, Antarctica
-
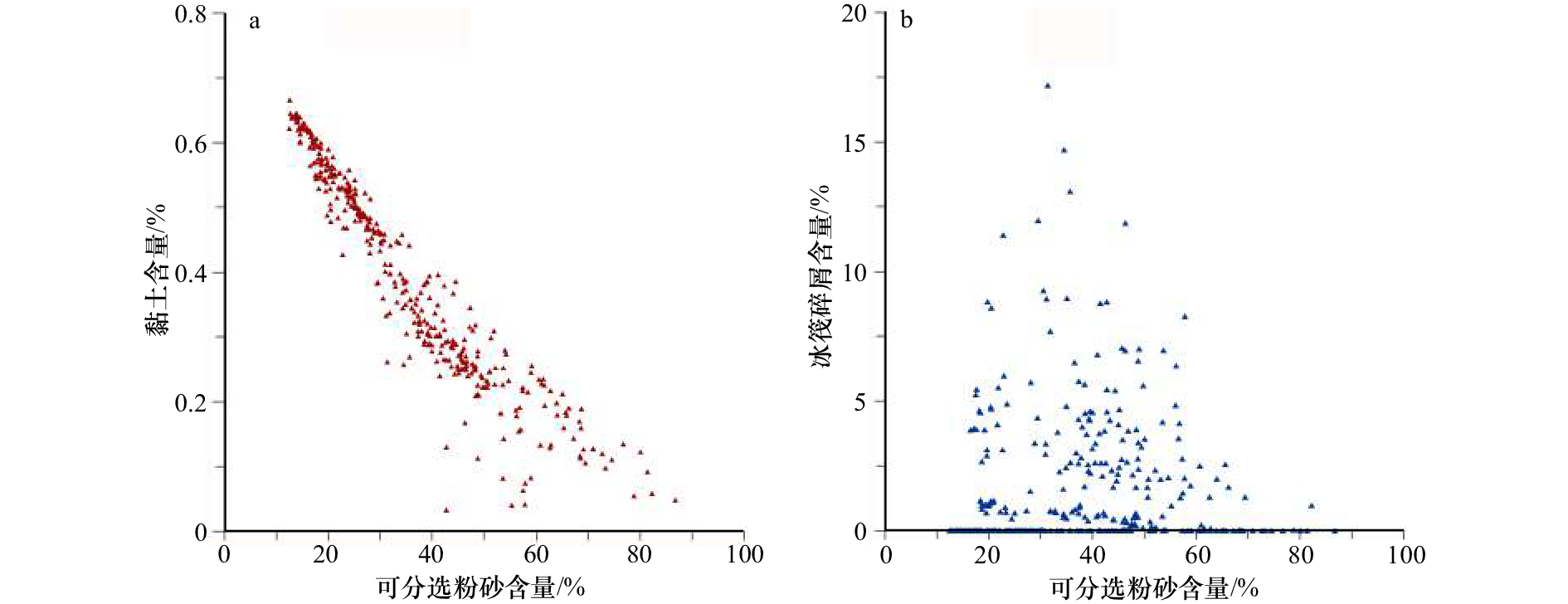
摘要: 本文通过对阿蒙森海西北部陆隆AMS01岩心沉积物颜色、粒度及地球化学等多种指标分析,重建了该地区氧同位素9期(MIS9,大约距今34万年)以来冰盖与古生产力演变历史,结果表明:(1)岩心沉积物粒度与古生产力替代指标表现出明显的冰期–间冰期旋回变化特征;(2)MIS9、MIS7和MIS5等间冰期沉积速率较小,沉积物呈褐色,冰筏碎屑含量低,生源组分含量高,反映出该时期阿蒙森海地区气候温暖,冰盖发生了大规模退缩,冰盖–冰架–冰山等陆源冰对沉积物的影响减弱,海冰覆盖减弱,有利于浮游植物的生长和繁殖;(3)MIS8c、MIS8a、MIS6、MIS2等冰期沉积速率大,沉积物呈灰色,沉积物随之变粗,冰筏碎屑含量高,生源组分含量低,说明该时期冰盖大幅扩张,陆隆区成为近冰盖/冰架沉积环境,海冰和冰山密集,海洋生产力显著降低;(4)冰期、间冰期内,冰盖与古生产力也有不同程度的波动;特别是MIS8b期发育浅褐色间冰阶沉积,冰筏碎屑含量低,生产力水平与间冰期基本持平,说明阿蒙森海地区冰盖、海洋对气候变化的响应比东南极地区敏感。Abstract: Core AMS01 dredged on the northwestern continental rise of the Amundsen Sea was used to reconstruct the history of ice sheet and paleoproductivity since MIS9 (about 34 ka BP) based on the analyses of color reflectance, grain size and geochemical proxies. The results show that: (1) Grain size and paleoproductivity proxies of the core exhibits evident glacial–interglacial cycles of Quaternary; (2) The interglacials such as MIS9, MIS7 and MIS5 have low sedimentation rates, brown sediments, low ice-rafted detritus (IRD) contents and high paleoproductivity, indicating warm climate, limited sea ice and large-scale retreat of the ice sheet in the Amundsen Sea sector; (3) Glacial ages such as MIS8c, MIS8a, MIS6 and MIS2 have relatively high sedimentation rates, gray sediments, high IRD and low biological components, which indicate the ice sheet expanded greatly to the edge of the continental shelf, and the continental rise became a proximal environment close to the grounded ice sheet and/or floating ice shelf with dense sea ice and icebergs, and significantly lowered marine productivity; (4) In the glacials and interglacials, ice sheet and paleoproductivity also have certain fluctuations, especially in MIS8b interstadial, the light brown sediments with low IRD and elevated marine productivity make it be like the environment of interglacial period, which indicates that the ice sheet and ocean in the Amundsen Sea sector are more sensitive to climate change than those in the East Antarctica.
-
Key words:
- West Antarctica /
- the Amundsen Sea /
- Late Quaternary /
- ice sheet /
- paleoproductivity
-
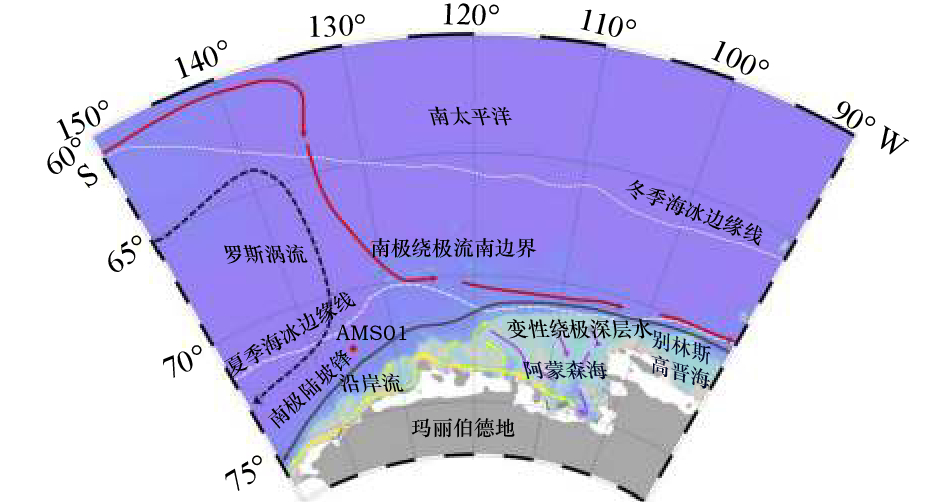
图 1 阿蒙森海取样站位与环流分布
红色圆点代表本文研究站位AMS01。海区环流综合文献[16-21]绘制。黑色实线代表南极陆坡锋(ASF)[17],紫色实线箭头代表变性绕极深层水(MCDW)[16, 18],黄色实线箭头代表沿岸流(CC)流向[16],黑色虚线箭头代表罗斯涡流(RG)方向[19],红色实线箭头代表南极绕极流南边界(SBACC)[20];白色点线和白色虚线分 别代表南极冬季海冰覆盖线(WSI)和夏季海冰覆盖线(SSI)[21]
Fig. 1 Map of the Amundsen Sea showing location of sediment core AMS01 and marine circulation
Sediment core AMS01 is marked by the red dot. The circulation is edited from references [16-21]. Black line indicates Antarctic Slope Front (ASF)[17]; Modified Circumpolar Deep Water (MCDW) [16, 18]and Coastal Current (CC)[16] are indicated by the purple and yellow arrows, respectively; black dashed arrow indicates the Ross Gyre (RG)[19]; red arrows indicate the Southern Boundary (SB) of Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC)[20]; winter sea ice (WSI) and summer sea ice (SSI) are indicated by white dotted line and dashed line, respectively[21]
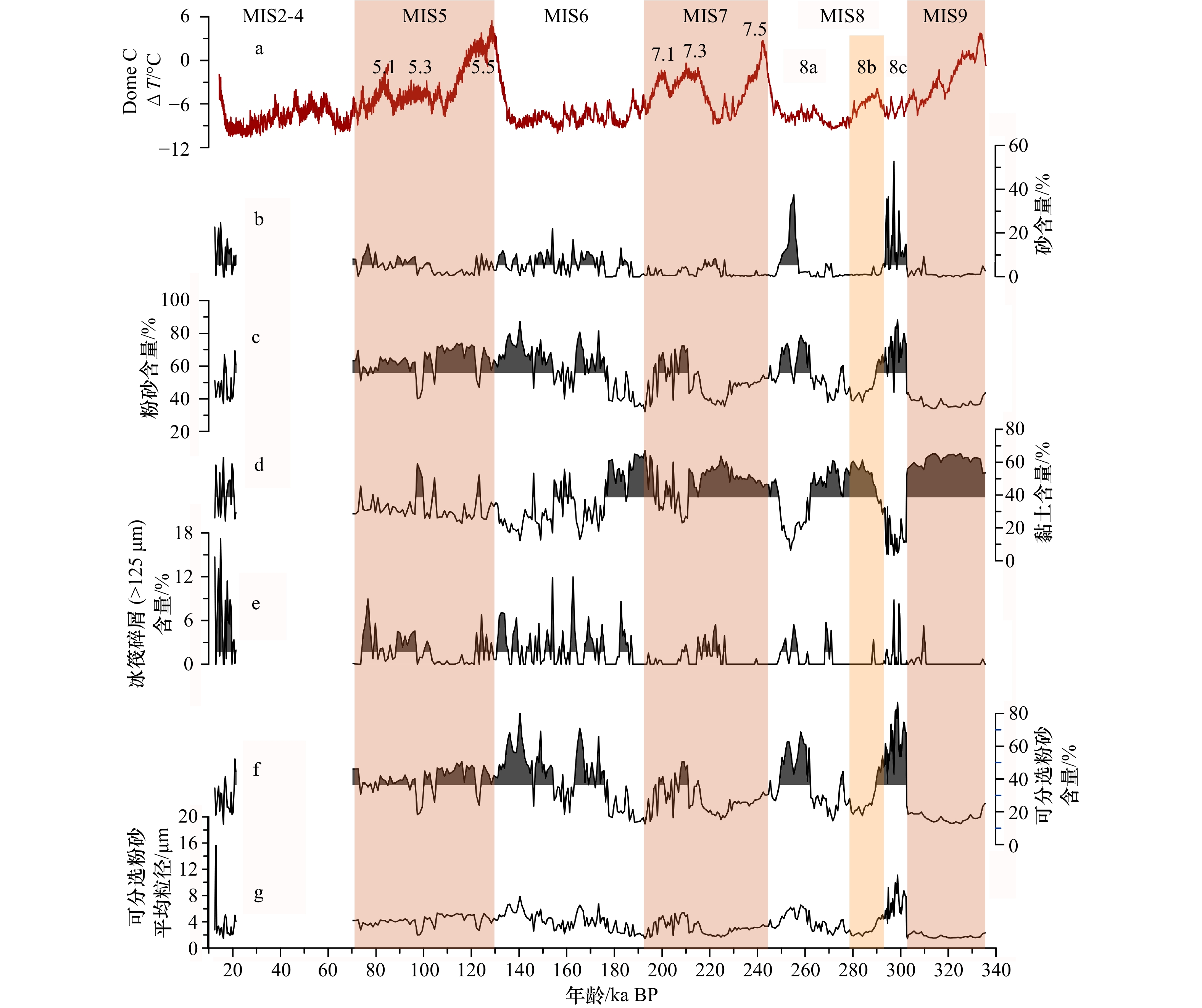
图 3 AMS01岩心粒度组成与冰筏碎屑含量变化
a. Dome C冰芯温差记录;b.砂含量;c.粉砂含量;d.黏土含量;e.冰筏碎屑(>125 μm)含量;f.可分选粉砂含量;g.可分选粉砂平均粒径
Fig. 3 Downcore variations of grain size and ice-rafted detritus in Core AMS01
a. Dome C △T record; b. sand content; c. silt content; d. clay content; e. ice-rafted detritus (>125 μm) content; f. sortable silt content; g. sortable silt mean size
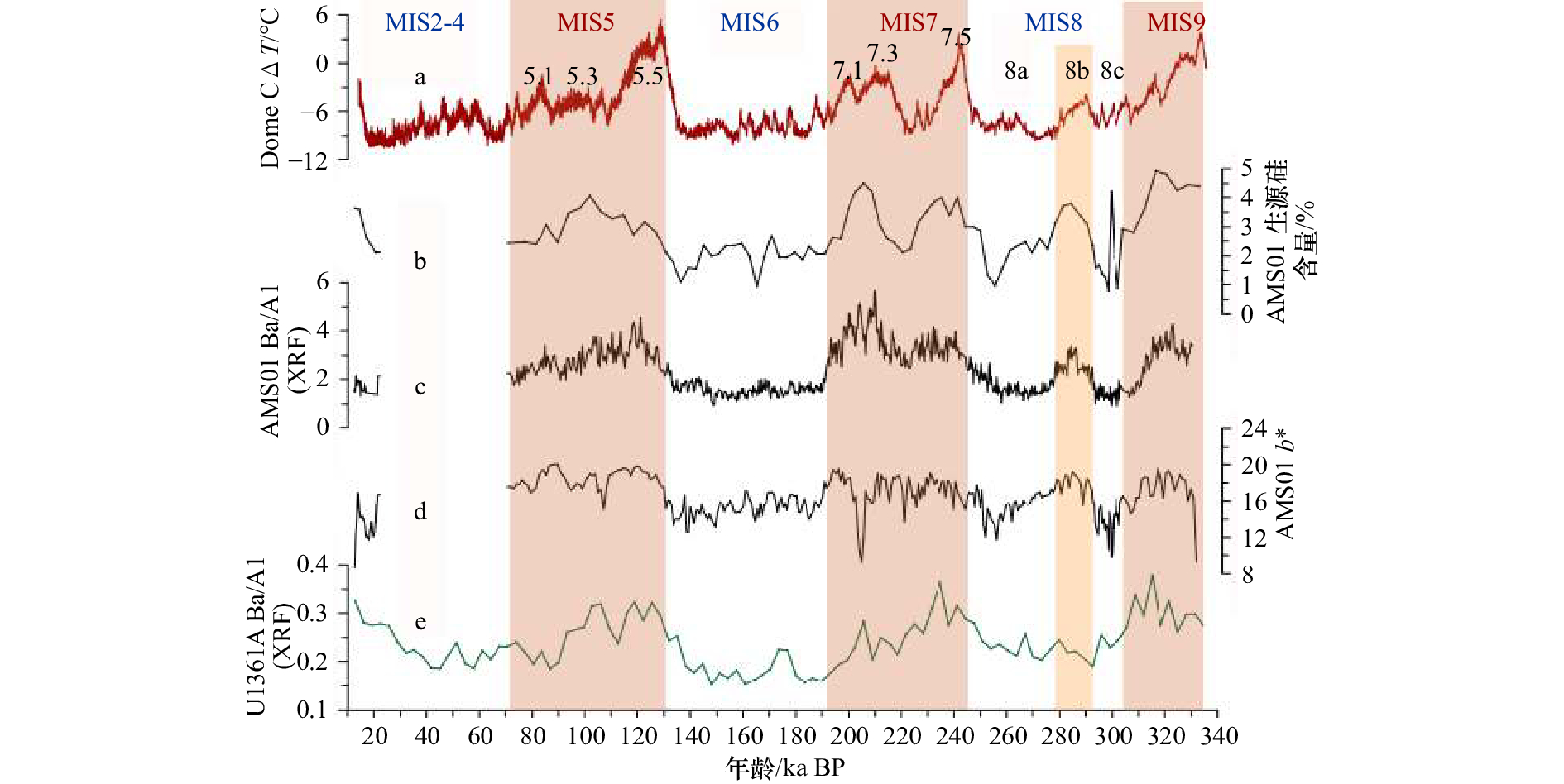
图 5 AMS01岩心多种生产力替代指标的变化及其与东南极IODP U1361A孔的对比
a. Dome C冰芯温差记录;b.AMS01岩心生源硅含量;c. AMS01岩心Ba/Al比值;d. AMS01岩心颜色反射率参数b*;e.U1361A岩心Ba/Al比值
Fig. 5 Downcore variation of paleoproductivity proxies in Core AMS01, and the comparison with IODP Core U1361A in East Antarctic
a. Dome C △T record; b. biogenic silica content in Core AMS01; c. Ba/Al in Core AMS01; d. b* in Core AMS01; e. Ba/Al in Core U1361A
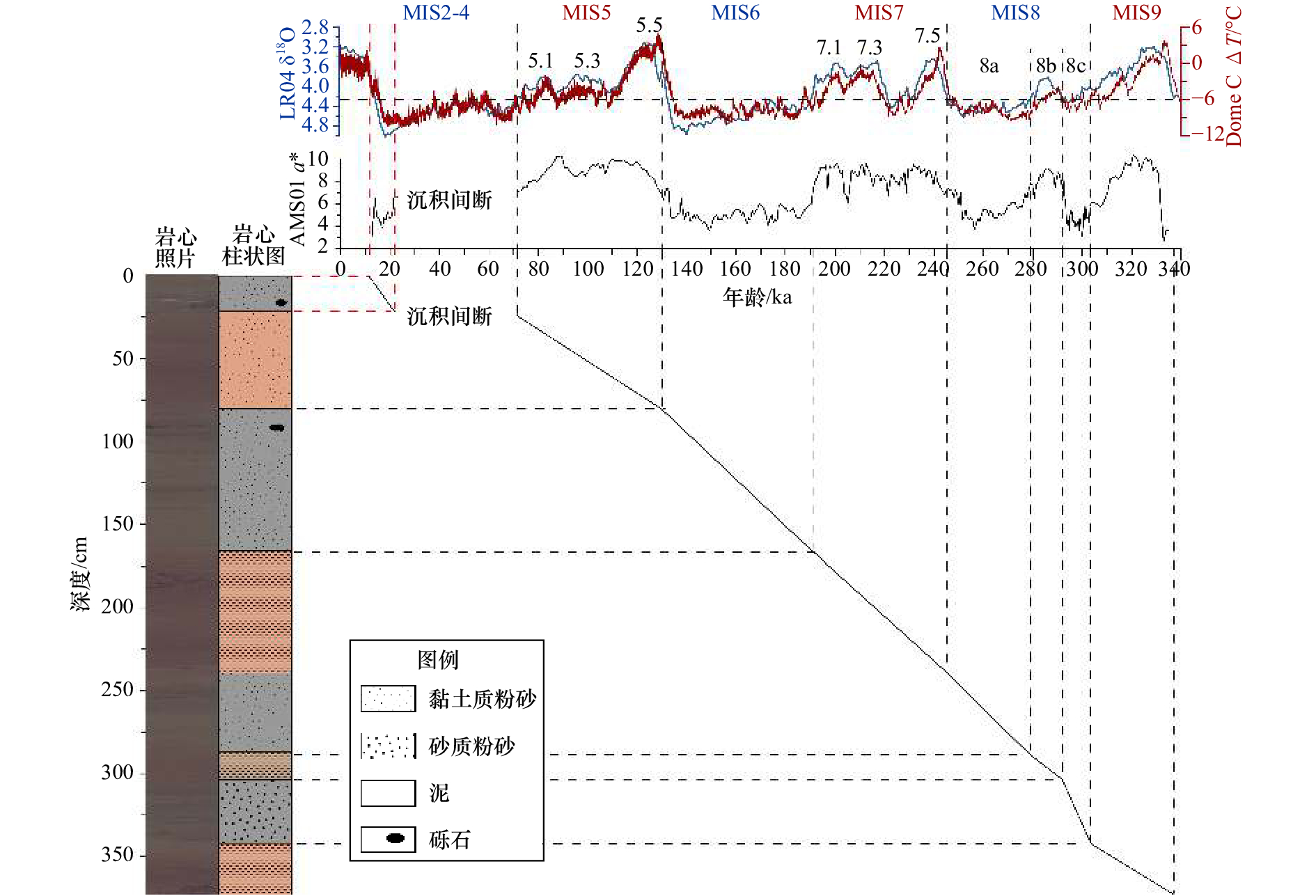
表 1 AMS01岩心AMS14C测年数据与年龄校正
Tab. 1 AMS14C and calibrated ages of Core AMS01
序号 深度/cm 测年材料 AMS14C年龄/a BP 碳储库年龄/a 日历年龄/a BP 1 0~2 有孔虫 12 480±40 1 300 12 680±94 2 20~22 有孔虫 18 860±60 1 300 20 700±200 3 36~38 有孔虫 35 250±250 1 300 37 990±412* 4 44~46 有孔虫 38 840±680 1 300 41 620±547* 注:*表示该年龄超出26 ka BP的日历年龄准确校正区间(建议校正区间),只作参考,不作为岩心年代控制点。 表 2 AMS01岩心各层段年龄与沉积速率估算
Tab. 2 The ages and calculated sedimentation rates for main sections in Core AMS01
控制点特征 深度
/cm年龄
/ka BP平均沉积速率
/cm·ka−1测年结果 1 12.68 — 测年结果 21 20.70 2.49 MIS2/MIS5地层分界 23 21.5/71 — MIS5/MIS6地层分界 80 130 0.97 MIS6/MIS7地层分界 165 191 1.39 MIS7/MIS8地层分界 238 245 1.35 MIS8a/MIS8b亚层分界 286 279 1.41 MIS8b/MIS8c亚层分界 303 292 1.31 MIS8/MIS9地层分界 340 303 3.36 MIS9底界 373 337 0.97 -
[1] Smith J A, Hillenbrand C D, Kuhn G, et al. Deglacial history of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet in the western Amundsen Sea Embayment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 30(5): 488−505. [2] 王亚凤, 温家洪, 刘吉英. 南极冰盖与冰川的快速变化[J]. 极地研究, 2006, 18(1): 63−74.Wang Yafeng, Wen Jiahong, Liu Jiying. Rapid changes of the Antarctic ice sheet and glaciers[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2006, 18(1): 63−74. [3] Pritchard H D, Ligtenberg S R M, Fricker H A, et al. Antarctic ice-sheet loss driven by basal melting of ice shelves[J]. Nature, 2012, 484(7395): 502−505. doi: 10.1038/nature10968 [4] Paolo F S, Fricker H A, Padman L. Volume loss from Antarctic ice shelves is accelerating[J]. Science, 2015, 348(6232): 327−331. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa0940 [5] Jenkins A, Shoosmith D, Dutrieux P, et al. West Antarctic Ice Sheet retreat in the Amundsen Sea driven by decadal oceanic variability[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2018, 11: 733−738. doi: 10.1038/s41561-018-0207-4 [6] Petit J R, Jouzel J, Raynaud D, et al. Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420,000 years from the Vostok ice core, Antarctica[J]. Nature, 1999, 399(6735): 429−436. doi: 10.1038/20859 [7] Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Cattani O, et al. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800,000 years[J]. Science, 2007, 317(5839): 793−796. doi: 10.1126/science.1141038 [8] Wilson D J, Bertram R A, Needham E F, et al. Ice loss from the East Antarctic Ice Sheet during late Pleistocene interglacials[J]. Nature, 2018, 561(7723): 383−386. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0501-8 [9] Larter R D, Anderson J B, Graham A G C, et al. Reconstruction of changes in the Amundsen Sea and Bellingshausen Sea sector of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 100: 55−86. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.10.016 [10] Hillenbrand C D, Smith J A, Hodell D A, et al. West Antarctic Ice Sheet retreat driven by Holocene warm water incursions[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7661): 43−48. doi: 10.1038/nature22995 [11] Scherer R P, Aldahan A, Tulaczyk S, et al. Pleistocene collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5373): 82−85. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5373.82 [12] Hillenbrand C D, Fütterer D K, Grobe H, et al. No evidence for a Pleistocene collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet from continental margin sediments recovered in the Amundsen Sea[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2002, 22(2): 51−59. doi: 10.1007/s00367-002-0097-7 [13] Hillenbrand C D, Kuhn G, Frederichs T. Record of a Mid-Pleistocene depositional anomaly in West Antarctic continental margin sediments: an indicator for ice-sheet collapse?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(13): 1147−1159. [14] Vaughan D G. West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse–the fall and rise of a paradigm[J]. Climatic Change, 2008, 91(1/2): 65−79. [15] Nitsche F O, Jacobs S S, Larter R D, et al. Bathymetry of the Amundsen Sea continental shelf: Implications for geology, oceanography, and glaciology[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2007, 8(10): 1−10. [16] Arneborg L, Wåhlin A K, Björk G, et al. Persistent inflow of warm water onto the central Amundsen shelf[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(12): 876−880. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1644 [17] Martinson D G. Antarctic circumpolar current's role in the Antarctic ice system: An overview[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2012, 335-336: 71−74. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.04.007 [18] Stlaurent P, Yager P L, Sherrell R M, et al. Pathways and supply of dissolved iron in the Amundsen Sea (Antarctica)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(9): 7135−7162. doi: 10.1002/2017JC013162 [19] Dotto T S, Alberto N G, Sheldon B, et al. Variability of the Ross Gyre, Southern Ocean: drivers and responses revealed by satellite altimetry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(12): 6195−6201. [20] Orsi A H, Whitworth T, Nowlin W D. On the Meridional Extent and Fronts of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1995, 42(5): 641−673. doi: 10.1016/0967-0637(95)00021-W [21] Comiso J C, Cavalieri D J, Markus T. Sea ice concentration, ice temperature, and snow depth using AMSR-E data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(2): 243−252. [22] Mortlock R A, Froelich P N. A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(9): 1415−1426. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90092-7 [23] Stuiver M, Reimer P J. Extended 14C data base and revised CALIB 3.0 14C age calibration program[J]. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35(1): 215−230. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200013904 [24] Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4): 1869−1887. doi: 10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947 [25] Berkman P A, Forman S L. Pre-bomb radiocarbon and the reservoir correction for calcareous marine species in the Southern Ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1996, 23(4): 363−366. doi: 10.1029/96GL00151 [26] Hillenbrand C D, Grobe H, Diekmann B, et al. Distribution of clay minerals and proxies for productivity in surface sediments of the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas (West Antarctica) – Relation to modern environmental conditions[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 193(3): 253−271. [27] Parkinson C L. Spatial patterns in the length of the sea ice season in the Southern Ocean, 1979-1986[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 1994, 99(C8): 16327−16339. doi: 10.1029/94JC01146 [28] van der Plicht, J Beck, J W Bard, et al. NOTCAL04—comparison/calibration 14C records 26–50 ka cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2004, 46: 1225−1238. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200033117 [29] Chiu T C, Fairbanks R G, Mortlock R A, et al. Extending the radiocarbon calibration beyond 26,000 years before present using fossil corals[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24(16): 1797−1808. [30] Fairbanks R G, Mortlock R A, Chiu T C, et al. Radiocarbon calibration curve spanning 0 to 50,000 years BP based on paired 230Th/234U/238U and 14C dates on pristine corals[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2005, 24(16): 1781−1796. [31] Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20(1): 1−17. [32] 刘合林, 陈志华, 葛淑兰, 等. 晚第四纪普里兹湾北部陆坡岩心沉积学记录及古海洋学意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(3): 209−217.Liu Helin, Chen Zhihua, Ge Shulan, et al. Late Quaternary sedimentary records and paleoceanographic implications from the core on continental slope off the Prydz Bay, East Antarctic[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(3): 209−217. [33] 赵仁杰, 陈志华, 刘合林, 等. 15 ka以来罗斯海陆架岩心沉积学记录及古海洋学意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(5): 78−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.05.008Zhao Renjie, Chen Zhihua, Liu Helin, et al. Sedimentary record and paleoceanographic implications of the core on the continental shelf off the Ross Sea since 15 ka[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(5): 78−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2017.05.008 [34] Witus A E, Branecky C M, Anderson J B, et al. Meltwater intensive glacial retreat in polar environments and investigation of associated sediments: example from Pine Island Bay, West Antarctica[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 85(2): 99−118. [35] McCave I N, Manighetti B, Robinson S G. Sortable silt and fine sediment size/composition slicing: parameters for palaeocurrent speed and palaeoceanography[J]. Paleoceanography, 1995, 10(3): 593−610. doi: 10.1029/94PA03039 [36] Mccave I N, Hall I R. Size sorting in marine muds: Processes, pitfalls, and prospects for paleoflow-speed proxies[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(10): 1−38. [37] Denis D, Crosta X, Schmidt S, et al. Holocene glacier and deep water dynamics, Adélie Land region, East Antarctica[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2009, 28(13): 1291−1303. [38] Noormets R, Dowdeswell J A, Larter R D, et al. Morphology of the upper continental slope in the Bellingshausen and Amundsen Seas – Implications for sedimentary processes at the shelf edge of West Antarctica[J]. Marine Geology, 2009, 258(1/4): 100−114. [39] Anderson J B, Shipp S S. The West Antarctic ice sheet: behavior and environment[J]. Antarctic Research Series, 2001, 77: 45−57. [40] Dowdeswell J A, Evans J, O Cofaigh C, et al. Morphology and sedimentary processes on the continental slope off Pine Island Bay, Amundsen Sea, West Antarctica[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(5/6): 606−619. [41] Dutton A, Carlson A E, Long A J, et al. Sea-level rise due to polar ice-sheet mass loss during past warm periods[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6244): 153−164. [42] Voosen P. Antarctic ice melt 125,000 years ago offers warning[J]. Science, 2018, 361(6421): 1339−1339. [43] Bonn W J, Gingele F X, Grobe H, et al. Palaeoproductivity at the Antarctic continental margin: opal and barium records for the last 400 ka[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1998, 139(3): 195−211. [44] Dymond J, Suess E, Lyle M. Barium in deep-sea sediment: A geochemical proxy for paleoproductivity[J]. Paleoceanography, 1992, 7(2): 163−181. doi: 10.1029/92PA00181 [45] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12−32. [46] Murray R W, Leinen M. Scavenged excess aluminum and its relationship to bulk titanium in biogenic sediment from the central equatorial Pacific Ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(20): 3869−3878. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(96)00236-0 [47] Anderson R F, Chase Z, Fleisher M Q, et al. The Southern Ocean's biological pump during the last glacial maximum[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2002, 49(9/10): 1909−1938. [48] Wolff E W, Fischer H, Fundel F, et al. Southern Ocean sea-ice extent, productivity and iron flux over the past eight glacial cycles[J]. Nature, 2006, 440(7083): 491−496. doi: 10.1038/nature04614 [49] 武力, 王汝建, 肖文申, 等. 东南极普里兹湾陆坡扇晚第四纪高分辨率地层年龄模式[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(3): 197−208.Wu Li, Wang Rujian, Xiao Wenshen, et al. High resolution age model of late Quaternary mouth fan at Prydz Trough, Eastern Antarctica[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2015, 35(3): 197−208. -




 下载:
下载: