Study on the response of hydrodynamic force and sedimentation in mangrove zone to wharf construction by a coupled model based on remote sensing enhancement
-
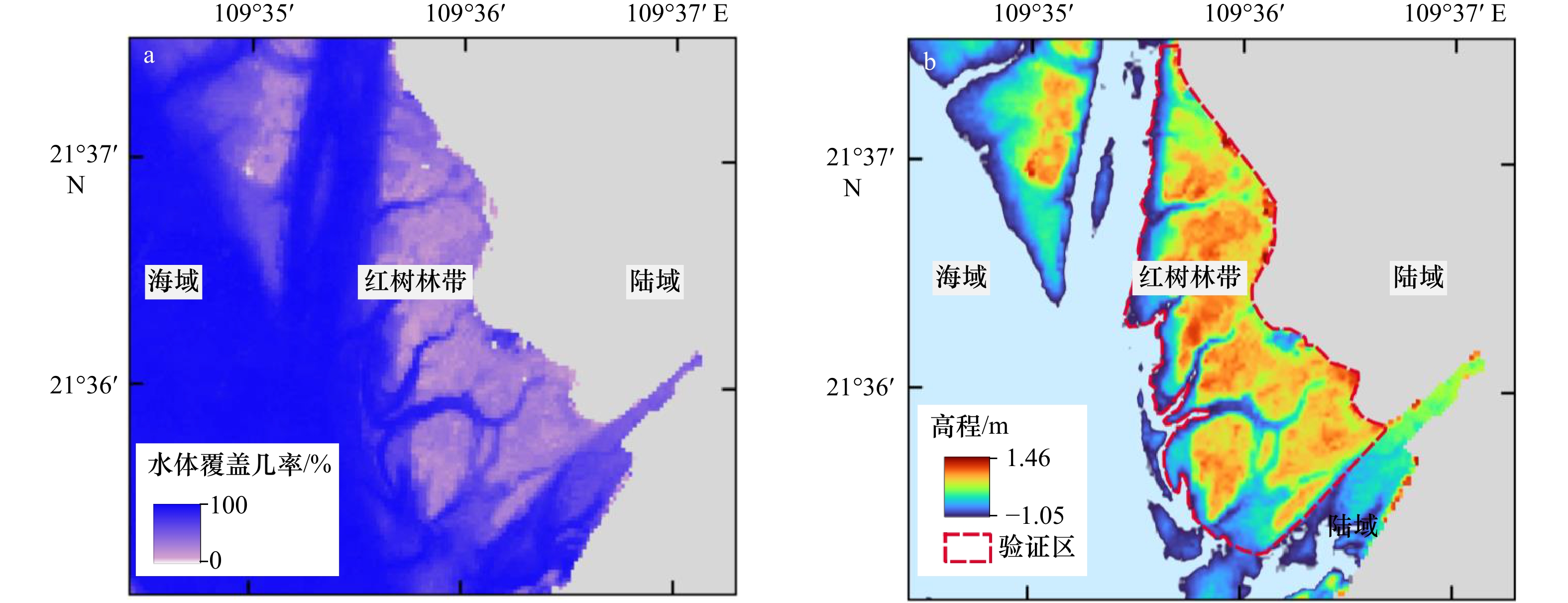
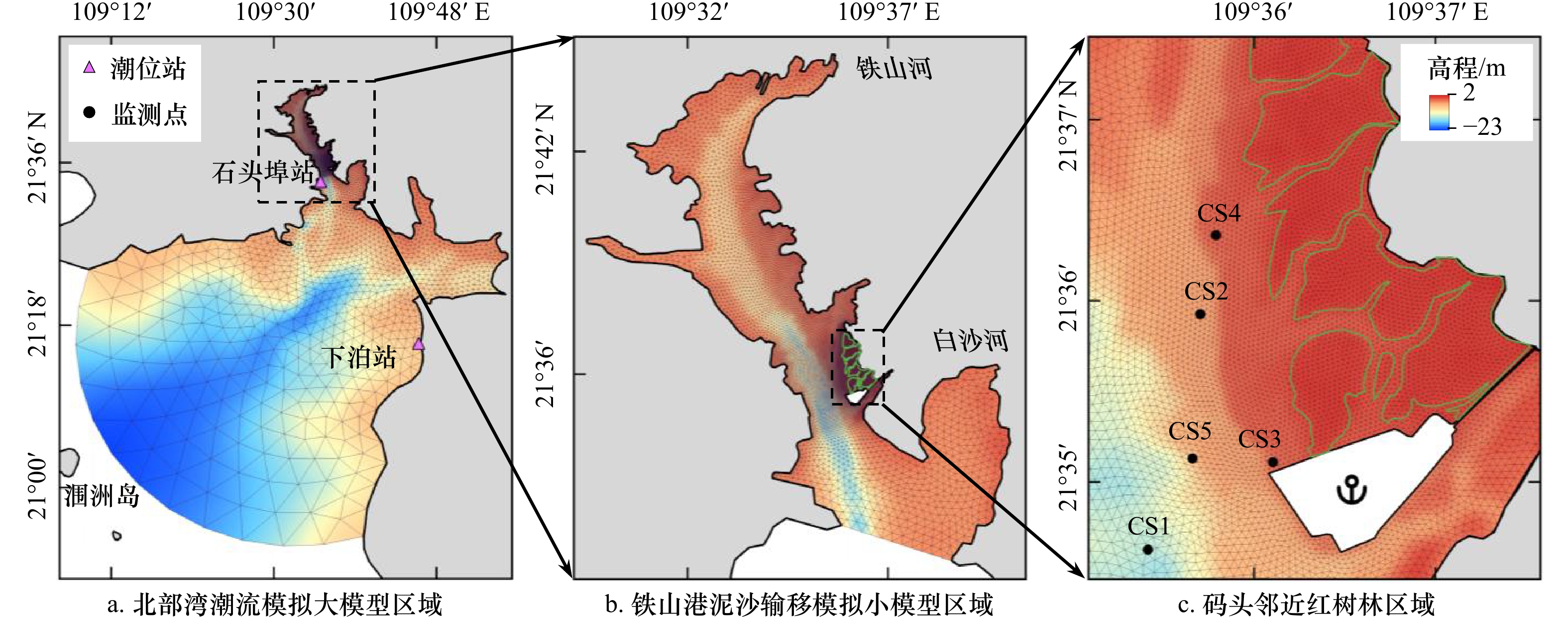
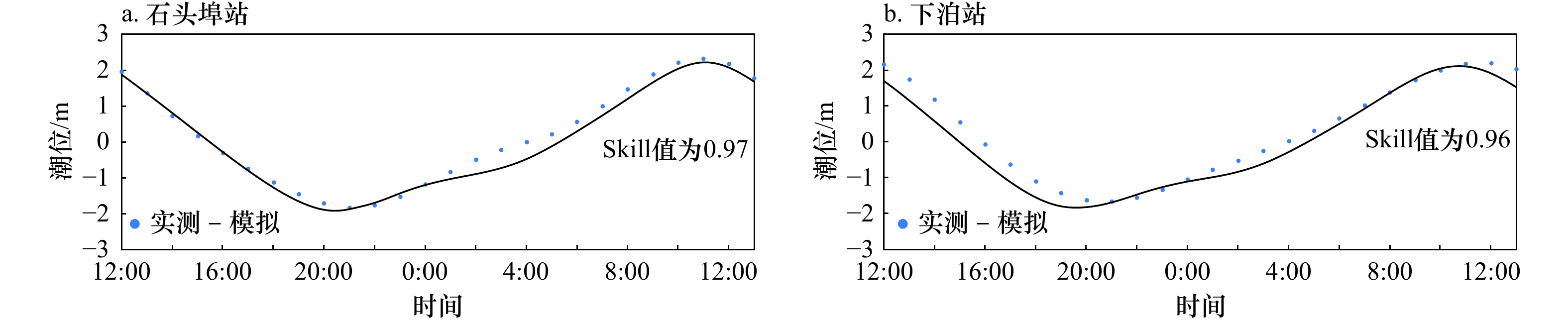
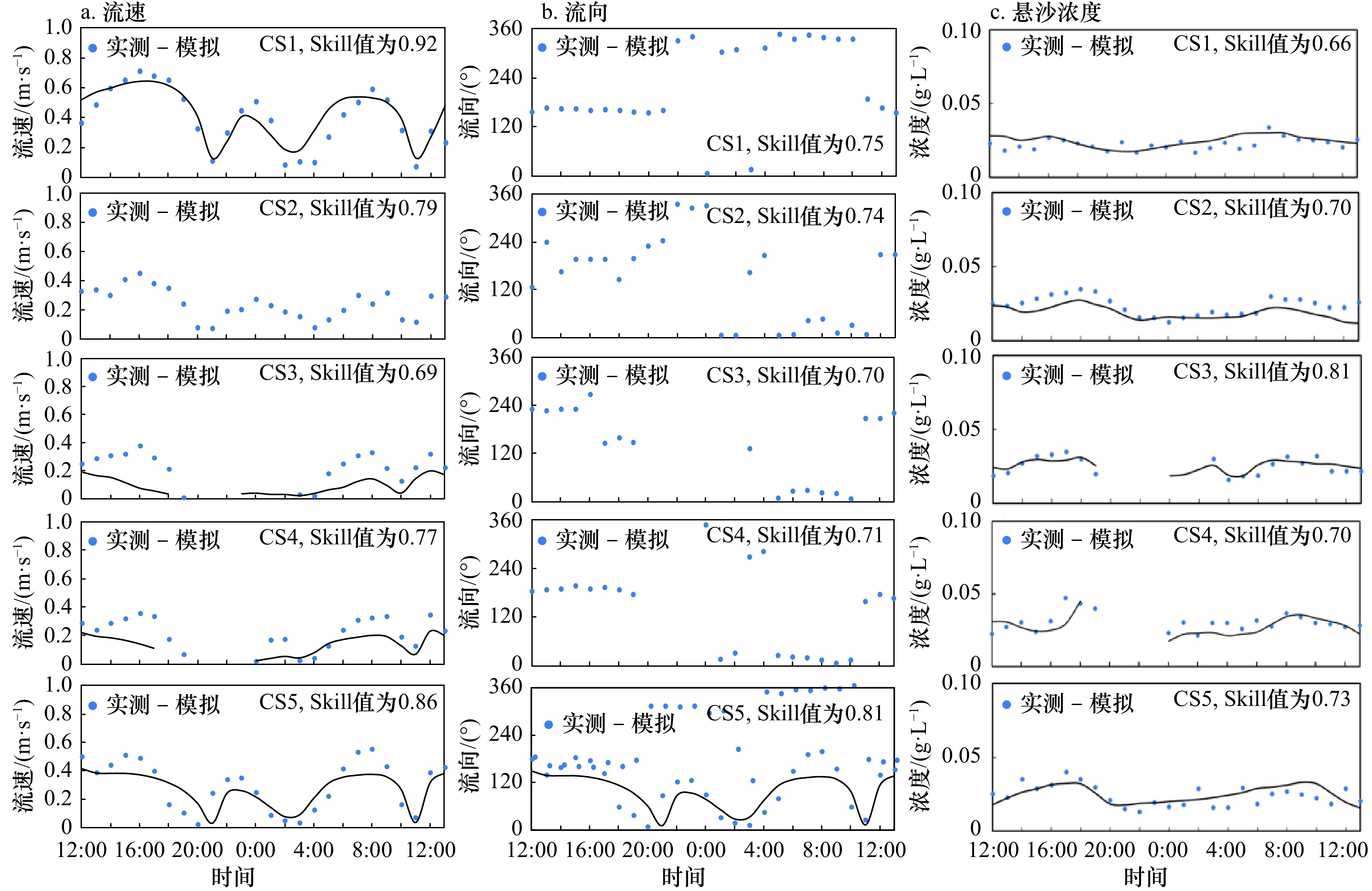
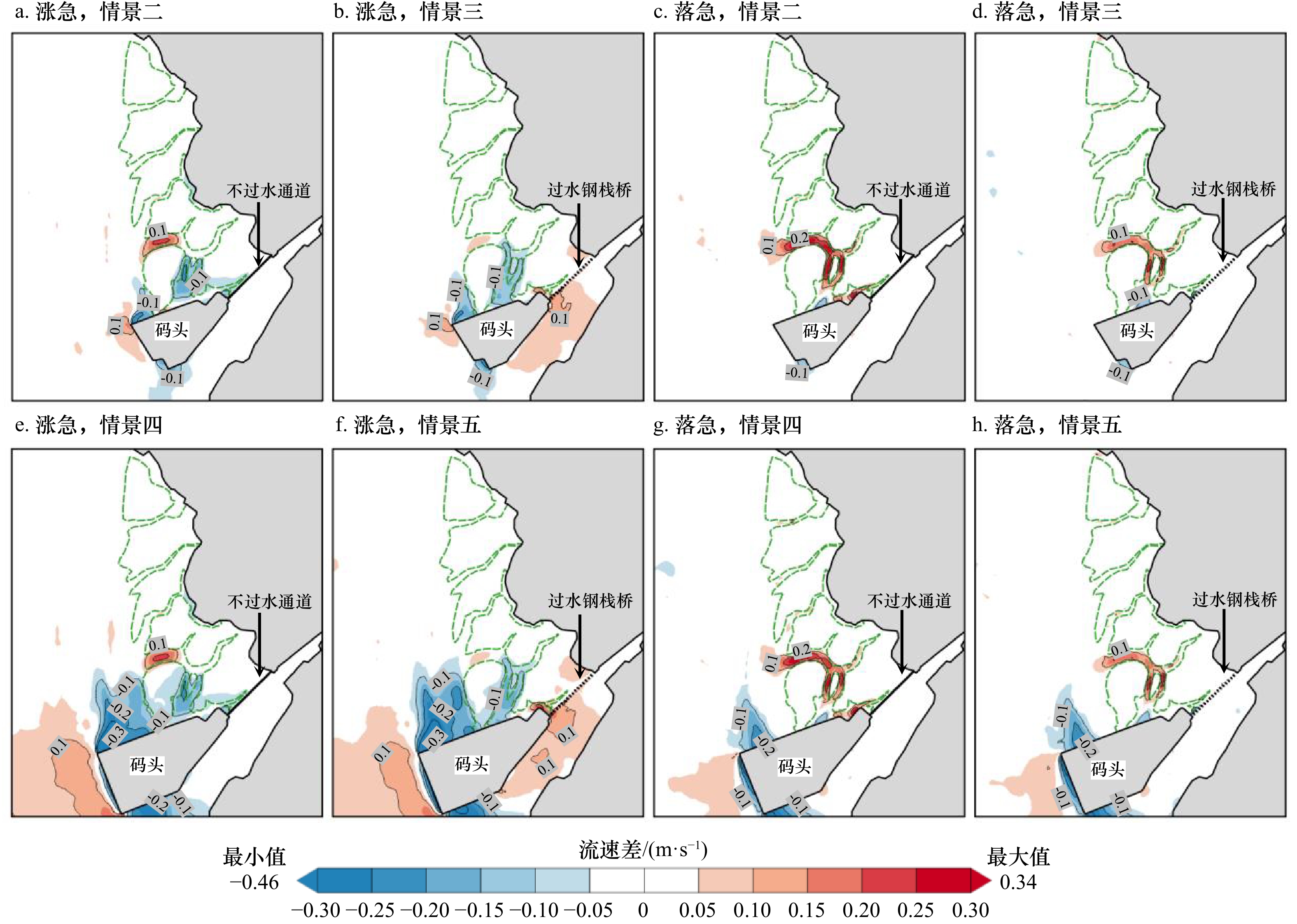
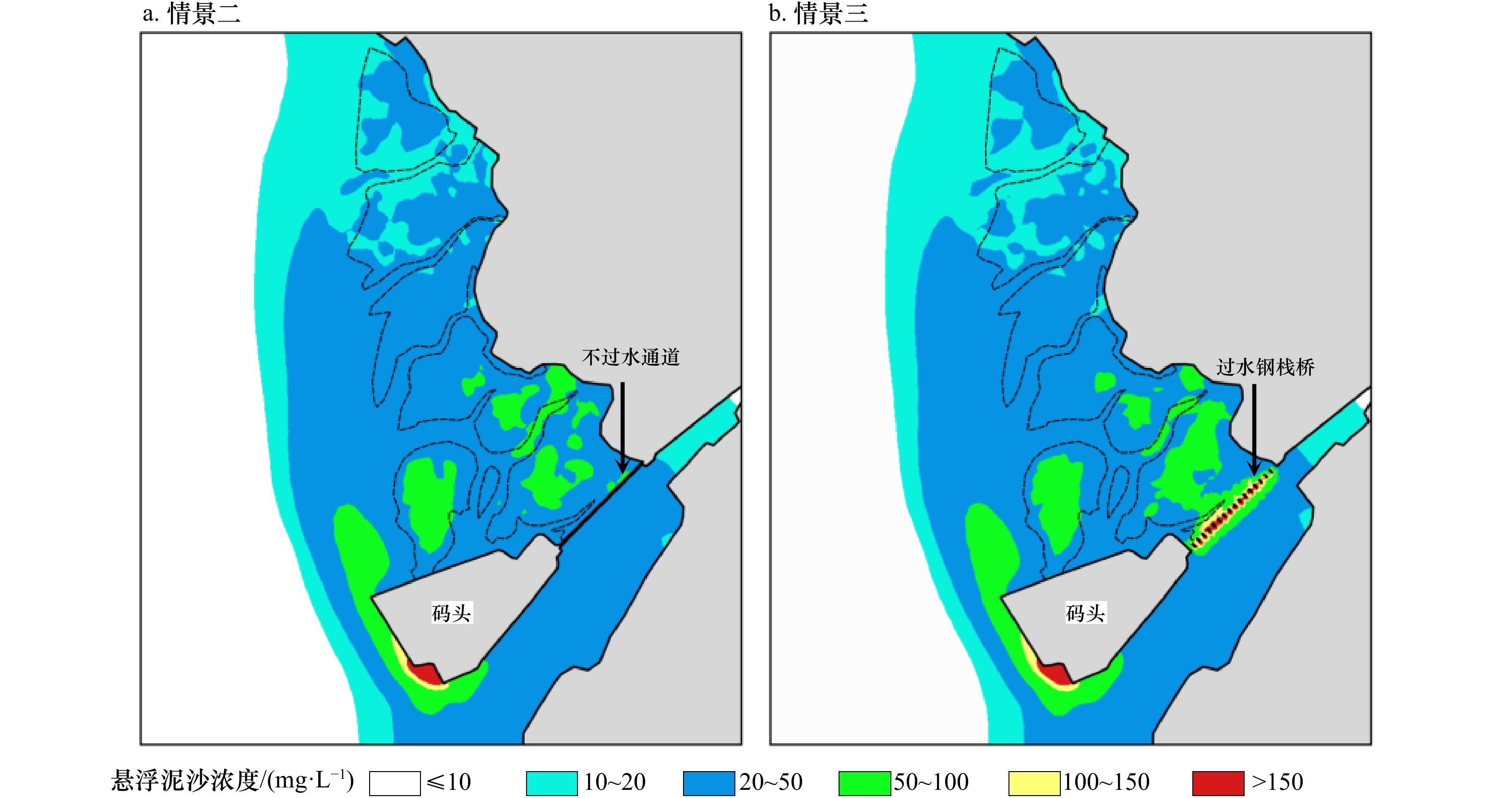
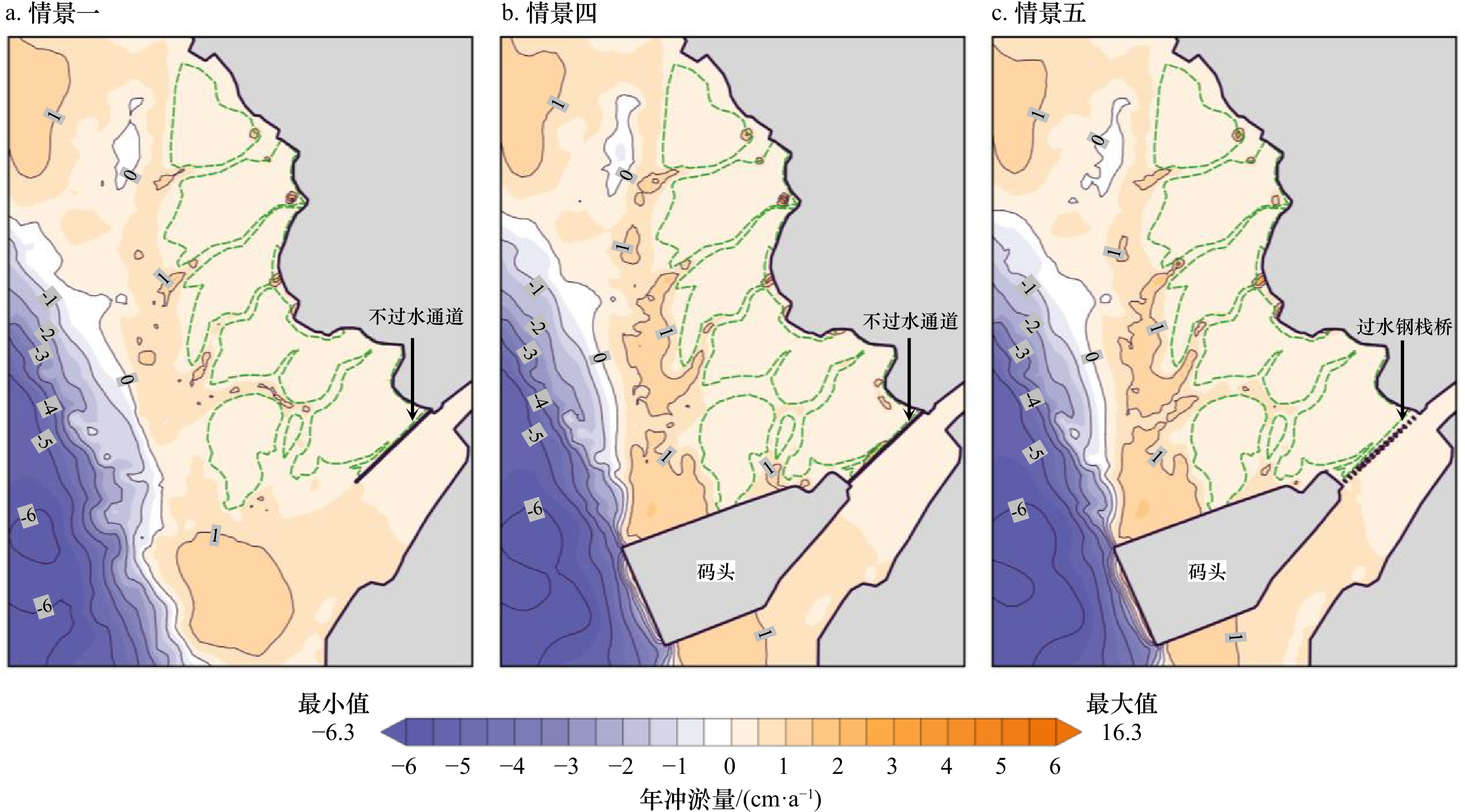
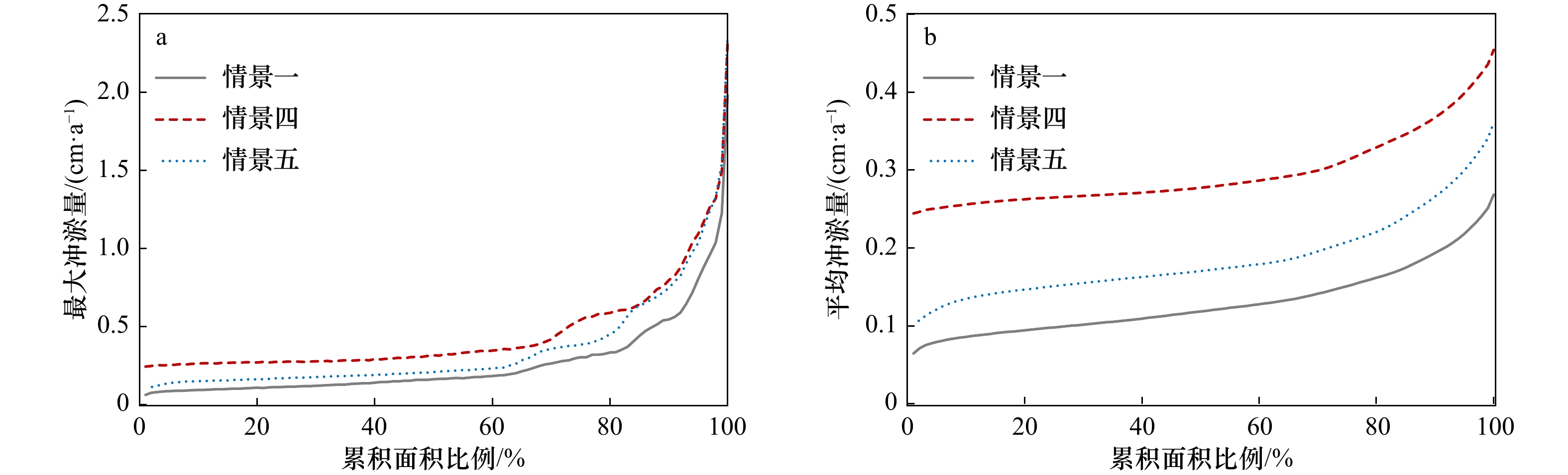
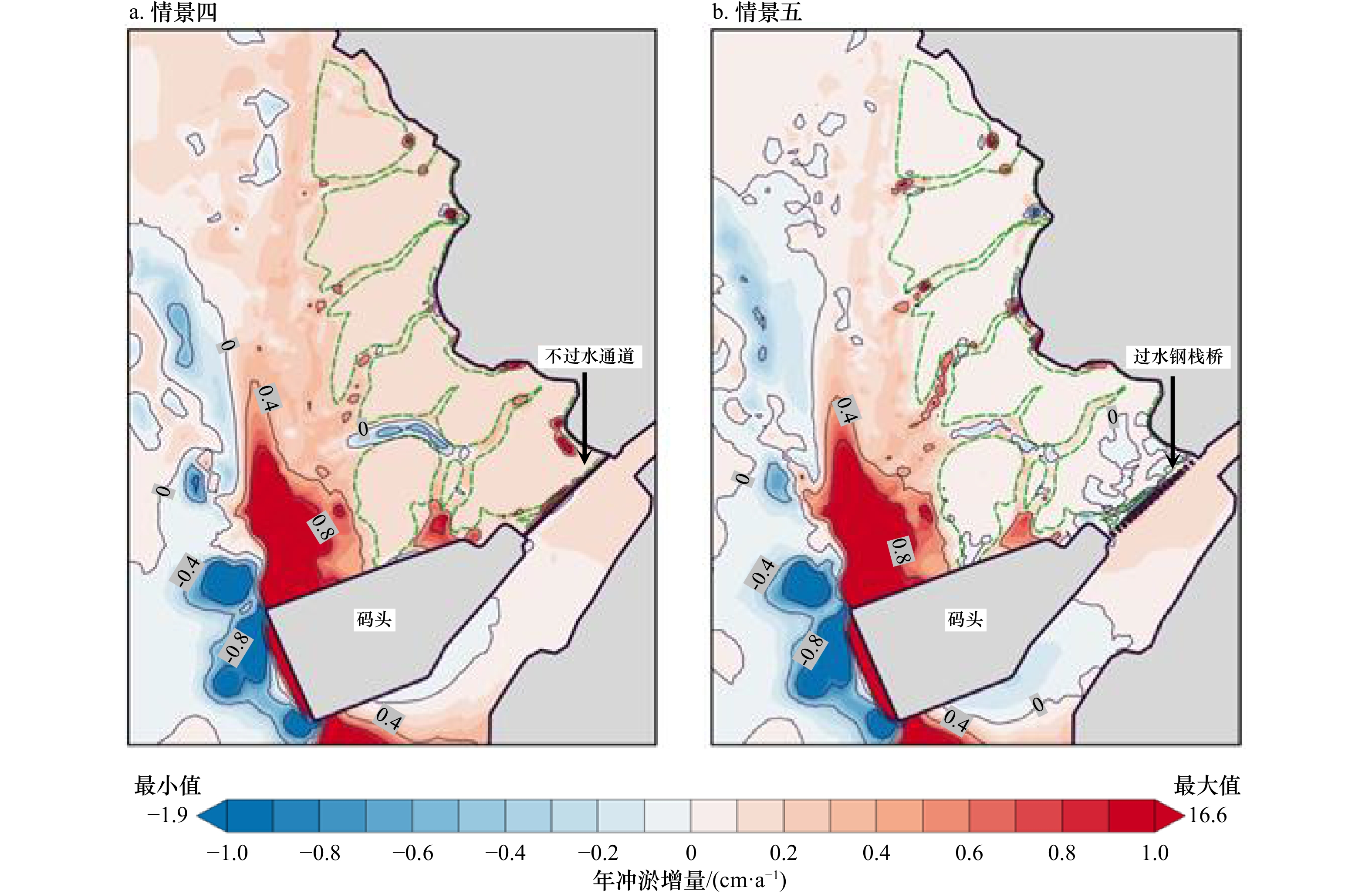
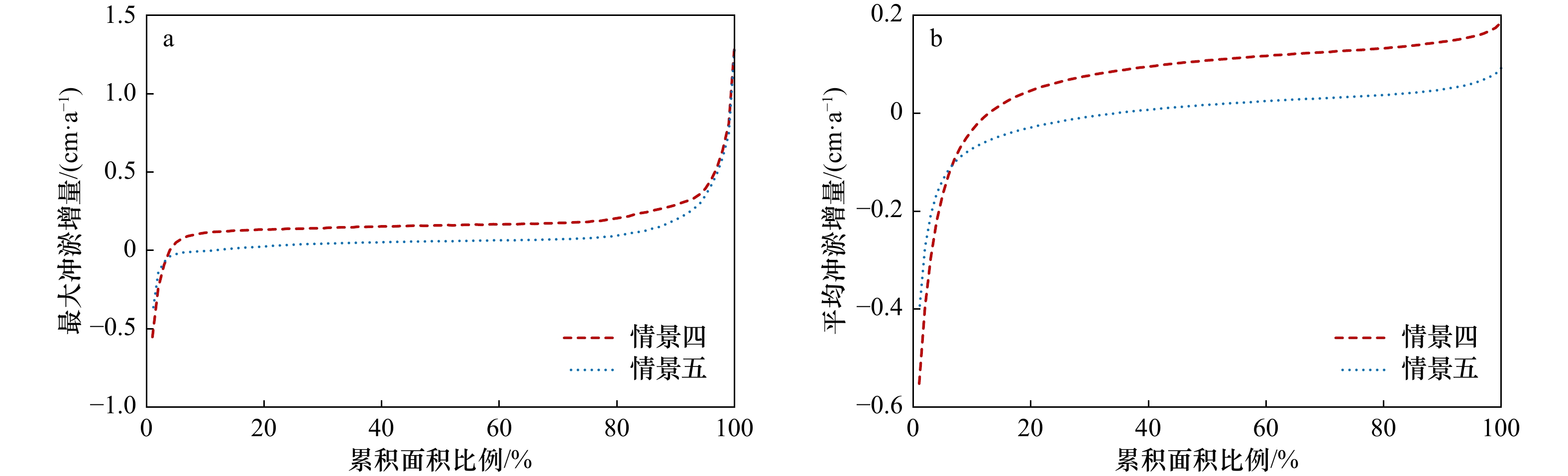
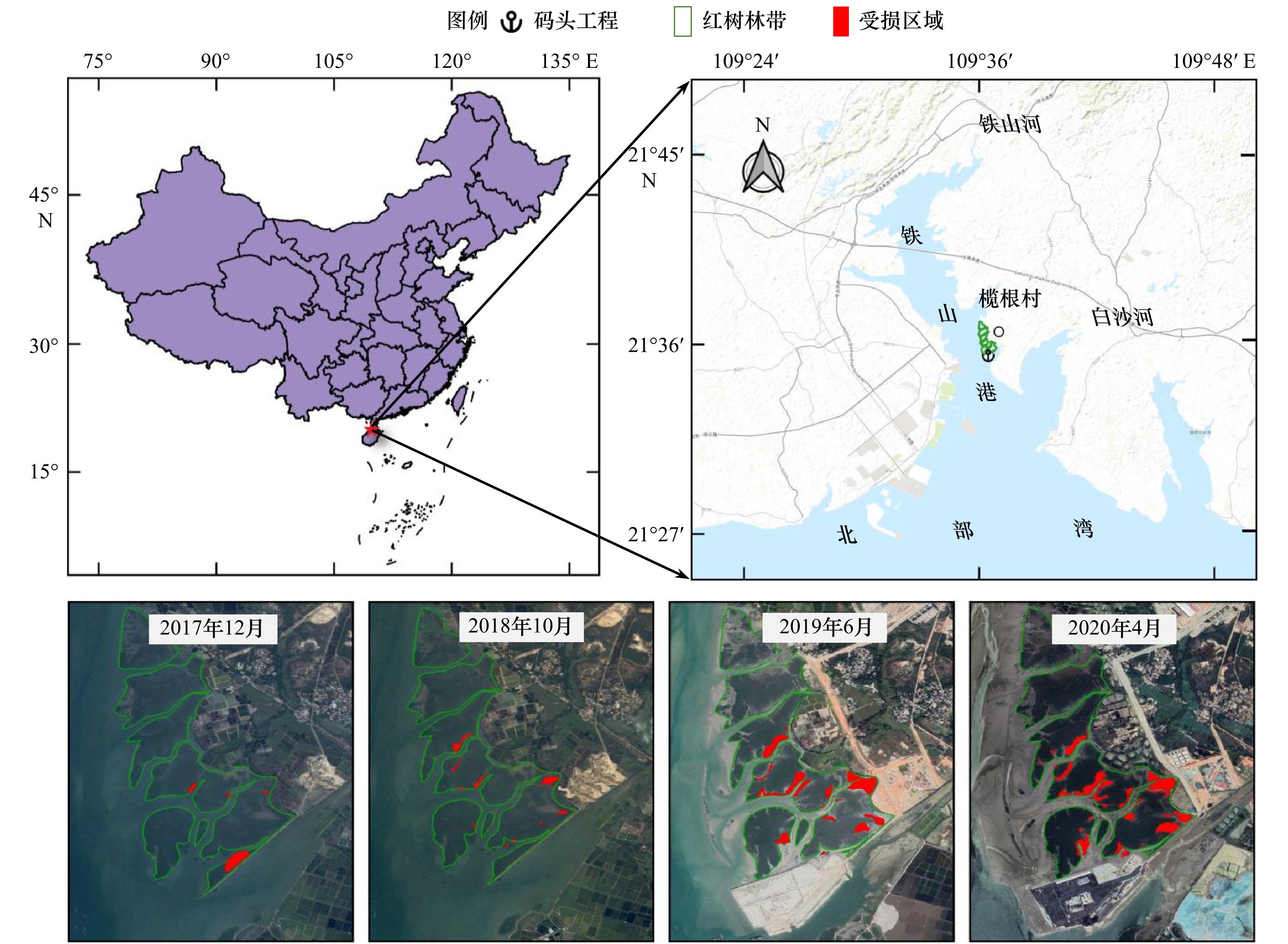
摘要: 南海北部湾铁山港码头建设期间,邻近区域红树林带植株出现受损死亡现象。本研究构建基于遥感增强包含红树林潮间带的海湾水沙嵌套模型,评估码头建设对红树林带潮流、泥沙输移及冲淤的影响。结果表明:海湾水沙嵌套模型可充分利用南海海流模拟信息,且精细化模拟了工程建设附近海域泥沙输移规律。采用全球地表水覆盖几率遥感反演数据与当地潮位的信息融合技术,为红树林带水沙模拟提供了可靠地形信息。码头建设主要影响红树林带南部潮流,涨急时流速减小,落急时部分潮沟通道流速增大。当进港方案更改为过水钢栈桥,红树林带东南部流速略有增加。码头施工期,红树林带69%~72%范围的悬浮泥沙浓度增量介于20~50 mg/L之间。码头建设前,红树林带泥沙平均冲淤量为0.27 cm/a;进港方案分别为不过水通道和过水钢栈桥,码头建设后红树林带淤积量增加的面积占比分别为96.6%和89.3%,平均冲淤量分别为0.45 cm/a和0.36 cm/a。过水钢栈桥替换不过水通道,红树林带冲淤增量下降了50.0%。研究结论可为潮间带水沙环境模拟和红树林带保护决策提供科学依据。Abstract: When the wharf project of Tieshan Port in Beibu Gulf was constructed, nearby mangrove plants were damaged. A coupled model of hydrodynamic force and sedimentation in the gulf including mangrove intertidal zone based on remote sensing enhancement was built. Impacts of the wharf on the tide, sediment transport, erosion and deposition in the mangrove zone were evaluated. Results showed that the model can make full use of the tidal simulation information in the South China Sea and can finely simulate the sediment transport principle nearby the wharf. In association with information fusion technology of remote sensing inversion of the cover probability of global surface water and local tidal levels, elevation data in mangrove zone were reliably obtained. The tides mainly in the southern of the mangrove zone were influenced by the wharf. The velocity decreased at the most rising tide, and that in the tidal channel increased at the most ebb tide. When the way to the wharf was transferred using a steel trestle, the velocity in the southeast of the mangrove zone increased slightly. During the construction period of the wharf, the increase of suspended sediment concentration varied from 20 mg/L to 50 mg/L in the range of 69% and 72% of the mangrove zone. Before the wharf construction, the average sediment deposition in the mangrove zone accounted for 0.27 cm/a. For two designed ways to the wharf, i.e. the road isolating tide and the steel trestle allowing tide passing, the average deposition accounted for 0.45 cm/a and 0.36 cm/a with the range of 96.6% and 89.3% in the mangrove zone respectively. Provided that the steel trestle to the wharf would be selected, the average increment of the deposition in the mangrove zone decreased by 50%. The conclusions can provide the scientific basis for the simulation of tide and sedimentation in intertidal zone and the decision of the mangrove protection.
-
Key words:
- coupled model /
- remote sensing enhancement /
- mangrove /
- suspended sediment /
- erosion and deposition /
- Tieshan Port
-
表 1 工程设计方案模拟情景
Tab. 1 Simulation scenarios of engineering design schemes
情景 工程方案 一 工程建设前,原有不过水便道延伸至拟建码头处 二 施工期(停工时建设规模),进港方案为不过水通道 三 施工期(停工时建设规模),进港方案为过水钢栈桥 四 工程建成后,进港方案为不过水通道 五 工程建成后,进港方案为过水钢栈桥 表 2 红树林带悬浮泥沙增量的浓度区间分布
Tab. 2 Distribution of the range for individual concentration of suspended sediment in mangrove zone
情景 10~20 mg/L 20~50 mg/L 50~100 mg/L 100~150 mg/L 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 二 0.484 16.8 2.069 71.9 0.324 11.3 0 0 三 0.518 18.0 1.991 69.2 0.366 12.7 0.002 0.1 -
[1] 韩倩倩, 牛振国, 吴孟泉, 等. 基于潮位校正的中国潮间带遥感监测及变化[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(4): 456−473. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00723Han Qianqian, Niu Zhenguo, Wu Mengquan, et al. Remote-sensing monitoring and analysis of China intertidal zone changes based on tidal correction[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(4): 456−473. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00723 [2] 张文开. 福建省潮间带滩涂资源的开发利用研究[J]. 资源科学, 2001, 23(3): 29−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2001.03.007Zhang Wenkai. A study on exploitation and utilization of tideland resources in Fujian Province[J]. Resources Science, 2001, 23(3): 29−32. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2001.03.007 [3] 张长宽, 陈欣迪. 海岸带滩涂资源的开发利用与保护研究进展[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(1): 25−33.Zhang Changkuan, Chen Xindi. Advances in development, utilization, and protection of coastal tidal flats[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 44(1): 25−33. [4] 蒋昌波, 李媛, 官志鑫, 等. 铁山湾建港前后水体交换能力的数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2013, 32(1): 81−86.Jiang Changbo, Li Yuan, Guan Zhixin, et al. Numerical simulation of water exchange capability before and after port construction in Tieshan Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(1): 81−86. [5] 谢卫明, 何青, 张迨, 等. 河口潮滩地貌和沉积物对人类工程的响应特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(5): 118−127.Xie Weiming, He Qing, Zhang Dai, et al. The response of morphplogy and sediment characteristics to human modification in an estuarine tidal flat[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(5): 118−127. [6] 李松喆. 人工岛对沙质海岸动力泥沙环境及岸滩冲淤演变的影响研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2021, 39(4): 144−153.Li Songzhe. Study on the influence of artificial island on dynamic sediment environment and beach erosion and deposition evolution of sandy coast[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(4): 144−153. [7] 肖哲宇, 戚洪帅, 蔡锋, 等. 人工岛建设对海口湾沉积特征与泥沙运移的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2022, 44(3): 137−146.Xiao Zheyu, Qi Hongshuai, Cai Feng, et al. The impact of artificial island construction on sedimentary characteristics and sediment transport in the Haikou Bay[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(3): 137−146. [8] 张再旺, 李甲亮, 隋涛, 等. 中国红树林湿地有机污染物研究进展[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(5): 232−240.Zhang Zaiwang, Li Jialiang, Sui Tao, et al. Organic contamination in mangrove ecosystems of China[J]. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(5): 232−240. [9] 陈国强, 刘影, 陈鹏. 海湾型城市湿地的动态变化及其退化因素分析[J]. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(3): 327−330.Chen Guoqiang, Liu Ying, Chen Peng. Analysis on the dynamic change and degradation factors of wetland in bay-type city[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science), 2007, 31(3): 327−330. [10] 王金华, 黄华梅, 贾后磊, 等. 粤港澳大湾区海岸带生态系统保护和修复策略[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(23): 8430−8439.Wang Jinhua, Huang Huamei, Jia Houlei, et al. Discussion on the strategies of coastal ecosystem protection and restoration in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(23): 8430−8439. [11] 郭伟, 朱大奎. 深圳围海造地对海洋环境影响的分析[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2005, 41(3): 286−296.Guo Wei, Zhu Dakui. Reclamation and its impact on marine environment in Shenzhen area, China[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2005, 41(3): 286−296. [12] 王晓明, 冯秀丽, 田动会, 等. 填海工程建设前后丹东港海域泥沙冲淤变化特征与成因分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(9): 41−49.Wang Xiaoming, Feng Xiuli, Tian Donghui, et al. Sediment scouring and deposition at the Dandong Port before and after the construction of reclamation project[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(9): 41−49. [13] Jiang Shenghui, Hu Rijun, Feng Xiuli, et al. Influence of the construction of the Yantai West Port on the dynamic sedimentary environment[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2018, 36(1): 43−51. [14] 王春玲, 武雅洁, 董启涛, 等. 日照豪迈码头港池布局对泥沙输移影响研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2019, 49(7): 110−117.Wang Chunling, Wu Yajie, Dong Qitao, et al. Study on the impacts of the sediment transport on the Rizhao Haomai Harbor’s layout[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(7): 110−117. [15] Cheng Zhixin, Jalon-Rójas I, Wang Xiaohua, et al. Impacts of land reclamation on sediment transport and sedimentary environment in a macro-tidal estuary[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 242: 106861. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106861 [16] 蔡家新, 潘国富, 陈培雄. 围海工程前后瓯飞滩冲淤变化特征及动力机制分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(3): 63−71.Cai Jiaxin, Pan Guofu, Chen Peixiong. Analysis of the characteristics and dynamic mechanism of scouring and silting changes in Oufei Tidal Flat before and after the reclamation project[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(3): 63−71. [17] Liu Yongxue, Li Manchun, Cheng Liang, et al. Topographic mapping of offshore sandbank tidal flats using the waterline detection method: a case study on the Dongsha sandbank of Jiangsu radial tidal sand ridges, China[J]. Marine Geodesy, 2012, 35(4): 362−378. doi: 10.1080/01490419.2012.699501 [18] 马洪羽, 丁贤荣, 葛小平, 等. 辐射沙脊群潮滩地形遥感遥测构建[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(3): 111−122.Ma Hongyu, Ding Xianrong, Ge Xiaoping, et al. Remote sensing and remote measuring approach to construct tidal flat terrain in the radial sand ridges[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(3): 111−122. [19] Kang Yanyan, Ding Xianrong, Xu Fan, et al. Topographic mapping on large-scale tidal flats with an iterative approach on the waterline method[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2017, 190: 11−22. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2017.03.024 [20] 祁雅莉, 付东洋, 刘大召, 等. 南海西北部英罗湾红树林保护区光滩近期冲淤变化分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(6): 6−14. doi: 10.11759/hykx20181115001Qi Yali, Fu Dongyang, Liu Dazhao, et al. Erosion-accretion analysis of bare flats outside the mangrove area in Yingluo Bay, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 2019, 43(6): 6−14. doi: 10.11759/hykx20181115001 [21] 陶艳成, 刘文爱, 潘良浩, 等. 遥感技术在受损红树林资源调查与监测中的应用[J]. 广西科学院学报, 2021, 37(3): 256−263.Tao Yancheng, Liu Wenai, Pan Lianghao, et al. Application of remote sensing technology in investigation and monitoring of damaged mangrove resource[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, 2021, 37(3): 256−263. [22] Tseng K H, Kuo C Y, Lin Tanghuang, et al. Reconstruction of time-varying tidal flat topography using optical remote sensing imageries[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 131: 92−103. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.07.008 [23] Pekel J F, Cottam A, Gorelick N, et al. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes[J]. Nature, 2016, 540(7633): 418−422. doi: 10.1038/nature20584 [24] Xu Hanqiu. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2006, 27(14): 3025−3033. doi: 10.1080/01431160600589179 [25] 裴木凤, 胡嘉镗, 高劲松, 等. 广西铁山港水体交换能力对填海和季风的响应研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2019(6): 34−40.Pei Mufeng, Hu Jiatang, Gao Jinsong, et al. Study on the response of water exchange capability in Tieshan Bay in Guangxi to the reclamation and monsoon[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019(6): 34−40. [26] Rahdarian A, Niksokhan M H. Numerical modeling of storm surge attenuation by mangroves in protected area of mangroves of Qheshm Island[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 145: 304−315. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.09.026 [27] Barros M L C, da Silva T D, da Cruz A G B, et al. Numerical simulation of wetland hydrodynamics and water quality[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2020, 42(8): 444. doi: 10.1007/s40430-020-02523-y [28] Willmott C J. On the validation of models[J]. Physical Geography, 1981, 2(2): 184−194. doi: 10.1080/02723646.1981.10642213 [29] He Wei, Zhang Jian, Yu Xiaodong, et al. Effect of runoff variability and sea level on saltwater intrusion: a case study of Nandu River Estuary, China[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(12): 9919−9934. doi: 10.1029/2018WR023285 [30] 张琴. 海洋工程施工悬浮泥沙源强及扩散规律研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(6): 176−184.Zhang Qin. Research overview on source and diffusion of suspended solids in ocean engineering construction[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(6): 176−184. [31] 戴志军, 周晓妍, 王杰, 等. 红树林潮滩沉积动力研究进展与展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 69−75. doi: 10.11978/YG2020007Dai Zhijun, Zhou Xiaoyan, Wang Jie, et al. Review and prospect of mangrove tidal flat sedimentary dynamics[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 69−75. doi: 10.11978/YG2020007 -




 下载:
下载: