Analysis on the variation characteristics of environmental factors and influencing factors in the process of Phaeocystis globosa bloom in the western waters of Hainan Island
-
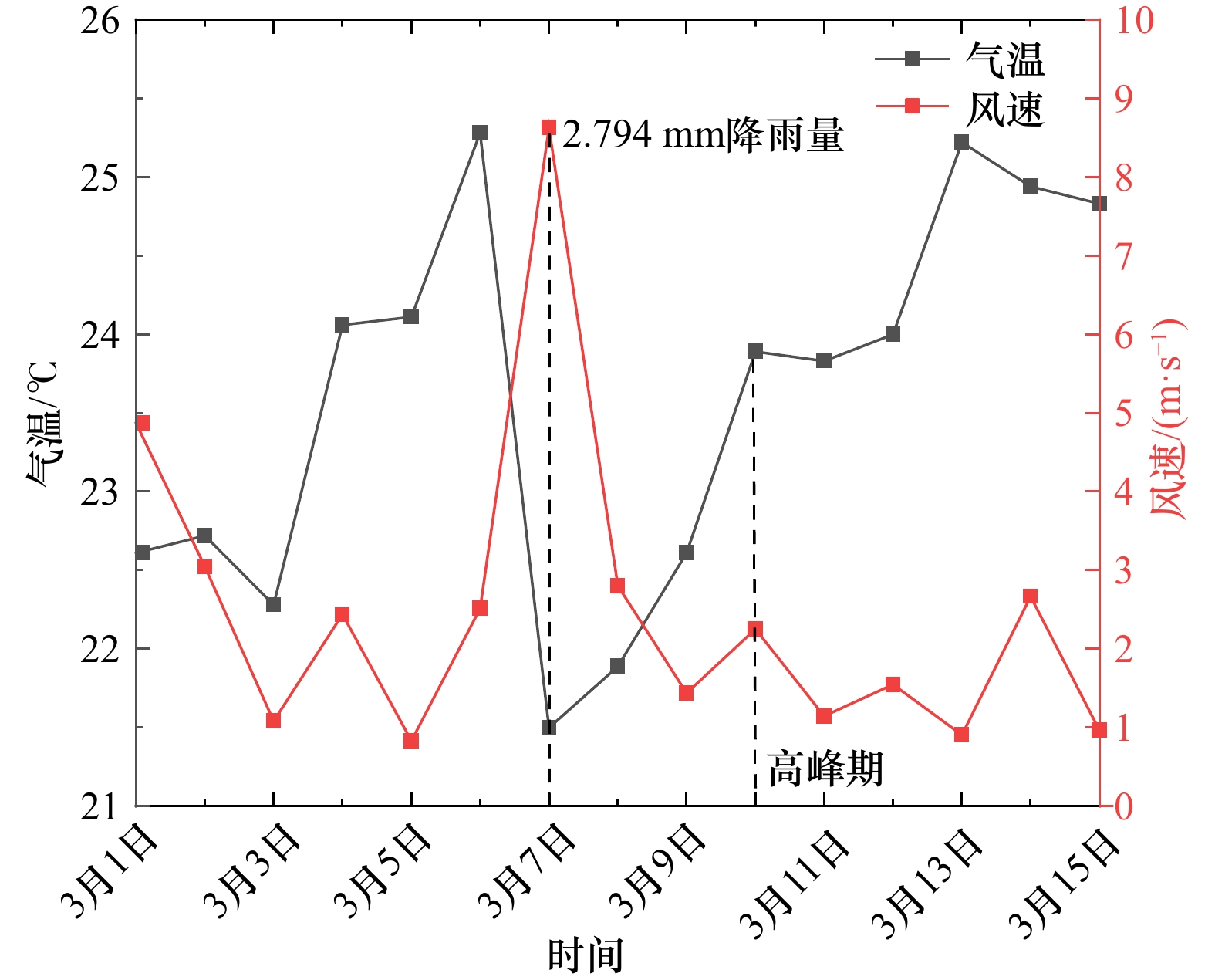
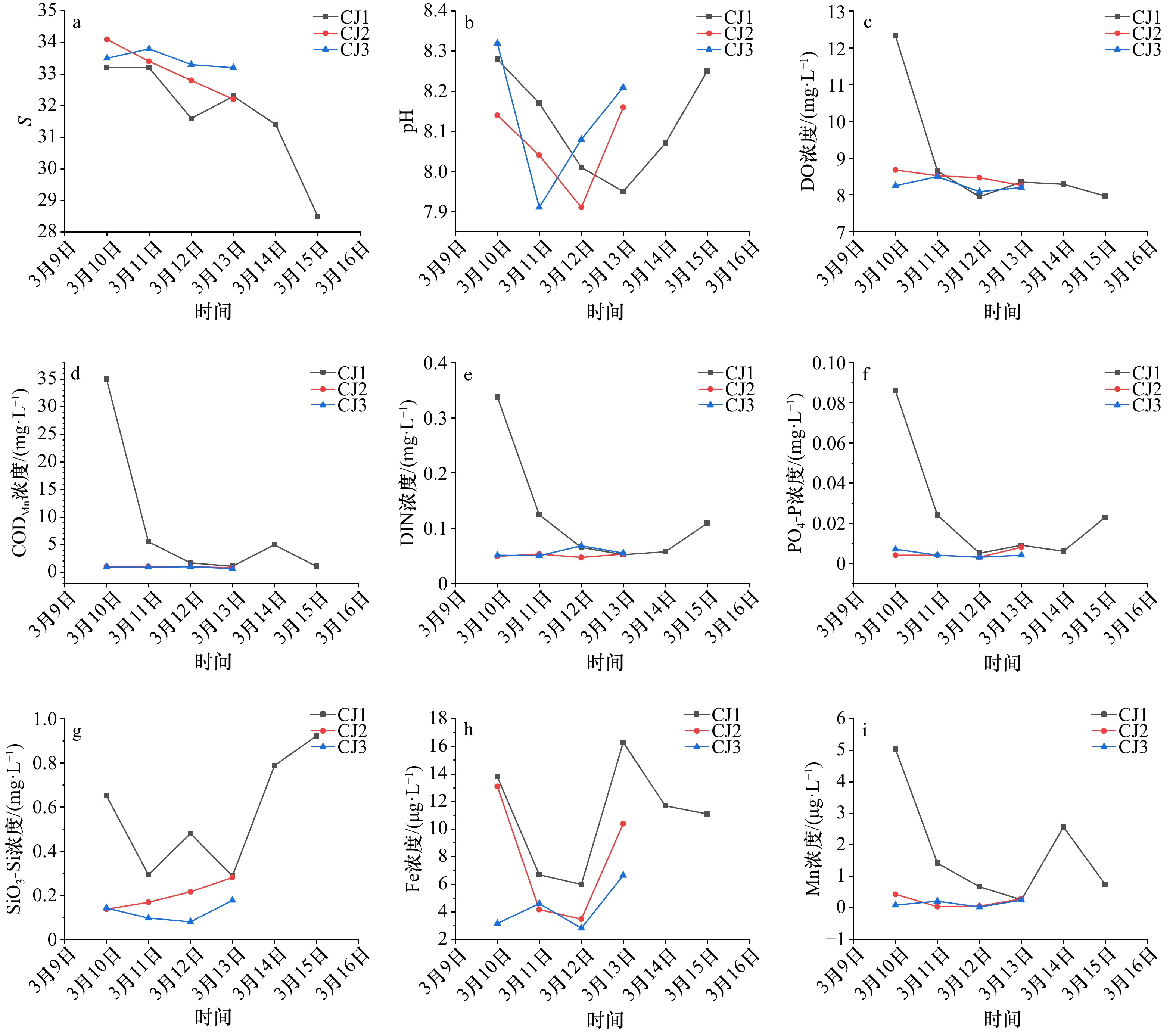
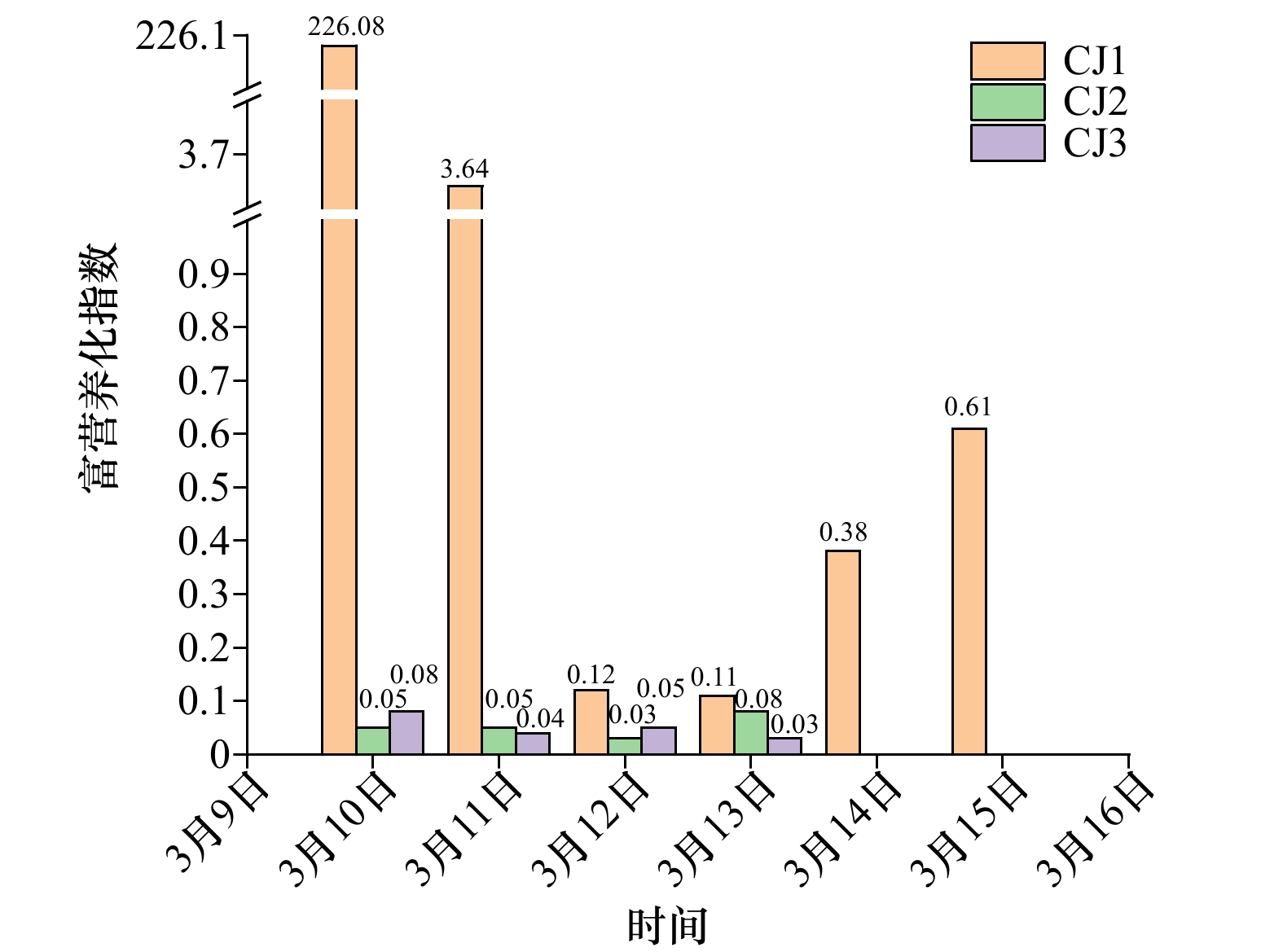
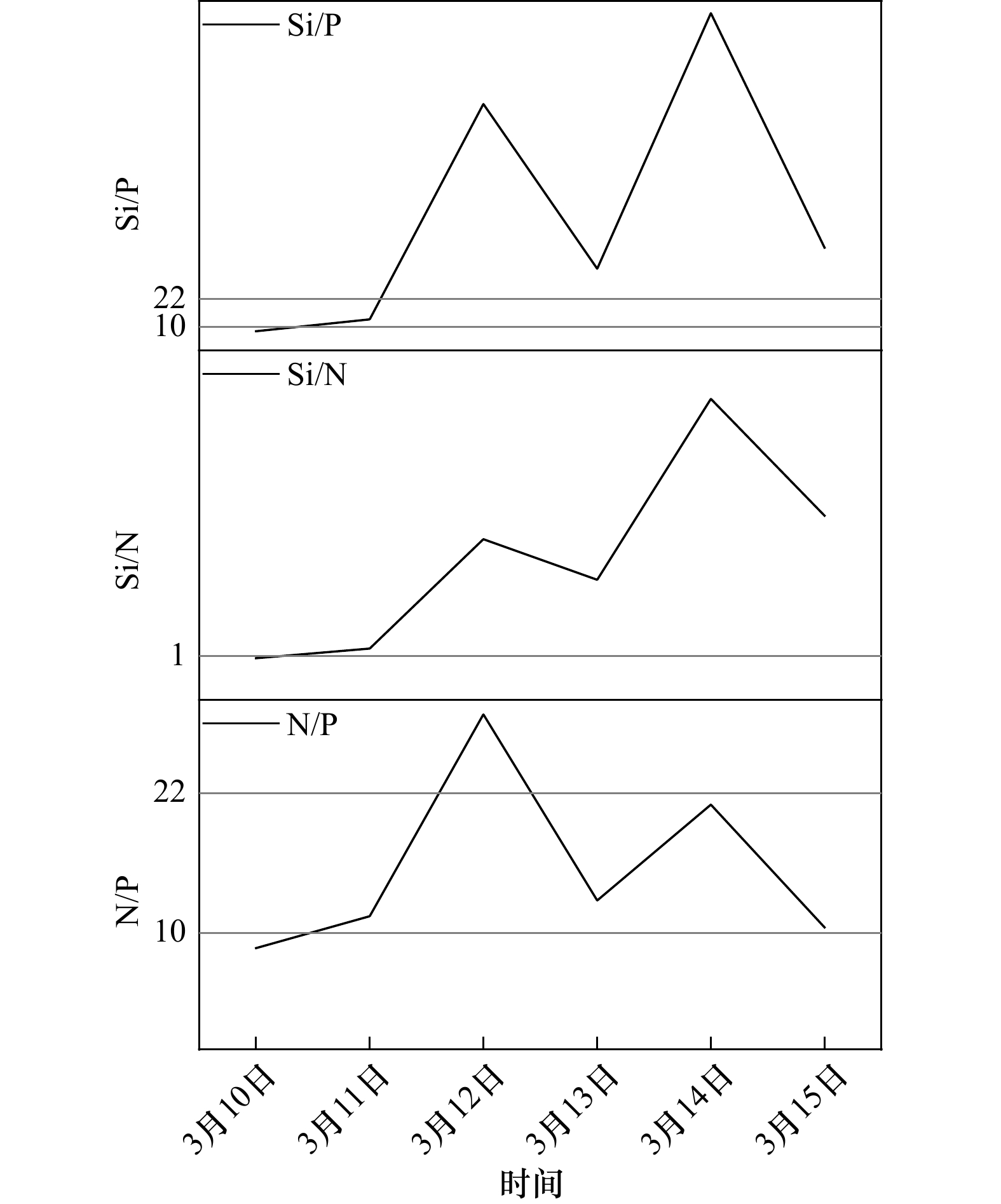
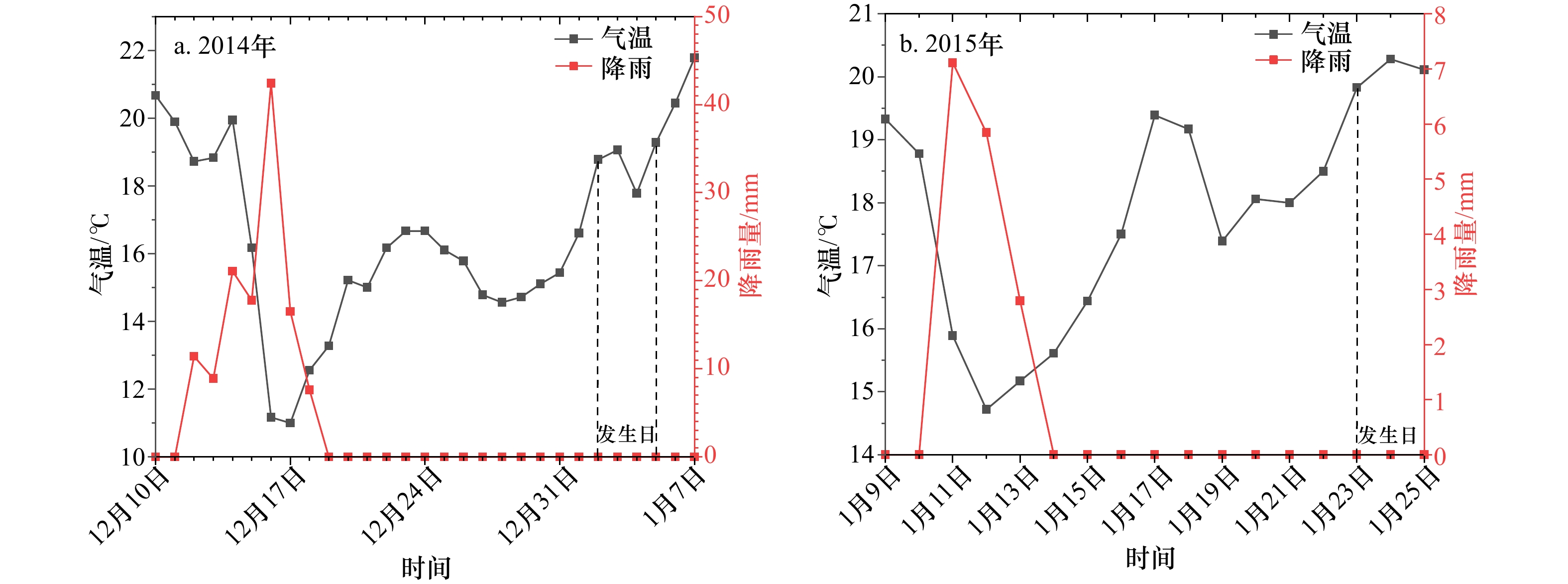
摘要: 通过2022年3月10−15日在海南岛西部昌江昌化沿岸海域开展为期6 d的现场跟踪调查,结合水文气象资料分析了本次球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)赤潮生消过程环境因子变化特征及影响因素。本次赤潮高峰期球形棕囊藻丰度及CODMn分别高达3.10×108 cells/L及35 mg/L,远高于其他海域报道记录。赤潮暴发前降雨及风浪扰动促进了陆源输入及沉积营养盐释放,为赤潮暴发提供物质条件。气温骤升诱导赤潮发生,更大潮差及较低风速为囊体沿岸聚集创造了有利的外部条件。赤潮消亡过程中,DIN、PO4-P、DO、CODMn及Mn浓度显著下降,其中DIN及PO4-P是本次赤潮消亡的限制因子,DO、CODMn及Mn为本次赤潮消亡的重要特征因子。黄色囊体出现破碎后,Chlorophyll a及SiO3-Si浓度也迅速下降,随后缓慢上升甚至高于高峰期浓度水平,此时以旋链角毛藻(Chaetoceros curvisetus)等代表的硅藻丰度逐渐增加。研究还初步探索了本次赤潮的基本生消过程,为进一步揭示本区域球形棕囊藻赤潮爆发机理提供重要参考依据。Abstract: Combined with hydrometeorological data, a six-day tracking survey was carried out in the coastal waters of Changhua Town, Changjiang County, western Hainan Island on March 10 to 15, 2022. And this study analyzed the variation characteristics of environmental factors and influencing factors in the process of Phaeocystis globose bloom. During the peak of the bloom, the abundance of Phaeocystis globosa and CODMn were as high as 3.10×108 cells/L and 35 mg/L, which were much higher than those reported in other areas. The rainfall and wind wave disturbance before the bloom promoted the terrestrial runoff and the release of sedimentary nutrients, which provided material conditions for the bloom. The sudden rise of temperature induces the bloom, and the larger tidal range and lower wind speed create favorable external conditions for the accumulation along the colony. During the elimination of the bloom, the concentrations of DIN, PO4-P, DO, CODMn and Mn decreased significantly, in which DIN and PO4-P were the limiting factors, and DO, CODMn and Mn were important characteristic factors. After the yellow colony broken, the concentrations of Chl a and SiO3-Si also decreased rapidly, and then slowly increased or even higher than the peak concentration level, when the diatom abundance represented by Chaetoceros curvisetus gradually increased. The study also preliminarily explores the basic generation and elimination process of the bloom, which provides an important reference for the further study of the bloom mechanism of P. globosa in this area.
-
Key words:
- Phaeocystis globose /
- colony /
- environmental factors /
- variation characteristics /
- influence factors
-
图 2 CJ1站位镜检及现场图
a, b. 囊体内无鞭毛不动细胞100×/400×;c. 游离的无鞭毛不动细胞400×;d. 具鞭毛游动细胞400× ;e. 高峰期赤潮水体;f. 黄色囊体;g. 透明囊体;h. 透明囊体碎片
Fig. 2 Microscopic examination and on-the-spot map of Station CJ1
a, b. Flagellar-less immobile cells in the colony 100×/400×; c. free flagellar-less immobile cells 400×; d. flagellar motile cells 400×; e. the bloom during the peak period; f. yellow colony; g. hyaline colony; h. hyaline colony fragment
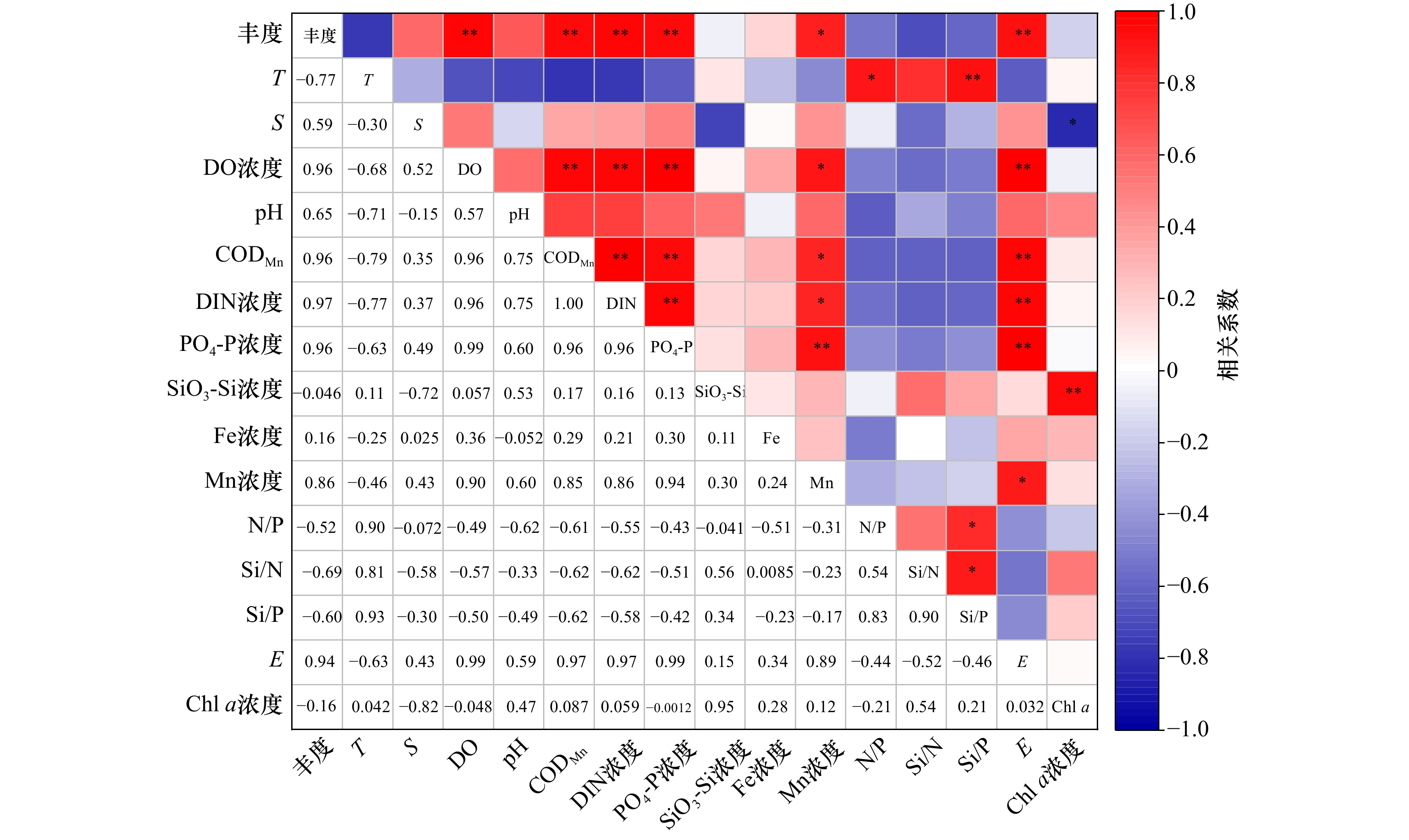
图 8 调查期间球形棕囊藻与环境因子的相关系数
**表示p<0.01,极显著性相关;*表示0.01<p<0.05,显著性相关;否则差异不显著
Fig. 8 Correlation coefficient between Phaeocystis globosa and environmental factors during the survey period
** represents extremely significant correlation at p<0.01, * represents significant correlation at 0.01<p<0.05, other no significant
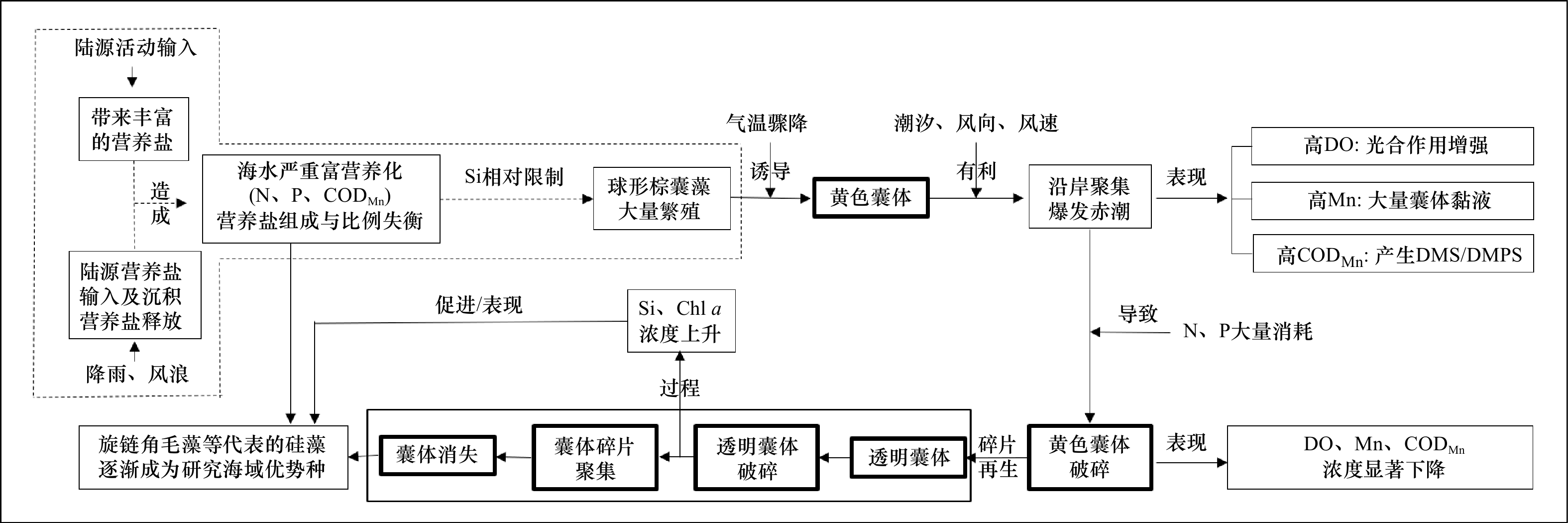
图 11 昌江昌化沿岸海域球形棕囊藻赤潮生消流程图
虚线框内的流程表示赤潮爆发前根据背景数据资料进行的推测,其余流程为现场跟踪调查的测定结果
Fig. 11 Flow map of generation and elimination of Phaeocystis globosa bloom in the coastal waters of Changhua, Changjiang
The flow in the dotted frame shows the conjecture based on the background data before the bloom, and the rest of the process is the results of the on-site follow-up investigation
表 1 调查期间CJ1站位浮游植物种类组成及丰度(单位:cells/L)逐日变化情况
Tab. 1 Daily variation of species composition and abundance (unit: cells/L) of phytoplankton in the Station CJ1 during the survey period
门类 种类 拉丁名 3月10日 3月11日 3月12日 3月13日 3月14日 3月15日 硅藻门 双眉藻 Amphora sp. − 2.67×103 − − − − 奇异棍形藻 Bacillaria paradoxa 3.33×104 − − − − − 中国盒形藻 Biddulphia sinensis 1.33×103 − − − 1.33×103 1.33×103 大洋角管藻 Cerataulina pelagica − − − 1.33×103 − − 窄隙角毛藻 Chaetoceros affinis − 1.33×103 − − − 6.40×104 绕孢角毛藻 Chaetoceros cinctus − − 2.67×104 2.80×104 − 1.20×105 扁面角毛藻 Chaetoceros compressus − − − − 1.87×104 − 旋链角毛藻 Chaetoceros curvisetus − − 1.20×104 1.60×104 − 1.27×105 柔弱角毛藻 Chaetoceros debilis − − 6.67×103 1.47×104 − 4.67×104 幷基角毛藻 Chaetoceros decipiens − − − − − 2.67×104 粗股角毛藻 Chaetoceros femur − − − 4.00×103 − − 洛氏角毛藻 Chaetoceros lorenzianus − 4.00×103 − 6.67×103 − 4.80×104 拟弯角毛藻 Chaetoceros pseudocurvisetus − − 1.33×103 3.20×104 − 4.13×104 暹罗角毛藻 Chaetoceros siamense − − 4.00×103 3.33×104 − 3.33×104 聚生角毛藻 Chaetoceros socialis − − − − − 9.33×103 角毛藻 Chaetoceros spp. − − 1.60×104 5.87×104 6.67×103 8.00×104 圆柱角毛藻 Chaetoceros teres − − 1.73×104 4.00×103 − 2.93×104 扭链角毛藻 Chaetoceros tortissimus − − − 1.47×104 − 4.93×104 圆筛藻 Coscinodiscus spp. 1.07×104 − 4.00×103 6.67×103 9.33×103 1.33×103 椭圆双壁藻 Diploneis elliptica 5.33×103 1.33×103 − − 8.00×103 4.00×103 太阳双尾藻 Ditylum sol − − 1.33×103 − − − 长角弯角藻 Eucampia cornuta − − − 1.33×103 − − 丹麦细柱藻 Leptocylindrus danicus 5.33×103 1.33×103 2.67×103 1.87×104 1.47×104 8.00×103 颗粒直链藻 Melosira granulata 2.93×104 − 1.33×104 − 1.07×105 2.67×104 念珠直链藻 Melosira moniliformis − − − − − 5.33×103 舟形藻 Navicula spp. 1.60×104 1.33×103 1.87×104 1.20×104 2.40×104 1.33×104 新月菱形藻 Nitzschia closterium 3.60×104 1.33×103 1.20×104 5.33×103 8.13×104 1.07×104 菱形藻 Nitzschia spp. 2.13×104 1.33×103 1.20×104 8.00×103 2.27×104 9.33×103 美丽斜纹藻 Pleurosigmaformosum 1.33×103 − − − 1.33×103 1.33×103 柔弱拟菱形藻 Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima 4.00×103 6.67×103 6.67×103 9.33×103 2.40×104 4.00×103 尖刺拟菱形藻 Pseudo-nitzschia pungens − 8.00×103 − 1.07×104 2.00×104 5.33×103 翼根管藻 Rhizosolenia alata − − − 1.33×103 − − 螺端根管藻 Rhizosolenia cochlea − − − 1.33×103 − − 厚刺根管藻 Rhizosolenia crassispina − − − − − 1.33×103 斯托根管藻 Rhizosolenia fragilissima − − 1.33×103 5.33×103 − 5.33×103 覆瓦根管藻 Rhizosolenia imbricata 1.33×103 − − − − − 刚毛根管藻 Rhizosolenia setigera 1.33×103 1.33×103 2.67×103 − − 6.67×103 中华根管藻 Rhizosolenia sinensis 2.67×103 − 2.67×103 − 2.67×103 1.33×103 笔尖根管藻 Rhizosolenia styliformis 1.33×103 − − − 1.33×103 − 中肋骨条藻 Skeletonema costatum − − 2.53×104 8.00×103 1.33×104 1.12×105 塔形冠盖藻 Stephanopyxis turris − − − − 8.00×103 − 芽形双菱藻 Surirella gemma − − − − 1.33×103 − 伽氏针杆藻 Synedra fulgens − − − − 2.67×103 − 针杆藻 Synedra spp. 6.67×103 − 1.20×104 9.33×103 1.33×104 4.00×103 肘状针杆藻 Synedra ulna − − 1.33×103 − 1.33×103 − 菱形海线藻 Thalassionema nitzschioides 6.67×103 − − 5.33×103 9.33×103 1.47×104 密联海链藻 Thalassiosira condensata 4.00×103 − − − 2.00×104 − 佛氏海毛藻 Thalassiothrix frauenfeldii − − − − 4.00×103 − 大龙骨藻 Tropidoneis maxima 1.33×103 − − − − 1.33×103 蓝藻门 红海束毛藻 Trichodesmillm erythraeum 2.53×104 − − − 8.67×104 − 黄藻门 海洋卡盾藻 Chattonella marina 1.07×104 4.00×103 − 4.00×103 8.00×103 5.33×103 金藻门 球形棕囊藻 Phaeocystis globosa 3.10×108 1.17×108 3.97×106 4.23×106 5.54×106 8.52×105 注:加粗字体表示球形棕囊藻名称及丰度,下划线加粗字体表示调查期间其他浮游植物第一优势种名称及丰度,−表示未鉴定出该物种。 -
[1] Wang Xiaodong, Song Huiyin, Wang Yan, et al. Research on the biology and ecology of the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa in China: progresses in the last 20 years[J]. Harmful Algae, 2021, 107: 102057. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102057 [2] Schoemann V, Becquevort S, Stefels J, et al. Phaeocystis blooms in the global ocean and their controlling mechanisms: a review[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2005, 53(1/2): 43−66. [3] Hamm C E. Architecture, ecology and biogeochemistry of Phaeocystis colonies[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2000, 43(3/4): 307−315. [4] 陈菊芳, 徐宁, 江天久, 等. 中国赤潮新记录种──球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学版), 1999, 20(3): 124−129.Chen Jufang, Xu Ning, Jiang Tianjiu, et al. A report of Phaeocystis globosa bloom in coastal water of Southeast China[J]. Journal of Ji'nan University (Natural Science), 1999, 20(3): 124−129. [5] 沈萍萍, 齐雨藻, 欧林坚. 中国沿海球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的分类、分布及其藻华[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(10): 146−162. doi: 10.11759/hykx20171225004Shen Pingping, Qi Yuzao, Ou Linjian. Phaeocystis globosa in coastal China: taxonomy, distribution, and its blooms[J]. Marine Sciences, 2018, 42(10): 146−162. doi: 10.11759/hykx20171225004 [6] 海南省海洋与渔业厅. 2003−2017年海南省海洋环境状况公报[R]. 海口: 海南省海洋与渔业厅, 2003−2017.Department of Ocean and Fisheries of Hainan Province. State of the marine environment in Hainan Province, 2003−2017[R]. Haikou: Department of Ocean and Fisheries of Hainan Province, 2003−2017. [7] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 17378.4−2007, 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. GB 17378.4−2007, The specification for marine monitoring−−Part 4: Seawater analysis[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [8] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB 17378.7−2007, 海洋监测规范 第7部分: 近海污染生态调查和生物监测[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. GB 17378.7−2007, The specification for marine monitoring−−Part 7: Ecological survey for offshore pollution and biological monitoring[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [9] 中华人民共和国环境保护部. HJ 442−2008, 近岸海域环境监测规范[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2009.Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. HJ 442−2008, Specification for offshore environmental monitoring[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2009. [10] 沈萍萍, 王艳, 齐雨藻, 等. 球形棕囊藻的生长特性及生活史研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2000, 24(6): 635−643. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2000.06.010Shen Pingping, Wang Yan, Qi Yuzao, et al. Growth characteristics and life cycle of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2000, 24(6): 635−643. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3207.2000.06.010 [11] 胡章喜, 邓蕴彦, 唐赢中. 我国北部湾球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa)的表面形态和细胞超微结构的电镜观察[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(3): 621−629. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180700180Hu Zhangxi, Deng Yunyan, Tang Yingzhong. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy observation on morphology and ultrastructure of Phaeocystis globosa from Beibu Gulf, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(3): 621−629. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180700180 [12] 徐轶肖, 何喜林, 张腾, 等. 北部湾棕囊藻藻华原因种分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6): 122−130.Xu Yixiao, He Xilin, Zhang Teng, et al. Causative species of Phaeocystis blooms in Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 122−130. [13] Dortch Q, Packard T T. Differences in biomass structure between oligotrophic and eutrophic marine ecosystems[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part A: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1989, 36(2): 223−240. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(89)90135-0 [14] Justić D, Rabalais N N, Turner R E. Stoichiometric nutrient balance and origin of coastal eutrophication[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1995, 30(1): 41−46. doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)00105-I [15] 施玉珍, 赵辉, 王喜达, 等. 珠江口海域营养盐和叶绿素a的时空分布特征[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2019, 39(1): 56−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2019.01.009Shi Yuzhen, Zhao Hui, Wang Xida, et al. Distribution characteristics of nutritive salts and chlorophyll a in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2019, 39(1): 56−65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2019.01.009 [16] 马奔, 赵辉. 夏季珠江口叶绿素a和营养盐分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(5): 707−716. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200244Ma Ben, Zhao Hui. Distribution characteristics of chlorophyll a and nutrients in the Pearl River Estuary in summer and their relationship with environmental factors[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(5): 707−716. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200244 [17] Wang Kang, Chen Baohong, Gao Yahui, et al. Harmful algal blooms caused by Phaeocystis globosa from 1997 to 2018 in Chinese coastal waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 173: 112949. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112949 [18] 李杰, 陆家昌, 赖俊翔, 等. 球形棕囊藻游离单细胞的密度与囊体形成的关系研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 2022, 40(1): 84−95. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2022.10084Li Jie, Lu Jiachang, Lai Junxiang, et al. Study on the relationship between solitary cell density and colony formation of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel[J]. Plant Science Journal, 2022, 40(1): 84−95. doi: 10.11913/PSJ.2095-0837.2022.10084 [19] 黄长江, 董巧香, 郑磊. 1997年底中国东南沿海大规模赤潮原因生物的形态分类与生态学特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1999, 30(6): 581−590. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.06.001Huang Changjiang, Dong Qiaoxiang, Zheng Lei. Taxonomic and ecological studies on a large scale Phaeocystis pouchetii bloom in the southeast coast of China during late 1997[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1999, 30(6): 581−590. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.06.001 [20] 王超, 李新辉, 赖子尼, 等. 珠江口球形棕囊藻(Phaeocysis globosa)赤潮后期的浮游植物群落结构特征研究[J]. 生态科学, 2010, 29(2): 140−146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2010.02.009Wang Chao, Li Xinhui, Lai Zini, et al. Study on phytoplankton community structure at the late stage of a Phaeocystis globosa bloom in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Ecological Science, 2010, 29(2): 140−146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8873.2010.02.009 [21] Smith W O Jr, Liu Xiao, Tang K W, et al. Giantism and its role in the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2014, 101: 95−106. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.12.005 [22] 庄万金. 厦门西海域赤潮发生区海水pH的分布及与赤潮的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1992, 11(3): 64−70.Zhuang Wanjin. Relationship between red tide outbreak and pH distribution in the res tide occurring area of Xiamen west barbor[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1992, 11(3): 64−70. [23] 石鑫, 宋金明, 李学刚, 等. 长江口邻近海域海水pH的季节变化及其影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(5): 1033−1042. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190200037Shi Xin, Song Jinming, Li Xuegang, et al. Seasonal change of pH in the waters off Changjiang River Estuary and its impact factors[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(5): 1033−1042. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190200037 [24] 刘悦, 李丽, 翟晓辉, 等. 深圳大鹏湾一次球形棕囊藻藻华的发生过程及成因分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(3): 164−171. doi: 10.11978/2021148Liu Yue, Li Li, Zhai Xiaohui, et al. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 164−171. doi: 10.11978/2021148 [25] 李波, 蓝文陆, 李天深, 等. 球形棕囊藻赤潮消亡过程环境因子变化及其消亡原因[J]. 生态学杂志, 2015, 34(5): 1351−1358. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.20150311.050Li Bo, Lan Wenlu, Li Tianshen, et al. Variation of environmental factors during Phaeocystis globosa blooms and its implications for the bloom decay[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2015, 34(5): 1351−1358. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.20150311.050 [26] 朱健, 李捍东, 王平. 环境因子对底泥释放COD、TN和TP的影响研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2009, 35(8): 44−49. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2009.08.011Zhu Jian, Li Handong, Wang Ping. The impact of environmental factors on COD, TN, TP release from sediment[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2009, 35(8): 44−49. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2009.08.011 [27] Liss P S, Malin G, Turner S M, et al. Dimethyl sulphide and Phaeocystis: a review[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 1994, 5(1): 41−53. doi: 10.1016/0924-7963(94)90015-9 [28] 齐雨藻, 徐宁, 王艳, 等. 中国赤潮研究的新进展——球形棕囊藻赤潮及其产硫的研究[J]. 中国基础科学, 2002(4): 25−30.Qi Yuzao, Xu Ning, Wang Yan, et al. Progress of studies on red tide in China——studies on Phaeocystis giobosa red tide and its DMS(DMSP) production[J]. China Basic Science, 2002(4): 25−30. [29] 屠建波, 张秋丰, 徐玉山, 等. 渤海湾天津近岸海域首次棕囊藻赤潮初探[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(3): 334−337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.016Tu Jianbo, Zhang Qiufeng, Xu Yushan, et al. Preliminary analysis of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel red tide in Tianjin coastal sea areas of Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30(3): 334−337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2011.03.016 [30] Xu Mingben, Zhang Rongcan, Jiang Fajun, et al. Spatiotemporal variation in phytoplankton and physiochemical factors during Phaeocystis globosa red-tide blooms in the Northern Beibu Gulf of China[J]. Water, 2022, 14(7): 1099. doi: 10.3390/w14071099 [31] 徐宁, 齐雨藻, 陈菊芳, 等. 球形棕囊藻(Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel)赤潮成因分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2003, 23(1): 113−118. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2003.01.022Xu Ning, Qi Yuzao, Chen Jüfang, et al. Analysis on the cause of Phaeocystis globosa Scherffel red tide[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2003, 23(1): 113−118. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2003.01.022 [32] 刘琦. 硅藻对球形棕囊藻生长与囊体形成的影响[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2019.Liu Qi. Effects of Diatom on the growth and colony formation in Phaeocystis globosa[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2019. [33] Wang Jinxiu, Kong Fanzhou, Geng Huixia, et al. CHEMTAX analysis of phytoplankton assemblages revealed potential indicators for blooms of haptophyte Phaeocystis globosa[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 131: 108177. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108177 [34] Riegman R, Noordeloos A A M, Cadée G C. Phaeocystis blooms and eutrophication of the continental coastal zones of the North Sea[J]. Marine Biology, 1992, 112(3): 479−484. doi: 10.1007/BF00356293 [35] Davidson A T, Marchant H J. Binding of manganese by Antarctic Phaeocystis pouchetii and the role of bacteria in its release[J]. Marine Biology, 1987, 95(3): 481−487. doi: 10.1007/BF00409577 [36] 苏芯莹, 陈波, 牙韩争, 等. 涠洲岛海域球形棕囊藻藻华过程中营养盐及浮游植物群落组成分析[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2022, 30(6): 863−873.Su Xinying, Chen Bo, Ya Hanzheng, et al. Analysis of nutrient and phytoplankton Community During Phaeocystis globosa bloom in Weizhou Island Waters[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2022, 30(6): 863−873. [37] 贺成, 宋书群, 李才文. 广西北部湾海域球形棕囊藻囊体时空分布及其影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(3): 630−643. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180800192He Cheng, Song Shuqun, Li Caiwen. The spatial-temperal distribution of Phaeocystis globosa colonies and related affecting factors in Guangxi Beibu Gulf[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(3): 630−643. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20180800192 [38] 李天深, 蓝文陆, 卢印思, 等. 近岸海域自动监测浮标在赤潮预警中的应用及其缺陷[J]. 海洋预报, 2015, 32(1): 70−78. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2015.01.011Li Tianshen, Lan Wenlu, Lu Yinsi, et al. Application of automatic monitoring buoy in early warning for algal blooms in offshore area[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2015, 32(1): 70−78. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2015.01.011 [39] Seuront L, Vincent D. Increased seawater viscosity, Phaeocystis globosa spring bloom and Temora longicornis feeding and swimming behaviours[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2008, 363: 131−145. doi: 10.3354/meps07373 [40] Kang Zhenjun, Yang Bin, Lai Junxiang, et al. Phaeocystis globosa bloom monitoring: based on P. globosa induced seawater viscosity modification adjacent to a nuclear power plant in Qinzhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2020, 19(5): 1207−1220. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-4481-6 -





 下载:
下载: