Occurrence phase and enrichment mechanism of platinum group elements in the Pacific cobalt-rich crusts
-
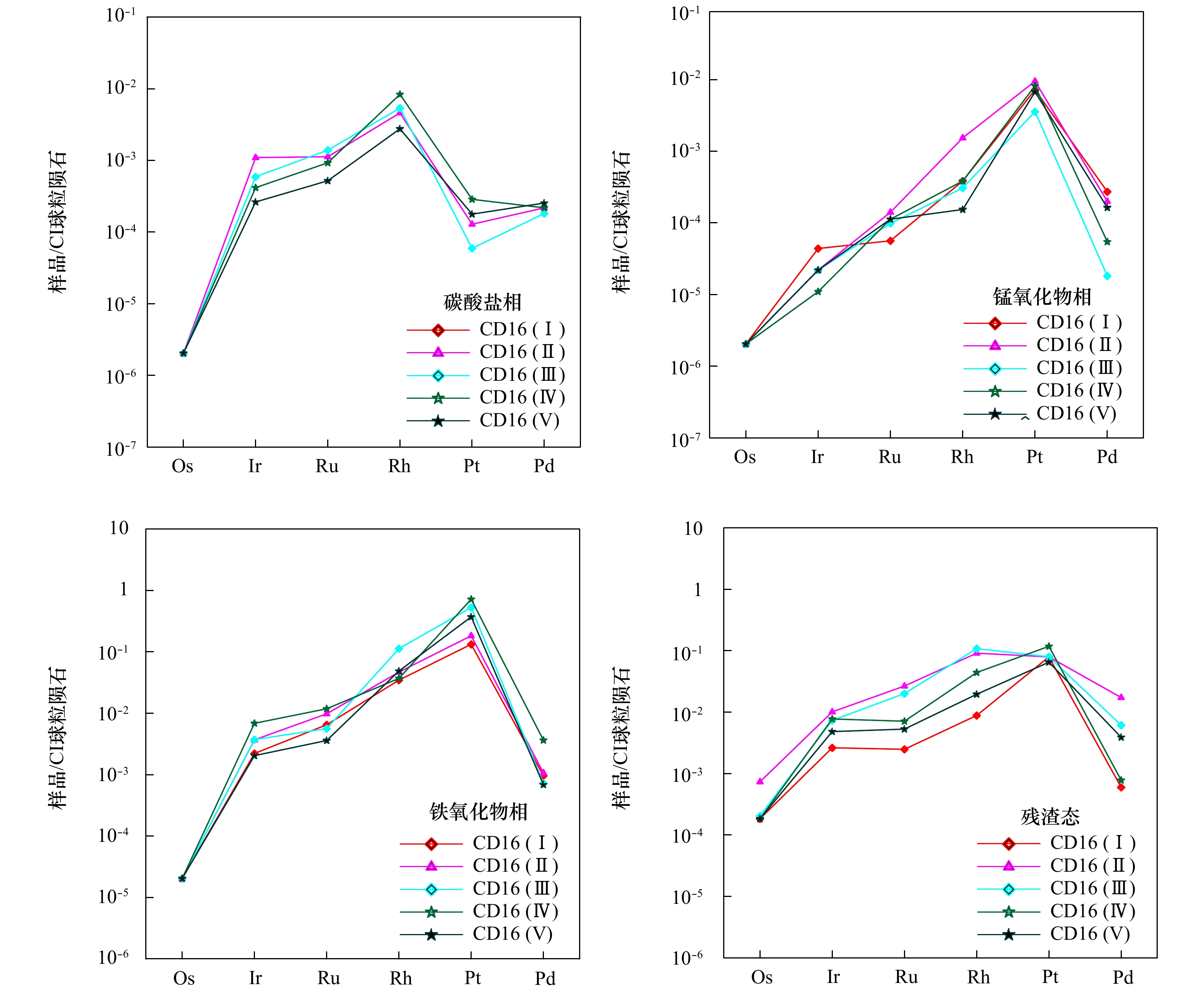
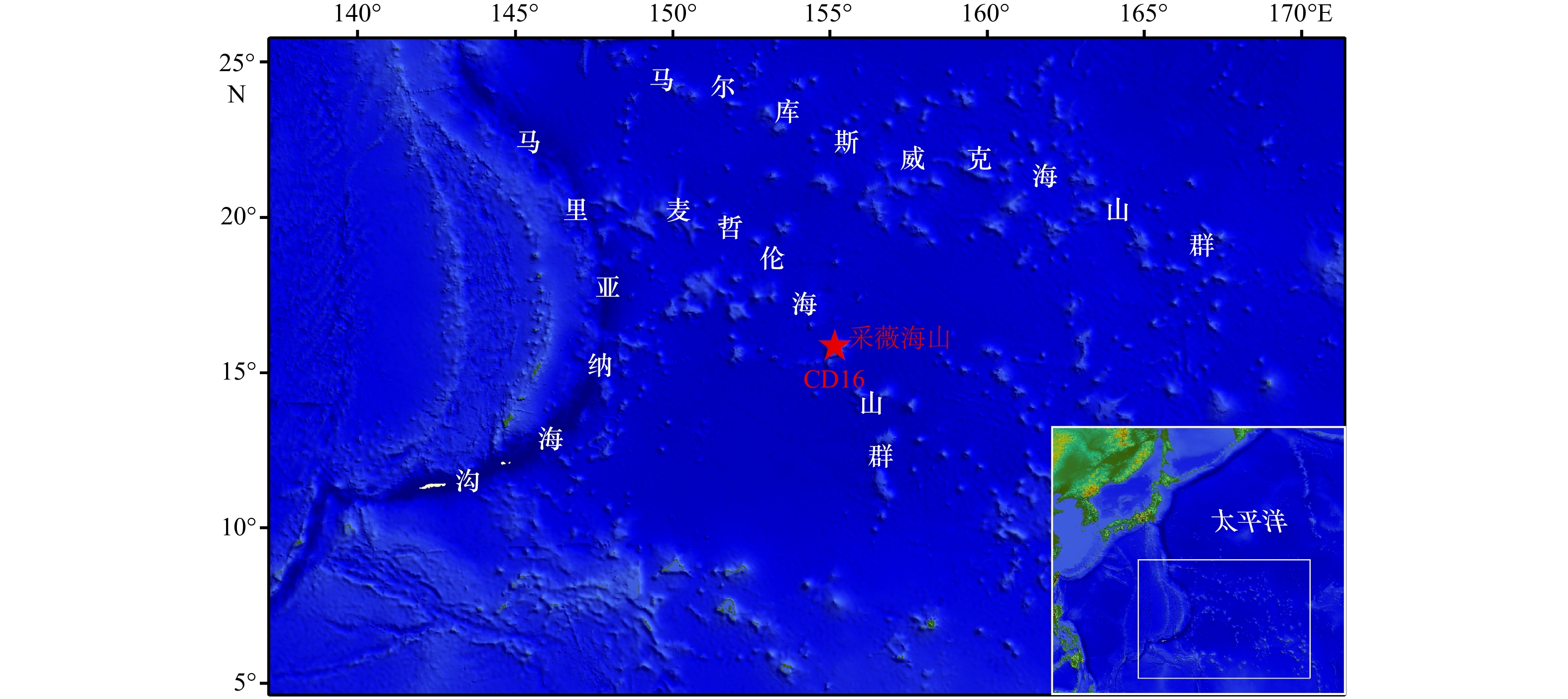
摘要: 通过选择性化学提取法,对太平洋采薇海山富钴结壳样品中铂族元素进行分级提取实验,利用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)测定了铂族元素含量。赋存状态结果显示,富钴结壳中铂族元素在各个化学相态中富集比例从大到小依次为:铁氧化物相、残渣态、锰氧化物相、碳酸盐相、吸附态,未磷酸盐化新壳层和磷酸盐化老壳层中铂族元素都主要赋存于铁氧化物相中,其富集比例为59.26%~82.19%,残渣态中磷酸盐对铂族元素具有一定的富集能力,其富集比例为17.23%~35.37%。不同类型地质体中铂族元素的赋存状态结果,也证实了富钴结壳和海山结核中铂族元素富集主要受到铁氧化物相和残渣态的影响。太平洋海山富钴结壳中铂族元素的富集机理推测为铁氧/氢氧化物胶体粒子的吸附作用,使海水中
${\rm PtCl}_4^{2-} $ 离子被吸附到铁氧化物相中,从而使富钴结壳中铂族元素富集。Abstract: Selective chemical extraction method was utilized to fractionally extract platinum group elements (PGE) in cobalt-rich crusts from Caiwei Seamount in the Pacific, and PGE contents were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Occurrence phase analysis results in cobalt-rich crusts show that the PGE enrichments in different phases conform to the following order: iron oxide phase, residual phase, manganese oxide phase, carbonate phase, adsorbed phase. PGE in the new non-phosphate layers and the old phosphate layers are mainly enriched in the iron oxide phase, with the enrichment ratio from 59.26% to 82.19%, and the phosphate in residual phase has certain enrichment ability for PGE, with the enrichment ratio from 17.23% to 35.37%. Meanwhile, occurrence phase analysis results in different geological bodies show that the PGE enrichment in cobalt-rich crusts and seamount nodules is mainly affected by iron oxide phase and residual phase. In addition, the enrichment mechanism of PGE in cobalt-rich crusts is presumed to the iron oxide/iron hydroxides colloid particles adsorption, and the soluble$ {\rm PtCl}_4^{2-}$ in seawater is adsorbed into the iron oxide phase, so PGE are enriched in cobalt-rich crusts. -
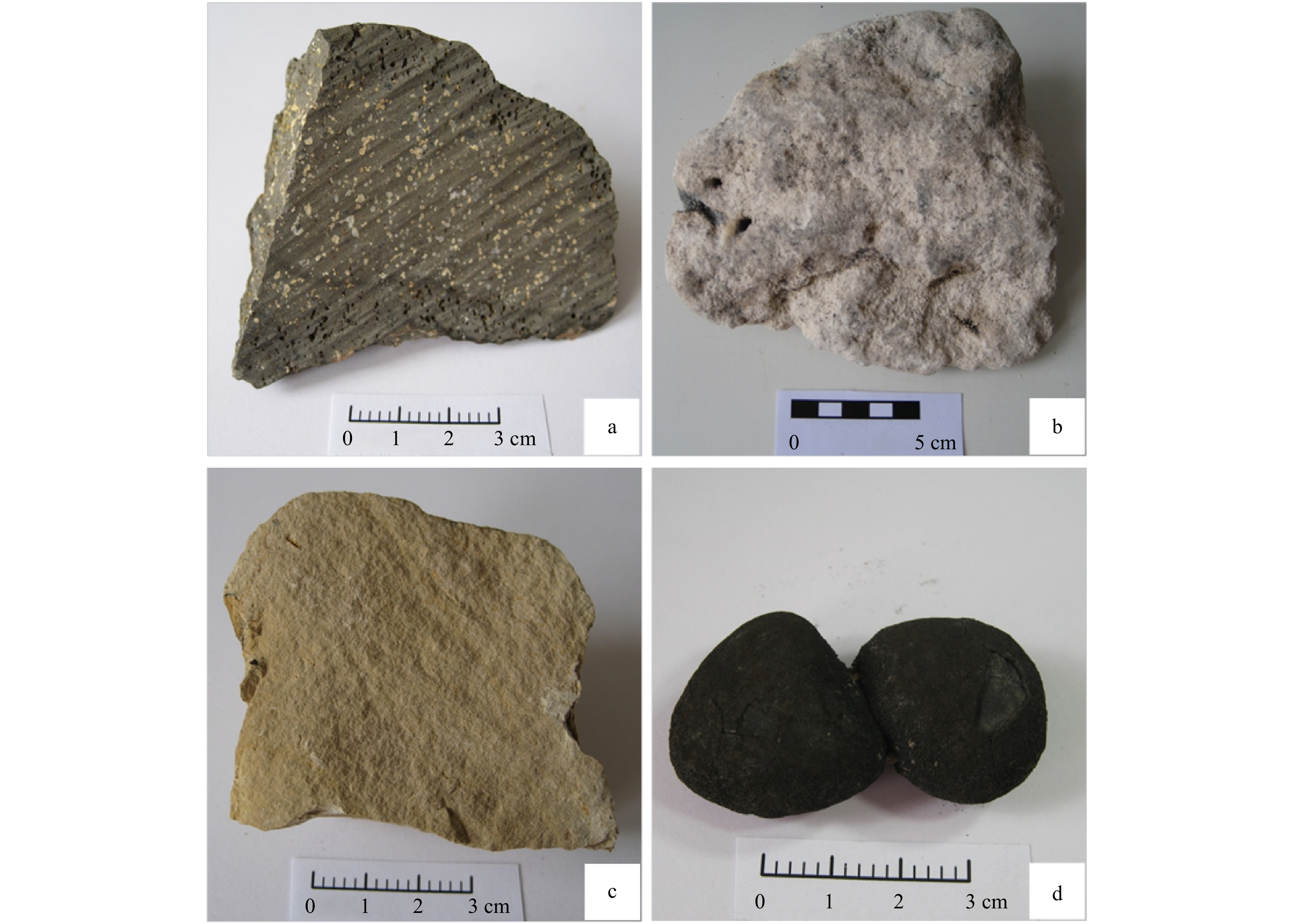
图 3 不同类型地质体样品照片
a. 玄武岩,气孔发育,多见白色杏仁体充填;b. 碳酸岩,由有孔虫壳体组成;c. 磷块岩,由微细晶粒或隐晶质矿物组成;d. 海山结核,椭球状结核体
Fig. 3 The photos of different geological bodies
a. Basalt, vesicular structure, filled with secondary minerals;b. carbonate rock, composed of foraminifera shells;c. phosphate rock, composed of fine crystal grains or cryptocrystalline minerals;d. seamount nodules, ellipsoidal nodule bodies
表 1 富钴结壳不同构造层样品描述
Tab. 1 Description of different structural layer in cobalt-rich crusts
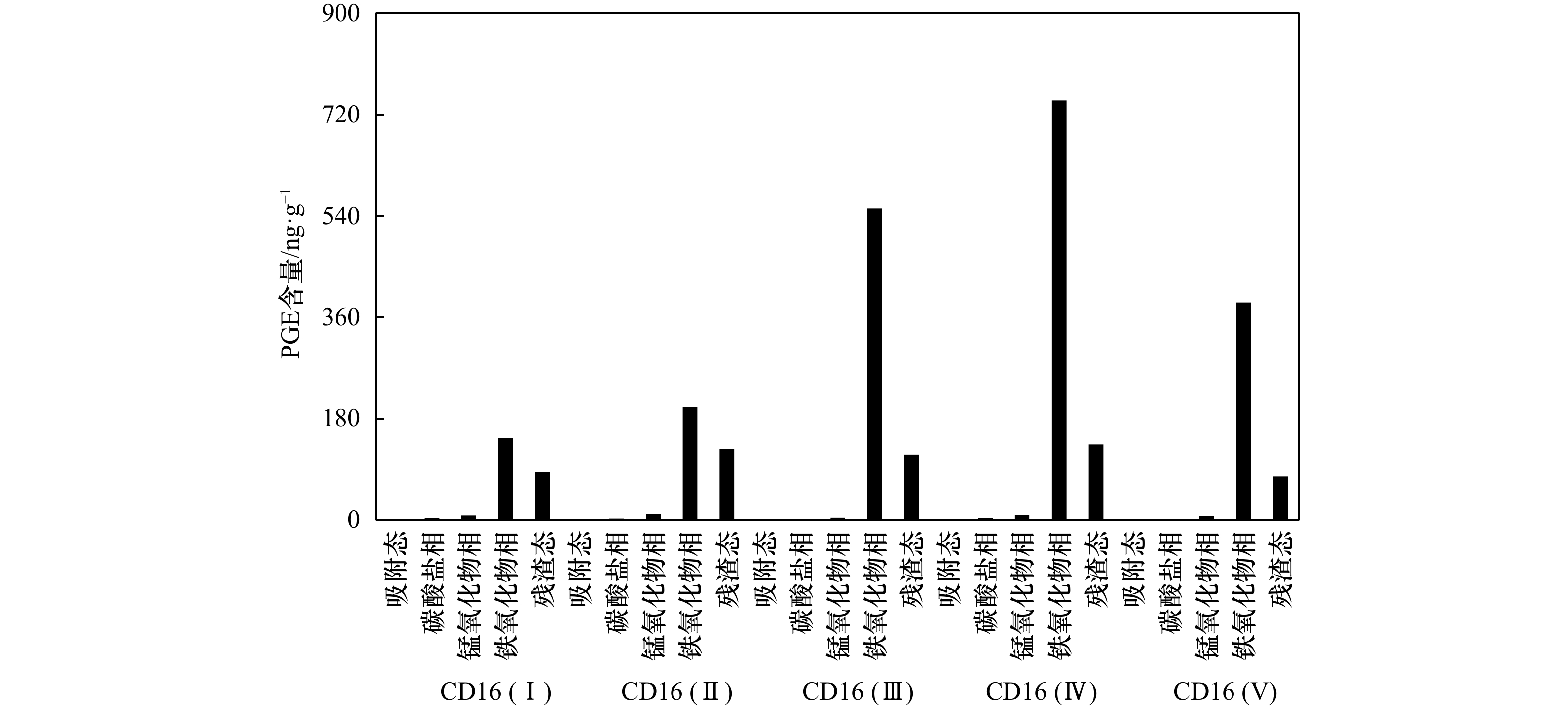
样品编号 构造层 深度/mm 样品描述 CD16(Ⅰ) 第Ⅰ构造层 0~16 致密,褐黑色,表层葡萄体状突起,以柱状构造为主 CD16(Ⅱ) 第Ⅱ构造层 16~26 致密,黑色,以柱状构造为主 CD16(Ⅲ) 第Ⅲ构造层 26~60 疏松,黄褐色,黏土较多,以树丛状构造为主 CD16(Ⅳ) 第Ⅳ构造层 60~88 致密,黑色,少量磷酸盐脉,以斑杂状构造为主 CD16(Ⅴ) 第Ⅴ构造层 88~98 致密,亮黑色,较多磷酸盐脉,以水平层纹状构造为主 表 2 富钴结壳不同构造层样品中铂族元素(PGE)含量
Tab. 2 Platinum group elements (PGE) contents of different structural layer in cobalt-rich crusts
样品 Ru含量/ng·g–1 Pd含量/ng·g–1 Ir含量/ng·g–1 Pt含量/ng·g–1 Rh含量/ng·g–1 Os含量/ng·g–1 PGE含量/ng·g–1 CD16(Ⅰ) 19.00 1.700 4.600 202.4 14.70 0.350 0 242.8 CD16(Ⅱ) 20.60 0.300 0 5.700 247.6 13.20 0.470 0 287.9 CD16(Ⅲ) 10.26 2.350 4.710 380.5 18.95 0.130 0 416.9 CD16(Ⅳ) 15.80 2.700 9.700 866.8 24.90 0.110 0 920.0 CD16(Ⅴ) 9.700 4.200 4.900 470.0 14.40 0.130 0 503.3 表 3 不同类型地质体中铂族元素(PGE)含量
Tab. 3 Platinum group elements (PGE) contents in different geological bodies
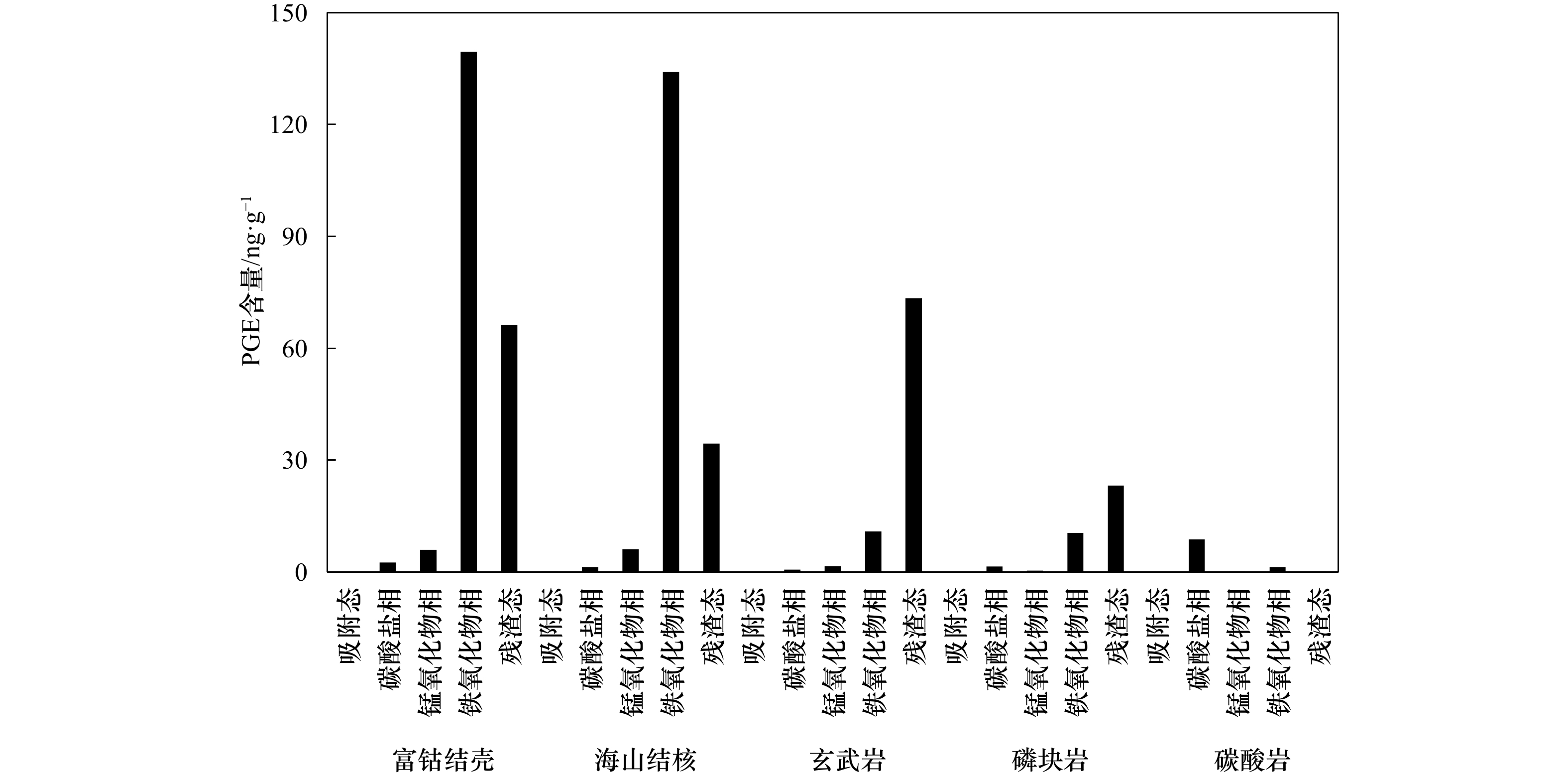
样品 Ru含量/ng·g–1 Pd含量/ng·g–1 Ir含量/ng·g–1 Pt含量/ng·g–1 Rh含量/ng·g–1 Os含量/ng·g–1 PGE含量/ng·g–1 碳酸岩 0.010 0 0.740 0 0.120 0 10.13 0.190 0 0.120 0 11.31 磷块岩 1.360 1.770 0.190 0 33.11 0.260 0 0.110 0 36.80 玄武岩 1.250 3.900 0.340 0 80.49 0.330 0 0.130 0 86.44 海山结核 16.42 2.970 2.290 164.9 0.680 0 0.610 0 187.9 富钴结壳 18.30 4.700 5.400 215.6 15.30 0.200 0 259.5 -
[1] 刘季花. 太平洋富钴结壳伴生有用元素分布特征及成矿远景评价[R]. 青岛: 国家海洋局第一海洋研究所, 2015: 1–238.Liu Jihua. Distribution characteristics and mineralization prospect evaluation of the associated useful elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Pacific Ocean[R]. Qingdao: The First Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2015: 1–238. [2] 王登红, 骆耀南, 屈文俊, 等. 中国西南铂族元素矿床地质、地球化学与找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 13–16.Wang Denghong, Luo Yaonan, Qu Wenjun, et al. Geology, Geochemistry and Exploration of PGE Deposits in SW China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 13–16. [3] 刘秉光. 中国PGE矿床类型分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2002, 38(4): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2002.04.001Liu Bingguang. Discussion on PGE deposit types in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2002, 38(4): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2002.04.001 [4] 梁有彬, 刘同有, 宋国仁, 等. 中国铂族元素矿床[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1998: 1–185.Liang Youbin, Liu Tongyou, Song Guoren, et al. Platinum Group Element Deposits in China[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1998: 1–185. [5] Yang K, Park H, Son S K, et al. Electron microscopy study on the formation of ferromanganese crusts, western Pacific Magellan Seamounts[J]. Marine Geology, 2019, 410: 32−41. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2019.01.001 [6] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224−233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045 [7] Zawadzki D, Maciąg Ł, Kotliński R A, et al. Geochemistry of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from the Perth Abyssal Plain (E Indian Ocean)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101: 520−531. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.08.004 [8] Maksimov S O, Safronov P P. Geochemical features and genesis of continental cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2018, 59(7): 745−762. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2018.07.003 [9] Hein J R, Conrad T, Mizell K, et al. Controls on ferromanganese crust composition and reconnaissance resource potential, Ninetyeast Ridge, Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 110: 1−19. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.11.006 [10] Marino E, González F J, Somoza L, et al. Strategic and rare elements in Cretaceous-Cenozoic cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from seamounts in the Canary Island Seamount Province (northeastern tropical Atlantic)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 41−61. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.005 [11] Goto K T, Nozaki T, Toyofuku T, et al. Paleoceanographic conditions on the São Paulo Ridge, SW Atlantic Ocean, for the past 30 million years inferred from Os and Pb isotopes of a hydrogenous ferromanganese crust[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2017, 146: 82−92. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2016.10.010 [12] Gueguen B, Rouxel O, Rouget M L, et al. Comparative geochemistry of four ferromanganese crusts from the Pacific Ocean and significance for the use of Ni isotopes as paleoceanographic tracers[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 189: 214−235. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.06.005 [13] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3/4): 331−351. [14] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113−5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4 [15] 白志民, 王英滨, 姜波, 等. 太平洋富钴结壳中稀土元素的赋存状态[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(2): 387−392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.02.008Bai Zhimin, Wang Yingbin, Jiang Bo, et al. Occurrence modes of REE in the Pacific cobalt-rich crusts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(2): 387−392. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.02.008 [16] 徐兆凯, 李安春, 于心科, 等. 东菲律宾海新型铁锰结壳中元素的赋存状态[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2008, 33(3): 329−336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.03.005Xu Zhaokai, Li Anchun, Yu Xinke, et al. Elemental occurrence phases of the new-type ferromanganese crusts from the East Philippine Sea[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 33(3): 329−336. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.03.005 [17] Khanchuk A I, Mikhailik P E, Mikhailik E V, et al. Peculiarities of the distribution of rare-earth elements and yttrium in mineral phases of the ferromanganese crusts from the Detroit guyot (Pacific Ocean)[J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2015, 465(2): 1243−1247. doi: 10.1134/S1028334X15120016 [18] Mohwinkel D, Kleint C, Koschinsky A. Phase associations and potential selective extraction methods for selected high-tech metals from ferromanganese nodules and crusts with siderophores[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 43: 13−21. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.01.010 [19] Qi L, Zhou M F, Wang C Y, et al. Evaluation of a technique for determining Re and PGEs in geological samples by ICP-MS coupled with a modified Carius tube digestion[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2007, 41(6): 407−414. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.41.407 [20] Qi Liang, Zhou Meifu, Wang C Y. Determination of low concentrations of platinum group elements in geological samples by ID-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(10): 1335−1339. doi: 10.1039/b400742e [21] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 李先国, 等. 富钴结壳中稀土元素化学相态分析方法及其应用[J]. 分析化学, 2015, 43(12): 1895−1900. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.150418Gao Jingjing, Liu Jihua, Li Xianguo, et al. Chemical phase analysis of rare earth elements in cobalt-rich crusts and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2015, 43(12): 1895−1900. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.150418 [22] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079−4094. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00231-7 [23] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[M]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 2000: 239–279. [24] Pan Jiahua, De Carlo E H, Yang Yi, et al. Effect of phosphatization on element concentration of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79(3): 349−355. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2005.79.issue-3 [25] 任向文, 石学法, 朱爱美, 等. 麦哲伦海山群MK海山富钴结壳稀土元素的赋存相态[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2011, 41(3): 707−714.Ren Xiangwen, Shi Xuefa, Zhu Aimei, et al. Existing phase of rare earth elements in Co-rich Fe-Mn crusts from seamount MK of magellan seamount cluster[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(3): 707−714. [26] 卜文瑞. 太平洋富钴结壳稀有气体地球化学特征及其成矿指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2008: 1–164.Bu Wenrui. Noble gas geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean and their significations for the formation of crusts[D]. Qingdao: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008: 1–164. [27] 何高文, 孙晓明, 杨胜雄, 等. 东太平洋CC区多金属结核铂族元素(PGE)地球化学及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(2): 164−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.02.006He Gaowen, Sun Xiaoming, Yang Shengxiong, et al. Platinum group elements (PGE) geochemistry of polymetallic nodules in CC zone, east Pacific Ocean[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(2): 164−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.02.006 [28] 杨胜雄, 龙晓军, 祁奇, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳矿物学和地球化学特征-以麦哲伦海山和马尔库斯-威克海山富钴结壳为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(2): 105−116.Yang Shengxiong, Long Xiaojun, Qi Qi, et al. The mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Co-rich crusts from the western Pacific: taking the Co-rich crusts from Magellan and Marcus-wake seamounts as an example[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(2): 105−116. [29] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳的稀土和铂族元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(10): 1745−1757.Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, Yao Huiqiang, et al. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from west Pacific Ocean Seamounts[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(10): 1745−1757. [30] McDonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223−253. [31] 孙晓明, 薛婷, 何高文, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳铂族元素(PGE)和Os同位素地球化学及其成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12): 3014−3026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.12.017Sun Xiaoming, Xue Ting, He Gaowen, et al. Platinum group elements (PGE) and Osisotopic geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean seamounts and their constraints on genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(12): 3014−3026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.12.017 [32] Halbach P, Kriete C, Prause B, et al. Mechanisms to explain the platinum concentration in ferromanganese seamount crusts[J]. Chemical Geology, 1989, 76(1/2): 95−106. [33] Hein J R, Mizell K, Koschinsky A, et al. Deep-ocean mineral deposits as a source of critical metals for high- and green-technology applications: comparison with land-based resources[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2013, 51: 1−14. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.12.001 [34] Hein J R, Koschinsky A. Deep-ocean ferromanganese crusts and nodules[M]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on Geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier, 2014: 273–291. [35] Bau M, Schmidt K, Koschinsky A, et al. Discriminating between different genetic types of marine ferro-manganese crusts and nodules based on rare earth elements and yttrium[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 381: 1−9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.05.004 [36] Jiang Xuejun, Lin Xuehui, Yao De, et al. Enrichment mechanisms of rare earth elements in marine hydrogenic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54(2): 197−203. doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4070-4 -






 下载:
下载: