The study of the influences of wave-current interaction on significant wave height under serious sea conditions
-
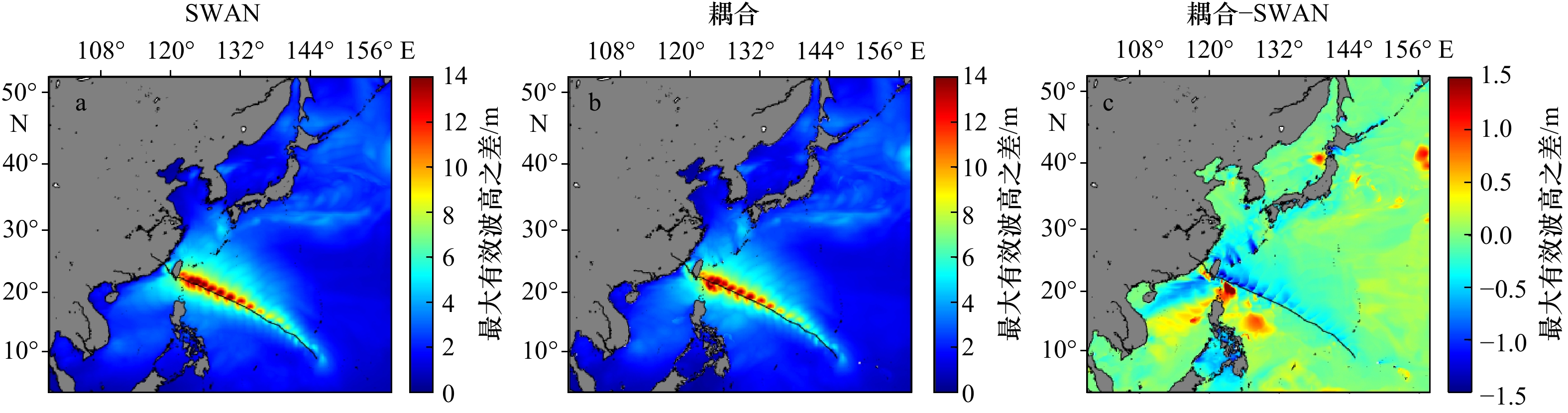
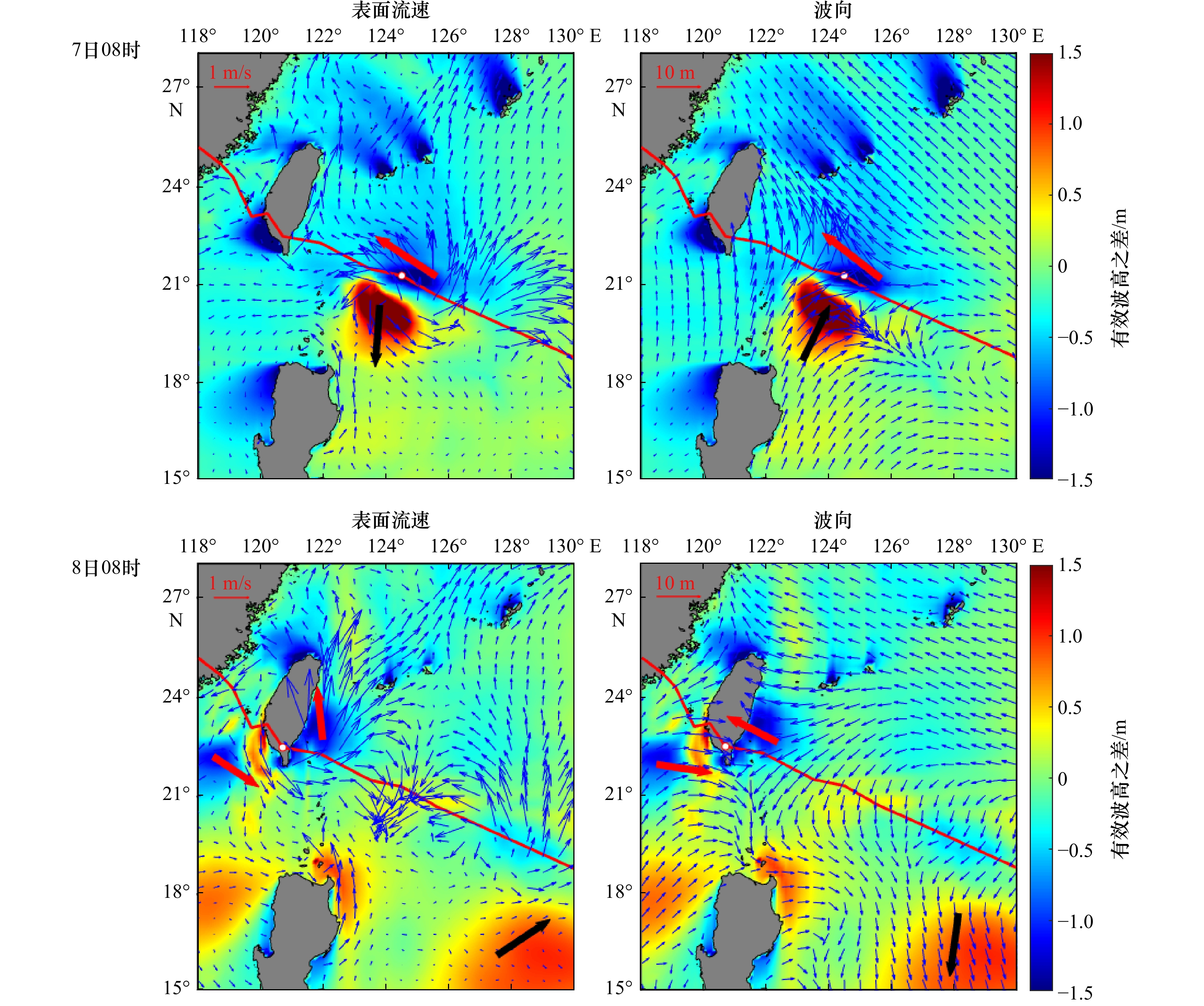
摘要: 波流相互作用作为非线性科学的前沿课题,一直受到国内外广大学者的关注。本文以2016年第1号超强台风“尼伯特”为例,基于波流耦合模式研究了台风影响期间强海况下波流相互作用对有效波高的影响。研究表明:(1)波流耦合模式可有效提高强海况下海浪的模拟精度;(2)波流相互作用对有效波高的影响与波向和流向之间的夹角关系密切:当波向与流向大致相同时,波流相互作用使有效波高减小;当波向与流向大致相反时,波流相互作用使有效波高增大;当波向与流向之间的夹角越接近90°时,波流相互作用对有效波高的影响越小。波流相互作用对有效波高的影响最大可达1.5 m。Abstract: As a frontier subject of nonlinear science, wave-current interaction has been studied by many scholars. This paper will explore the wave-current interaction under the serious sea conditions in the Northwest Pacific during the influenced by No.1 super Typhoon “Nepartak” in 2016. The results indicate that wave-current coupling model can effectively improve the simulation accuracy of significant wave height (SWH) under serious sea conditions. The influence of wave-current interaction on SWH is closely related to the angle between wave direction and sea surface current direction: when wave direction is close to current direction, wave-current interaction will decrease the SWH; in those areas where the wave and the current have the opposite direction, wave-current interaction will increase the SWH; the closer the angle between the wave and the current is to 90°, the less influence wave-current interaction has on the SWH. The maximum SWH difference whether including wave-current interaction or not is about 1.5 m.
-
表 1 波−流耦合模式交换的变量
Tab. 1 Variables of wave−current coupling mode exchange
耦合子模式 SWAN波浪模式 ROMS海洋模式 交换的变量 Dwave波向 zeta自由表面高度 Hwave有效波高 VEL_x表层流速x方向的分量 Lwave平均波长 VEL_y表层流速y方向的分量 Pwave_bot底部的波浪周期 …… Pwave_top 表层峰谱周期 …… 表 2 各浮标处分析风速和观测风速的标准偏差与平均绝对误差(单位:m/s )
Tab. 2 The standard deviation and mean absolute error of the analyzed and the observed wind speed at each buoy (unit: m/s)
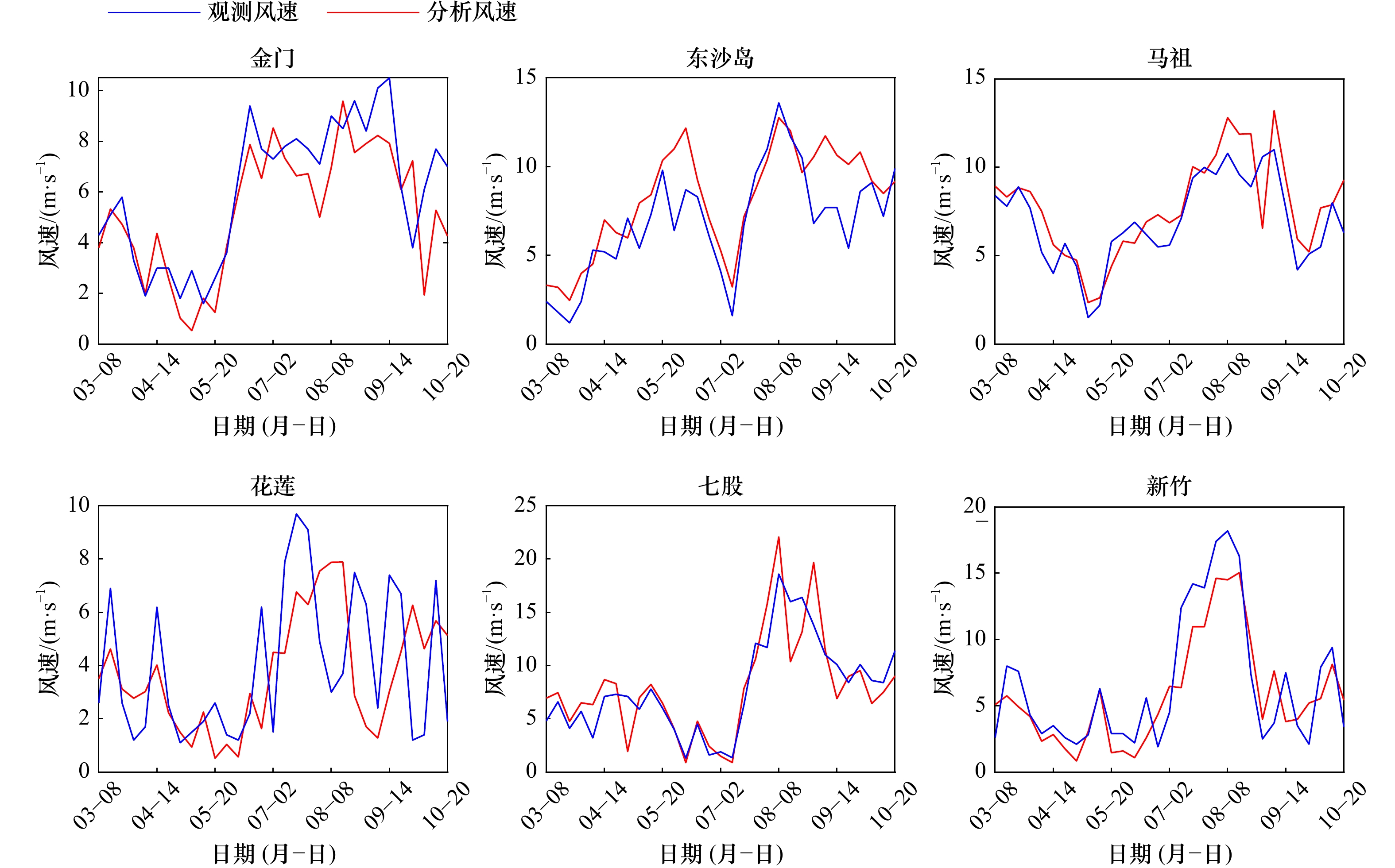
金门 东沙岛 马祖 花莲 七股 新竹 平均值 标准偏差 1.708 6 2.104 6 1.642 5 2.854 1 2.462 5 3.503 4 2.379 2 平均绝对误差 1.343 4 1.650 1 1.284 2 2.341 5 1.785 7 2.037 3 1.740 3 表 3 模拟和观测有效波高的统计变量比较
Tab. 3 Comparison of statistical variables between simulated significane wave height and observed significant wave height
统计变量 金门 东沙岛 马祖 花莲 七股 新竹 相关系数 SWAN 0.952 4 0.784 0 0.904 3 0.965 0 0.763 6 0.945 6 耦合 0.966 3 0.828 4 0.919 5 0.962 2 0.873 8 0.961 6 标准偏差 SWAN 0.107 1 2.065 0 0.633 5 4.776 5 3.300 0 2.379 1 耦合 0.494 4 1.648 0 0.064 2 1.729 4 1.691 5 1.548 8 平均绝对误差 SWAN 0.107 1 2.065 0 0.633 5 4.776 5 3.300 0 2.379 1 耦合 0.494 4 1.648 0 0.064 2 1.729 4 1.691 5 1.548 8 -
[1] Wang Pengcheng, Sheng Jinyu. A comparative study of wave-current interactions over the eastern Canadian shelf under severe weather conditions using a coupled wave-circulation model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(7): 5252−5281. doi: 10.1002/2016JC011758 [2] Kemp P H, Simons R R. The interaction between waves and a turbulent current: waves propagating with the current[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1982, 116: 73−89. [3] Longuet-Higgins M S, Stewart R W. Changes in the form of short gravity waves on long waves and tidal currents[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1960, 8(4): 565−583. doi: 10.1017/S0022112060000803 [4] Longuet-Higgins M S, Stewart R W. Radiation stress and mass transport in gravity waves, with application to “surf beats”[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1962, 13(4): 481−504. doi: 10.1017/S0022112062000877 [5] Whitham G B. A general approach to linear and non-linear dispersive waves using a lagrangian[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1965, 22(2): 273−283. doi: 10.1017/S0022112065000745 [6] Rretherton F P, Garret C J R. Wavetrains in inhomogeneous moving media[J]. Phys Oceanogr, 1968, 25: 1333−1349. [7] Dietrich J C, Tanaka S, Westerink J J, et al. Performance of the unstructured-mesh, SWAN+ADCIRC model in computing hurricane waves and surge[J]. Journal of Scientific Computing, 2012, 52(2): 468−497. doi: 10.1007/s10915-011-9555-6 [8] Pietrafesa L J, Xie L, Dickey D A, et al. The North Carolina State University coastal and estuary storm surge and flood prediction system[J]. Ecosystems and Sustainable Development, 2003, 63: 100−109. [9] Warner J C, Armstrong B, He R Y, et al. Development of a coupled ocean–atmosphere–wave–sediment transport (COAWST) modeling system[J]. Ocean Modelling, 2010, 35(3): 230−244. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2010.07.010 [10] Kumar N, Voulgaris G, Warner J C. Implementation and modification of a three-dimensional radiation stress formulation for surf zone and rip-current applications[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2011, 58(12): 1097−1117. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2011.06.009 [11] 桂祈军, 沙文钰. 黄渤海春季浪流耦合数值模拟[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 6(1): 71−75.Gui Qijun, Sha Wenyu. Numerical simulation of coupling wave-current in Huang-hai and Bo-hai sea in spring[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2005, 6(1): 71−75. [12] 刘永玲, 王秀芹, 王淑娟. 波浪对风暴潮影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2007(S1): 1-7.Liu Yongling, Wang Xiuqin, Wang Shujuan. A numerical study of the influence of waves on storm surges[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2007, (S1): 1−7. [13] 张志远, 宋顺强, 刘利, 等. 浪流耦合模式数值模拟及检验分析[J]. 海洋技术, 2011, 30(4): 87−92.Zhang Zhiyuan, Song Shunqiang, Liu Li, et al. Numerical simulation and verification of the wave-circulation coupled model[J]. Ocean Technology, 2011, 30(4): 87−92. [14] 夏波, 张庆河, 蒋昌波. 基于非结构网格的波流耦合数值模式研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2013, 44(6): 1451−1456.Xia Bo, Zhang Qinghe, Jiang Changbo. A coupled wave-current numerical model on unstructured grids[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2013, 44(6): 1451−1456. [15] Yang Jingling, Jiang Shaocai, Wu Junshan, et al. Effects of wave-current interaction on the waves, cold-water mass and transport of diluted water in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2020, 39(1): 25−40. doi: 10.1007/s13131-019-1529-9 [16] Shan Zhigang, Zhu Zhipeng, Wang Dong, et al. Numerical modeling of the dynamic response of an elastoplastic seabed under wave-current interactions[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2023, 22(1): 43−52. doi: 10.1007/s11802-023-5076-9 [17] Li Zhao, Li Shuiqing, Hou Yijun, et al. Typhoon-induced wind waves in the northern East China Sea during two typhoon events: the impact of wind field and wave-current interaction[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2022, 40(3): 934−949. doi: 10.1007/s00343-021-1089-7 -





 下载:
下载: