Component changes and control factors of detrital minerals in riverbed, estuary and beach of short source rivers: taking the Xin’an River in Shandong Peninsula as an example
-
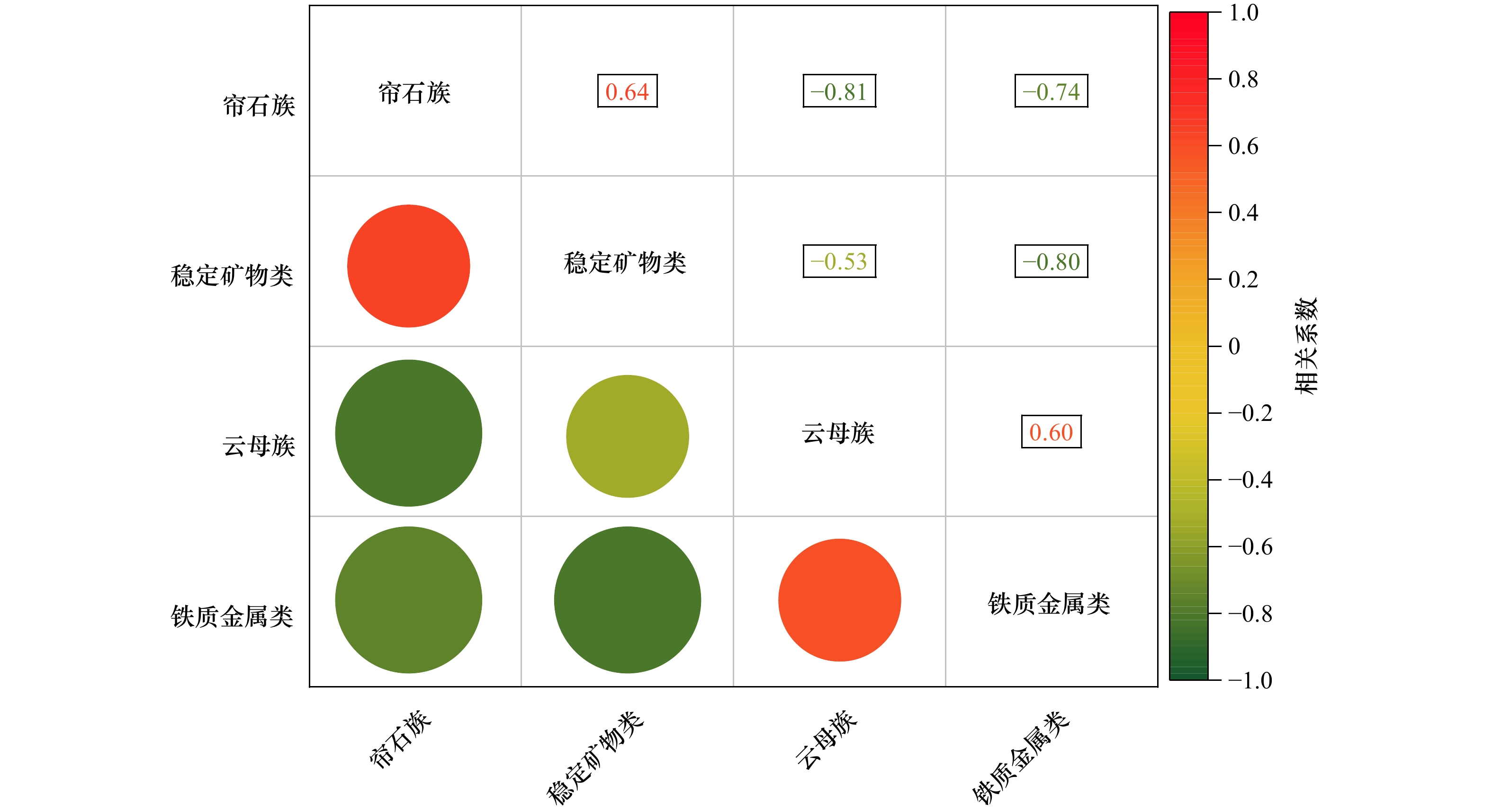
摘要: 山东半岛诸多小河沉积物大多来源明确,矿物沉积分异相对较小,对其研究能为大河入海物源分析提供区域相似性,也可为黄、渤海陆架沉积提供山东半岛物质来源特征。本文以山东半岛东北部短源小河辛安河为例,对取自河床、河口、海滩的表层沉积样品的碎屑矿物分布规律进行了多粒级分析。研究表明,辛安河流域和海滩沉积物多为中砂和细砂,全样重矿物含量中等,在1.47%~8.19%之间。出现重矿物27种,轻矿物8种,主要重矿物为普通角闪石(41.7%)、绿帘石(16.7%)、阳起石(10.6%)和褐铁矿(6.7%),主要轻矿物为石英(49.0%)、斜长石(26.5%)和钾长石(20.7%),这些矿物的含量在河床、河口和海滩远高于其他碎屑矿物,且矿物组合保持不变,相对含量变幅不大;非主要矿物种类与碎屑粒径存在显著的非线性相关关系。辛安河矿物种类和含量受控于区域岩性物源,即酸性、中酸性侵入岩和区域变质岩。闪石族矿物在辛安河不同地貌中的相对稳定输出是其同宗同源属性所在,矿物组成变化主要受水动力控制下的粒度分选影响。山东半岛短源河流虽碎屑矿物种类和含量不尽相同,但它们来源于相似的地质地貌和岩石类型,矿物组成变化的主要控制因素为区域物源和粒度分选,其次为沉积环境差异。相比而言,黄河闪石族矿物的低含量、云母族和碳酸盐类矿物在特定粒级的高含量有别于半岛南北两侧的河源物质。Abstract: Most of the small rivers in the Shandong Peninsula have clear sediment sources and relatively small mineral deposition differentiation, and their study can provide regional similarities for the analysis of the sources of large rivers into the sea, as well as the characteristics of the material sources in the Shandong Peninsula for the deposition of the Yellow Sea shelf and Bohai Sea shelf. In this paper, the distribution patterns of detrital minerals in surface sediment samples taken from riverbeds, estuaries and beaches were analysed at multiple grain levels, taking the Xin’an River, a small short-source river in the northeastern part of the Shandong Peninsula, as an example. The study shows that the Xin’an River basin and beach sediments are mostly medium and fine sands, with moderate heavy mineral content in the whole sample, ranging from 1.47% to 8.19%. Twenty-seven heavy minerals and eight light minerals occur, with the main heavy minerals hornblende (41.7%), chlorite (16.7%), actinolite (10.6%) and limonite (6.7%) and the main light minerals quartz (49.0%), plagioclase (26.5%) and potassium feldspar (20.7%), which are much more abundant than the other detrital minerals in the riverbed, estuary and beach, and the mineral assemblage remains constant, with less significant variation in relative content between them, while there is a significant non-linear correlation between non-dominant mineral species and clastic grain size. Mineral species and content in the Xin’an River are controlled by the regional lithological sources, i.e. acidic and moderately acidic intrusive rocks and regional metamorphic rocks, and the relatively stable output of amphibole group minerals across the different features of the Xin’an River is responsible for their homogeneity. The short source rivers of the Shandong Peninsula are derived from similar geological features and rock types, although the types and content of detrital minerals vary. The main controlling factors for mineral composition variation are regional sources and particle size sorting, followed by sedimentary environmental differences. In contrast, the high content of mica group and carbonate minerals in a specific grain size and the low content of amphibole group minerals are the aspects that distinguish the Huanghe River from the river source materials in the northern and southern coastal waters of the Shandong Peninsula.
-
图 5 山东半岛主要河流碎屑重矿物组合在不同沉积环境的变化趋势
不稳定矿物包括闪石族和帘石族;云母族、稳定矿物和铁质金属矿物与文中分类相同;未标注广粒级的粒级Φ为3~4;*数据引自参考文献[52]
Fig. 5 Variation trend of detrital heavy mineral assemblies in main rivers from the Shandong Peninsula to sea in different sedimentary environments
Unstable minerals include amphiboles and epidotes; mica, stabilized and ferrous metal minerals are classified as in this paper; unmarked wide grain size Φ with 3 to 4; *data cited from reference [52]
图 6 山东半岛入海小河和黄河重矿物组合入海前后对比
*黄河数据引自参考文献[7, 53];其他河流数据引自参考文献[52]
Fig. 6 Comparison of heavy mineral assemblages of small rivers on the Shandong Peninsula and the Huanghe River before and after entering the sea
*The Huanghe River data are cited from references [7, 53] ; other river data are cited from reference [52]
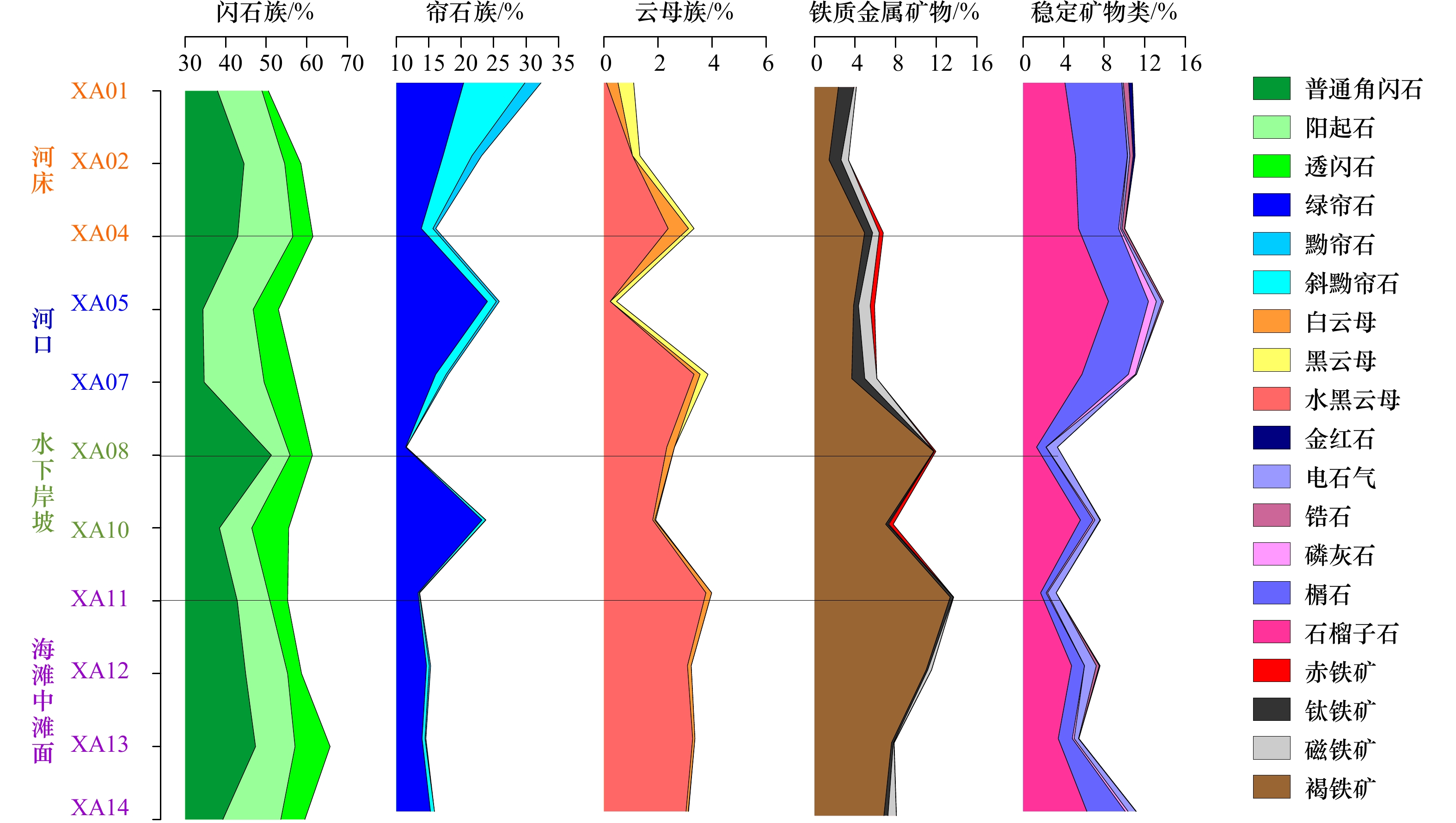
表 1 采样点位
Tab. 1 Sampling point location
样点号 经纬度位置 地貌位置 XA01 37°24′20″N,121°32′18″E 辛安河大桥西北侧河床 XA02 37°24′09″N,121°32′19″E 辛安河大桥西北侧河床 XA04 37°20′47″N,121°27′49″E 北水桃林村桥下边滩 XA05 37°26′15″N,121°33′12″E 辛安河特大桥西南侧河口 XA07 37°26′14″N,121°33′06″E 辛安河特大桥西南侧河口 XA08 37°26′30″N,121°32′59″E 水下岸坡远处 XA10 37°26′29″N,121°33′01″E 海滩沿岸槽谷 XA11 37°26′28″N,121°33′00″E 海滩中滩面 XA12 37°26′28″N,121°33′02″E 海滩中滩面 XA13 37°26′28″N,121°33′06″E 海滩中滩面 XA14 37°26′27″N,121°33′10″E 海滩中滩面 表 2 辛安河沉积物粒度参数
Tab. 2 Grain size parameters of the Xin’an River sediments
粒度参数 XA01 XA02 XA04 XA05 XA07 XA08 XA10 XA11 XA12 XA13 XA14 平均粒径 4.82 3.74 0.93 1.46 1.64 1.44 1.98 1.27 1.60 1.73 1.72 标准偏差 0.95 1.73 1.65 0.91 0.68 0.56 0.62 0.65 0.58 0.54 0.56 偏态 0.24 0.24 0.27 −0.28 −0.17 0.02 −0.48 0.15 −0.18 −0.16 −0.25 峰度 1.04 1.14 1.31 0.84 0.80 0.76 1.03 0.8 0.73 0.43 0.21 表 3 辛安河不同粒级重矿物含量差异
Tab. 3 Difference of heavy mineral content of different grain size fractions in the Xin’an River
样品位置 样品
编号广粒级重矿物在全样中的含量/%(加权值) Φ为3~4粒级含量/% Φ为3~4重矿物在全样中
的含量/%
(加权值)Φ为3~4重矿物在该粒级
中的含量/%河床 XA01 2.01 2.98 0.07 3.92 XA02 4.06 15.73 1.12 27.65 XA04 2.51 1.86 0.21 8.29 河口 XA05 6.11 0.63 0.11 1.88 XA07 8.19 0.37 0.05 0.62 水下岸坡 XA08 2.59 0.08 0.01 0.69 海滩槽谷 XA10 3.27 1.68 0.25 7.91 中滩面 XA11 1.48 0.09 0.01 0.60 XA12 2.43 0.09 0.02 0.77 XA13 1.83 0.27 0.07 3.54 XA14 2.96 0.16 0.04 1.44 表 4 辛安河沉积物重矿物加权百分数(%)
Tab. 4 Heavy mineral weighted percentages for the Xin’an River sediments (%)
矿物 XA01 XA02 XA04 XA05 XA07 XA08 XA10 XA11 XA12 XA13 XA14 普通角闪石 37.96 44.51 42.93 34.37 34.69 51.25 38.45 42.84 44.91 47.34 39.29 透闪石 1.58 4.01 4.96 6.23 7.74 5.52 9.10 4.38 3.45 8.65 5.93 阳起石 10.96 10.02 13.59 12.38 14.77 4.59 7.96 8.04 10.34 9.73 14.28 绿帘石 20.37 17.20 13.85 24.04 16.08 11.44 23.20 13.36 14.65 13.97 15.26 黝帘石 2.48 1.48 0.44 0.44 0.33 − 0.05 0.07 0.22 0.14 − 斜黝帘石 9.44 4.46 1.78 1.38 1.61 0.09 0.55 0.17 0.41 0.44 0.61 黑云母 0.58 0.27 0.20 0.23 0.29 − 0.04 − − − 0.01 白云母 0.42 − 0.75 − 0.23 0.28 0.07 0.21 0.14 0.08 0.08 水黑云母 0.10 1.06 2.38 0.23 3.33 2.33 1.81 3.77 3.09 3.28 3.04 石榴子石 4.12 5.16 5.46 8.41 5.80 1.33 5.65 1.72 4.78 3.46 6.28 榍石 5.61 5.12 3.95 3.94 4.58 0.93 1.24 0.55 1.27 1.39 3.78 磷灰石 − 0.02 0.18 0.78 0.68 0.02 0.18 0.13 0.01 0.18 0.28 电气石 0.14 0.23 0.15 0.54 0.10 1.10 0.50 0.85 1.16 0.43 0.78 锆石 0.54 0.32 0.25 0.16 − − 0.05 − 0.29 0.04 0.03 金红石 0.37 0.19 0.03 − − − − − 0.09 − − 透辉石 0.18 0.87 0.15 0.17 0.80 − − − − − − 钛铁矿 1.53 1.18 0.79 0.49 1.29 0.04 0.21 0.31 0.16 0.18 0.40 磁铁矿 0.24 0.73 0.65 1.16 1.19 0.03 0.10 0.03 0.37 0.06 0.83 褐铁矿 2.35 1.43 4.93 3.85 3.66 11.75 7.01 13.37 11.00 7.59 6.84 赤铁矿 − − 0.40 0.43 − 0.15 0.43 − 0.01 0.02 0.01 风化碎屑 0.99 1.40 1.87 0.77 2.49 7.96 2.57 9.42 2.84 2.58 1.83 岩屑 0.03 0.36 0.24 − 0.22 1.99 0.83 0.58 0.82 0.21 0.41 注:“−”表示未测得数据,仅在某一粒级偶尔出现的矿物未作计算。 表 5 辛安河沉积物轻矿物加权含量百分数(%)
Tab. 5 Weighted percentage of light minerals in the Xin’an River sediments (%)
矿物 XA01 XA02 XA04 XA05 XA07 XA08 XA10 XA11 XA12 XA13 XA14 石英 66.36 51.56 41.81 52.82 46.72 44.60 47.01 46.67 45.38 50.58 46.89 斜长石 18.07 25.95 29.17 25.83 29.56 25.62 27.19 28.28 29.89 25.97 26.65 钾长石 11.80 18.09 23.45 17.73 17.57 26.26 22.84 22.83 22.11 20.69 24.35 白云母 1.84 0.89 1.19 0.50 0.37 0.14 0.04 − 0.10 0.15 0.06 风化云母 1.91 3.19 2.54 1.41 2.50 0.92 1.54 0.55 0.63 0.97 0.83 方解石 0.01 − − 0.01 0.05 0.10 0.02 0.05 0.20 − 0.13 岩屑 0.01 0.25 1.12 1.33 1.90 2.26 1.22 1.27 1.26 1.33 0.85 风化碎屑 0.01 0.07 0.72 0.39 1.23 0.05 − 0.36 0.43 0.05 0.25 注:“−”表示未测得数据,仅在某一粒级偶尔出现的矿物未作计算。 表 6 碎屑矿物因子载荷矩阵
Tab. 6 Clastics mineral factor load matrix
碎屑矿物 因子1 因子2 因子3 普通角闪石 −0.25 −0.92 −0.04 透闪石 0.09 −0.07 −0.70 阳起石 0.41 0.79 −0.17 绿帘石 0.63 −0.19 −0.58 黝帘石 0.80 0.28 −0.34 黑云母 0.41 0.81 −0.06 白云母 −0.02 −0.16 −0.05 石榴子石 −0.08 0.90 0.15 磷灰石 −0.64 0.38 −0.28 电气石 −0.80 −0.33 0.23 锆石 −0.32 0.00 0.88 金红石 0.56 0.20 0.11 透辉石 0.76 0.45 −0.11 自生碳酸盐 −0.05 −0.16 0.02 钛铁矿 0.01 0.04 0.81 磁铁矿 −0.36 −0.11 0.80 褐铁矿 −0.86 −0.19 0.31 赤铁矿 0.04 −0.02 0.01 特征值 6.78 3.65 2.62 累计贡献 0.25 0.47 0.66 -
[1] Garzanti E, Andò S, France-Lanord C, et al. Mineralogical and chemical variability of fluvial sediments: 1. Bedload sand (Ganga-Brahmaputra, Bangladesh)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 299(3/4): 368−381. [2] Garzanti E, Andò S, Vezzoli G. Settling equivalence of detrital minerals and grain-size dependence of sediment composition[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 273(1/2): 138−151. [3] 方建勇, 陈坚, 王爱军, 等. 台湾海峡表层沉积物的粒度和碎屑矿物分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(5): 91−99.Fang Jianyong, Chen Jian, Wang Aijun, et al. The distribution characteristics of grain size and mineral of surface sediment in the Taiwan Strait[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(5): 91−99. [4] 孙白云. 黄河、长江和珠江三角洲沉积物中碎屑矿物的组合特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1990, 10(3): 23−34.Sun Baiyun. Detrital mineral assemblages in the Huanghe, Changjiang and Zhujiang River Delta sediments[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1990, 10(3): 23−34. [5] Milliman J D, Syvitski J P M. Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: the importance of small mountainous rivers[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1992, 100(5): 525−544. doi: 10.1086/629606 [6] 杨守业, 印萍. 自然环境变化与人类活动影响下的中小河流沉积物源汇过程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(1): 1−10.Yang Shouye, Yin Ping. Sediment source-to-sink processes of small mountainous rivers under the impacts of natural environmental changes and human activities[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 2018, 38(1): 1−10. [7] 林晓彤, 李巍然, 时振波. 黄河物源碎屑沉积物的重矿物特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23(3): 17−21.Lin Xiaotong, Li Weiran, Shi Zhenbo. Characteristics of mineralogy in the clastic sediments from the Yellow River Provenance, China[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23(3): 17−21. [8] 王中波, 杨守业, 李日辉, 等. 黄河水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及沉积动力环境约束[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(4): 73−85.Wang Zhongbo, Yang Shouye, Li Rihui, et al. Detrital mineral composition of the sediments from Huanghe and its hydrodynamic environmental constraints[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(4): 73−85. [9] Jin Bingfu, Wang Mengyao, Yue Wei, et al. Heavy mineral variability in the Huanghe River sediments as determined by the multiple-window strategy[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(85): 1−16. doi: 10.3390/min9020085 [10] 樊水淼, 金秉福, 王昕, 等. 云母在黄河口段沉积物中的形状系数与等效沉积[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2021, 37(5): 31−38.Fan Shuimiao, Jin Bingfu, Wang Xin, et al. Mica shape factor and its equivalent sedimentation in the Sediments of the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2021, 37(5): 31−38. [11] 金秉福, 党丽丽, 孔庆祥, 等. 黄河和长江沉积角闪石亲石元素地球化学特征对比与物源辨识[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(1): 149−165. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.098Jin Bingfu, Dang Lili, Kong Qingxiang, et al. Comparison of geochemical characteristics of Lithophile Elements of Amphibole: identification of estuarine sediment provenance, Huanghe River and Changjiang River[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(1): 149−165. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2020.098 [12] 王中波, 杨守业, 李萍, 等. 长江水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(4): 570−578.Wang Zhongbo, Yang Shouye, Li Ping, et al. Detrital mineral compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and their tracing implications[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(4): 570−578. [13] 窦衍光, 王昆山, 王国庆, 等. 长江水下三角洲沉积物碎屑矿物研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(4): 22−26, 31.Dou Yanguang, Wang Kunshan, Wang Guoqing, et al. Research of detrital minerals in the sediment of sub-aqueous Yangtze Delta[J]. Marine Science, 2007, 31(4): 22−26, 31. [14] 潘大东, 王张华, 陈艇, 等. 长江口表层沉积物矿物磁性分区特征及其沉积环境指示意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 37(5): 101−111.Pan Dadong, Wang Zhanghua, Chen Ting, et al. Mineral magnetic characteristics of surficial sediments and their implications for identifying sedimentary environments at the Changjiang River Mouth[J]. Marine Science, 2015, 37(5): 101−111. [15] Yue Wei, Jin Bingfu, Zhao Baocheng. Transparent heavy minerals and magnetite geochemical composition of the Yangtze River sediments: implication for provenance evolution of the Yangtze Delta[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2018, 364: 42−52. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.12.006 [16] Cascalho J, Fradique C. Chapter 3 The sources and hydraulic sorting of heavy minerals on the Northern Portuguese continental margin[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 2007, 58: 75−110. [17] Pang Hongli, Pan Baotian, Garzanti E, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of modern Yellow River sediments: Implications for weathering and provenance[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 488: 76−86. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.04.010 [18] Garzanti E, Andò S. Heavy minerals for junior woodchucks[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(148): 2−25. doi: 10.3390/min9030148 [19] Morton A C. Geochemical studies of detrital heavy minerals and their application to provenance research[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1991, 57(1): 31−45. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1991.057.01.04 [20] Weckwerth P, Chabowski M. Heavy minerals as a tool to reconstruct river activity during the Weichselian glaciation (Toruń Basin, Poland)[J]. Geologos, 2013, 19(1/2): 25−46. [21] Eker C S, Sipahi F, Gümüş M K. Tracing provenance and chemical weathering changes in Ankara Stream sediments, central Turkey: geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic evidence[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2018, 138: 367−382. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.11.034 [22] 王利波, 李军, 赵京涛, 等. 辽东湾表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布及其对物源和沉积物扩散的指示意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(2): 66−74.Wang Libo, Li Jun, Zhao Jingtao, et al. Detrital mineral assemblages and distributions as indicators of provenance and dispersal pattern in surface sediments from Liaodong Bay, Bohai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(2): 66−74. [23] 邓凯, 杨守业, 王中波, 等. 台湾山溪性小河流碎屑重矿物组成及其示踪意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(3): 531−542.Deng Kai, Yang Shouye, Wang Zhongbo, et al. Detrital heavy mineral assemblages in the river sediments from Taiwan and its implications for sediment provenance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(3): 531−542. [24] Li Guangxue, Wei Helong, Yue Shuhong, et al. Sedimentation in the Yellow River Delta, part II: suspended sediment dispersal and deposition on the subaqueous delta[J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 149(1/4): 113−131. [25] Liu Jian, Saito Y, Wang Hong, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 236(3/4): 165−187. [26] 窦衍光, 李军, 杨守业. 山东半岛东部海域表层沉积物元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2012, 34(1): 109−119.Dou Yanguang, Li Jun, Yang Shouye. Element compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in offshore areas of the eastern Shandong Peninsula in China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2012, 34(1): 109−119. [27] Qin Yachao, Xue Chunting, Jiang Xuejun. Tidal current-dominated depositional environments in the central-northern Yellow Sea as revealed by heavy-mineral and grain-size dispersals[J]. Marine Geology, 2018, 398: 59−72. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2018.01.004 [28] 张维武. 山东省辛安河上游砂金矿床成矿地质特征[J]. 黄金, 1989, 10(12): 7−12.Zhang Weiwu. The metallogenic geological characteristics of placer gold deposit in upper reaches of Xin’an River, Shandong Province[J]. Gold, 1989, 10(12): 7−12. [29] 金秉福, 王孟瑶, 王昆山, 等. 长江口和黄东海沉积物单矿物分选的常用方法和流程[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(1): 163−174.Jin Bingfu, Wang Mengyao, Wang Kunshan, et al. Methods of single mineral separation for sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2019, 39(1): 163−174. [30] 王孟瑶, 金秉福, 岳伟. 长江口表层沉积物重矿物在不同粒级中的分布与研究意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(11): 89−100.Wang Mengyao, Jin Bingfu, Yue Wei. Patterns of heavy mineral combination in different grain-size categories and their sedimentary significance: a case study for surfical sediments in the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(11): 89−100. [31] Mange M A, Maurer H F W. Heavy Minerals in Colour[M]. London: Chapman & Hall, 1992. [32] 杨立建, 马小川, 贾建军, 等. 近百年来黄河改道及输沙量变化对山东半岛泥质楔沉积物粒度特征的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(1): 78−89.Yang Lijian, Ma Xiaochuan, Jia Jianjun, et al. Impacts of channel shifts and interannual sediment load reducing of the Yellow River on the grain size characteristics of sediments in the Shandong mud wedge over the past 100 years[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(1): 78−89. [33] 刘宝珺. 沉积岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1980.Liu Baojun. Sedimentary Petrology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1980. [34] Morton A, Hallsworth C, Strogen D. Evolution of provenance in the NE Atlantic rift: the Early-Middle Jurassic succession in the Heidrun Field, Halten Terrace, offshore Mid-Norway[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(7): 1100−1117. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.07.006 [35] Garzanti E, Andò S, Vezzoli G. Grain-size dependence of sediment composition and environmental bias in provenance studies[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 277(3/4): 422−432. [36] Garzanti E, Andò S, Vezzoli G, et al. Petrology of the Namib Sand Sea: long-distance transport and compositional variability in the wind-displaced Orange Delta[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 112(3/4): 173−189. [37] Wang Mengyao, Jin Bingfu, Gao Jianhua, et al. Identification of sediment provenance in the South Yellow Sea using detrital amphibole geochemistry[J]. Marine Geology, 2022, 450: 106857. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2022.106857 [38] 张凯棣, 李安春, 董江, 等. 东海表层沉积物碎屑矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示[J]. 沉积学报, 2016, 34(5): 902−911.Zhang Kaidi, Li Anchun, Dong Jiang, et al. Detrital mineral distributions in surface sediments of the East China Sea: implications for sediment provenance and sedimentary environment[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2016, 34(5): 902−911. [39] 王孔海. 山东烟台地区晚太古代胶东群变质岩系原岩恢复及其地质意义[C]//中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所文集. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社, 1983: 14−36.Wang Konghai. Primary rock restoration for metamorphic rocks of late Archean Jiaodong Group and its significance in Yantai, Shandong Province[C]//Bull Shenyang institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Press, 1983: 14−36. [40] 李学杰, 汪品先, 廖志良, 等. 南海西部表层沉积物碎屑矿物分布特征及其物源[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(1): 123−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.013Li Xuejie, Wang Pinxian, Liao Zhiliang, et al. Distribution of clastic minerals of surface sediments in the western South China Sea and their provenance[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(1): 123−130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.01.013 [41] 杨东宁, 袁东星. 主成分分析法用于厦门西港和香港维多利亚港沉积物样品分类研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1998, 17(3): 61−66.Yang Dongning, Yuan Dongxing. Application of principal component analysis to sediment sample classification[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1998, 17(3): 61−66. [42] Cojan I, Renard M. Sedimentology[M]. Netherlands: CRC Press, 2020. [43] 刘炳辰, 金秉福, 王萌, 等. 内蒙古五岔沟地区洮儿河流域重矿物特征分析[J]. 世界地质, 2013, 32(1): 69−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.01.009Liu Bingchen, Jin Bingfu, Wang Meng, et al. Analysis of the characteristics of heavy minerals in Taoer River area, Wuchagou region in Inner Mongolia[J]. Global Geology, 2013, 32(1): 69−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2013.01.009 [44] 胡修棉. 物源分析的一个误区: 砂粒在河流搬运过程中的变化[J]. 古地理学报, 2017, 19(1): 175−184. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.01.014Hu Xiumian. A misunderstanding in provenance analysis: sand changes of mineral, roundness, and size in flowing-water transportation[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2017, 19(1): 175−184. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2017.01.014 [45] 石勇, 高建华, 刘强, 等. 陆架环流作用下的北黄海中北部细颗粒物质输运[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(4): 53−63.Shi Yong, Gao Jianhua, Liu Qiang, et al. Fine sediment transport in north-central of Yellow Sea: the role of continental shelf circulation[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(4): 53−63. [46] 林旭, 赵希涛, 吴中海, 等. 渤海湾周缘主要河流钾长石物源示踪指标研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 10−18.Lin Xu, Zhao Xitao, Wu Zhonghai, et al. Source tracing elements of K-feldspars of main rivers around Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 10−18. [47] Jin Bingfu, Wang Mengyao, Yue Wei, et al. Comparative analysis of heavy mineral characteristics of sediments from the Huanghe River and the Changjiang River based on the multiple-window grain size strategy[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2021, 216: 104326. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2020.104326 [48] 常丽华, 陈曼云, 金巍, 等. 透明矿物薄片鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2014.Chang Lihua, Chen Manyun, Jin Wei, et al. Manual of Transparent Mineral Thin Section Identification[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2014. [49] 刘雪亚, 王荃. 中国地质图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2002.Liu Xueya, Wang Quan. Geological Atlas of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2002. [50] 赵珊茸. 结晶学及矿物学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004.Zhao Shanrong. Crystallography and Mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004. [51] 金秉福, 张云吉, 宋键. 长江三角洲第一硬土层中微结核的矿物化学特征及其成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2007, 27(3): 9−15.Jin Bingfu, Zhang Yunji, Song Jian. Characteristics of mineral chemistry and formation of the micro-nodules in the first stiff clay layer in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2007, 27(3): 9−15. [52] 宁泽, 韩宗珠, 林学辉, 等. 山东半岛南部近岸海域碎屑矿物对中小河流的物源响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(4): 57−68.Ning Ze, Han Zongzhu, Lin Xuehui, et al. Provenance response of detrital minerals from medium and small rivers in offshore Southern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(4): 57−68. [53] 王昆山, 石学法, 蔡善武, 等. 黄河口及莱州湾表层沉积物中重矿物分布与来源[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(6): 1−8.Wang Kunshan, Shi Xuefa, Cai Shanwu, et al. Distribution and provenance of the surface sediments of the Yellow River Mouth and Laizhou Bay deduced from heavy minerals[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(6): 1−8. [54] 王艳君, 金秉福. 黄河河口段与海河河口段沉积物碳酸盐对比分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2017, 41(7): 94−104. doi: 10.11759/hykx20161208001Wang Yanjun, Jin Bingfu. Comparative analysis of carbonates in sediments of the Yellow River and the Haihe River estuaries[J]. Marine Sciences, 2017, 41(7): 94−104. doi: 10.11759/hykx20161208001 -





 下载:
下载: