Research on the structure and characteristics of Chongming Island adjacent waters ecosystem based on Rpath
-
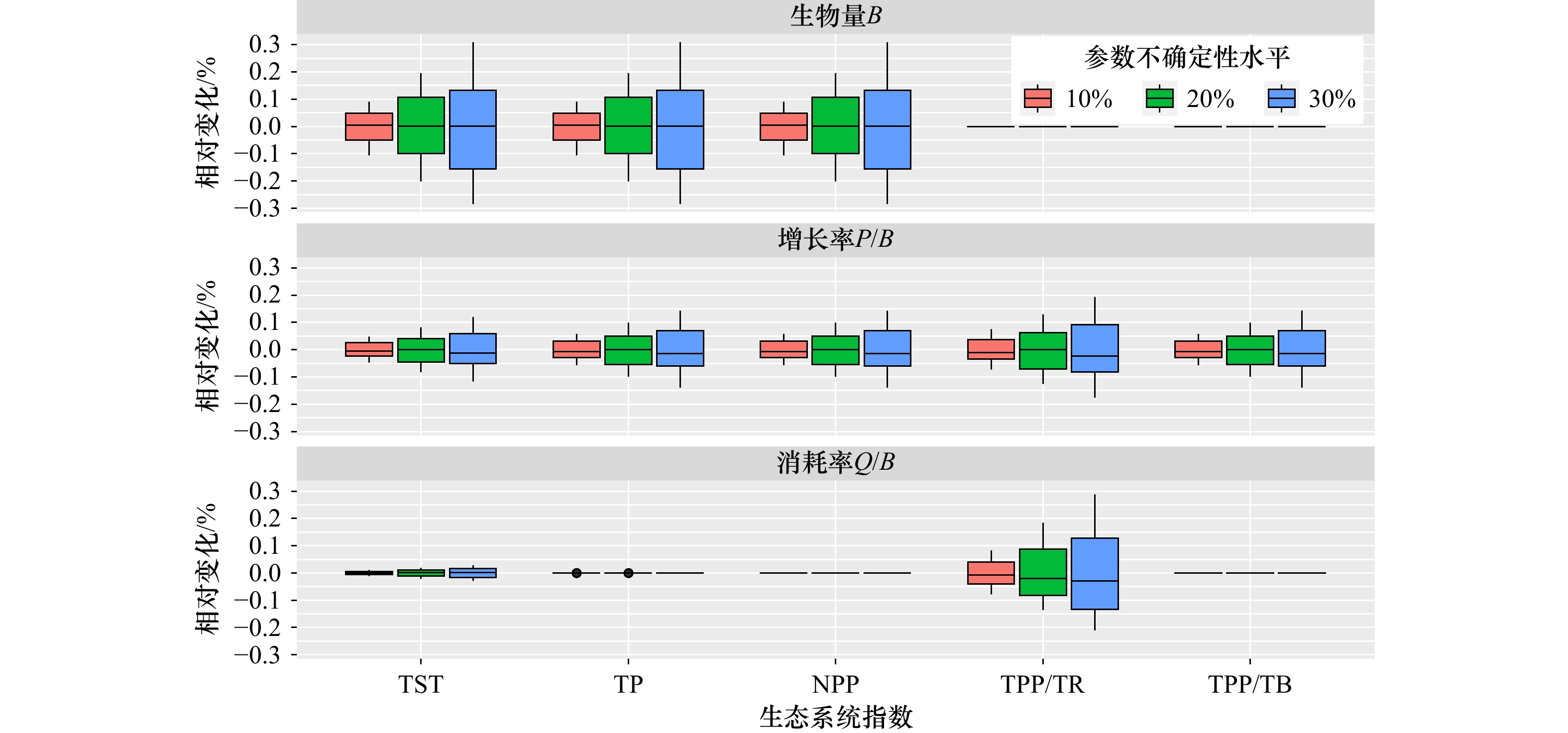
摘要: 本研究根据2020年11月,2021年1月、4月及8月在崇明岛周边海域的渔业调查数据,使用开源程序Rpath构建了包括22个功能群的物质平衡模型,对该海域生态系统结构和特征进行研究。结果表明:崇明岛周边海域生态系统各功能群营养级范围为1~4.32。小型底栖生物的生态转换效率最低(0.01),说明其到高营养级的能量转换存在瓶颈,是影响该海域底层食物链营养传递效率的关键节点。生态系统总体特征分析表明,该生态系统总规模为2 909.42 t/(km2·a),低于附近海域生态系统规模。浮游植物对生态系统总初级生产力的贡献为60%,是该生态系统的主要营养来源。生态系统总初级生产量/总呼吸量为1.99、系统杂食性指数为0.18,表明生态系统成熟度较低,食物网简单,受干扰后恢复能力较差。模型敏感性分析表明,功能群生物量是影响模型输出准确程度的主要指标。本研究结果可以为该海域生态系统水平的禁捕效果评估工作提供基准参考。Abstract: Based on the comprehensive fishery survey in the Chongming Island adjacent waters in November 2020, January 2021, April 2021, and August 2021, we used an open-source program Rpath to build a mass balance model containing 22 functional groups for this area. The ecosystem structure and characteristics in this sea area were then studied. Results showed that the trophic level for these 18 functional groups ranged from 1 to 4.32, with the highest trophic level of bottom carnivorous fish. The ecological transfer efficiency of small benthic organisms is the lowest (0.01), suggesting a bottleneck in their energy transfer to higher trophic levels and indicated it was the bottleneck to limit the energy transfer in the benthic food chain. The analysis of the overall characteristics of the ecosystem shows that the total system throughput of the Chongming Island adjacent waters ecosystem was 2 909.42 t/(km2·a), which was lower than that of the nearby marine ecosystem. Phytoplankton contributes 60% of the energy to the total primary productivity of the ecosystem and was the main nutrient source of this ecosystem. The total primary production/total respiration is 1.99 and the system omnivorous index is 0.18. This indicate that the Chongming Island adjacent waters ecosystem has low maturity, simple trophic interaction, and low recovery ability after disturbance. Sensitivity analysis showed that functional group biomass was the main index that affected the accuracy of ecosystem model output. The results of this study can provide a reference for the evaluation of the effect of the Changjiang River fishing ban.
-
Key words:
- Chongming Island adjacent waters /
- mass balance model /
- Rpath /
- ecosystem characteristics
-
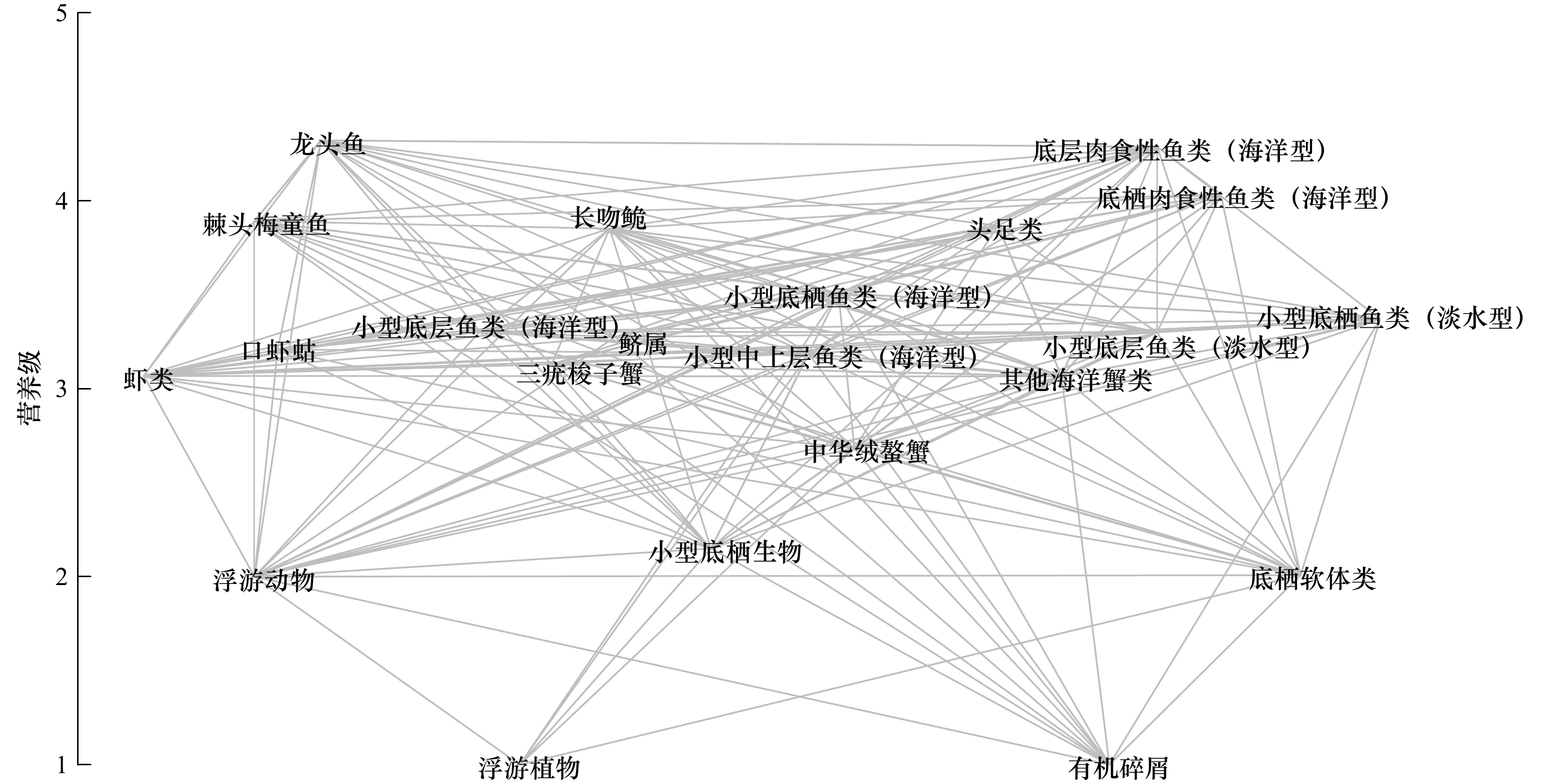
表 1 崇明岛周边海域生态系统各功能群物种组成
Tab. 1 Species composition of each functional groups for the Chongming Island adjacent waters ecosystem model
编号 功能群 主要种类 1 浮游植物 硅藻、甲藻等 2 浮游动物 桡足类、毛颚类、甲壳类幼体、中国毛虾(Acetes chinensis)等 3 虾类 脊尾白虾(Exopalaemon carinicauda)、秀丽白虾(E. modestus)、周氏新对虾(Joyneris shrimp)、日本沼虾(Macrobrachium nipponense)、细鳌沼虾(M. superbum)、安氏白虾(Palaemon annandalei)、葛氏长臂虾(P. gravieri)、巨指长臂虾(P. macrodactylus)、哈氏仿对虾(Parapenaeopsis hardwickii)、东海红虾(Plesionika izumiae)、中华管鞭虾(Solenocera crassicornis)等 4 口虾蛄
口虾蛄(Oratosquilla oratoria) 5 其他海洋蟹类
双斑蟳(Charybdis bimaculata)、日本蟳(C. japonica)、无齿螳臂相手蟹(Chiromantes dehaani)、狭颚绒螯蟹(Eriocheir leptognathus)、日本平家蟹(Heikeopsis japonica)、红线黎明蟹(Matuta planipes)、狭颚新绒螯蟹(Neoeriocheir leptognathus)等 6 三疣梭子蟹
三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus) 7 中华绒螯蟹 中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis) 8 小型中上层鱼类 鳓(Ilisha elongata)、鲻(Mugil cephalus)、黄鲫(Setipinna taty)等 9 鲚属
凤鲚(Coilia mystus)、刀鲚(C. nasus) 10 棘头梅童鱼
棘头梅童鱼(Collichthys lucidus) 11 龙头鱼
龙头鱼(Harpodon nehereus) 12 长吻鮠 长吻鮠(Leiocassis longirostris) 13 小型底层鱼类
(海洋型)皮氏叫姑鱼(Johnius belangerii)、暗纹东方鲀(Takifugu obscurus)等 14 小型底层鱼类
(淡水型)黄颡鱼(Pelteobaggrus fulvidraco)、光泽黄颡鱼(P. nitidus)、似鳊(Pseudobrama simoni)、长蛇鮈(Saurogobio dumerili)等 15 底层肉食性鱼类
(海洋型)中国花鲈(Lateolabrax japonicus)、鮸(Miichthys miiuy)等 16 小型底栖鱼类
(海洋型)窄体舌鳎(Cynoglossus gracilis)、鮻(Liza haematocheila)、睛尾蝌蚪虾虎鱼(Lophiogobius ocellicauda)、狼牙鳗虾虎鱼(Odontamblyopus rubicundus)、矛尾复虾虎鱼(Synechogobius hasta)、孔虾虎鱼(Trypauchen vagina)等 17 小型底栖鱼类
(淡水型)香斜棘鱼衔(Repomucenus olidus)、髭缟虾虎鱼(Tridentiger barbatus)等 18 底栖肉食性鱼类
(海洋型)斑尾刺虾虎鱼(Acanthogobius ommaturus)、细鳞鯻(Terapon jarbua)等 19 头足类 日本无针乌贼(Sepiella japonica)等 20 底栖软体类 河蚬(Corbicula fluminea)、红带织纹螺(Nassarius succinctus)、纵肋织纹螺(N. variciferus)、毛蚶(Scapharca subcrenata)、蛏子(Sinonovacula constricta)等 21 小型底栖生物 多毛类、棘皮类、腔肠类、钩虾类、等足类、端足类等 22 有机碎屑 包括悬浮颗粒有机物及沉积物中有机碎屑 表 2 崇明岛周边海域Rpath模型功能群输入参数
Tab. 2 Input parameters of Rpath model function group for Chongming Island adjacent waters ecosystem
编号 功能群 营养级 生物量/(t·km−2) 生产量/
生物量消费量/
生物量生态营养效率 捕捞量/
(t·km−2)杂食性
指数1 浮游植物 1.00 5.600 0 200.000 − 0.46 − − 2 浮游动物 2.00 4.000 0 25.000 180.000 0.26 − − 3 虾类 3.07 0.049 4 7.600 28.900 0.98 0.000 004 0.05 4 口虾蛄 3.21 0.000 05 8.000 28.900 0.32 − 0.16 5 其他海洋蟹类 3.07 0.004 5.650 26.900 0.95 0.000 022 0.25 6 三疣梭子蟹 3.13 0.013 7 3.500 11.000 0.20 0.000 233 0.16 7 中华绒螯蟹 2.68 0.002 9 4.000 15.000 0.80 0.000 046 0.36 8 小型中上层鱼类 3.19 0.048 1 2.370 7.900 0.34 0.000 233 0.31 9 鲚属 3.28 0.010 5 1.590 5.296 0.42 0.000 473 0.36 10 棘头梅童鱼 3.89 0.011 3 1.600 6.060 0.75 0.000 937 0.24 11 龙头鱼 4.32 0.003 2 1.890 6.770 0.38 0.000 341 0.22 12 长吻鮠 3.85 0.029 5 0.958 4.700 0.38 0.000 201 0.25 13 小型底层鱼类(海洋型) 3.30 0.005 1.754 6.400 0.95 0.000 004 0.15 14 小型底层鱼类(淡水型) 3.30 0.011 0 1.754 6.400 0.48 0.000 086 0.13 15 底层肉食性鱼类(海洋型) 4.29 0.014 5 0.600 4.700 0.33 0.000 099 0.28 16 小型底栖鱼类(海洋型) 3.51 0.024 3 1.220 4.600 0.75 − 0.52 17 小型底栖鱼类(淡水型) 3.37 0.006 1.220 4.600 0.95 − 0.33 18 底栖肉食性鱼类(海洋型) 4.03 0.000 2 0.958 4.700 0.90 0.000 002 0.19 19 头足类 3.87 0.002 3.000 10.000 0.95 0.000 002 0.27 20 小型底栖生物 2.15 4.900 0 9.280 33.000 0.01 − 0.13 21 底栖软体类 2.01 0.100 0 4.540 17.128 0.69 − 0.01 22 有机碎屑 1.00 36.200 0 − − 0.38 − − 注:加粗值由Rpath模型估算得出;“−”代表无相关统计资料。 表 3 崇明岛周边海域生态系统总特征参数表
Tab. 3 General characteristic parameters of Chongming Island adjacent waters cosystem
特征参数 数值 总消耗量/(t·km−2·a−1) 866.14 总输出量/(t·km−2·a−1) 557.45 呼吸的总流量/(t·km−2·a−1) 562.55 流入碎屑的总流量/(t·km−2·a−1) 903.28 系统总流通量/(t·km−2·a−1) 2 909.42 总生产量/(t·km−2·a−1) 1 266.65 总净初级生产量/(t·km−2·a−1) 1 120.00 净系统生产量/(t·km−2·a−1) 557.45 总初级生产量/总呼吸(TPP/TR) 1.99 总初级生产量/总生物量(TPP/TB) 75.50 总生物量(除去碎屑)/(t·km−2·a−1) 14.83 总捕捞量/(t·km−2·a−1) 0.002 7 Pedigree指数 0.573 系统杂食性指数 0.18 浮游植物贡献比 0.6 有机碎屑贡献比 0.4 -
[1] 罗秉征. 河口及近海的生态特点与渔业资源[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 1992(1): 24−30.Luo Bingzheng. Ecological characteristics and fishery resources of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent sea areas[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Valley, 1992(1): 24−30. [2] 池连宝. 长江口及邻近海域低氧区的时空变化特征与关键过程研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2019.Chi Lianbao. The spatial-temporal distributions and key processes of hypoxia off the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. [3] 王金辉, 徐韧, 秦玉涛, 等. 长江口基础生物资源现状及年际变化趋势分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 36(5): 821−828.Wang Jinhui, Xu Ren, Qin Yutao, et al. The basic biological resources and variation during the last decades in the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(5): 821−828. [4] 王远超. 长江口及其邻近海域能流网络结构与年际动态[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2019.Wang Yuanchao. Modelling the structure and interannual dynamics of energy flows in Yangtze Eestuary and its adjacent waters[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. [5] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 农业农村部关于设立长江口禁捕管理区的通告[J]. 中华人民共和国农业农村部公报, 2020(12): 92−93.Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Notice on the Establishment of a Fishing Ban Management Area in the Yangtze River Estuary by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China[J]. Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China, 2020(12): 92−93. [6] 马凤娇, 杨彦平, 方弟安, 等. 长江禁捕后长江口刀鲚资源特征[J]. 水生生物学报, 2022, 46(10): 1580−1590.Ma Fengjiao, Yang Yanping, Fang Di’an, et al. Characteristics of Coilia nasus resources after fishing ban in the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2022, 46(10): 1580−1590. [7] Ulanowicz R E, Puccia C J. Mixed trophic impacts in ecosystems[J]. Coenoses, 1990, 5(1): 7−16. [8] Christensen V, Walters C J, Pauly D. Ecopath with Ecosim: a user’s guide[EB/OL]. [2023−05−01]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267193103 [9] Heymans J J, Coll M, Link J S, et al. Best practice in Ecopath with Ecosim food-web models for ecosystem-based management[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2016, 331: 173−184. [10] 王玮, 王俊杰, 左平, 等. 基于Ecopath模型的西南黄海生态系统结构和能量流动分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(4): 528−539.Wang Wei, Wang Junjie, Zuo Ping, et al. Analysis of structure and energy flow in southwestern Yellow Sea ecosystem based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 528−539. [11] 任晓明, 刘阳, 徐宾铎, 等. 基于Ecopath模型的海州湾及邻近海域生态系统结构研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(6): 101−109.Ren Xiaoming, Liu Yang, Xu Binduo, et al. Ecosystem structure in the Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters based on Ecopath model[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(6): 101−109. [12] Taghavimotlagh S A, Vahabnezhad A, Shojaei M G. A trophic model of the coastal fisheries ecosystem of the northern Persian Gulf using a mass balance Ecopath model[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2021, 42: 101639. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101639 [13] Lucey S M, Gaichas S K, Aydin K Y. Conducting reproducible ecosystem modeling using the open source mass balance model Rpath[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 427: 109057. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109057 [14] Whitehouse G A, Aydin K Y. Assessing the sensitivity of three Alaska marine food webs to perturbations: an example of Ecosim simulations using Rpath[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2020, 429: 109074. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109074 [15] Han Dongyan, Zhang Chongliang, Xue Ying, et al. Impacts of sample size for stomach content analysis on the estimation of ecosystem indices[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2020, 39(8): 53−61. [16] 张效嘉. 长江口近海能流网络分析与鱼类群落研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所), 2015.Zhang Xiaojia. Energy network analysis and fish community in adjacent waters of Yangtze Estuary[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [17] 徐超, 王思凯, 赵峰, 等. 基于Ecopath模型的长江口生态系统营养结构和能量流动研究[J]. 海洋渔业, 2018, 40(3): 309−318.Xu Chao, Wang Sikai, Zhao Feng, et al. Trophic structure and energy flow of the Yangtze Estuary ecosystem based on the analysis with Ecopath model[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2018, 40(3): 309−318. [18] 王殿常, 吴兴华, 丁玲, 等. 基于Ecopath模型的长江口生态系统结构与功能分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12(2): 417−425.Wang Dianchang, Wu Xinghua, Ding Ling, et al. A preliminary analysis of the ecosystemstructure and function of the Yangtze Estuary based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2022, 12(2): 417−425. [19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中华人民共和国推荐性国家标准: 海洋调查规范 第 6 部分 海洋生物调查 :GB/T 12763.6−2007 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. National Standard (Recommended) of the People’s Republic of China: Specifications for oceanographic survey. Part 6: Marine biological survey: GB/T 12763.6−2007 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [20] 国家海洋局. 海洋监测规范 第 6 部分: 生物体分析: GB 17378.6−2007[S]. 北京: 标准出版社, 2007.National Marine Data and Information Service. Specifications for marine monitoring. Part 6: Organism analysis: GB 17378.6−2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007. [21] 中国环境科学研究院. 近岸海域环境监测规范: HJ 442−2008[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2008.Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences. Specifications for offshore environmental monitoring: HJ 442−2008[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2008. [22] Gulland J A. The Fish Resources of the Ocean[M]. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1971. [23] 欧阳力剑, 郭学武. 东、黄海主要鱼类Q/B值与种群摄食量研究[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2010, 31(2): 23−29.Ouyang Lijian, Guo Xuewu. Studies on the Q/B values and food consumption of major fishes in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Science, 2010, 31(2): 23−29. [24] Funtowicz S O, Ravetz J R. Uncertainty and Quality in Science for Policy[M]. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990. [25] Guesnet V, Lassalle G, Chaalali A, et al. Incorporating food-web parameter uncertainty into Ecopath-derived ecological network indicators[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2015, 313: 29−40. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.05.036 [26] Odum E P. The strategy of ecosystem development[J]. Science, 1969, 164(3877): 262−270. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.262 [27] Wickham H. Data Analysis[M]. Houston, Texas, USA: Springer Cham, 2016. [28] 林群, 金显仕, 郭学武, 等. 基于Ecopath模型的长江口及毗邻水域生态系统结构和能量流动研究[J]. 水生态学杂志, 2009, 30(2): 28−36.Lin Qun, Jin Xianshi, Guo Xuewu, et al. Study on the structure and energy flow of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters ecosystem based on Ecopath model[J]. Journal of Hydroecology, 2009, 30(2): 28−36. [29] 赵晨. 长江口海洋牧场示范区海域生态系统结构与功能研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2019.Zhao Chen. Analysis of ecosystem structure and function in the Yangtze Estuary Marine Ranch[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2019. [30] 刘志豪, 韩东燕, 高春霞, 等. 基于捕食者CPUE权重的浙江南部近海龙头鱼摄食习性分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(4): 482−492.Liu Zhihao, Han Dongyan, Gao Chunxia, et al. Feeding habits of Bombay ducks (Harpadon nehereus) in the offshorewaters of southern Zhejiang, based on predator CPUE weighting[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(4): 482−492. [31] 潘绪伟, 程家骅. 长江口外海域龙头鱼营养生态学特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 2011, 18(5): 1132−1140.Pan Xuwei, Cheng Jiahua. Feeding ecology of Harpadon nehereus in areas adjacent to Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2011, 18(5): 1132−1140. [32] 庄平, 罗刚, 张涛, 等. 长江口水域中华鲟幼鱼与6种主要经济鱼类的食性及食物竞争[J]. 生态学报, 2010, 30(20): 5544−5554.Zhuang Ping, Luo Gang, Zhang Tao, et al. Food comparison among juvenile Acipenser sinensis and other six economic fishes in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2010, 30(20): 5544−5554. [33] 韩东燕, 薛莹, 纪毓鹏, 等. 胶州湾5虾虎鱼类的营养和空间生态位[J]. 中国水产科学, 2013, 20(1): 148−156. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2013.00148Han Dongyan, Xue Ying, Ji Yupeng, et al. Trophic and spatial niche of five gobiid fishes in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2013, 20(1): 148−156. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2013.00148 [34] Morissette L. Complexity, cost and quality of ecosystem models and their impact on resilience: a comparative analysis, with emphasis on marine mammals and the Gulf of St. Lawrence[D]. Vancouver: University of British Columbia, 2007. [35] Ulanowicz R E. Growth and Development, Ecosystems Phenomenology[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1986. -




 下载:
下载: