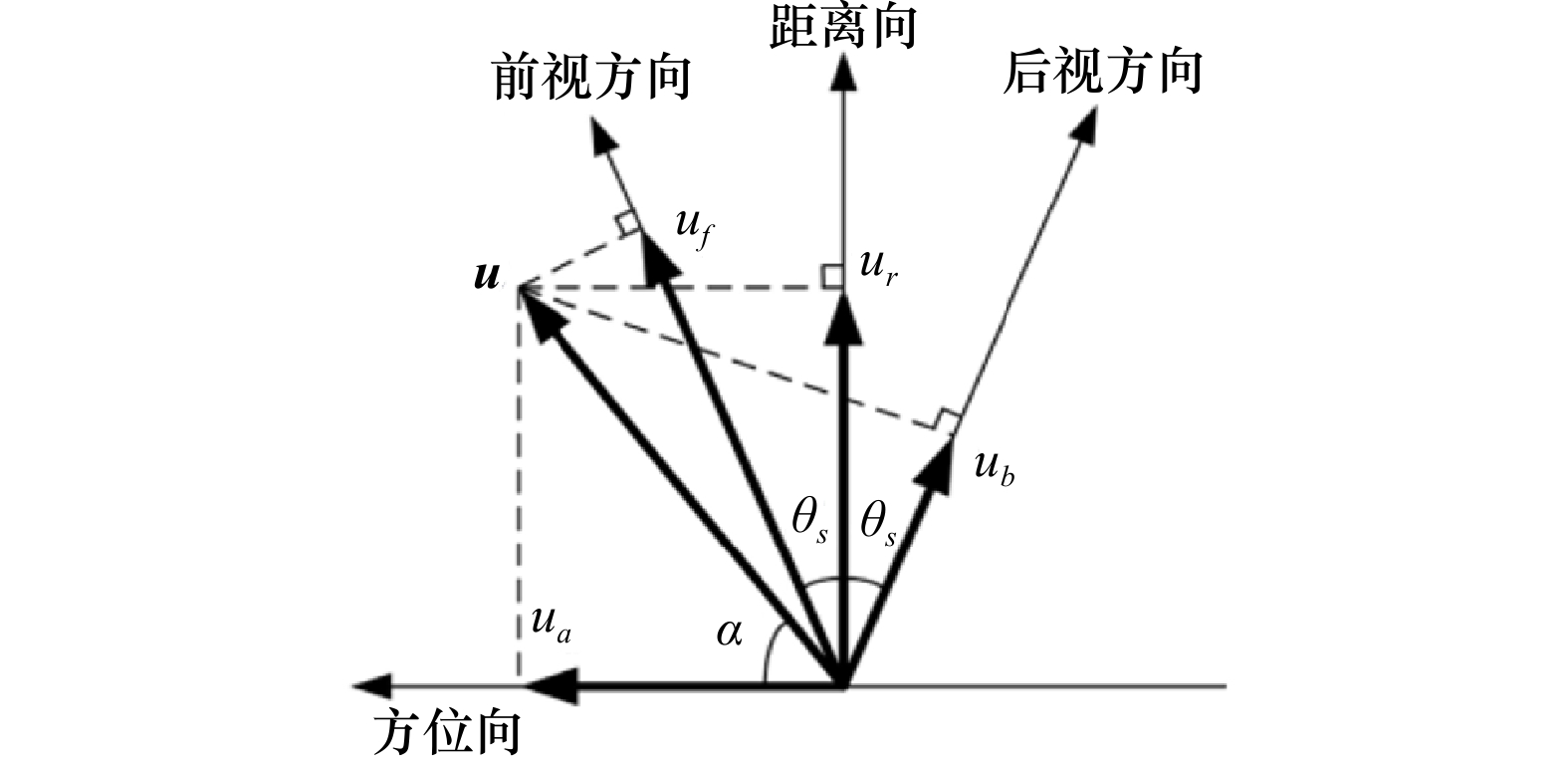
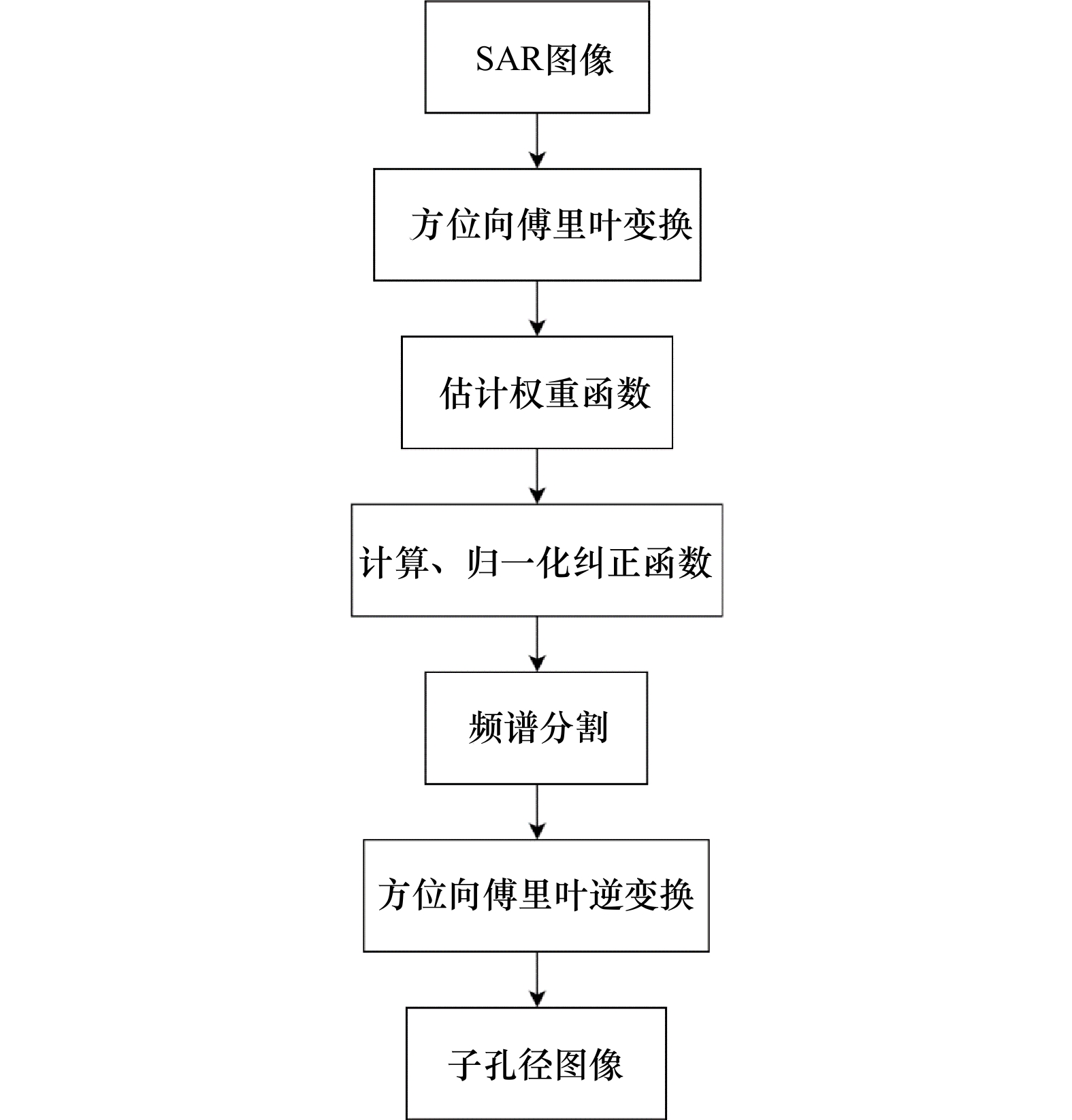
Two-dimensional sea surface current field inversion based on SAR sub-aperture decomposition
-
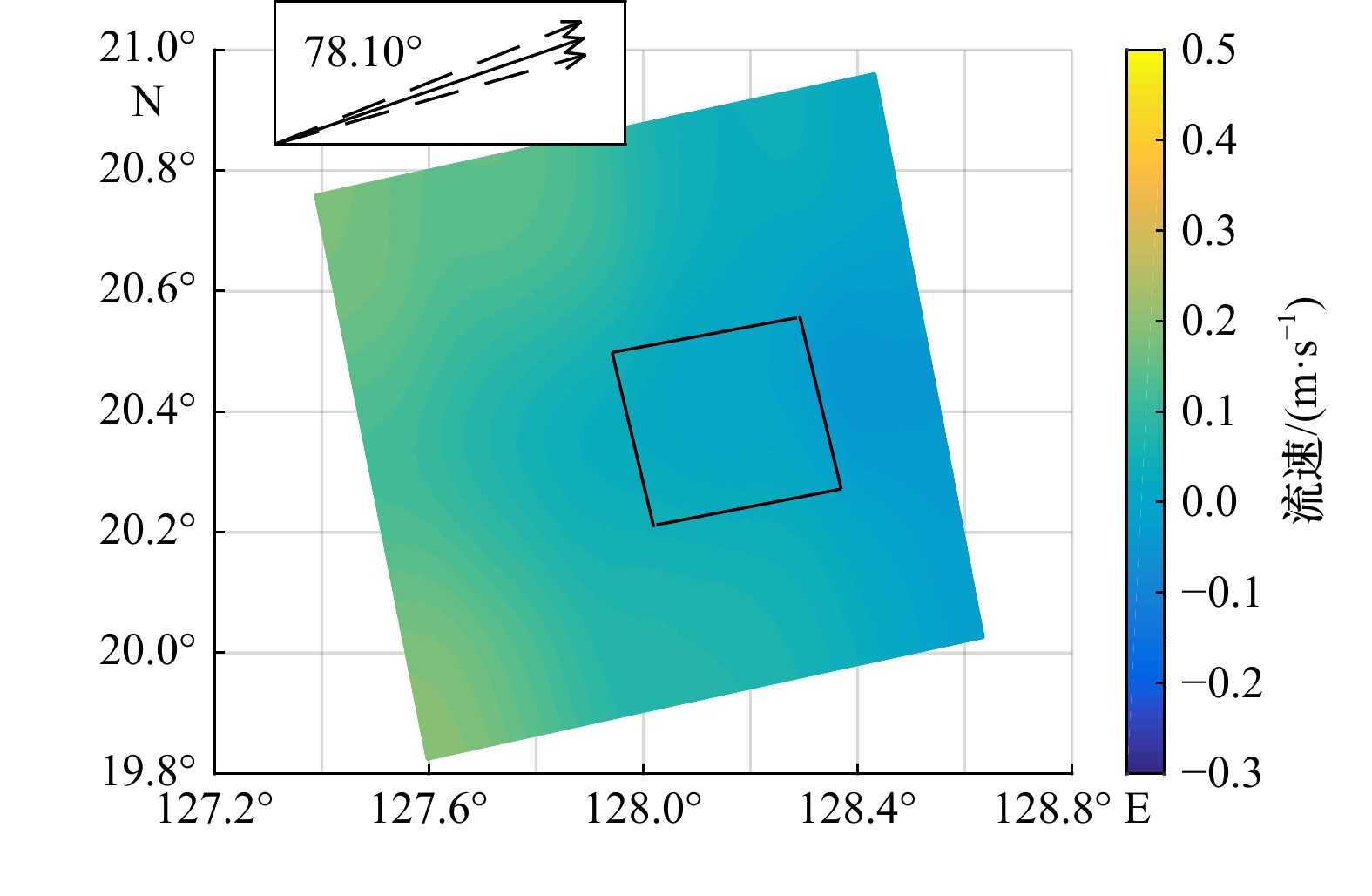
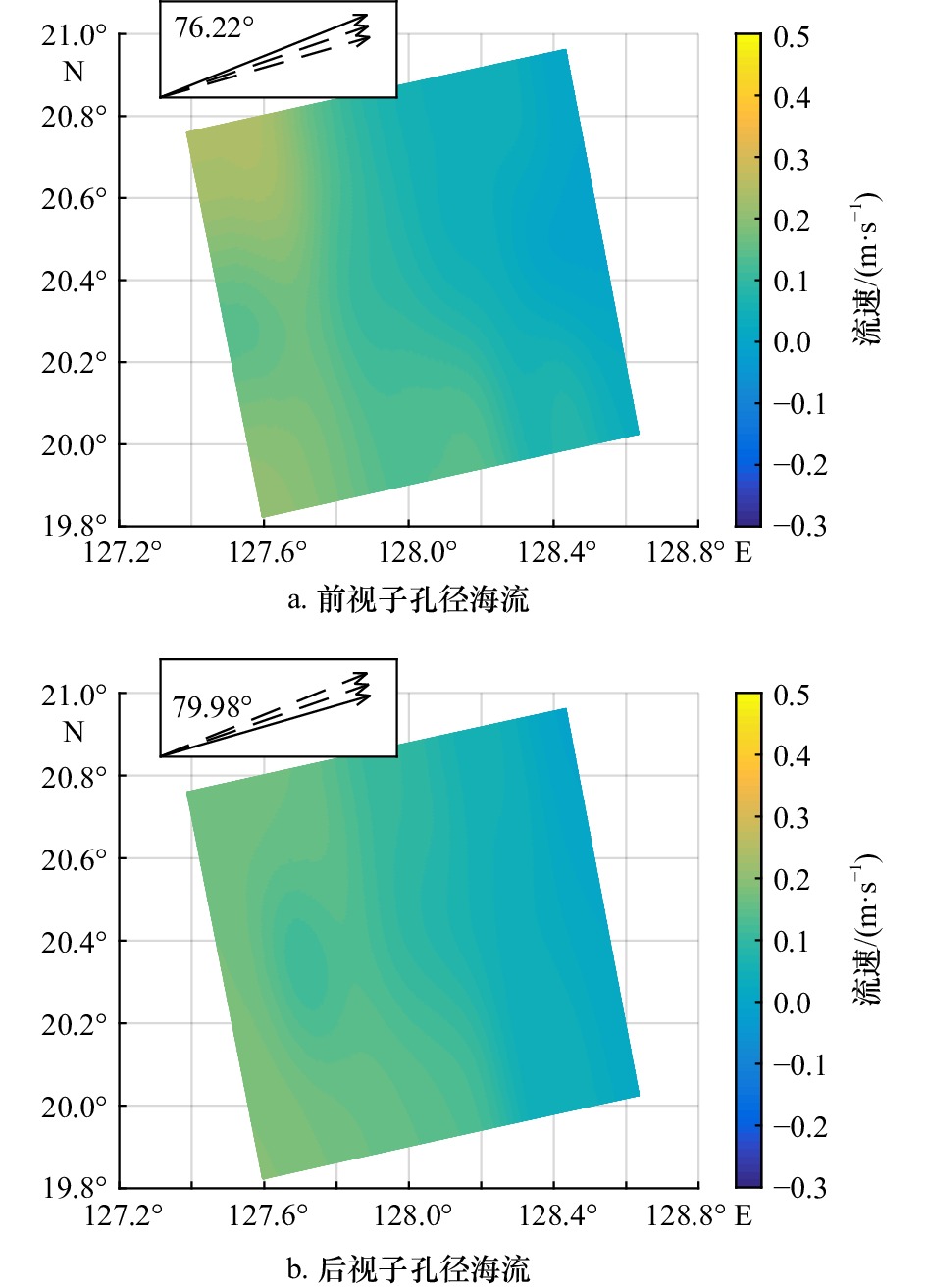
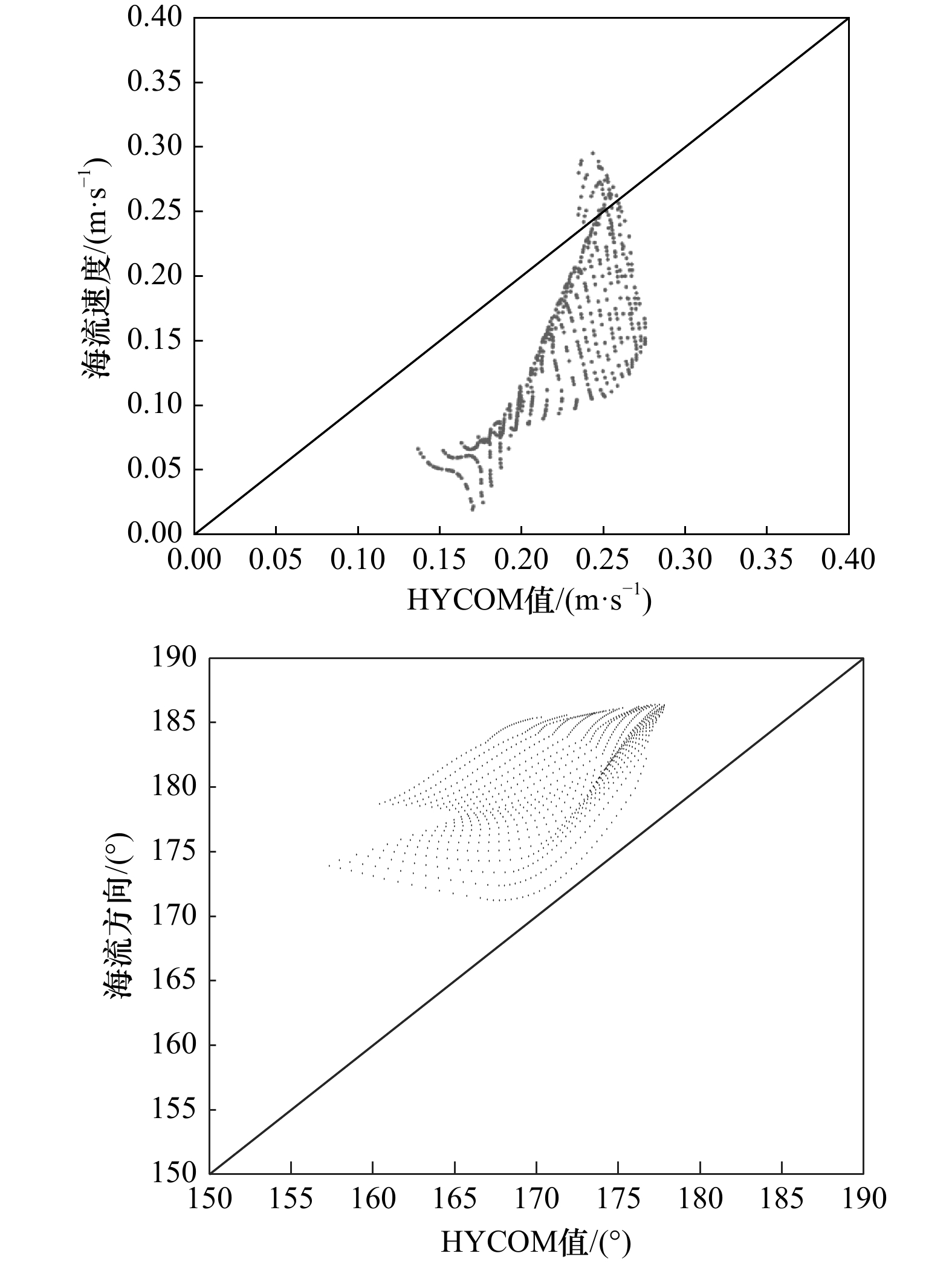
摘要: 对Radarsat-2和Sentinel-1A分别观测的两个海域的单景SAR图像进行子孔径分解,各自得到不同方位角上的两幅SAR子孔径图像。使用多普勒质心频移法分别对不同方位角的两幅SAR图像进行海流反演,并进行海流矢量合成,采用经过时空匹配的HYCOM模式数据对反演结果进行检验,结果表明:Radarsat-2观测的SAR图像分解的两幅子孔径SAR图像矢量合成后的海流与HYCOM模式数据相比,速度均方根值为0.09 m/s,相关系数为0.64;方向均方根值为10.49°,相关系数为0.78。Sentinel-1A观测的SAR图像分解的两幅子孔径SAR图像矢量合成后的海流与HYCOM模式数据相比,速度均方根值为0.06 m/s,相关系数为0.82;方向均方根值为2.85°,相关系数为0.86。由此可见,基于单景SAR分解的两幅子孔径SAR图像可以有效反演二维海流。其反演精度与雷达视向和真实海流矢量的方向有关,二者的角度越小,反演海流矢量的精度越高。Abstract: Two single-scene SAR images observed by Radarsat-2 and Sentinel-1A were decomposed to obtain a pair of SAR sub-aperture images at different azimuth-angles, respectively. Doppler centroid anomaly method was used to invert the sea surface current of two sub-aperture images with different azimuth angles. The current field was obtained by vector synthesis. The inversion results were verified by the HYCOM model data with spatio-temporal matching. The results show that the root mean square (RMS) of the current velocity between the synthesized result by two sub-aperture images of Radarsat-2 and the HYCOM model data is 0.09 m/s, and the correlation coefficient is 0.64. The RMS of current direction is 10.49° and the correlation coefficient is 0.78 of this group data. As for the results of the Sentinel-1A image, the RMS of the current velocity is 0.06 m/s, and the correlation coefficient is 0.82. The RMS of the current direction is 2.85°, and the correlation coefficient is 0.86. It can be seen that the two-dimensional ocean currents field can be effectively inverted based on the two sub-aperture SAR images that decomposed from single-scene SAR image. The inversion accuracy is related to the relative direction of the radar’s looking direction and the real current vector. The inversion accuracy of the sea surface current field can be higher when the relative angle is small.
-
Key words:
- SAR /
- sub-aperture /
- Doppler centroid anomaly /
- two-dimensional current field /
- HYCOM
-
表 1 反演海流矢量与HYCOM值统计结果
Tab. 1 Statistical results of inverted current vector and HYCOM values
速度 方向 平均偏差 −0.08 m/s 9.98° 均方根差 0.09 m/s 10.49° 相关系数 0.64 0.78 表 2 合成海流矢量与HYCOM值统计结果
Tab. 2 Statistical results of synthesized current vector and HYCOM values
速度 方向 平均偏差 −0.05 m/s 2.72° 均方根差 0.06 m/s 2.85° 相关系数 0.82 0.86 -
[1] Chapron B, Collard F, Ardhuin F. Direct measurements of ocean surface velocity from space: interpretation and validation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C7): C07008. [2] Goldstein R M, Zebker H A. Interferometric radar measurement of ocean surface currents[J]. Nature, 1987, 328(6132): 707−709. doi: 10.1038/328707a0 [3] Yuan Xinzhe, Lin Mingsen, Han Bing, et al. Observing sea surface current by gaofen-3 satellite along-track interferometric SAR experimental mode[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7762−7770. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3099105 [4] Yoshida T, Ouchi K, Yang C S. Application of MA-ATI SAR for estimating the direction of moving water surface currents in Pi-SAR2 images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 2724−2730. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3060008 [5] Yoshida T, Ouchi K, Yang C S. Validation of MA-ATI SAR theory using numerical simulation for estimating the direction of moving targets and ocean currents[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(4): 677−681. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2983160 [6] Li Yan, Chong Jinsong, Li Zongze. A simulation method of two-dimensional sea-surface current field for trajectory crossing spaceborne SAR[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(12): 5900. doi: 10.3390/app12125900 [7] 候富城, 孟俊敏, 张晰, 等. 利用多普勒频移反演ASAR海表面流速[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2019, 37(2): 274−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.02.011Hou Fucheng, Meng Junmin, Zhang Xi, et al. Using the doppler shift method to retrieve the ASAR sea surface velocity[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2019, 37(2): 274−283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.02.011 [8] 张夏荣, 黄云仙, 赵现斌. 基于星载SAR多普勒速度反演海表流场算法的研究[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 2016, 33(1): 1−7. doi: 10.19441/j.cnki.issn1006-009x.2016.01.001Zhang Xiarong, Huang Yunxian, Zhao Xianbin. Study of ocean surface current inversion algorithm based on space-borne synthetic aperture radar dopplervelocity[J]. Meteorological, Hydrological and Marine Instruments, 2016, 33(1): 1−7. doi: 10.19441/j.cnki.issn1006-009x.2016.01.001 [9] 杨小波. 基于ASAR的时变海表面流场反演研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016.Yang Xiaobo. Sea surface current retrieval based on ASAR data[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. [10] 宋小霞, 王静, 储小青. 基于多普勒频移的SAR海表流场反演[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2019, 34(2): 293−302.Song Xiaoxia, Wang Jing, Chu Xiaoqing. Estimation of sea surface velocities from SAR images using the Doppler shift[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2019, 34(2): 293−302. [11] Mouche A A, Collard F, Chapron B, et al. On the use of Doppler shift for sea surface wind retrieval from SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(7): 2901−2909. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2174998 [12] 马琳, 潘宗序, 黄钟泠, 等. 基于子孔径与全孔径特征学习的SAR多通道虚假目标鉴别[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 159−172. doi: 10.12000/JR20106Ma Lin, Pan Zongxu, Huang Zhongling, et al. Multichannel false-target discrimination in SAR images based on sub-aperture and full-aperture feature learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 159−172. doi: 10.12000/JR20106 [13] Ferro-Famil L, Reigber A, Pottier E, et al. Scene characterization using sub-aperture polarimetric SAR data analysis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Toronto: IEEE, 2002: 417−419. [14] Li Yan, Chong Jinsong, Sun Kai, et al. Accuracy and error analysis of vector measurement of ocean surface current by multi-aperture along-track interferometric SAR[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 207551−207562. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3038449 [15] Li Yan, Chong Jinsong, Sun Kai, et al. Measuring ocean surface current in the kuroshio region using gaofen-3 SAR data[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(16): 7656. doi: 10.3390/app11167656 -




 下载:
下载: