Characteristics of small medusae community correlated with environmental factors in the southwest of Bohai Sea
-
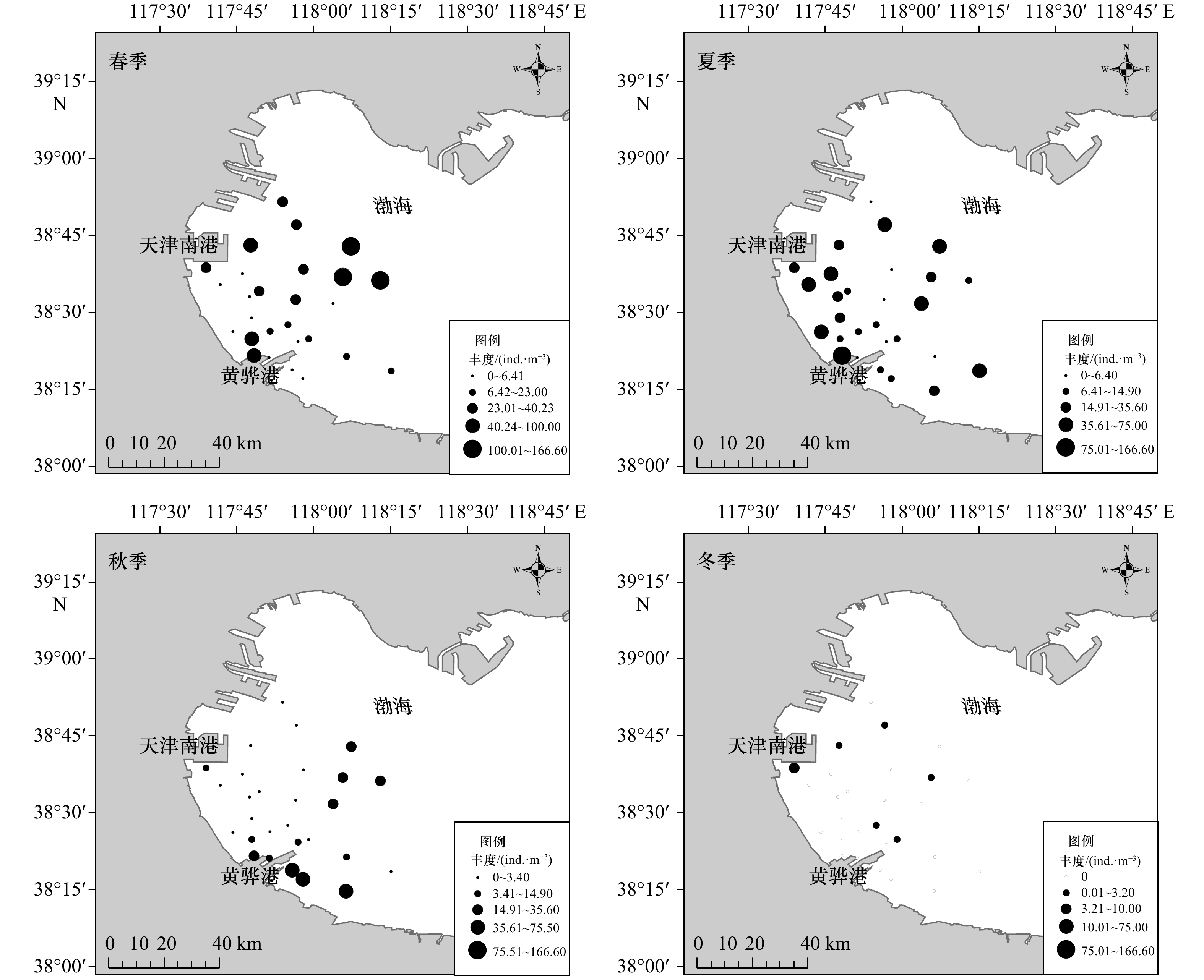
摘要: 根据2020年8月至2021年5月对渤海西南部浮游动物调查的4个航次数据,分析该海域水螅水母、栉水母群落结构和季节变化特征,讨论了环境因子对小型水母丰度的影响。研究发现,渤海西南部小型水母种类组成和丰度分布存在季节变化,全年调查共发现小型水母13种,11种水螅水母、2种栉水母;春、夏、秋、冬该海域水母种数分别为4种、9种、7种和2种,丰度均值分别为30.74 ind./m3、30.78 ind./m3、12.08 ind./m3、0.57 ind./m3;优势种为嵊山秀氏水母(Sugiura chengshanense)、八斑芮氏水母(Rathkea octopunctata)、锡兰和平水母(Eirene ceylonensis)、半球美螅水母(Clytia hemisphaerica)、球型侧腕水母(Pleurobrachia globosa),优势种季节更替率平均为91.67%,呈现明显季节演替。水温和盐度是影响渤海西南部小型水母丰度季节变化的主要环境因子,春季水温回升及适宜营养盐含量促进小型水母生长繁殖,夏季桡足类为小型水母提供了丰富的饵料促进其生长,秋季群落主要受盐度的影响。根据渤海西南部小型水母风险种分布情况,推测夏季和秋季风险种旺发对拟建核电存在风险。Abstract: According to the data of four voyages of zooplankton survey in the southwest of Bohai Sea from August 2020 to May 2021, the community structure and seasonal variation of small medusae were analyzed, and the effects of environmental factors on the abundance of small medusae were discussed. There were seasonal variations in species composition and abundance distribution of small medusae in the southwest of Bohai Sea, a total of 13 species of small medusae were found throughout the year, including 11 species of hydromedusae and 2 species of ctenophores. The number of medusae species in spring, summer, autumn and winter were 4, 9, 7 and 2 species respectively. The mean abundance values were 30.74 ind./m3, 30.78 ind./m3, 12.08 ind./m3 and 0.57 ind./m3 respectively. The dominant species were Sugiura chengshanense, Rathkea octopunctata, Eirene ceylonensis, Clytia hemisphaerica, Pleurobrachia globosa. The average seasonal replacement rate of dominant species was 91.67%, showing obvious seasonal succession. Water temperature and salinity were main environmental factor affecting the seasonal variation of total abundance of small medusae in the southwest of Bohai Sea. The increase of water temperature and nutrients in spring promote the growth and reproduction of small medusae. In summer, copepods provided rich bait for small medusae to promote its growth, the community was mainly affected by salinity in autumn. According to the risk species of small medusae in the southwest of Bohai Sea, it was speculated that the peak of risk species in summer and autumn was a risk to the planned nuclear power.
-
Key words:
- hydromedusae /
- ctenophores /
- seasonal variation /
- environmental factor /
- zooplankton copepods /
- Bohai Sea
-
图 3 渤海西南部小型水母与环境因子的CCA排序
WT:水温;DIN:无机氮;DIP:磷酸盐;DO:溶解氧;S:盐度;COD:化学需氧量;Copepods:桡足类
Fig. 3 CCA ordination of small medusae and environmental factors in southwest of Bohai Sea
WT: Water temperature; DIN: dissolved inorganic nitrogen; DIP: dissolved inorganic phosphorus; DO: dissolved oxygen: S: salinity; COD: chemical oxygen demand; Copepods: Copepods
表 1 环境要素分析方法
Tab. 1 Analysis methods of environmental factors
序号 环境要素 方法 1 pH pH计法 2 溶解氧含量 碘量法 3 化学需氧量 碱性高锰酸钾法 4 磷酸盐含量 流动分析法 5 无机氮含量 流动分析法 表 2 不同季节水母种类组成名录
Tab. 2 Species composition of medusae in different seasons
序号 类群 学名 拉丁学名 夏季 秋季 冬季 春季 1 水螅水母 高手水母 Bougainvillia sp. + − − − 2 水螅水母 八斑芮氏水母 Rathkea octopunctata − − + + 3 水螅水母 灯塔水母 Turritopsis nutricula + − − − 4 水螅水母 小介螅水母 Hydractinia minima − − − + 5 水螅水母 薮枝螅水母属 Obelia spp. + + − − 6 水螅水母 嵊山秀氏水母 Sugiura chengshanense + + − + 7 水螅水母 四手触丝水母 Lovenella assimilis − + − − 8 水螅水母 锡兰和平水母 Eirene ceylonensis + − − − 9 水螅水母 细颈和平水母 Eirene menoni + + − − 10 水螅水母 半球美螅水母 Clytia hemisphaerica + + − + 11 水螅水母 四枝管水母 Proboscidactyla flavicirrata + − + − 12 栉水母 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa + + − − 13 栉水母 蝶水母 Ocyropsis crystallina − + − − 注:+表示检出,−表示未检出。 表 3 各季节水母优势种及优势度指数
Tab. 3 The dominant species and dominant degree of medusae in different seasons
种类 季节 优势度 丰度占比/% 出现率/% 球型侧腕水母 夏季 0.39 45.52 86.21 锡兰和平水母 夏季 0.27 35.17 75.86 半球美螅水母 夏季 0.08 11.59 65.52 球型侧腕水母 秋季 0.69 83.95 82.76 八斑芮氏水母 冬季 0.18 87.27 20.69 嵊山秀氏水母 春季 0.32 58.56 55.17 八斑芮氏水母 春季 0.05 26.15 17.24 表 4 不同季节浮游动物丰度及海水环境要素平均值
Tab. 4 Average values of zooplankton abundance and seawater environmental factors in different seasons
参数 夏季 秋季 冬季 春季 p 浮游动物丰度/(ind.·m−3) 180.20±105.56 96.85±671.91 163.92±568.7 2 078.68±171.69 ** 桡足类丰度/(ind.·m−3) 53.80±422.22 5.05±19.61 85.64±275.83 1 678.11±162.11 ** 水温/℃ 27.69±5.37 12.56±2.1 2.69±4.41 17.16±7.17 ** 盐度 30.95±1.24 31.24±2.02 31.96±1.54 31.46±1.83 ** pH 8.09±0.24 8.28±0.45 8.21±0.4 8.12±0.14 ** 溶解氧含量/(mg·L−1) 7.04±1.87 8.93±3.42 11.44±2.72 7.52±2.76 ** 化学需氧量/(mg·L−1) 1.193±1.47 1.20±1.50 1.41±1.82 1.01±0.77 ** 磷酸盐含量/(μg·L−1) 10.94±66.02 4.185±9.04 8.99±14.34 3.89±5.14 ** 无机氮含量/(μg·L−1) 315.43±856.2 143.921±621.5 248.09±722.6 77.25±199.5 ** 注:**代表p<0.01。 -
[1] 中国科学院中国动物志编辑委员会. 中国动物志−无脊椎动物−第二十七卷−刺胞动物门, 水螅虫纲管水母亚纲 钵水母纲[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.Editorial Committee of Zoology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Invertebrata, Vol.27 Phylum Cnidaria Class Hydrozoa Subclass Siphonophorae Class Scyphomedusae[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. [2] 张芳, 孙松, 李超伦. 海洋水母类生态学研究进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(2): 121−130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.001Zhang Fang, Sun Song, Li Chaolun. Advances in the study of marine jellyfish ecology[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(2): 121−130. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.001 [3] Richardson A J, Bakun A, Hays G C, et al. The jellyfish joyride: causes, consequences and management responses to a more gelatinous future[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 2009, 24(6): 312−322. [4] 高倩, 陈佳杰, 徐兆礼, 等. 长江口及邻近海域浮游水螅水母、管水母和栉水母的丰度分布与季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(22): 7328−7337.Gao Qian, Chen Jiajie, Xu Zhaoli, et al. Abundance distribution and seasonal variation of medusae, siphonophores, and ctenophores in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(22): 7328−7337. [5] 孙松. 水母暴发研究所面临的挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(3): 257−261.Sun Song. Challenges in the Jellyfish bloom research[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 2012, 27(3): 257−261. [6] Purcell J E, Sturdevant M V. Prey selection and dietary overlap among zooplanktivorous jellyfish and juvenile fishes in Prince William Sound, Alaska[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2001, 210: 67−83. doi: 10.3354/meps210067 [7] Purcell J E, Uye S I, Lo W T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: a review[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 350: 153−174. doi: 10.3354/meps07093 [8] 韩瑞, 纪平, 赵懿珺, 等. 滨海核电厂取水堵塞事件调研及分析[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 44(S1): 75−80. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2018.0265Han Rui, Ji Ping, Zhao Yijun, et al. The investigation and analysis on cooling water blockages of Costal Nuclear Power Plants[J]. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 2018, 44(S1): 75−80. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2018.0265 [9] 李聪. 我国水母灾害研究现状与展望[J]. 渔业研究, 2018, 40(2): 156−162.Li Cong. Review on the current situation and perspective of Chinese jellyfish disasters’ research[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2018, 40(2): 156−162. [10] 王卫成. 胶州湾浮游动物功能群长期变化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2017.Wang Weicheng. Long-term changes of zooplankton functional groups in Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. [11] 张芳, 李超伦, 孙松, 等. 水母灾害的形成机理、监测预测及防控技术研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(6): 1187−1195. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171000258Zhang Fang, Li Chaolun, Sun Song, et al. Progress on studying jellyfish bloom, and the monitoring and control[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(6): 1187−1195. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20171000258 [12] 邓邦平, 刘衡, 王洪波, 等. 福建宁德晴川湾海域水母群落特征及其潜在生态风险分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(4): 128−136.Deng Bangping, Liu Heng, Wang Hongbo, et al. Analysis on the community characteristics and potential ecological risk of jellyfish in the Qingchuan Bay of Ningde, Fujian Province[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(4): 128−136. [13] 李浩然, 刘光兴, 马静, 等. 夏、秋季黄河口及邻近水域浮游动物群落特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2018, 37(5): 631−639. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180502Li Haoran, Liu Guangxing, Ma Jing, et al. Community characteristics of zooplankton in the Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent area in summer and autumn[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2018, 37(5): 631−639. doi: 10.12111/j.cnki.mes20180502 [14] 黄旭光, 郭东晖, 肖武鹏, 等. 九龙江口春季微型浮游生物数量变动及其与小型水母消长的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 579−583. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203026026Huang Xuguang, Guo Donghui, Xiao Wupeng, et al. The relationship between quantitative changes of microplankton and population dynamics of small medusa in the Jiulong River Estuary in spring of 2011[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 579−583. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203026026 [15] 唐娅菲. 滨海核电运行安全典型致灾生物研究——以宁德核电为例[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2018.Tang Yafei. Study on typical disaster-causing organisms of coastal nuclear power operation safety: taking Ningde nuclear power as an example[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2018. [16] 张朝文, 关春江, 徐鹏, 等. 辽东湾东部海域核电冷源取水区的风险生物分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(1): 41−45. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190107Zhang Chaowen, Guan Chunjiang, Xu Peng, et al. Analysis on risk organisms for the cold source water of nuclear power plantin the eastern waters of Liaodong Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2019, 38(1): 41−45. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190107 [17] Lalli C M, Parsons T R. Biological Oceanography: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Burlington, USA: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997. [18] 张晓举, 温若冰, 于海洋. 渤海湾南部水域春秋季强壮滨箭虫摄食压力变化的初步研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2013, 32(4): 434−439. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.04.011Zhang Xiaoju, Wen Ruobing, Yu Haiyang. Preliminary study on the variations of Aidanosagitta crassa feeding pressure in southern Bohai Bay during spring and autumn[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2013, 32(4): 434−439. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.04.011 [19] 高文胜, 刘宪斌, 张秋丰, 等. 渤海湾近岸海域浮游动物多样性[J]. 海洋科学, 2014, 38(4): 55−60. doi: 10.11759/hykx20120503001Gao Wensheng, Liu Xianbin, Zhang Qiufeng, et al. Species diversity of zooplankton in the coastal area of Bohai Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 2014, 38(4): 55−60. doi: 10.11759/hykx20120503001 [20] 吴春勇. 近海核电厂地下水放射性污染环境影响评价[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2018.Wu Chunyong. Groundwater environmental impact assessment of the radioactive contamination in offshore NPP[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2018. [21] 陈亚瞿, 徐兆礼, 王云龙, 等. 长江口河口锋区浮游动物生态研究Ⅰ.生物量及优势种的平面分布[J]. 中国水产科学, 1995, 2(1): 49−58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.1995.01.003Chen Yaqu, Xu Zhaoli, Wang Yunlong, et al. An ecological study on zooplankton in plume front zone of Changjiang(Yangtze) River estuarine area I. biomass distribution of dominant species[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 1995, 2(1): 49−58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.1995.01.003 [22] 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 贾晓平, 等. 大亚湾海域浮游动物种类组成和优势种的季节变化[J]. 水产学报, 2013, 37(8): 1213−1119. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38591Du Feiyan, Wang Xuehui, Jia Xiaoping, et al. Seasonal succession of zooplankton species composition and dominant species in the Daya Bay, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2013, 37(8): 1213−1119. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2013.38591 [23] 马喜平, 高尚武. 渤海水母类生态的初步研究——种类组成、数量分布与季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2000, 20(4): 533−540. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.04.001Ma Xiping, Gao Shangwu. The ecology of medusae in the Bohai Sea—Species composition, quantitative distribution and seasonal variation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2000, 20(4): 533−540. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2000.04.001 [24] 冯颂, 孙松, 李超伦, 等. 胶州湾半球美螅水母(Clytia hemisphaerica)数量周年变动及对浮游动物摄食压力估算[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 464−470. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203010010Feng Song, Sun Song, Li Chaolun, et al. Annual changes in Clytia hemisphaerica abundance and its grazing pressure on zooplankton population in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 464−470. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203010010 [25] 刘西汉, 石雅君, 姜会超, 等. 曹妃甸邻近海域浮游动物群落时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(4): 114−125. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200601004Liu Xihan, Shi Yajun, Jiang Huichao, et al. Spatial and temporal variations of zooplankton community and their influential factors in Caofeidian coastal waters[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(4): 114−125. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200601004 [26] 蒋双, 陈介康. 黄渤海水螅水母、管水母和栉水母的地理分布[J]. 海洋通报, 1994, 13(3): 17−23.Jiang Shuang, Chen Jiekang. Geographical distribution of Hydromedusae, Siphonophore and Ctenophora in Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1994, 13(3): 17−23. [27] 陈洪举, 刘光兴. 夏季长江口及邻近海域水母类生态特征研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2010, 34(4): 17−24.Chen Hongju, Liu Guangxing. Ecological characteristics of medusa in the Changjiang River Estuary and its adjacent waters in summer[J]. Marine Sciences, 2010, 34(4): 17−24. [28] 徐兆礼, 张凤英, 罗民波. 东海栉水母(Ctenophora)生态特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2006, 25(11): 1301−1305. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.11.001Xu Zhaoli, Zhang Fengying, Luo Minbo. Ecological characters of Ctenophora in East China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2006, 25(11): 1301−1305. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2006.11.001 [29] 张金标. 我国东南近岸海域球型侧腕水母的分布和丰度[J]. 海洋学报, 1983, 5(S1): 840−846.Zhang Jinbiao. Distribution and abundance of Pleurobrachia globosa in the coastal waters of China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1983, 5(S1): 840−846. [30] 张金标. 中国海域水螅水母类区系的初步分析[J]. 海洋学报, 1979, 1(1): 127−137.Zhang Jinbiao. A preliminary analysis on the Hydromedusae Fauna of the China Sea areas[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1979, 1(1): 127−137. [31] 孙松, 张芳, 李超伦, 等. 黄海小型水母的分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(3): 429−437. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203005005Sun Song, Zhang Fang, Li Chaolun, et al. The distribution pattern of small medusae in the Yellow Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(3): 429−437. doi: 10.11693/hyhz201203005005 [32] 时永强. 黄海浮游动物功能群年际变化研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2015.Shi Yongqiang. Interannual changes of zooplankton functional groups in the Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [33] 张国辉, 宋和航, 穆阳阳. 北方核电厂取水口堵塞原因分析及改进措施评价[J]. 核动力工程, 2019, 40(5): 111−117. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2019.05.0111Zhang Guohui, Song Hehang, Mu Yangyang. Reason analysis and improvement measures evaluation for water intake blockage at Northern Nuclear Power Plants[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2019, 40(5): 111−117. doi: 10.13832/j.jnpe.2019.05.0111 [34] 於凡, 许波涛, 吴昕, 等. 基于核电冷源安全的海洋生物调查及筛选评价方法研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(1): 139−143. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190239Yu Fan, Xu Botao, Wu Xin, et al. Study on the method of marine organisms investigation, screening and evaluation based on nuclear power plant cold source safety[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(1): 139−143. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190239 [35] Sun Song, Sun Xiaoxia, Jenkinson I R. Preface: giant jellyfish blooms in Chinese waters[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2015, 754(1): 1−11. doi: 10.1007/s10750-015-2320-3 [36] 郑向荣, 李燕, 张海鹏, 等. 河北沿海大型水母生物量调查[J]. 河北渔业, 2014(1): 15−18, 42.Zheng Xiangrong, Li Yan, Zhang Haipeng et al. Investigation of macro-jellyfish biomass in the Hebei coast[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2014(1): 15−18, 42. [37] 袁晓博, 刘志亮, 薛力园, 等. 秦皇岛海域水母灾害发生规律及研究进展[J]. 河北渔业, 2021(6): 12−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2021.06.004Yuan Xiaobo, Liu Zhiliang, Xue Liyuan, et al. Review on the occurrence regularity and current situation of jellyfish disaster in Qinhuangdao coastal area[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2021(6): 12−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2021.06.004 [38] 王朋鹏, 张芳, 孙松, 等. 2018年6月渤海大型水母分布特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(1): 85−94. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190500085Wang Pengpeng, Zhang Fang, Sun Song, et al. Distribution of giant jellyfish in the Bohai Sea in June 2018[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(1): 85−94. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20190500085 [39] Molinero J C, Casini M, Buecher E. The influence of the Atlantic and regional climate variability on the long-term changes in gelatinous carnivore populations in the northwestern Mediterranean[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2008, 53(4): 1456−1467. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.4.1456 [40] Gibbons M J, Richardson A J. Patterns of jellyfish abundance in the North Atlantic[M]//Pitt K A, Purcell J E. Jellyfish Blooms: Causes, Consequences, and Recent Advances. Dordrecht: Springer, 2008: 51−65. [41] Fraser J H. The ecology of the ctenophore Pleurobrachia pileus in Scottish waters[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 1970, 33(2): 149−168. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/33.2.149 [42] 姜会超, 陈海刚, 宋秀凯, 等. 莱州湾金城海域浮游动物群落结构及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319.Jiang Huichao, Chen Haigang, Song Xiukai, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Jincheng area of Laizhou Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(22): 7308−7319. [43] 姜会超, 刘宁, 高继庆, 等. 烟台四十里湾浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327.Jiang Huichao, Liu Ning, Gao Jiqing, et al. Zooplankton community structure in Sishili Bay and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(4): 1318−1327. [44] Mills C E. Density is altered in hydromedusae and ctenophores in response to changes in salinity[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 1984, 166(1): 206−215. doi: 10.2307/1541442 [45] Ma X P, Purcell J E. Temperature, salinity, and prey effects on polyp versus medusa bud production by the invasive hydrozoan Moerisia lyonsi[J]. Marine Biology, 2005, 147(1): 225−234. doi: 10.1007/s00227-004-1539-8 [46] Purcell J E. Dietary composition and diel feeding patterns of epipelagic siphonophores[J]. Marine Biology, 1981, 65(1): 83−90. doi: 10.1007/BF00397071 [47] 林义, 邹清, 王航俊, 等. 温州沿岸海域春、夏季浮游动物群落特征及与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2021, 38(6): 51−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.06.009Lin Yi, Zou Qing, Wang Hangjun, et al. Characteristics of zooplankton community structure and its response to environment factors in the Wenzhou coastal waters during spring and summer[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2021, 38(6): 51−59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2021.06.009 [48] 周强, 王云忠, 齐继光, 等. 环境因子对4种常见观赏性水母生长发育影响的研究进展[J]. 湖南农业科学, 2019(10): 120−124.Zhou Qiang, Wang Yunzhong, Qi Jiguang, et al. Research progress in effect of environmental factors on growth and development of four common ornamental jellyfish[J]. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 2019(10): 120−124. [49] 曲长凤, 宋金明, 李宁. 水母旺发的诱因及对海洋环境的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2014, 25(12): 3701−3712. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20141009.005Qu Changfeng, Song Jinming, Li Ning. Causes of jellyfish blooms and their influence on marine environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2014, 25(12): 3701−3712. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20141009.005 -




 下载:
下载: