An algorithm for extracting airborne LiDAR bathymetric travel time in water column based on seabed echo enhancement
-
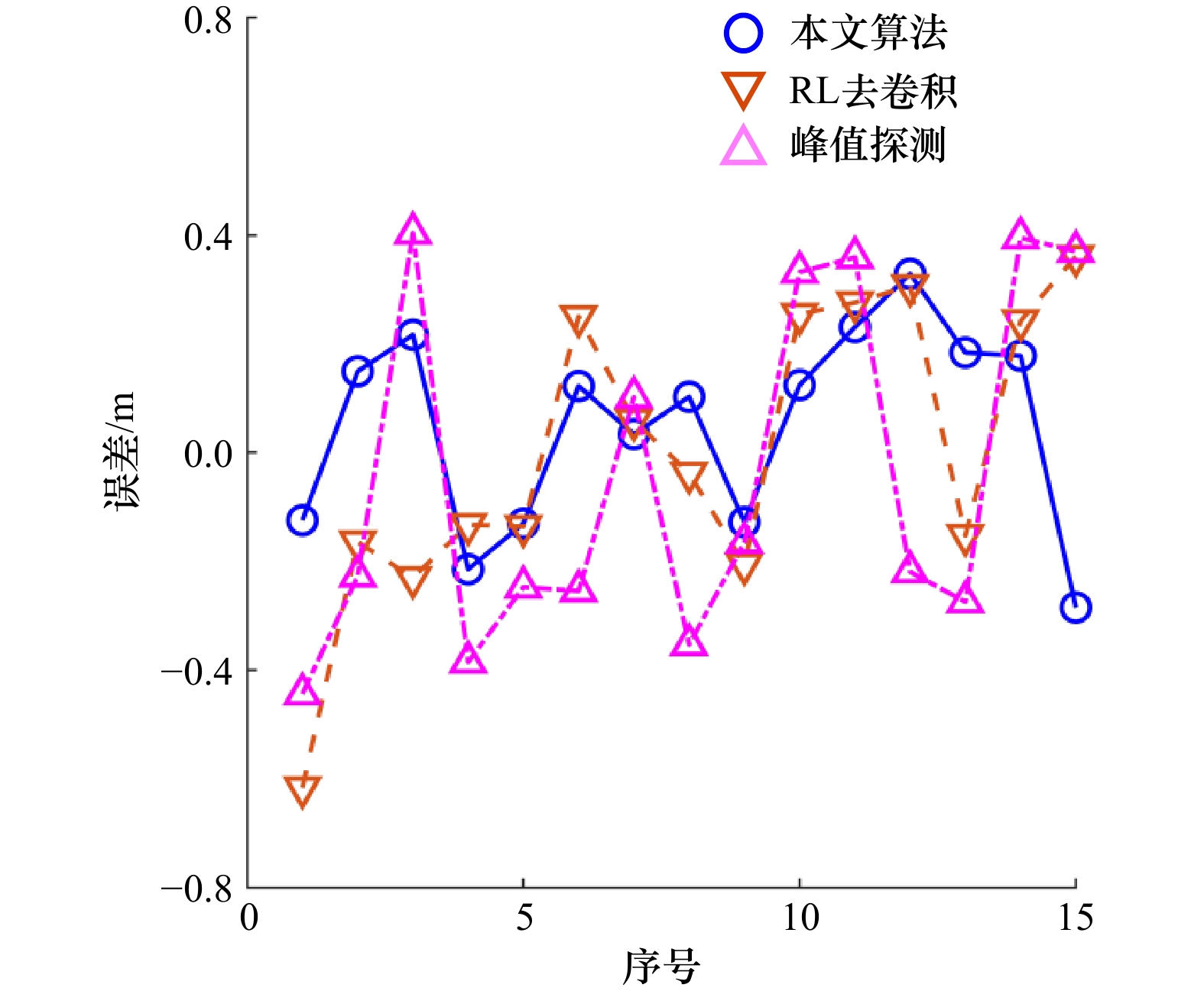
摘要: 机载LiDAR测深(Airborne LiDAR Bathymetry, ALB)技术具有高精度、高效率、强机动性、水陆两用等优势,特别适合海岸带、海岛礁等浅水海域复杂地形的快速探测。激光穿透水体时能量将迅速衰减,导致部分海底回波难以有效提取,海底真实位置判别困难。为此,本文提出一种基于回波增强的机载LiDAR测深水体旅行时提取算法。通过Gold去卷积算法来恢复目标横截面形状,确定海底初始回波范围;随后采用双指数函数拟合水体后向散射有效范围,进而求取波形漫衰减系数Kd值;最后结合海底激光雷达方程,利用Kd值对海底初始回波范围内波形进行增强,并利用高斯函数分解增强后回波,确定海底位置参数,从而实现ALB波形的水体旅行时提取。利用青岛胶州湾RIEGL VQ-840-G ALB实验数据对本文算法的可行性进行验证,将本文算法与理查德森-露西(Richardson-Lucy,RL)去卷积模型、峰值探测模型进行了比对,结果表明本文算法与单波束同名点之间高程误差的均方根误差(Root Mean Square Error, RMSE)为18.5 cm,较上述两种算法分别降低了29.9%、41.4%。因此,本文算法具有可行性,能够满足ALB波形的水体旅行时高精度提取,可为机载LiDAR测深数据精细化处理提供一定技术支撑。Abstract: The airborne LiDAR bathymetry (ALB) technology has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, strong mobility and dual use of water and land. It is especially suitable for the rapid detection of complex terraforming in shallow waters such as coastal zones, islands and reefs. When the laser penetrates the water, the energy will attenuate rapidly, which makes it difficult to extract part of the seabed echo effectively and distinguish the true position of the sea bottom. Therefore, an airborne LiDAR bathymetric travel time in the water column extraction algorithm based on echo enhancement is proposed in this paper. The Gold deconvolution algorithm was used to restore the cross section shape of the target and determine the initial range of the seabed. Then, the effective range of backscattering was fitted by double exponential function, and the diffuse attenuation coefficient Kd was obtained. Finally, combined with the seabed LiDAR equation, the waveform in the initial range of the seabed is enhanced by Kd value, and the enhanced echo is decomposed by Gaussian function to determine the seabed position parameters, so as to realize the travel time in the water column extraction of ALB waveform. The feasibility of the proposed algorithm was verified by using the experimental data of RIEGL VQ-840-G ALB in Qingdao Jiaozhou Bay, and the proposed algorithm was compared with the Richardson-Lucy deconvolution model and the peak detection model. The results show that the root mean square error (RMSE) between the proposed algorithm and the single-beam point with the same name is 18.5 cm, which is 29.9% and 41.4% lower than the above two algorithms, respectively. Therefore, the proposed algorithm is feasible and can satisfy the high precision extraction of ALB waveform during water column traveling, which can provide certain technical support for the fine processing of airborne LiDAR bathymetry data.
-
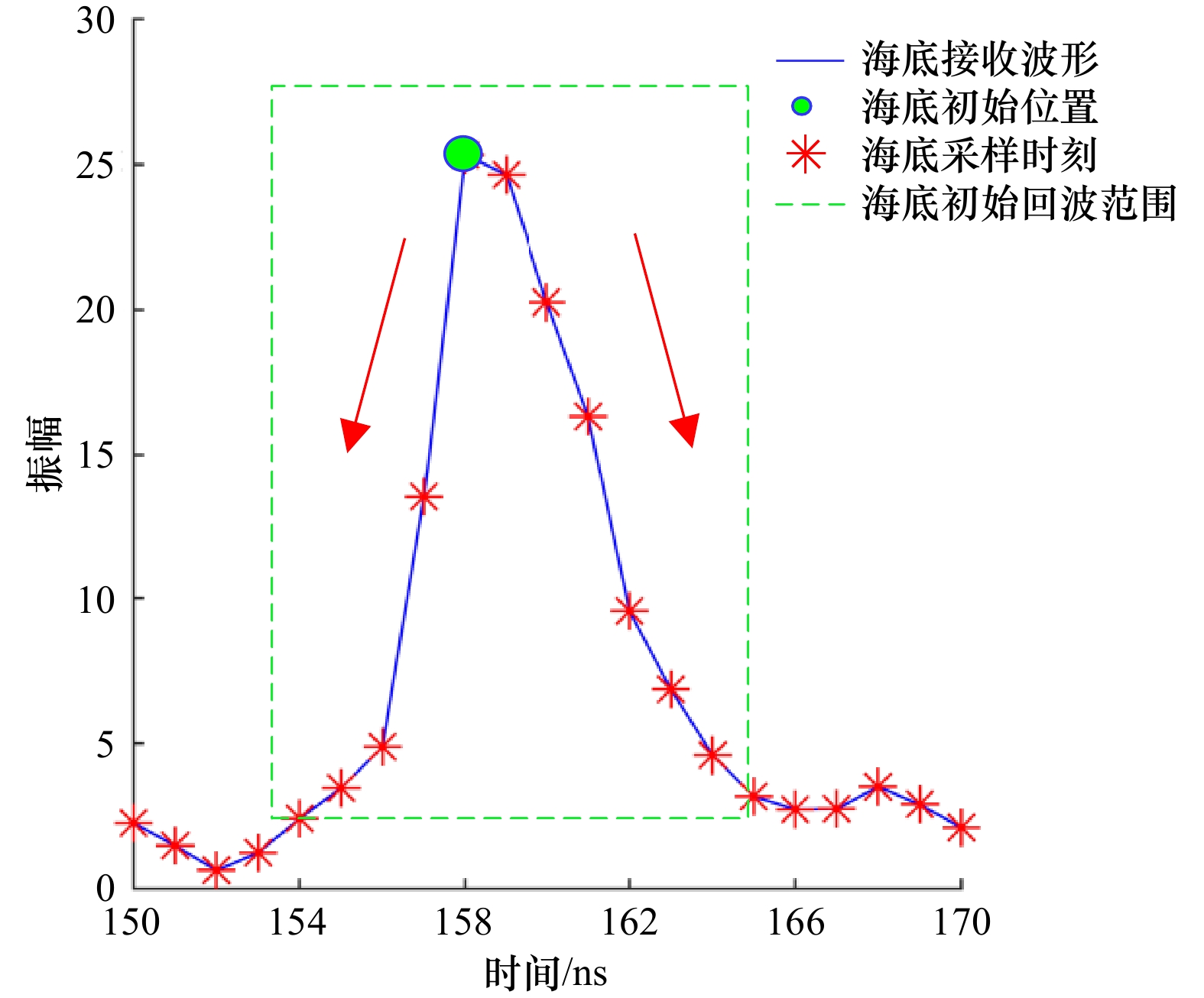
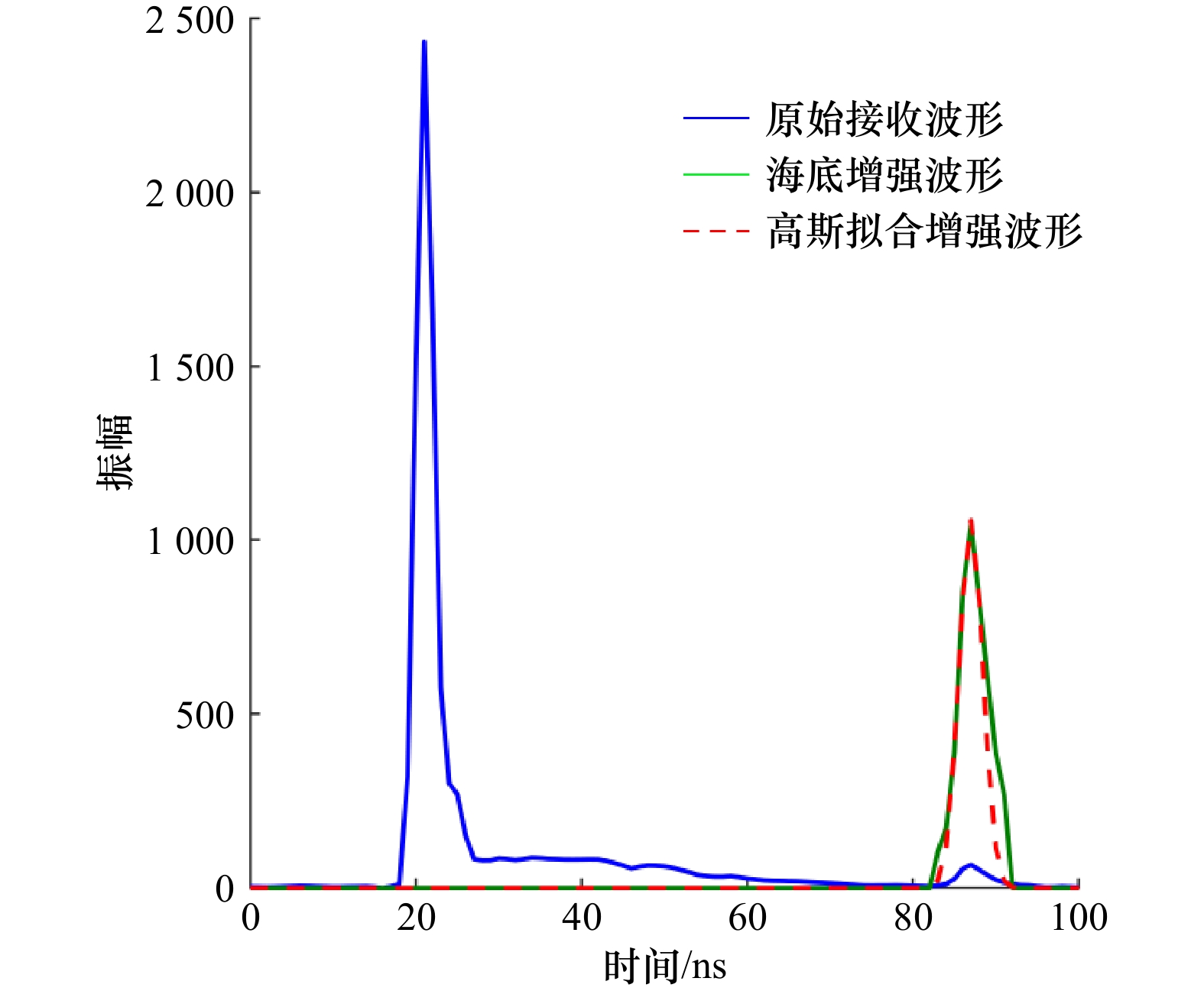
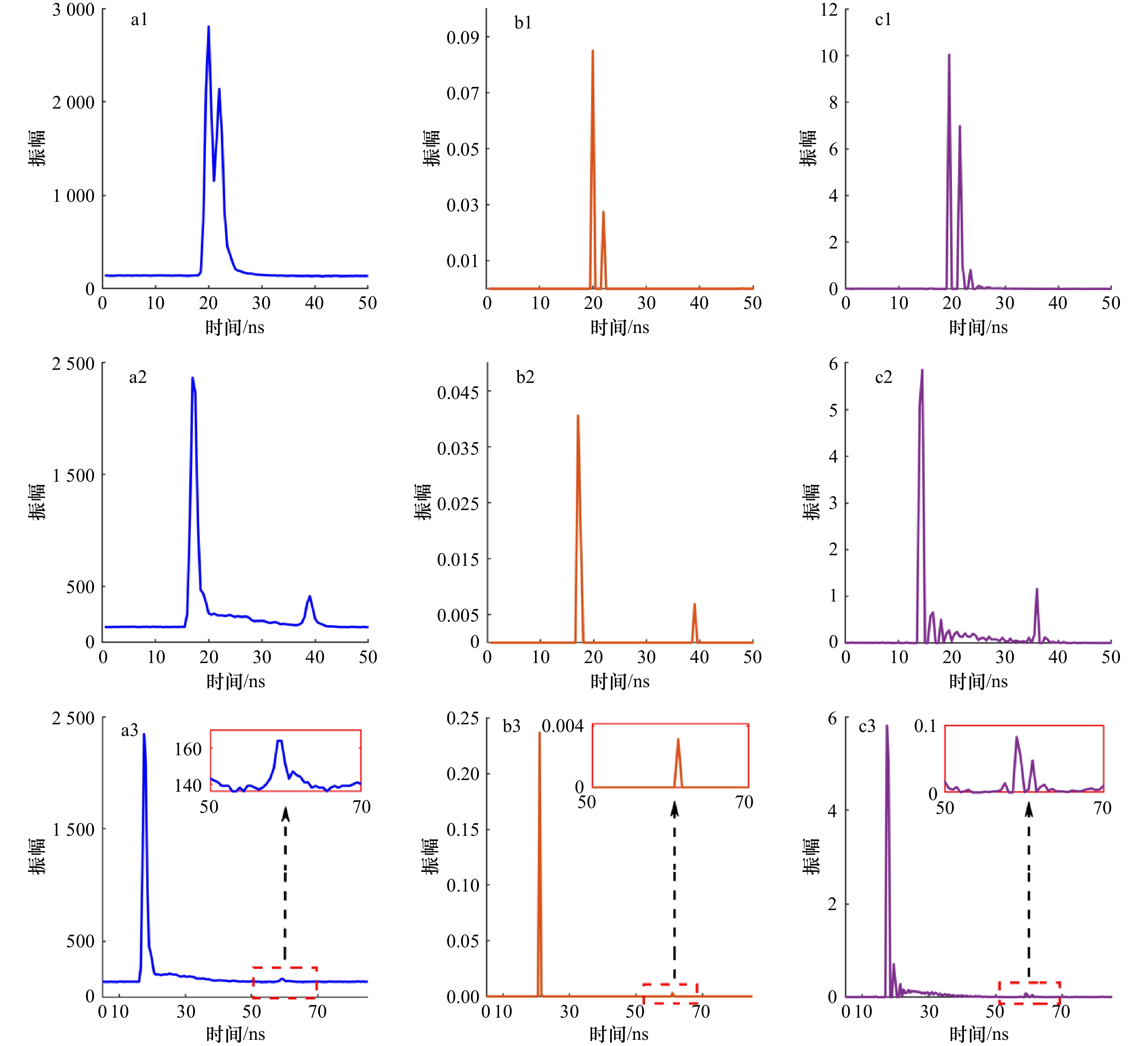
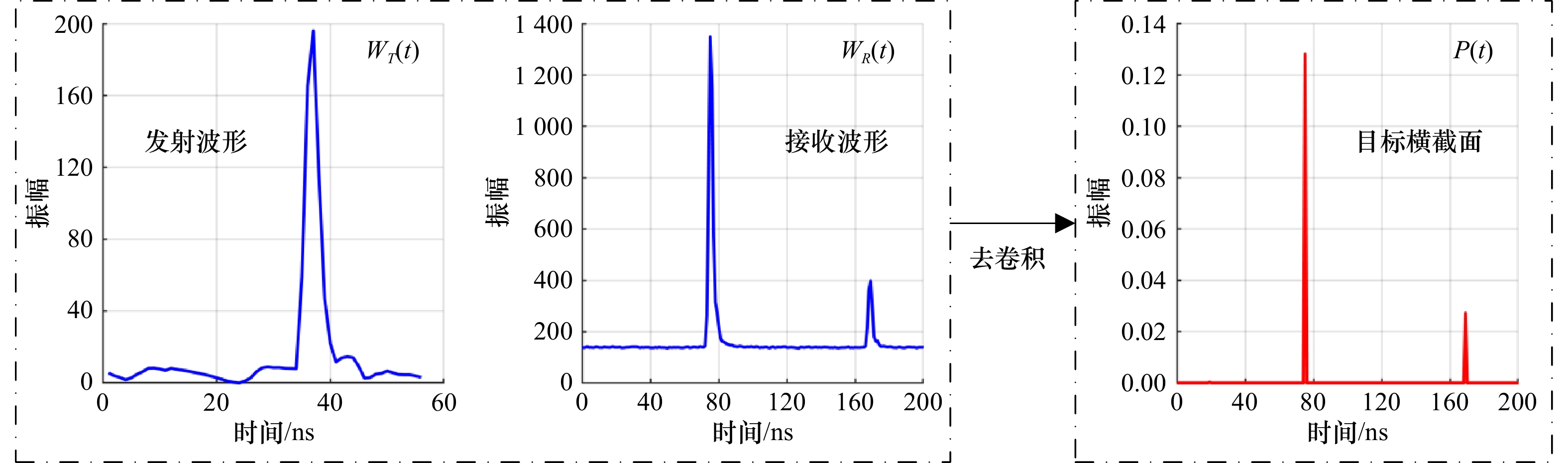
图 7 3类典型波形的目标横截面恢复结果
a1–a3为极浅水波形、常规波形、微弱波形;b1–b3为Gold去卷积所恢复对应目标横截面;c1–c3为RL去卷积所恢复对应目标横截面
Fig. 7 Target cross section restoration results of three types of typical waveforms
a1–a3. Extremely shallow water waveform, conventional waveform, weak waveform; b1–b3. Gold deconvolution recovered corresponding target cross section; c1–c3. RL deconvolution restores corresponding target cross sections
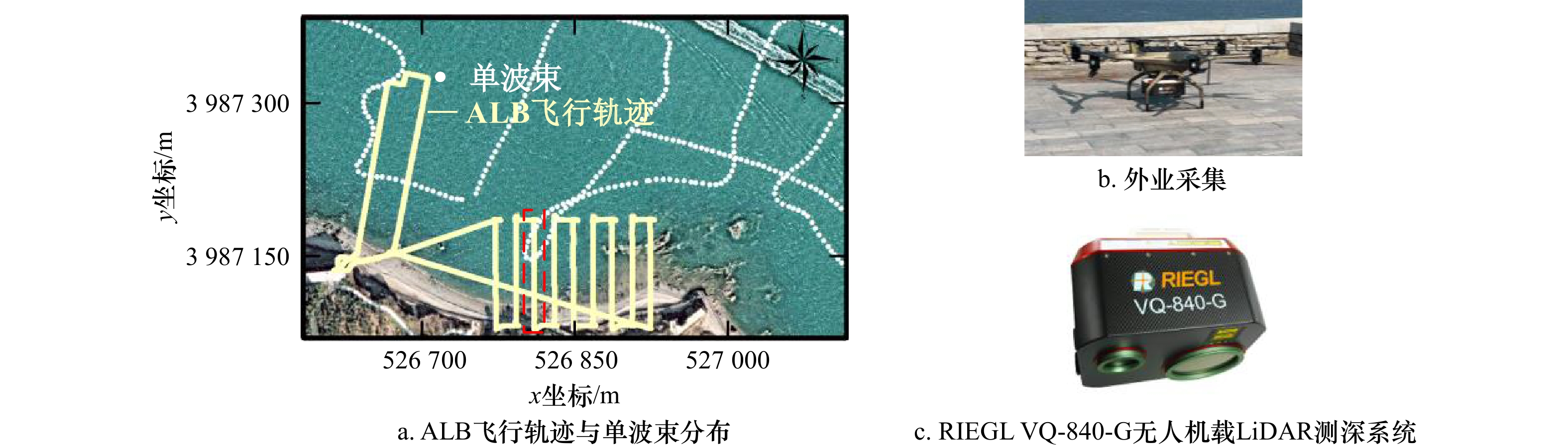
表 1 RIEGL VQ-840-G无人机载LiDAR测深系统主要技术参数指标
Tab. 1 Main technical parameters of RIEGL VQ-840-G UAV-borne LiDAR bathymetry system
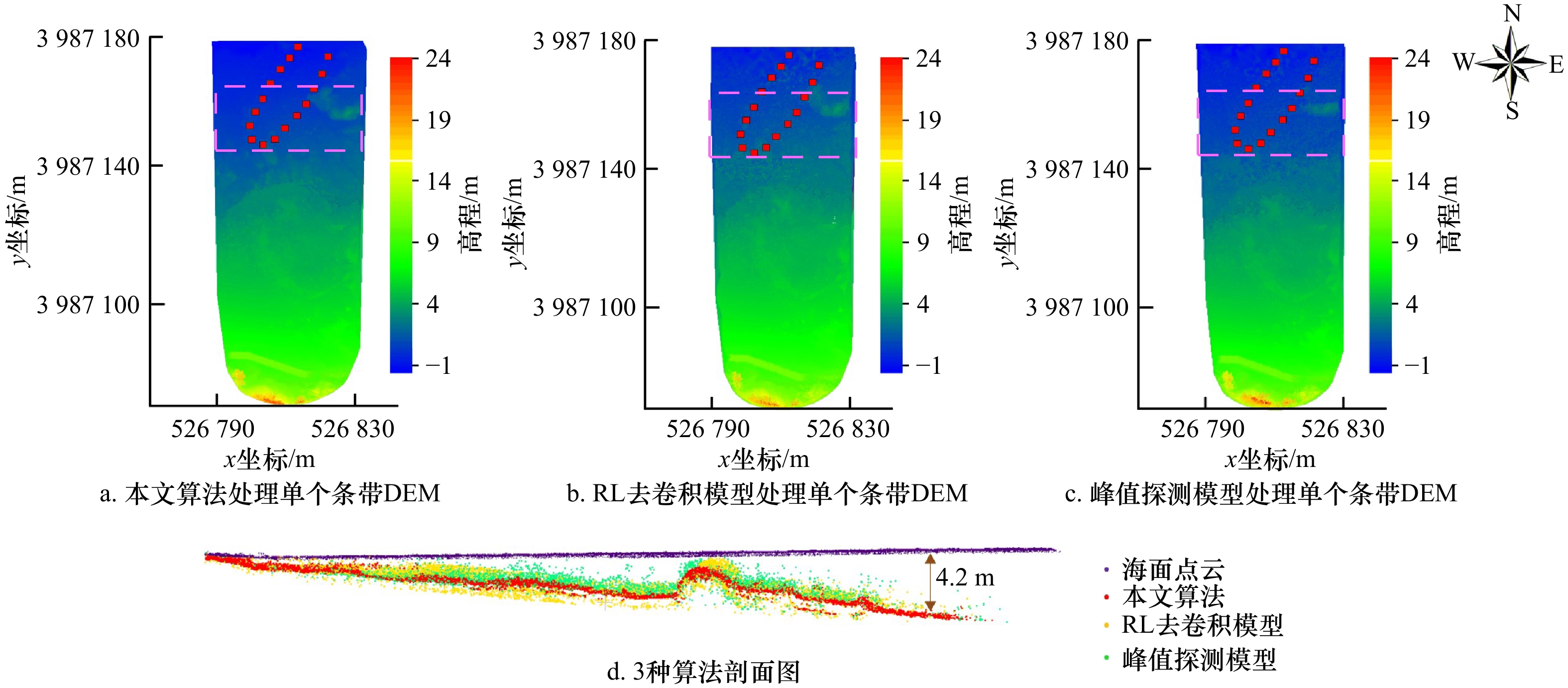
参数 指标 扫描频率 200 kHz(可调节) 最大穿透深度 2.5 Secchi @ 50 kHz 视场角 40° 测点密度 > 100 pts/m2 光斑 10 cm @ 100 m航高 重量 12 kg 表 2 3种算法所生成点云的点密度统计
Tab. 2 Point density statistics of point clouds generated by the three algorithms
算法 平均密度/(point·m−2) 本文算法 271 RL去卷积 192 峰值探测 185 -
[1] 刘焱雄, 郭锴, 何秀凤, 等. 机载激光测深技术及其研究进展[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2017, 42(9): 1185−1194.Liu Yanxiong, Guo Kai, He Xiufeng, et al. Research progress of airborne laser bathymetry technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(9): 1185−1194. [2] 王越. 机载激光浅海测深技术的现状和发展[J]. 测绘地理信息, 2014, 39(3): 38−42.Wang Yue. Current status and development of airborne laser bathymetry technology[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2014, 39(3): 38−42. [3] 刘永明, 邓孺孺, 秦雁, 等. 机载激光雷达测深数据处理与应用[J]. 遥感学报, 2017, 21(6): 982−995.Liu Yongming, Deng Ruru, Qin Yan, et al. Data processing methods and applications of airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 21(6): 982−995. [4] 宿殿鹏, 阳凡林, 陈亮, 等. 无人机载LiDAR测深系统进行海岸带测绘的可行性分析[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 41(5): 11−20.Su Dianpeng, Yang Fanlin, Chen Liang, et al. Feasibility analysis of UAV-airborne LiDAR bathymetry system for coastal zone mapping[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 41(5): 11−20. [5] Wang Chisheng, Li Qingquan, Liu Yanxiong, et al. A comparison of waveform processing algorithms for single-wavelength LiDAR bathymetry[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 101: 22−35. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.11.005 [6] Song Yue, Li Houpu, Zhai Guojun, et al. Comparison of multichannel signal deconvolution algorithms in airborne LiDAR bathymetry based on wavelet transform[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 16988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96551-w [7] 黄田程, 陶邦一, 贺岩, 等. 国产机载激光雷达测深系统的波形处理方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(8): 082808.Huang Tiancheng, Tao Bangyi, He Yan, et al. Waveform processing methods in domestic airborne lidar bathymetry system[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(8): 082808. [8] 贺岩, 胡善江, 陈卫标, 等. 国产机载双频激光雷达探测技术研究进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(8): 082801.He Yan, Hu Shanjiang, Chen Weibiao, et al. Research progress of domestic airborne dual-frequency LiDAR detection technology[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(8): 082801. [9] 王丹菂, 徐青, 邢帅, 等. 一种由粗到精的机载激光测深信号检测方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(8): 1148−1159.Wang Dandi, Xu Qing, Xing Shuai, et al. A coarse-to-fine signal detection method for airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(8): 1148−1159. [10] Qi Chao, Ma Yue, Su Dianpeng, et al. A method to decompose airborne LiDAR bathymetric waveform in very shallow waters combining deconvolution with curve fitting[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 7004905. [11] Ding Kai, Li Qingquan, Zhu Jiasong, et al. An improved quadrilateral fitting algorithm for the water column contribution in airborne bathymetric LiDAR waveforms[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 552. doi: 10.3390/s18020552 [12] Wagner W, Ullrich A, Ducic V, et al. Gaussian decomposition and calibration of a novel small-footprint full-waveform digitising airborne laser scanner[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2006, 60(2): 100−112. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2005.12.001 [13] Chauve A, Mallet C, Bretar F, et al. Processing full-waveform LiDAR data: modelling raw signals[C]//ISPRS Workshop Laser Scanning and SilviLaser (LS SL). Espoo: HAL, 2007: 102−107. [14] Hofton M A, Minster J B, Blair J B. Decomposition of laser altimeter waveforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(4): 1989−1996. doi: 10.1109/36.851780 [15] 亓超, 周丰年, 吴敬文, 等. 基于机载LiDAR测深水体波形的漫衰减系数提取方法[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(1): 147−154.Qi Chao, Zhou Fengnian, Wu Jingwen, et al. Extraction method for diffuse attenuation coefficient based on airborne LiDAR bathymetric water column waveform[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(1): 147−154. [16] 王丹菂, 徐青, 邢帅, 等. 机载激光测深去卷积信号提取方法的比较[J]. 测绘学报, 2018, 47(2): 161−169. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170501Wang Dandi, Xu Qing, Xing Shuai, et al. Comparison of signal extraction method for airborne LiDAR bathymetry based on deconvolution[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(2): 161−169. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170501 [17] Richardson W H. Bayesian-based iterative method of image restoration[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1972, 62(1): 55−59. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.62.000055 [18] Lucy L B. An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 1974, 79: 745. doi: 10.1086/111605 [19] Morháč M, Kliman J, Matoušek V, et al. Efficient one- and two-dimensional gold deconvolution and its application to γ-ray spectra decomposition[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 1997, 401(2/3): 385−408. [20] Wu Jiaying, Van Aardt J A N, McGlinchy J, et al. A robust signal preprocessing chain for small-footprint waveform LiDAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3242−3255. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2178420 [21] Zhou Tan, Popescu S C, Krause K, et al. Gold–A novel deconvolution algorithm with optimization for waveform LiDAR processing[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 129: 131−150. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.04.021 [22] Zhou Guoqing, Long Shuhua, Xu Jiasheng, et al. Comparison analysis of five waveform decomposition algorithms for the airborne LiDAR echo signal[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7869−7880. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3096197 [23] Schwarz R, Mandlburger G, Pfennigbauer M, et al. Design and evaluation of a full-wave surface and bottom-detection algorithm for LiDAR bathymetry of very shallow waters[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 150: 1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.02.002 [24] Mader D, Richter K, Westfeld P, et al. Potential of a non-linear full-waveform stacking technique in airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. PFG-Journal of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science, 2021, 89(2): 139−158. doi: 10.1007/s41064-021-00147-y [25] Richter K, Maas H G, Westfeld P, et al. An approach to determining turbidity and correcting for signal attenuation in airborne LiDAR bathymetry[J]. PFG–Journal of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science, 2017, 85(1): 31−40. doi: 10.1007/s41064-016-0001-0 [26] 宋越, 李厚朴, 翟国君. 机载激光测深波形去噪算法对比分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(2): 270−278.Song Yue, Li Houpu, Zhai Guojun. Comparative analysis of airborne laser bathymetric waveforms denoising algorithms[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(2): 270−278. [27] 江虹, 苏阳. 一种改进的小波阈值函数去噪方法[J]. 激光与红外, 2016, 46(1): 119−122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2016.01.023Jiang Hong, Su Yang. Denoising method based on improved wavelet threshold function[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2016, 46(1): 119−122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2016.01.023 [28] Morháč M, Matoušek V, Kliman J. Efficient algorithm of multidimensional deconvolution and its application to nuclear data processing[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2003, 13(1): 144−171. doi: 10.1016/S1051-2004(02)00011-8 [29] Ding Kai, Wang Chisheng, Tao Ming, et al. A new algorithm for retrieving diffuse attenuation coefficient based on big LiDAR bathymetry data[C]//11th International Symposium on Cyberspace Safety and Security. Guangzhou: Springer, 2019: 133−142. [30] Guenther G C, LaRocque P E, Lillycrop W J. Multiple surface channels in scanning hydrographic operational airborne LiDAR Survey (SHOALS) airborne LiDAR[C]//Proceedings of SPIE 2258, Ocean Optics XII. Bergen: SPIE, 1994: 422−430. [31] Eren F, Pe’eri S, Rzhanov Y, et al. Bottom characterization by using airborne LiDAR bathymetry (ALB) waveform features obtained from bottom return residual analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 206: 260−274. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.12.035 [32] 郭锴, 刘焱雄, 徐文学, 等. 机载激光测深波形分解中LM与EM参数优化方法比较[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(1): 117−131.Guo Kai, Liu Yanxiong, Xu Wenxue, et al. Comparison of LM and EM parameter optimization methods for airborne laser bathymetric full-waveform decomposition[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2020, 49(1): 117−131. [33] 申二华, 张永生, 李凯. 圆扫描式机载激光测深系统定位模型与仿真分析[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(2): 0214001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0214001Shen Erhua, Zhang Yongsheng, Li Kai. Positioning model and simulation of conical scanning airborne laser bathymetry system[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(2): 0214001. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0214001 [34] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 17501−2017, 海洋工程地形测量规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 17501−2017, Specification for marine engineering topographic surveying[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. -




 下载:
下载: