Distribution coefficients of trace elements between Merulinidae coral aragonite skeletons and seawater in the Weizhou Island, the northern South China Sea: Species and Rayleigh dependencies
-
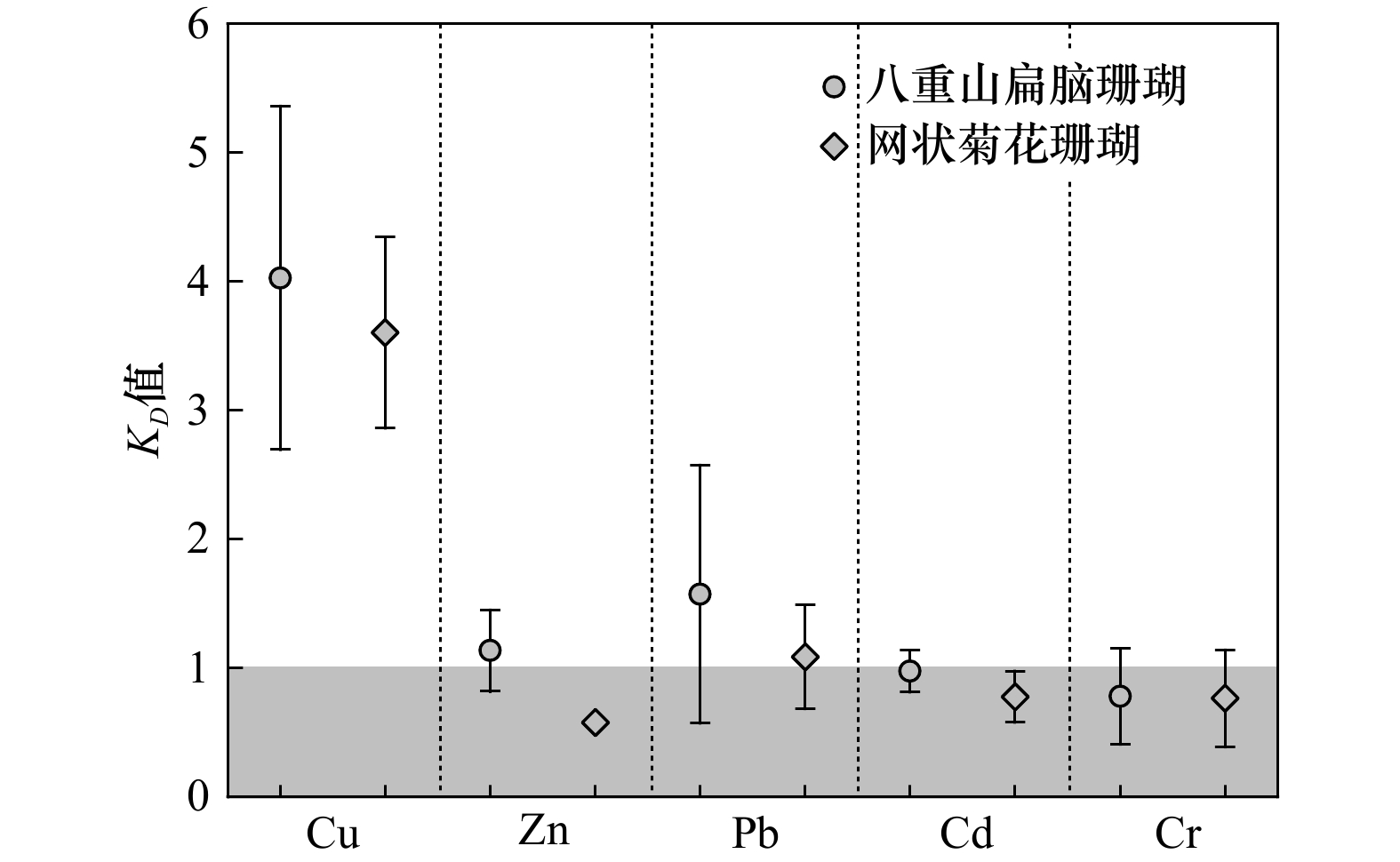
摘要: 微量元素在珊瑚文石骨骼和海水间的分配过程是控制海水中微量元素进入珊瑚骨骼的关键环节,表征该分配过程的分配系数(KD)常用于时间序列上的海水微量元素含量重建。由于缺乏珊瑚和海水的原位研究,我们对珊瑚文石骨骼与海水之间微量元素的分配行为的了解非常有限,这严重阻碍了我们对于准确的海水化学定量数据的获取。本研究中,我们选取了南海北部涠洲岛海域的两种典型的造礁石珊瑚种(网状菊花珊瑚(Goniastrea retiformis)和八重山扁脑珊瑚(Platygyra yaeyamaensis))和周围原位表层海水中的5种微量元素(Cu、Zn、Pb、Cd和Cr)进行研究,估算了这些微量元素在珊瑚文石骨骼和海水之间的分配系数。研究结果表明:各个微量元素在网状菊花珊瑚和八重山扁脑珊瑚文石骨骼和海水间的分配系数分别为3.65和3.49(Cu);0.57和0.97(Zn);1.06和1.42(Pb);0.88和1.01(Cd);0.66和0.60(Cr)。结合前人报道的各个种属珊瑚的分配系数,我们发现不同珊瑚种属Cu、Zn、Pb和Cd的KD值存在显著差异,而Cr的KD值差异则相对较小。此外,微量元素KD值还在一定程度上受到瑞利分馏的影响,该影响与KD值的大小有关。本研究为珊瑚文石骨骼和海水间分配系数提供了较为准确的KD值,为未来的珊瑚研究提供了重要的基础数据,并扩展了我们对海洋生物成因矿物晶格的化学特征的认识。Abstract: The distribution process of trace elements between coral aragonite skeletons and seawater is a key link to control the incorporating of trace elements in seawater into coral skeletons. The distribution coefficient (KD) characterizing this distribution process is often used to reconstruct the contents of trace elements in seawater in time series. Lacking of in situ research on corals and seawater, the limited knowledge related to the distribution behavior of trace elements between coral aragonite skeletons and seawater seriously hindered our acquisition of accurate chemical quantitative data on seawater. In this study we selected two typical reef-building coral species (Goniastrea retiformis and Platygyra yaeyamaensis) and five trace elements (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd and Cr) in the surrounding in-situ surface seawater of Weizhou Island in the northern South China Sea, and estimated the distribution coefficients of these trace elements between the coral aragonite skeleton and seawater. Results revealed that the KD value of G. retiformis for Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Cr was 3.65, 0.57, 1.06, 0.88, 0.66 respectively; the KD value of P. yaeyamaensis was 3.49, 0.97, 1.42, 1.01, 0.60 respectively. We found a significant difference among different coral species in the KD values of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd, but no significant difference for Cr. The results indicate that the KD values of trace elements are affected by the Rayleigh fractionation, which is related to the numerical values of KD. The study provided relatively accurate KD values for coral aragonite skeleton and seawater, represented important basic data for future research on coral reefs, and expanded our knowledge of chemical signature in biogenic lattices associated with marine organism.
-
Key words:
- in situ seawater /
- Rayleigh fractionation /
- trace element /
- Merulinidae coral /
- South China Sea
-
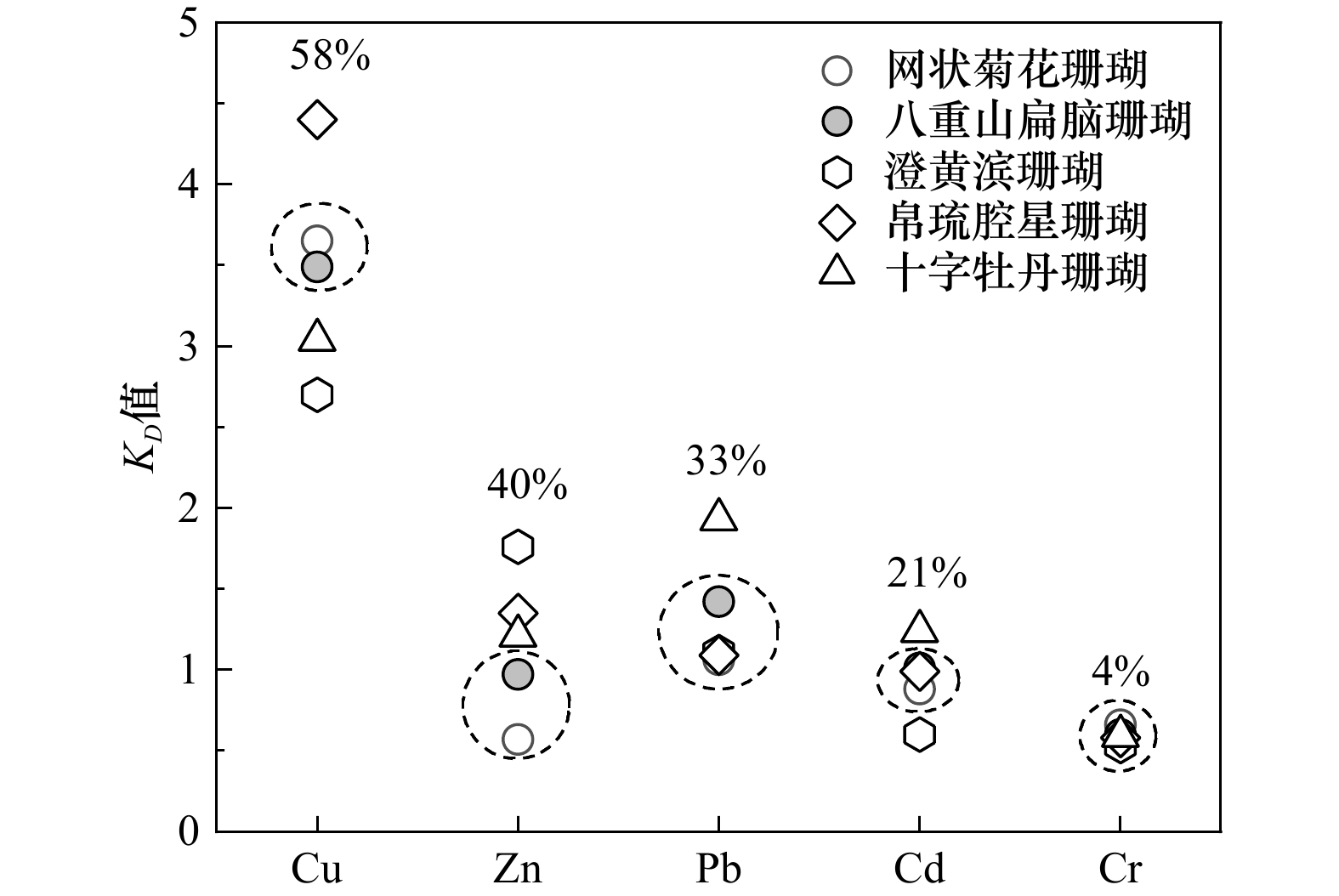
图 5 涠洲岛海域不同种属珊瑚微量元素的KD值
虚线圈标记了本研究估算的珊瑚属KD值位置,数字为相对标准偏差
Fig. 5 Distribution coefficients KD of trace elements for various species of corals from the seawater in the Weizhou Island
The broken circles represent the distribution coefficients KD of Pavona corals, and the numbers are relative standard deviations
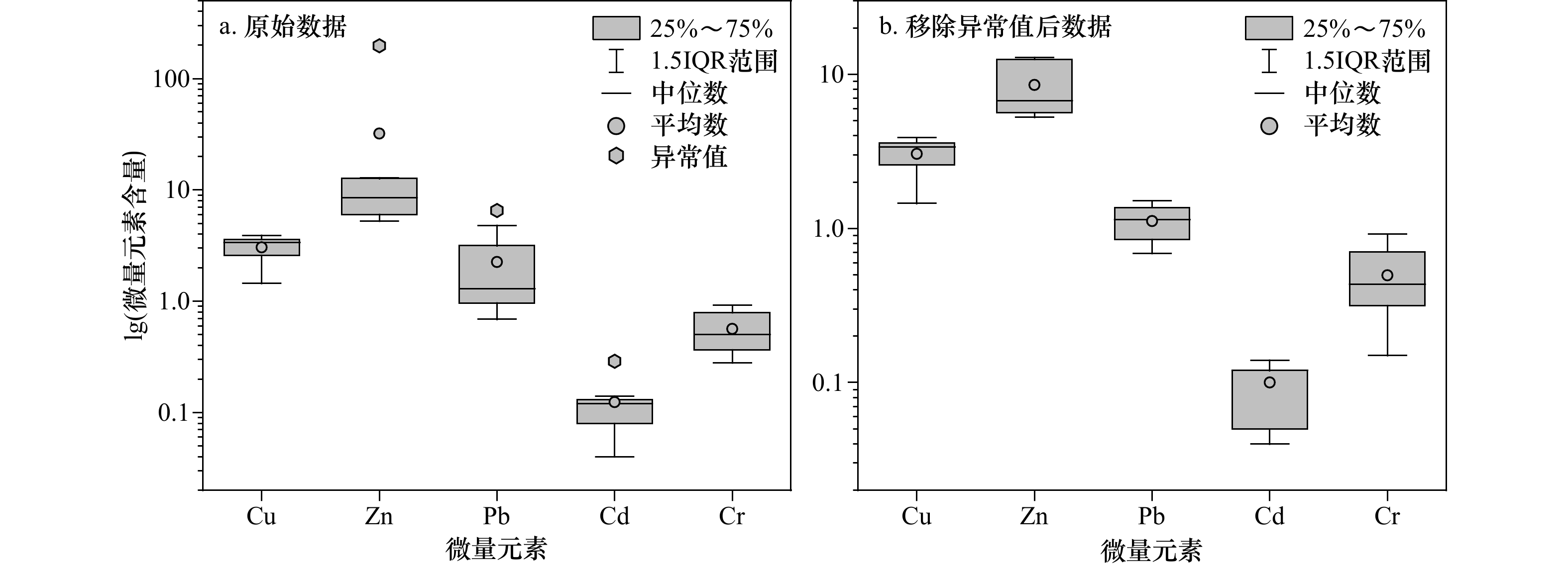
表 1 本研究采集的涠洲岛珊瑚文石骨骼微量元素含量(单位:μg/g)
Tab. 1 The contents of trace elements (unit: μg/g) in coral skeletons collected in Weizhou Island
珊瑚种类 位置 珊瑚采集点位 Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr 网状菊花珊瑚 (Goniastrea retiformis) W1 W1-1 3.40 197.40 1.08 0.11 0.35 W3 W3-1a 3.33 6.71 1.37 0.14 0.49 W3-2 2.60 5.63 0.69 0.12 0.90 W3-1b 3.69 12.87 1.51 0.29 0.51 八重山扁脑珊瑚(Platygyra yaeyamaensis) W4 W4-2 1.45 5.26 0.85 0.05 0.28 W5 W5-2 3.49 12.52 6.52 0.12 0.92 W5-1 2.56 6.41 4.80 0.04 0.38 W6 W6-1 3.89 10.29 1.21 0.12 0.68 注:斜体为移除的异常值。 表 2 南海不同海域珊瑚骨骼微量元素平均含量(单位:μg/g)
Tab. 2 Average content of trace elements in coral skeletons in the Souch China Sea (unit: μg/g)
位置 珊瑚种类 Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr 参考文献 广西涠洲岛 网状菊花珊瑚(Goniastrea retiformis) 3.11 6.17 1.05 0.12 0.58 本研究 八重山扁脑珊瑚(Platygyra yaeyamaensis) 3.02 9.47 1.19 0.08 0.55 本研究 广西涠洲岛 澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea) 2.70 19.23 1.58 0.09 0.72 文献[29] 帛琉腔星珊瑚(Coelastrea palauensis) 3.74 27.71 1.52 0.16 0.98 文献[29] 十字牡丹珊瑚 (Pavona decussata) 2.52 17.6 2.51 0.15 0.54 文献[29] 西沙永兴岛 帛琉腔星珊瑚(Coelastrea palauensis) 2.34 21.11 − 0.09 − 文献[30] 鹿角杯形珊瑚(Pocillopora damicornis) 3.81 26.41 − 0.14 − 文献[30] 西沙永兴岛 澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea) 1.27 2.56 0.36 0.0025 0.30 文献[31] 广东大亚湾 澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea) 11.7 16.9 1.02 0.10 1.08 文献[32] 小角刺柄珊瑚(Hydnophora microconos) 7.71 3.74 1.84 − − 文献[33] 马来西亚沙巴 标准盘星珊瑚 (Favia speciosa) 8.72 4.69 1.79 − − 文献[33] 团块滨珊瑚(Porites lobata) 6.97 4.12 1.37 − − 文献[33] 注:“−”代表无数据。 表 3 从涠洲岛采集的海水pH、SST(单位:℃)、表层海水盐度(SSS)和溶解微量元素含量(单位:μg/L),以及基于高分辨率珊瑚数据的调整系数[21]
Tab. 3 The pH, SST (unit: °C), surface sea salinity (SSS) and the contents (unit: μg/L) of dissolved trace elements of the seawater samples collected from Weizhou Island, as well as the adjustment coefficients based on the high resolution coral data [21]
位置 pH SST SSS Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr W1-1 8.42 27.6 32.0 0.96 10.66 0.92 0.11 0.90 W1-2 8.46 27.8 31.9 1.16 11.53 0.52 0.12 0.92 W3-1 8.37 27.1 32.6 0.93 8.41 0.69 0.068 0.70 W3-2 8.39 27.3 32.5 1.01 8.03 0.80 0.07 0.79 W4-1 8.88 27.3 32.2 0.40 3.25 0.19 0.021 0.67 W4-2 8.93 27.4 32.7 0.41 3.92 0.24 0.024 0.70 W5-1 8.45 27.2 32.4 0.88 4.83 0.24 0.046 0.58 W5-2 8.59 27.6 32.8 1.05 5.75 0.56 0.05 0.66 W6-1 8.43 27.6 31.9 0.55 8.35 1.23 0.042 0.99 W6-2 8.46 27.8 32.0 0.60 8.9 1.62 0.046 1.00 平均值 8.53 27.5 32.3 0.82 7.23 0.65 0.051 0.79 一类海水水质标准 5 20 1 1 50 调整系数 0.85 0.61 0.63 0.38 0.80 表 4 涠洲岛两种珊瑚中微量元素的分配系数及其他珊瑚种属参考值对比
Tab. 4 The comparison of calculated distribution coefficients for trace metals among two species of corals from Weizhou Island and reference values of other coral species
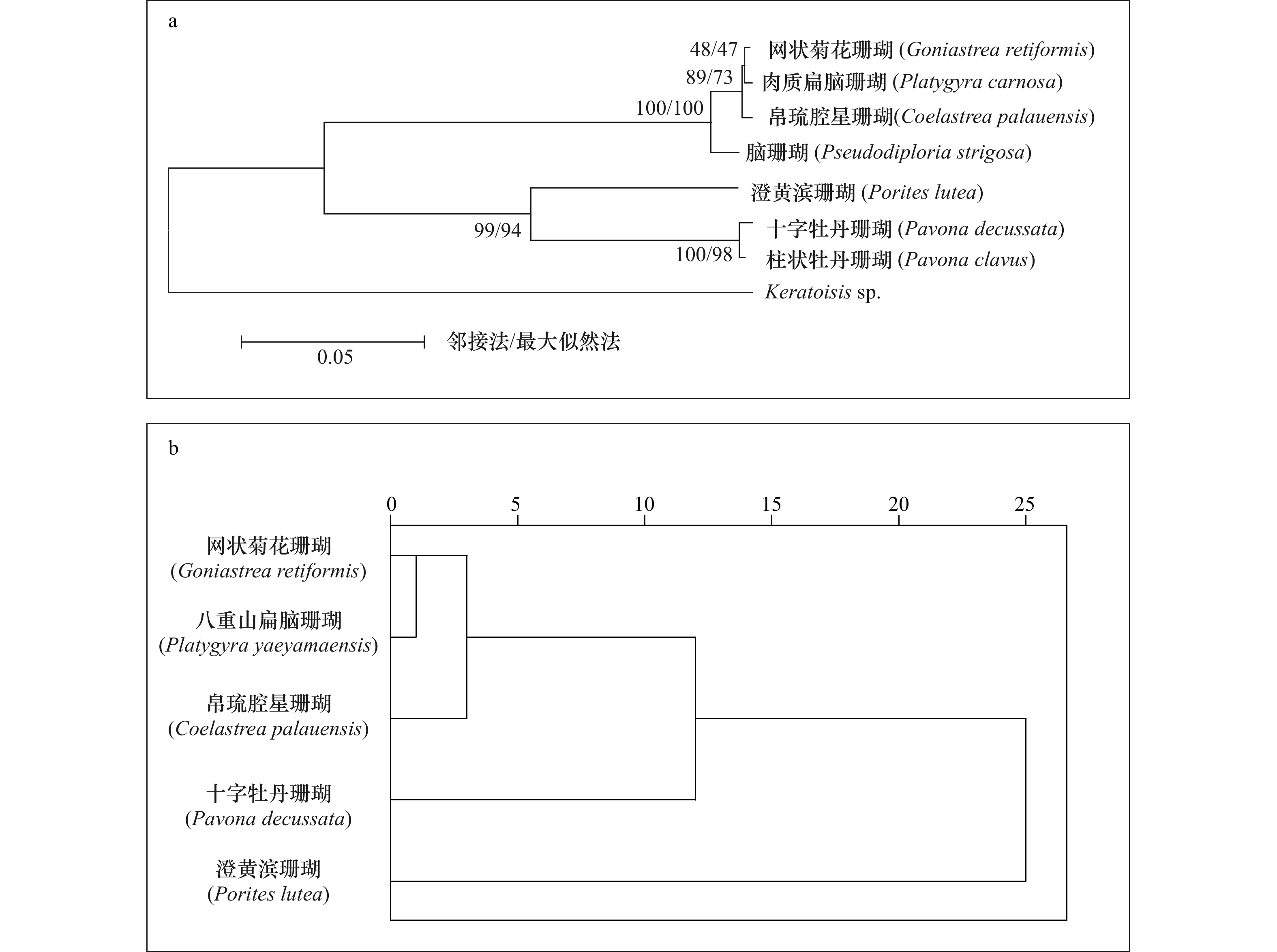
珊瑚物种 位置 Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr 本研究 网状菊花珊瑚(Goniastrea retiformis) W1-1 4.32 − 1.06 0.55 0.45 W3-1 3.65 0.59 1.50 0.90 0.66 W3-2 2.84 0.56 0.70 0.88 1.18 平均值 3.60 0.57 1.08 0.78 0.76 中值 3.65 0.57 1.06 0.88 0.66 八重山扁脑珊瑚(Platygyra yaeyamaensis) W3-1 3.49 0.96 1.42 − 0.60 W4-2 3.55 0.97 2.64 1.01 0.38 W5-1 3.48 1.42 − 0.75 1.06 W5-2 3.22 1.52 − 1.01 1.27 W6-1 6.40 0.80 0.66 1.13 0.58 平均值 4.03 1.13 1.58 0.98 0.78 中值 3.49 0.97 1.42 1.01 0.60 参考值 澄黄滨珊瑚(Porites lutea)[21] 2.70 1.76 1.11 0.60 0.53 帛琉腔星珊瑚(Coelastrea palauensis)[21] 4.40 1.35 1.09 0.99 0.58 十字牡丹珊瑚(Pavona decussata)[21] 3.04 1.21 1.93 1.24 0.59 柱状牡丹珊瑚(Pavona clavus) 0.36[17] 0.7~1.3[19], 1 [7, 12], 0.76[20] 脑珊瑚(Pseudodiploria strigosa) 1[7] 2.3[12] -
[1] Forget G, Ferreira D. Global ocean heat transport dominated by heat export from the tropical Pacific[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2019, 12(5): 351−354. doi: 10.1038/s41561-019-0333-7 [2] Gagan M K, Ayliffe L K, Beck J W, et al. New views of tropical paleoclimates from corals[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(1/5): 45−64. [3] Thompson D M. Environmental records from coral skeletons: a decade of novel insights and innovation[J]. WIRES Climate Change, 2022, 13(1): e745. [4] Saha N, Webb G E, Zhao J X. Coral skeletal geochemistry as a monitor of inshore water quality[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 566–567: 652−684. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.066 [5] Yu Kefu. Coral reefs in the South China Sea: their response to and records on past environmental changes[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(8): 1217−1229. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4449-5 [6] Shen G T. Lead and cadmium geochemistry of corals: reconstruction of historic perturbations in the upper ocean[D]. Cambridge, Mass, United States: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1986. [7] Shen G T, Boyle E A. Determination of lead, cadmium and other trace metals in annually-banded corals[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 67(1/2): 47−62. [8] Sholkovitz E, Shen G T. The incorporation of rare earth elements in modern coral[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(13): 2749−2756. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00170-5 [9] Wyndham T, McCulloch M, Fallon S, et al. High-resolution coral records of rare earth elements in coastal seawater: biogeochemical cycling and a new environmental proxy[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(9): 2067−2080. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.11.004 [10] Barnard L A, Macintyre I G, Pierce J W. Possible environmental index in tropical reef corals[J]. Nature, 1974, 252(5480): 219−220. doi: 10.1038/252219a0 [11] Hanna R G, Muir G L. Red sea corals as biomonitors of trace metal pollution[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 1990, 14(2/3): 211−222. [12] Shen G T, Boyle E A. Lead in corals: reconstruction of historical industrial fluxes to the surface ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1987, 82(3/4): 289−304. [13] Kelly A E, Reuer M K, Goodkin N F, et al. Lead concentrations and isotopes in corals and water near Bermuda, 1780–2000[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 283(1/4): 93−100. [14] Quinby-Hunt M S, Turehian K K. Distribution of elements in sea water[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 1983, 64(14): 130. doi: 10.1029/EO064i014p00130 [15] Liu Yi, Li Xiaohua, Zeng Zhen, et al. Annually-resolved coral skeletal δ138/134Ba records: a new proxy for oceanic Ba cycling[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2019, 247: 27−39. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2018.12.022 [16] Zhang Ting, Sun Ruoyu, Liu Yi, et al. Copper and Zinc isotope signatures in scleratinian corals: implications for Cu and Zn cycling in modern and ancient ocean[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2022, 317: 395−408. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.10.014 [17] Linn L J, Delaney M L, Druffel E R M. Trace metals in contemporary and seventeenth-century Galapagos coral: records of seasonal and annual variations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(2): 387−394. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90327-H [18] Livingston H D, Thompson G. Trace element concentrations in some modern corals[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 1971, 16(5): 786−796. doi: 10.4319/lo.1971.16.5.0786 [19] Shen G T, Sanford C L. Trace element indicators of climate variability in reef-building corals[J]. Elsevier Oceanography Series, 1990, 52: 255−283. [20] Grottoli A G, Matthews K A, Palardy J E, et al. High resolution coral Cd measurements using LA-ICP-MS and ID-ICP-MS: calibration and interpretation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2013, 356: 151−159. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.08.024 [21] Jiang Wei, Yu Kefu, Wang Ning, et al. Distribution coefficients of trace metals between modern coral-lattices and seawater in the northern South China Sea: species and SST dependencies[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 187: 104082. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104082 [22] Sadler J, Webb G E, Nothdurft L D, et al. Geochemistry-based coral palaeoclimate studies and the potential of ‘non-traditional’ (non-massive Porites) corals: recent developments and future progression[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2014, 139: 291−316. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.10.002 [23] 樊祺诚, 孙谦, 龙安明, 等. 北部湾涠洲岛及斜阳岛火山地质与喷发历史研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1529−1537. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.06.011Fan Qicheng, Sun Qian, Long Anming, et al. Geology and eruption history of volcanoes in Weizhou Island and Xieyang Island, Northern Bay[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(6): 1529−1537. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.06.011 [24] 王文欢, 余克服, 王英辉. 北部湾涠洲岛珊瑚礁的研究历史、现状与特色[J]. 热带地理, 2016, 36(1): 72−79. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002806Wang Wenhuan, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui. A review on the research of coral reefs in the Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf[J]. Tropical Geography, 2016, 36(1): 72−79. doi: 10.13284/j.cnki.rddl.002806 [25] 黄林韬, 黄晖, 江雷. 中国造礁石珊瑚分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 2020, 28(4): 515−523. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019384Huang Lintao, Huang Hui, Jiang Lei. A revised taxonomy for Chinese hermatypic corals[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2020, 28(4): 515−523. doi: 10.17520/biods.2019384 [26] Hoeksema B W, Cairns S. World list of scleractinia, 2020[EB/OL]. [2023−01−01]. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1363. [27] 杨华, 王少鹏, 余克服, 等. 南海北部珊瑚生长区海水重金属污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 253−260. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2017.02.010Yang Hua, Wang Shaopeng, Yu Kefu, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in seawater of coral growing regions in the northern South China Sea[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(2): 253−260. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2017.02.010 [28] Xie Sirong, Jiang Wei, Sun Yinan, et al. Interannual variation and sources identification of heavy metals in seawater near shipping lanes: evidence from a coral record from the northern South China Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 854: 158755. [29] 王宁, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 涠洲岛珊瑚骨骼重金属水平及其生物富集效应[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 44(2): 570−579. doi: 10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2019.0570Wang Ning, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Concentrations and bioaccumulation effects of heavy metals in coral skeletons from Weizhou Island[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 44(2): 570−579. doi: 10.13624/j.cnki.issn.1001-7445.2019.0570 [30] 彭加喜, 刘金铃, 徐向荣, 等. 西沙永兴岛珊瑚重金属水平及其富集效应[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2014, 33(6): 848−853. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2014.06.006Peng Jiaxi, Liu Jinling, Xu Xiangrong, et al. Heavy metal levels in coral skeletons from Yongxing Island and their enrichment effects[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2014, 33(6): 848−853. doi: 10.13634/j.cnki.mes.2014.06.006 [31] Song Yinxian, Yu Kefu, Zhao Jianxin, et al. Past 140-year environmental record in the northern South China Sea: evidence from coral skeletal trace metal variations[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2014, 185: 97−106. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.10.024 [32] 彭子成, 刘军华, 刘桂建, 等. 广东省电白县大放鸡岛滨珊瑚的重金属含量及其意义[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2003, 19(11): 5−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.11.002Peng Zicheng, Liu Junhua, Liu Guijian, et al. Interannual variability of the heavy metal contents in the porites lutea coral from Dafangji Island of Dianbai county and their implications[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2003, 19(11): 5−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2003.11.002 [33] Mokhtar M B, Praveena S M, Aris A Z, et al. Trace metal (Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni and Zn) accumulation in Scleractinian corals: a record for Sabah, Borneo[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2012, 64(11): 2556−2563. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.030 [34] 徐轶肖, 谢谊, 赵鹏, 等. 北部湾涠洲岛海水重金属污染现状研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2018, 27(5): 908−915. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.05.016Xu Yixiao, Xie Yi, Zhao Peng, et al. Heavy metal pollution of seawater in Weizhou Island, Beibu Gulf of Guangxi[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 27(5): 908−915. doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2018.05.016 [35] Akagi T, Hashimoto Y, Fu Fengfu, et al. Variation of the distribution coefficients of rare earth elements in modern coral-lattices: species and site dependencies[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(10): 2265−2273. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.12.014 [36] Reuer M K, Boyle E A, Cole J E. A mid-twentieth century reduction in tropical upwelling inferred from coralline trace element proxies[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 210(3/4): 437−452. [37] Nothdurft L D, Webb G E, Kamber B S. Rare earth element geochemistry of Late Devonian reefal carbonates, Canning Basin, western Australia: confirmation of a seawater REE proxy in ancient limestones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 68(2): 263−283. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00422-8 [38] Zhong Shaojun, Mucci A. Partitioning of rare earth elements (REEs) between calcite and seawater solutions at 25°C and 1 atm, and high dissolved REE concentrations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(3): 443−453. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)00381-U [39] Kuffner I B, Jokiel P L, Rodgers K S, et al. An apparent “vital effect” of calcification rate on the Sr/Ca temperature proxy in the reef coral Montipora capitata[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13(8): Q08004. [40] Gaetani G A, Cohen A L. Element partitioning during precipitation of aragonite from seawater: a framework for understanding paleoproxies[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(18): 4617−4634. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.07.008 [41] Gagnon A C, Adkins J F, Erez J. Seawater transport during coral biomineralization[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 329−330: 150−161. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2012.03.005 [42] Inoue M, Gussone N, Koga Y, et al. Controlling factors of Ca isotope fractionation in scleractinian corals evaluated by temperature, pH and light controlled culture experiments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 167: 80−92. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.06.009 -




 下载:
下载: