Study on the hydrodynamics of undular tidal bore over the uneven seabed
-
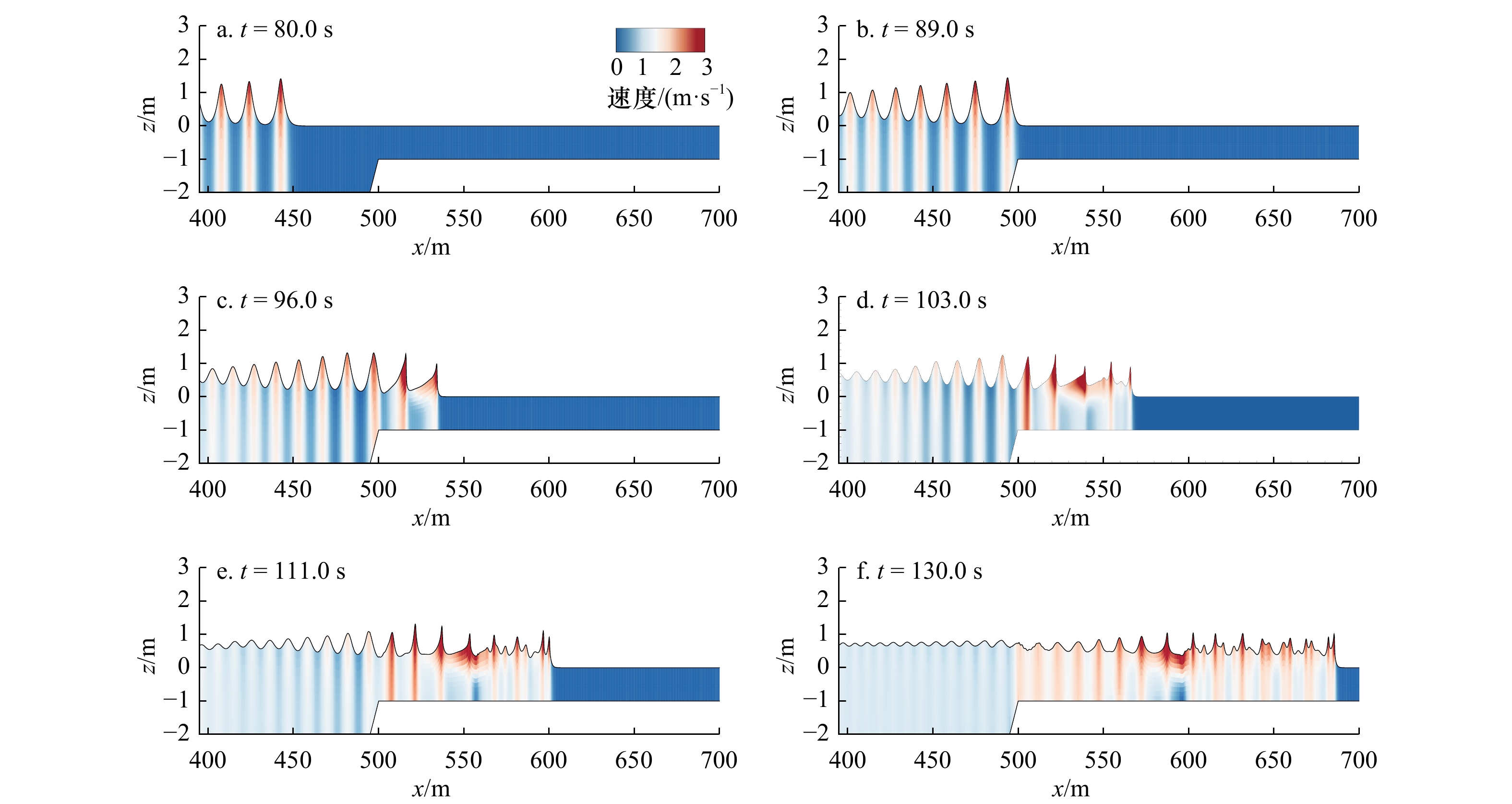
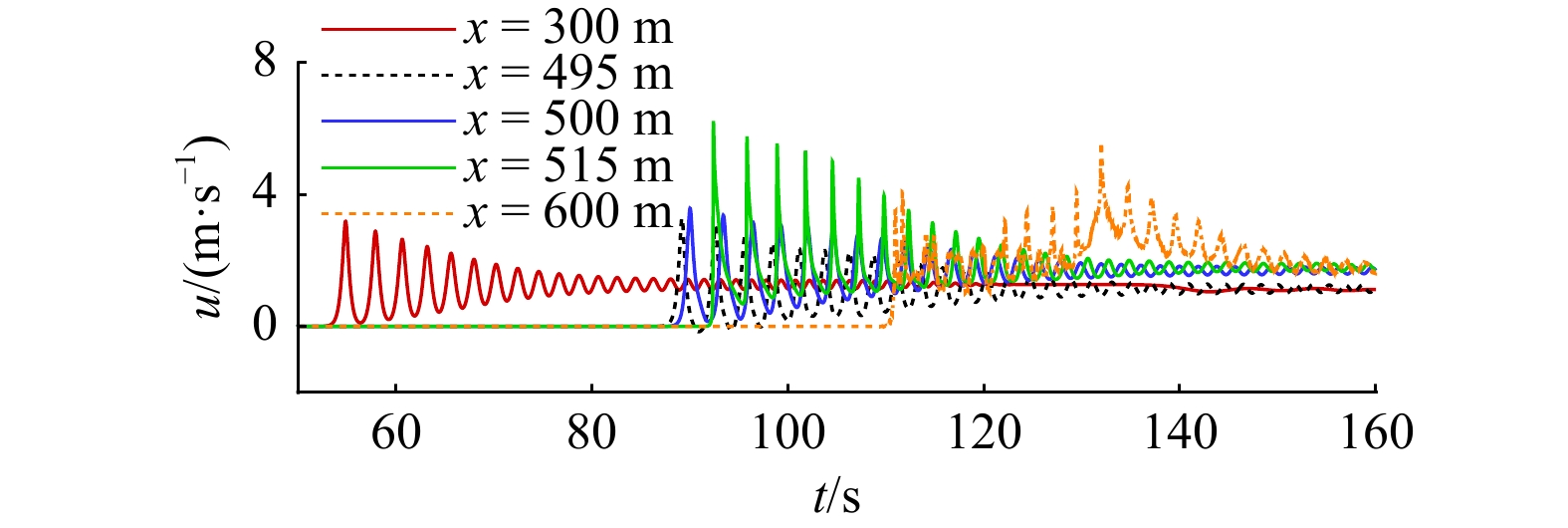
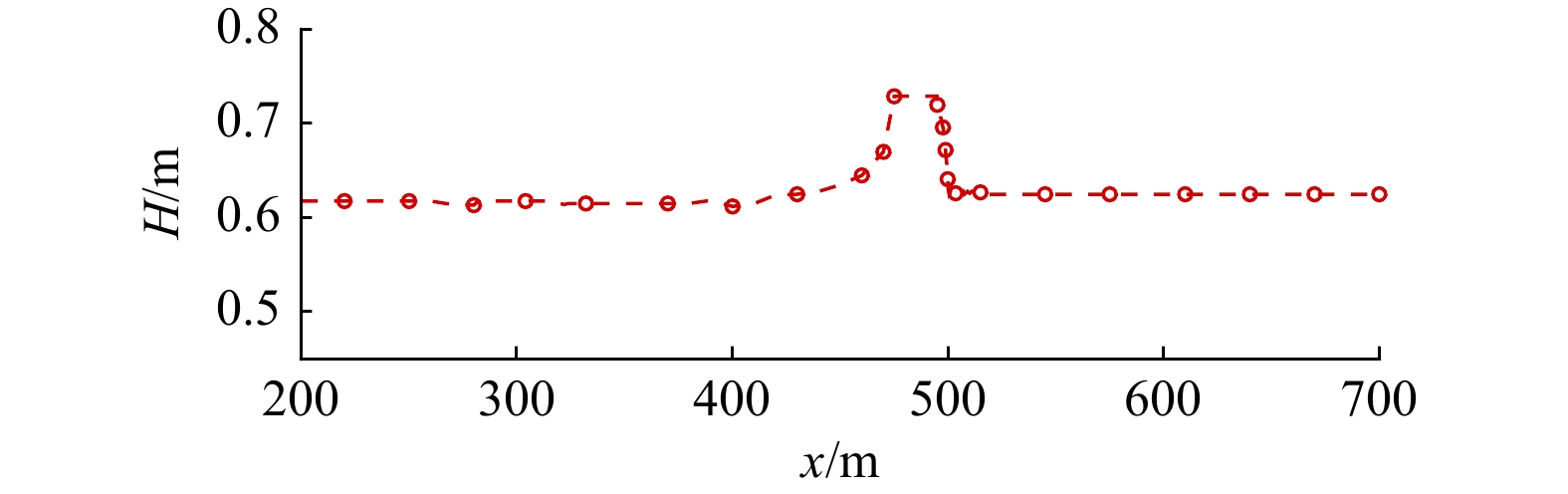
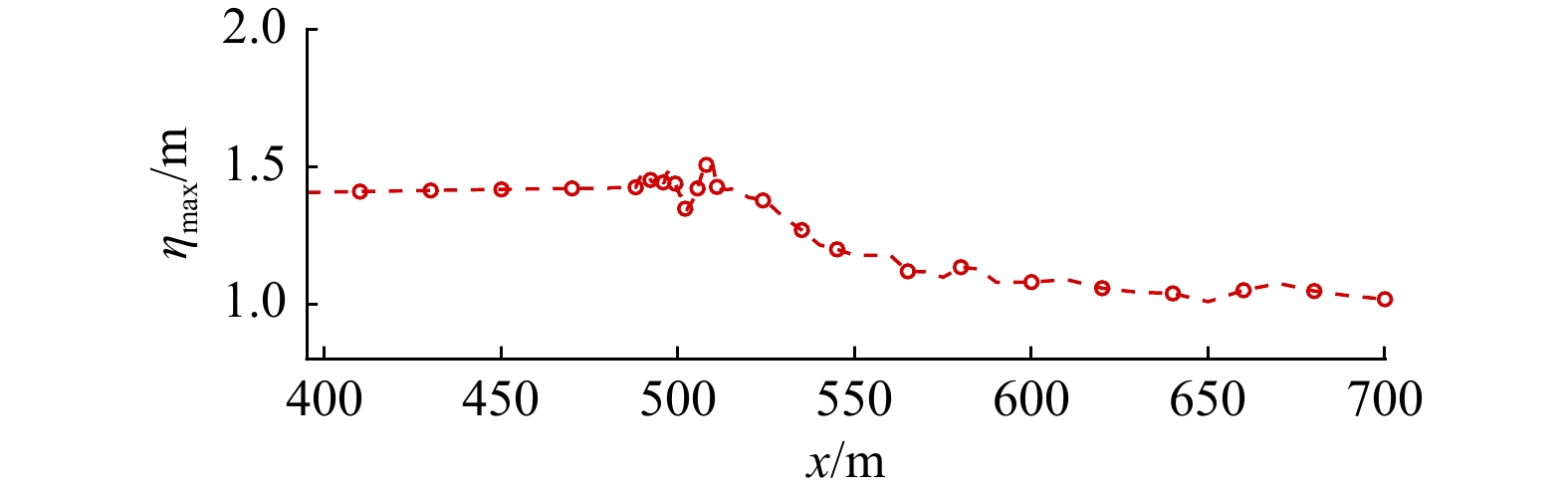
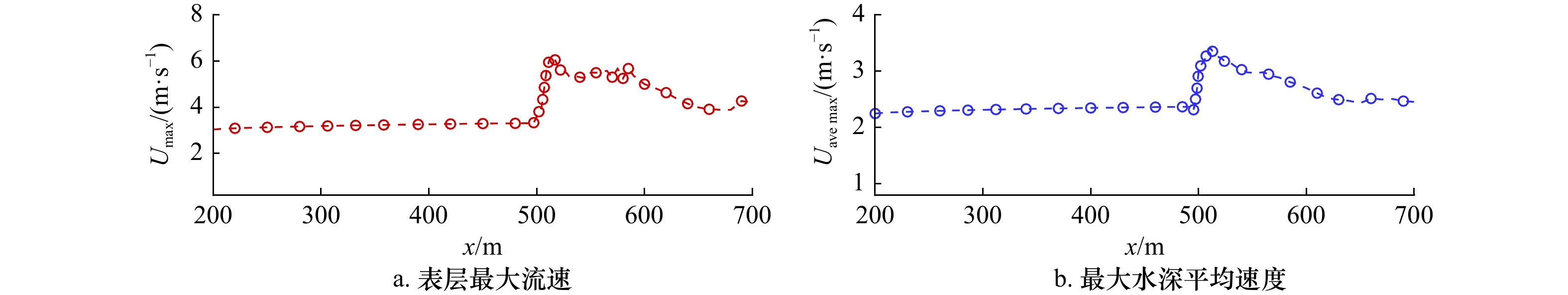
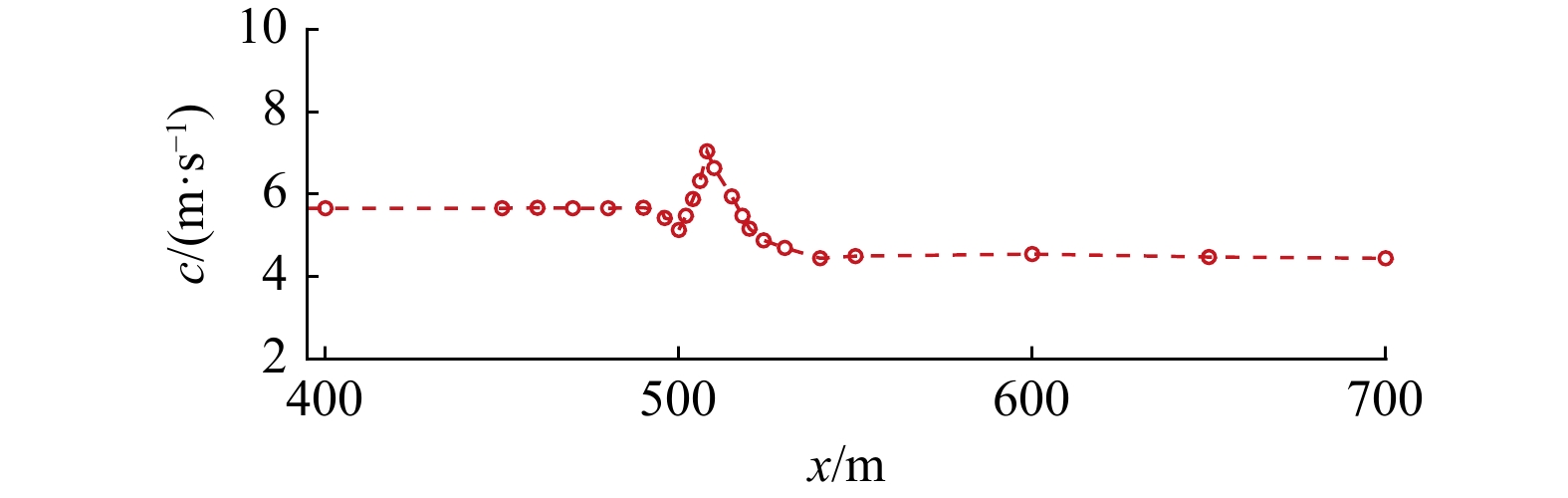
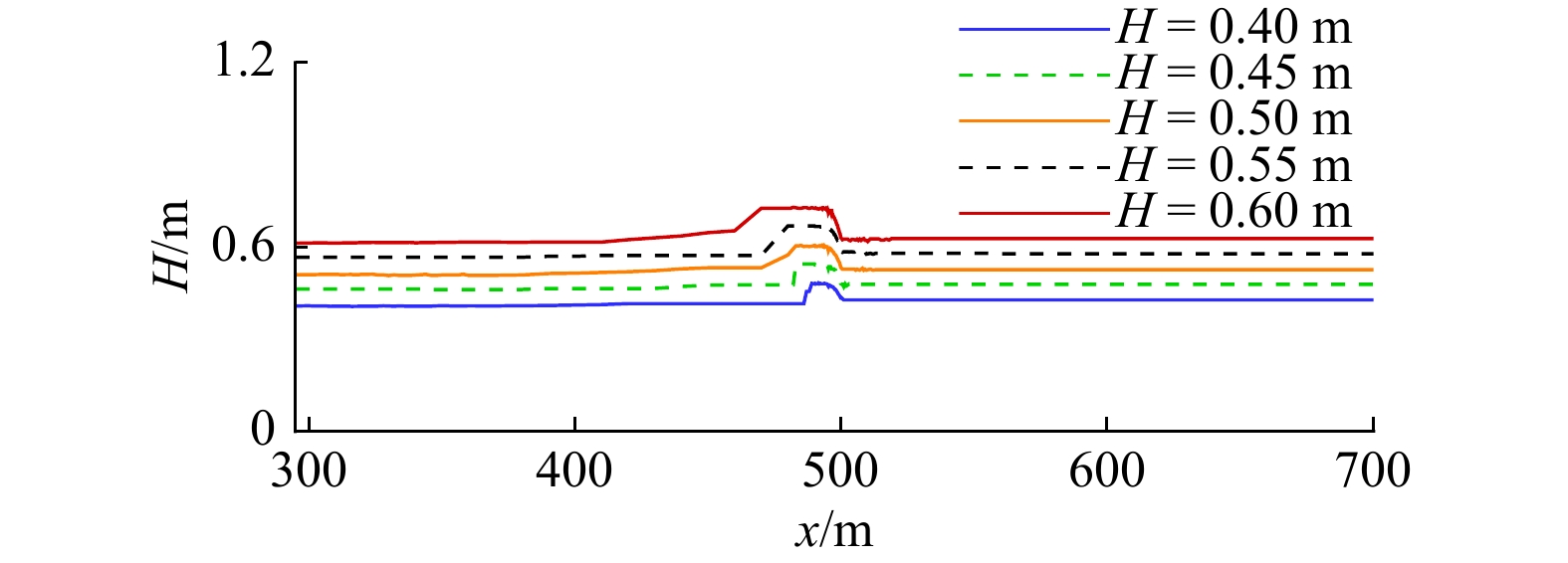
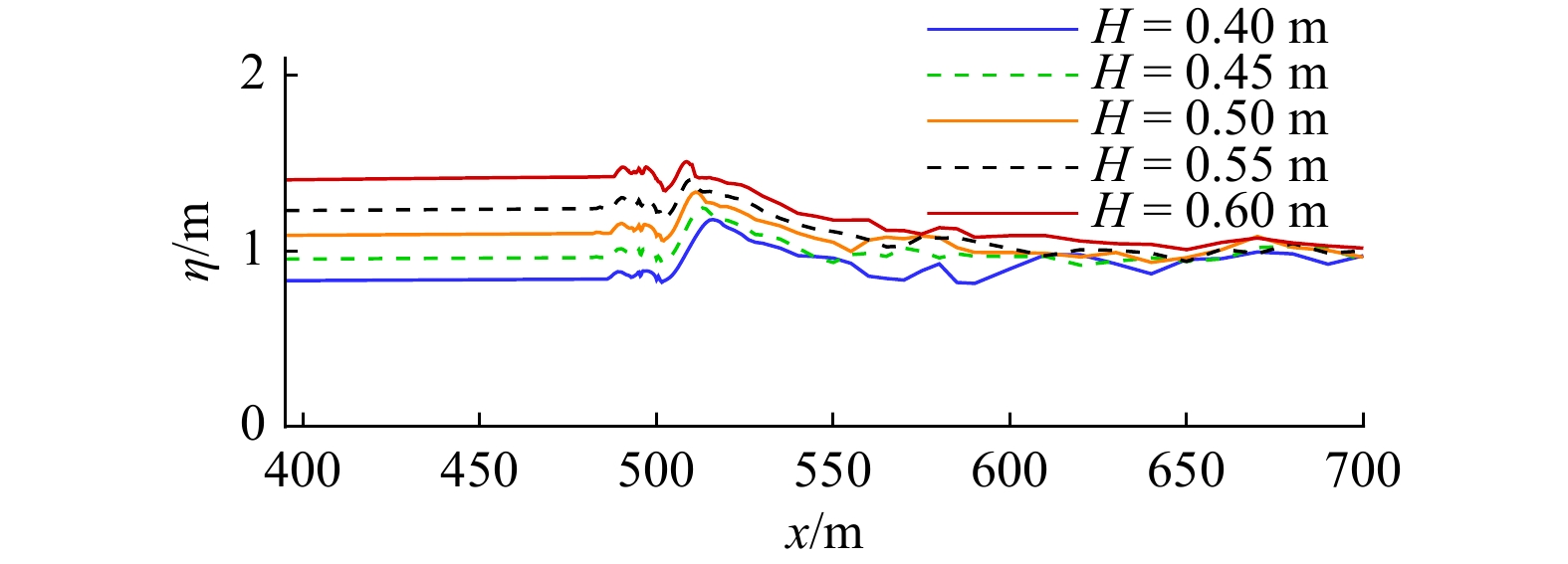
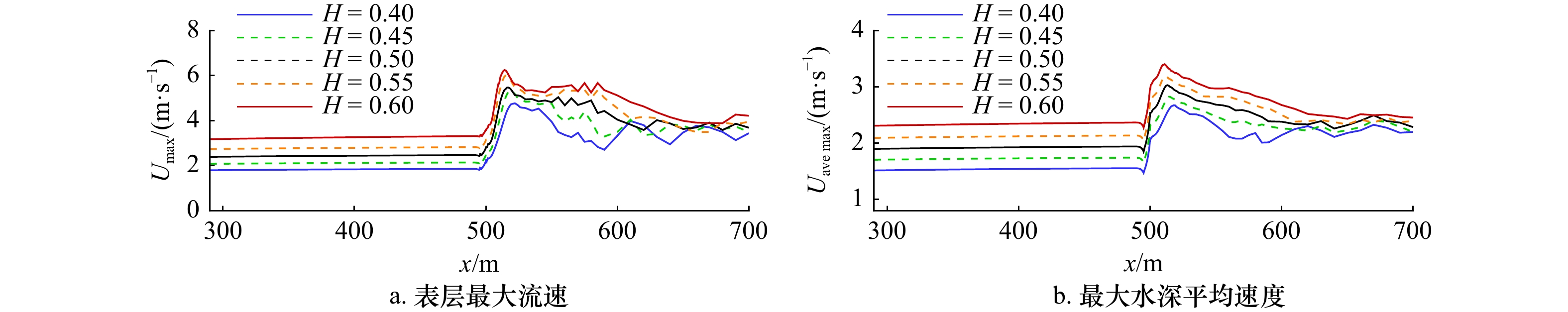
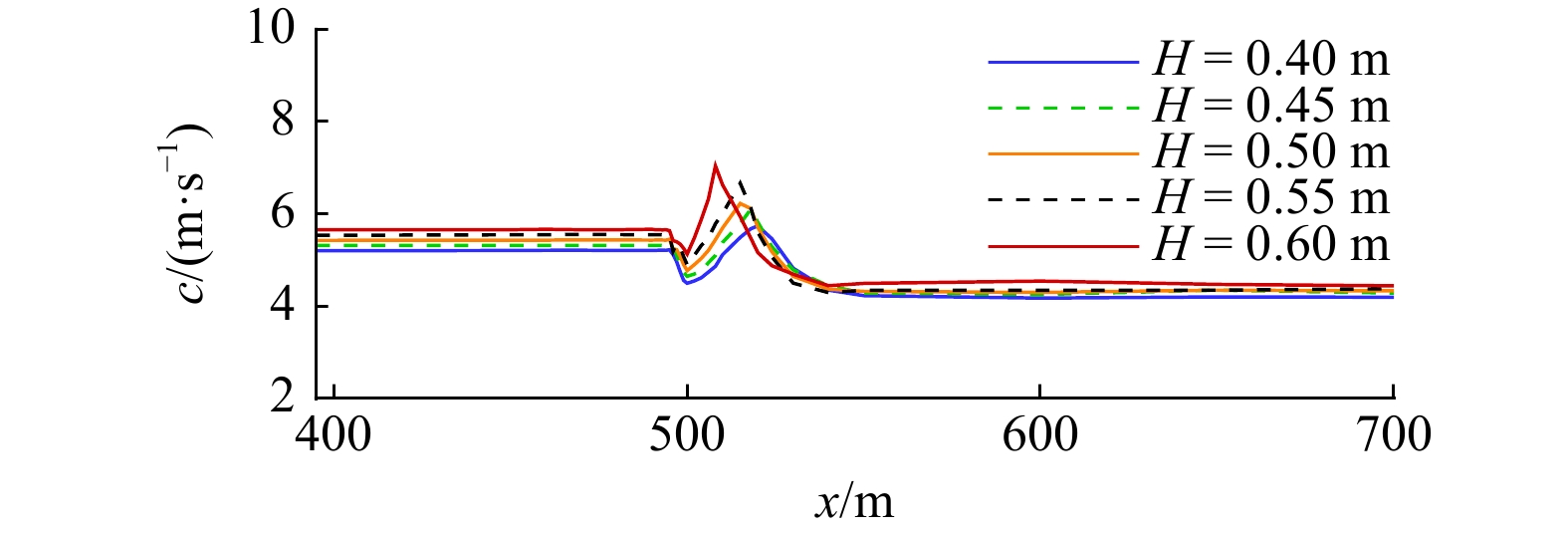
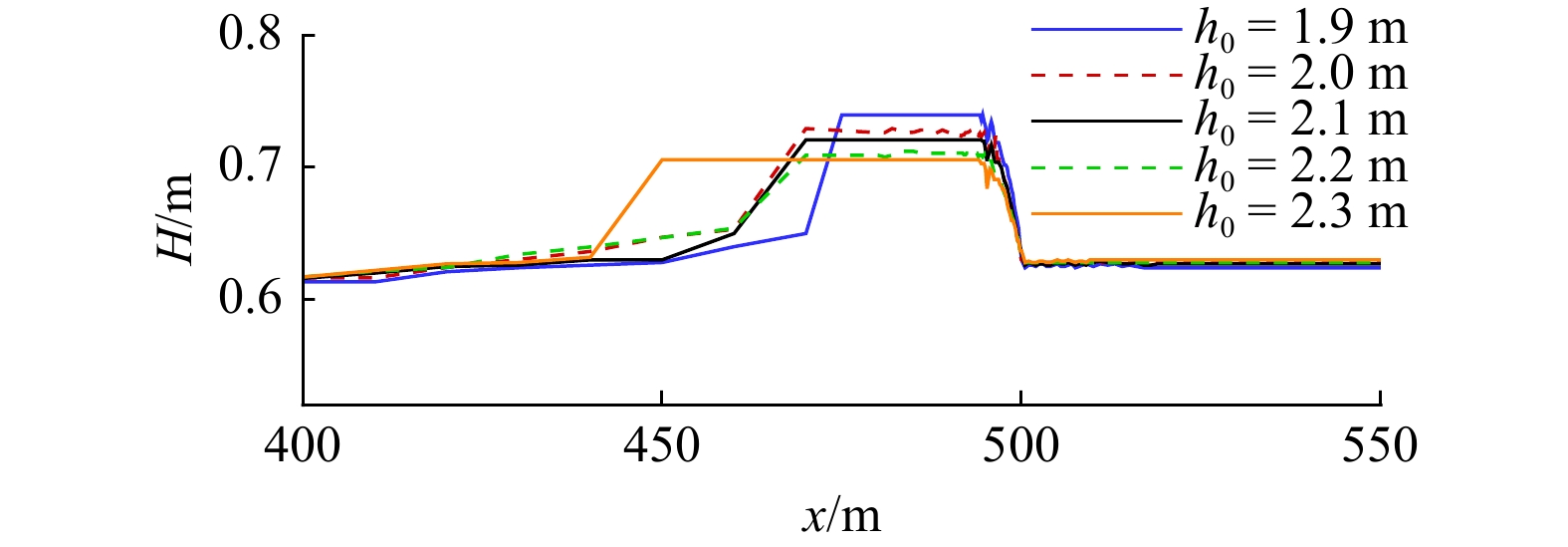
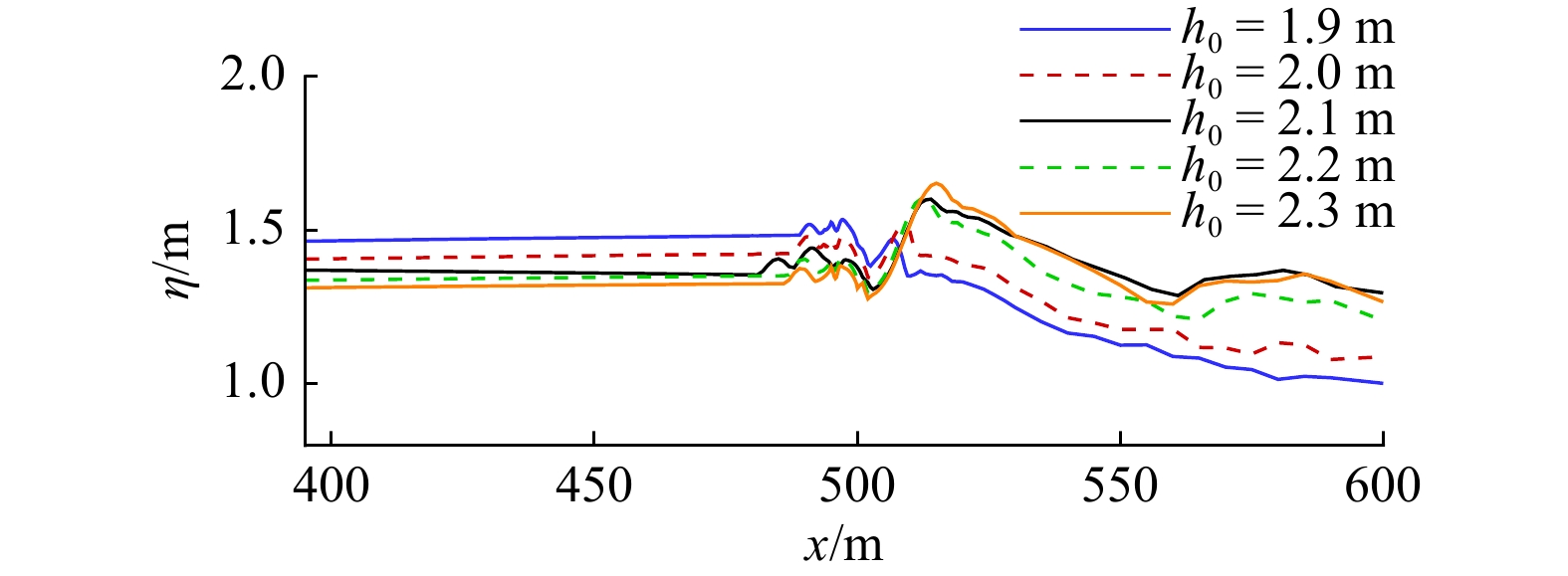
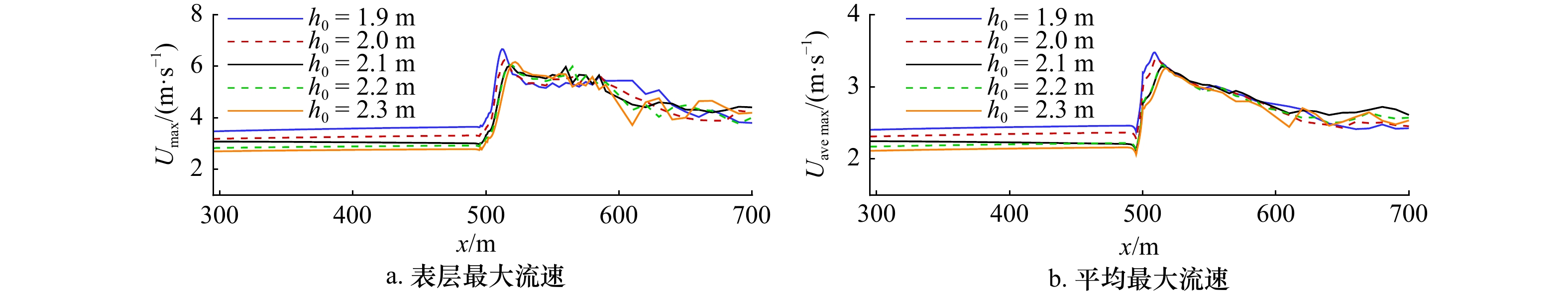
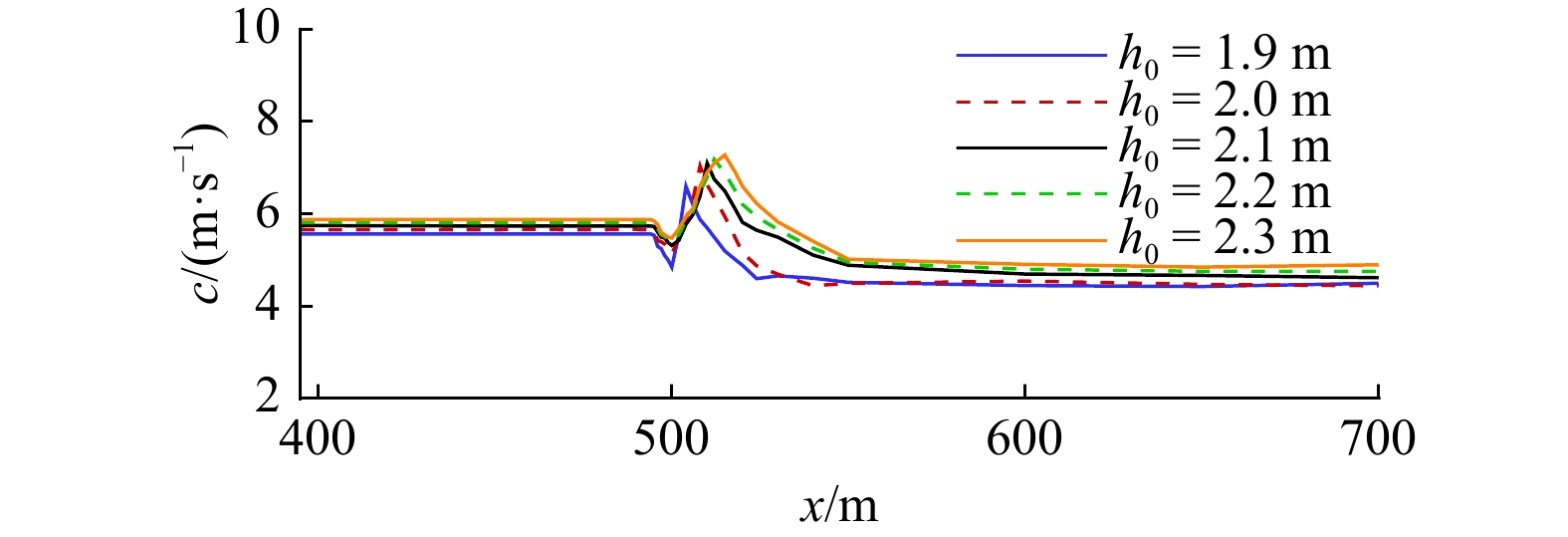
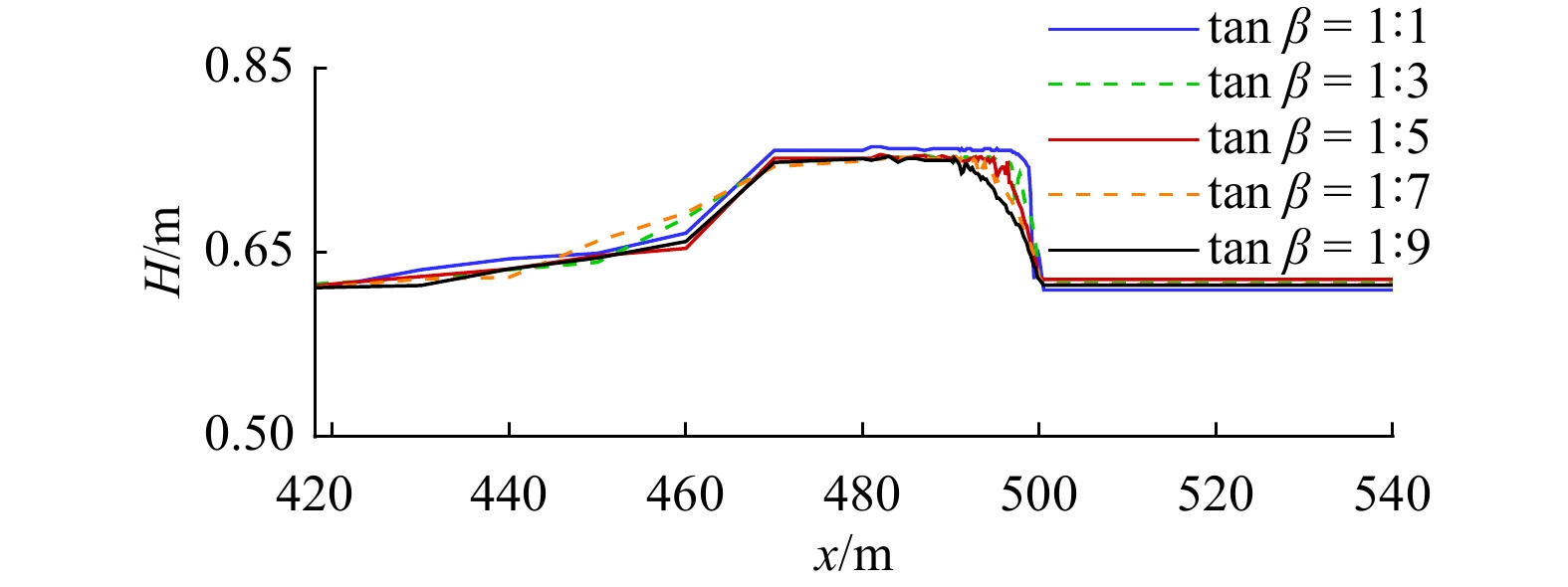
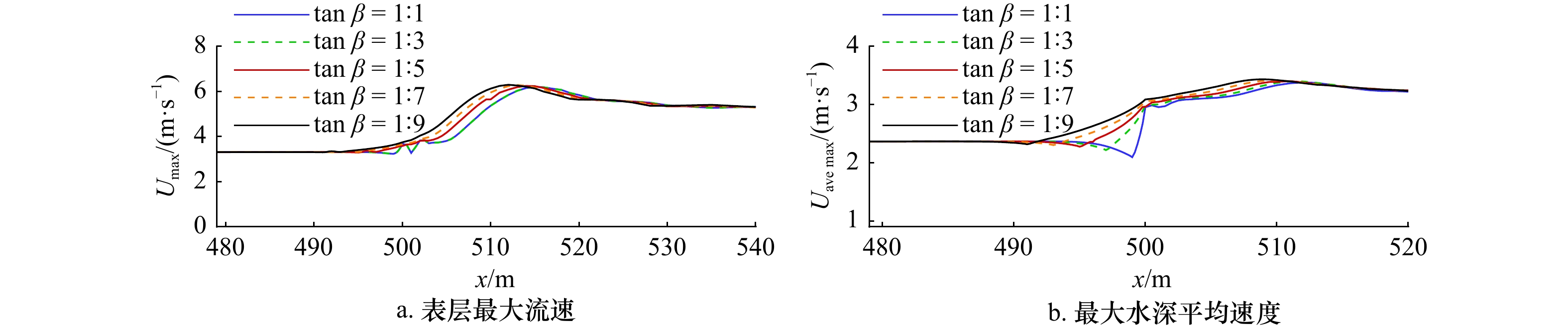
摘要: 本文采用非静压单相流模型(NHWAVE)研究了波状涌潮在变化地形上的传播演变特性。通过设置合理的计算工况,系统分析了涌潮高度、潮前水深和斜坡坡度对波状涌潮水动力特性的影响。计算结果表明,涌潮高度和潮前水深对波状涌潮在变化地形上的水动力特性影响显著,不同的地形坡度对波状涌潮水动力特性影响较小。变化地形的存在可导致涌潮高度显著增大,引起沿程最大水位的剧烈变化,并且使涌潮传播速度降低。随涌潮高度的逐渐增加,斜坡前后潮差持续增大,同时表层速度与水深平均速度均呈现增大趋势。当增加潮前水深时,斜坡前后潮差减小,表层速度与水深平均速度单调递减。本文研究成果对于正确认识波状涌潮在变化地形上的传播演变规律有一定的参考意义,为波状涌潮河段涉水建筑物的工程设计及安全评估提供了科学依据。Abstract: In this study, hydrodynamic characteristics of transformation and breaking processes of the undular tidal bore on the uneven seabed have been numerically investigated by applying a nonhydrostatic numerical wave model (NHWAVE). Effects of tidal bore height, initial water depth and bed slope on the hydrodynamics of tidal bore are discussed in detail. Research findings indicates that the tidal bore height and initial water depth have significant effects on the transformation and breaking processes of the undular tidal bore on the uneven seabed. However, different bed slope on the undular tidal bore hydrodynamic characteristics of the influence of less. The existence of bed slope can lead to a significant increase in the height of the undular tidal bore, causing dramatic changes in the maximum water level along the range, and make the tidal bore propagation speed is reduced. The average speed of water depth tends to increase with the tidal bore height, as well as the height difference between the upstream and downstream tidal bore height. When increasing the water depth, the tidal difference between the upstream and downstream tidal bore height decreases, and the surface velocity decreases monotonically with the average velocity of water depth. The research findings drawn from this study can have certain reference significances for the accurate understanding of the hydrodynamics of tidal bore on the uneven seabed. It provides a scientific basis for the engineering design and safety assessment of wading buildings in the tidal river section.
-
Key words:
- undular tidal bore /
- uneven seabed /
- nonhydrostatic wave model /
- numerical simulation
-
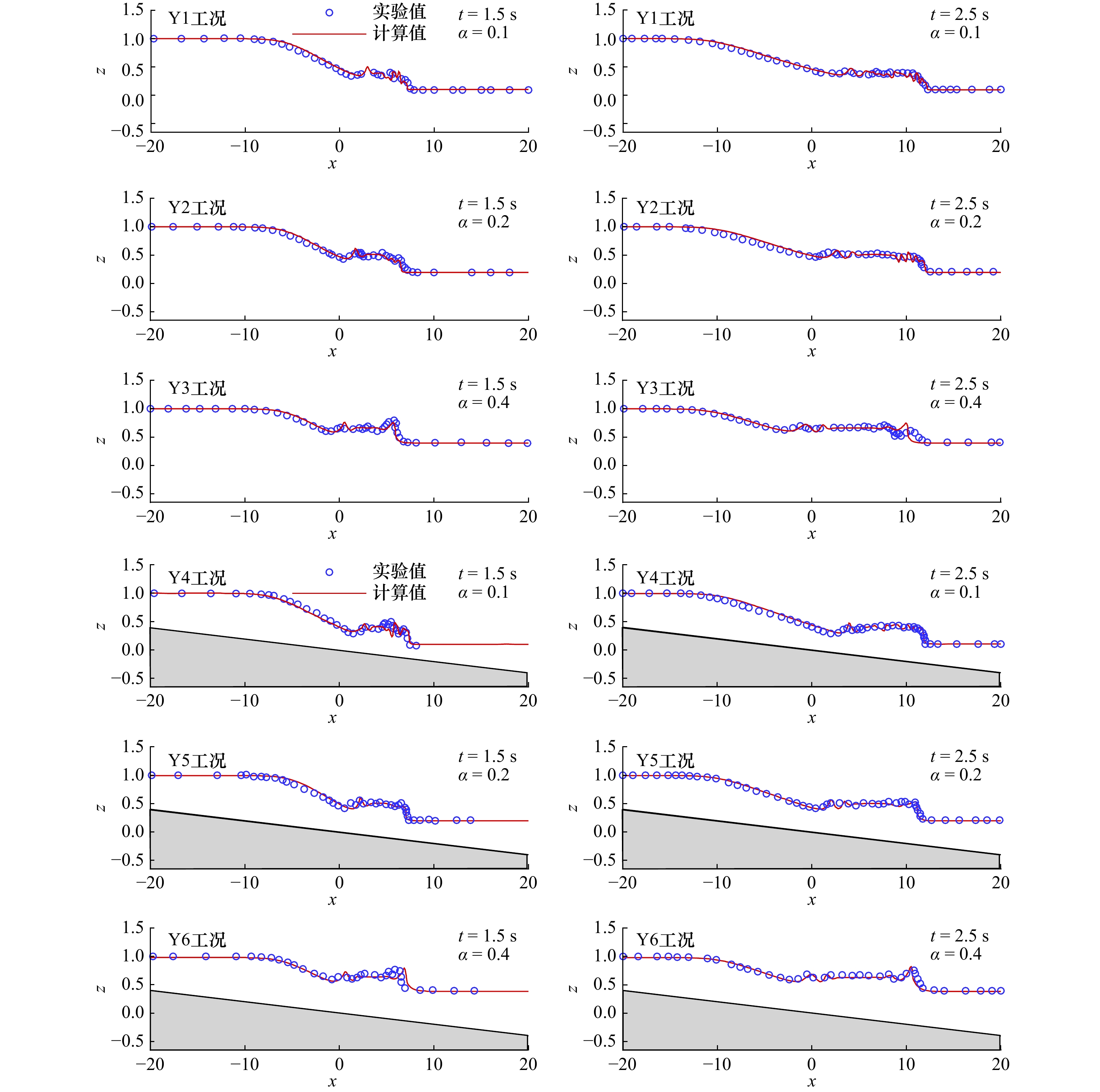
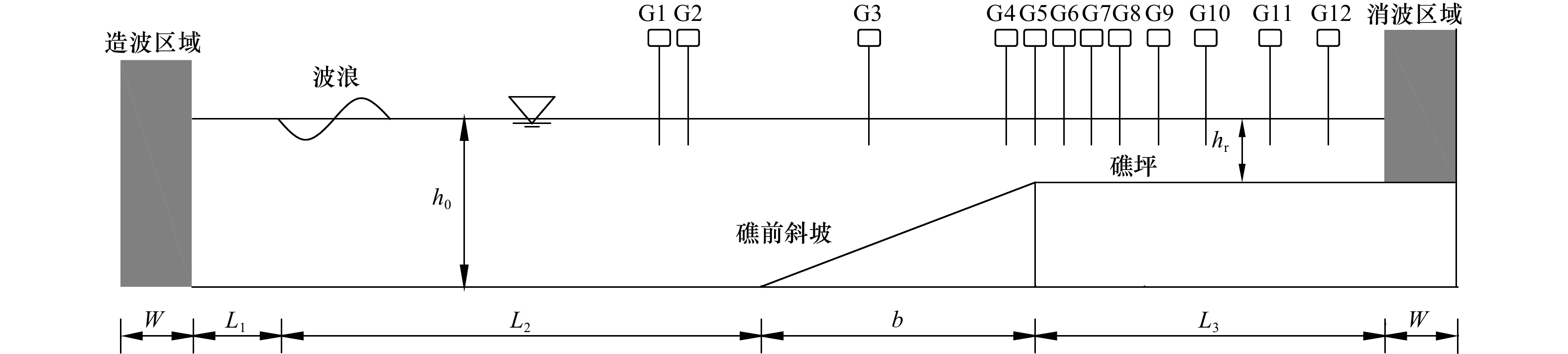
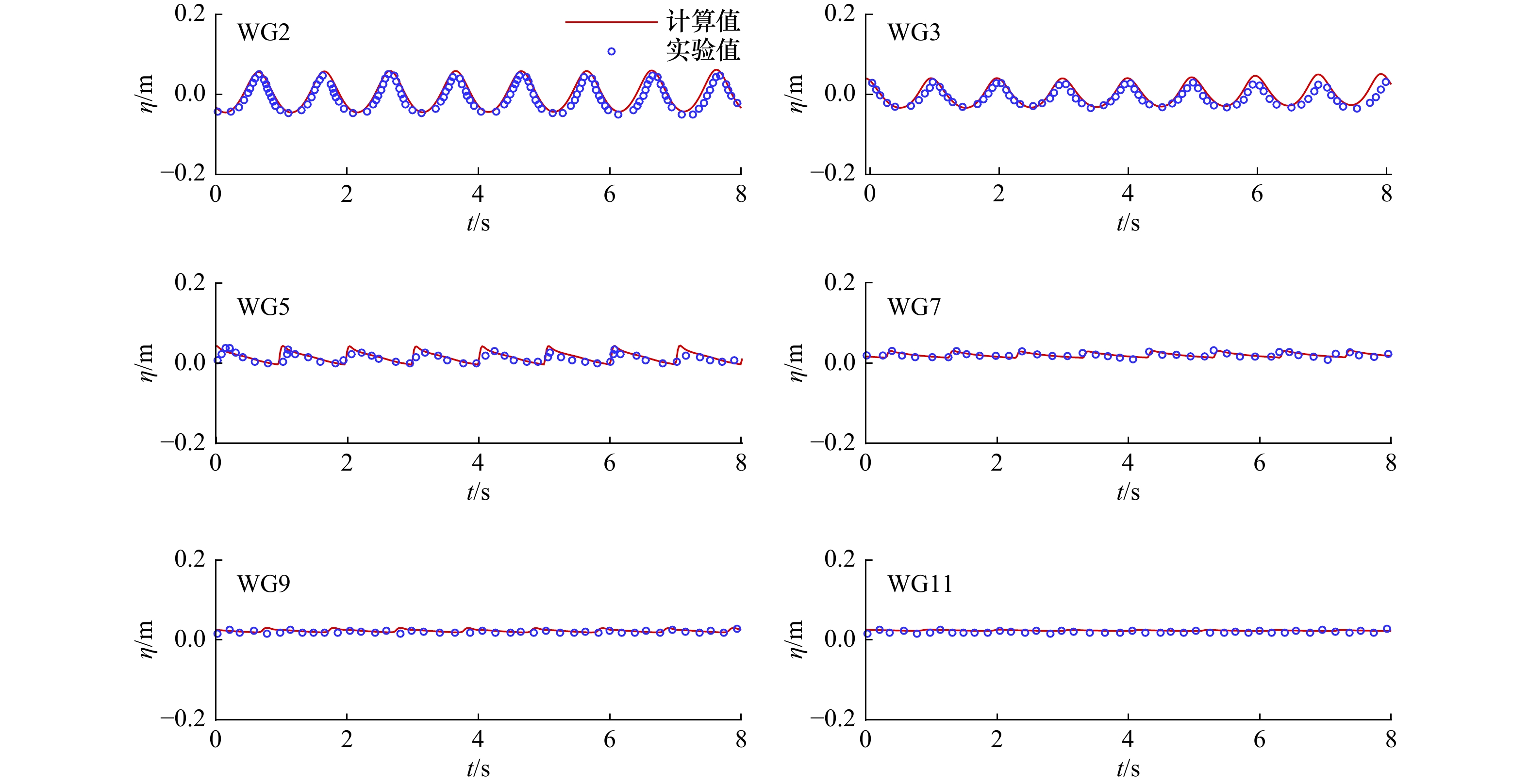
表 1 实验工况
Tab. 1 Experimental setups
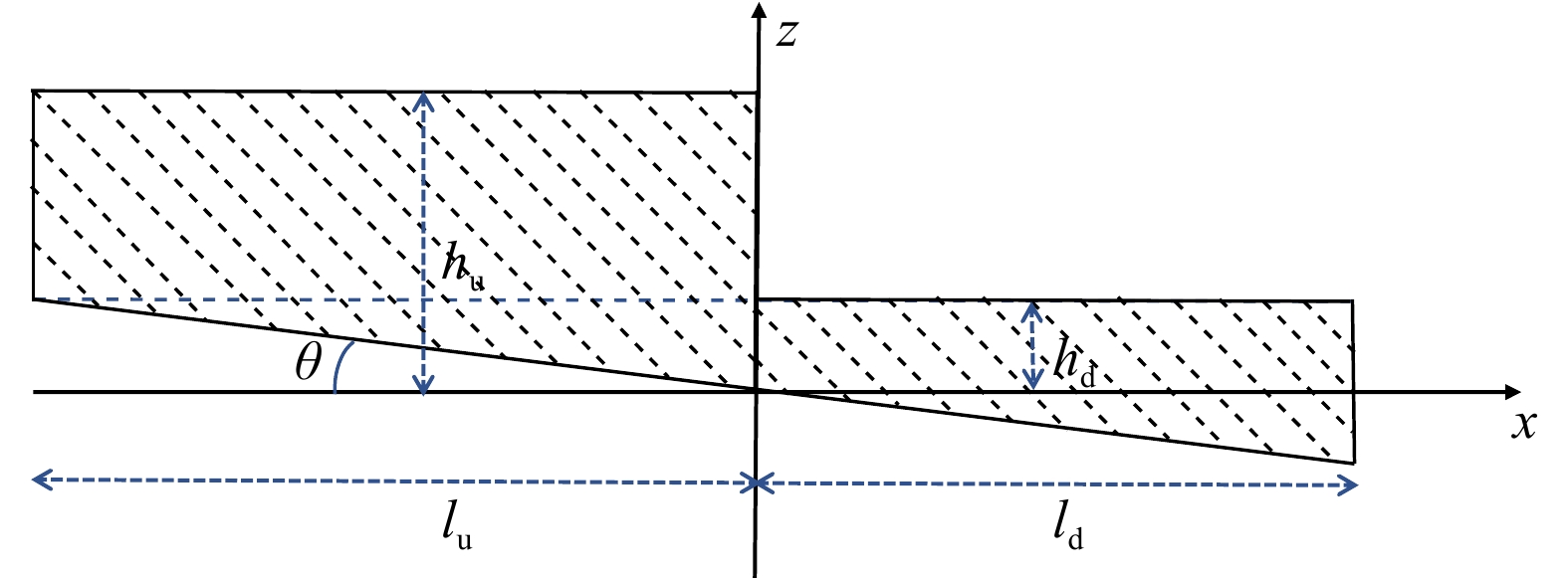
工况编号 $ {h}_{\mathrm{u}} $/m $ {h}_{\mathrm{d}} $/m $ \theta $/(°) Y1 0.4 0.04 0 Y2 0.4 0.08 0 Y3 0.4 0.16 0 Y4 0.4 0.04 0.02 Y5 0.4 0.08 0.02 Y6 0.4 0.16 0.02 表 2 数值模拟工况设置
Tab. 2 Parameter setup of numerical simulation
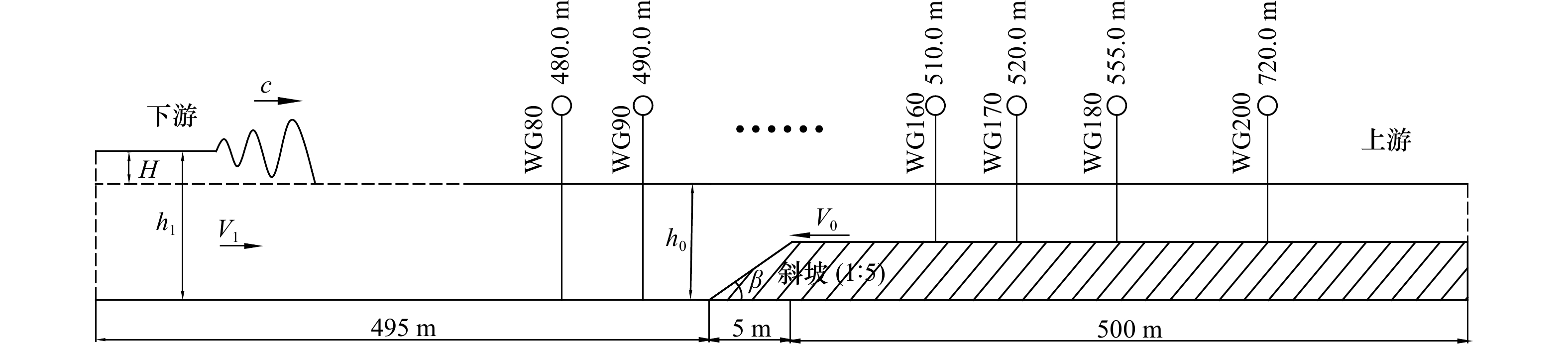
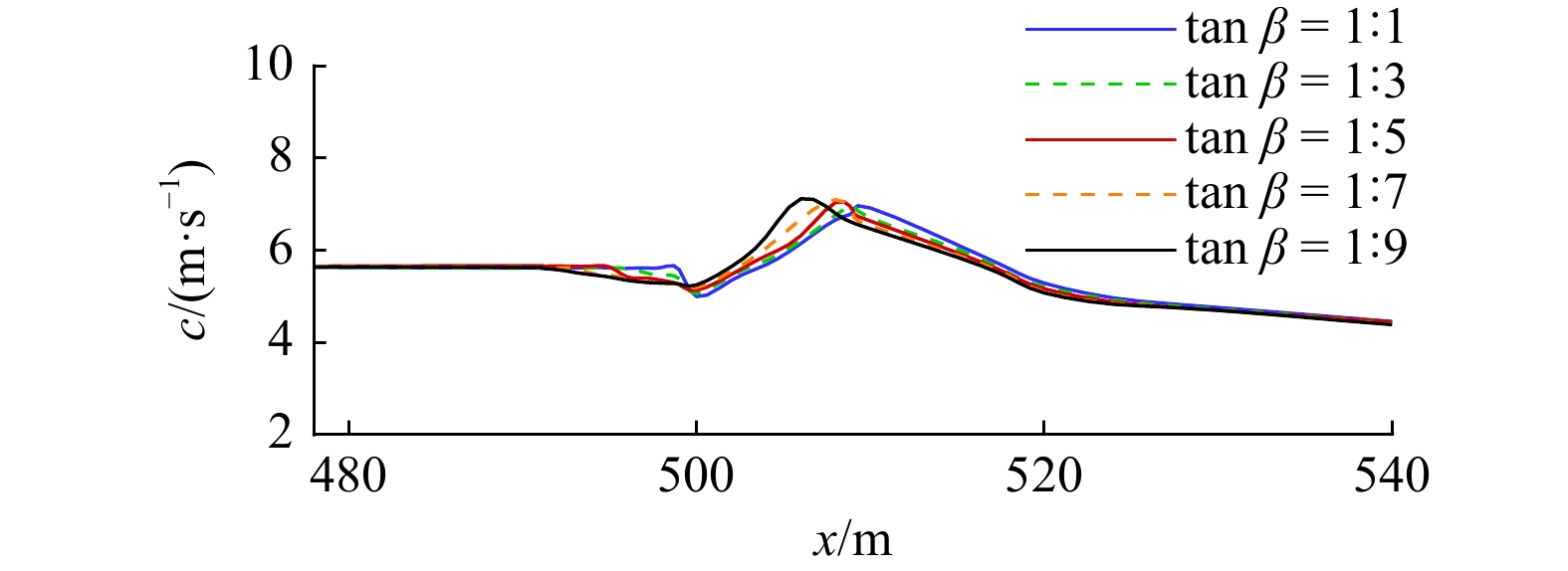
工况 涌潮高度H/m 潮前水深h0/m 底坡坡度tan β 弗劳德数Fr A1 0.60 2.0 1∶5 1.220 A2 0.40 2.0 1∶5 1.150 A3 0.45 2.0 1∶5 1.167 A4 0.50 2.0 1∶5 1.185 A5 0.55 2.0 1∶5 1.204 B1 0.60 1.9 1∶5 1.234 B2 0.60 2.1 1∶5 1.212 B3 0.60 2.2 1∶5 1.203 B4 0.60 2.3 1∶5 1.194 C1 0.60 2.0 1∶1 1.220 C2 0.60 2.0 1∶3 1.220 C3 0.60 2.0 1∶7 1.220 C4 0.60 2.0 1∶9 1.220 -
[1] 戚蓝, 肖厅厅, 张芝永, 等. 涌潮水流CFD数值模拟[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2019(3): 32−40.Qi Lan, Xiao Tingting, Zhang Zhiyong, et al. Numerical simulation of tidal bore based on CFD method[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2019(3): 32−40. [2] 林炳尧. 钱塘江涌潮的特性[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 87, 130.Lin Bingyao. Characteristics of Qiantang River Tide[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 87, 130. [3] 黄静, 潘存鸿, 陈刚, 等. 涌潮的水槽模拟及验证[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2013(2): 1−8.Huang Jing, Pan Cunhong, Chen Gang, et al. Experimental simulation and validation of the tidal bore in the flume[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2013(2): 1−8. [4] 潘存鸿, 鲁海燕, 曾剑. 钱塘江涌潮特性及其数值模拟[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2008(2): 1−9.Pan Cunhong, Lu Haiyan, Zeng Jian. Characteristic and numerical simulation of tidal bore in Qiantang River[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2008(2): 1−9. [5] 林伟栋, 赵西增, 叶洲腾, 等. 涌潮运动的CFD模拟研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2017, 32(6): 696−703.Lin Weidong, Zhao Xizeng, Ye Zhouteng, et al. Numerical simulation of tidal bore using CFD model[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2017, 32(6): 696−703. [6] 林炳尧, 黄世昌, 毛献忠. 波状水跃和波状涌潮的分析[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 1998, 13(1): 106−115.Lin Bingyao, Huang Shichang, Mao Xianzhong. Analyses of undular hydraulic jump and undular bore[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 1998, 13(1): 106−115. [7] Chanson H. Current knowledge in tidal bores and their environmental, ecological and cultural impacts[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 2011, 11(1): 77−98. doi: 10.1007/s10652-009-9160-5 [8] 刘文虎, 朱小华, 张钟哲, 等. 钱塘江涌潮观测及其动力学特性研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2015, 30(5): 567−572.Liu Wenhu, Zhu Xiaohua, Zhang Zhongzhe, et al. Observation and dynamic characteristics of tidal bore in Qiantang River, China[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2015, 30(5): 567−572. [9] Wolanski E, Williams D, Spagnol S, et al. Undular tidal bore dynamics in the Daly Estuary, Northern Australia[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 60(4): 629−636. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.03.001 [10] Simpson J H, Fisher N R, Wiles P. Reynolds stress and TKE production in an estuary with a tidal bore[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2004, 60(4): 619−627. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2004.03.006 [11] 岳书波, 曾剑, 陈永平, 等. 涌潮潮头掺气的模型试验研究[J]. 工程科学与技术, 2018, 50(1): 28−35.Yue Shubo, Zeng Jian, Chen Yongping, et al. Investigation of aeration of tidal bore front by physical experiments[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2018, 50(1): 28−35. [12] 潘存鸿, 鲁海燕. 二维浅水间断流动数值模型在涌潮模拟中的应用[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2009, 43(11): 2107−2113.Pan Cunhong, Lu Haiyan. 2D numerical model for discontinuous shallow water flows and application to simulation of tidal bore[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2009, 43(11): 2107−2113. [13] 潘存鸿, 鲁海燕, 于普兵, 等. 钱塘江二维涌潮数值模拟及其应用[J]. 浙江水利科技, 2008(2): 4−8.Pan Cunhong, Lu Haiyan, Yu Pubing, et al. 2D numerical simulation of bore on Qiantang River and its application[J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics, 2008(2): 4−8. [14] 黄婷, 张怀, 石耀霖. 基于Boussinesq型方程的钱塘江涌潮数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(1): 79−95.Huang Ting, Zhang Huai, Shi Yaolin. Numerical simulation of the tidal bore in the Qiantang River based on Boussinesq-type equations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(1): 79−95. [15] 谢东风, 潘存鸿, 陆波, 等. 基于实测资料的钱塘江涌潮水动力学特性研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2012, 27(5): 501−508.Xie Dongfeng, Pan Cunhong, Lu Bo, et al. A study on the hydrodynamic characteristics of the Qiantang tidal bore based on field data[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2012, 27(5): 501−508. [16] 张巍, 贺治国, 谈利明, 等. 基于定点连续观测的钱塘江涌潮特性研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2017, 32(2): 253−259.Zhang Wei, He Zhiguo, Tan Liming, et al. Dynamic characteristics of Qiantang tidal bore based on field observations at a fixed location[J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2017, 32(2): 253−259. [17] Yeh H H, Mok K M. On turbulence in bores[J]. Physics of Fluids A: Fluid Dynamics, 1990, 2(5): 821−828. doi: 10.1063/1.857630 [18] Treske A. Undular bores (favre-waves) in open channels-experimental studies[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1994, 32(3): 355−370. doi: 10.1080/00221689409498738 [19] Miahr H C. Physical modelling of the flow field in an UNDULAR tidal bore[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 2005, 43(3): 234−244. doi: 10.1080/00221680509500118 [20] 杨火其, 潘存鸿, 周建炯, 等. 涌潮水力学特性试验研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2008, 26(4): 136−138.Yang Huoqi, Pan Cunhong, Zhou Jianjiong, et al. Experiment study on hydraulic properties of tidal bore[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2008, 26(4): 136−138. [21] 赵雪华. 钱塘江涌潮的一维数学模型[J]. 水利学报, 1985(1): 50−54.Zhao Xuehua. A one-dimensional mathematical model of the surge of Qiantang River[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1985(1): 50−54. [22] 潘存鸿. 三角形网格下求解二维浅水方程的和谐Godunov格式[J]. 水科学进展, 2007, 18(2): 204−209.Pan Cunhong. Well-balanced Godunov-type scheme for 2D shallow water flow with triangle mesh[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2007, 18(2): 204−209. [23] 潘存鸿, 徐昆. 三角形网格下求解二维浅水方程的KFVS格式[J]. 水利学报, 2006, 37(7): 858−864.Pan Cunhong, Xu Kun. Kinetic flux vector splitting scheme for solving 2-D shallow water equations with triangular mesh[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 37(7): 858−864. [24] Landrini M, Colagrossi A, Greco M, et al. Gridless simulations of splashing processes and near-shore bore propagation[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 591: 183−213. doi: 10.1017/S0022112007008142 [25] Li Jing, Liu Huaxing, Tan S K. Lagrangian modeling of tidal bores passing through bridge piers[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2010, 22(1): 496−502. [26] Furuyama S I, Chanson H. A numerical study of open channel flow hydrodynamics and turbulence of the tidal bore and dam-break flows[J]. Hydraulic Model, 2008. [27] 赵渭军, 赵刚, 李永和. 钱塘江海塘护塘建筑物技术演进[J]. 浙江水利科技, 2015, 43(2): 34−37.Zhao Weijun, Zhao Gang, Li Yonghe. Investigation on facilities for protecting Qiantang Estuary seadyke[J]. Zhejiang Hydrotechnics, 2015, 43(2): 34−37. [28] 杨火其, 杨永楚, 庄娟芳. 钱塘江河口斜坡式土堤水下防护面板稳定性试验[J]. 水利水运工程学报, 2001(3): 65−68.Yang Huoqi, Yang Yongchu, Zhuang Juanfang. Stability experiment of underwater face-plate on sloping dyke in Qiantangjiang Estuary[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2001(3): 65−68. [29] 陈伟, 倪舒娴, 袁淼. 钱塘江海塘建设的历史沿革[J]. 浙江建筑, 2018, 35(9): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3707.2018.09.001Chen Wei, Ni Shuxian, Yuan Miao. Historical evolution of seawall construction for the Qiantang River[J]. Zhejiang Construction, 2018, 35(9): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3707.2018.09.001 [30] Ma Gangfeng, Kirby J T, Shi Fengyan. Numerical simulation of tsunami waves generated by deformable submarine landslides[J]. Ocean Modelling, 2013, 69: 146−165. doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2013.07.001 [31] Liu Wenjun, Wang Bo, Guo Yakun, et al. Experimental investigation on the effects of bed slope and tailwater on dam-break flows[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 590: 125256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125256 [32] Zhang Fengjie, Wang Bo, Guo Yakun. Experimental study of the dam-break waves in triangular channels with a sloped wet bed[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 255: 111399. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111399 [33] Yao Yu, Huang Zhenhua, Monismith S G, et al. 1DH Boussinesq modeling of wave transformation over fringing reefs[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2012, 47: 30−42. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.03.010 -




 下载:
下载: