Geochemistry and source of platinum group elements in cobalt-rich crusts from Caiwei Seamounts in the western Pacific
-
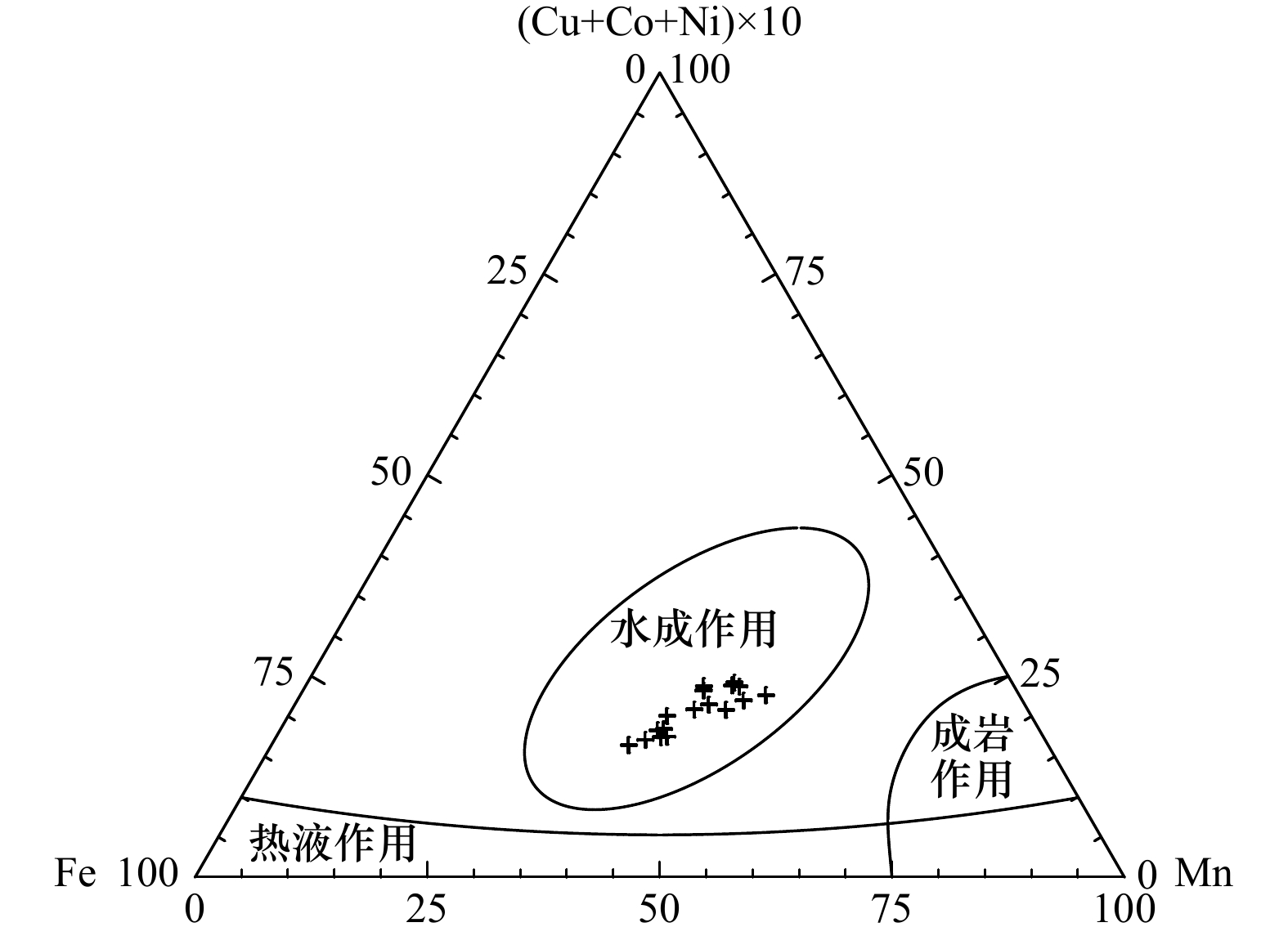
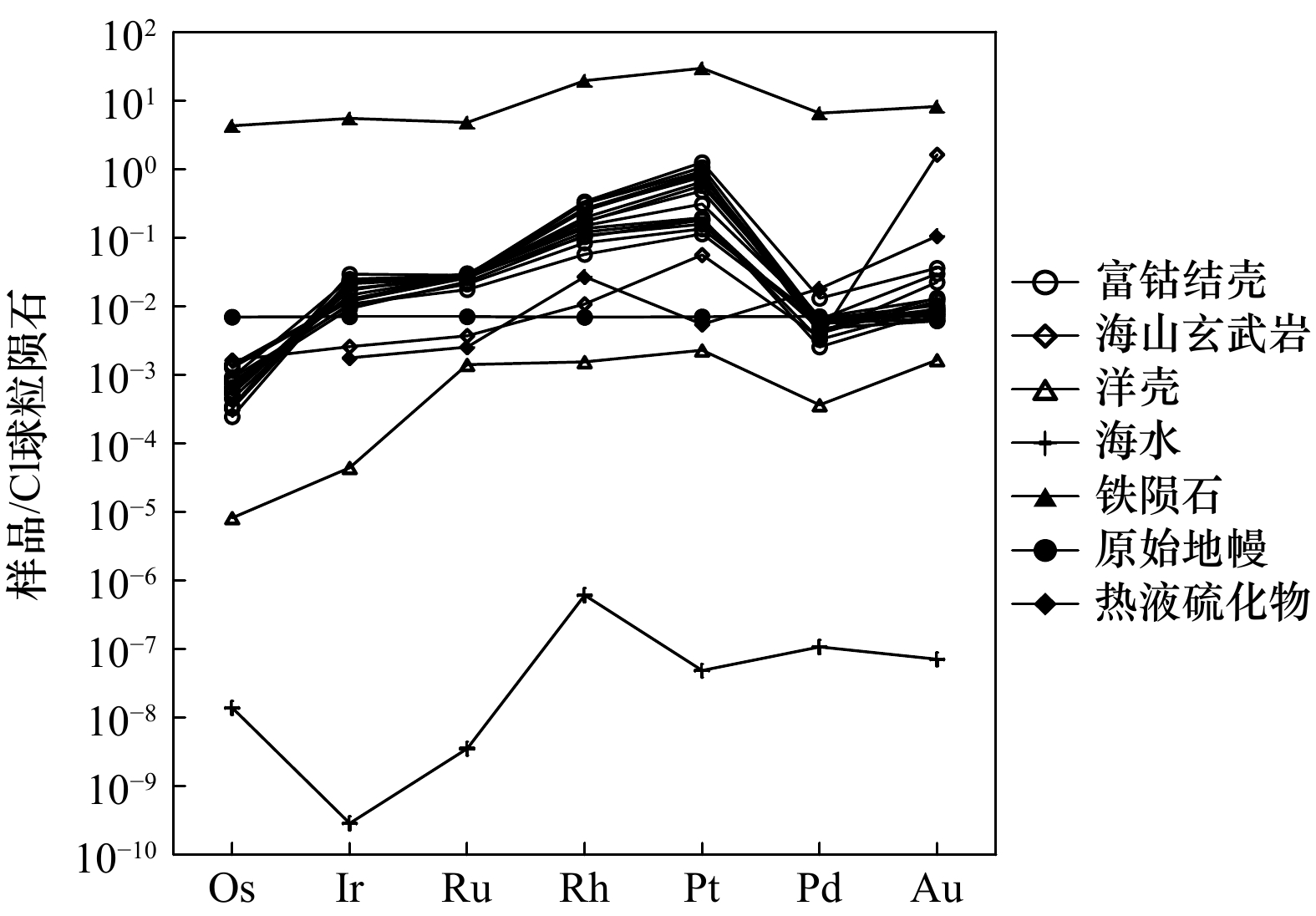
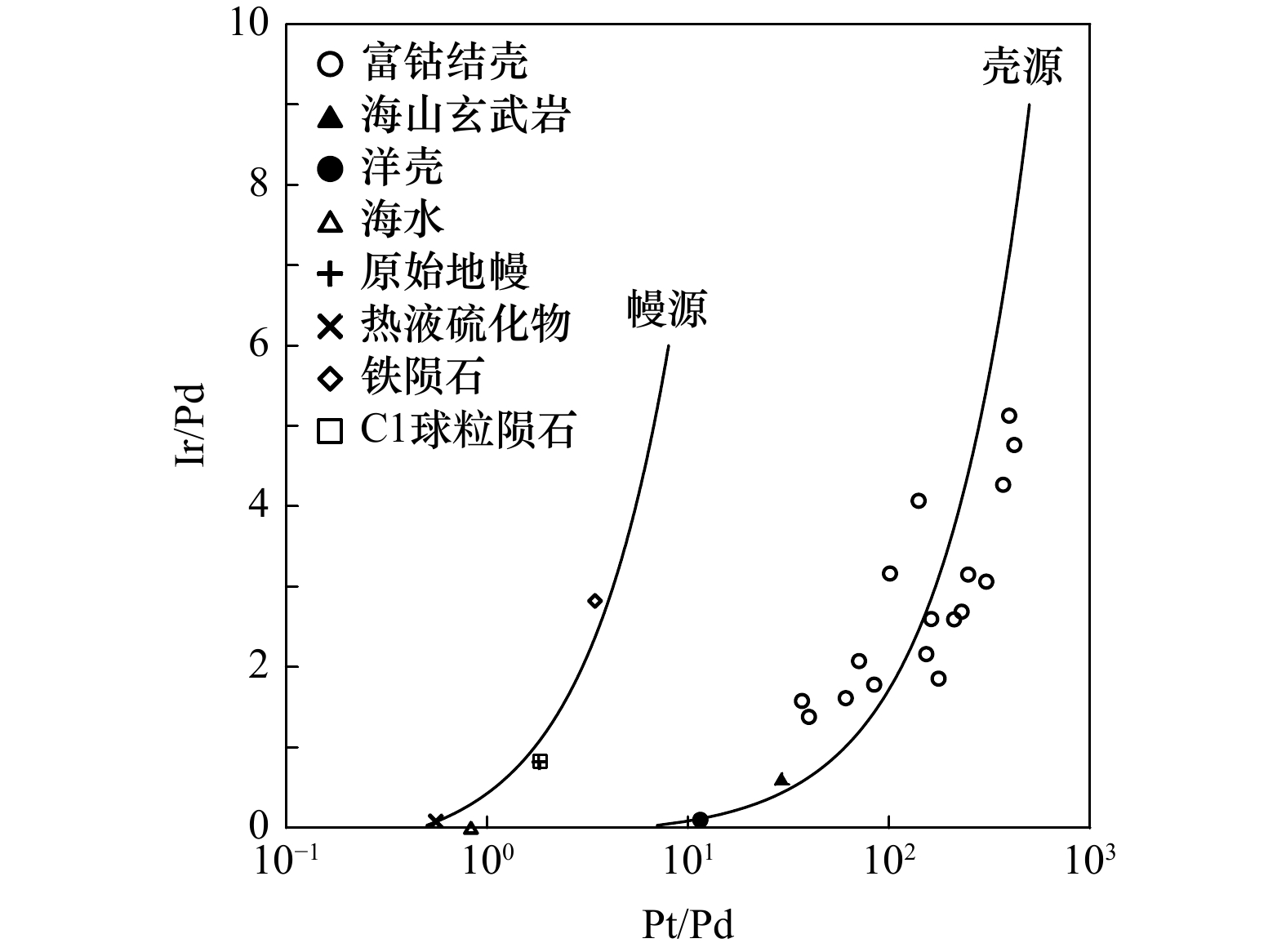
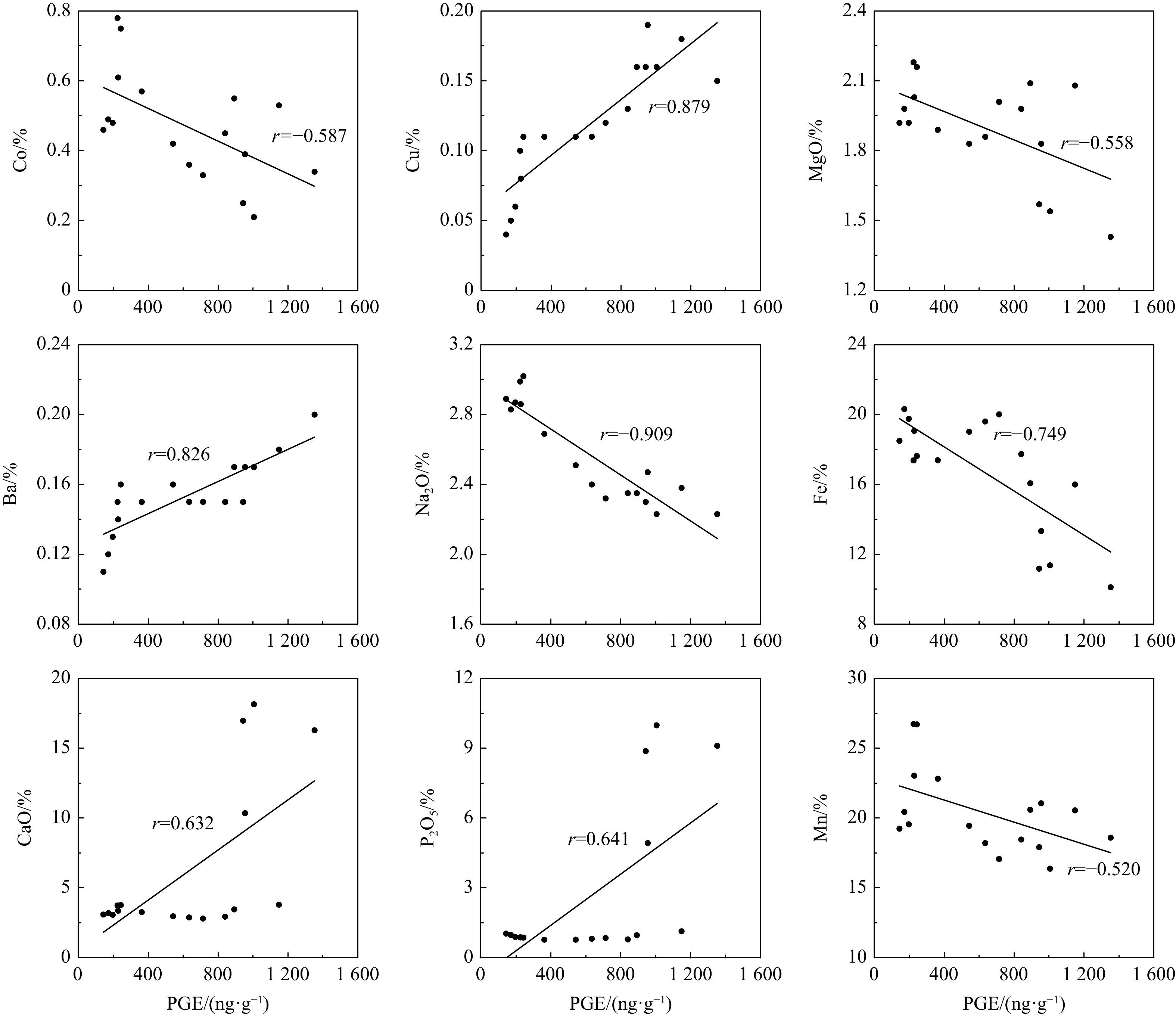
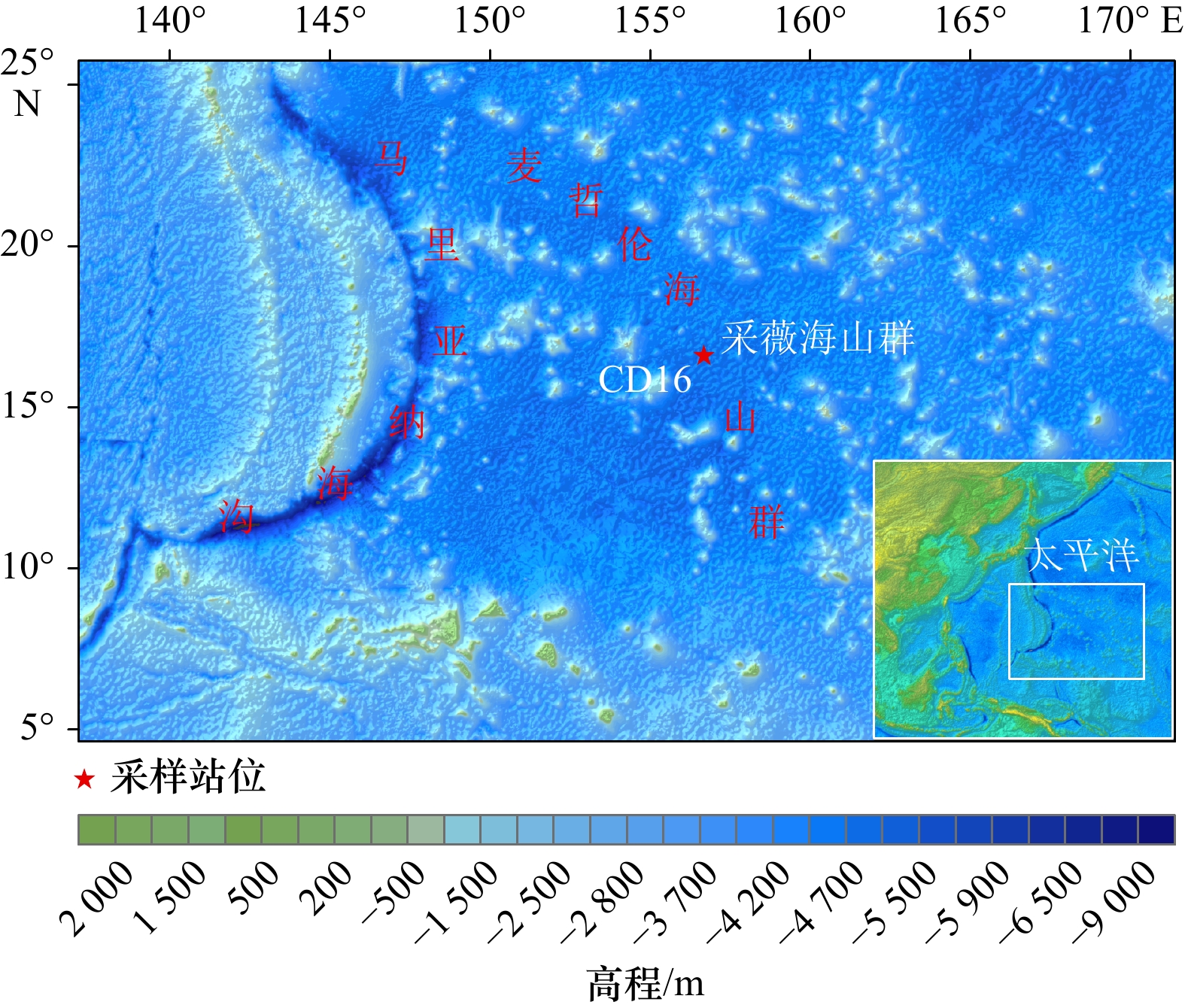
摘要: 为探讨富钴结壳铂族元素的来源,以西太平洋采薇海山群富钴结壳样品为研究对象,利用X射线衍射法、等离子体发射光谱法和质谱法,对富钴结壳样品进行了矿物组成、主量元素和铂族元素含量分析。研究表明,富钴结壳的主要结晶矿物为水羟锰矿,次要矿物有石英、斜长石、钾长石和碳氟磷灰石,同时含有大量非晶态铁氧/氢氧化物。富钴结壳中Mn和Fe含量最高,且明显富集铂族元素,铂族总量为142~1 352 ng/g,其中Pt为114~1 268 ng/g,占铂族总量的80%以上。老壳层的铂族元素含量高于新壳层,老壳层发生了磷酸盐化作用。富钴结壳的铂族元素之间发生了分异作用,Pd组(PPGE)含量高于Ir组(IPGE)。铂族元素配分模式显示Pt正异常和Pd负异常,具有Pt富集而Pd亏损特征,推测富钴结壳的铂族元素来源于洋壳蚀变过程中海山玄武岩和海水之间的水−岩反应。富钴结壳的铂族元素与CaO、P2O5、Ba和Cu正相关,推测铂族元素赋存于磷酸盐矿物相中。富钴结壳生长剖面从上到下,由新到老,铂族元素含量呈逐渐增加趋势,海水氧化性环境和高海洋生产力可增进磷酸盐化作用,从而进一步促进了铂族元素的富集。该研究对于揭示富钴结壳铂族元素的来源具有一定的参考价值。Abstract: To explore the source of platinum group elements (PGE) in cobalt-rich crusts, the samples from Caiwei Seamounts in western Pacific were chosen as the research object, for which XRD, ICP-OES and ICP-MS were used to analyze the mineral composition, major elements contents and PGE contents in cobalt-rich crusts. The results showed that, the main crystalline minerals were vernadites in cobalt-rich crusts, and the minor minerals included quartz, plagioclase, potassium feldspar and carbon fluoride apatite. Also many amorphous ferric minerals were contained in cobalt-rich crusts. In addition, Mn and Fe contents were the highest in cobalt-rich crusts, and PGE were enriched in cobalt-rich crusts. PGE contents were 142−1352 ng/g, and Pt contents were 114−1268 ng/g, in which Pt accounted for more than 80%. PGE contents in the old layers were higher than that in the new layers. And the phosphatization appeared in the old crust layers. Moreover, there was an obvious contrast in PGE of cobalt-rich crusts, Pd group (PPGE) contents were more than Ir group (IPGE). PGE diagrams showed the positive Pt anomalies and negative Pd anomalies. And Pt was enriched and Pd was poor in cobalt-rich crusts. Meanwhile, PGE in cobalt-rich crusts were probably derived from the reaction between seamount basalt and seawater during the oceanic shell erosion process. PGE had positive correlation with CaO, P2O5, Ba and Cu, so PGE were probably enriched in the phosphate phase. In addition, the growth profile of cobalt-rich crust was from top to bottom and from new to old, PGE contents increased gradually. Therefore, oxidative marine environment and high marine productivity had a positive impact on phosphatization, which further promoted the enrichment of PGE. This study provided a certain reference value for revealing the source of PGE in cobalt-rich crusts.
-
Key words:
- the western Pacific /
- Caiwei Seamounts /
- cobalt-rich crusts /
- platinum group elements /
- geochemistry /
- source
-
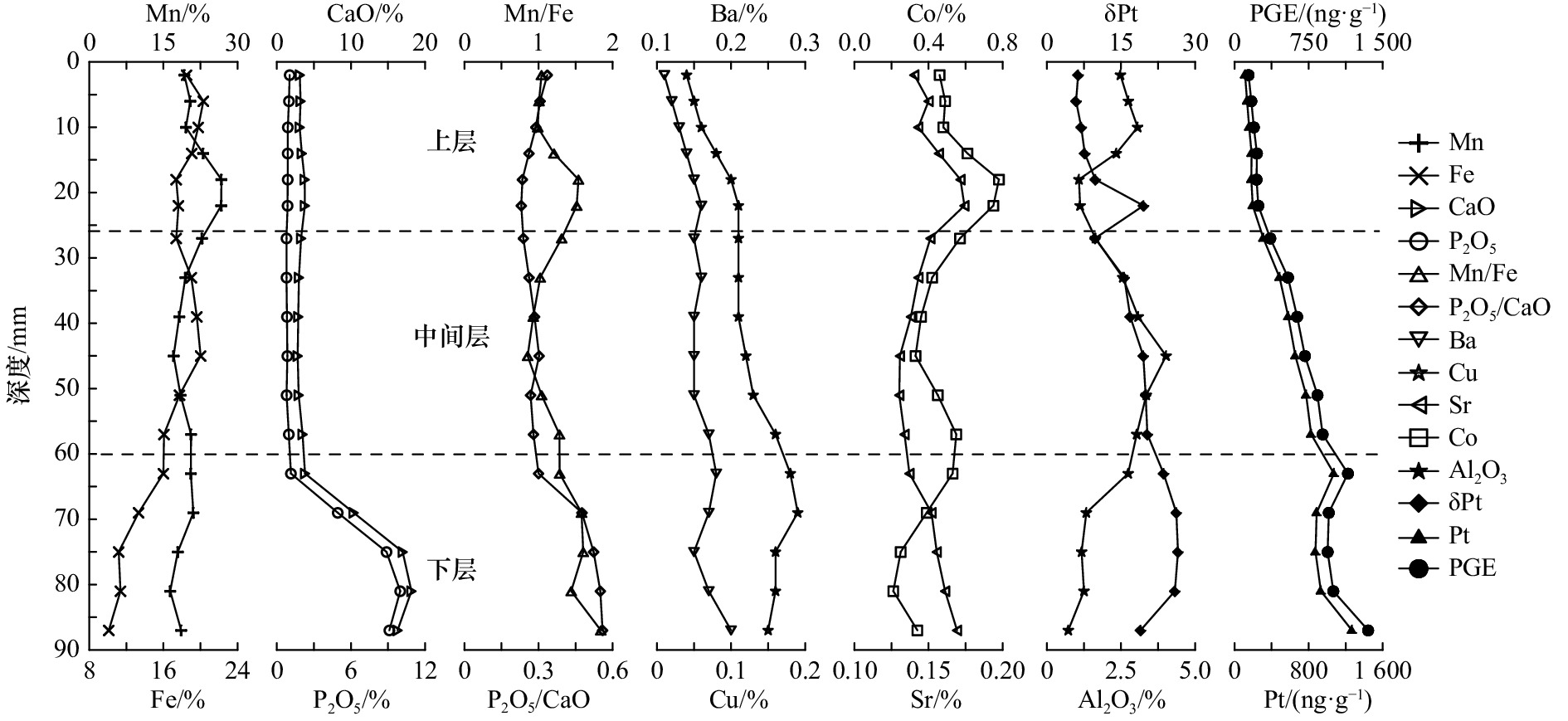
表 1 富钴结壳CD16样品描述
Tab. 1 The description of cobalt-rich crusts CD16
样品号 构造层 深度/mm 样品描述 CD16(1) 较致密层 0~4 表面有葡萄体状突起,树丛顶部 CD16(2) 4~8 树丛状构造,黑褐色 CD16(3) 8~12 树丛状构造,黑褐色 CD16(4) 12~16 树丛状构造,黑褐色 CD16(5) 16~20 柱状构造,黑色 CD16(6) 20~24 柱状构造,黑色 CD16(7) 疏松层 24~30 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(8) 30~36 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(9) 36~42 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(10) 42~48 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(11) 48~54 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(12) 54~60 树枝状构造,黄褐色,较多黏土杂质 CD16(13) 致密层 60~66 斑杂状构造,黑色,有磷酸盐脉 CD16(14) 66~72 柱状构造,黑色,有磷酸盐脉 CD16(15) 72~78 柱状构造,黑色,有磷酸盐脉 CD16(16) 78~84 柱状构造,黑色,有磷酸盐脉 CD16(17) 84~90 层纹状构造,黑色,较多磷酸盐脉 表 2 富钴结壳样品中常量元素含量
Tab. 2 Major elements contents of cobalt-rich crusts
样品号 Mn/% Fe/% CaO/% P2O5/% Al2O3/% Na2O/% K2O/% MgO/% TiO2/% Co/% Cu/% Ni/% Ba/% Sr/% Mn/Fe CaO/P2O5 CD16(1) 19.25 18.50 3.10 1.04 2.48 2.89 0.66 1.92 1.33 0.46 0.04 0.30 0.11 0.14 1.04 2.98 CD16(2) 20.45 20.32 3.20 0.98 2.75 2.83 0.73 1.98 1.44 0.49 0.05 0.32 0.12 0.15 1.01 3.27 CD16(3) 19.56 19.76 3.08 0.89 3.06 2.87 0.77 1.92 1.47 0.48 0.06 0.34 0.13 0.14 0.99 3.46 CD16(4) 23.04 19.07 3.37 0.88 2.34 2.86 0.70 2.03 1.59 0.61 0.08 0.42 0.14 0.16 1.21 3.83 CD16(5) 26.74 17.38 3.75 0.88 1.08 2.99 0.60 2.18 1.84 0.78 0.10 0.53 0.15 0.17 1.54 4.26 CD16(6) 26.71 17.63 3.78 0.87 1.12 3.02 0.62 2.16 2.07 0.75 0.11 0.53 0.16 0.17 1.52 4.34 CD16(7) 22.82 17.39 3.27 0.78 1.64 2.69 0.65 1.89 2.08 0.57 0.11 0.42 0.15 0.15 1.31 4.19 CD16(8) 19.45 19.02 2.98 0.78 2.56 2.51 0.75 1.83 2.08 0.42 0.11 0.34 0.16 0.14 1.02 3.82 CD16(9) 18.21 19.61 2.89 0.82 3.08 2.40 0.83 1.86 1.97 0.36 0.11 0.31 0.15 0.14 0.93 3.52 CD16(10) 17.08 20.02 2.81 0.85 4.02 2.32 0.99 2.01 1.83 0.33 0.12 0.28 0.15 0.13 0.85 3.31 CD16(11) 18.47 17.74 2.95 0.79 3.35 2.35 0.91 1.98 1.88 0.45 0.13 0.33 0.15 0.13 1.04 3.73 CD16(12) 20.60 16.07 3.47 0.97 3.03 2.35 0.93 2.09 2.21 0.55 0.16 0.40 0.17 0.13 1.28 3.58 CD16(13) 20.56 16.00 3.80 1.14 2.74 2.38 0.90 2.08 2.15 0.53 0.18 0.43 0.18 0.14 1.28 3.33 CD16(14) 21.07 13.33 10.36 4.93 1.33 2.47 0.57 1.83 1.64 0.39 0.19 0.49 0.17 0.15 1.58 2.10 CD16(15) 17.92 11.18 16.98 8.88 1.17 2.30 0.50 1.57 1.31 0.25 0.16 0.41 0.15 0.16 1.60 1.91 CD16(16) 16.38 11.37 18.16 9.99 1.25 2.23 0.47 1.54 1.30 0.21 0.16 0.36 0.17 0.16 1.44 1.82 CD16(17) 18.60 10.11 16.29 9.11 0.72 2.23 0.48 1.43 1.62 0.34 0.15 0.35 0.20 0.17 1.84 1.79 最小值 16.38 10.11 2.81 0.78 0.72 2.23 0.47 1.43 1.30 0.21 0.04 0.28 0.11 0.13 0.85 1.79 最大值 26.74 20.32 18.16 9.99 4.02 3.02 0.99 2.18 2.21 0.78 0.19 0.53 0.20 0.17 1.84 4.34 平均值 20.41 16.74 6.13 2.62 2.22 2.57 0.71 1.90 1.75 0.47 0.12 0.39 0.15 0.15 1.26 3.25 表 3 富钴结壳样品中铂族元素含量
Tab. 3 Platinum group elements (PGE) contents in cobalt-rich crusts
样品号 Os/
(ng·g−1)Ir/
(ng·g−1)Ru/
(ng·g−1)Rh/
(ng·g−1)Pt/
(ng·g−1)Pd/
(ng·g−1)PGE/
(ng·g−1)PPGE/
(ng·g−1)IPGE/
(ng·g−1)PPGE/
IPGEPt/Pd Pt/Ir Pd/Ir δPt δPd CD16(1) 0.39 4.90 12.4 7.40 114 3.10 142 126 17.7 7.11 36.9 23.3 0.63 6.32 0.21 CD16(2) 0.44 4.70 15.0 10.9 136 3.40 170 151 20.1 7.51 39.9 28.9 0.72 5.91 0.19 CD16(3) 0.37 4.20 16.2 14.0 158 2.60 196 176 20.8 8.47 60.9 37.7 0.62 6.95 0.15 CD16(4) 0.62 5.40 18.4 15.6 184 2.60 227 203 24.4 8.33 70.9 34.1 0.48 7.66 0.14 CD16(5) 0.69 5.70 19.7 13.4 182 1.80 223 198 26.1 7.61 101 31.9 0.32 9.81 0.08 CD16(6) 0.65 5.70 20.1 17.7 197 1.40 242 217 26.5 8.20 140 34.5 0.25 10.5 0.06 CD16(7) 0.32 6.60 19.9 19.5 312 3.70 362 336 26.8 12.5 84.4 47.3 0.56 9.73 0.13 CD16(8) 0.28 7.80 21.3 22.6 487 3.00 542 513 29.4 17.5 162 62.4 0.38 15.6 0.08 CD16(9) 0.26 8.20 18.8 21.9 581 3.79 634 608 27.2 22.3 153 70.8 0.46 16.9 0.08 CD16(10) 0.22 8.10 18.8 25.5 657 3.12 713 687 27.1 25.4 211 81.2 0.39 19.5 0.08 CD16(11) 0.27 9.84 19.5 33.7 774 3.12 840 812 29.6 27.4 248 78.6 0.32 20.0 0.07 CD16(12) 0.16 9.69 18.4 32.3 828 3.60 892 865 28.2 30.6 230 85.4 0.37 20.3 0.07 CD16(13) 0.16 10.79 19.2 41.1 1073 3.52 1148 1122 30.2 37.2 305 99.5 0.33 23.6 0.04 CD16(14) 0.16 10.25 20.8 33.5 887 2.40 954 925 31.3 29.6 370 86.5 0.23 26.2 0.04 CD16(15) 0.45 11.33 19.8 34.5 875 2.21 943 913 31.6 28.9 396 77.2 0.19 26.5 0.04 CD16(16) 0.12 10.58 18.9 40.9 932 2.22 1005 979 29.6 33.1 420 88.1 0.21 25.9 0.03 CD16(17) 0.17 13.36 20.0 43.6 1268 7.19 1352 1324 33.5 39.5 176 94.9 0.54 19.0 0.06 最小值 0.12 4.20 12.4 7.40 114 1.40 142 126 17.7 7.11 36.9 23.3 0.19 5.91 0.03 最大值 0.69 13.4 21.3 43.6 1268 7.19 1352 1324 33.5 39.5 420 99.5 0.72 26.5 0.21 平均值 0.34 8.07 18.7 25.2 567 3.10 623 597 27.1 20.7 189 62.5 0.41 15.9 0.09 注:Pd组(PPGE)=Rh+Pt+Pd+Au,Ir组(IPGE)=Os+Ir+Ru,δPt=$ {{{\rm{Pt}}}_{{\rm{N}}}} $/$ {\sqrt{{{\rm{Rh}}}_{{\rm{N}}}\cdot{{\rm{Pd}}}_{{\rm{N}}}} }$,δPd=$ {{{\rm{Pd}}}_{{\rm{N}}}} $/$ {\sqrt{{\rm{Pt}}_{{\rm{N}}}\cdot{\rm{Au}}_{{\rm{N}}}} }$,RhN、PtN、PdN、AuN均为C1球粒陨石标准化值;C1球粒陨石数据引自文献[29]。 表 4 富钴结壳与其他地质体铂族元素富集倍数
Tab. 4 The enrichment factors of platinum group elements (PGE) in cobalt-rich crusts and other geological bodies
富集倍数 Os Ir Ru Rh Pt Pd PGE 富钴结壳 0.34 8.07 18.7 25.2 567 3.10 1.77 洋壳 0.004 0.02 1.0 0.2 2.3 0.2 3.72 地壳 1 1 1 1 5 10 19 海山玄武岩 0.8 1.17 2.63 1.4 56.41 1.92 64.33 海水 6.8 0.1 2.5 79 49 59 196 热液硫化物 − 0.8 1.8 3.5 5.5 9.9 22 原始地幔 3.4 3.2 5 0.9 7.1 3.9 24 f(洋壳) 84 403 19 126 247 16 167 f(地壳) 0.3 8.1 19 25 113 0.31 33 f(海山玄武岩) 0.4 6.9 7.1 18 10 1.6 9.7 f(海水) 0.05 81 7.5 0.32 12 0.05 3.2 f(热液硫化物) − 10.1 10 7.2 103 0.31 28 f(原始地幔) 0.10 2.5 3.7 28 80 0.8 26 注:“−”表示无数据;海水铂族元素单位为fg/g,其他单位均为ng/g;富钴结壳数据为表3中平均值;地壳数据引自文献[5];原始地幔数据引自文献[29];洋壳数据引自文献[30];海山玄武岩数据引自文献[31];海水数据引自文献[32];热液硫化物数据引自文献[33]。 表 5 富钴结壳元素之间相关系数矩阵表
Tab. 5 Correlation matrix of elements in cobalt-rich crusts
元素 Mn Fe CaO P2O5 Al2O3 Na2O K2O MgO TiO2 Co Cu Ni Ba Sr Rh Pt PGE Mn 1 Fe 0.233 1 CaO –0.389 –0.927** 1 P2O5 –0.431 –0.917** 0.998** 1 Al2O3 –0.382 0.708** –0.659** –0.630** 1 Na2O 0.754** 0.562* –0.536* –0.556* –0.105 1 K2O –0.151 0.662** –0.736** –0.719** 0.924** –0.109 1 MgO 0.637** 0.722** –0.853** –0.874** 0.426 0.593* 0.605* 1 TiO2 0.374 0.288 –0.539* –0.553* 0.243 –0.056 0.554* 0.531* 1 Co 0.936** 0.447 –0.623** –0.653** –0.093 0.774** 0.136 0.805** 0.472 1 Cu –0.198 –0.718** 0.544* 0.525* –0.286 –0.742** –0.095 –0.317 0.275 –0.337 1 Ni 0.813** -0.266 0.077 0.021 –0.640** 0.366 –0.380 0.325 0.271 0.625** 0.332 1 Ba –0.058 –0.673** 0.493* 0.487* –0.388 –0.624** –0.162 –0.348 0.394 –0.172 0.844** 0.310 1 Sr 0.491* –0.474 0.513* 0.487* –0.893** 0.301 –0.840** –0.268 –0.293 0.238 0.038 0.598* 0.238 1 Rh –0.458 –0.771** 0.655** 0.658** –0.208 –0.874** –0.098 –0.534* 0.103 –0.535* 0.904** 0.026 0.847** 0.004 1 Pt –0.524* –0.748** 0.631** 0.640** –0.153 –0.910** –0.057 –0.558* 0.090 –0.590* 0.877** –0.066 0.823** –0.060 0.976** 1 PGE –0.520* –0.749** 0.632** 0.641** –0.157 –0.909** –0.059 –0.558* 0.093 –0.587* 0.879** –0.062 0.826** –0.056 0.978** 1.000** 1 注:相关系数为Pearson简单系数,n=17;**表示置信度P为99%;*表示置信度P为95%。 -
[1] Hein J R, Conrad T, Mizell K, et al. Controls on ferromanganese crust composition and reconnaissance resource potential, Ninetyeast Ridge, Indian Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2016, 110: 1−19. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2015.11.006 [2] Halbach P E, Jahn A, Cherkashov G. Marine Co-rich ferromanganese crust deposits: description and formation, occurrences and distribution, estimated world-wide resources[M]//Sharma R. Deep-Sea Mining. Cham: Springer, 2017: 65−141. [3] Astakhova N V. Noble metals in ferromanganese crusts from Marginal Seas of the Northwest Pacific[J]. Oceanology, 2017, 57(4): 558−567. doi: 10.1134/S0001437017040014 [4] Marino E, González F J, Somoza L, et al. Strategic and rare elements in Cretaceous-Cenozoic cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts from seamounts in the Canary Island Seamount Province (northeastern tropical Atlantic)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 87: 41−61. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.005 [5] 刘英俊, 曹励明. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 1−281.Liu Yingjun, Cao Liming. Introduction to Elemental Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1987: 1−281. [6] Koschinsky A, Hein J R, Kraemer D, et al. Platinum enrichment and phase associations in marine ferromanganese crusts and nodules based on a multi-method approach[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 539: 119426. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119426 [7] 王登红, 骆耀南, 屈文俊, 等. 中国西南铂族元素矿床地质、地球化学与找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 1-335.Wang Denghong, Luo Yaonan, Qu Wenjun, et al. Geology, Geochemistry and Exploration of PGE Deposits in SW China[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2007: 1−335. [8] Josso P, Rushton J, Lusty P, et al. Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic paleoceanography from North-east Atlantic ferromanganese crust microstratigraphy[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 422: 106122. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106122 [9] Sousa I M C, Santos R V, Koschinsky A, et al. Mineralogy and chemical composition of ferromanganese crusts from the Cruzeiro do Sul Lineament-Rio Grande Rise, South Atlantic[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2021, 108: 103207. doi: 10.1016/j.jsames.2021.103207 [10] Azami K, Hirano N, Machida S, et al. Rare earth elements and yttrium (REY) variability with water depth in hydrogenetic ferromanganese crusts[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 493: 224−233. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.045 [11] Josso P, Parkinson I, Horstwood M, et al. Improving confidence in ferromanganese crust age models: a composite geochemical approach[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 513: 108−119. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.003 [12] Jiang Xiaodong, Sun Xiaoming, Chou Y M, et al. Geochemistry and origins of carbonate fluorapatite in seamount Fe-Mn crusts from the Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 423: 106135. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106135 [13] Maeno M Y, Ohashi H, Yonezu K, et al. Sorption behavior of the Pt (II) complex anion on manganese dioxide (δ-MnO2): a model reaction to elucidate the mechanism by which Pt is concentrated into a marine ferromanganese crust[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2016, 51(2): 211−218. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0599-7 [14] Josso P, Lusty P, Chenery S, et al. Controls on metal enrichment in ferromanganese crusts: temporal changes in oceanic metal flux or phosphatisation?[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021, 308: 60−74. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.06.002 [15] Halbach P, Sattler C D, Teichmann F, et al. Cobalt-rich and platinum-bearing manganese crust deposits on seamount: nature, formation, and metal potential[J]. Marine Mining, 1989, 8(1): 23−29. [16] 姚德, 张丽洁, Wiltshire J C, 等. 富Co铁锰结壳铂族元素与铼−锇同位素组成及其意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2002, 22(3): 53−58. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2002.03.008Yao De, Zhang Lijie, Wiltshire J C, et al. PGE and Re-Os isotope compositions and their significances of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2002, 22(3): 53−58. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2002.03.008 [17] 孙晓明, 薛婷, 何高文, 等. 西太平洋海底海山富钴结壳惰性气体同位素组成及其来源[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(9): 2331−2340. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.09.008Sun Xiaoming, Xue Ting, He Gaowen, et al. Noble gases isotopic compositions and sources of cobalt-rich crusts from West Pacific Ocean seamounts[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(9): 2331−2340. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.09.008 [18] 赵宏樵, 赵建如. 富钴结壳中贵金属元素的特征[J]. 现代地质, 2007, 21(4): 654−658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.010Zhao Hongqiao, Zhao Jianru. Characteristics of noble metal elements in cobalt-rich crusts[J]. Geoscience, 2007, 21(4): 654−658. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2007.04.010 [19] 任江波, 何高文, 姚会强, 等. 西太平洋海山富钴结壳的稀土和铂族元素特征及其意义[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(10): 1745−1757.Ren Jiangbo, He Gaowen, Yao Huiqiang, et al. Geochemistry and significance of REE and PGE of the cobalt-rich crusts from West Pacific Ocean seamounts[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(10): 1745−1757. [20] 卜文瑞. 太平洋富钴结壳稀有气体地球化学特征及其成矿指示意义[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2008: 1−164.Bu Wenrui. Noble gas geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean and their significations for the formation of crusts[D]. Qingdao: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008: 1−164. [21] Qi Liang, Zhou Meifu, Wang C Y. Determination of low concentrations of platinum group elements in geological samples by ID-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(10): 1335−1339. doi: 10.1039/b400742e [22] Qi Liang, Zhou Meifu, Wang C Y, et al. Evaluation of a technique for determining Re and PGEs in geological samples by ICP-MS coupled with a modified Carius tube digestion[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2007, 41(6): 407−414. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.41.407 [23] Hein J R, Koschinsky A, Bau M, et al. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts in the Pacific[M]//Cronan D S. Handbook of Marine Mineral Deposits. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2000: 239−279. [24] Hein J R. Cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts: global distribution, composition, origin and research activities[C]//Minerals Other than Polymetallic Nodules of the International Seabed Area. Kingston Jamaica: International Seabed Authority, 2004: 188−256. [25] Koschinsky A, Stascheit A, Bau M, et al. Effects of phosphatization on the geochemical and mineralogical composition of marine ferromanganese crusts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(19): 4079−4094. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00231-7 [26] 杨胜雄, 龙晓军, 祁奇, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳矿物学和地球化学特征——以麦哲伦海山和马尔库斯–威克海山富钴结壳为例[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2016, 46(2): 105−116.Yang Shengxiong, Long Xiaojun, Qi Qi, et al. The mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Co-rich crusts from the western Pacific: taking the Co-rich crusts from Magellan and Marcus-wake seamounts as an example[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(2): 105−116. [27] 潘家华, 刘淑琴, 杨忆, 等. 西太平洋海山磷酸盐的常量、微量和稀土元素地球化学研究[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 48(5): 534−541. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.05.012Pan Jiahua, Liu Shuqin, Yang Yi, et al. Research on geochemical characteristics of major, trace and rare-earth elements in phosphates from the West Pacific seamounts[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 48(5): 534−541. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2002.05.012 [28] Bonatti E, kraemer T, Rydell H. Classification and genesis of submarine iron-manganese deposits[M]//Horn D R. Ferromanganese Deposits on the Ocean Floor. Washington: National Science Foundation, 1972: 149−166. [29] McDonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223−253 [30] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Press, 1985: 1−312. [31] 孙晓明, 薛婷, 何高文, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳铂族元素(PGE)和Os同位素地球化学及其成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12): 3014−3026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.12.017Sun Xiaoming, Xue Ting, He Gaowen, et al. Platinum group elements (PGE) and Os isotopic geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean seamounts and their constraints on genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(12): 3014−3026. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2006.12.017 [32] Glasby G P. Incorporation of transition and platinum group elements (PGE) in Co-rich Mn crusts at Afanasiy-Nikitin Seamount (AFS) in the equatorial S Indian Ocean[J]. Resource Geology, 2010, 60(2): 212−215. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2010.00128.x [33] Pašava J, Vymazalová A, Petersen S, et al. PGE distribution in massive sulfides from the pacmanus hydrothermal field, eastern Manus Basin, Papua New Guinea: implications for PGE enrichment in some ancient volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2004, 39(7): 784−792. doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0442-z [34] 何高文, 孙晓明, 杨胜雄, 等. 东太平洋CC区多金属结核铂族元素(PGE)地球化学及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(2): 164−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.02.006He Gaowen, Sun Xiaoming, Yang Shengxiong, et al. Platinum group elements (PGE) geochemistry of polymetallic nodules in CC zone, East Pacific Ocean[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(2): 164−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.02.006 [35] Jiang Shaoyong, Yang Jinghong, Ling Hongfei, et al. Re-Os isotopes and PGE geochemistry of black shales and intercalated Ni-Mo polymetallic sulfide bed from the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation, South China[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2003, 13(10): 788−794. doi: 10.1080/10020070312331344440 [36] 何高文, 赵祖斌, 朱克超, 等. 西太平洋富钴结壳资源[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001: 1−92.He Gaowen, Zhao Zubin, Zhu Kechao, et al. Cobalt-Rich Crust Resources in the West Pacific[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2001: 1−92. [37] Koschinsky A, Halbach P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: genetic implications[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(24): 5113−5132. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00358-4 [38] Koschinsky A, Hein J R. Uptake of elements from seawater by ferromanganese crusts: solid-phase associations and seawater speciation[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 198(3/4): 331−351. [39] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 张辉, 等. 太平洋海山富钴结壳中铂族元素赋存状态与富集机理[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 115−124.Gao Jingjing, Liu Jihua, Zhang Hui, et al. Occurrence phase and enrichment mechanism of platinum group elements in the Pacific cobalt-rich crusts[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 115−124. [40] 高晶晶, 刘季花, 张辉, 等. 太平洋徐福海山富钴结壳稀土元素和铂族元素赋存状态研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(11): 77−87.Gao Jingjing, Liu Jihua, Zhang Hui, et al. Occurrence phases of rare earth elements and platinum group elements in cobalt-rich crusts from the Seamount Xufu in the Pacific[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(11): 77−87. [41] 任向文, 石学法, 朱爱美, 等. 麦哲伦海山群MK海山富钴结壳稀土元素的赋存相态[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(3): 707−714. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2011.03.039Ren Xiangwen, Shi Xuefa, Zhu Aimei, et al. Existing phase of rare earth elements in Co-rich Fe-Mn crusts from seamount MK of Magellan seamount cluster[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(3): 707−714. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2011.03.039 [42] 崔迎春, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 70 Ma以来风尘活动在太平洋铁锰结壳中的记录[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2012, 42(2): 393−399. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2012.02.024Cui Yingchun, Shi Xuefa, Liu Jihua, et al. Records of past 70 Ma dust activities in ferromanganese crusts from Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2012, 42(2): 393−399. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2012.02.024 [43] 李江山, 石学法, 刘季花, 等. 古海洋环境演化对富钴结壳稀土元素富集的制约[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2011, 29(5): 622−629.Li Jiangshan, Shi Xuefa, Liu Jihua, et al. Constraints of paleoceanographic environmental evolution on REEs enrichment in Co-rich crust[J]. Journal of the Chinese Society of Rare Earths, 2011, 29(5): 622−629. [44] 任向文, 刘季花, 石学法, 等. 麦哲伦海山群M海山富钴结壳成因与成矿时代: 来自地球化学和Co地层学的证据[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(6): 65−74.Ren Xiangwen, Liu Jihua, Shi Xuefa, et al. Genesis and ore-forming stages of Co-rich ferromanganese crusts from Seamount M of Magellan Seamounts: evidence from geochemistry and Co chronology[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(6): 65−74. [45] 侯晓帆, 王珍岩, 李文建, 等. 西太平洋卡罗琳洋脊CM4海山铁锰结壳矿物学和地球化学特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(5): 1118−1126. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20191000193Hou Xiaofan, Wang Zhenyan, Li Wenjian, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of ferromanganese crusts of Caroline ridge CM4 guyot in the western Pacific[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(5): 1118−1126. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20191000193 -




 下载:
下载: