The role of ecological factors in the progress of the green tide in the Yellow Sea
-
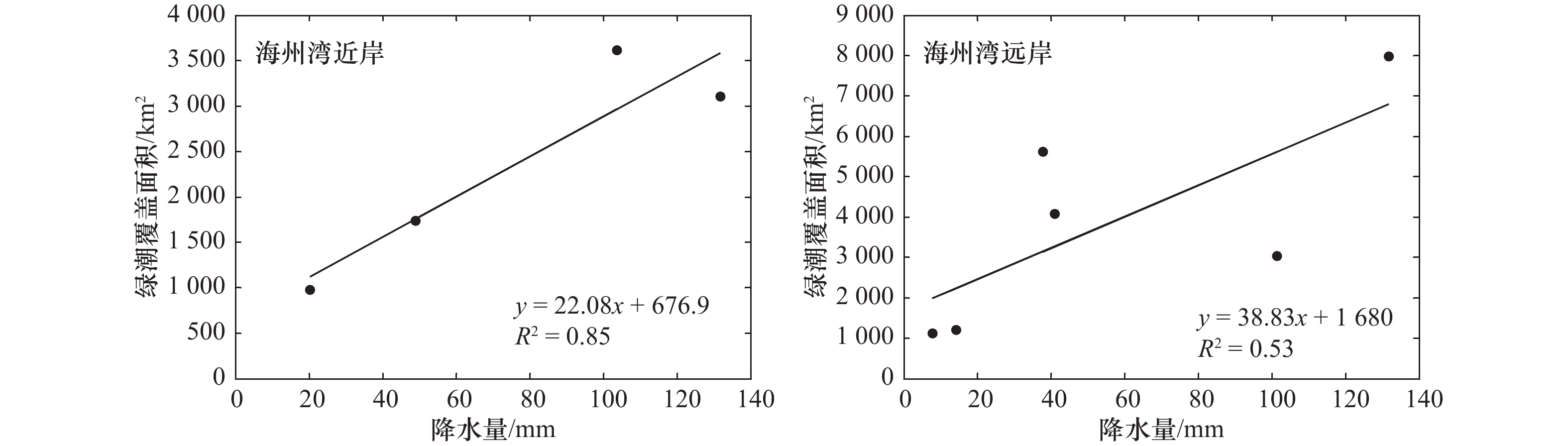
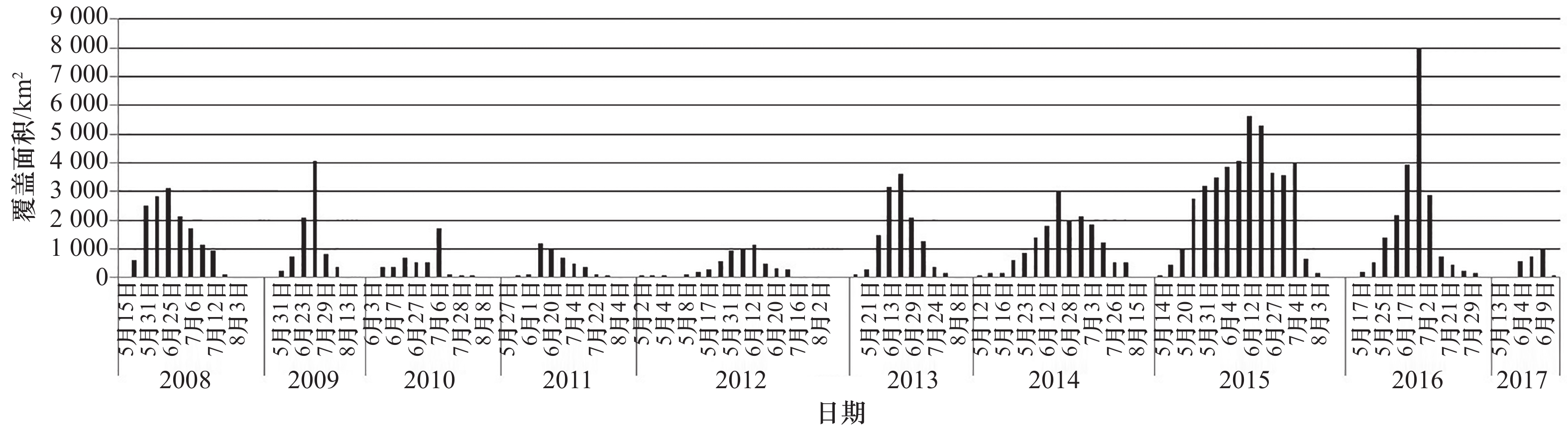
摘要: 2008–2017年南黄海海域连续10 a发生绿潮,影响周边沿海城市养殖、旅游和航运安全等。研究绿潮生消过程及其影响因素对于理解黄海绿潮分布特征,开展绿潮灾害的预防与治理有重要意义。本文主要采用MODIS L1B数据,通过归一化植被指数提取绿潮信息。根据逐年绿潮覆盖面积的变化特征,将绿潮生消过程分为3个阶段:触发阶段、快速发展阶段、消衰阶段,分析了海表温度、降水和光照在绿潮生消过程中的作用。结果表明:在触发阶段,温度达到15°C后,有效降水可以刺激绿潮的触发,在降水后的半个月内可以通过MODIS影像发现绿潮。在快速发展阶段,绿潮所在位置海表面温度为16~21°C,适宜绿潮的快速生长;太阳短波辐射集中在250~280 W/m2范围内;降水量是影响绿潮生长规模的一个重要因素,降水量少时绿潮覆盖面积峰值明显较小,而出现绿潮覆盖面积最大值的2016年降水量也极高。在消衰阶段,海表温度上升至22~26°C,绿潮在卫星影像中消失时,平均海表温度超过26°C,最高温度可达27.48°C,较高的海表面温度是导致绿潮消亡的主要原因之一;太阳短波辐射集中在240~260 W/m2,略低于快速发展阶段光照范围;降水量在该阶段相对充足不再影响绿潮的生长。Abstract: The green tide occurred in the South Yellow Sea for 10 a from 2008 to 2017, affecting aquaculture, tourism and the safety of shipping in surrounding coastal cities. Studying the progress of the green tide and their influencing factors are of vital significance for understanding the distribution characteristics of the green tide in the South Yellow Sea and for preventing and controlling the green tide disaster. MODIS L1B data is used in this paper and normalized difference vegetation index is applied to extract related information of the green tide. According to the variation characteristics of the coverage area of the green tide, the whole progress of the green tide is divided into three stages: trigger stage, fast development stage and depletion stage. And the effects of sea surface temperature, precipitation and short-wave radiation on the variation of the green tide were analyzed. The results show that in the trigger stage, when the temperature is over 15℃, effective precipitation can stimulate the triggering of the green tide. The green tide can be detected by MODIS image within half a month following the effective precipitation. In the fast development stage, the sea surface temperature at the location of the green tide is 16–21℃, which is suitable for the rapid growth of the green tide. The solar short-wave radiation is concentrated in the range of 250~280 W/m2, and the precipitation is important for the growth of the green tide during this stage. The peak coverage area of the green tide is low when precipitation is small, while the precipitation is extremely high in 2016 when the peak coverage area is the largest. During the depletion stage, the sea surface temperature rises to 22–26℃. When the green tide disappears, the average sea surface temperature exceeds 26℃, and the highest temperature reaches 27.48℃. The high sea surface temperature is one of the main factors for the demise of the green tide. The solar short-wave radiation is concentrated at 240–260 W/m2, which is slightly lower than that in the fast development stage. The precipitation is relatively sufficient in this stage and no longer affects the growth of the green tide.
-
表 1 2008–2017年温度、降水与绿潮触发关系
Tab. 1 The relationship between temperature, precipitation and the green tide trigger from 2008 to 2017
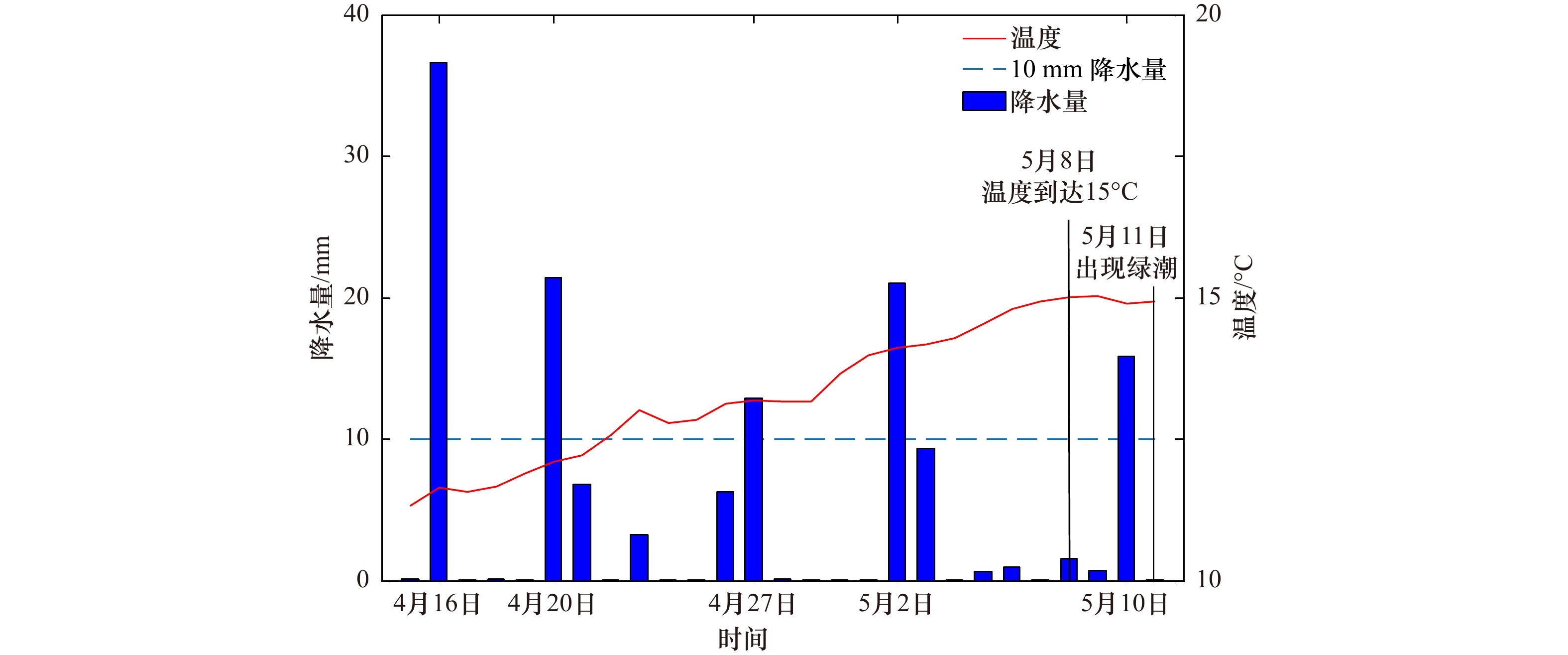
年份 降水日期 温度达到15℃日期 降水与适宜温度的间隔天数/d 是否为有效降水 绿潮出现日期 首次有效降水与绿潮首发的间隔天数/d 2008 5月4日 5月11日 7 √ 5月15日 11 2009 4月20日 5月7日 17 × 5月26日 10 5月16日 9 √ 5月20日 13 √ 2010 4月18日 5月14日 26 × 6月3日 17 4月19日 25 × 4月21日 23 × 5月17日 3 √ 5月22日 8 √ 2011 5月11日 5月10日 1 √ 5月27日 16 2012 4月21日 5月7日 16 × 5月6日 12 4月24日 13 √ 2013 5月9日 5月12日 3 √ 5月21日 12 2014 4月26日 5月11日 15 √ 5月12日 16 5月11日 0 √ 2015 5月2日 5月11日 9 √ 5月14日 12 2016 4月16日 5月8日 22 × 5月11日 14 4月20日 18 × 4月27日 11 √ 5月2日 6 √ 5月10日 2 √ 2017 5月4日 5月7日 3 √ 5月13日 9 5月8日 1 √ 5月12日 5 √ 表 2 2008–2017年绿潮快速增加阶段绿潮密集区域内海表面温度、太阳短波辐射、降水统计表
Tab. 2 Sea surface temperature, solar short-wave radiation, and precipitation in the intensive areas in the fast development stage of green tide from 2008 to 2017
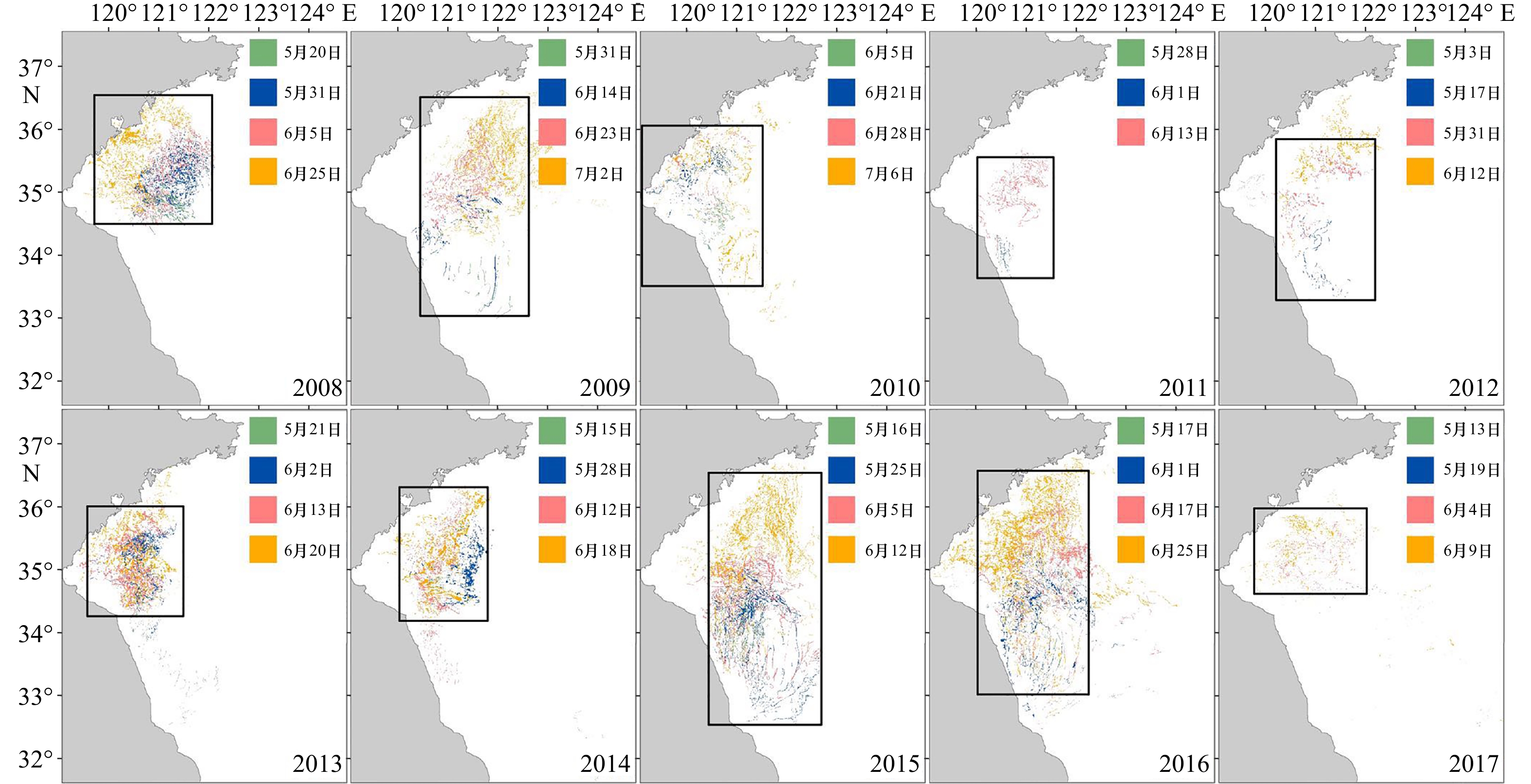
快速发展阶段时间 海表面温度/℃ 太阳短波辐射/W·m–2 降水量/mm 2008 5月20日至6月25日 17.38 258.89 131.81 2009 5月31日至7月2日 20.39 276.84 41.11 2010 6月5日至7月6日 20.66 275.34 49.03 2011 5月28日至6月13日 17.52 276.40 14.15 2012 5月3日至6月12日 16.75 282.09 7.86 2013 5月21日至6月20日 17.42 259.60 103.72 2014 5月15日至6月18日 17.75 266.58 101.49 2015 5月16日至6月12日 17.51 272.49 37.81 2016 5月17日至6月25日 18.72 252.12 131.70 2017 5月19日至6月9日 18.30 284.89 20.22 表 3 2008–2017年绿潮消衰阶段研究区域内海表面温度、太阳短波辐射、降水统计
Tab. 3 Sea surface temperature, solar shortwave radiation, and precipitation within the study areas in the green tide depletion stage from 2008 to 2017
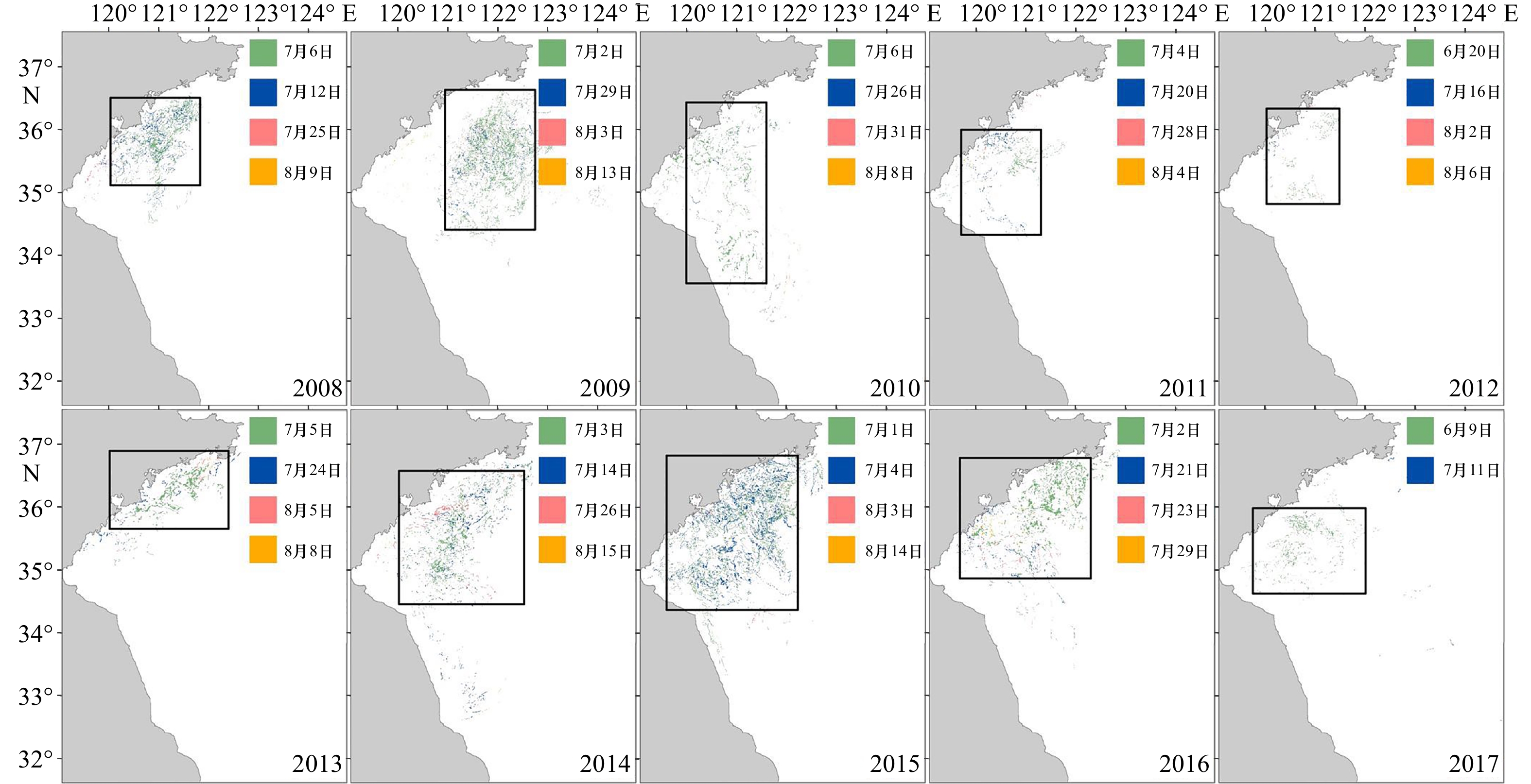
衰退时间 海表面温度/℃ 太阳短波辐射/W·m–2 降水量/mm 2008年7月6日至8月9日 24.29 235.68 131.10 2009年7月2日至8月13日 24.56 239.41 181.66 2010年7月6日至8月8日 25.46 254.23 94.77 2011年7月4日至8月4日 23.38 211.44 268.90 2012年6月20日至8月6日 23.75 249.93 201.95 2013年7月5日至8月8日 25.08 241.53 104.59 2014年7月3日至8月15日 24.66 244.85 85.06 2015年7月1日至8月14日 24.79 241.47 142.87 2016年7月2日至7月29日 24.72 246.71 84.22 2017年6月9日至7月11日 22.50 262.97 93.56 -
[1] 崔琳琳, 胡松, 杨红, 等. 绿潮早期聚集期间天气过程分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2014, 33(6): 941−946.Cui Linlin, Hu Song, Yang Hong, et al. Weather process analysis for the period during the early aggregation of green tide[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2014, 33(6): 941−946. [2] 温连杰, 江崇波, 马兆江, 等. 山东省2010–2014年海洋灾害概况及防御对策建议[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(6): 98−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.06.018Wen Lianjie, Jiang Chongbo, Ma Zhaojiang, et al. The general situation of marine disasters in Shandong Province during 2010–2014 and the defense strategies[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(6): 98−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.06.018 [3] 田晓玲, 霍元子, 陈丽平, 等. 江苏如东近海绿潮藻分子检测与类群演替分析[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(4): 309−317.Tian Xiaoling, Huo Yuanzi, Chen Liping, et al. Molecular detection and analysis of green seaweeds from Rudong coasts in Jiangsu Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(4): 309−317. [4] 刘峰. 黄海绿潮的成因以及绿潮浒苔的生理生态学和分子系统学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2010.Liu Feng. The causes of green tides in the Yellow Sea, and ecophysiological and phylogenetic analysis of the bloom-forming alga, Ulva prolifera[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010. [5] Taylor R, Fletcher R L, Raven J A. Preliminary studies on the growth of selected ‘green tide’ algae in laboratory culture: effects of irradiance, temperature, salinity and nutrients on growth rate[J]. Botanica Marina, 2001, 44(4): 327−336. [6] 韩红宾, 韦章良, 霍元子, 等. 温度与光照强度对浒苔孢子/配子放散和萌发的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 2015, 37(6): 517−524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2015.06.006Han Hongbin, Wei Zhangliang, Huo Yuanzi, et al. Effects of temperature and light intensity on the release and germination of Ulva prolifera spores/gametes[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2015, 37(6): 517−524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2015.06.006 [7] 孟晓智, 苏贵森, 卓品利, 等. 温度和光照强度对浒苔生长和光合生理特性的影响[J]. 生物学杂志, 2018, 35(4): 49−52, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2018.04.049Meng Xiaozhi, Su Guisen, Zhuo Pinli, et al. Combined effects of temperature and light intensity on the growth and physiological performances of Ulva prolifera[J]. Journal of Biology, 2018, 35(4): 49−52, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2018.04.049 [8] 忻丁豪, 任松, 何培民, 等. 黄海海域浒苔属(Enteromorpha)生态特征初探[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2009, 28(2): 190−192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2009.02.018Xin Dinghao, Ren Song, He Peimin, et al. Preliminary study on experimental ecology of Enteromorpha in Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2009, 28(2): 190−192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2009.02.018 [9] 李瑞香, 吴晓文, 韦钦胜, 等. 不同营养盐条件下浒苔的生长[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009, 27(2): 211−216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.011Li Ruixiang, Wu Xiaowen, Wei Qinsheng, et al. Growth of Enteromorpha prolifera under different uutrient conditions[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2009, 27(2): 211−216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2009.02.011 [10] Zhang Guosen, Zhang Jing, Liu Sumei. Characterization of nutrients in the atmospheric wet and dry deposition observed at the two monitoring sites over Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry, 2007, 57(1): 41−57. doi: 10.1007/s10874-007-9060-3 [11] 郭伟, 赵亮, 李秀梅. 黄海绿潮分布年际变化特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(12): 36−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.12.004Guo Wei, Zhao Liang, Li Xiumei. The interannual variation of green tide in the Yellow Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(12): 36−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.12.004 [12] 宋伟. 苏北浅滩定生绿藻的鉴定、生理特征及群落演替研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2014.Song Wei. Studies on species identification, physiological characteristics and community succession of attached green algae on Subei shoal[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2014. [13] 衣立, 张苏平, 殷玉齐. 2009年黄海绿潮浒苔爆发与漂移的水文气象环境[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2010, 40(10): 15−23.Yi Li, Zhang Suping, Yin Yuqi. Influnce of environmental hydro-meteorological conditions to Enteromorpha prolifera blooms in Yellow Sea, 2009[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(10): 15−23. [14] Zhang Jing, Liu Min’guang. Observations on nutrient elements and sulphate in atmospheric wet depositions over the northwest Pacific coastal oceans—Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1994, 47(2): 173−189. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(94)90107-4 [15] 张国森. 大气的干、湿沉降以及对东、黄海海洋生态系统的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004.Zhang Guosen. Atmospheric dry and wet deposition and impact on the marine ecosystem of Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004. [16] Zhang J, Chen S Z, Yu Z G, et al. Factors influencing changes in rainwater composition from urban versus remote regions of the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1999, 104(D1): 1631−1644. doi: 10.1029/1998JD100019 [17] 李鸿妹. 营养盐与黄海浒苔绿潮暴发关系的探究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Li Hongmei. Relationship between nutrients and the occurrence of macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [18] 刘素美, 黄薇文, 张经, 等. 青岛地区大气沉降物的化学成分研究——Ⅰ. 微量元素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1991, 10(4): 21−28.Liu Sumei, Huang Weiwen, Zhang Jing, et al. Chemical composition analysis of atmospheric deposition at Qingdao—Ⅰ. Trace elements[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1991, 10(4): 21−28. [19] 陈月红. 温度、光照对浒苔生长及其硝酸还原酶活力的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Chen Yuehong. Effects of temperature and solar radiation on the growth and nitrate reductase activity of Ulva prolifera[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [20] Cui Jianjun, Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, et al. Adaptability of free-floating green tide algae in the Yellow Sea to variable temperature and light intensity[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 101(2): 660−666. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.033 [21] 吴青, 张建恒, 赵升, 等. 黄海绿潮漂浮浒苔对高光强胁迫生态适应机制研究[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2016, 25(1): 97−105. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20150301380Wu Qing, Zhang Jianheng, Zhao Sheng, et al. An adjustment mechanism to high light intensity for free-floating Ulva in the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2016, 25(1): 97−105. doi: 10.12024/jsou.20150301380 [22] Zhang Jianheng, Huo Yuanzi, Zhang Zhenglong, et al. Variations of morphology and photosynthetic performances of Ulva prolifera during the whole green tide blooming process in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2013, 92: 35−42. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2013.08.009 [23] 李彦之. 环境因子对黄海浒苔发展的影响[J]. 现代农业科技, 2018(15): 194−198, 201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2018.15.122Li Yanzhi. Effect of environmental factors on growth of Enteromorpha prolifera in Yellow Sea[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018(15): 194−198, 201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2018.15.122 [24] Jin Song, Liu Yongxue, Sun Chao, et al. A study of the environmental factors influencing the growth phases of Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135: 1016−1025. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.08.035 [25] Kim J H, Kang E J, Park M G, et al. Effects of temperature and irradiance on photosynthesis and growth of a green-tide-forming species (Ulva linza) in the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Applied Phycology, 2011, 23(3): 421−432. doi: 10.1007/s10811-010-9590-y [26] 辛蕾, 丁一, 王宁, 等. 基于遥感的黄海绿潮覆盖面积受表层温盐的影响分析[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2018, 34(3): 210−215.Xin Lei, Ding Yi, Wang Ning, et al. Effect on Green Tide coverage area in the Yellow Sea by surface water temperature and salinity based on remote sensing[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2018, 34(3): 210−215. [27] 张广宗, 吴孟泉, 孙晓, 等. 南黄海浒苔漂移轨迹年际变化规律及驱动因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(5): 1084−1093.Zhang Guangzong, Wu Mengquan, Sun Xiao, et al. The inter-annual drift and driven force of Ulva prolifera bloom in the Southern Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(5): 1084−1093. [28] Nordby Ø. Optimal conditions for meiotic spore formation in Ulva mutabilis Føyn[J]. Botanica Marina, 1977, 20(1): 19−28. -




 下载:
下载: