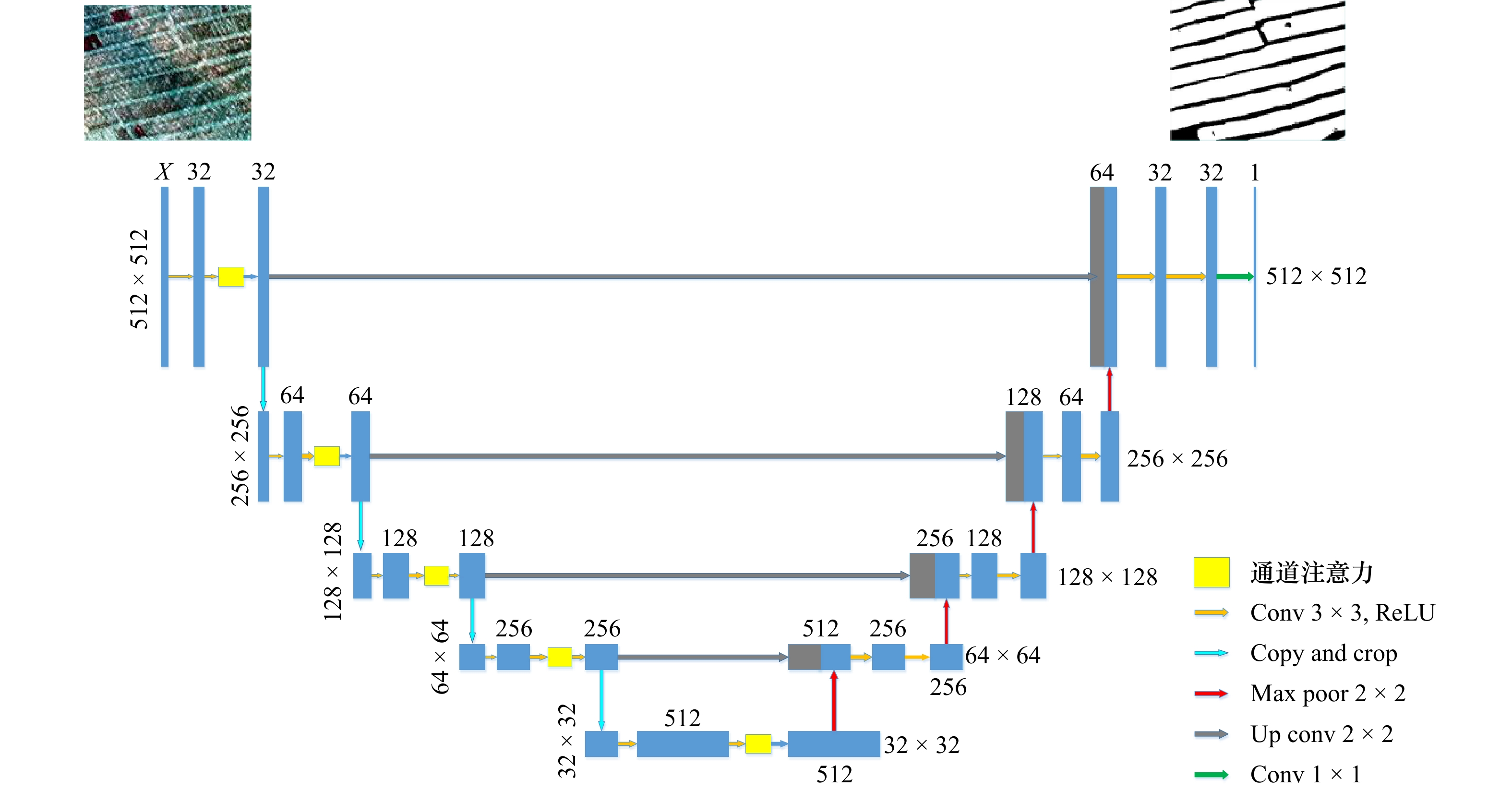
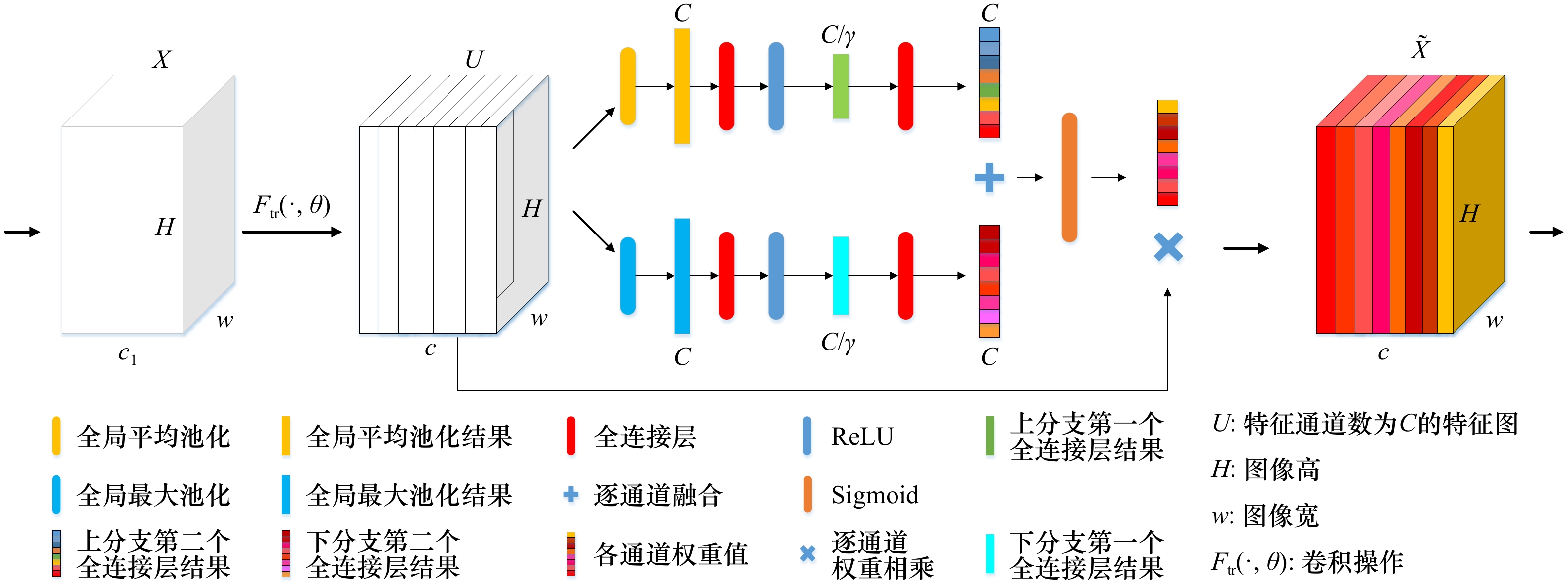
Extraction of the raft aquaculture area based on convolutional neural networks and data fusion
-
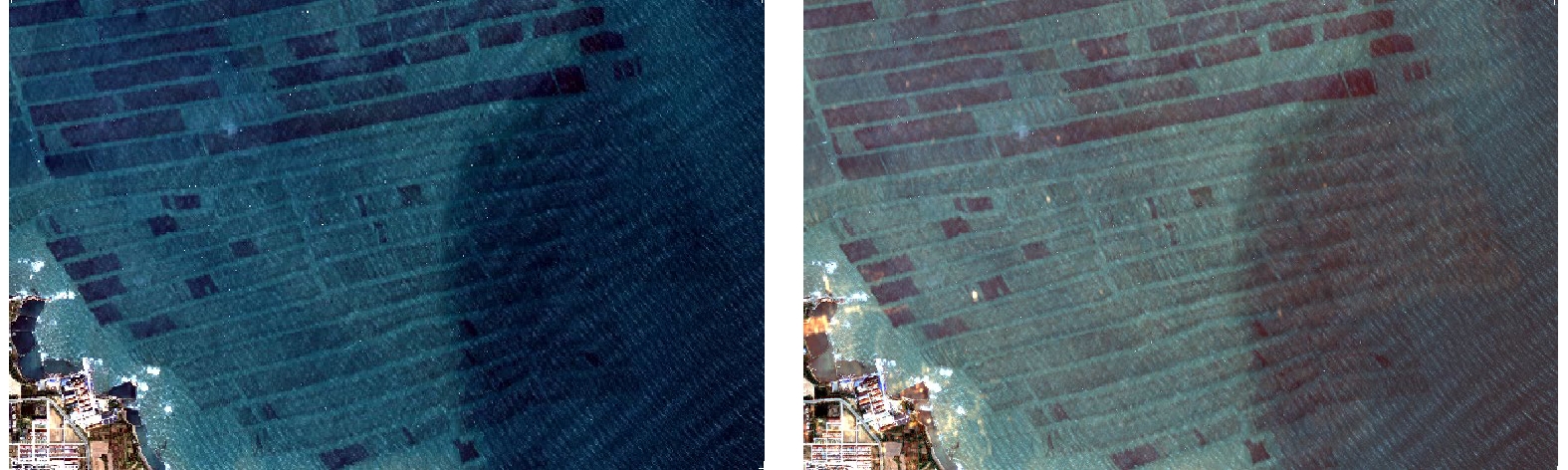
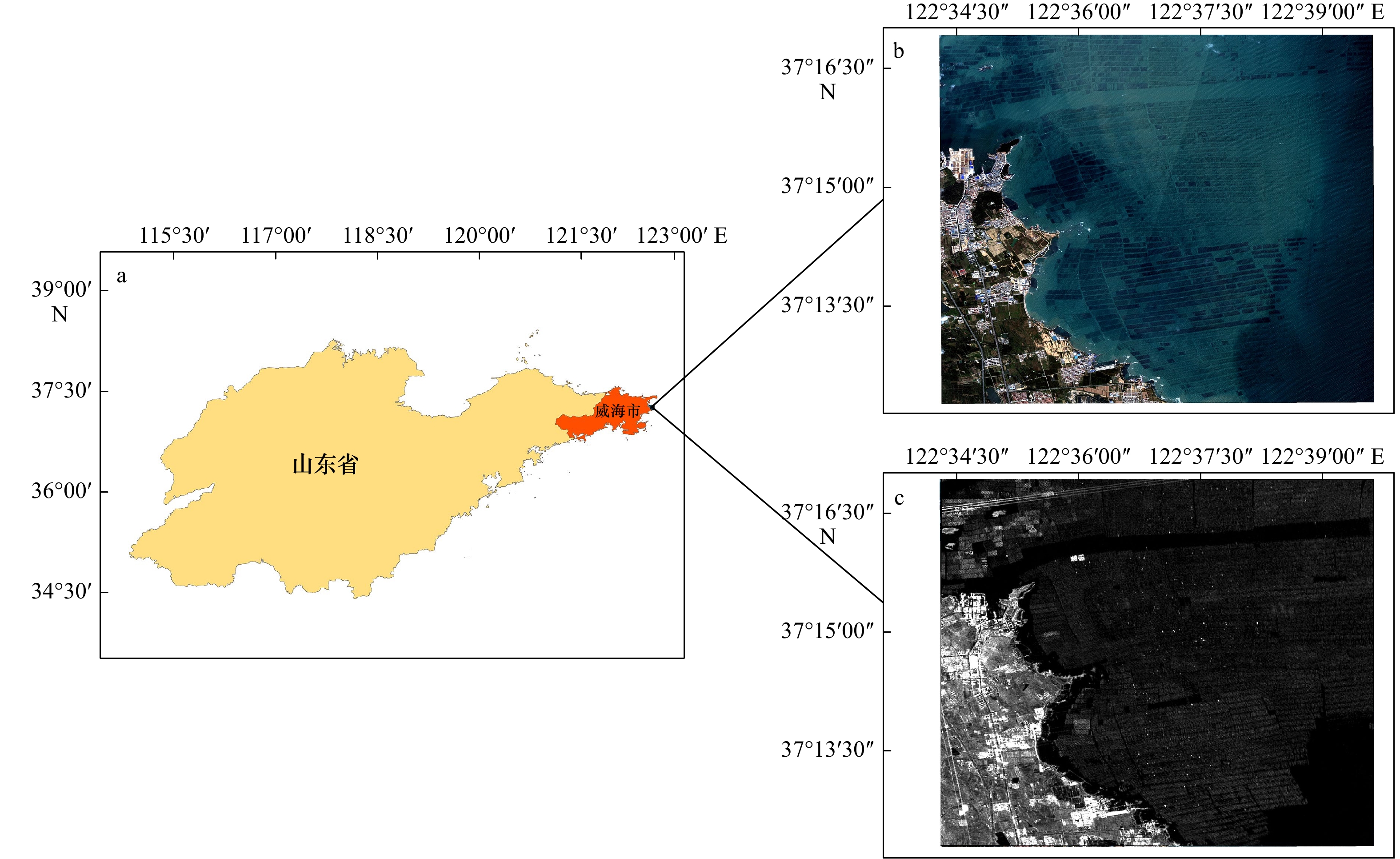
摘要: 准确提取海水筏式养殖区信息对于海洋资源管理和环境监测具有重要意义,但是筏式养殖区养殖筏因淹没于水中常出现数据弱信号区域的现象,导致仅凭光学影像提取精度较低。因此,本文以威海荣成湾为研究区域,通过添加通道注意力机制改进U-Net神经网络并结合高分2号光学影像光谱信息以及高分3号雷达影像纹理信息,尝试提高筏式养殖区提取精度。结果表明:(1)无论是对于单一的光学影像还是光学和雷达影像融合影像,添加通道注意力机制的U-Net神经网络预测结果总体精度都会提高,提高幅度在2.21%~4.12%之间。(2)利用改进后的U-Net神经网络处理融合数据,总体精度达到95.75%,相对于仅用高分2号影像的精度高4.3%;(3)对于弱信号区域,利用改进网络以及融合数据提取的总体精度和Kappa系数分别为91.61%和0.827 7。该方法可以对海洋筏式养殖区弱信号区域进行有效提取,能够为海洋养殖面积统计以及海洋环境检测提供技术支持。Abstract: Accurate extraction of marine raft aquaculture area information is of great significance for marine resource management and environmental monitoring. But the raft culture area is often submerged in water with weak data signal areas, resulting in low extraction accuracy based on optical images alone. Therefore, this paper takes Weihai Rongcheng Bay as the research area, and improves the U-Net neural network by adding channel attention mechanism to combine the spectral information of GF-2 optical image and the texture information of GF-3 radar image, trying to improve the extraction accuracy of raft aquaculture area. The results show that: (1) Whether it is a single optical image or a fusion image of optical and radar images, the overall accuracy of the prediction results of the U-Net neural network with channel attention mechanism will be improved, with an increase of 2.21%−4.12%. (2) Using the improved U-Net neural network to process the fusion data, the overall accuracy is 95.75%, which is 4.3% higher than that of only using GF-2 image. (3) For weak signal region, the overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient of extraction based on improved network and data fusion are 91.61% and 0.827 7, respectively. This method can effectively extract the weak signal area of marine raft aquaculture area, and can provide technical support for marine aquaculture area statistics and marine environment detection.
-
Key words:
- raft aquaculture area /
- weak signal area /
- channel attention mechanism /
- U-Net /
- image fusion
-
表 1 混淆矩阵
Tab. 1 Confusion matrix
真实值 模型预测结果 正例 反例 正例 TP FN 反例 FP TN 表 2 U-Net与SE_U-Net模型预测结果精度评估
Tab. 2 Evaluation of the extraction result for U-Net and SE_U-Net model
模型 GF2 GF23S GF23B U-Net 总体精度/% 85.30 87.47 91.33 Kappa系数 0.708 7 0.751 0 0.826 8 SE_U-Net 总体精度/% 89.42 89.68 93.71 Kappa系数 0.788 7 0.794 3 0.874 0 表 3 不同数据集预测精度
Tab. 3 Prediction accuracy for different datasets
数据集 类别 召回率/
%精确率/
%错分
率/%漏分
率/%F1分数 GF2 背景 95.08 88.61 11.39 4.92 91.73 养殖区 80.54 91.14 8.86 19.46 85.51 GF23S 背景 97.11 93.78 6.22 2.89 95.42 养殖区 89.74 95.12 4.88 10.26 92.35 GF23B 背景 96.96 96.16 3.84 3.04 96.56 养殖区 93.84 95.10 4.90 6.16 94.50 表 4 不同数据集预测结果精度评估
Tab. 4 Evaluation of the extraction result for different datasets
数据集 总体精度/% Kappa系数 GF2 89.47 0.772 9 GF23S 94.27 0.877 7 GF23B 95.75 0.910 2 表 5 弱信号区域预测结果精度评估
Tab. 5 Evaluation of the extraction result of the weak signal areas
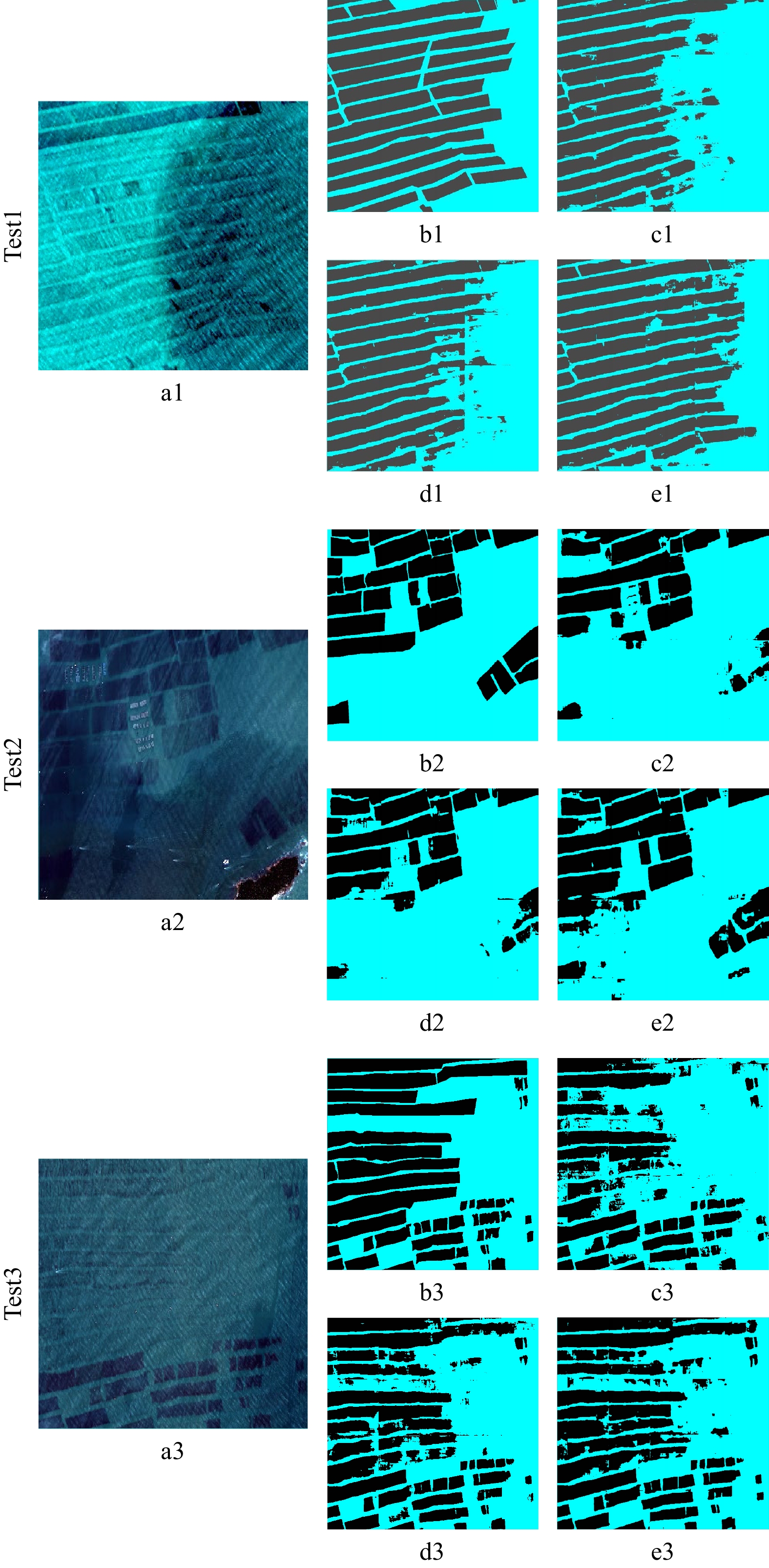
测试区 数据集 总体精度/% Kappa系数 Test1 GF2 81.41 0.6334 GF23S 84.75 0.6965 GF23B 91.61 0.8277 Test2 GF2 89.52 0.7463 GF23S 91.79 0.8052 GF23B 94.30 0.8717 Test3 GF2 82.40 0.6428 GF23S 88.18 0.7620 GF23B 91.59 0.8309 -
[1] Gu Yangguang, Lin Qin, Jiang Shijun, et al. Metal pollution status in Zhelin Bay surface sediments inferred from a sequential extraction technique, South China Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2014, 81(1): 256−261. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.01.030 [2] Han Qingxi, Wang Yueqi, Zhang Yong, et al. Effects of intensive scallop mariculture on macrobenthic assemblages in Sishili Bay, the northern Yellow Sea of China[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2013, 718(1): 1−15. doi: 10.1007/s10750-013-1590-x [3] Wartenberg R, Feng Limin, Wu Jiajun, et al. The impacts of suspended mariculture on coastal zones in China and the scope for integrated multi-trophic aquaculture[J]. Ecosystem Health and Sustainability, 2017, 3(6): 1340268. doi: 10.1080/20964129.2017.1340268 [4] Kang Y H, Hwang J R, Chung I K, et al. Development of a seaweed species-selection index for successful culture in a seaweed-based integrated aquaculture system[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2013, 12(1): 125−133. doi: 10.1007/s11802-013-1928-z [5] Cheng Bo, Liang Chenbin, Liu Xunan, et al. Research on a novel extraction method using deep learning based on GF-2 images for aquaculture areas[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(9): 3575−3591. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1706009 [6] 钟勇. 基于深度学习的筏式养殖区识别与检测方法[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学, 2019.Zhong Yong. Recognition and detection method of raft aquaculture area based on deep learning[D]. Qingdao: Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2019. [7] 杨英宝, 江南, 殷立琼, 等. 太湖围湖利用及网围养殖的遥感调查与分析[J]. 农村生态环境, 2005, 21(3): 25−28.Yang Yingbao, Jiang Nan, Yin Liqiong, et al. Remote sensing investigation and analysis of ponding and enclosure culture in Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2005, 21(3): 25−28. [8] 刘晓, 黄海军, 杨曦光, 等. 基于SPOT影像的筏式养殖区提取方法研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2013, 38(2): 41−43. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2013.02.033Liu Xiao, Huang Haijun, Yang Xiguang, et al. Method to extract raft-cultivation area based on SPOT image[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(2): 41−43. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2013.02.033 [9] 胡园园, 范剑超, 王钧. 广义统计区域合并的SAR图像浮筏养殖信息提取[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2017, 22(5): 610−621.Hu Yuanyuan, Fan Jianchao, Wang Jun. Modifying generalized statistical region merging for unsupervised extraction of floating raft aquaculture in SAR images[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2017, 22(5): 610−621. [10] Cui Yishuo, Zhang Xuehong, Jiang Nan, et al. Remote sensing identification of marine floating raft aquaculture area based on sentinel-2A and DEM data[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9: 955858. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.955858 [11] Hu Fan, Xia Guisong, Hu Jingwen, et al. Transferring deep convolutional neural networks for the scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(11): 14680−14707. doi: 10.3390/rs71114680 [12] Kussul N, Lavreniuk M, Skakun S, et al. Deep learning classification of land cover and crop types using remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(5): 778−782. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2681128 [13] Li Erzhu, Xia Junshi, Du Peijun, et al. Integrating multilayer features of convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5653−5665. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2711275 [14] Ding Lei, Tang Hao, Lorenzo Bruzzone. LANet: Local attention embedding to improve the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 426−435. [15] Lu Yimin, Shao Wei, Sun Jie. Extraction of offshore aquaculture areas from medium-resolution remote sensing images based on deep learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(19): 3854. doi: 10.3390/rs13193854 [16] Cui Bin’ge, Fei Dong, Shao Guanghui, et al. Extracting raft aquaculture areas from remote sensing images via an improved U-net with a PSE structure[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(17): 2053. doi: 10.3390/rs11172053 [17] Zhang Yi, Wang Chengyi, Ji Yuan, et al. Combining segmentation network and nonsubsampled contourlet transform for automatic marine raft aquaculture area extraction from sentinel-1 images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(24): 4182. doi: 10.3390/rs12244182 [18] 李连伟, 张源榆, 岳增友, 等. 基于全卷积网络模型的高分遥感影像内陆网箱养殖区提取[J]. 山东科学, 2022, 35(2): 1−10. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2022.02.001Li Lianwei, Zhang Yuanyu, Yue Zengyou, et al. Extracting inland cage aquacultural areas from high-resolution remote sensing images using fully convolutional networks model[J]. Shandong Science, 2022, 35(2): 1−10. doi: 10.3976/j.issn.1002-4026.2022.02.001 [19] 于慧男. 基于光学影像与SAR影像融合的海洋浮筏养殖区提取[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.Yu Huinan. Extracting marine floating raft region based on fusion of optical image and radar image[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. [20] 陈家长, 孟顺龙, 胡庚东, 等. 空心菜浮床栽培对集约化养殖鱼塘水质的影响[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2010, 26(2): 155−159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.02.011Chen Jiazhang, Meng Shunlong, Hu Gengdong, et al. Effect of ipomoea aquatica cultivation on artificial floating rafts on water quality of intensive aquaculture ponds[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2010, 26(2): 155−159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4831.2010.02.011 [21] 耿杰, 范剑超, 初佳兰, 等. 基于深度协同稀疏编码网络的海洋浮筏SAR图像目标识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 593−604.Geng Jie, Fan Jianchao, Chu Jialan, et al. Research on marine floating raft aquaculture SAR image target recognition based on deep collaborative sparse coding network[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 593−604. [22] 张瑞, 刘国祥, 于慧男, 等. 基于SAR和光学影像融合的近海浮筏养殖区提取方法: 202010128207.2[P]. 2020−06−26.Zhang Rui, Liu Guoxiang, Yu Huinan, et al. Extraction method of offshore floating raft aquaculture area based on SAR and optical image fusion. 202010128207.2[P]. 2020−06−26. [23] 武易天. 基于遥感影像的近海岸水产提取方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院遥感与数字地球研究所), 2017.Wu Yitian. Research on coastal aquaculture detection using remote sensing images[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2017. [24] 邵亚奎, 朱长明, 张新, 等. 国产高分卫星遥感影像融合方法比较与评价[J]. 测绘通报, 2019(6): 5−10.Shao Yakui, Zhu Changming, Zhang Xin, et al. Comparison of diffirent fusion methods and their performance evaluation to high spatial resolution remote sensing data of GF[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2019(6): 5−10. [25] 福建省统计局, 国家统计局福建调查总队. 福建统计年鉴2016[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2016.Fujian Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Survey Office of the National Bureau of Statistics in Fujian. Fujian Statistical Yearbook 2016[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2016. [26] 刘海江, 张建辉, 何立环, 等. 我国县域尺度生态环境质量状况及空间格局分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2010, 26(6): 62−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2010.06.017Liu Haijiang, Zhang Jianhui, He Lihuan, et al. Analysis of the status and spatial distribution patterns of county-level eco-environmental quality of China[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2010, 26(6): 62−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2010.06.017 [27] 王井利, 马畅, 张宁. 基于遥感归一化指数的生态环境破坏和恢复能力的监测与评价[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(4): 676−683.Wang Jingli, Ma Chang, Zhang Ning. Monitoring and evaluation of ecological environmental damage and recovery capability based on remote sensing image normalization index[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science), 2018, 34(4): 676−683. [28] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich: Springer, 2015: 234−241. [29] Hu Jie, Shen Li, Sun Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 7132−7141. [30] Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 3−19. [31] Liu Chenxi, Jiang Tao, Zhang Zhen, et al. Extraction method of offshore mariculture area under weak signal based on multisource feature fusion[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(2): 99. doi: 10.3390/jmse8020099 [32] Jiang Zongchen, Ma Yi. Accurate extraction of offshore raft aquaculture areas based on a 3D-CNN model[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(14): 5457−5481. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1737340 -




 下载:
下载: