Factors affecting the thickness of gas hydrate stability zones in the Huaguang Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要: 为了探讨琼东南盆地华光凹陷海底天然气水合物稳定带的分布规律,定量研究了静水压力、底水温度、地温梯度和气源组分对水合物稳定带的影响程度。在此基础上,分析了华光凹陷现今甲烷水合物稳定带的厚度分布。最后,综合各因素的历史演化过程,初步探讨了华光凹陷1.05 Ma BP以来天然气水合物稳定带的演化。结果表明:(1)气源组分和海底温度的变化对研究区内水合物稳定带的影响较大;水合物稳定带厚度与海底温度呈良好的线性负相关性。(2)水深超过600 m的海域具备形成天然气水合物的温压条件;超过600 m水深的海域水合物稳定带厚度大部分超过 100 m,其中西北部稳定带的最大厚度超过300 m,是有利的水合物勘探区。(3)华光凹陷1.05 Ma BP以来天然气水合物稳定带厚度经历了快速增厚–窄幅变化–快速减薄和恢复的过程。麻坑群与水合物稳定变化敏感区在空间上具有较好的叠合关系。结合前人的研究成果,推测其形成与天然气水合物的分解释放有关。Abstract: In order to study the distribution of gas hydrate stable zones (GHSZ) in the Huaguang Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin, the important factors affecting GHSZ's thickness are quantitatively studied, including hydrostatic pressure, bottom water temperature, geothermal gradient and gas source composition. Then, it analyzes that the thickness distribution of the present methane GHSZ in Huaguang Sag. Finally, based on the historical evolution process of above various factors, the evolution of gas hydrate stabilization zone since 1.05 Ma BP in this area is preliminarily discussed. The results show that: (1) the gas source composition and seabed temperature have a great influence on the GHSZ in the study area, and the thickness of GHSZ has a good linear negative correlation with seabed temperature; (2) the temperature and pressure conditions for gas hydrate formation are available in the Huaguang Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin, where water depth is more than 600 m, the thickness of the hydrate stability zone is more than 100 m; the thickest GHSZ is located in the northwest of the study area, with a maximum thickness of more than 300 m; it is a favorable hydrate exploration area; (3) the methane GHSZ has gone through stable stage, relatively quick incrassation, gently changing stage, and quickly attenuating and recovery stage since 1.05 Ma BP. There is a good superposition relationship between the pockmark group and the sensitive area of GHSZ. Combined with previous research results, it is concluded that their formation is related to the decomposition and release of natural gas hydrate.
-
Key words:
- gas hydrate /
- thickness of gas hydrate stable zones /
- distribution /
- evolution /
- Huaguang Sag /
- Qiongdongnan Basin
-
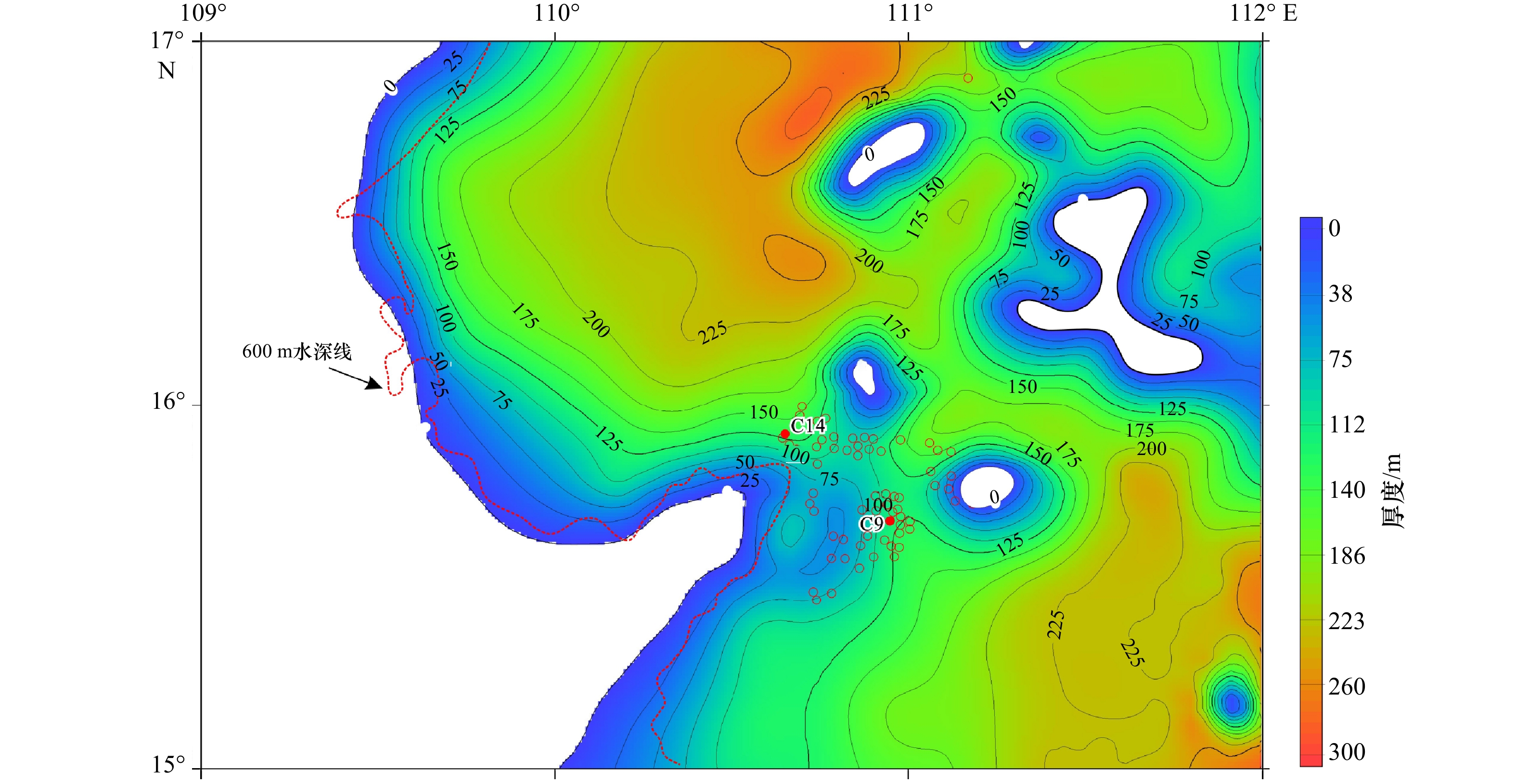
图 1 琼东南盆地(a)和研究区(b)的位置图及琼东南盆地地层综合柱状图(c)(据文献[17-18]修改)
Fig. 1 The locations and structural units of the Qiongdongnan Basin and the studying area (a) (modified from Shan et al[17]), bathymetric map of the studying area (b) (data from National Geophysical Data Center website) and generalized stratigraphic column for the Qiongdongnan Basin (c) (modified from Yang et al[18])
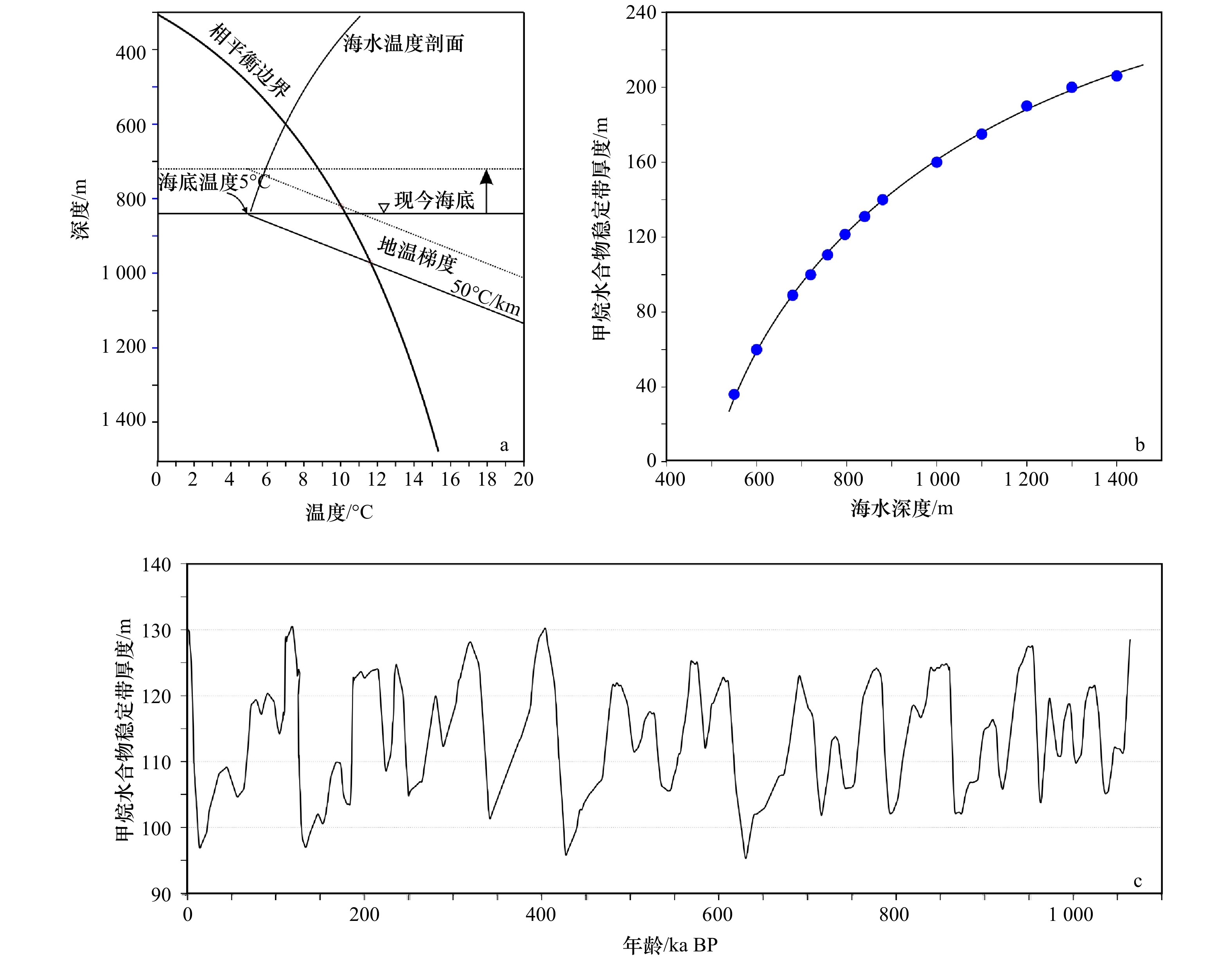
图 2 海平面变化对天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响
a. 海平面下降120 m时,C14站位的甲烷水合物稳定带厚度变化;b. 海水深度与水合物稳定带厚度的关系;c. 1.05 Ma BP以来,C14站位处水合 物稳定带厚度变化特征(只考虑海平面变化的影响)
Fig. 2 Effect of sea-level change on the thickness of gas hydrate stable zones
a. The thickness of methane hydrate stable zone at C14 station decreases by about 30 m when sea level drops by 120 m; b. the relationship between the water depth and the thickness of hydrate stable zone; c. thickness variation characteristics of methane hydrate stable zone at C14 station since 1.05 Ma BP (only considering the influence of sea level change)
图 3 海底温度对天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响
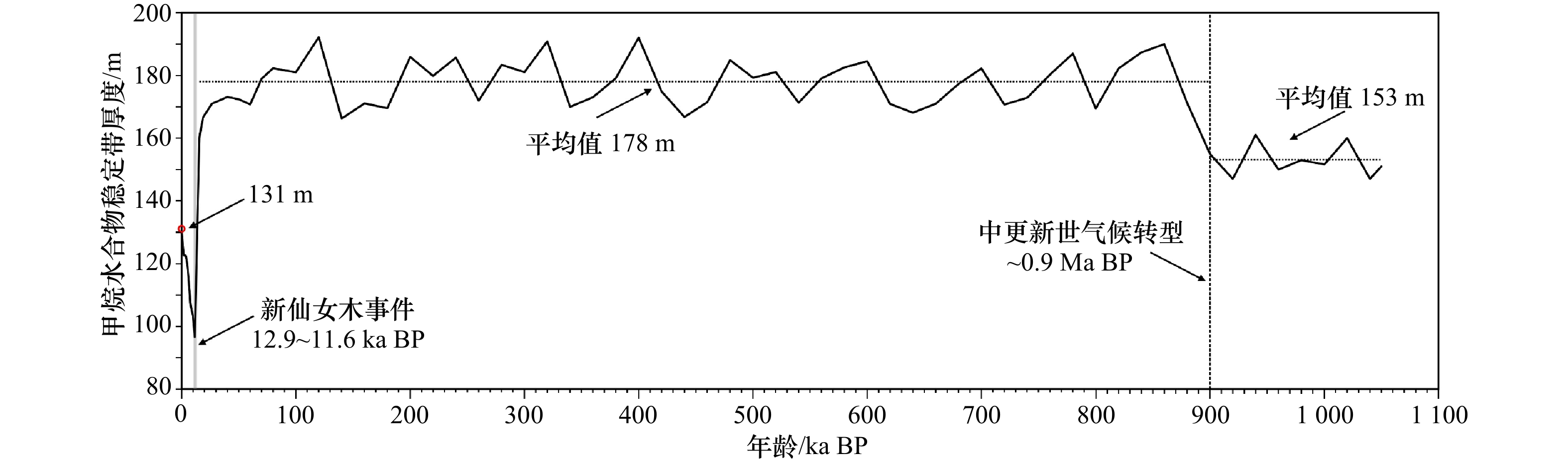
a. 不同海底温度下天然气水合物稳定带厚度的变化;b. 海底温度与水合物稳定带厚度的关系;c. ODP1148站位底栖有孔虫δ18O曲线(据 Jian等[28])和6 Ma BP以来海底温度变化趋势(注意中更新世气候转型,只考虑海底温度甲烷水合物稳定带厚度增大38.4 m)
Fig. 3 Effect of seafloor temperature on the thickness of gas hydrate stable zones
a. Thickness variation of gas hydrate stable zone under different seafloor temperatures; b. functional relationship between seafloor temperature and thickness of gas hydrate stable zone; c. trends of benthic foraminifera δ18O curve (after Jian et al[28]) and seafloor temperature change at ODP 1148 station since 6 Ma BP (at the Middle Pleistocene Revolution, the thickness of the methane hydrate stabilization zone increases by 38.4 m if only the seafloor temperature is taken into account)
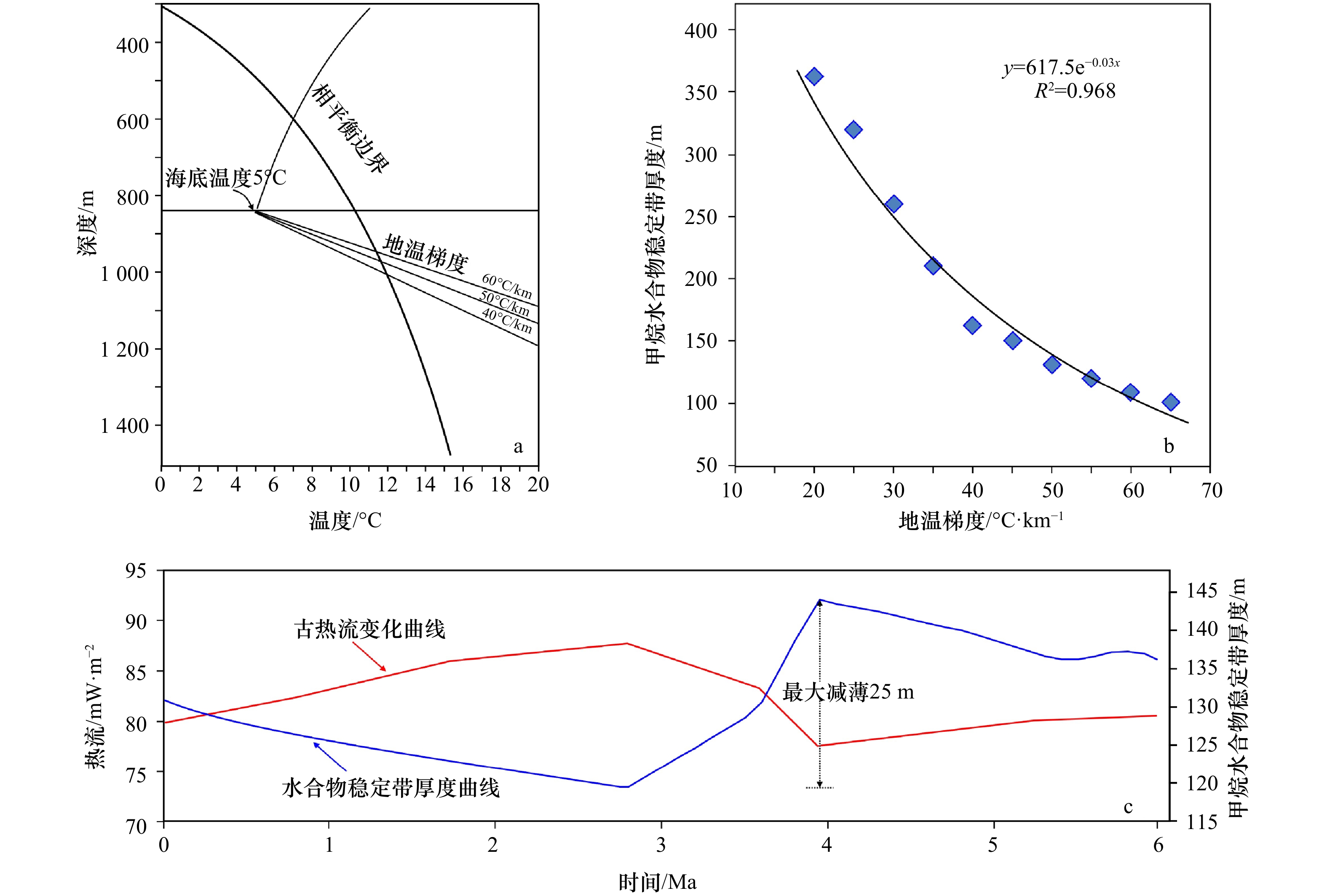
图 4 地温梯度对天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响
a. 不同地温梯度下甲烷水合物稳定带厚度变化;b. 地温梯度与甲烷水合物厚度的关系
Fig. 4 Effect of geothermal gradient on the thickness of gas hydrate stable zones
a. Thickness variation of methane hydrate stable zone under different geothermal gradients; b. relationship between geothermal gradient and methane hydrate stable zone thickness
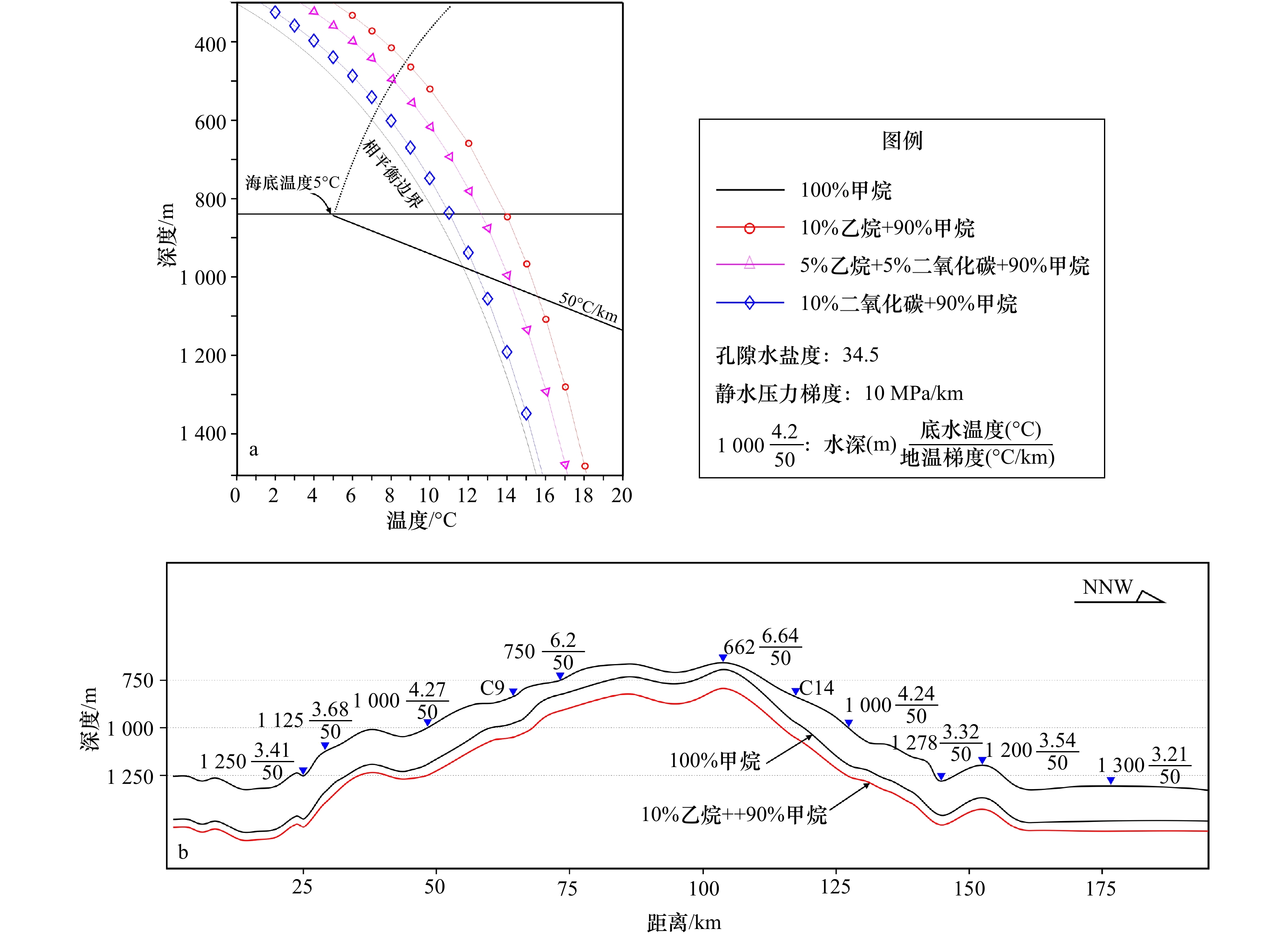
图 5 气源组分变化对天然气水合物稳定带厚度的影响
a. 不同气体成分水合物的相平衡曲线;b. 过麻坑区剖面不同气体组分形成的水合物的稳定带底界深度(剖面位置见图1)
Fig. 5 Effect of gas composition on the thickness of gas hydrate stable zones
a. Phase equilibrium curves of gas hydrates with different gas components; b. the depth of stable zone base for hydrates with different gas components arcoss pockmark area (see Fig. 1 for profile location)
-
[1] Majorowicz J, Safanda J, Osadetz K. Inferred gas hydrate and permafrost stability history models linked to climate change in the Beaufort-Mackenzie Basin, Arctic Canada[J]. Climate of the Past, 2012, 8(2): 667−682. [2] Riboulot V, Ker S, Sultan N, et al. Freshwater lake to salt-water sea causing widespread hydrate dissociation in the Black Sea[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 117. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02271-z [3] Handwerger A L, Rempel A W, Skarbek R M. Submarine landslides triggered by destabilization of high-saturation hydrate anomalies[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2017, 18(7): 2429−2445. doi: 10.1002/ggge.v18.7 [4] 宋海斌, 江为为, 张岭. 海洋天然气水合物的地球物理研究(Ⅳ): 双似海底反射[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2003, 18(3): 497−502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2003.03.027Song Haibin, Jiang Weiwei, Zhang Ling. Geophysical researches on marine gas hydrates (Ⅳ): double bottom simulating reflections[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2003, 18(3): 497−502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2003.03.027 [5] Zander T, Haeckel M, Berndt C, et al. On the origin of multiple BSRs in the Danube deep-sea fan, Black Sea[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 462: 15−25. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2017.01.006 [6] 陈芳, 陆红锋, 刘坚, 等. 南海东北部陆坡天然气水合物多期次分解的沉积地球化学响应[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2016, 41(10): 1619−1629.Chen Fang, Lu Hongfeng, Liu Jian, et al. Sedimentary geochemical response to gas hydrate episodic release on the northeastern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2016, 41(10): 1619−1629. [7] 叶黎明, 初凤友, 葛倩, 等. 新仙女木末期南海北部天然气水合物分解事件[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(6): 1299−1308.Ye Liming, Chu Fengyou, Ge Qian, et al. A rapid gas hydrate dissociation in the Northern South China Sea since the Late Younger Dryas[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2013, 38(6): 1299−1308. [8] 金春爽, 汪集旸, 卢振权. 南海西沙海槽6 Ma以来天然气水合物稳定带演化初探[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(1): 156−162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.013Jin Chunshuang, Wang Jiyang, Lu Zhenquan. A tentative discussion on the evolution of the natural gas hydrates stable zone in Xisha Trough of South China Sea since 6 Ma B.P.[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2011, 30(1): 156−162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.01.013 [9] 龚跃华, 杨胜雄, 王宏斌, 等. 琼东南盆地天然气水合物成矿远景[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2018, 48(4): 1030−1042.Gong Yuehua, Yang Shengxiong, Wang Hongbin, et al. Prospect of gas hydrate resources in Qiong Dongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Earth Science Edition, 2018, 48(4): 1030−1042. [10] 陈多福, 李绪宣, 夏斌. 南海琼东南盆地天然气水合物稳定域分布特征及资源预测[J]. 地球物理学报, 2004, 47(3): 483−489. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.03.018Chen Duofu, Li Xuxuan, Xia Bin. Distribution of gas hydrate stable zones and resource prediction in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2004, 47(3): 483−489. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2004.03.018 [11] 杨力, 刘斌, 徐梦婕, 等. 南海北部琼东南海域活动冷泉特征及形成模式[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(7): 2905−2914. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0374Yang Li, Liu Bin, Xu Mengjie, et al. Characteristics of active cold seepages in Qiongdongnan Sea Area of the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(7): 2905−2914. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0374 [12] 孙春岩, 吴能有, 牛滨华, 等. 南海琼东南盆地气态烃地球化学特征及天然气水合物资源远景预测[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(1): 95−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.01.011Sun Chunyan, Wu Nengyou, Niu Binhua, et al. Geochemical characteristics of gaseous hydrocarbons and hydrate resource prediction in the Qiong-Dongnan Basin of the South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(1): 95−100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.01.011 [13] 王秀娟, 吴时国, 王大伟, 等. 琼东南盆地多边形断层在流体运移和天然气水合物成藏中的作用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(1): 122−128.Wang Xiujuan, Wu Shiguo, Wang Dawei, et al. The role of polygonal faults in fluid migration and gas hydrate reservoir forming in Southeast Hainan Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 45(1): 122−128. [14] 梁金强, 王宏斌, 苏丕波, 等. 天然气水合物成藏的控制因素研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018.Liang Jinqiang, Wang Hongbin, Su Pibo, et al. Study on Controlling Factors of Gas Hydrate Reservoir Formation[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018. [15] 朱继田, 裴健翔, 孙志鹏, 等. 琼东南盆地新构造运动及其对晚期油气成藏的控制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(4): 649−656.Zhu Jitian, Pei Jianxiang, Sun Zhipeng, et al. Feature of neotectonism and its control on late hydrocarbon accumulation in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(4): 649−656. [16] Schimanski A, Stattegger K. Deglacial and Holocene evolution of the Vietnam shelf: stratigraphy, sediments and sea-level change[J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 214(4): 365−387. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2004.11.001 [17] 单竞男, 张功成, 吴景富, 等. 南海北缘琼东南盆地热结构与莫霍面温度[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(8): 2102−2109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.08.017Shan Jingnan, Zhang Gongcheng, Wu Jingfu, et al. Thermal structure and Moho temperature of Qiongdongnan Basin, northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(8): 2102−2109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.08.017 [18] 杨涛涛, 吴敬武, 王彬, 等. 琼东南盆地华光凹陷构造特征及沉积充填[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(5): 13−18.Yang Taotao, Wu Jingwu, Wang Bin, et al. Structural pattern and sediment filling in Huaguang Sag of southern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(5): 13−18. [19] Zeng Lili, Wang Qiang, Xie Qiang, et al. Hydrographic field investigations in the Northern South China Sea by open cruises during 2004-2013[J]. Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(6): 607−615. doi: 10.1007/s11434-015-0733-z [20] Luo Min, Dale A W, Wallmann K, et al. Estimating the time of pockmark formation in the SW Xisha Uplift (South China Sea) using reaction-transport modeling[J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 364: 21−31. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.03.006 [21] 翟普强, 陈红汉, 谢玉洪, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区超压演化与油气运移模拟[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版), 2013, 44(10): 4187−4201.Zhai Puqiang, Chen Honghan, Xie Yuhong, et al. Modelling of evolution of overpressure system and hydrocarbon migration in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2013, 44(10): 4187−4201. [22] 郝诒纯, 陈平富, 万晓樵, 等. 南海北部莺歌海-琼东南盆地晚第三纪层序地层与海平面变化[J]. 现代地质, 2000, 14(3): 237−245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2000.03.001Hao Yichun, Chen Pingfu, Wan Xiaoqiao, et al. Late Tertiary sequence stratigraphy and sea level changes in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2000, 14(3): 237−245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2000.03.001 [23] Shao Lei, Cui Yuchi, Qiao Peijun, et al. Sea-level changes and carbonate platform evolution of the Xisha Islands (South China Sea) since the Early Miocene[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 485: 504−516. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.07.006 [24] Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R. Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic[J]. Science, 1987, 235: 1156−1166. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156 [25] 余克服, 陈特固. 南海北部晚全新世高海平面及其波动的海滩沉积证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(6): 138−145. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.06.015Yu Kefu, Chen Tegu. Beach sediments from northern South China Sea suggest high and oscillating sea level during the Late Holocene[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(6): 138−145. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.06.015 [26] Bintanja R, van de Wal R S W, Oerlemans J. Modelled atmospheric temperatures and global sea levels over the past million years[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7055): 125−128. doi: 10.1038/nature03975 [27] Kennett J P, Cannariato K G, Hendy I L, et al. Carbon isotopic evidence for methane hydrate instability during quaternary interstadials[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5463): 128−133. [28] Jian Zhimin, Cheng Xinrong, Zhao Quanhong, et al. Oxygen isotope stratigraphy and events in the northern South China Sea during the last 6 million years[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2001, 44(10): 952−960. doi: 10.1007/BF02907088 [29] 黄宝琦, 翦知湣, 赵泉鸿, 等. 晚上新世以来南海北部深部水团演化[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2005, 30(5): 529−533.Huang Baoqi, Jian Zhimin, Zhao Quanhong, et al. Variations in deep-water masses from the Northern South China Sea since the Late Pliocene[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2005, 30(5): 529−533. [30] Siddall M, Hönisch B, Waelbroeck C, et al. Changes in deep Pacific temperature during the mid-Pleistocene transition and Quaternary[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(1/2): 170−181. [31] Shao Lei, Li Xuejie, Geng Jianhua, et al. Deep water bottom current deposition in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(7): 1060−1066. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0015-y [32] Zahn R, Mix A C. Benthic foraminiferal δ18O in the ocean’s temperature-salinity-density field: constraints on Ice Age thermohaline circulation[J]. Paleoceanography, 1991, 6(1): 1−20. doi: 10.1029/90PA01882 [33] He Lijuan, Wang Kelin, Xiong Liangping, et al. Heat flow and thermal history of the South China Sea[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2001, 126(3/4): 211−220. [34] 米立军, 袁玉松, 张功成, 等. 南海北部深水区地热特征及其成因[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(1): 27−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.01.005Mi Lijun, Yuan Yusong, Zhang Gongcheng, et al. Characteristics and genesis of geothermal field in deep-water area of the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(1): 27−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.01.005 [35] 宋洋, 赵长煜, 张功成, 等. 南海北部珠江口与琼东南盆地构造–热模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(12): 3057−3069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.007Song Yang, Zhao Changyu, Zhang Gongcheng, et al. Research on tectono–thermal modeling for Qiongdongnan Basin and Pearl River Mouth Basin in the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(12): 3057−3069. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.12.007 [36] Wang Zhenfeng, Shi Xiaobin, Yang Jun, et al. Analyses on the tectonic thermal evolution and influence factors in the deep-water Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(12): 107−117. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0580-9 [37] 施小斌, 王振峰, 蒋海燕, 等. 张裂型盆地地热参数的垂向变化与琼东南盆地热流分布特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(3): 939−952. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150320Shi Xiaobin, Wang Zhenfeng, Jiang Haiyan, et al. Vertical variations of geothermal parameters in rifted basins and heat flow distribution features of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(3): 939−952. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150320 [38] Nissen S S, Hayes D E, Yao Bochu, et al. Gravity, heat flow, and seismic constraints on the processes of crustal extension: northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1995, 100(B11): 22447−22483. [39] Collett T S. Energy resource potential of natural gas hydrates[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1971−1992. [40] Tréhu A M, Ruppel C, Holland M, et al. Gas hydrates in marine sediments: lessons from scientific ocean drilling[J]. Oceanography, 2006, 19(4): 124−142. doi: 10.5670/oceanog [41] Sloan E D, Koh C A, Sum A K. Gas hydrate stability and sampling: the future as related to the phase diagram[J]. Energies, 2010, 3(12): 1991−2000. doi: 10.3390/en3121991 [42] Milkov A V, Claypool G E, Lee Y J, et al. Gas hydrate systems at Hydrate Ridge offshore Oregon inferred from molecular and isotopic properties of hydrate-bound and void gases[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(4): 1007−1026. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2004.08.021 [43] 苏新, 陈芳, 于兴河, 等. 南海陆坡中新世以来沉积物特性与气体水合物分布初探[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(1): 1−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.001Su Xin, Chen Fang, Yu Xinghe, et al. A pilot study on Miocene through Holocene sediments from the continental slope of the South China Sea in correlation with possible distribution of gas hydrates[J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(1): 1−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.01.001 [44] Waseda A. Organic carbon content, bacterial methanogenesis, and accumulation processes of gas hydrates in marine sediments[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1998, 32(3): 143−157. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.32.143 [45] 刘正华, 陈红汉. 琼东南盆地天然气成因类型及其烃源探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2011, 33(6): 639−644. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.06.015Liu Zhenghua, Chen Honghan. Origin mechanism and source rock for natural gas in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2011, 33(6): 639−644. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2011.06.015 [46] 陈萍, 方念乔. 天然气体水合物在地质作用过程中变化的探讨[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(4): 441−445.Chen Ping, Fang Nianqiao. Study on changes of gas-hydrate under various geological processes[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2002, 27(4): 441−445. [47] 董伟良, 黄保家. 东方1-1气田天然气组成的不均一性与幕式充注[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1999, 26(2): 15−18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1999.02.005Dong Weiliang, Huang Baojia. Heterogeneity of natural gases and the episodic charging process: a case study for Dongfang 1-1 gas field, Yinggehai Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26(2): 15−18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1999.02.005 [48] Hao Fang, Li Sitian, Sun Yongchuan, et al. Geology, compositional heterogeneities, and geochemical origin of the Yacheng gas field, Qiongdongnan basin, South China Sea[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(7): 1372−1384. [49] 高媛, 曲希玉, 杨希冰, 等. 琼东南盆地乐东–陵水凹陷中新统储层流体包裹体特征及成藏期研究[J]. 海相油气地质, 2018, 23(1): 83−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2018.01.010Gao Yuan, Qu Xiyu, Yang Xibing, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and accumulation period of Miocene reservoir in Ledong–Lingshui sag of Qiongdongnan basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2018, 23(1): 83−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2018.01.010 [50] 贾元琴, 胡沛青, 张铭杰, 等. 琼东南盆地崖城地区流体包裹体特征和油气充注期次分析[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(1): 189−196.Jia Yuanqin, Hu Peiqing, Zhang Mingjie, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and their constraints on timing of hydrocarbon filling in the Yacheng area of Qiongdongnan basin, South China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(1): 189−196. [51] Sun Qiliang, Wu Shiguo, Hovland M, et al. The morphologies and genesis of mega-pockmarks near the Xisha Uplift, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(6): 1146−1156. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.003 -





 下载:
下载: