Experimental study on settlement of rod coral sand in stagnant water
-
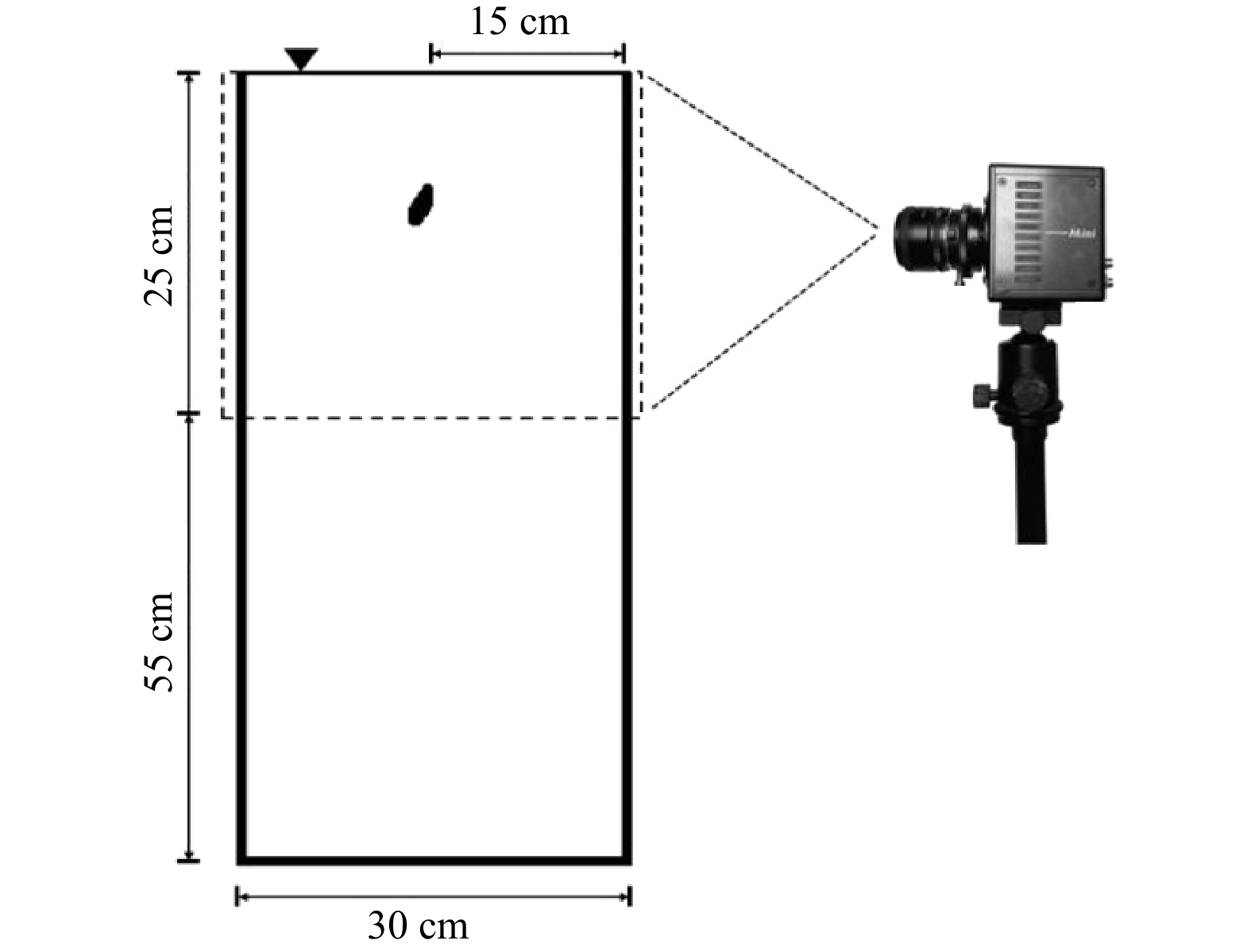
摘要: 沉降速度是珊瑚砂的一个重要物理参数。由于柱状珊瑚砂与其他形状的珊瑚砂有着明显的差异,套用现有珊瑚砂的沉速公式进行计算并不合适。本文选取柱状珊瑚砂进行单颗粒沉降试验,研究静水中柱状珊瑚砂沉降速度及其影响因素,通过讨论分析不同的等效粒径和形状系数对柱状珊瑚砂沉降速度的影响,发现柱状珊瑚砂的沉降速度与等容粒径和Corey形状系数密切相关,基于本文试验数据推求了适用于计算柱状珊瑚砂沉降速度的经验公式,丰富了海岸泥沙理论。Abstract: The settling velocity is an important physical parameter of coral sand. Because of the rod coral sand is obviously different from other shapes of coral sand, it is not suitable to apply the settling velocity formula of the existing coral sand for calculation. The rod coral sand was selected to study the settling velocity and its influencing factors for single particle settlement experiment in stagnant water in this study. By analyzing the effects of different equivalent particle sizes and shape coefficients on the settling velocity of rod coral sand, it is found that the settling velocity of rod coral sand is strongly correlated with the diameter of the volume-equivalent sphere and Corey shape coefficient. Based on the experimental data, an empirical formula suitable for calculating the settling velocity of rod coral sand is deduced, which enriches the theory of coastal sediment.
-
Key words:
- rod coral sand /
- settling velocity /
- drag coefficient /
- shape coefficient
-
表 1 不同等效粒径和形状系数方案设计
Tab. 1 Programmes of different equivalent particle sizes and shape coefficients
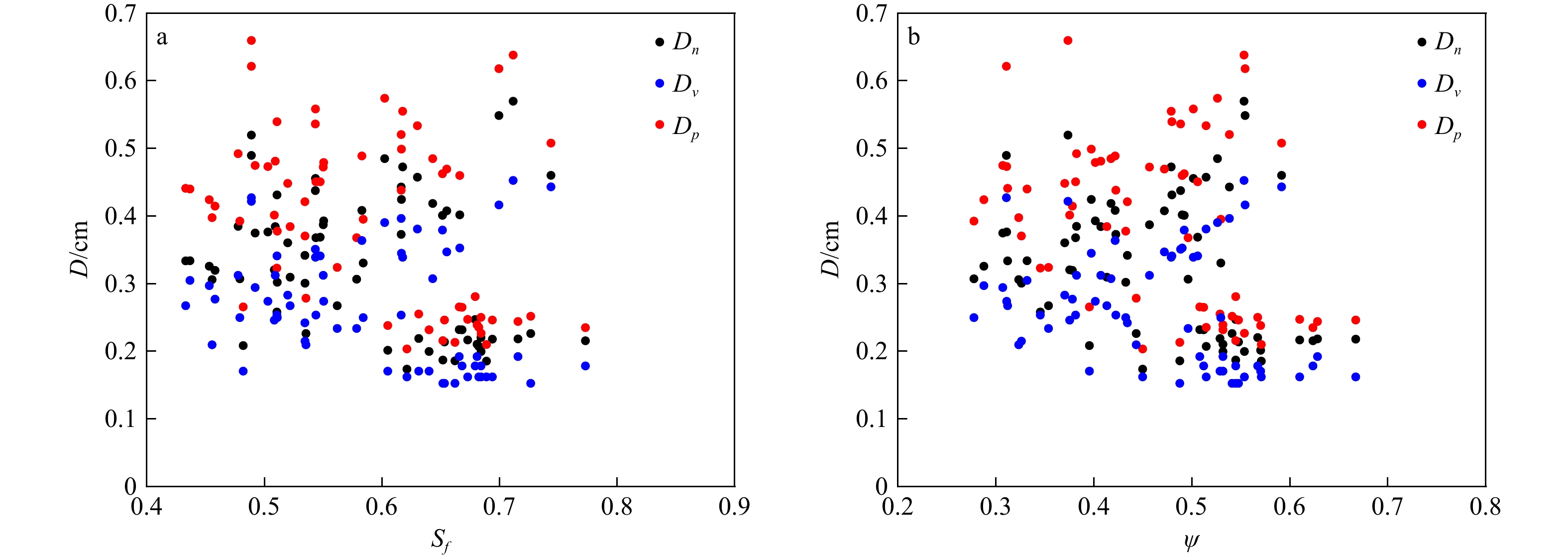
组次 等效粒径 形状系数 1 轴平均粒径 Corey形状系数 2 轴平均粒径 Wang形状系数 3 等容粒径 Corey形状系数 4 等容粒径 Wang形状系数 5 投影粒径 Corey形状系数 6 投影粒径 Wang形状系数 表 2 Corey形状系数离散程度
Tab. 2 Dispersions of Corey shape coefficient
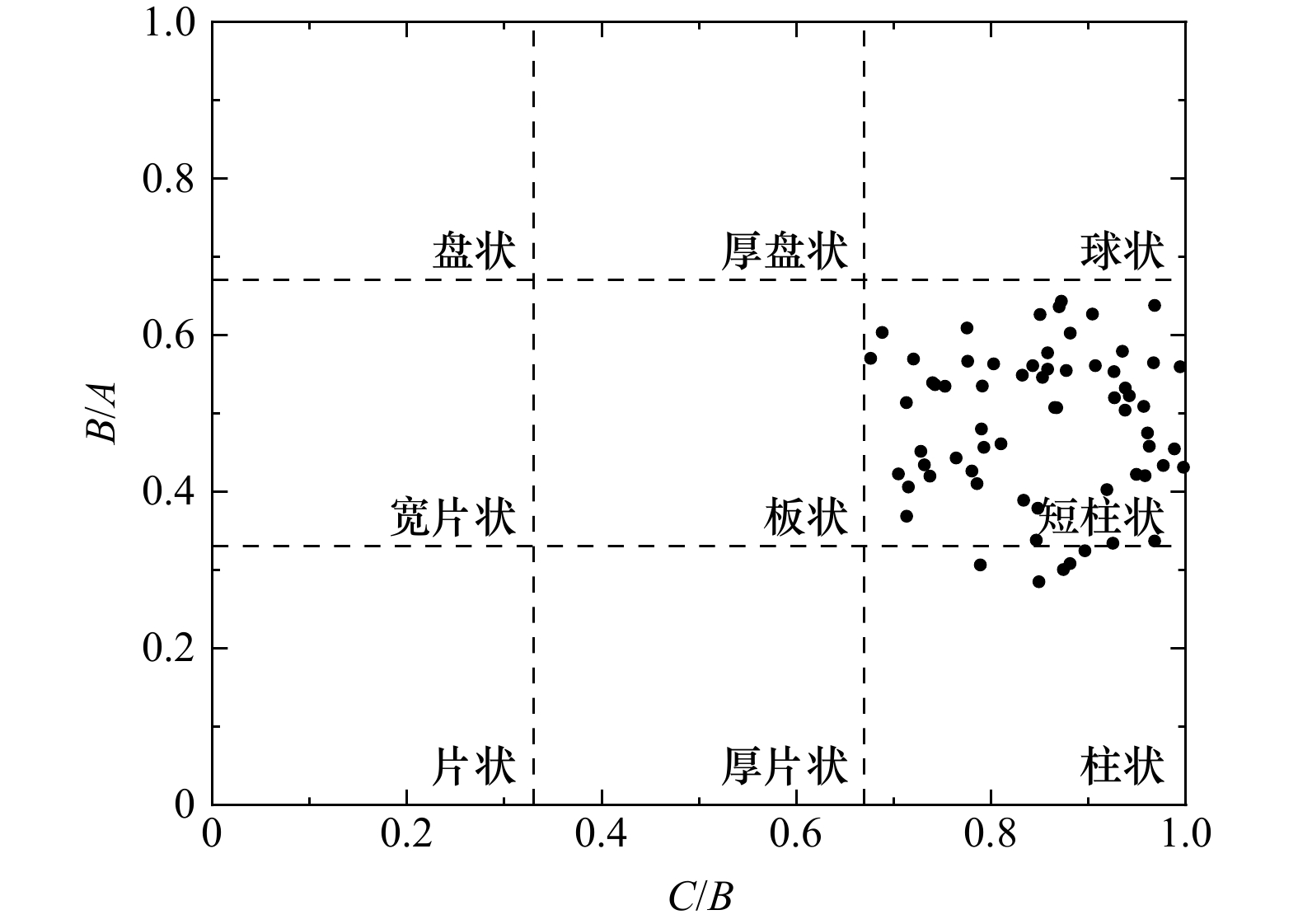
粒径大小 Dn<0.20 Dn <0.25 Dn <0.30 Dn <0.35 第25百分位数 0.635 0.637 0.623 0.511 第75百分位数 0.685 0.685 0.684 0.680 四分位差 0.050 0.048 0.059 0.169 注:Dn单位:cm。 表 3 不同形状系数与沉降速度相关系数
Tab. 3 Correlation coefficients of shape coefficients and settling velocitys
形状系数 粗颗粒沉降速度/(cm·s−1) 细颗粒沉降速度/(cm·s−1) Corey形状系数 0.634 0.277 Wang形状系数 0.562 0.238 表 4 柱状珊瑚砂不同等效粒径和形状参数拟合公式对照
Tab. 4 Comparison of fitting formulas for rod coral sand with different equivalent particle sizes and shape coefficients
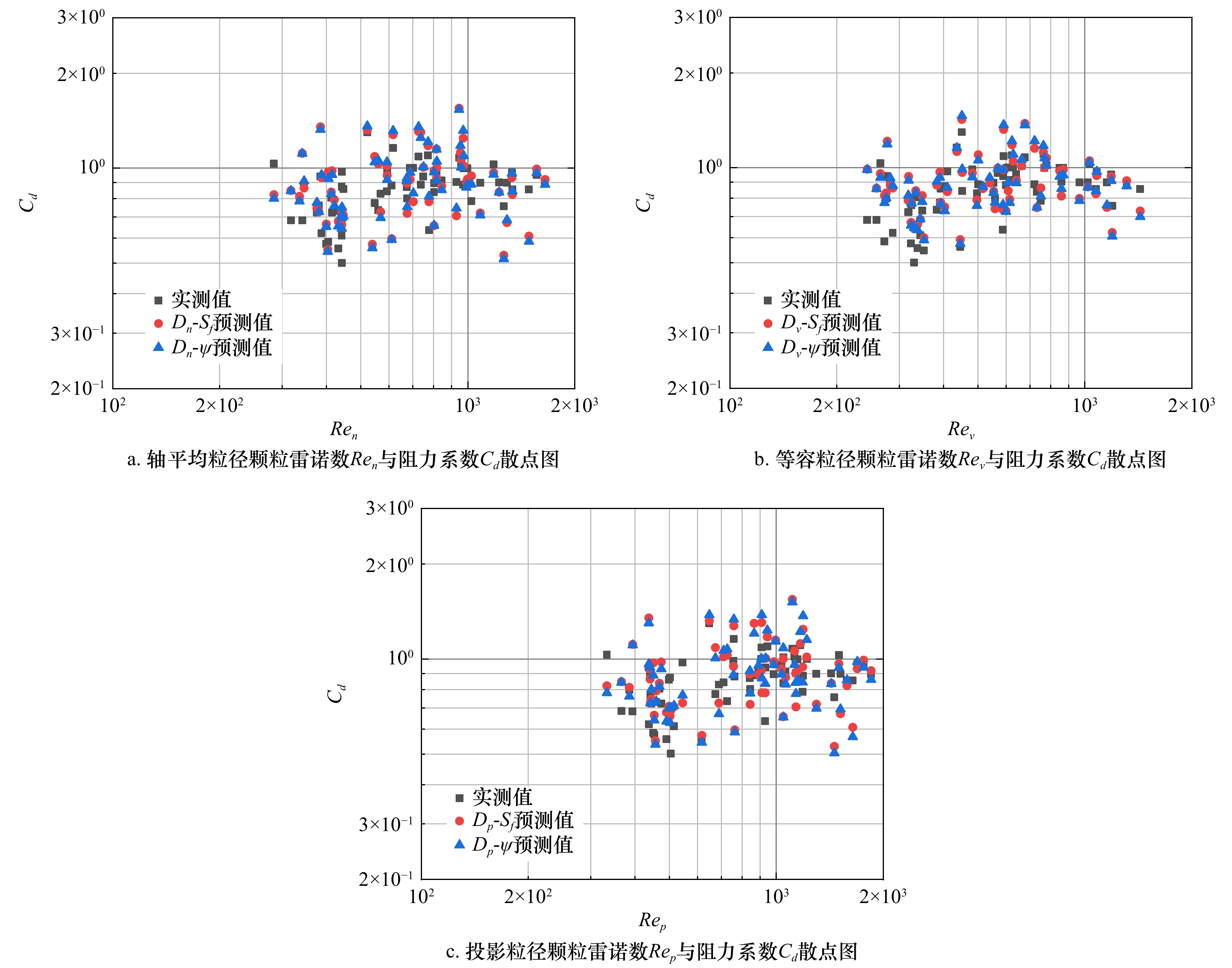
组次 V/A拟合公式 R2 沉降速度拟合公式 1 ${\dfrac{V}{ { {A_p} } } = 0.381S_{ f}^{0.434}{D_n} }$ 0.735 ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.762\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.434}{D_n} }$ 2 $ {\dfrac{V}{{{A_p}}} = 0.366{\psi ^{0.243}}{D_n}} $ 0.726 $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.732\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.243}}{D_n}} $ 3 ${\dfrac{V}{ { {A_p} } } = 0.473S_{ f}^{0.428}{D_v} }$ 0.897 ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.946\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.428}{D_v} }$ 4 $ {\dfrac{V}{{{A_p}}} = 0.452{\psi ^{0.234}}{D_v}} $ 0.886 $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.904\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.234}}{D_v}} $ 5 ${\dfrac{V}{ { {A_p} } } = 0.380S_{ f}^{0.765}{D_p} }$ 0.735 ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.760\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.765}{D_p} }$ 6 $ {\dfrac{V}{{{A_p}}} = 0.355{\psi ^{0.435}}{D_p}} $ 0.708 $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.710\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.435}}{D_p}} $ 表 5 不同等效粒径和形状参数拟合公式对照
Tab. 5 Comparison of fitting formulas for rod coral sand with different equivalent particle sizes and shape coefficients
组次 阻力系数Cd拟合公式 沉降速度ω拟合公式 1 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 403 \nu }}{{D_n^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 3.34} \right)^{ - 4.58}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 205 \nu }}{{D_n^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.13} \right)^{0.405}}} $ ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.762\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.434}{D_n} }$ 2 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 725 \nu }}{{D_n^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 4.82} \right)^{ - 2.77}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 226 \nu }}{{D_n^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.14} \right)^{0.416}}} $ $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.732\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.243}}{D_n}} $ 3 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 108 \nu }}{{D_v^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 2.39} \right)^{ - 11.60}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 74.5 \nu }}{{D_v^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.03} \right)^{0.601}}} $ ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.946\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.428}{D_v} }$ 4 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 172 \nu }}{{D_v^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 2.95} \right)^{ - 13.50}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 95.3 \nu }}{{D_v^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.05} \right)^{0.486}}} $ $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.904\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.234}}{D_v}} $ 5 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 210 \nu }}{{D_p^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 2.00} \right)^{ - 15.70}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 182 \nu }}{{D_p^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.09} \right)^{0.533}}} $ ${ {\omega ^2} = 0.760\dfrac{ {\left( { {\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g} }{ {\rho {C_d} } }S_{ f}^{0.765}{D_p} }$ 6 $ {{C_d} = {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 778 \nu }}{{D_p^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 4.57} \right)^{ - 14.12}} + {\left( {\dfrac{{ - 249 \nu }}{{D_p^{1.5} \times {g^{0.5}}}} + 1.14} \right)^{0.436}}} $ $ {{\omega ^2} = 0.710\dfrac{{\left( {{\rho _s} - \rho } \right)g}}{{\rho {C_d}}}{\psi ^{0.435}}{D_p}} $ 表 6 沉降速度计算误差表
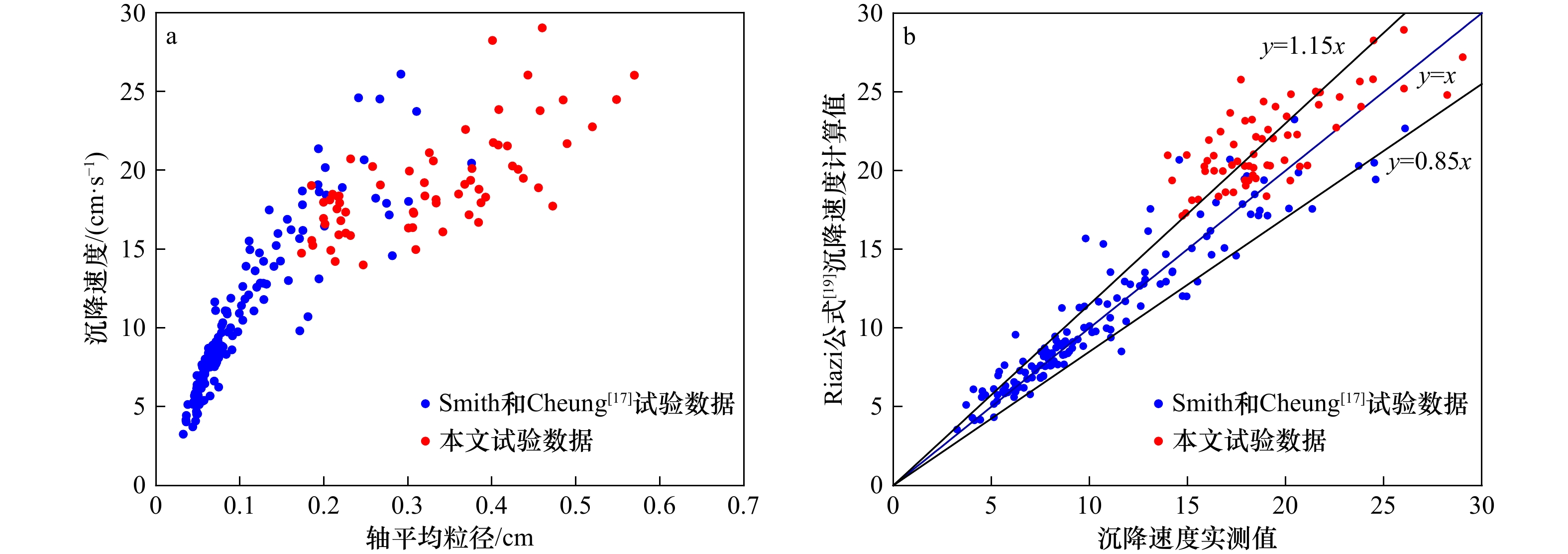
Tab. 6 Calculation error of the settling velocity
Eave RMSE Wang公式[18] 0.1346 3.1869 本文公式训练组 0.0714 1.7608 本文公式验证组 0.1191 2.6018 -
[1] 孙宗勋. 南沙群岛珊瑚砂工程性质研究[J]. 热带海洋, 2000, 19(2): 1−8.Sun Zongxun. Engineering properties of coral sands in Nansha Islands[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2000, 19(2): 1−8. [2] 沈扬, 冯照雁, 邓珏, 等. 南海珊瑚砂地基承载力模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(5): 1281−1290. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1316Shen Yang, Feng Zhaoyan, Deng Jue, et al. Model test on bearing capacity of coral sand foundation in the South China Sea[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(5): 1281−1290. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1316 [3] Yang Yongkang, Yang Wu, Feng Chunyan. Experimental research on geotechnical engineering characteristics of coral reef in Xisha Islands[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 783(1): 012052. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/783/1/012052 [4] Ye Jianhong, Shan Jipeng, Zhou Haoran, et al. Numerical modelling of the wave interaction with revetment breakwater built on reclaimed coral reef islands in the South China Sea—Experimental verification[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 235: 109325. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.109325 [5] Lokier S W, Fiorini F. Temporal evolution of a carbonate coastal system, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates[J]. Marine Geology, 2016, 381: 102−113. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2016.09.001 [6] Milliman J D, Müller G, Förstner F. Recent Sedimentary Carbonates: Part 1 Marine Carbonates[M]. New York: Springer, 2012: 4. [7] Wang Xing, Wu Yang, Cui Jie, et al. Shape characteristics of coral sand from the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(10): 803. doi: 10.3390/jmse8100803 [8] 王新志. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁工程地质特性及大型工程建设可行性研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院岩土力学研究所, 2008: 82.Wang Xinzhi. Study on engineering geological properties of coral reefs and feasibility of large project construction on Nansha Islands[D]. Wuhan: Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008: 82. [9] Wu Xuehui, Cai Yuanqiang, Xu Sifa, et al. Effects of size and shape on the crushing strength of coral sand particles under diametral compression test[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(2): 1829−1839. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01972-y [10] Lade P V, Liggio C D Jr, Nam J. Strain rate, creep, and stress drop-creep experiments on crushed coral sand[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2009, 135(7): 941−953. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000067 [11] 李小梅, 王芳, 韩林, 等. 珊瑚砂蠕变特性的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(11): 2124−2130.Li Xiaomei, Wang Fang, Han Lin, et al. Experimental study on creep properties of coral sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(11): 2124−2130. [12] 薛鹏, 周先齐, 蔡燕燕, 等. 饱和珊瑚砂三轴蠕变特性及经验模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(S2): 255−260.Xue Peng, Zhou Xianqi, Cai Yanyan, et al. Triaxial creep characteristics and empirical model for saturated coral sand[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(S2): 255−260. [13] 吕亚茹, 王冲, 黄厚旭, 等. 珊瑚砂细观颗粒结构及破碎特性研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2021, 42(2): 352−360. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0938Lü Yaru, Wang Chong, Huang Houxu, et al. Study on particle structure and crushing behaviors of coral sand[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(2): 352−360. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0938 [14] 孙越, 肖杨, 周伟, 等. 钙质砂和石英砂压缩下的颗粒破碎与形状演化[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(6): 1061−1068.Sun Yue, Xiao Yang, Zhou Wei, et al. Particle breakage and shape evolution of calcareous and quartz sands under compression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 1061−1068. [15] Bian C, Chen J, Jiang C B, et al. Threshold of motion of coral sediment under currents in flume experiments[J/OL]. Sedimentology, (2023-01-28). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/sed.13082. [16] Chen J, Yao Z, Jiang C B, et al. Experiment study of the evolution of coral sand particle clouds in water[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2022, 36(5): 720−733. doi: 10.1007/s13344-022-0064-1 [17] Smith D A, Cheung K F. Settling characteristics of calcareous sand[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 479−483. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:6(479) [18] Wang Yin, Zhou Lingxin, Wu Ye, et al. New simple correlation formula for the drag coefficient of calcareous sand particles of highly irregular shape[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 326: 379−392. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.12.004 [19] Riazi A, Vila-Concejo A, Salles T, et al. Improved drag coefficient and settling velocity for carbonate sands[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 9465. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65741-3 [20] Li Yanan, Yu Qian, Gao Shu, et al. Settling velocity and drag coefficient of platy shell fragments[J]. Sedimentology, 2020, 67(4): 2095−2110. doi: 10.1111/sed.12696 [21] 金智涛, 郑建国, 张君, 等. 颗粒形状对珊瑚砂和石英砂沉降影响的试验研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2021, 40(4): 447−454.Jin Zhitao, Zheng Jianguo, Zhang Jun, et al. Experimental study on the influence of particle shape on the settlement of coral sand and quartz sand[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2021, 40(4): 447−454. [22] Stokes G G. On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums[J]. Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 1901, 9: 1−141. [23] Dyer K R. Coastal and Estuarine Sediment Dynamics[M]. Chichester: Wiley, 1986: 358. [24] Dietrich W E. Settling velocity of natural particles[J]. Water Resources Research, 1982, 18(6): 1615−1626. doi: 10.1029/WR018i006p01615 [25] Wu Weiming, Wang S S Y. Formulas for sediment porosity and settling velocity[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2006, 132(8): 858−862. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2006)132:8(858) [26] 李大鸣, 吕小海, 焦润红. 泥沙静水沉降阻力系数[J]. 水利学报, 2004(1): 1−5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.01.001Li Daming, Lü Xiaohai, Jiao Runhong. Resistance coefficient of sediment deposition in still water[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004(1): 1−5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.01.001 [27] Maiklem W R. Some hydraulic properties of bioclastic carbonate grains[J]. Sedimentology, 1968, 10(2): 101−109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1968.tb01102.x [28] Corey A T. Influence of shape on the fall velocity of sand grains[D]. Colorado: Colorado State University, 1949: 29. [29] Zingg T. Beitrag zur schotteranalyse[D]. Zurich: Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, 1935: 124. [30] Kim D, Son Y, Park J. Prediction of settling velocity of nonspherical soil particles using digital image processing[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2018: 4647675. -




 下载:
下载: