Laboratory experimental study on the lateral melting process of ice layer
-
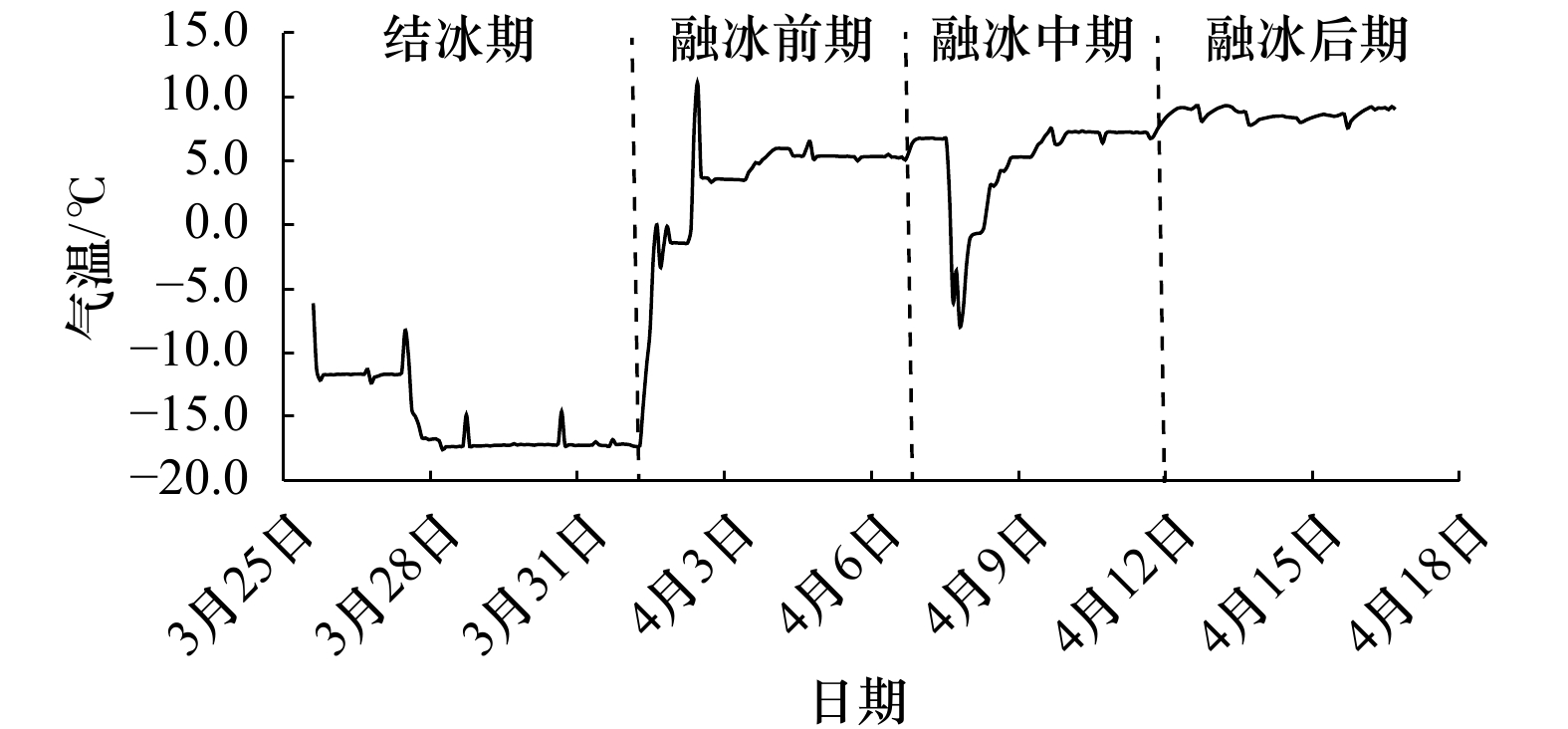
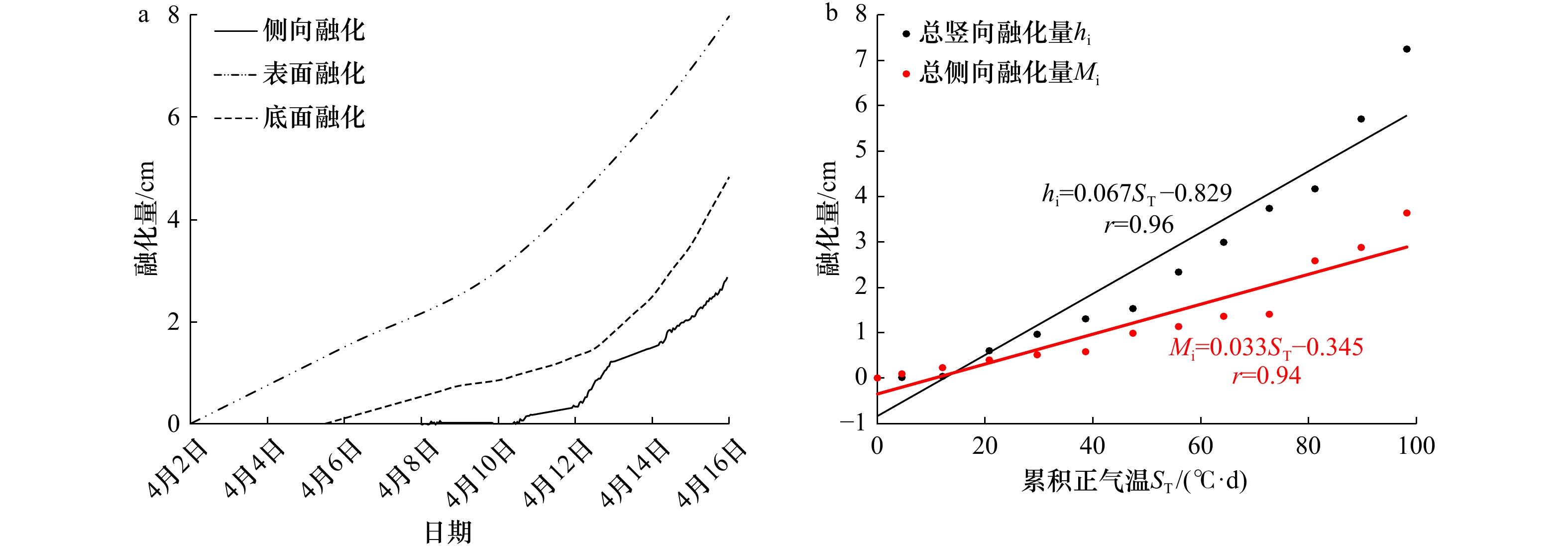
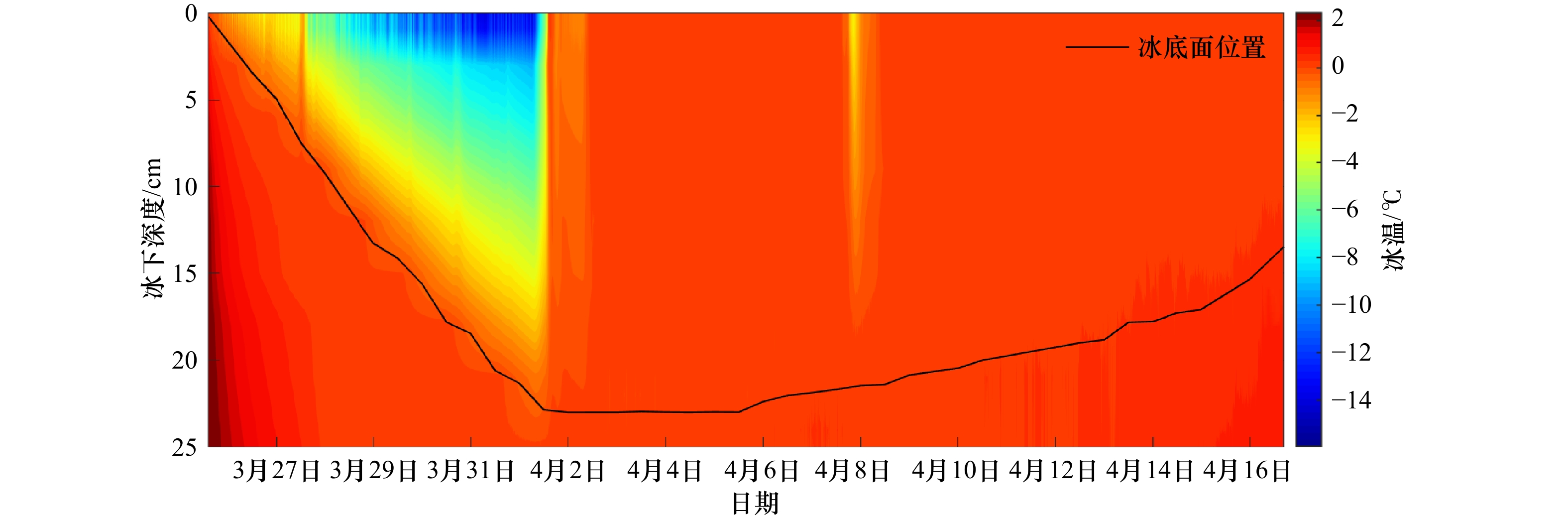
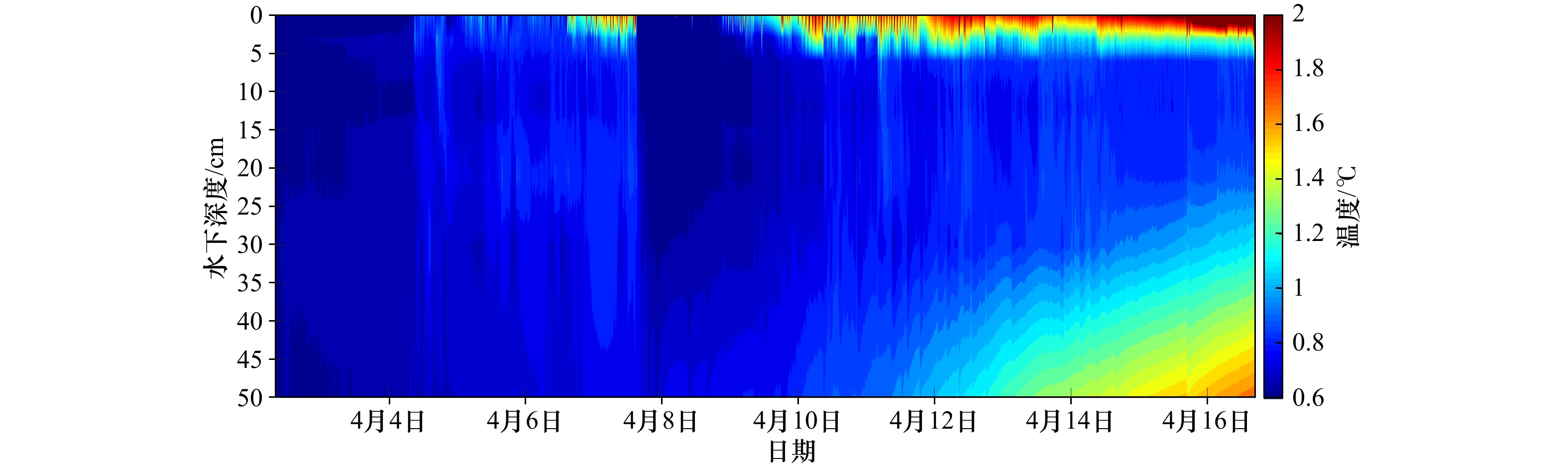
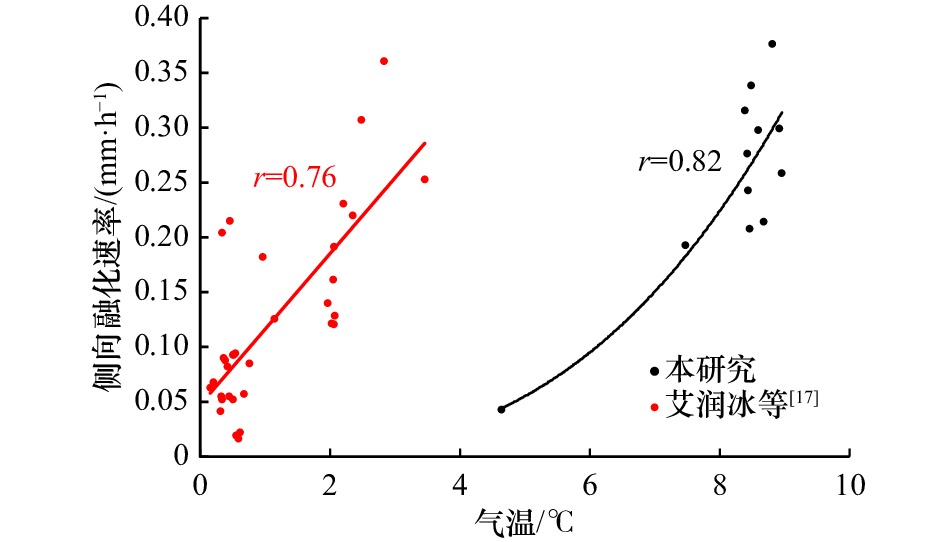
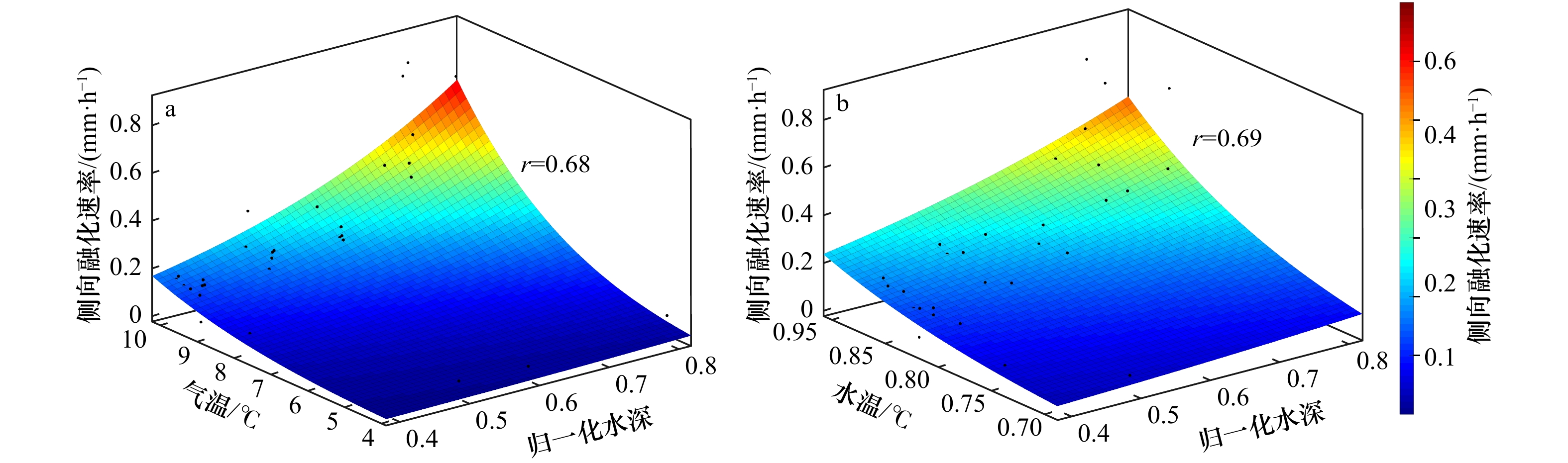
摘要: 为了探究冰层侧向融化过程,定量分析影响冰层侧向融化的主导因素,在低温实验室水槽内实施了浮冰融化实验。同步测量了冰底面和表面生消过程、浮冰侧向融化过程,同时记录了实验室气温、冰样内部不同深度处的冰温及开阔水域不同深度处的水温,利用相关分析方法研究了不同要素之间的关系及其对浮冰侧向融化速率的影响规律。结果表明,融冰前期冰样内部不同深度处的侧向融化缓慢且均匀,平均融化速率为0.05 mm/h;融冰中后期不同深度处的侧向融化速率显著增加且不再均匀,平均融化速率为0.15 mm/h。平均侧向融化速率与气温的相关系数较好(r=0.82),优于其与平均水温(r=0.74)和水–冰温度差(r=0.48)的相关系数。建立侧向融化速率随温度(气温、水温)和深度变化的定量关系,可以准确描述浮冰侧向融化过程的非均匀性。同时验证了进行非均匀性侧向融化试验技术的可行性,为更加接近北极真实情况考虑风速和光源条件的海冰试验奠定了基础。Abstract: In order to investigate the melting process at the ice-water lateral interface and to quantify the dominant factors affecting the lateral melting rate of ice layer, an ice melting experiment was carried out in a low-temperature water tank. Simultaneous measurements of the ice bottom and surface processes and the lateral melting process of the ice layer were carried out, while the laboratory air temperature, ice temperature at different depths inside the ice samples and water temperature at different depths in open water were recorded, the relationships between different elements and their influence patterns on the lateral melting rate of ice were investigated using correlation analysis methods. The results show that the lateral melting rate at different depths inside the ice samples was slow and uniform in the early stage of melting, with an average melting rate of 0.05 mm/h. The lateral melting rate at different depths in the middle and late stages of melting increased significantly and was no longer uniform, with an average melting rate of 0.15 mm/h. The correlation coefficient of the average lateral melting rate and air temperature (r=0.82) was better than that between the average water temperature (r=0.74) and the water-ice temperature difference (r=0.48). The quantitative relationships of lateral melting rate with temperature (air temperature, water temperature) and depth were established to accurately describe the non-uniformity of the lateral melting process of ice layer. It also verifies the feasibility of conducting non-uniform lateral melting test techniques, and lays the foundation for sea ice tests that more closely resemble real Arctic conditions considering wind speed and light source conditions.
-
Key words:
- lateral melting rate /
- temperature /
- water depth /
- parameterization /
- low temperature experiment
-
表 1 冰样三面融化对比
Tab. 1 Comparison of melting on three sides of the ice layer
冰样位置 融化厚度/cm 平均融化速率/(mm·h–1) 融化体积占比/% 表面 8 0.24 57.7 底面 5 0.15 36.1 侧面 3 0.09 6.2 -
[1] Deser C, Walsh J E, Timlin M S. Arctic sea ice variability in the context of recent atmospheric circulation trends[J]. Journal of Climate, 2000, 13(3): 617−633. doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<0617:ASIVIT>2.0.CO;2 [2] Screen J A, Simmonds I. The central role of diminishing sea ice in recent Arctic temperature amplification[J]. Nature, 2010, 464(7293): 1334−1337. doi: 10.1038/nature09051 [3] Holland M M, Bitz C M, Tremblay B. Future abrupt reductions in the summer Arctic sea ice[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(23): L23503. doi: 10.1029/2006GL028024 [4] Overland J E, Wood K R, Wang Muyin. Warm Arctic-cold continents: climate impacts of the newly open Arctic Sea[J]. Polar Research, 2011, 30(1): 15787. doi: 10.3402/polar.v30i0.15787 [5] Perovich D K, Polashenski C. Albedo evolution of seasonal Arctic sea ice[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(8): L08501. [6] Malinka A, Zege E, Istomina L, et al. Reflective properties of melt ponds on sea ice[J]. The Cryosphere, 2018, 12(6): 1921−1937. doi: 10.5194/tc-12-1921-2018 [7] Schröder D, Feltham D L, Flocco D, et al. September Arctic sea-ice minimum predicted by spring melt-pond fraction[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014, 4(5): 353−357. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2203 [8] Wang Q, Danilov S, Jung T, et al. Sea ice leads in the Arctic Ocean: model assessment, interannual variability and trends[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(13): 7019−7027. doi: 10.1002/2016GL068696 [9] Zubov N N. Arctic Ice[M]. San Diego: Navy Electronics Laboratory, 1963. [10] Josberger E G. Laminar and turbulent boundary layers adjacent to melting vertical ice walls in salt water[D]. Seattle: University of Washington, 1979. [11] Perovich D K. On the summer decay of a sea ice cover[D]. Seattle: University of Washington, 1983. [12] Steele M. Sea ice melting and floe geometry in a simple ice-ocean model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1992, 97(C11): 17729−17738. doi: 10.1029/92JC01755 [13] 李志军, 王智群, 王庆凯, 等. 浮冰界面融化速率参数化方案的实验室研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(7): 162−172.Li Zhijun, Wang Zhiqun, Wang Qingkai, et al. Laboratory study on parameterization of ice floe melt rate at ice-air and ice-water interfaces[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(7): 162−172. [14] 雷瑞波, 李志军, 程斌, 等. 夏季北冰洋浮冰–水道热力学特征现场观测研究[J]. 极地研究, 2010, 22(3): 286−295.Lei Ruibo, Li Zhijun, Cheng Bin, et al. Observations on the thermodynamics mechanism of the floe-lead system in the Arctic Ocean during summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2010, 22(3): 286−295. [15] 王庆凯, 李志军, 曹晓卫, 等. 实测冰–水侧向界面热力学融化速率[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2016, 14(6): 81−86.Wang Qingkai, Li Zhijun, Cao Xiaowei, et al. Analysis of measured thermodynamic melting rate of lateral interface between ice and water[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2016, 14(6): 81−86. [16] 王庆凯, 方贺, 李志军, 等. 湖冰侧、底部融化现场观测与热力学分析[J]. 水利学报, 2018, 49(10): 1207−1215.Wang Qingkai, Fang He, Li Zhijun, et al. Field investigations on lateral and bottom melting of lake ice and thermodynamic analysis[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(10): 1207−1215. [17] 艾润冰, 谢涛, 刘彬贤, 等. 基于气温的浮冰侧向融化速率参数化方案实验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(5): 150−158.Ai Runbing, Xie Tao, Liu Binxian, et al. An experimental study on parametric scheme of lateral melting rate of ice layer based on temperature[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(5): 150−158. [18] Tsamados M, Feltham D, Petty A, et al. Processes controlling surface, bottom and lateral melt of Arctic sea ice in a state of the art sea ice model[J]. Philosophical transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2015, 373(2052): 20140167. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2014.0167 [19] Bilello M A. Maximum thickness and subsequent decay of lake, river, and fast sea ice in Canada and Alaska[R]. Hanover: U. S. Army, Corps of Engineers, Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, 1980. [20] Josberger E G, Martin S. A laboratory and theoretical study of the boundary layer adjacent to a vertical melting ice wall in salt water[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1981, 111: 439−473. doi: 10.1017/S0022112081002450 -





 下载:
下载: