Analysis of the relationships between zooplankton and temperature-salinity based on RDA and GAMs model in coastal East China Sea
-
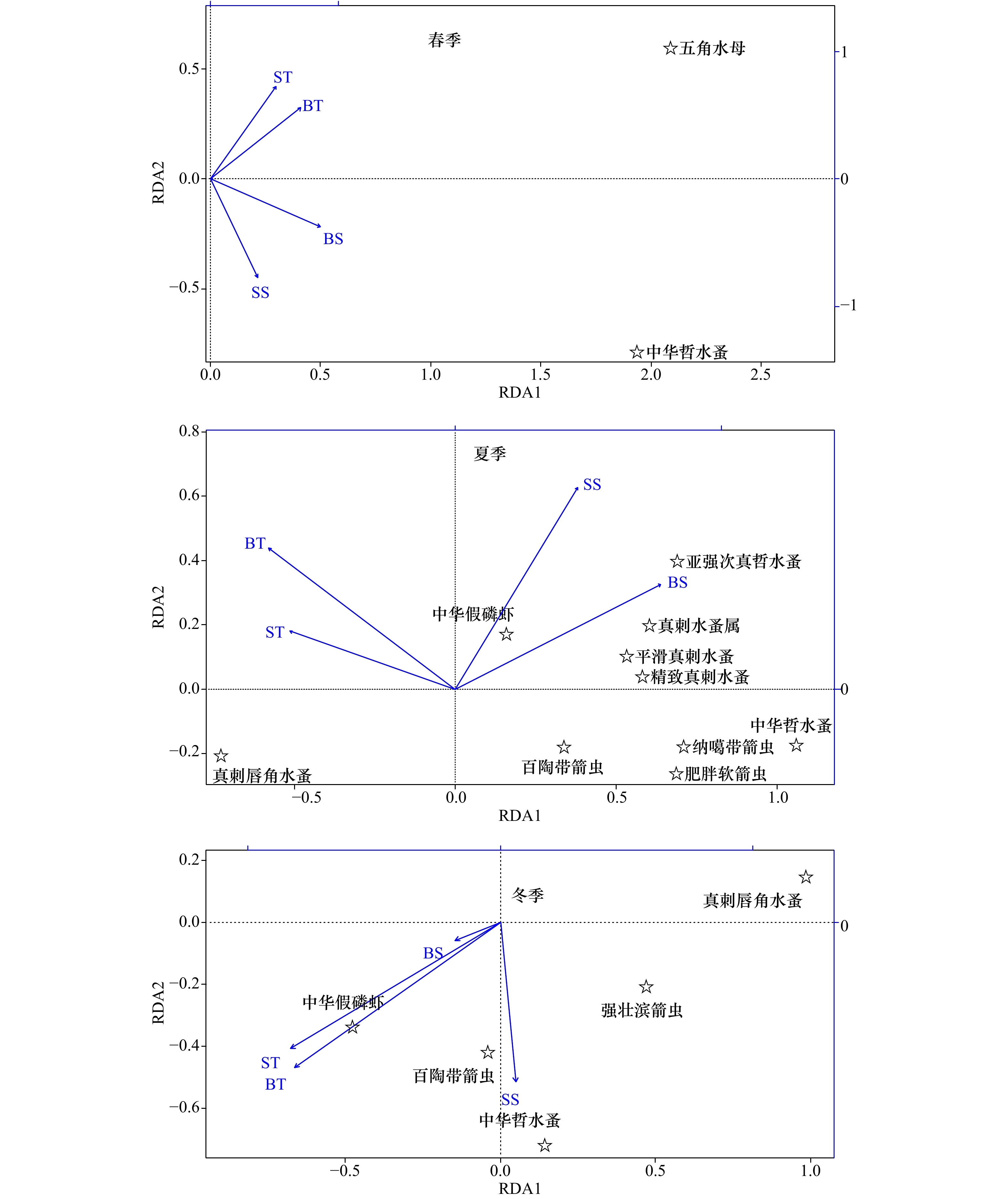
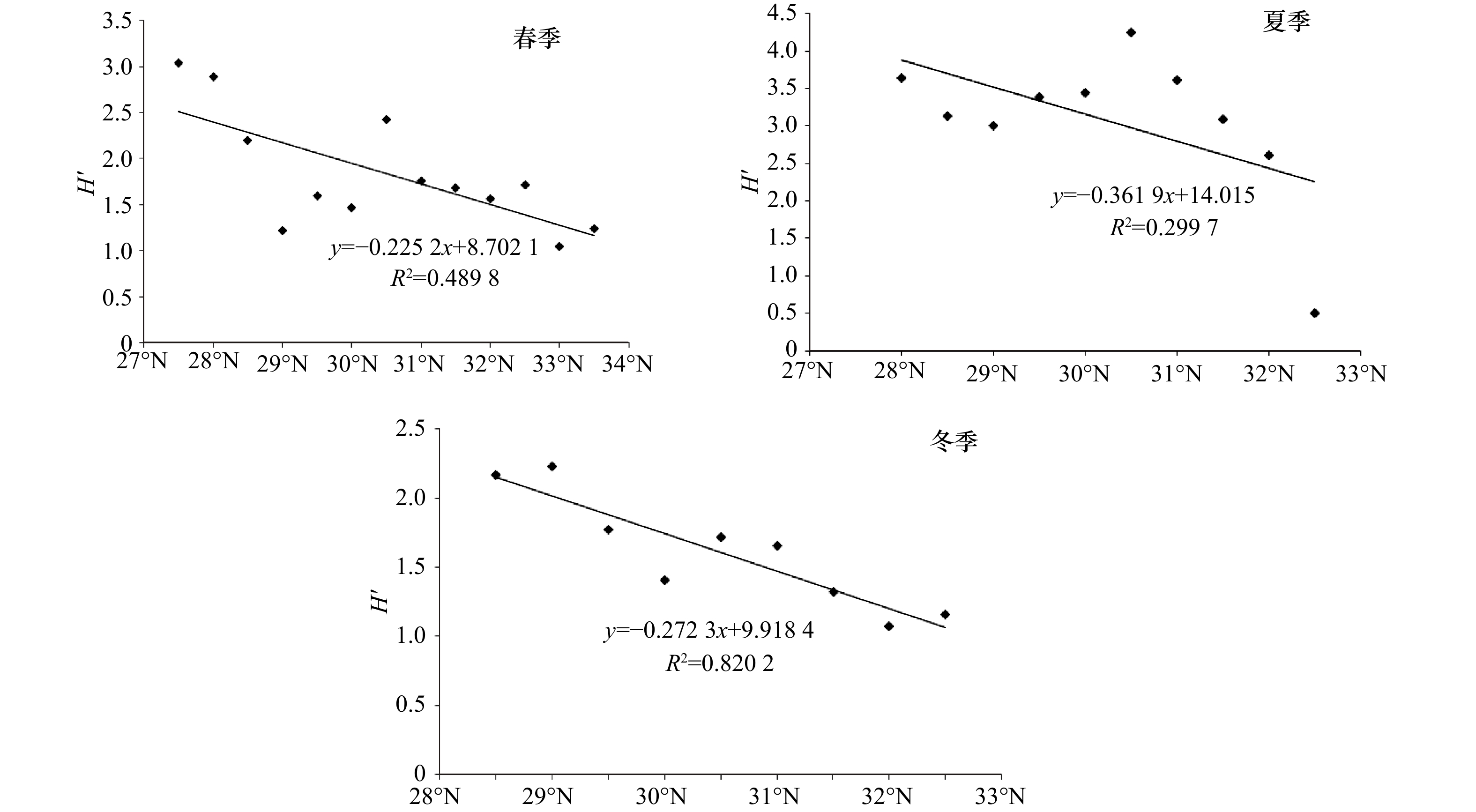
摘要: 为进一步探讨东海近岸海域浮游动物季节演替与温盐的变化关系,根据2013年5月(春季)、8月(夏季)和12月(冬季)东海近岸海域3个航次的浮游动物调查资料,利用冗余分析模型分析了优势种与温盐的变化关系,广义加性模型分析了生物多样性参数与温盐之间的关系。结果表明:(1)优势种季节演替较为明显,由春季2种演替成夏季10种,再更替为冬季5种,春季和冬季优势种的种类和生态类群相对单一,夏季较为丰富。(2)优势种时空分布是综合多层环境因子的结果,如春季中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus)与表层盐度和底层盐度正相关,夏季与表层温度和底层温度负相关,冬季与表层盐度正相关;春季五角水母(Muggiaea atlantica)与底层温度、底层盐度呈现较好的正相关;夏季盐度是决定暖水性和高温高盐性优势种分布的关键因子,且呈现较强的正相关;冬季真刺唇角水蚤(Labidocera euchaeta)、强壮滨箭虫(Aidanosagitta crassa)与表层温度关系密切,并呈现较强的负相关。(3)春季和冬季香农–威纳指数多样性指数与纬度呈负相关。(4)温度和盐度对生物多样性参数影响显著,但季节上又呈现出差异。Abstract: In order to further explore the changes in relationships between seasonal succession of zooplankton and temperature-salinity in coastal East China sea, zooplankton survey data of three voyages in May (spring), August (summer) and December (winter) of 2013 were analyzed. Redundancy analysis model (RDA) was used to analyze the relationship between the changes of the dominant species and temperature-salinity, then the general algebraic modeling system (GAMs) was applied to analyze the relationship between temperature-salinity and parameters of the biological diversity. Results show that the dominant species’ succession changes seasonally from spring (2 kinds) to summer (10 kinds), then becomes 5 kinds in winter. Dominant species and the ecological groups are relatively single in spring and winter, but rich in summer. The temporal and spatial distribution of dominant species are the results of a comprehensive multi-level of environmental factors. For example, Calanus sinicus positively relates to surface salinity and bottom salinity in spring, negatively relates to surface temperature and bottom temperature in summer, positively relates to surface salinity in winter. Muggiaea atlantica presents better positive correlations with bottom temperature and bottom salinity in spring. What’s more, salinity is the key factor to determine the distribution of dominant species like warm water species and high temperature-salinity groups in summer, it also presents strong positive correlations. Labidocera euchaeta and Aidanosagitta crassa have strong negative correlations with surface temperature in winter. Shannon-Wiener diversity index negatively correlates with latitude in spring and winter. Biodiversity parameters are significantly affected by the temperature and salinity, but the influence presents differences seasonally.
-
Key words:
- East China Sea /
- zooplankton /
- dominant species /
- biodiversity parameters /
- temperature /
- salinity
-
表 1 东海近岸海域浮游动物优势种的优势度(Y≥0.02)、平均丰度
Tab. 1 The dominance of dominant species (Y≥0.02), average abundance in coastal waters of East China Sea
优势种 春季 夏季 冬季 种类 生态类群 Y 丰度均值/ind.·m–3 Y 丰度均值/ind.·m–3 Y 丰度均值/ind.·m–3 中华假磷虾 近岸低盐种 / / 0.03 5.72 0.03 0.53 强壮滨箭虫 近岸低盐种 / / / / 0.02 0.45 肥胖软箭虫 暖水种 / / 0.03 7.53 / / 百陶带箭虫 亚热带近海种 / / 0.05 11.20 0.03 0.58 纳噶带箭虫 亚热带近海种 / / 0.03 9.72 / / 中华哲水蚤 广温种 0.82 500.18 0.10 26.86 0.65 7.03 五角水母 暖水低盐种 0.04 39.70 / / / / 亚强次真哲水蚤 高温高盐种 / / 0.03 9.10 / / 精致真刺水蚤 暖水广盐种 / / 0.03 8.28 / / 平滑真刺水蚤 暖水种 / / 0.02 9.86 / / 真刺水蚤属 / / / 0.04 17.50 / / 真刺唇角水蚤 低盐种 / / 0.04 14.90 0.05 1.11 注:“/”表示非优势种。 表 2 东海近岸海域浮游动物优势种平均丰度区域分布(单位:ind./m3)
Tab. 2 Regional distribution of dominant species’ average abundance of zooplankton in coastal waters of East China Sea(unit: ind./m3)
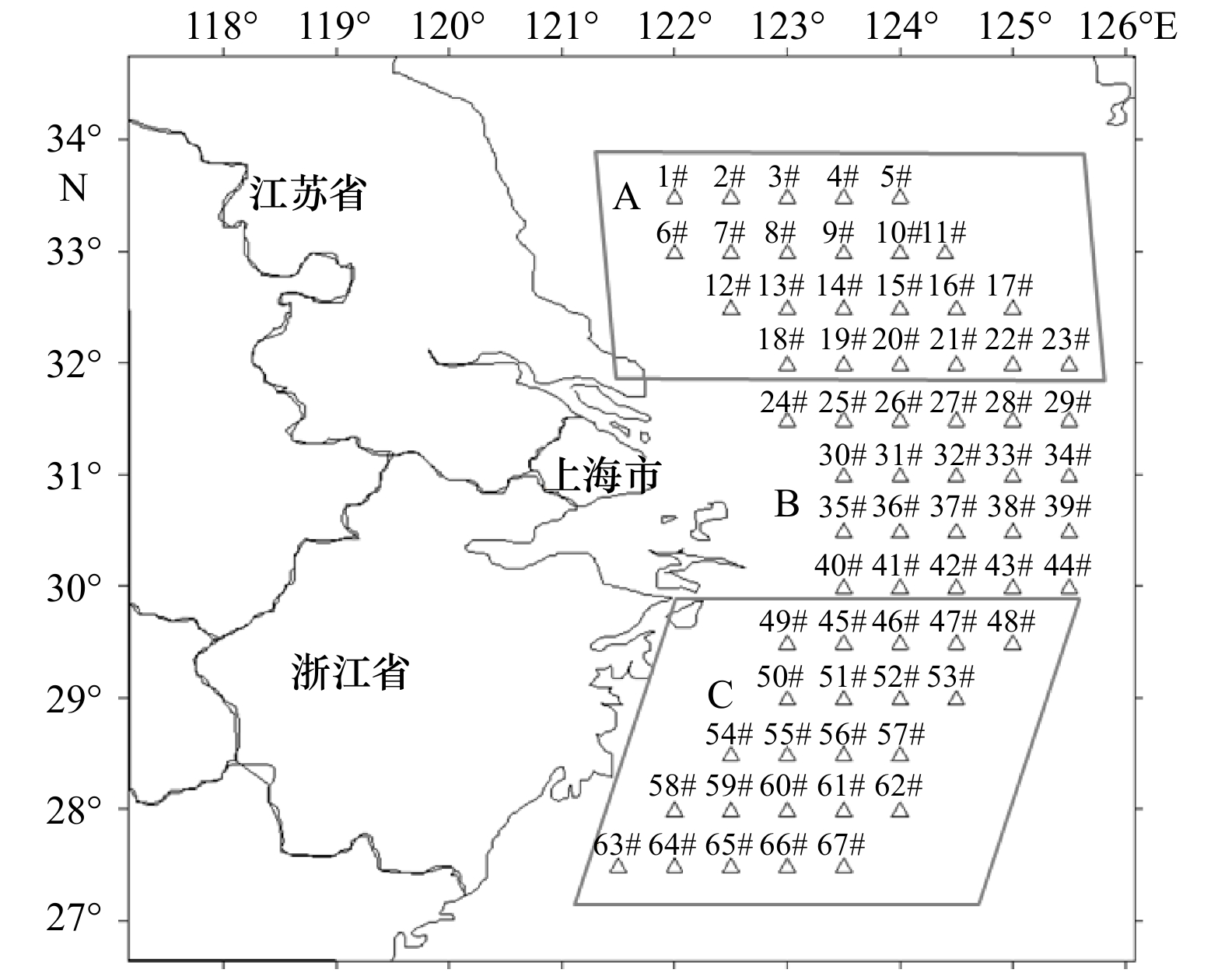
春季 夏季 冬季 A B C A B C A B C 中华假磷虾 / / / 6.25 6.48 7.54 0.25 0.62 1.71 强壮滨箭虫 / / / / / / 0.52 1.35 0 肥胖软箭虫 / / / 3.10 13.50 8.23 / / / 百陶带箭虫 / / / 2.36 22.28 12.42 0.71 1.21 0.75 纳噶带箭虫 / / / 3.13 21.98 15.45 / / / 中华哲水蚤 662.63 184.75 645.29 3.45 41.45 57.47 6.14 10.12 3.43 五角水母 125.84 34.73 82.26 / / / / / / 亚强次真哲水蚤 / / / 0 6.93 22.80 / / / 精致真刺水蚤 / / / 2.40 8.08 17.07 / / / 平滑真刺水蚤 / / / 3.60 16.60 28.81 / / / 真刺水蚤属 / / / 0 26.25 57.29 / / / 真刺唇角水蚤 / / / 51.17 15.92 1.31 2.76 1.40 0 注:A. 东海北部近岸水域;B. 长江口及其邻近水域;C. 东海中南部近岸水域; “/”表示非优势种。 表 3 RDA前两轴排序分析及蒙特卡洛检验结果
Tab. 3 Results by RDA ordination with the first two axis and Monte Carlo permutation test in herb layer
春季 夏季 冬季 RDA1 RDA 2 RDA 1 RDA 2 RDA 1 RDA 2 ST 0.512 0.727** –0.623* 0.219 –0.823** –0.522 SS 0.368 –0.769** 0.460 0.759** 0.070 –0.630* BT 0.709** 0.559 –0.702** 0.531 0.093 –0.727** BS 0.861** –0.374 0.772** 0.395 –0.179 –0.078 总被分析环境因子解释比例 43.21% 4.08% 15.10% 1.40% 14.77% 8.54% 注:ST表示表层温度;SS 表示表层盐度;BT 表示底层温度;BS 表示底层盐度;*表示 P<0.05;**表示 P<0.01。 表 5 不同季节生物多样性参数与温盐关系GAMs模型分析结果
Tab. 5 Results of relations in biodiversity parameters and temperature-salinity based on GAMs model in different season
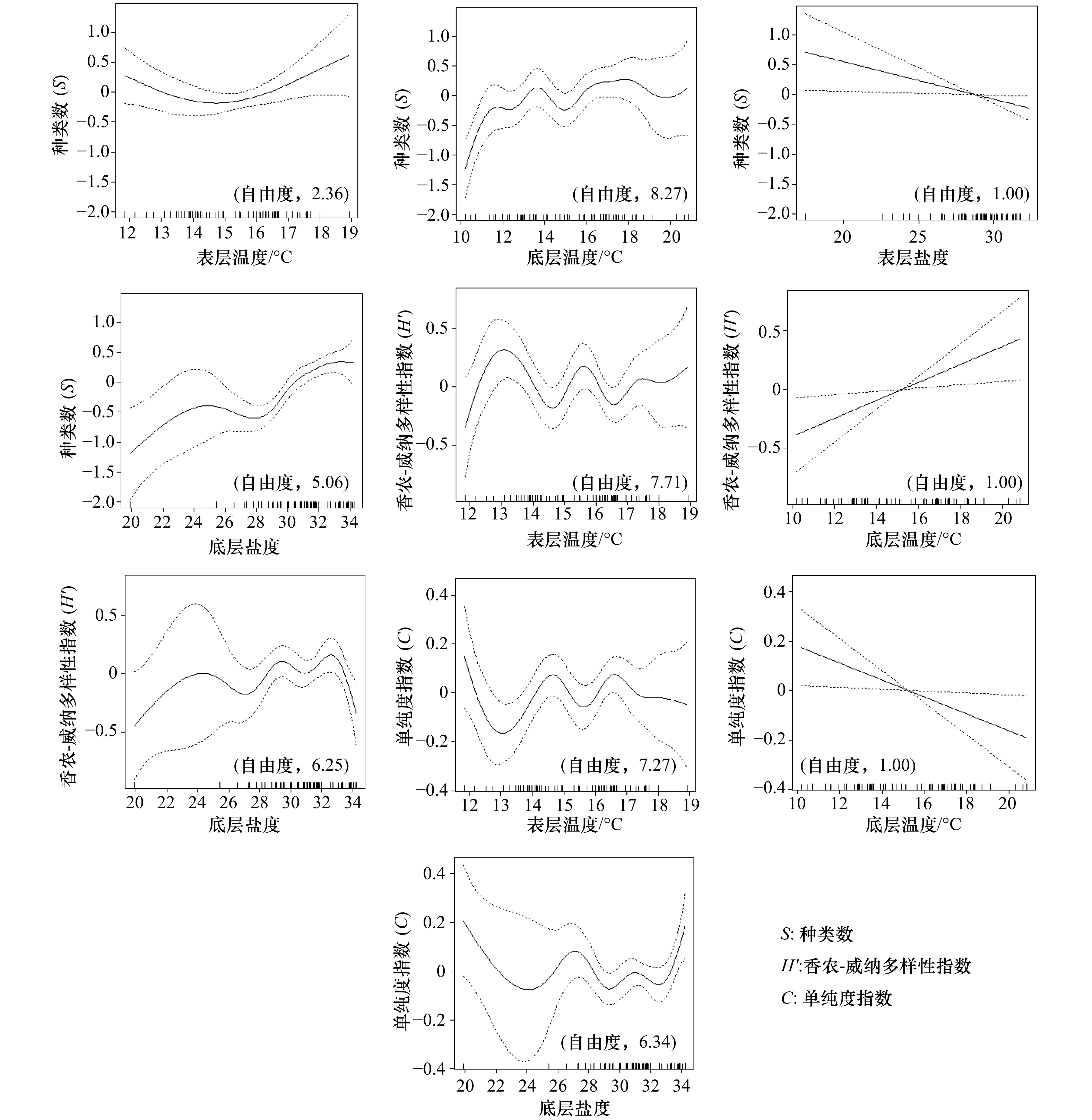
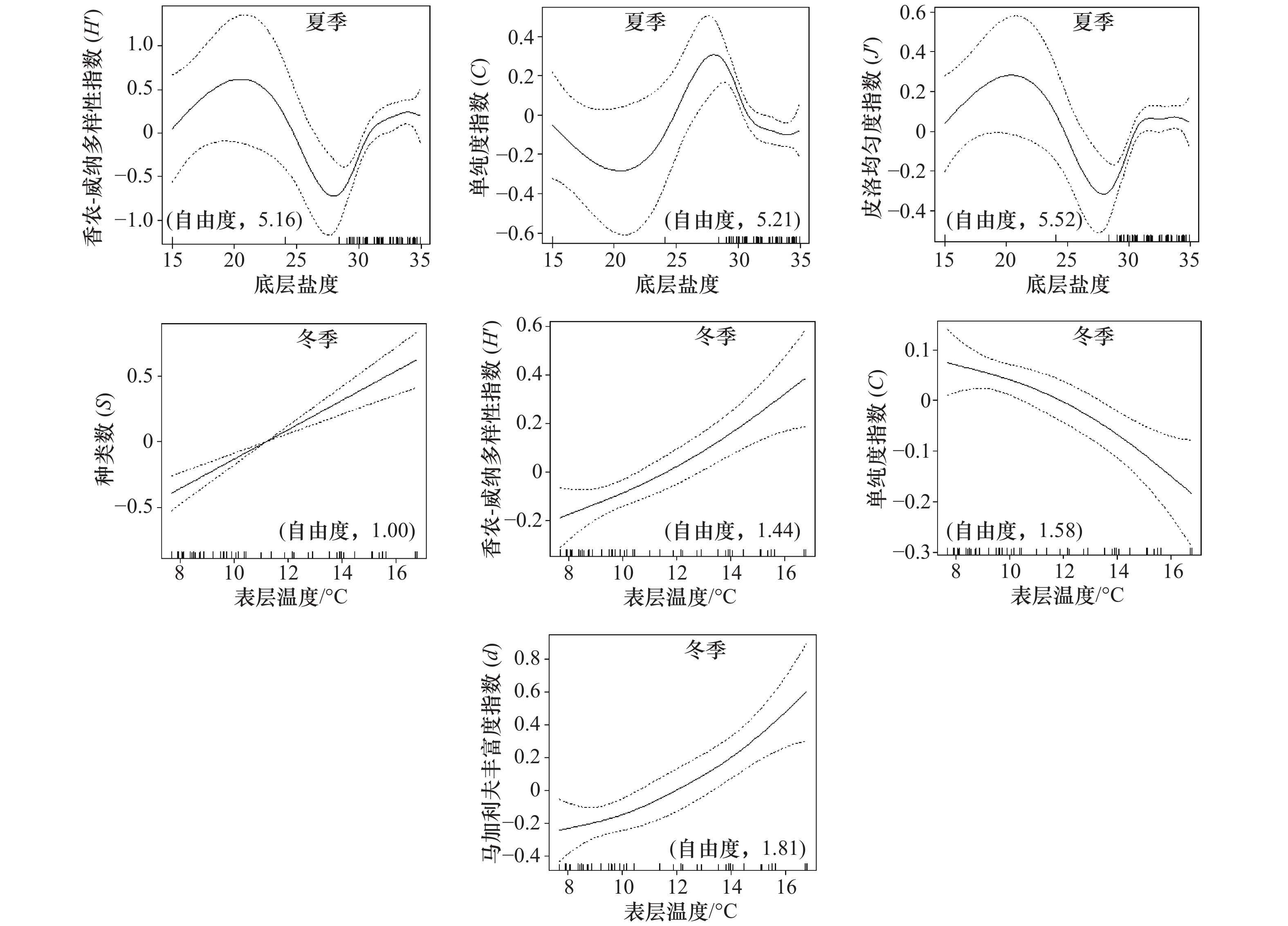
种类数S 多样性指数H′ 单纯度指数C 均匀度指数J′ 丰富度指数d 春季 环境因子 ST+SS+BT+BS ST+ BT+BS ST+ BT+BS ST+ SS+BS / AIC值 31.00 4.95 83.29 90.55 / 偏差解释比例/% 82.4 62.7 57.2 66.8 / 夏季 环境因子 / BS BS BS SS AIC值 / 34.19 50.31 61.65 29.35 偏差解释比例/% / 49.4 49.0 48.8 16.5 冬季 环境因子 ST+SS ST ST / ST AIC值 12.04 11.57 50.67 / 34.36 偏差解释比例/% 68.3 31.6 27.4 / 37.5 注:ST表示表层温度;SS表示表层盐度;BT表示底层温度;BS表示底层盐度。AIC赤池信息准则。“/”表示无数据。 表 4 不同区域内的环境参数
Tab. 4 Environmental parameters in different areas
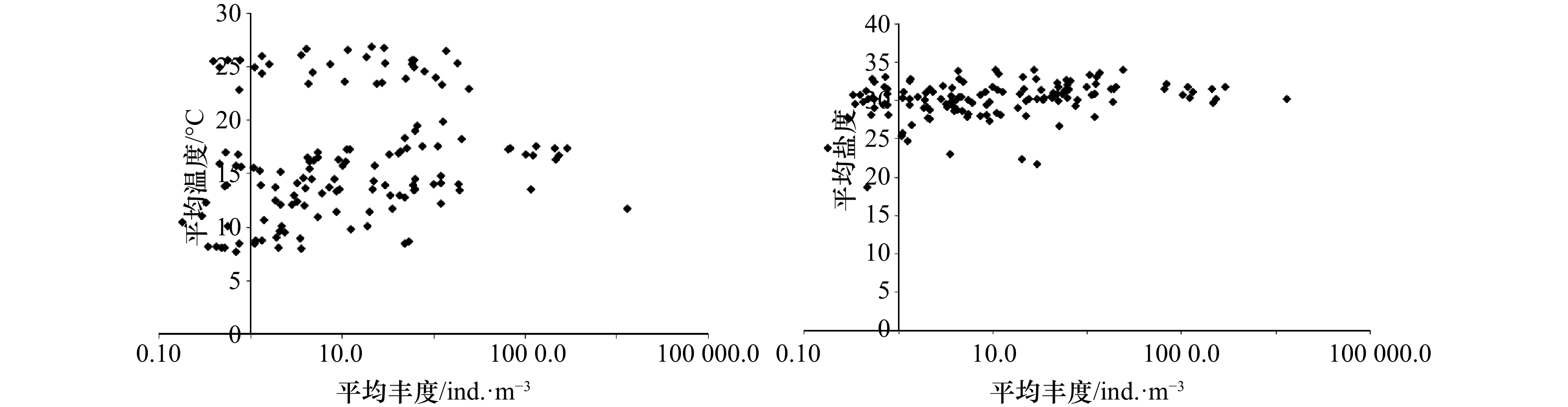
季节 区域 平均表温/℃ 平均表盐 平均底温/℃ 平均底盐 春季 A 13.7±0.78 30.2±1.07 12.6±1.27 30.6±0.95 B 15.7±0.88 26.4±3.06 15.5±1.72 30.7±3.56 C 17.0±0.74 29.3±1.45 17.9±1.39 31.3±2.38 夏季 A 26.3±0.75 29.9±0.83 26.5±0.76 29.8±0.67 B 25.7±0.65 28.3±5.00 23.3±2.28 31.0±4.58 C 26.2±0.70 32.0±1.21 25.2±2.47 32.6±1.21 冬季 A 8.3±0.52 30.1±0.88 8.6±0.52 30.2±0.68 B 11.8±2.59 29.8±2.95 17.0±2.78 29.4±4.15 C 12.9±2.27 29.5±1.72 13.3±2.38 29.7±1.82 注:A. 东海北部近岸水域; B. 长江口及邻近水域; C. 东海中南部近岸海域。 -
[1] 邓邦平, 徐韧, 刘材材, 等. 夏季黄海南部和东海近海浮游动物群落分布特征[J]. 南方水产科学, 2015, 11(4): 11−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2015.04.002Deng Bangping, Xu Ren, Liu Caicai, et al. Distribution characteristics of zooplankton communities in offshore waters of the southern Yellow Sea and the East China Sea in summer[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2015, 11(4): 11−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2015.04.002 [2] 杜明敏, 刘镇盛, 王春生, 等. 中国近海浮游动物群落结构及季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(17): 5407−5418.Du Mingmin, Liu Zhensheng, Wang Chunsheng, et al. The seasonal variation and community structure of zooplankton in China sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(17): 5407−5418. [3] 高倩, 徐兆礼, 庄平. 长江口北港和北支浮游动物群落比较[J]. 应用生态学报, 2008, 19(9): 2049−2055.Gao Qian, Xu Zhaoli, Zhuang Ping. Comparison of mesozooplankton communities in north channel and north branch of Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2008, 19(9): 2049−2055. [4] 刘镇盛. 长江口及其邻近海域浮游动物群落结构和多样性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Liu Zhensheng. Community structure and biodiversity of zooplankton in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [5] 林景宏, 陈明达, 陈瑞祥. 南黄海和东海浮游端足类的分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 1995, 17(5): 117−123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1995.05.009Lin Jinghong, Chen Mingda, Chen Ruixiang. Distribution characteristics of pelagic Amphipoda in south Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1995, 17(5): 117−123. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.1995.05.009 [6] 齐衍萍. 夏、冬季黄东海浮游动物群落生态学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.Qi Yanping. Study on the community ecology of zooplankton in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea in summer and winter[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2008. [7] 左涛. 东、黄海浮游动物群落结构研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2003.Zuo Tao. Community structure of zooplankton in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2003. [8] Mazumder D, Saintilan N, Williams R J. Trophic relationships between itinerant fish and crab larvae in a temperate Australian saltmarsh[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 2006, 57(2): 193−199. doi: 10.1071/MF05040 [9] Zhou Shuchan, Jin Binsong, Guo Li, et al. Spatial distribution of zooplankton in the intertidal marsh creeks of the Yangtze River Estuary, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2009, 85(3): 399−406. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2009.09.002 [10] 张光星, 陈石泉, 陈丹丹, 等. 海南岛近岸海域夏初浮游动物与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(12): 125−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.12.013Zhang Guangxing, Chen Shiquan, Chen Dandan, et al. The relationship between zooplankton and the environmental factors in the coastal waters of Hainan Island in the early summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(12): 125−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2014.12.013 [11] Chang K H, Amano A, Miller T W, et al. Pollution study in Manila Bay: eutrophication and its impact on plankton community[M]//Obayashi Y, Isobe T, Subramanian A, et al. Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry–Environmental Research in Asia. Tokyo: Terrapub, 2009, 261–267. [12] 陈涛, 王云龙, 廖勇. 象山港人工鱼礁区浮游动物种类组成及群落结构特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(7): 41−46. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130910001Chen Tao, Wang Yunlong, Liao Yong. The species composition and community structure of zooplankton in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(7): 41−46. doi: 10.11759/hykx20130910001 [13] 郭沛涌, 沈焕庭, 刘阿成, 等. 长江河口浮游动物的种类组成、群落结构及多样性[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 23(5): 892−900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.05.008Guo Peiyong, Shen Huanting, Liu Acheng, et al. The species composition, community structure and diversity of zooplankton in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 23(5): 892−900. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2003.05.008 [14] 张壮丽, 叶孙忠. 福建海区浮游动物种类组成及数量分布特点[J]. 南方水产, 2005, 1(6): 34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2005.06.005Zhang Zhuangli, Ye Sunzhong. The species composition and quantity distribution characteristics of zooplankton in Fujian sea area[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2005, 1(6): 34−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2005.06.005 [15] 王晓娟. 福建近岸海域夏季浮游动物的数量和分布[J]. 海峡科学, 2013, 12(6): 19−21, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8683.2013.06.007Wang Xiaojuan. The quantity and distribution of zooplankton at Fujian offshore in summer[J]. Straits Science, 2013, 12(6): 19−21, 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8683.2013.06.007 [16] 徐兆礼, 晁敏, 陈亚瞿. 东海浮游动物生物量分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2004, 26(3): 93−101. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.03.011Xu Zhaoli, Chao Min, Chen Yaqu. Distribution characteristics of zooplankton biomass in the East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2004, 26(3): 93−101. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2004.03.011 [17] 丁峰元, 李圣法, 董婧, 等. 春季东海区近海浮游动物群落结构及其影响因子[J]. 海洋渔业, 2005, 27(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.01.005Ding Fengyuan, Li Shengfa, Dong Jing, et al. Preliminary study on the zooplankton community structure and its influential factors in the offshore waters of the East China Sea in spring[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2005, 27(1): 26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.01.005 [18] 高瑜, 江志兵, 杜萍, 等. 乐清湾春季浮游生物群落和环境因子分布特征[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2012, 33(6): 82−89.Gao Yu, Jiang Zhibing, Du Ping, et al. Characteristics of plankton community and its relations with environmental factors in Yueqing Bay[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2012, 33(6): 82−89. [19] 李纯厚, 贾晓平, 蔡文贵. 南海北部浮游动物多样性研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 2004, 11(2): 139−146. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2004.02.010Li Chunhou, Jia Xiaoping, Cai Wengui. Diversity of marine zooplankton in the north of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2004, 11(2): 139−146. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2004.02.010 [20] 于雯雯, 刘培廷, 高银生, 等. 春夏季吕泗渔场水产种质资源保护区浮游动物分布特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2013, 32(10): 2744−2749.Yu Wenwen, Liu Peiting, Gao Yinsheng, et al. Distribution characteristics of zooplankton in national aquatic germplasm conservation area in Lüsi fishing ground of east China in spring and summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2013, 32(10): 2744−2749. [21] 骆鑫, 曾江宁, 徐晓群, 等. 舟山海域夏、秋季浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(24): 8194−8204.Luo Xin, Zeng Jiangning, Xu Xiaoqun, et al. Distribution of zooplankton in the Zhoushan sea and its relationship with environmental factors in summer and autumn[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(24): 8194−8204. [22] 张冬融, 徐佳奕, 徐兆礼, 等. 杭州湾南岸海域春秋季浮游动物分布特征与主要环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(8): 2115−2123.Zhang Dongrong, Xu Jiayi, Xu Zhaoli, et al. Distribution pattern of zooplankton in the south part of Hangzhou Bay during spring and autumn in relation to main environmental factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(8): 2115−2123. [23] 赵坤, 吴波, 尤庆敏, 等. 长江口九段沙附近水域浮游动物时空分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(5): 374−379.Zhao Kun, Wu Bo, You Qingmin, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of zooplankton and its relation with environmental factors in Jiuduansha inshore waters of Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2015, 15(5): 374−379. [24] 朱延忠, 刘录三, 郑丙辉, 等. 春季长江口及毗邻海域浮游动物空间分布及与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(1): 59−65.Zhu Yanzhong, Liu Lusan, Zhen Binghui, et al. Relationship between spatial distribution of zooplankton and environmental factors in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters in spring[J]. Marine Sciences, 2011, 35(1): 59−65. [25] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T12763.6-2007, 海洋调查规范 第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 12763.6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [26] 王晓. 南黄海浮游动物群落及环境因子对其分布影响的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Wang Xiao. Studies on zooplankton community and the effects of environmental factors on its distribution in the southern Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [27] 姜会超, 陈海刚, 宋秀凯, 等. 莱州湾金城海域浮游动物群落结构及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319.Jiang Huichao, Chen Haigang, Song Xiukai, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Jincheng area of Laizhou Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319. [28] 徐晓群, 曾江宁, 陈全震, 等. 乐清湾海域浮游动物群落分布的季节变化特征及其环境影响因子[J]. 海洋学研究, 2012, 30(1): 34−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.01.005Xu Xiaoqun, Zeng Jiangning, Chen Quanzhen, et al. Seasonal variations of zooplankton community distribution and environmental impact factors in Yueqing Bay[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2012, 30(1): 34−40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.01.005 [29] 林元烧, 李松. 厦门港中华哲水蚤生活周期的初步研究[J]. 厦门大学学报:自然科学版, 1984, 23(1): 111−116.Lin Yuanshao, Li Song. A preliminary study on the life cycle of Calanus sinicus (Brodsky) in Xiamen Harbour[J]. Journal of Xiamen University: Natural Science, 1984, 23(1): 111−116. [30] Uye S I. Temperature-dependent development and growth of Calanus sinicus (Copepoda: Calanoida) in the laboratory[J]. Hydrobiologia, 1988, 167–168(1): 285−293. doi: 10.1007/BF00026316 [31] 徐兆礼, 李云. 长江口中华哲水蚤对不同温度和盐度的适应[C]//2008年中国水产学会学术年会论文摘要集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008.Xu Zhaoli, Li Yun. Adaptation of Calanus sinicus (Copepoda, Crustacea) to temperature and salinity in the Changjiang Estuary[C]//Fisheries of Academic Annual Meeting Abstract Set of China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008. [32] 黄加祺, 郑重. 温度和盐度对厦门港几种桡足类存活率的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1986, 17(2): 161−167.Huang Jiaqi, Zheng Zhong. The effects of temperature and salinity on the survival of some Copepods from Xiamen Harbour[J]. Oceanology et Limnologia Sinica, 1986, 17(2): 161−167. [33] 许振祖, 黄加祺, 林茂, 等. 中国刺胞动物门水螅虫总纲[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2014: 833-834.Xu Zhenzu, Huang Jiaqi, Lin Mao, et al. The Superclass Hydrozoa of the Phylum Cnidaria in China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2014: 833-834. [34] 齐衍萍, 陈洪举, 朱延忠, 等. 福建罗源湾浮游动物群落特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2010, 40(1): 39−46.Qi Yanping, Chen Hongju, Zhu Yanzhong, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community in Luoyuan Bay, Fujian[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(1): 39−46. [35] 孙鲁峰, 柯昶, 徐兆礼, 等. 上升流和水团对浙江中部近海浮游动物生态类群分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(6): 1811−1821.Sun Lufeng, Ke Chang, Xu Zhaoli, et al. The influence of upwelling and water mass on the ecological group distribution of zooplankton in Zhejiang coastal waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(6): 1811−1821. [36] 孙鲁峰, 孙岳, 徐兆礼. 椒江口海域浮游动物群落季节变化特征[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2014, 23(1): 131−138.Sun Lufeng, Sun Yue, Xu Zhaoli. The study on the seasonal variations of zooplankton community in Jiaojiang coastal waters[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2014, 23(1): 131−138. [37] 张海景. 春夏季苏北浅滩浮游动物生态特征的分析研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2011.Zhang Haijing. Ecological characteristics of zooplankton in the Northern Jiangsu Shoal in spring and summer[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2011. [38] 彭鹏飞, 李绪录, 蔡钰灿. 珠江口万山群岛海域秋春季浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(18): 170−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.18.062Peng Pengfei, Li Xulu, Cai Yucan. Distributing characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship to environmental factors in Wanshan islands sea of the Pearl River Estuary in fall and spring[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(18): 170−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.18.062 [39] 龚玉艳, 杨玉滔, 范江涛, 等. 南海北部陆架斜坡海域夏季浮游动物群落的空间分布[J]. 南方水产科学, 2017, 13(5): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.05.002Gong Yuyan, Yang Yutao, Fan Jiangtao, et al. Spatial distribution of zooplankton in continental slope of northern South China Sea in summer[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2017, 13(5): 8−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2017.05.002 -




 下载:
下载: