Analysis of the influence of temperature, salinity and depth variations on beam footprint coordinates
-
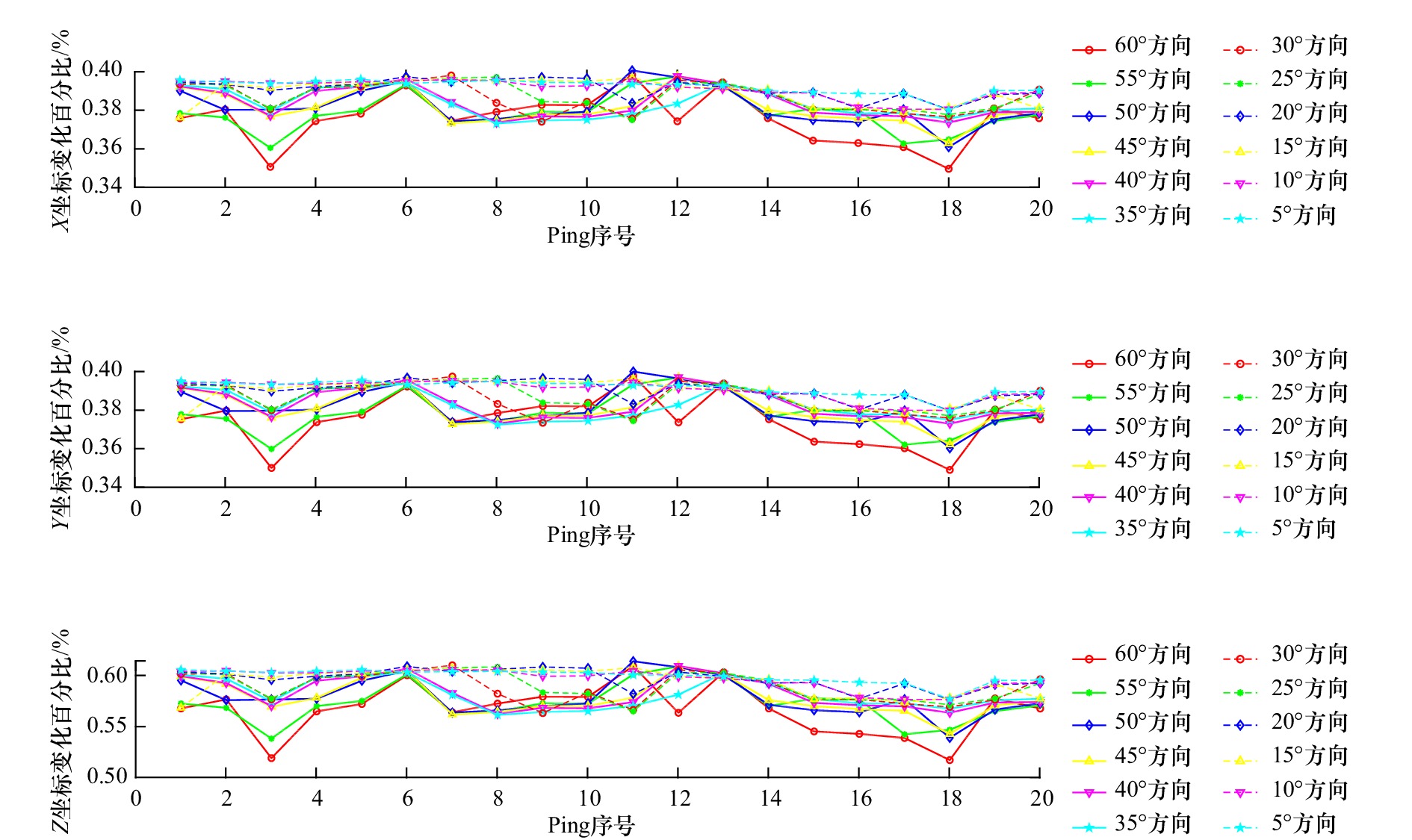
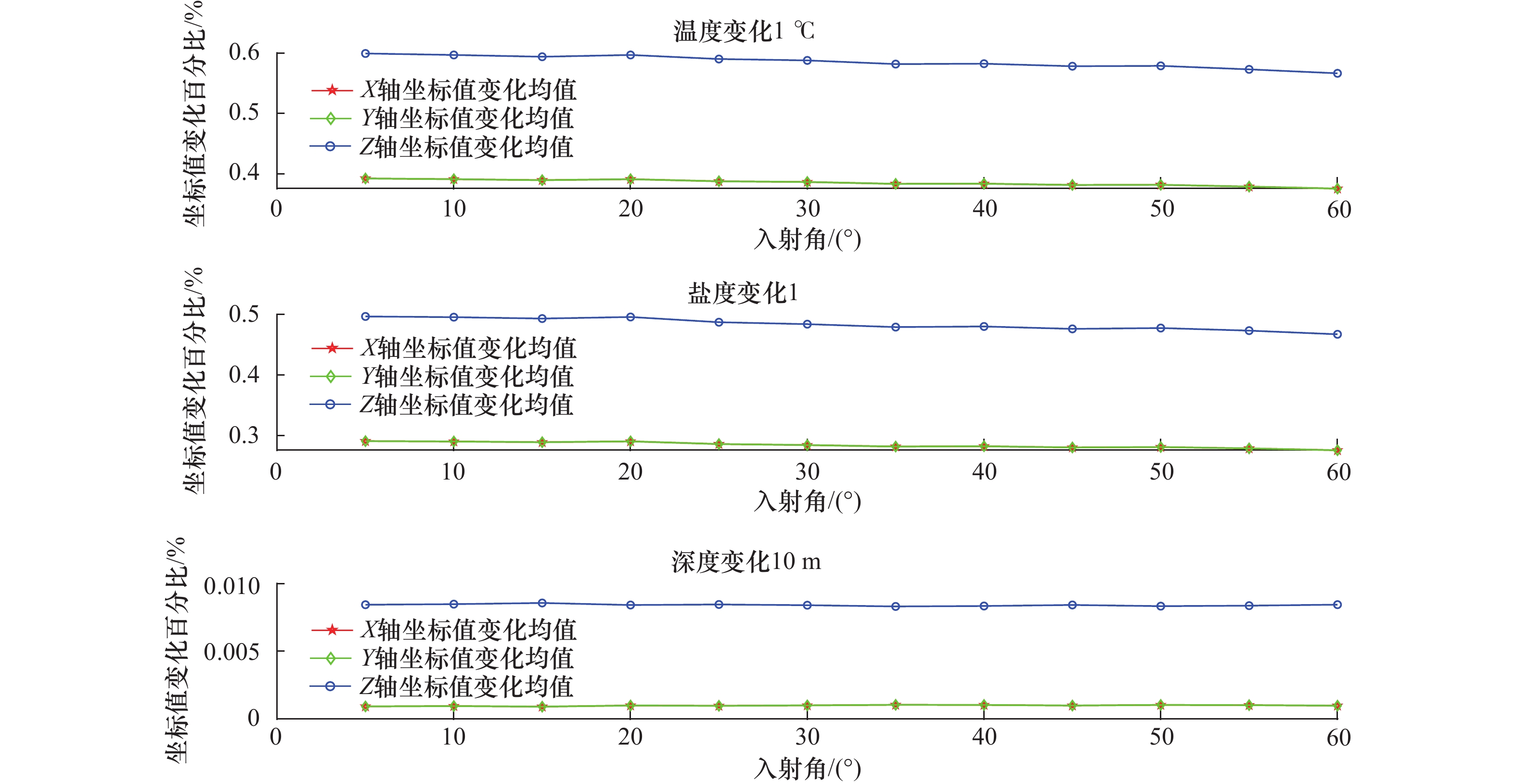
摘要: 在多波束测深中,温盐深剖面数据的准确性对测量精度起到非常重要的作用,而在实际测量中,温盐深误差又不可避免地存在。为了分析温盐深变化对波束脚印坐标的影响规律并将其影响值量化,本文在声速剖面间接测量数据的基础上,选择精度较高、适应性较强的声速经验公式推导其误差公式,计算温盐深变化所引起的声速误差值,并且在常梯度声线跟踪模型的基础上推导出声波旅行轨迹的水平位移和垂直位移误差公式,然后结合声速剖面计算出声速误差对波束脚印坐标的影响程度。实验结果表明,温度变化对声速的影响最大,盐度和深度依序次之;温度、盐度、深度3个参量的变化引起波束脚印Z坐标的变化量均大于X、Y坐标,最高可达变化前深度的0.6%。温度和盐度的变化引起的三轴坐标值变化量随入射角的增大而减小,而深度变化引起的三轴坐标值变化量几乎不随入射角的变化而变化。本文研究结果可为温盐深误差对多波束测深精度评估工作提供借鉴作用。Abstract: The multi-beam echo sounder is usually used in bathymetry activity, the accuracy of temperature, salinity and depth profile data play a very important role in the bathymetry. Unfortunately, those errors among the temperature, salinity and depth data were inevitably brought into the measurement. To analyze the influence of temperature, salinity and depth variations on beam footprint coordinates and quantify its influence value, then, on basis of the indirect measurement data of sound velocity profile, the empirical formula of sound velocity with high precision and strong adaptability were selected to deduce their error formula, and the error value of sound velocity caused by temperature, salinity and depth variation was calculated. On the basis of constant-gradient sound ray tracing model, the horizontal and vertical displacement error formulas of sound wave travel path were derived, and then the influence value of acoustic velocity error on beam footprint coordinates was calculated by combining with sound velocity profile. The experimental results show that temperature has the greatest influence on sound velocity, followed by salinity and depth. The variations of temperature, salinity and depth cause the Z-coordinate variation of the beam footprint to be larger than the X and Y coordinates, up to 0.6% of the depth before the change. The variation of three-dimensional coordinates caused by temperature and salinity decreases with the increase of incident angle, however, the variation of three-dimensional coordinates caused by depth hardly changes with the change of incident angle. The results of this paper can be used for reference to evaluate the accuracy of multi-beam bathymetry with temperature, salinity and depth error.
-
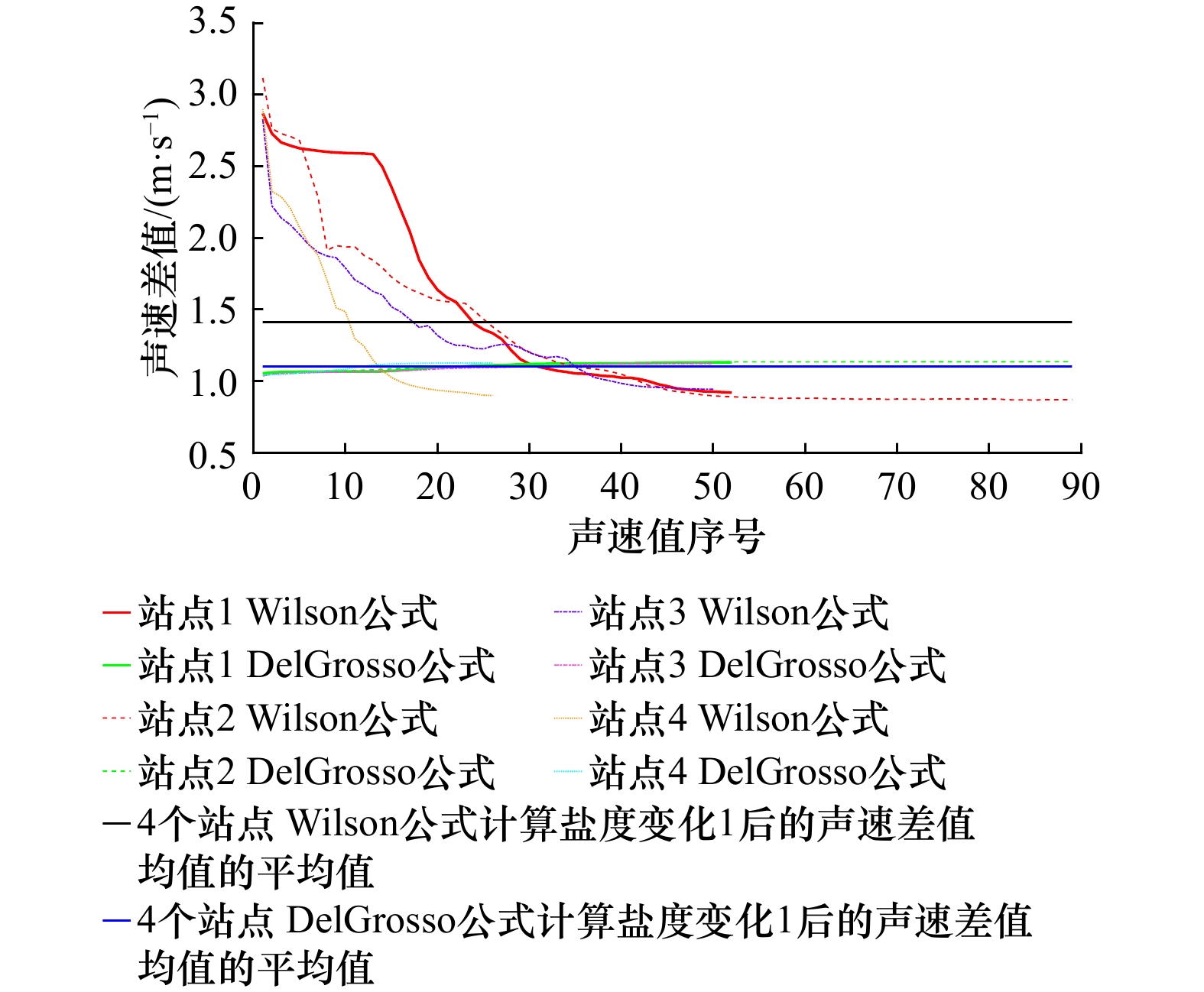
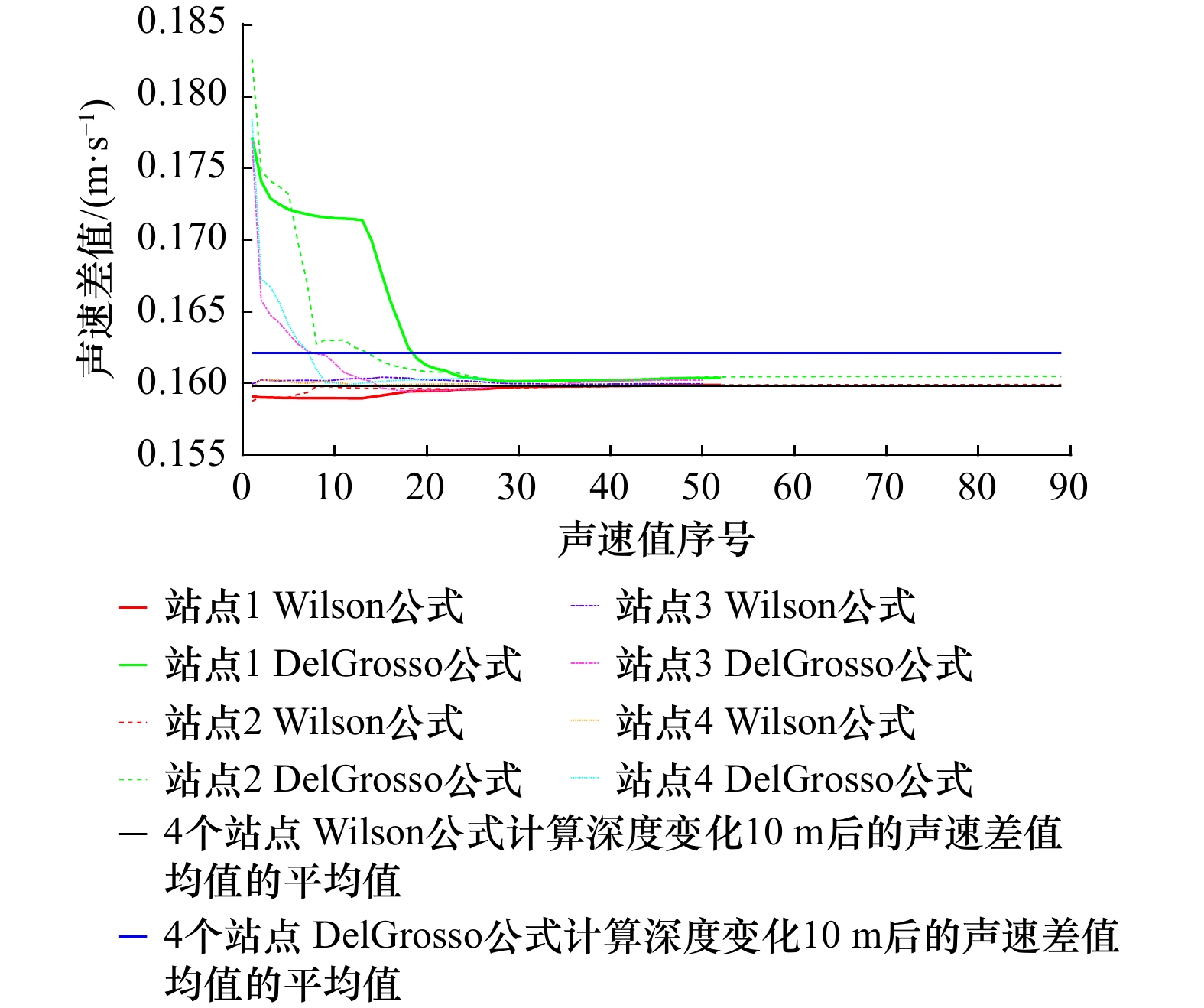
表 1 4个站点2种声速经验公式计算的声速变化均值
Tab. 1 The mean value of sound velocity variation calculated by two empirical sound velocity formulas at four stations
参量变化值 Wilson公式计算值/(m·s–1) DelGrosso公式计算值/(m·s–1) 温度变化1℃ 2.582 2.572 盐度变化1 1.408 1.102 深度变化10 m 0.160 0.162 -
[1] 肖付民, 黄毅, 张永厚, 等. 表层声速误差对多波束测深数据的影响分析[J]. 海洋测绘, 2021, 41(1): 27−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2021.01.006Xiao Fumin, Huang Yi, Zhang Yonghou, et al. Analysis of surface sound speed errors on multibeam sounding data[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2021, 41(1): 27−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2021.01.006 [2] 朱庆, 李德仁. 多波束测深数据的误差分析与处理[J]. 武汉测绘科技大学学报, 1998, 23(1): 1−4, 46.Zhu Qing, Li Deren. Error analysis and processing of multibeam soundings[J]. Journal of Wuhan Technical University of Surveying and Mapping, 1998, 23(1): 1−4, 46. [3] 朱小辰, 刘雁春, 肖付民, 等. 海道测量多波束声速改正精确模型研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2011, 31(1): 1−3, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.01.001Zhu Xiaochen, Liu Yanchun, Xiao Fumin, et al. Rigorous model of multibeam echosounding system sounding velocity correction[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2011, 31(1): 1−3, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2011.01.001 [4] 张志伟, 暴景阳, 肖付民, 等. 利用模拟退火算法反演多波束测量声速剖面[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版, 2018, 43(8): 1234−1241. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20160304Zhang Zhiwei, Bao Jingyang, Xiao Fumin, et al. Inversion of sound velocity profile in multibeam survey based on simulated annealing algorithm[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(8): 1234−1241. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20160304 [5] 杨永红, 王翠杰. 基于压强和深度的两种不同声速计算方法比较[J]. 海洋测绘, 2015, 35(3): 64−66.Yang Yonghong, Wang Cuijie. Comparison of two methods for calculating ocean sound speed profiles based on pressure and depth[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2015, 35(3): 64−66. [6] 吴碧, 陈长安, 林龙. 声速经验公式的适用范围分析[J]. 声学技术, 2014, 33(6): 504−507.Wu Bi, Chen Chang’an, Lin Long. Analysis of applicable scope of empirical equation for sound velocity[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2014, 33(6): 504−507. [7] 张启国, 陈献, 刘强. 远海多波束水深测量中声速剖面获取方法研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2019, 39(5): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.05.001Zhang Qiguo, Chen Xian, Liu Qiang. Research on the method of the sound speed profile acquisition in deep sea multi-beam sounding[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2019, 39(5): 1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2019.05.001 [8] 朱小辰, 肖付民, 刘雁春, 等. 表层声速对多波束测深影响的研究[J]. 海洋测绘, 2007, 27(2): 23−25, 29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2007.02.006Zhu Xiaochen, Xiao Fumin, Liu Yanchun, et al. Research on the influence of surface sound velocity in multibeam echo sounding[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2007, 27(2): 23−25, 29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2007.02.006 [9] 刘胜旋. 关于表层声速对多波束测深影响及改正的探讨[J]. 海洋测绘, 2009, 29(6): 26−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.06.007Liu Shengxuan. The correction and effect of surface sound velocity on the multibeam echosounding[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2009, 29(6): 26−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2009.06.007 [10] Meinen C S, Watts D R. Further evidence that the sound-speed algorithm of Del Grosso is more accurate than that of Chen and Millero[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1997, 102(4): 2058−2062. doi: 10.1121/1.419655 [11] Del Grosso V A. New equation for the speed of sound in natural waters (with comparisons to other equations)[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1974, 56(4): 1084−1091. doi: 10.1121/1.1903388 [12] Wilson W D. Speed of sound in sea water as a function of temperature, pressure, and salinity[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1960, 32(6): 641−644. doi: 10.1121/1.1908167 [13] 刘伯胜, 雷家煜. 水声学原理[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 1993: 23.Liu Bosheng, Lei Jiayu. Principles of Underwater Acoustics[M]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press, 1993: 23. [14] Barnard T E. Geometrically derived ray-theory results and direct verification of the pekeris solution for unbounded constant-gradient media[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2012, 37(2): 244−254. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2012.2188161 [15] Ogasawara H, Mori K, Nakamura T. Reciprocal sound propagation experiment in very shallow water area of hashirimizu port[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 49(7S): 07HG15. [16] Ramezani H, Jamali-Rad H, Leus G. Target localization and tracking for an isogradient sound speed profile[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(6): 1434−1446. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2235432 [17] 赵建虎, 刘经南. 多波束测深及图像数据处理[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2008: 125-127.Zhao Jianhu, Liu Jingnan. Multibeam Bathymetry and Image Data Process[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2008: 125−127. [18] 何林帮, 赵建虎, 张红梅, 等. 顾及姿态角的多波束声线精确跟踪方法[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2015, 36(1): 46−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.201312038He Linbang, Zhao Jianhu, Zhang Hongmei, et al. A precise multibeam sound ray tracking method taking into account the attitude angle[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2015, 36(1): 46−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.201312038 -





 下载:
下载: