Sequencing and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of green abalone (Haliotis fulgens)
-
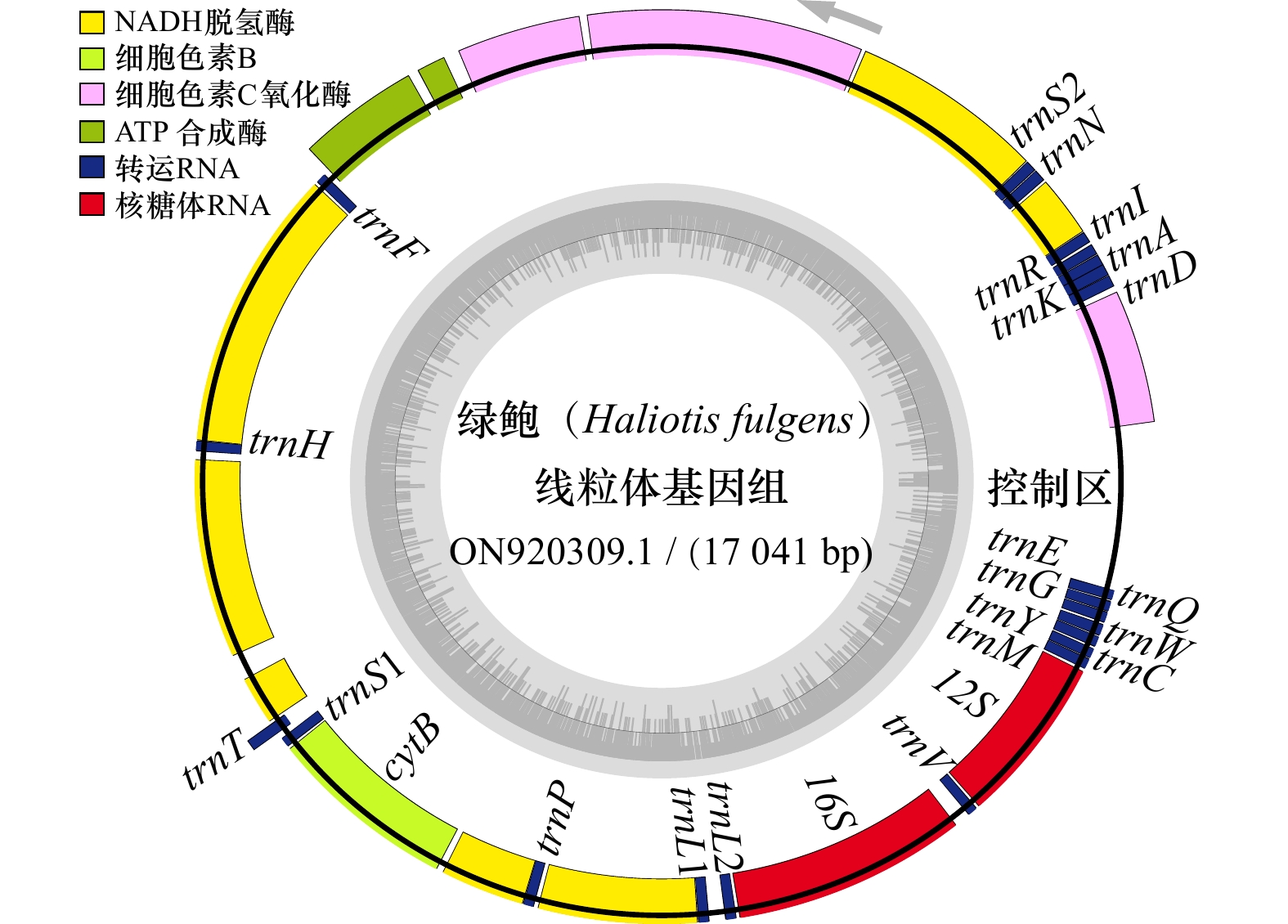
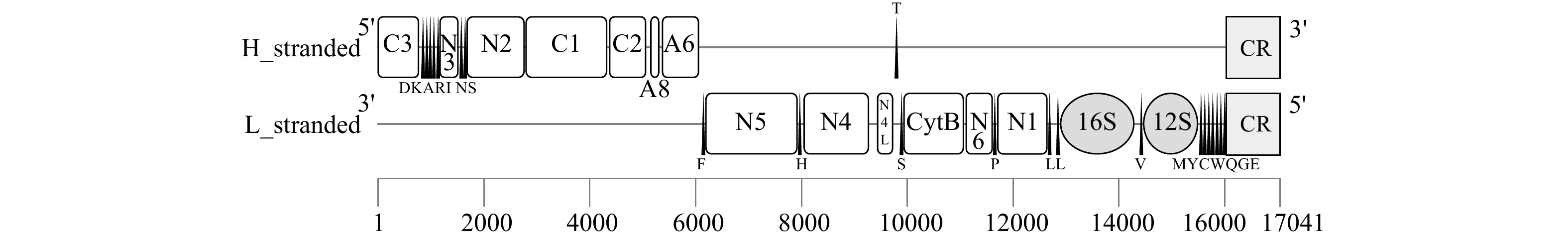
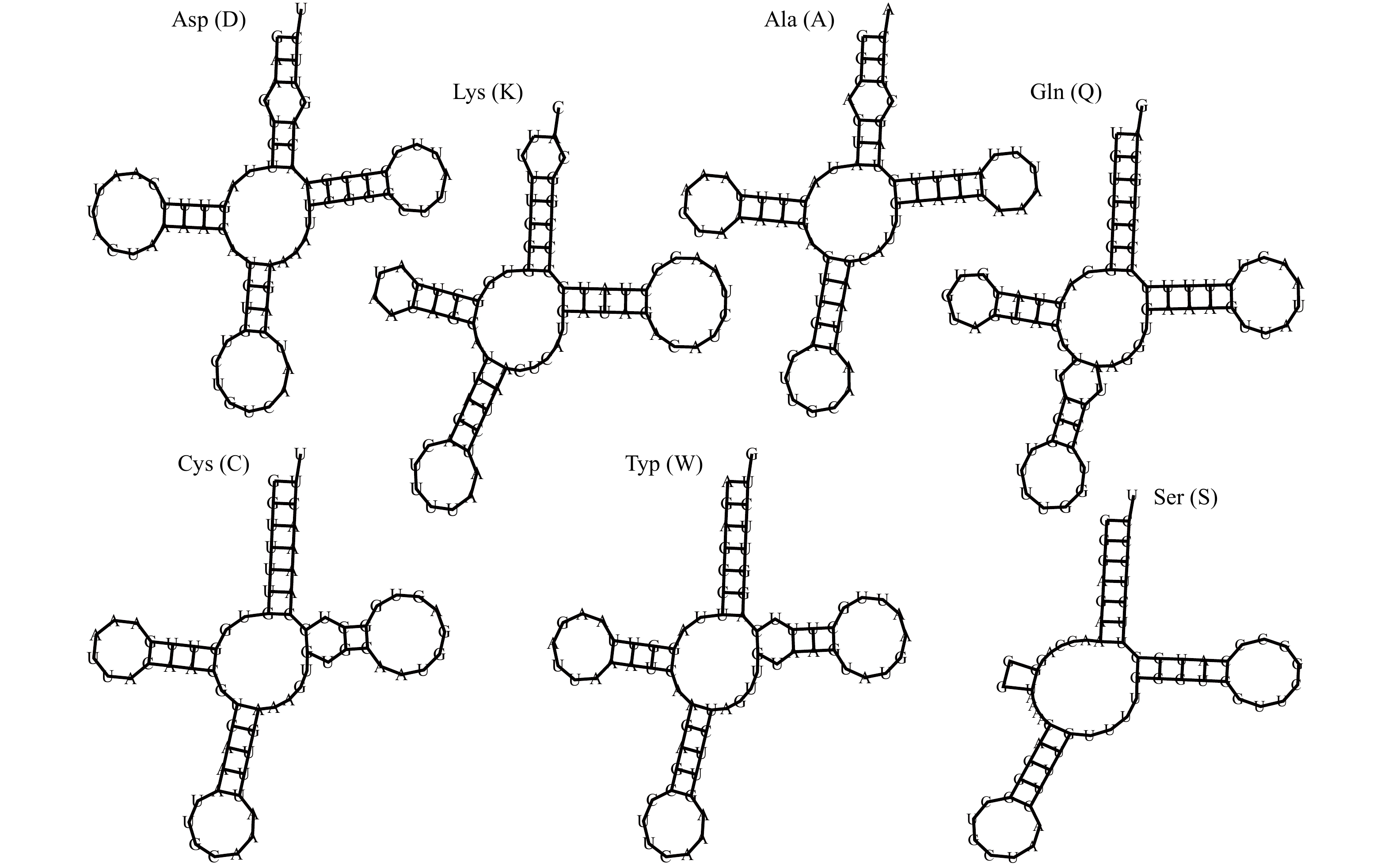
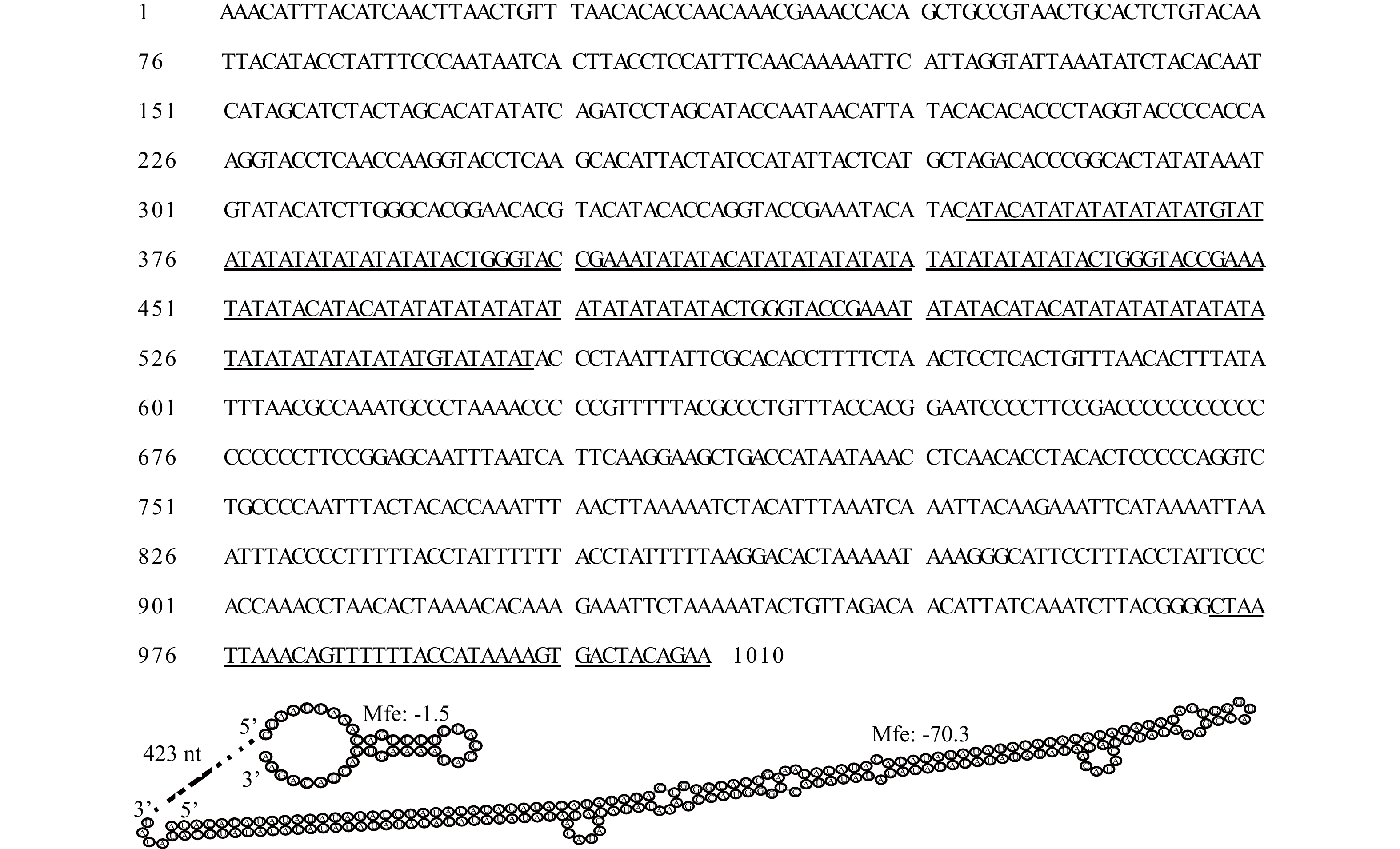
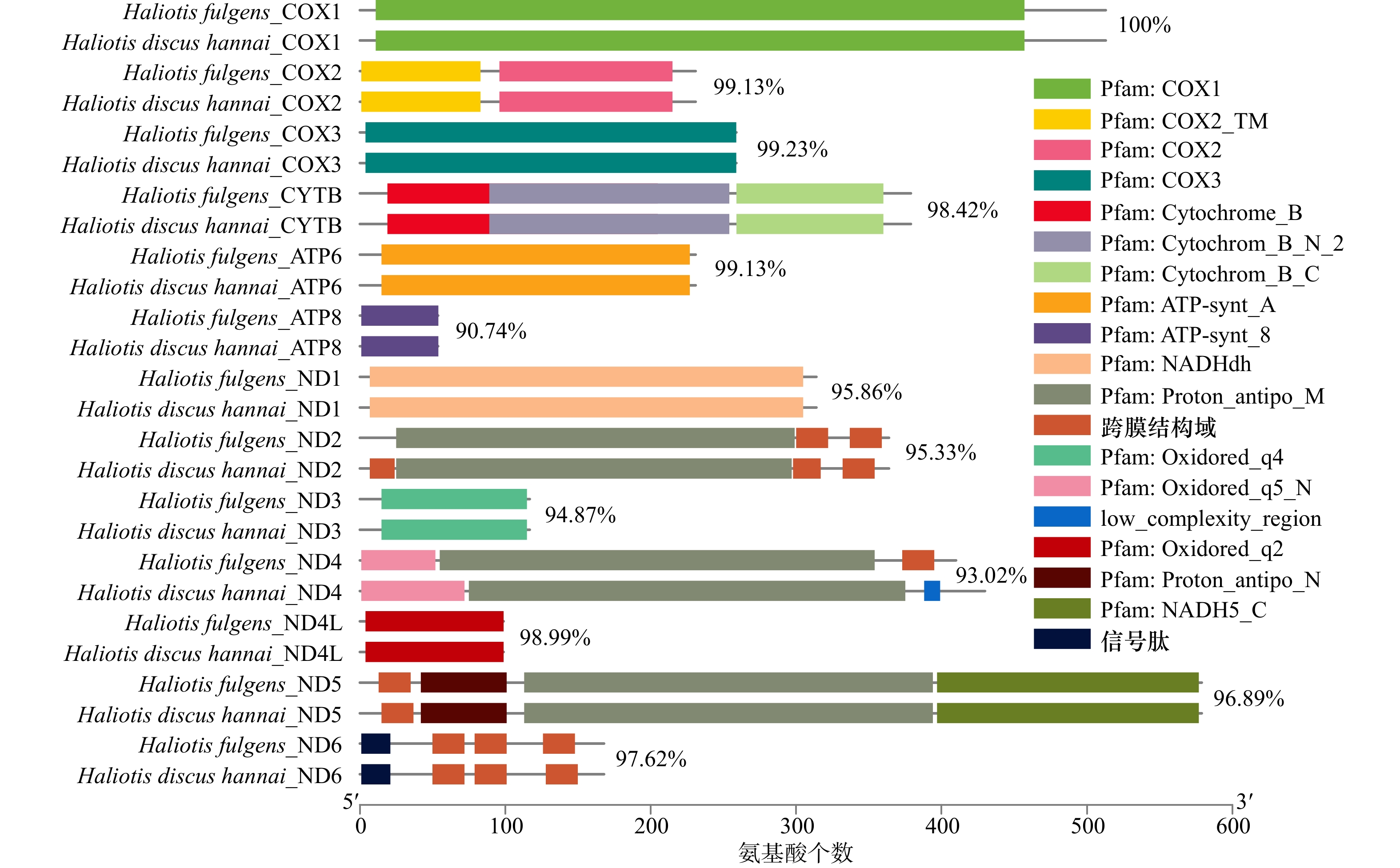
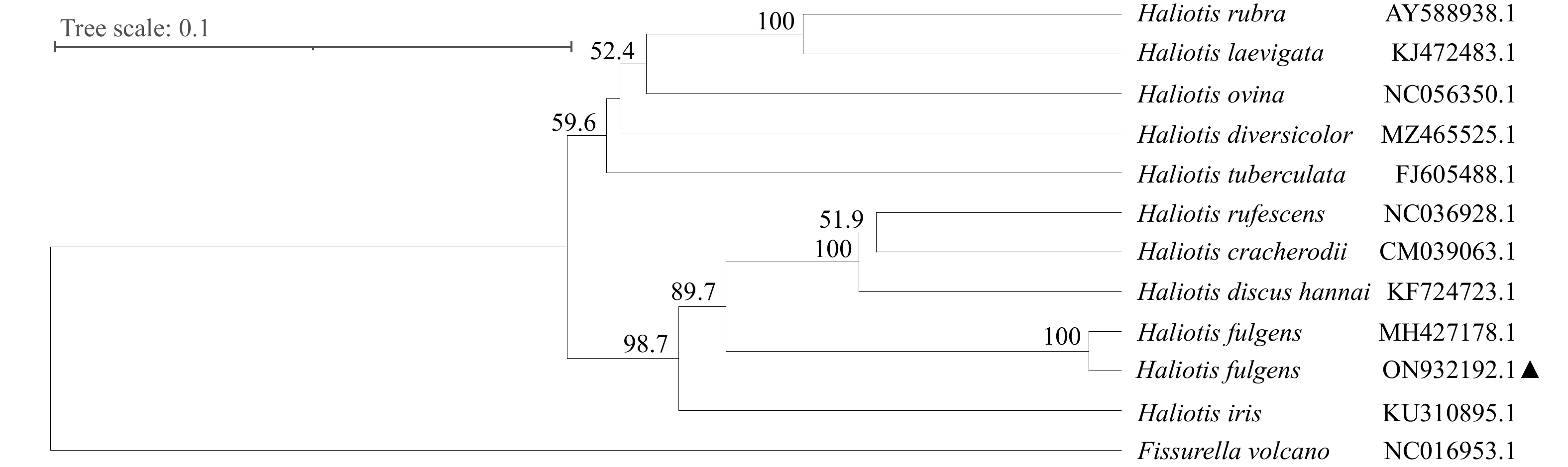
摘要: 为高效鉴别鲍属物种和更好地管理和保护鲍种质资源,本研究通过高通量测序获得了养殖绿鲍(Haliotis fulgens)稚贝的线粒体基因组全序列,并对其序列和结构特征进行分析。结果表明,绿鲍线粒体基因组全长17 041 bp,含有37个编码基因,其中蛋白质编码基因13个、tRNA基因22个、rRNA基因2个。13个蛋白质编码基因均以AUG为起始密码子,以UAG或UAA为终止密码子。除tRNA-Ser(AGN)外的21个tRNA基因可折叠成典型三叶草结构。分析发现tRNA-Glu和COX3间存在富含A+T的非编码区,其内含有2个带回文序列的发卡结构。基于已报道的10个鲍属线粒体基因组全序列构建系统发育树,发现绿鲍与皱纹盘鲍(Haliotis discus hannai)、红鲍(Haliotis rufescens)、黑鲍(Haliotis cracherodii)聚为一支。将绿鲍与皱纹盘鲍13个线粒体编码蛋白的结构域比较,发现二者ND2、ND4的跨膜结构域数量存在差异,这是否与二者的高温耐受性差异有关,有待进一步研究。总之,绿鲍线粒体基因组全序列的首次获取和分析,丰富了鲍类细胞遗传信息,为分类、种质鉴定与种质资源保护提供了基础数据和参考。Abstract: To identify abalone species effectively for better management and protection of abalone germplasm resources, we have obtained the complete mitochondrial genome of juvenile green abalone (Haliotis fulgens) through high-throughput sequencing, and its sequences and structural characteristics are analyzed accordingly. The results show that the mitogenome of H. fulgens is 17 041 bp in total length and encoded 37 genes, including 13 protein coding genes, 22 transfer RNA (tRNA) genes and 2 ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes. The 13 protein coding genes used AUG as the starting codon and UAA or UAG as the termination codon. Twenty-one tRNA genes other than tRNA-Ser(AGN) could be folded into a typical cloverleaf structure. There is a rich A+T non-coding region between tRNA-Glu and COX3, with two hairpin structures containing palindromes in it. A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on the reported complete mitochondrial genome sequences of Haliotis genus species, and phylogenetic analysis shows that H. fulgens is clustered with H. discus hannai, H. rufescens and H. cracherodii. Comparing the domains of 13 proteins of mitogenome of H. fulgens and H. discus hannai, we found the number of transmembrane domains of ND2 or ND4 dehydrogenase subunits were different in them. Whether this is related to the difference of high temperature tolerance between them needs further study. In brief, the first acquisition and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of H. fulgens has enriched the abalone cellular genetic information, and provided basic data and references for abalone species classification, germplasm identification, and protection of germplasm resources of H. fulgens as well.
-
Key words:
- Haliotis fulgens /
- mitochondrial genome /
- genome composition /
- phylogeny /
- domain
-
表 1 已报道鲍属贝类线粒体基因组
Tab. 1 The complete mitochondrial genomes reported of Haliotis genus for analysis
物种 长度/bp GC含量/% GenBank登录号 皱纹盘鲍(Haliotis discus hannai) 16 886 39.6 KF724723.1 黑足鲍(Haliotis iris) 17 131 40.2 KU310895.1 黑唇鲍(Haliotis rubra) 16 907 40.9 AY588938.1 绿唇鲍(Haliotis laevigata) 16 545 42.2 KJ472483.1 欧洲疣鲍(Haliotis tuberculata) 15 938 39.5 FJ605488.1 杂色鲍(Haliotis diversicolor) 16 543 40.1 MZ465525.1 羊鲍(Haliotis ovina) 16 531 40.7 NC056350.1 红鲍(Haliotis rufescens) 16 646 39.7 NC036928.1 黑鲍(Haliotis cracherodii) 18 391 37.7 CM039063.1 表 2 绿鲍线粒体基因组注释结果
Tab. 2 The results of the complete mitochondrial genome annotation for Haliotis fulgens
基因 长度/bp 定位 间隔区/bp 反密码子 密码子 编码链 起始位点 终止位点 起始密码子 终止密码子 COX3 780 1 780 0 − AUG UAA H trnD 73 812 884 31 GUC − − H trnK 72 884 955 −1 UUU − − H trnA 69 951 1 019 −5 UGC − − H trnR 66 1 021 1 086 1 UCG − − H trnI 70 1 099 1 168 12 GAU − − H ND3 354 1 171 1 524 2 − AUG UAA H trnN 71 1 537 1 607 12 GUU − − H trnS 67 1 611 1 677 3 GCU − − H ND2 1 095 1 681 2 775 3 − AUG UAA H COX1 1 542 2 795 4 336 19 − AUG UAA H COX2 696 4 375 5 070 38 − AUG UAG H ATP8 165 5 155 5 319 84 − AUG UAA H ATP6 696 5 374 6 069 54 − AUG UAA H trnF 68 6 113 6 180 43 GAA − − L ND5 1 740 6 195 7 934 14 − AUG UAA L trnH 68 7 935 8 002 0 GUG − − L ND4 1 233 8 050 9 282 47 − AUG UAA L ND4L 300 9 438 9 737 155 − AUG UAG L trnT 70 9 762 9 831 24 UGU − − H trnS 67 9 858 9 924 26 UGA − − L CYTB 1 140 9 937 11 076 12 − AUG UAG L ND6 507 11 114 11 620 37 − AUG UAG L trnP 67 11 621 11 687 0 UGG − − L ND1 945 11 710 12 654 22 − AUG UAG L trnL 68 12 656 12 723 1 UAA − − L trnL 68 12 814 12 881 90 UAG − − L 16S 1 400 12 898 14 297 16 − − − L trnV 66 14 390 14 455 92 AAC − − L 12S 1 033 14 469 15 501 13 − − − L trnM 70 15 516 15 585 14 CAU − − L trnY 68 15 588 15 655 2 GUA − − L trnC 70 15 664 15 733 8 GCA − − L trnW 73 15 737 15 809 3 UCA − − L trnQ 70 15 820 15 889 10 UUG − − L trnG 68 15 892 15 959 2 UCC − − L trnE 68 15 964 16 031 4 UUC − − L 注:trn表示rRNA,后面的大写字母表示该tRNA转运的氨基酸;16S和12S为rRNA基因;−代表无密码子。 表 3 鲍属线粒体基因组碱基组成
Tab. 3 Composition and skewness in the mitochondrial genomes of Haliotis genus species
物种 碱基组成/% AT偏移 GC偏移 A T C G A+T 线粒体全基因组 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 36.2 24.4 26.5 12.9 60.6 0.195 −0.345 皱纹盘鲍 Haliotis discus hannai 35.4 25.0 26.1 13.5 60.4 0.172 −0.318 黑足鲍 Haliotis iris 35.9 23.9 26.8 13.4 59.8 0.201 −0.333 黑唇鲍 Haliotis rubra 34.6 24.5 26.7 14.2 59.1 0.171 −0.306 绿唇鲍 Haliotis laevigata 23.9 33.9 14.9 27.3 57.8 −0.173 0.294 欧洲疣鲍 Haliotis tuberculata 34.8 25.7 25.8 13.6 60.5 0.150 −0.310 杂色鲍 Haliotis diversicolor 35.2 24.7 26.4 13.7 59.9 0.175 −0.317 羊鲍 Haliotis ovina 34.8 24.5 27.4 13.4 59.3 0.174 −0.343 红鲍 Haliotis rufescens 35.4 24.9 25.9 13.7 60.3 0.174 −0.308 黑鲍 Haliotis cracherodii 26.6 35.7 13.5 24.2 62.3 −0.146 0.284 蛋白质编码基因 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 23.4 36.3 19.1 21.2 59.7 −0.216 0.052 皱纹盘鲍 Haliotis discus hannai 23.4 36.3 19.2 21.1 59.7 −0.216 0.047 黑足鲍 Haliotis iris 22.5 36.0 19.6 21.9 58.5 −0.231 0.055 黑唇鲍 Haliotis rubra 22.3 35.1 19.9 22.6 57.4 −0.223 0.064 绿唇鲍 Haliotis laevigata 22.2 34.5 20.4 22.8 56.7 −0.217 0.056 欧洲疣鲍 Haliotis tuberculata 23.7 36.1 18.9 21.3 59.8 −0.207 0.060 杂色鲍 Haliotis diversicolor 23.2 35.9 19.1 21.8 59.1 −0.215 0.066 羊鲍 Haliotis ovina 22.6 35.8 19.3 22.2 58.4 −0.226 0.070 红鲍 Haliotis rufescens 23.5 36.0 19.3 21.2 59.5 −0.210 0.047 黑鲍 Haliotis cracherodii 23.2 35.9 19.4 21.6 59.1 −0.215 0.054 tRNA基因 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 28.1 31.0 16.9 24.0 59.1 −0.050 0.174 皱纹盘鲍 Haliotis discus hannai 28.2 30.5 17.3 24.0 58.7 −0.039 0.162 黑足鲍 Haliotis iris 27.6 30.6 17.5 24.3 58.2 −0.052 0.163 黑唇鲍 Haliotis rubra 27.5 30.4 17.4 24.8 57.9 −0.050 0.175 绿唇鲍 Haliotis laevigata 27.3 30.7 17.1 24.9 58.0 −0.059 0.186 欧洲疣鲍 Haliotis tuberculata 28.7 31.0 17.0 23.3 59.7 −0.039 0.156 杂色鲍 Haliotis diversicolor 27.2 30.8 17.2 24.9 58.0 −0.062 0.183 羊鲍 Haliotis ovina 27.5 31.2 17.0 24.4 58.7 −0.063 0.179 红鲍 Haliotis rufescens 28.3 30.5 17.4 23.8 58.8 −0.037 0.155 黑鲍 Haliotis cracherodii 28.0 30.8 17.1 24.1 58.8 −0.048 0.170 rRNA基因 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 26.1 35.1 13.4 25.4 61.2 −0.147 0.309 皱纹盘鲍 Haliotis discus hannai 27.2 35.2 13.1 24.5 62.4 −0.128 0.303 黑足鲍 Haliotis iris 25.8 35.7 12.9 25.6 61.5 −0.161 0.330 黑唇鲍 Haliotis rubra 26.2 34.9 13.6 25.3 61.1 −0.142 0.301 绿唇鲍 Haliotis laevigata 26.3 33.9 14.3 25.6 60.2 −0.126 0.283 欧洲疣鲍 Haliotis tuberculata 28.0 34.4 13.2 24.4 62.4 −0.103 0.298 杂色鲍 Haliotis diversicolor 27.1 35.1 13.2 24.5 62.2 −0.129 0.300 羊鲍 Haliotis ovina 25.8 34.6 13.5 26.1 60.4 −0.146 0.318 红鲍 Haliotis rufescens 27.3 34.9 13.3 24.5 62.2 −0.122 0.296 黑鲍 Haliotis cracherodii 27.1 35.0 13.3 24.6 62.1 −0.127 0.298 假定控制区 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 37.6 29.4 24.6 8.4 67.0 0.122 −0.491 表 4 绿鲍13个蛋白质编码基因密码子平均使用频率
Tab. 4 Total codon average usage in the thirteen protein coding genes for Haliotis fulgens
密码子 数量 使用率 密码子 数量 使用率 密码子 数量 使用率 密码子 数量 使用率 UCU(S) 95 2.11 GUU(V) 127 1.60 ACU(T) 67 1.48 CAA(Q) 44 1.19 UCC(S) 58 1.29 GUA(V) 75 0.94 ACA(T) 66 1.46 CAG(Q) 30 0.81 UCA(S) 52 1.15 GUG(V) 74 0.93 ACC(T) 36 0.80 CAU(H) 46 1.15 AGU(S) 50 1.11 GUC(V) 42 0.53 ACG(T) 12 0.27 CAC(H) 34 0.85 AGG(S) 38 0.84 UUA(L) 151 1.56 UUU(T) 216 1.38 AAA(K) 46 1.12 AGA(S) 34 0.75 UUG(L) 148 1.53 UUC(T) 98 0.62 AAG(K) 36 0.88 AGC(S) 18 0.40 CUA(L) 115 1.19 UAU(Y) 86 1.33 UGA(W) 60 1.10 UCG(S) 16 0.35 CUU(L) 74 0.77 UAC(Y) 43 0.67 UGG(W) 49 0.90 CGA(R) 29 1.81 CUC(L) 59 0.61 GGA(G) 92 1.31 GAA(E) 50 1.10 CGU(R) 19 1.19 CUG(L) 33 0.34 GGG(G) 92 1.31 GAG(E) 41 0.90 CGG(R) 9 0.56 GCU(A) 94 1.55 GGU(G) 69 0.99 GAC(D) 40 1.08 CGC(R) 7 0.44 GCC(A) 63 1.04 GGC(G) 27 0.39 GAU(D) 34 0.92 CCA(P) 61 1.64 GCA(A) 58 0.96 AAU(N) 77 1.29 AUG(M) 88 1.05 CCU(P) 52 1.40 GCG(A) 27 0.45 AAC(N) 42 0.71 AUA(M) 80 0.95 CCG(P) 20 0.54 UGU(C) 45 1.50 AUU(I) 145 1.19 UAA 8 1.23 CCC(P) 16 0.43 UGC(C) 15 0.50 AUC(I) 98 0.81 UAG 5 0.77 注:黑体表示偏好密码子。 表 5 基于线粒体全序列的10种鲍种间核酸相似性
Tab. 5 Nucleotide sequence identity among 10 species of abalone based on whole mitochondrial genome
物种 核酸相似性/% 绿鲍 Haliotis fulgens 100 皱纹盘鲍 Haliotis discus hannai 89.15 100 黑足鲍 Haliotis iris 82.86 83.41 100 黑唇鲍 Haliotis rubra 80.94 80.97 80.73 100 绿唇鲍 Haliotis laevigata 80.80 80.66 80.23 91.89 100 欧洲疣鲍 Haliotis tuberculata 81.51 81.39 81.32 83.84 83.37 100 杂色鲍 Haliotis diversicolor 81.03 80.77 80.16 83.09 82.80 82.59 100 羊鲍 Haliotis ovina 80.10 79.95 79.06 82.14 81.92 81.36 81.54 100 红鲍 Haliotis rufescens 88.16 90.94 83.41 81.51 81.12 81.61 81.59 80.75 100 黑鲍 Haliotis cracherodii 87.90 90.03 83.46 81.25 80.98 81.19 80.64 80.55 91.62 100 -
[1] 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 2022中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2022.Fishery and Fishery Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fisheries Technology Extension Center, China Society of Fisheries. 2022 China Fishery Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2022. [2] Franchini P, Slabbert R, Merwe M V D, et al. Karyotype and genome size estimation of Haliotis midae: estimators to assist future studies on the evolutionary history of Haliotidae[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2010, 29(4): 945−950. doi: 10.2983/035.029.0428 [3] Geiger D L. Distribution and biogeography of the recent Haliotidae (Gastropoda: Vetigastropoda) world-wide[J]. Bollettino Malacologico, 1999, 35: 57−118. [4] 赖龙玉, 严正凛. 鲍遗传育种研究进展[J]. 福建农业学报, 2013, 28(12): 1303−1309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.12.023Lai Longyu, Yan Zhenglin. Advances in genetics and breeding of abalone[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 28(12): 1303−1309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0384.2013.12.023 [5] 王子臣. 红鲍、绿鲍引种初步成功[J]. 大连水产学院学报, 1986(6): 93−94.Wang Zichen. Transplantations of American abalones, Haliotis rufescens and H. fulgens from U. S. A. to China[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 1986(6): 93−94. [6] 许国领, 劳赞, 杨小立. 美国绿鲍驯育和人工育苗[J]. 热带海洋, 1989, 8(3): 75−81.Xu Guoling, Lao Zan, Yang Xiaoli. A preliminary summary on the climatization and seed culture of green abalone[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 1989, 8(3): 75−81. [7] 范飞龙. 绿鲍的引种及与皱纹盘鲍的种间杂交研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2012.Fan Feilong. The introduction of Haliotis fulgens and the research of hybridization between Haliotis fulgens and Haliotis discus hannai[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2012. [8] 郭勍. 皱纹盘鲍与绿鲍杂交、回交后代的分子鉴定及性腺发育的初步研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2015.Guo Qing. Molecular identification of Haliotis discus hannai, Haliotis fulgens and their hybrids and backcross and the preliminary research of gonadal development of them[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2015. [9] You Weiwei, Guo Qing, Fan Feilong, et al. Experimental hybridization and genetic identification of Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai and green abalone H. fulgens[J]. Aquaculture, 2015, 448: 243−249. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.05.043 [10] Jex A R, Hall R S, Littlewood D T J, et al. An integrated pipeline for next-generation sequencing and annotation of mitochondrial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, 38(2): 522−533. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp883 [11] Robinson N A, Hall N E, Ross E M, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Haliotis laevigata (Gastropoda: Haliotidae) using MiSeq and HiSeq sequencing[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part A, 2016, 27(1): 437−438. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2014.900611 [12] Yang E C, Nam B H, Noh S J, et al. Complete mitochondrial genome of Pacific abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) from Korea[J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 2015, 26(6): 917−918. doi: 10.3109/19401736.2013.863289 [13] 张国范, 常亚青, 赵艳. 海洋动物线粒体DNA研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 1997(1): 25−28.Zhang Guofan, Chang Yaqing, Zhao Yan. A perspective of mitochondrial DNA research in marine animals[J]. Marine Sciences, 1997(1): 25−28. [14] 周传江, 马爱喆, 汪曦, 等. 鱼类线粒体基因组研究进展[J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(2): 74−82. doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2019.02.012Zhou Chuanjiang, Ma Aizhe, Wang Xi, et al. Progress on fish mitochondrial genome[J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(2): 74−82. doi: 10.16366/j.cnki.1000-2367.2019.02.012 [15] 梁日深, 杨杰銮, 谢瑞琳, 等. 巨石斑鱼与斜带石斑鱼线粒体基因组测序及物种有效性分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 52(6): 50−61.Liang Rishen, Yang Jieluan, Xie Ruilin, et al. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Epinephelus tauvina and E. coioides and their species validity[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2022, 52(6): 50−61. [16] 朱雷宇, 朱志煌, 朱陇强, 等. 龙虾科物种线粒体基因组特征和系统发育分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2022, 29(4): 525−534.Zhu Leiyu, Zhu Zhihuang, Zhu Longqiang, et al. Characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome in Palinuridae[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2022, 29(4): 525−534. [17] 李加爱, 陈丽彬, 柳斌彬, 等. 钝齿蟳线粒体基因组全序列测定及系统发育分析[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(3): 198−208.Li Jiaai, Chen Libin, Liu Binbin, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Charybdis hellerii (Brachyura: Portunidae) and phylogenetic analysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2021, 40(3): 198−208. [18] 颜成瑞, 苗菁, 叶莹莹. 14种帘蛤科贝类线粒体基因组特征与系统进化分析[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 40(4): 285−292.Yan Chengrui, Miao Jing, Ye Yingying. Mitochondrial genomic characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of 14 species of Veneridae[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2021, 40(4): 285−292. [19] 史宝, 柳学周, 刘永山, 等. 黄条鰤线粒体全基因组测序及结构特征分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(3): 405−415. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18365Shi Bao, Liu Xuezhou, Liu Yongshan, et al. Complete sequence and gene organization of the mitochondrial genome of Seriola aureovittata[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(3): 405−415. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18365 [20] 毛明光, 顾杰, 刘瑞婷, 等. 太平洋鳕线粒体全基因组测序及结构特征分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 2019, 43(1): 17−26. doi: 10.7541/2019.003Mao Mingguang, Gu Jie, Liu Ruiting, et al. Analysis of complete mitochondrial genome sequences of Gadus macrocephalus[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2019, 43(1): 17−26. doi: 10.7541/2019.003 [21] 杜诗雨, 张康琴, 潘达, 等. 格氏束腰蟹(Somanniathelphusa grayi)的线粒体基因组序列测定和基因顺序进化研究[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2022, 45(1): 86−95.Du Shiyu, Zhang Kangqin, Pan Da, et al. The mitochondrial genome of Somanniathelphusa grayi and the evolution of gene order[J]. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 45(1): 86−95. [22] 韩振勇. 丽蚌属线粒体基因组双单亲遗传研究与淡水蚌系统进化分析[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016.Han Zhenyong. Research of DUI in lamprotula mtDNA and phylogenomics analysis of unionoida[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. [23] Zhong Shengping, Huang Guoqiang, Liu Yonghong, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of marine gastropod Melo melo (Neogastropoda: Volutoidea)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 2019, 4(2): 4161−4162. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1693293 [24] Maynard B T, Kerr L J, Mckiernan J M, et al. Mitochondrial DNA sequence and gene organization in the Australian blacklip abalone Haliotis rubra (Leach)[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2005, 7(6): 645−658. doi: 10.1007/s10126-005-0013-z [25] Van Wormhoudt A, Le Bras Y, Huchette S. Haliotis marmorata from Senegal; a sister species of Haliotis tuberculata: morphological and molecular evidence[J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2009, 37(6): 747−755. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2009.12.020 [26] Xin Yi, Ren Jianfeng, Liu Xiao. Mitogenome of the small abalone Haliotis diversicolor Reeve and phylogenetic analysis within Gastropoda[J]. Marine Genomics, 2011, 4(4): 253−262. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2011.06.005 [27] Guo Zhansheng, Ding Yi, Han Leng, et al. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai[J]. Mitochondrial DNA Part B, 2019, 4(1): 717−718. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2018.1495125 [28] 房孝宁. 皱纹盘鲍、黑足鲍及杂交F1代线粒体基因组测序及系统发育价值的研究[D]. 威海: 山东大学, 2016.Fang Xiaoning. Research on sequencing of mitogenome and phylogenetic analysis within Haliotis discus hannai Ino, Haliotis iris martyn and hybrid F1[D]. Weihai: Shandong University, 2016. [29] 逯峰. 羊鲍线粒体全基因组序列测定及幼体附着影响因素的分析[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2020.Lu Feng. Sequencing and analysis of complete mitochondrial genome of Haliotis ovina[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2020. [30] Gutiérrez-Gonzalez J L, Cruz P, Rio-Portilla M A D, et al. Genetic structure of green abalone Haliotis fulgens population off Baja California, Mexico[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2007, 26(3): 839−846. doi: 10.2983/0730-8000(2007)26[839:GSOGAH]2.0.CO;2 [31] Mejía-Ruíz P, Perez-Enriquez R, Mares-Mayagoitia J A, et al. Population genomics reveals a mismatch between management and biological units in green abalone (Haliotis fulgens)[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8: e9722. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9722 [32] Moore J D, Juhasz C I, Robbins T T, et al. Green abalone, Haliotis fulgens infected with the agent of withering syndrome do not express disease signs under a temperature regime permissive for red abalone, Haliotis rufescens[J]. Marine Biology, 2009, 156(11): 2325−2330. doi: 10.1007/s00227-009-1260-8 [33] Mazariegos-Villarreal A, Casas-Valdez M, Siqueiros-Beltrones D A, et al. Changes in the natural diet of green abalone Haliotis fulgens during the 1997 to 1998 El Niño event in Baja California Sur, Mexico[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2012, 31(3): 795−800. doi: 10.2983/035.031.0325 [34] Serviere-Zaragoza E, Pérez-Estrada C J, Aranda D A. Status of the digestive gland and feed index in juvenile green abalone Haliotis fulgens fed rehydrated macroalgae[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2016, 22(4): 767−775. doi: 10.1111/anu.12295 [35] Tripp-Valdez M A, Harms L, Pörtner H O, et al. De novo transcriptome assembly and gene expression profile of thermally challenged green abalone (Haliotis fulgens: Gastropoda) under acute hypoxia and hypercapnia[J]. Marine Genomics, 2019, 45: 48−56. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2019.01.007 [36] Calderón-Liévanos S, Lluch-Cota S E, Hernández-Saavedra N Y, et al. Responses of the green abalone Haliotis fulgens (Philippi, 1845) to sudden and recurring extreme environmental variations[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 2021, 40(1): 127−136. [37] Vélez-Arellano N, Valenzuela-Quiñonez F, García-Domínguez F A, et al. Long-term analysis on the spawning activity of green (Haliotis fulgens) and pink (Haliotis corrugata) abalone along the central west coast of Baja California[J]. Fisheries Research, 2020, 228: 105588. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105588 [38] Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, et al. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2018, 35(6): 1547−1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096 [39] Donath A, Jühling F, Al-Arab M, et al. Improved annotation of protein-coding genes boundaries in metazoan mitochondrial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(20): 10543−10552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz833 [40] Benson G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, 27(2): 573−580. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.2.573 [41] Greiner S, Lehwark P, Bock R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(W1): W59−W64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz238 [42] Chen Chengjie, Chen Hao, Zhang Yi, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Molecular Plant, 2020, 13(8): 1194−1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 [43] Xu Kefeng, Kanno M, Yu Hong, et al. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Zhikong scallop Chlamys farreri (Bivalvia: Pectinidae)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2011, 38(5): 3067−3074. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-9974-8 [44] Saccone C, De Giorgi C, Gissi C, et al. Evolutionary genomics in Metazoa: the mitochondrial DNA as a model system[J]. Gene, 1999, 238(1): 195−209. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00270-X [45] Perna N T, Kocher T D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1995, 41(3): 353−358. doi: 10.1007/BF01215182 [46] Yu Hong, Li Qi. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of Crassostrea nippona: comparative and phylogenomic studies on seven commercial Crassostrea species[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(2): 999−1009. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0825-z [47] Brown W M. The mitochondrial genome of animals[M]//MacIntyre R J. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. New York: Plenum, 1985: 95−130. [48] 远洋. 九种异齿亚纲贝类线粒体基因组研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013.Yuan Yang. Studies on complete mitochondrial genomes of nine subclass Heterodonta species[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2013. [49] Terrett J A, Miles S, Thomas R H. Complete DNA sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Cepaea nemoralis (Gastropoda: Pulmonata)[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 1996, 42(2): 160−168. doi: 10.1007/BF02198842 [50] Jannotti-Passos L K, Ruiz J C, Caldeira R L, et al. Phylogenetic analysis of Biomphalaria tenagophila (Orbigny, 1835) (Mollusca: Gastropoda)[J]. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 2010, 105(4): 504−511. [51] Crick F H C. Codon-anticodon pairing: the wobble hypothesis[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1966, 19(2): 548−555. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(66)80022-0 [52] Ren Jianfeng, Liu Xiao, Jiang Feng, et al. Unusual conservation of mitochondrial gene order in Crassostreaoysters: evidence for recent speciation in Asia[J]. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 2010, 10: 394. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-394 [53] Ren Jianfeng, Shen Xin, Jiang Feng, et al. The mitochondrial genomes of two scallops, Argopecten irradians and Chlamys farreri (Mollusca: Bivalvia): the most highly rearranged gene order in the family Pectinidae[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 2010, 70(1): 57−68. doi: 10.1007/s00239-009-9308-4 [54] Wolstenholme D R. Animal mitochondrial DNA: structure and evolution[J]. International Review of Cytology, 1992, 141: 173−216. [55] 孟学平, 申欣, 赵娜娜, 等. 漳州西施舌线粒体基因组全序列: 腔蛤蜊属(Coelomactra)存在新种的证据[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(3): 204−214.Meng Xueping, Shen Xin, Zhao Nana, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of Zhangzhou Coelomactra antiquata: the evidence of a new species in genus Coelomactra (Mollusca: Mactridae)[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(3): 204−214. [56] Uda K, Komeda Y, Koyama H, et al. Complete mitochondrial genomes of two Japanese precious corals, Paracorallium japonicum and Corallium konojoi (Cnidaria, Octocorallia, Coralliidae): notable differences in gene arrangement[J]. Gene, 2011, 476(1/2): 27−37. [57] Leigh J, Lang B F. Mitochondrial 3′ tRNA editing in the jakobid Seculamonas ecuadoriensis: a novel mechanism and implications for tRNA processing[J]. RNA, 2004, 10(4): 615−621. doi: 10.1261/rna.5195504 [58] 蒋文枰, 李家乐, 郑润玲, 等. 褶纹冠蚌线粒体基因组全序列分析[J]. 遗传, 2010, 32(2): 153−162. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2010.00153Jiang Wenping, Li Jiale, Zheng Runling, et al. Analysis of complete mitochondrial genome of Cristaria plicata[J]. Hereditas (Beijing), 2010, 32(2): 153−162. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2010.00153 [59] 李云峰, 李梦遥, 王健, 等. 仿刺参线粒体全基因组序列结构及比较研究[J]. 水产科学, 2012, 31(8): 454−462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2012.08.002Li Yunfeng, Li Mengyao, Wang Jian, et al. Comparative structure of complete mitochondrial genome in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J]. Fisheries Science, 2012, 31(8): 454−462. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2012.08.002 [60] Yamazaki N, Ueshima R, Terrett J A, et al. Evolution of pulmonate gastropod mitochondrial genomes: comparisons of gene organizations of Euhadra, Cepaea and Albinaria and implications of unusual tRNA secondary structures[J]. Genetics, 1997, 145(3): 749−758. doi: 10.1093/genetics/145.3.749 [61] Boore J L. Animal mitochondrial genomes[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, 27(8): 1767−1780. doi: 10.1093/nar/27.8.1767 [62] Segovia R, Pett W, Trewick S, et al. Extensive and evolutionarily persistent mitochondrial tRNA editing in velvet worms (phylum onychophora)[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2011, 28(10): 2873−2881. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr113 [63] Hoffmann R J, Boore J L, Brown W M. A novel mitochondrial genome organization for the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis[J]. Genetics, 1992, 131(2): 397−412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.397 [64] Yuan Yang, Li Qi, Kong Lingfeng, et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of the grand jackknife clam, Solen grandis (Bivalvia: Solenidae): a novel gene order and unusual non-coding region[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2012, 39(2): 1287−1292. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0861-8 [65] Milbury C A, Gaffney P M. Complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the eastern oyster Crassostrea virginica[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 2005, 7(6): 697−712. doi: 10.1007/s10126-005-0004-0 [66] La Roche J, Snyder M, Cook D I, et al. Molecular characterization of a repeat element causing large-scale size variation in the mitochondrial DNA of the sea scallop Placopecten magellanicus[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 1990, 7(1): 45−64. [67] Dreyer H, Steiner G. The complete sequences and gene organisation of the mitochondrial genomes of the heterodont bivalves Acanthocardia tuberculata and Hiatella arctica–and the first record for a putative atpase subunit 8 gene in marine bivalves[J]. Frontiers in Zoology, 2006, 3: 13. doi: 10.1186/1742-9994-3-13 [68] 宋文涛, 高祥刚, 李云峰, 等. 双壳贝类线粒体基因组结构的比较[J]. 遗传, 2009, 31(11): 1127−1134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2009.01127Song Wentao, Gao Xianggang, Li Yunfeng, et al. Comparison of mitochondrial genomes of bivalves[J]. Hereditas (Beijing), 2009, 31(11): 1127−1134. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1005.2009.01127 -




 下载:
下载: