Different growth of red Noctiluca scintillans from Pingtan coast waters feeding on several diet algae
-
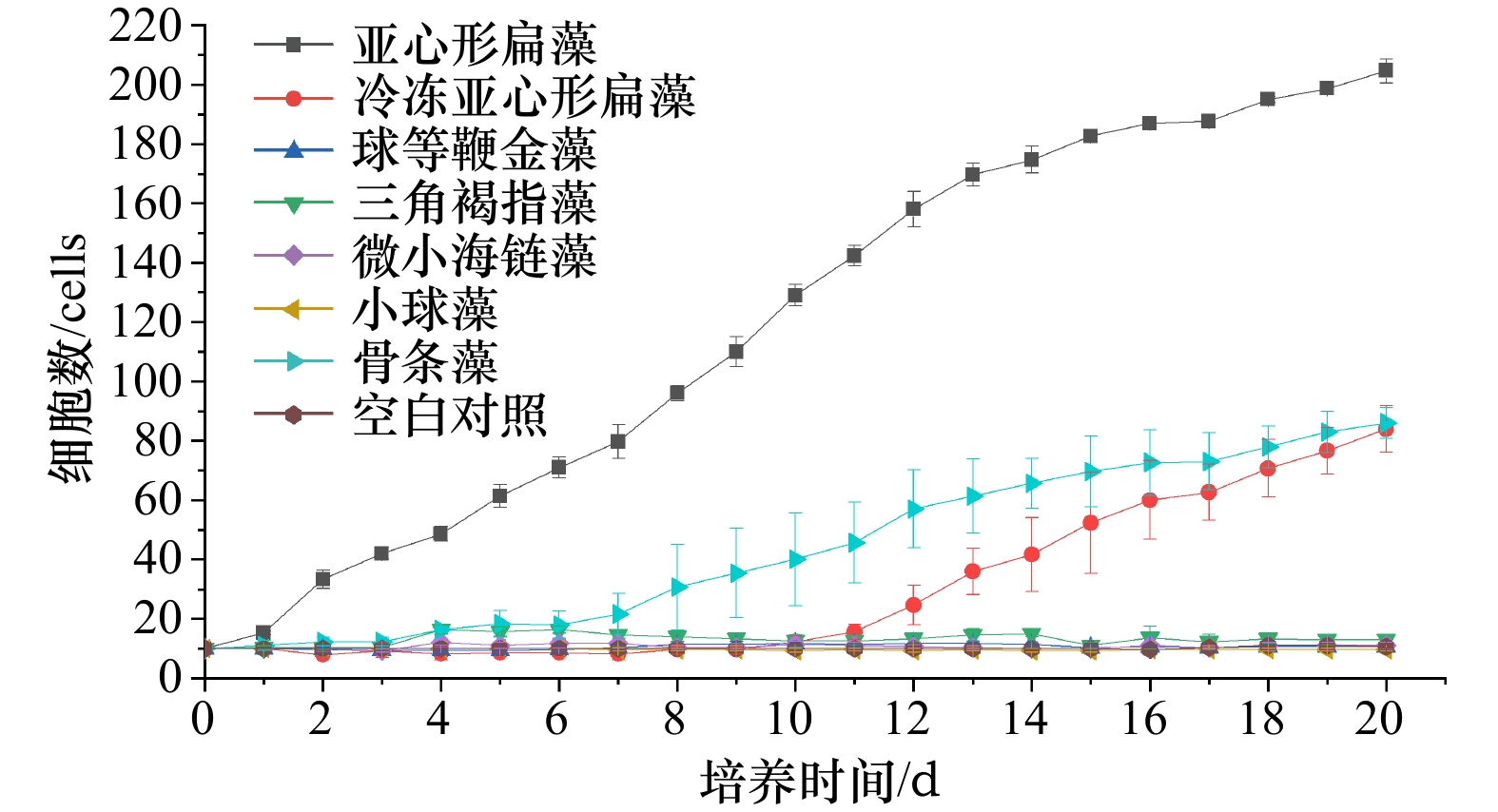
摘要: 夜光藻(Noctiluca scintillans)藻华是我国近海常见的生态灾害,其暴发机制尚不明确。为探究营养条件在其形成机制中的作用,本文分析了几种常见饵料藻与同海域硅藻培养下夜光藻的种群增长,同时探究模拟海水混合与营养盐水平对其种群增长的影响。结果发现,不同饵料藻培养下,夜光藻种群增长有着显著差异,其中亚心形扁藻(Platymonas subcordiformis)组中夜光藻的平均增长率为(0.151±0.001)d−1,远高于其他饵料藻。海水混合对夜光藻种群增长有一定的促进作用,模拟海水混合时,部分实验组中夜光藻增长率显著高于静置实验组,其中微小海链藻(Thalassiosira minima)培养下的夜光藻种群增长率为(0.136±0.001)d−1,远高于除亚心形扁藻以外的其他实验组。随着营养盐水平的增加,与亚心形扁藻共培养的夜光藻种群增长出现明显的先增强后减弱的趋势,拟合结果表明,其种群增长符合Boltzmann模型,并与营养盐水平相关。结果表明,海水混合与营养盐输入引起的平潭海域微藻的快速繁殖在当地夜光藻藻华的形成机制中可能起着重要的作用。Abstract: Blooms of red Noctiluca scintillans is an annual eco-disaster in coastal waters of China, but the mechanism of outbreak of N. scintillans is still unclear. To explore the role of nutrient conditions in the formation of N. scintillans blooms, the population growth of N. scintillans feeding several diet algae, including common diet algae and local diatoms, were investigated under standing water, mixing water and different inorganic nutrient levels. Results showed that there were significant differences in population growth of N. scintillans under different diets. Population growth of N. scintillans was fastest in Platymonas subcordiformis treatment, with growth rate of (0.151±0.001) d−1. N. scintillans growth significantly increased in mixing water when feeding on some diet algae. The population growth rate of N. scintillans in Thalassiosira minima treatment was (0.136±0.001) d−1, which was much higher than growth rate of N. scintillans in other algae treatment except in P. subcordiformis treatment. Growth rate and maximum population of N. scintillans cultured with P. subcordiformis firstly increased and then decreased with increasing inorganic nutrient levels, and results suggested that its growth fitted the Boltzmann model, with parameters were highly related to inorganic nutrients. Results indicated that proliferation of local diet algae, such as Thalassiosira species, leading by nutrients input in spring, combined with mixing of seawater, might play an important role in the formation of massive N. scintillans bloom in Pingtan coastal waters.
-
Key words:
- Noctiluca scintillans /
- population growth /
- bloom mechanism /
- inorganic nutrient levels
-
表 1 不同培养条件下夜光藻种群平均增长率
Tab. 1 Mean growth rate of Noctiluca scintillans feeding by different algal in standing and mixing simulated situation
饵料藻类 静置条件下增长率/d−1 海水混合条件下增长率/d−1 亚心形扁藻 0.151±0.001d 0. 152±0d 冷冻亚心形扁藻 0.106±0.005b 0.105±0.004b 球等鞭金藻 0.003±0.003a 0.101±0.002b 三角褐指藻 0.013±0.006a 0.101±0.004b 微小海链藻 0.005±0.005a 0.137±0.001c 小球藻 −0.002±0.003a −0.002±0.003a 骨条藻 0.108±0.003b 0.105±0.002b 空白对照(灭菌海水) 0.003±0.003a 0.000±0.005a 注:上标字母不同表示差异显著,p<0.05为显著。 表 2 夜光藻种群动态Boltzmann拟合参数
Tab. 2 Parameters of Boltzmann fitting on population dynamics of Noctiluca scintillans
f/2组 f/4组 f/8组 f/16组 f/32组 对照组 K/(cells·mL−1) 44.61±4.11 164.56±5.43 184.65±3.19 103.74±2.38 77.22±2.29 46.53±1.61 t0/d 12.67±0.88 11.05±0.31 7.79±0.17 7.19±0.20 6.96±0.31 6.48±0.36 dt 3.23±0.53 2.56±0.23 1.73±0.15 1.12±0.17 1.71±0.27 1.57±0.31 R2 0.929 3 0.979 1 0.983 3 0.961 9 0.942 9 0.912 5 表 3 夜光藻种群动态Boltzmann拟合参数与营养盐稀释倍数的拟合
Tab. 3 Fitting of dilution ratio with parameters of Boltzmann fitting on population dynamics of Noctiluca scintillans
拟合方式 拟合参数 R2 K 高斯 B=41.00±6.69 xc=0.36±0.01 w=0.32±0.02 A=72.76±5.76 0.994 0 t0 线性 a=6.57±0.39 b=6.57±0.82 0.941 7 dt 线性 c=1.38±0.18 d=1.90±0.38 0.863 0 -
[1] GEOHAB. Global ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms science plan[Z/OL]. [2021−10−19]. http://www.jodc.go.jp/info/ioc_doc/Other/124638e.pdf. [2] Glibert P M. Harmful algae at the complex nexus of eutrophication and climate change[J]. Harmful Algae, 2020, 91: 101583. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.03.001 [3] Xiao Xi, Agustí S, Pan Yaoru, et al. Warming amplifies the frequency of harmful algal blooms with eutrophication in Chinese coastal waters[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(22): 13031−13041. [4] Harrison P J, Furuya K, Glibert P M, et al. Geographical distribution of red and green Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2011, 29(4): 807−831. doi: 10.1007/s00343-011-0510-z [5] Piontkovski S A, Serikova I M, Evstigneev V P, et al. Seasonal blooms of the dinoflagellate algae Noctiluca scintillans: Regional and global scale aspects[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2021, 44: 101771. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101771 [6] Zhang Shuwen, Xia Xiaomin, Ke Ying, et al. Population dynamics and interactions of Noctiluca scintillans and Mesodinium rubrum during their successive blooms in a subtropical coastal water[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 755: 142349. [7] 胡翠林, 金海卫, 李振华, 等. 赤潮生物夜光藻的研究进展[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2015, 34(4): 379−386.Hu Cuilin, Jin Haiwei, Li Zhenhua, et al. Research advance of Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2015, 34(4): 379−386. [8] 自然资源部. 中国海洋灾害公报(1989–2020)[EB/OL]. [2021–10–01]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2020nzghyzhgb/, 1990–2021.Ministry of Natural Resources. Bulletin of China marine disaster 1989–2020[EB/OL]. [2021–10–01]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2020nzghyzhgb/, 1990–2021. [9] 梁玉波. 中国赤潮灾害调查与评价(1933–2009)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2012.Liang Yubo. Investigation and Evaluation of Red Tide in China 1933–2009[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2012. [10] Qi Lin, Tsai S F, Chen Yanlong, et al. In search of red Noctiluca scintillans blooms in the East China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(11): 5997−6004. doi: 10.1029/2019GL082667 [11] Wang Weicheng, Sun Song, Sun Xiaoxia, et al. Seasonal phenology of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney) in Jiaozhou Bay and adjacent coastal Yellow Sea, China[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2018, 36(4): 1280−1293. doi: 10.1007/s00343-018-6350-3 [12] Liu Lusan, Zhou Juan, Zheng Binghui, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of red tide outbreaks in the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent waters, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2013, 72(1): 213−221. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.04.002 [13] 钱宏林. 广东沿海的赤潮生物与赤潮研究[C]//第一届中国赤潮研究与防治学术研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国海洋学会, 2005.Qian Honglin. The red tide organisms and red tide study of the coastal waters of Guangdong[C]//Proceedings of the First Symposium of Red Tide Research and Control of China. Beijing: Chinese Society of Oceanography, 2005. [14] Raj K D, Mathews G, Obura D O, et al. Low oxygen levels caused by Noctiluca scintillans bloom kills corals in Gulf of Mannar, India[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 22133. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79152-x [15] 马继先, 于学颖, 李丽芳, 等. 钦州湾海域夜光藻赤潮发生区水文气象因子变化研究[J]. 广东化工, 2017, 44(7): 90−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2017.07.040Ma Jixian, Yu Xueying, Li Lifang, et al. Study on the change of environmental factors during Noctiluca scintillans red tide in Qinzhou Bay[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2017, 44(7): 90−92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2017.07.040 [16] 付仲, 侯雁彬, 郗艳娟, 等. 秦皇岛海域夜光藻种群密度与环境因子的关系[J]. 河北渔业, 2015(10): 31−35, 82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2015.10.009Fu Zhong, Hou Yanbin, Xi Yanjuan, et al. Study on the relationship between population density of Noctiluca scintillans and environmental factors in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2015(10): 31−35, 82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2015.10.009 [17] 黄长江, 齐雨藻. 南海大鹏湾夜光藻种群生态及其赤潮成因分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1997, 28(3): 245−255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1997.03.004Huang Changjiang, Qi Yuzao. The population ecology and causative mechanisms of red tide of Noctiluca scintillans in Dapeng Bay, the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1997, 28(3): 245−255. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1997.03.004 [18] Sarma V V S S, Patil J S, Shankar D, et al. Shallow convective mixing promotes massive Noctiluca scintillans bloom in the northeastern Arabian Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 138: 428−436. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.11.054 [19] 万艳. 适宜平潭海域夜光藻赤潮发生的水温和气象条件统计分析[J]. 海洋预报, 2020, 37(6): 65−73.Wan Yan. Statistical analysis of water temperature and meteorological conditions favorable for the occurrence of Noctiluca scintillans red tide in Pingtan sea area[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2020, 37(6): 65−73. [20] Xiang Chenhui, Tan Yehui, Zhang Huangchen, et al. The key to dinoflagellate (Noctiluca scintillans) blooming and outcompeting diatoms in winter off Pakistan, northern Arabian Sea[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 694: 133396. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.202 [21] 田达玮, 宋书群, 陈田田, 等. 胶州湾夜光藻种群动态及其大量繁殖的生态机制[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2017, 48(2): 276−284.Tian Dawei, Song Shuqun, Chen Tiantian, et al. Noctiluca scintillans blooming in the Jiaozhou Bay: population dynamics and ecological mechanism[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2017, 48(2): 276−284. [22] 尹翠玲, 张秋丰, 邹涛, 等. 渤海湾天津近岸海域夜光藻赤潮生消过程初探[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2013(2): 99−104.Yin Cuiling, Zhang Qiufeng, Zou Tao, et al. Analysis for Noctiluca scintillans red tide in Bohai Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013(2): 99−104. [23] Nishitani G, Shiromoto M, Sato-Okoshi W, et al. Molecular approach for analysis of in situ feeding by the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Harmful Algae, 2020, 99: 101928. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101928 [24] Kitatsuji S, Yamaguchi H, Asahi T, et al. Does Noctiluca scintillans end the diatom bloom in coastal water?[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 2019, 510: 10−14. doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2018.09.006 [25] Hallegraeff G M, Albinsson M, Dowdney J, et al. Prey preference, environmental tolerances and ichthyotoxicity by the red-tide dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans cultured from Tasmanian waters[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2019, 41(4): 407−418. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbz037 [26] Stauffer B A, Gellene A G, Rico D, et al. Grazing of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans on dinoflagellate and raphidophyte prey[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 2017, 80(2): 193−207. doi: 10.3354/ame01849 [27] Zhang Shuwen, Liu Hongbin, Guo Cui, et al. Differential feeding and growth of Noctiluca scintillans on monospecific and mixed diets[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2016, 549: 27−40. doi: 10.3354/meps11702 [28] 吴玉霖, 周成旭, 张永山. 夜光藻的室内培养[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(2): 165−167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.009Wu Yulin, Zhou Chengxu, Zhang Yongshan. Laboratory culture of Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney)[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(2): 165−167. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.009 [29] 周成旭, 吴玉霖, 邹景忠. 夜光藻的营养动力学[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1994, 25(2): 152−157. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.006Zhou Chengxu, Wu Yulin, Zou Jingzhong. Nutrient dynamics of Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney)[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1994, 25(2): 152−157. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1994.02.006 [30] Guillard R R, Ryther J H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella Nana Hustedt, and Detonula Confervacea (Cleve) Gran[J]. Canada Journal of Microbiology, 1962, 8: 229−239. doi: 10.1139/m62-029 [31] 孙军, 刘东艳. 浮游植物生物量研究: I. 浮游植物生物量细胞体积转化法[J]. 海洋学报, 1999, 21(2): 75−85.Sun Jun, Liu Dongyan. Study on phytoplankton biomass I. Phytoplankton measurement biomass from cell volume or plasma volume[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1999, 21(2): 75−85. [32] 徐韧, 沈竑, 王桂兰, 等. 夜光藻的实验室培养及对其带触手二分裂现象的观察[J]. 水产学报, 1995, 19(3): 268−271.Xu Ren, Shen Hong, Wang Guilan, et al. Laboratory culture and observation of equal binary fission with tentacle in Noctiluca scintillans (Macartney)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 1995, 19(3): 268−271. [33] Buskey E J. Growth and bioluminescence of Noctiluca scintillans on varying algal diets[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1995, 17(1): 29−40. doi: 10.1093/plankt/17.1.29 [34] Nakamura Y. Growth and grazing of a large heterotrophic dinoflagellate, Noctiluca scintillans, in laboratory cultures[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 1998, 20(9): 1711−1720. doi: 10.1093/plankt/20.9.1711 [35] Gomes H D R, McKee K, Mile A, et al. Influence of light availability and prey type on the growth and photo-physiological rates of the mixotroph Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5: 374. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00374 [36] Zhang Shuwen, Liu Hongbin, Chen Bingzhang, et al. Effects of diet nutritional quality on the growth and grazing of Noctiluca scintillans[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2015, 527: 73−85. doi: 10.3354/meps11219 [37] Uhlig G, Sahling G. Long-term studies on Noctiluca scintillans in the German Bight population dynamics and red tide phenomena 1968–1988[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1990, 25(1/2): 101−112. [38] Omori M, Hamner W M. Patchy distribution of zooplankton: Behavior, population assessment and sampling problems[J]. Marine Biology, 1982, 72(2): 193−200. doi: 10.1007/BF00396920 [39] 董婧, 王文波, 刘海映. 辽宁近海浮游植物与夜光藻赤潮的关系[J]. 水产科学, 2000, 19(1): 17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2000.01.004Dong Jing, Wang Wenbo, Liu Haiying. Relation between red tide caused by Notiluca scienllans and phytoplankton at sea near Liaoning[J]. Fisheries Science, 2000, 19(1): 17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2000.01.004 [40] Sato N E, Hernández D, Viñas M D. Feeding habits of Noctiluca scintillans in coastal waters off Buenos Aires Province, Argentina[J]. Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research, 2010, 38(3): 403−412. [41] Zhang Shuwen, Harrison P J, Song Shuqun, et al. Population dynamics of Noctiluca scintillans during a bloom in a semi-enclosed bay in Hong Kong[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 121(1/2): 238−248. -





 下载:
下载: