Temporal and spatial changes in chlorophyll a concentrations in the Bohai Sea in the past two decades
-
摘要: 浮游植物作为食物链的基础,对海洋生态系统具有重要作用。渤海作为我国最大的内海和重要渔业生物的产卵场、育幼场和索饵场,该区浮游植物研究具有重要意义。叶绿素a浓度是反映浮游植物生物量的重要指标。利用Google Earth Engine平台,对1997–2010年的宽视场海洋观测传感器(SeaWiFS)叶绿素a浓度数据和2002–2018年的水色卫星中分辨率成像光谱仪传感器(MODIS Aqua)叶绿素a浓度数据进行合并,并研究其时空变化特征。研究表明,近20年来,渤海全年叶绿素a浓度增加了14.1%,且增加显著。叶绿素a浓度在所有季节都呈现增加趋势;除11月外,其他各月都呈现稳定或增加趋势。从滦河入河口沿岸至渤海海峡的渤海中部,叶绿素a浓度增加较明显。同时也分析了海洋表面温度、风速和降水量数据。夏季渤海周边区域降水量和风速增加以及秋季海表温度的降低都有助于同季叶绿素a浓度的升高。渤海浮游植物可能受陆源营养物质输入影响较大。
-
关键词:
- 叶绿素a浓度 /
- 降水 /
- 海洋表面温度 /
- 风速 /
- SeaWiFS /
- MODIS Aqua /
- Google Earth Engine /
- 渤海
Abstract: Phytoplankton, as the base of the oceanic food chain, plays a fundamental role in marine ecosystems. Since the Bohai Sea, the largest inner sea in China, is an important spawning ground and nursery field as well as a feeding ground for marine creatures, it is critical to understand variations of phytoplankton in the area. Chlorophyll a (Chl a) concentration is an important proxy for phytoplankton biomass. Chl a derived from both the Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS) from 1997 to 2010 and the MODerate resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) sensor on satellite Aqua from 2002 to 2018 were combined into one time series to investigate the spatial and temporal variability of Chl a concentrations in the Bohai Sea using Google Earth Engine. Annual Chl a concentrations increased significantly by 14.1% in the study area over the past two decades. Chl a concentrations in every season and in all months except November have stagnated or increased. Chl a concentrations increased mainly in the middle part of the sea. Sea surface temperature (SST), wind speed and precipitation were also analyzed. Increases in precipitation over the land around the Bohai Sea and wind speed in summer, as well as decrease in SST in autumn, all contributed to the rises of Chl a concentrations. Nutrients from land may play an important role in phytoplankton growth.-
Key words:
- chlorophyll a concentration /
- precipitation /
- sea surface temperature /
- wind speed /
- SeaWiFS /
- MODIS Aqua /
- Google Earth Engine /
- Bohai Sea
-
表 1 叶绿素a浓度数据
Tab. 1 Chlorophyll a concentration data
卫星 传感器 时间范围 时间分辨率 空间分辨率 Aqua MODIS 2002年7月4日至
2018年8月29日日值 4 km×4 km SeaStar SeaWiFS 1997年9月4日至
2010年12月11日日值 10 km×10 km 表 2 近20 年渤海全年与各季节叶绿素a浓度变化
Tab. 2 Changes in annual and seasonal chlorophyll a concentration in the Bohai Sea over the past two decades
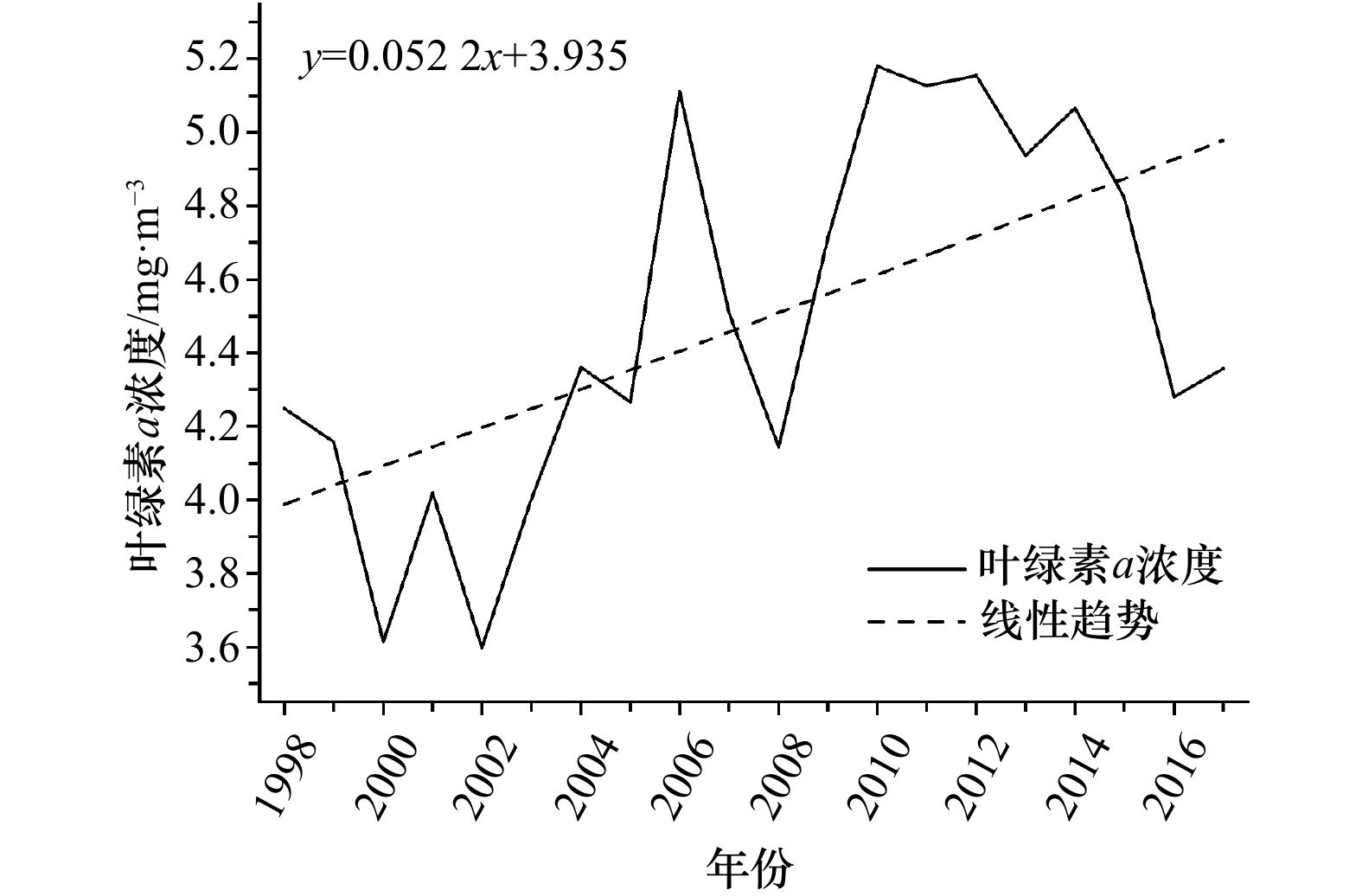
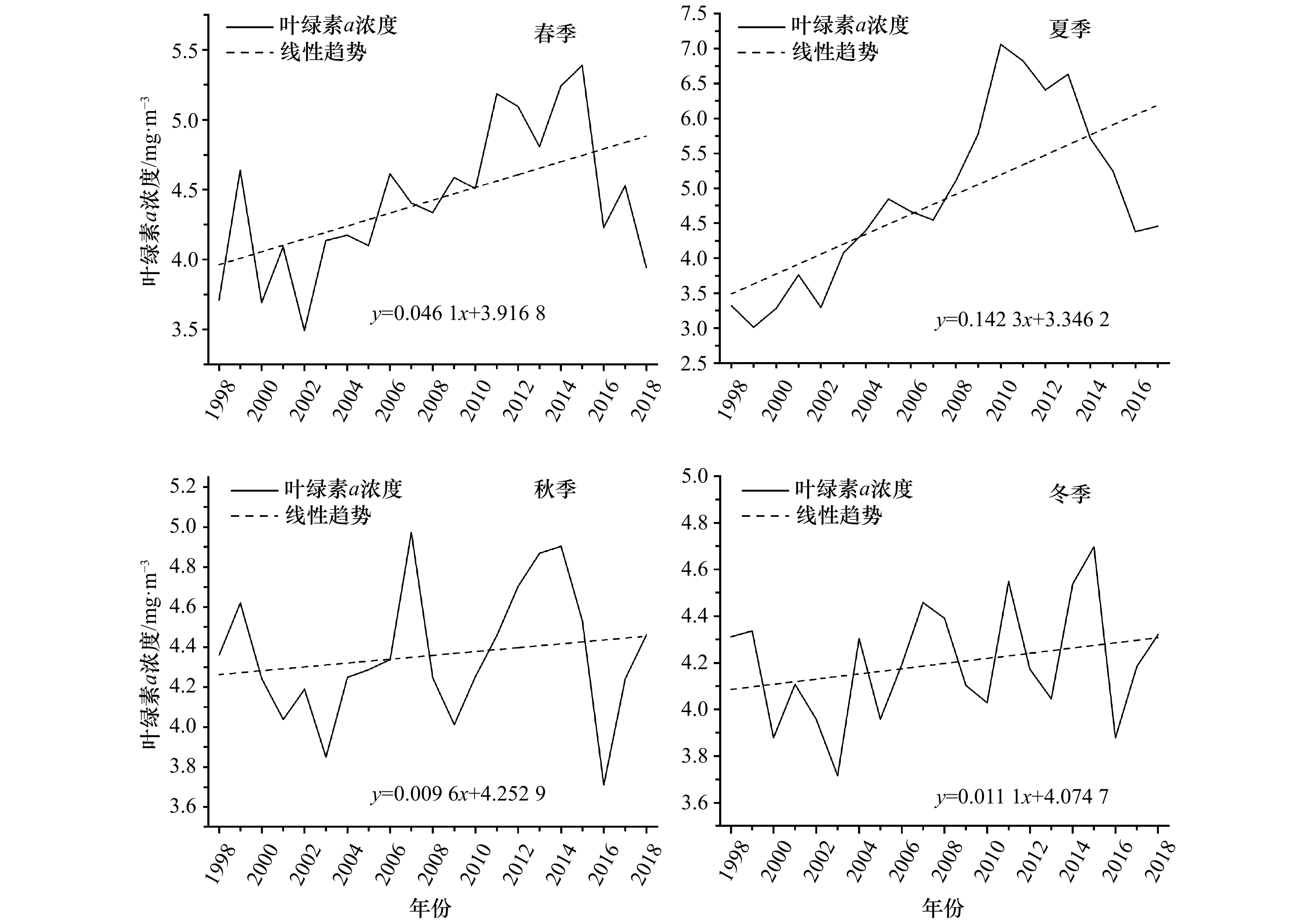
全年 春(3–5月) 夏(6–8月) 秋(9–11月) 冬(12–次年2月) 时间范围 1998–2017年 1998–2018年 1998–2017年 1997–2017年 1998–2018年 变化趋势/mg·m–3·a–1 0.052 2* 0.046 1* 0.142 3* 0.009 6 0.011 1 变化量 14.1% 15.2% 44.8% 2.5% 2.5% 注:线性趋势采用F检验,*表示99%的置信水平。 表 3 近20年渤海月值叶绿素a浓度变化
Tab. 3 Changes in monthly chlorophyll a concentration in the Bohai Sea over the past two decades
月份 1月 2月 3月 4月 5月 6月 时间范围 1998–2018年 1998–2018年 1998–2018年 1998–2018年 1998–2018年 1998–2018年 变化趋势/mg·m–3·a–1 0.013 5 0.019 6 0.010 9 0.045 3* 0.082 0* 0.098 7* 变化量 5.4% 6.6% 5.1% 11.0% 30.6% 37.5% 月份 7月 8月 9月 10月 11月 12月 时间范围 1998–2018年 1997–2017年 1997–2017年 1997–2017年 1997–2017年 1997–2017年 变化趋势/mg·m–3·a–1 0.140 5* 0.153 6* 0.042 3* 0.006 8 –0.020 3 0.000 2 变化量 52.2% 47.1% 10.9% –0.1% –4.9% 0 注:线性趋势采用F检验,*表示99%的置信水平。 表 4 近20年渤海降水量、海洋表面温度和风速变化
Tab. 4 Changes in precipitation, sea surface temperature and wind speed in the Bohai Sea over the past two decades
环境因子 时间 与叶绿素a浓度相关系数 线性趋势 时间范围 降水量 全年 0.14 0.32 mm/a 1998–2016年 降水量 夏季 0.15 0.61 mm/a 1998–2016年 降水量 2月 0.20 0.22 mm/a 1998–2016年 降水量 6月 0.08 0.70 mm/a 1998–2016年 降水量 7月 0.06 1.38 mm/a 1998–2016年 海洋表面温度 秋季 0.15 –0.01 °C/a 1997–2017年 风速 6月 0.36 0.03 m/(s·a) 1998–2017年 风速 7月 0.35 0.04 m/(s·a) * 1998–2017年 风速 夏季 0.28 0.02 m/(s·a) 1998–2017年 注:线性趋势采用F检验;*表示95%的置信水平。 -
[1] Boyce D G, Lewis M R, Worm B. Global phytoplankton decline over the past century[J]. Nature, 2010, 466(7306): 591−596. doi: 10.1038/nature09268 [2] 栾青杉, 康元德, 王俊. 渤海浮游植物群落的长期变化(1959~2015)[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(4): 9−18.Luan Qingshan, Kang Yuande, Wang Jun. Long-term changes in the phytoplankton community in the Bohai Sea (1959~2015)[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(4): 9−18. [3] Blondeau-Patissier D, Gower J F R, Dekker A G, et al. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2014, 123: 123−144. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.12.008 [4] 康元德, 吕培顶, 张坤诚. 渤海湾浮游植物光合作用强度的测定[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1982(4): 47−51.Kang Yuande, Lv Peiding, Zhang Kuncheng. The determination of phytoplankton photosynthesis in the Bohai Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1982(4): 47−51. [5] 吕培顶, 费尊乐, 毛兴华, 等. 渤海水域叶绿素a的分布及初级生产力的估算[J]. 海洋学报, 1984, 6(1): 90−98.Lv Peiding, Fei Zunle, Mao Xinghua, et al. The distribution of chlorophyll a and the estimation of primary productivity in the Bohai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1984, 6(1): 90−98. [6] 费尊乐, 毛兴华, 朱明远, 等. 渤海生产力研究——I. 叶绿素a的分布特征与季节变化[J]. 海洋学报, 1988, 10(1): 99−106.Fei Zunle, Mao Xinghua, Zhu Mingyuan, et al. Study of productivity in the Bohai Sea I: Distribution of chlorophyll a concentration and its seasonal variability[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1988, 10(1): 99−106. [7] 吕瑞华, 夏滨, 李宝华, 等. 渤海水域初级生产力10年间的变化[J]. 黄渤海海洋, 1999, 17(3): 80−86.Lv Ruihua, Xia Bin, Li Baohua, et al. The fluctuations of primary productivity in Bohai Sea waters over ten years[J]. Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai seas, 1999, 17(3): 80−86. [8] 孙军, 刘东艳, 柴心玉, 等. 1998~1999年春秋季渤海中部及其邻近海域叶绿素a浓度及初级生产力估算[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 23(3): 517−526. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.03.016Sun Jun, Liu Dongyan, Chai Xinyu, et al. The chlorophyll a concentration and estimating of primary productivity in the Bohai Sea in 1998~1999[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(3): 517−526. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.03.016 [9] 邹芳睿. 渤海湾分级叶绿素对营养盐浓度变化的响应[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2009.Zou Fangrui. Response of classified chlorophyll to changes of concentrations of nutrients in Bohai Bay[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2009. [10] 刘丽雪, 王玉珏, 邸宝平, 等. 2012年春季渤海中部及邻近海域叶绿素a与环境因子的分布特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(12): 8−15. doi: 10.11759/hykx20140123002Liu Lixue, Wang Yujue, Di Baoping, et al. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a and environmental factors in the Bohai Sea in spring of 2012[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(12): 8−15. doi: 10.11759/hykx20140123002 [11] 周凤霞, 高学鲁, 庄文, 等. 莱州湾沿岸河流对邻近海域表层水体中Chl a浓度的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(2): 184−189.Zhou Fengxia, Gao Xuelu, Zhuang Wen, et al. The impact of rivers on the Chl a concentrations in coastal surface waters of the Laizhou Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(2): 184−189. [12] 黄海燕, 杨翼, 杨璐, 等. 2004-2015年夏季渤海湾生态监控区网采浮游植物变化研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(1): 115−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.01.013Huang Haiyan, Yang Yi, Yang Lu, et al. Study on dynamics of net-phytoplankton in Bohai Bay ecological monitoring area in summer from 2004 to 2015[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2018, 40(1): 115−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.01.013 [13] 周艳蕾, 张传松, 石晓勇, 等. 黄渤海海水中叶绿素a的分布特征及其环境影响因素[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11): 4259−4265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.11.031Zhou Yanlei, Zhang Chuansong, Shi Xiaoyong, et al. Distribution characteristics of chlorophyll a and its influencing environmental factors in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(11): 4259−4265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.11.031 [14] Wei Hao, Sun Jun, Moll A, et al. Phytoplankton dynamics in the Bohai Sea—observations and modelling[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2004, 44(3/4): 233−251. [15] 王毅波, 孙延瑜, 王彩霞, 等. 夏季渤海网采浮游植物群落和叶绿素a分布特征及其对渔业资源的影响[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, doi: 10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20180514001Wang Yibo, Sun Yanyu, Wang Caixia, et al. Distribution of net-phytoplankton community and chlorophyll a in the Bohai Sea in summer and its impacts on fishery resources[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, doi: 10.19663/j.issn2095-9869.20180514001 [16] 檀赛春, 石广玉. 中国近海初级生产力的遥感研究及其时空演化[J]. 地理学报, 2006, 61(11): 1189−1199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.11.008Tan Saichun, Shi Guangyu. Remote sensing for ocean primary productivity and its spatio-temporal variability in the China Seas[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(11): 1189−1199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2006.11.008 [17] 许士国, 富砚昭, 康萍萍. 渤海表层叶绿素a时空分布及演变特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(6): 898−903, 924.Xu Shiguo, Fu Yanzhao, Kang Pingping. Seasonal and interannual variations of Chlorophyll a in Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2015, 34(6): 898−903, 924. [18] 李爽兆. 基于MODIS数据和水动力学模型的渤海叶绿素分布特性研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2017.Li Shuangzhao. Study of chlorophyll distribution in Bohai Sea based on MODIS data and hydrodynamic model[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2017. [19] Zhang Hailong, Qiu Zhongfeng, Sun Deyong, et al. Seasonal and interannual variability of satellite-derived chlorophyll-a (2000-2012) in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 582. doi: 10.3390/rs9060582 [20] Fu Yanzhao, Xu Shiguo, Liu Jianwei. Temporal-spatial variations and developing trends of Chlorophyll-a in the Bohai Sea, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 173: 49−56. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.02.016 [21] Liu Dongyan, Wang Yueqi. Trends of satellite derived chlorophyll-a (1997-2011) in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China: effects of bathymetry on seasonal and inter-annual patterns[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2013, 116: 154−166. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2013.07.003 [22] Shi Wei, Wang Menghua. Satellite views of the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea, and East China Sea[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2012, 104: 30−45. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2012.05.001 [23] Ning Xiuren, Lin Chuanlan, Su Jilan, et al. Long-term environmental changes and the responses of the ecosystems in the Bohai Sea during 1960-1996[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2010, 57(11/12): 1079−1091. [24] NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Ocean Ecology Laboratory, Ocean Biology Processing Group. Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Aqua Ocean Color Data, NASA OB[DB/OL]. [2018-1-15/2018-9-20]. Greenbelt, MD, USA: NASA Ocean Biology Distibuted Active Archive Center (OB.DAAC). https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/10.5067/AQUA/MODIS/L3M/CHL/2018/ [25] NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Ocean Ecology Laboratory, Ocean Biology Processing Group. Sea-viewing wide field-of-view sensor (SeaWiFS) Data, NASA OB[DB/OL]. [2018-2-15/2018-9-20]. Greenbelt, MD, USA: NASA Ocean Biology Distibuted Active Archive Center (OB.DAAC). https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/10.5067/ORBVIEW-2/SEAWIFS/L3B/CHL/2018/ [26] Harris I, Jones P D, Osborn T J, et al. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations-the CRU TS3. 10 Dataset[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2014, 34(3): 623−642. doi: 10.1002/joc.3711 [27] Clayson, Carol, Anne, et al. NOAA climate data record ocean surface bundle (OSB) climate data record (CDR) of sea surface temperature-WHOI, version 2[DB/OL]. [2016-09-30/2018-9-24]. Asheville, North Carolina, USA: NOAA National Climatic Data Center. https://data.nodc.noaa.gov/cgi-bin/iso?id=gov.noaa.ncdc:C00972 [28] Mann H B. Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 1945, 13(3): 245−259. doi: 10.2307/1907187 [29] Kendall M G. Rank Correlation Methods[M]. 4th ed. London: Charles Griffen, 1975. [30] Moore C M, Mills M M, Arrigo K R, et al. Processes and patterns of oceanic nutrient limitation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(9): 701−710. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1765 [31] 王震, 李宜良, 赵鹏. 环渤海地区海洋渔业经济可持续发展对策研究[J]. 中国渔业经济, 2015, 33(1): 38−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-590X.2015.01.008Wang Zhen, Li Yiliang, Zhao Peng. A study on the countermeasures of sustainable development of Bohai marine fishery economy[J]. Chinese Fisheries Economics, 2015, 33(1): 38−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-590X.2015.01.008 [32] 郭永坚, 罗昭林, 朱长波, 等. 水产养殖对流沙湾浮游植物群落特征的影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 2015, 11(2): 57−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2015.02.008Guo Yongjian, Luo Zhaolin, Zhu Changbo, et al. Influence of aquaculture on characteristics of phytoplankton community in Liusha Bay[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2015, 11(2): 57−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2015.02.008 -





 下载:
下载: