Observation of physical variables of coastal wetland and response of wetland system under the influence of typhoon process
-
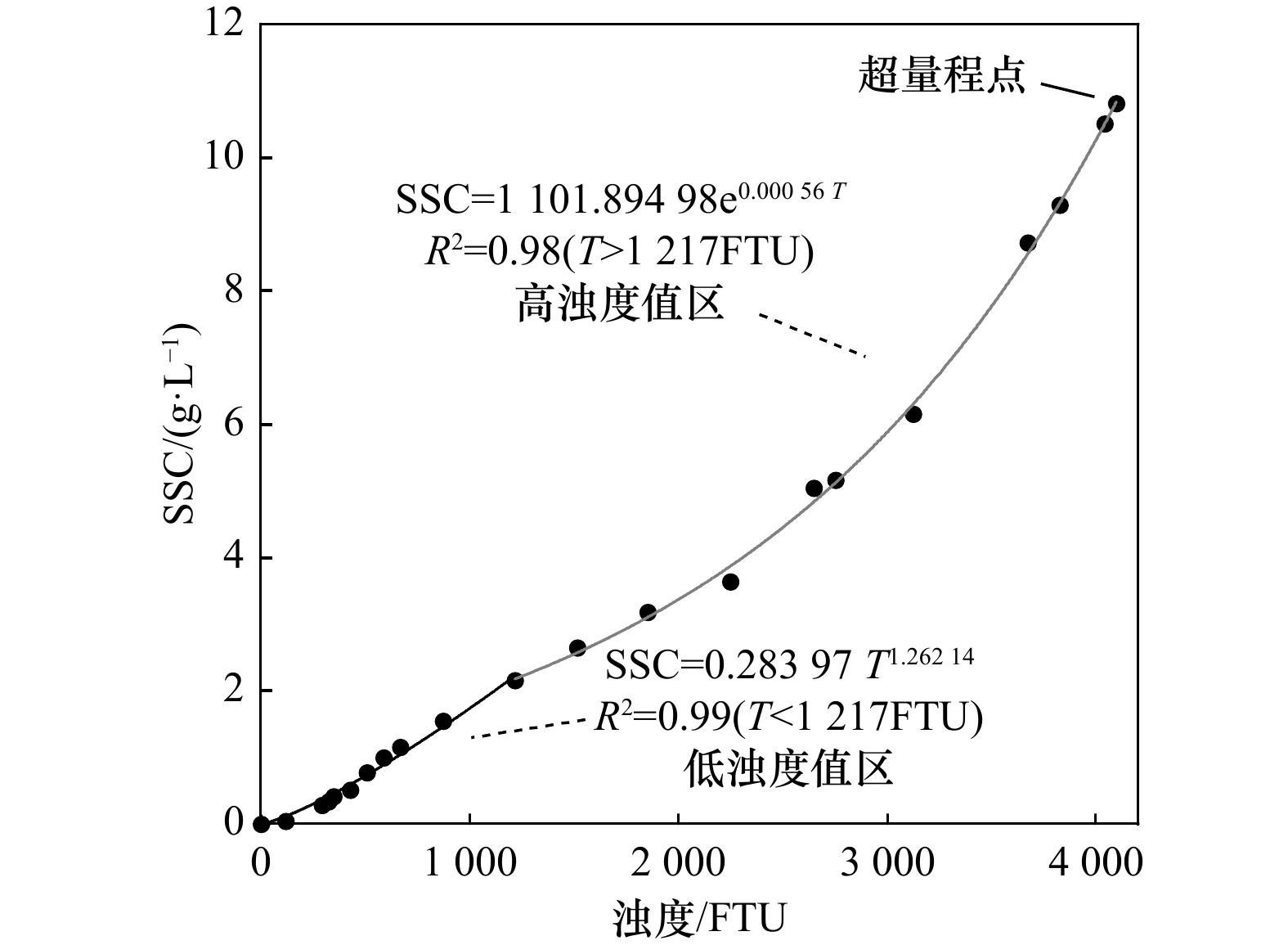
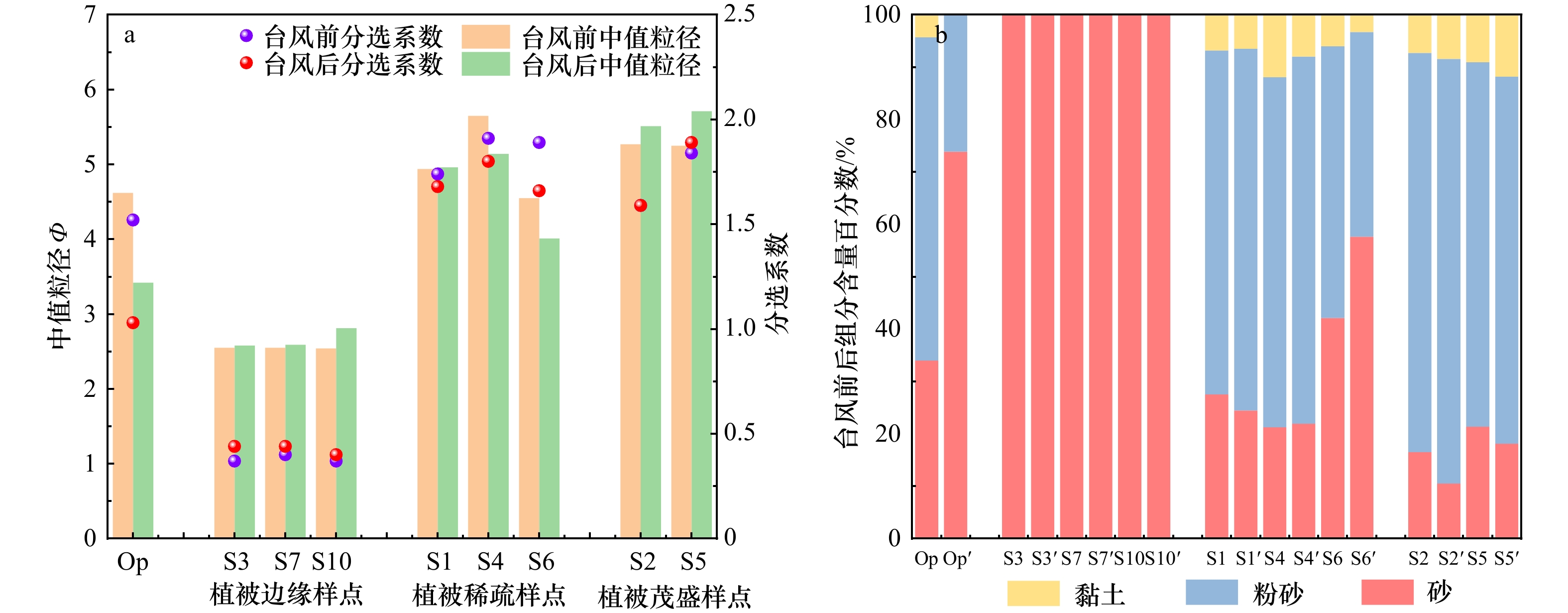
摘要: 如何研究台风等极端天气事件影响下的湿地系统响应过程,进而提出有效的生态完整性维护和管理方案,对关键区域的湿地管理及生态安全维护具有重要意义。本文于2021年9月“灿都”台风期间在南汇东滩南岸设置水动力观测点,采集表层沉积物、测量滩面高程并用无人机获得植被影像,运用ArcGIS空间分析,探讨了台风过程影响下的南汇东滩水动力、滩面沉积变化与植被分布面积响应。结果表明:台风中,观测点近底层平均流速为0.23 m/s,植被边缘平均有效波高和波能是台风前后的1.54倍和2.14倍,近底层1 m的滩面出现“高悬沙浓度层”(>10 g/L)且存在时长为8.13 h。台风后高程低于4 m的稀疏海三棱藨草和互花米草滩面侵蚀0~4.8 cm,高程高于4 m的茂盛互花米草和芦苇滩面淤积0~14.7 cm;研究区植被分布面积共减少1 827.67 m2,减少量占台风前植被总量的1.63%,其中侵蚀滩面植被分布面积减少31.9%,淤积滩面减少68.1%。对台风过程影响后的湿地管理,可以总结为:(1)湿地在台风过程后滩面基本表现为明显的侵蚀、淤积区域共存的特征;(2)对高程低于4 m的侵蚀滩面,建议确定植被适宜生长的高程,结合台风过程冲淤变化通过“微生物膜”和植被斑块移植的方法消浪、固滩和促淤,加速湿地在台风过程影响后的修复。Abstract: How to study the response process of wetland system under the influence of extreme weather events such as typhoon, and then put forward effective ecological integrity maintenance and management schemes is of great significance to wetland management and ecological security maintenance in key areas. In this paper, during the process of “Chanthu” Typhoon in September 2021, hydrodynamic observation points were set up on the South Bank of Nanhui east tidal flat, surface sediments were collected, tidal flat surface elevation was measured, and vegetation images were obtained by unmanned aerial vehicle. Using ArcGIS spatial analysis, the hydrodynamic and sedimentary changes of Nanhui east tidal flat and the response of tidal flat surface elevation, surface sediments and vegetation distribution area were discussed. The results show that the average effective wave height and wave energy at the edge of the vegetation are 1.54 times and 2.14 times in the typhoon, the average current velocity near the bottom layer is 0.23 m/s, and a “high suspended sediment concentration layer” (>10 g/L) with a thickness of more than 1 m appears on the tidal flat for 8.13 h. After the typhoon, the tidal flat surface of Scirpus mariqueter and Spartina alterniflora distributed sparsely below 4 m eroded 0−4.8 cm, and the tidal flat surface with lush growth of Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis above 4 m deposited 0−14.7 cm. The distribution area of vegetation in the study area decreased by 1827.67 m2, accounting for 1.63% of the total vegetation before the typhoon, including 31.9% of the eroded tidal flat vegetation and 68.1% of the deposited tidal flat vegetation. The wetland management after the typhoon process can be summarized as follows: (1) The wetland basically shows the characteristics of coexistence of erosion and accretion areas after the typhoon process; (2) For the tidal flat surface with an elevation lower than 4 m, it is suggested to determine the elevation suitable for vegetation growth, combine the erosion and deposition changes during the typhoon process, and use the “microbial film” and vegetation patch transplantation to dissipate waves, consolidate the tidal flat and promote accretion, so as to accelerate the rapid restoration of the wetland after the impact of the typhoon process.
-
Key words:
- typhoon /
- coastal wetlands /
- hydrodynamic force /
- deposition /
- response process
-
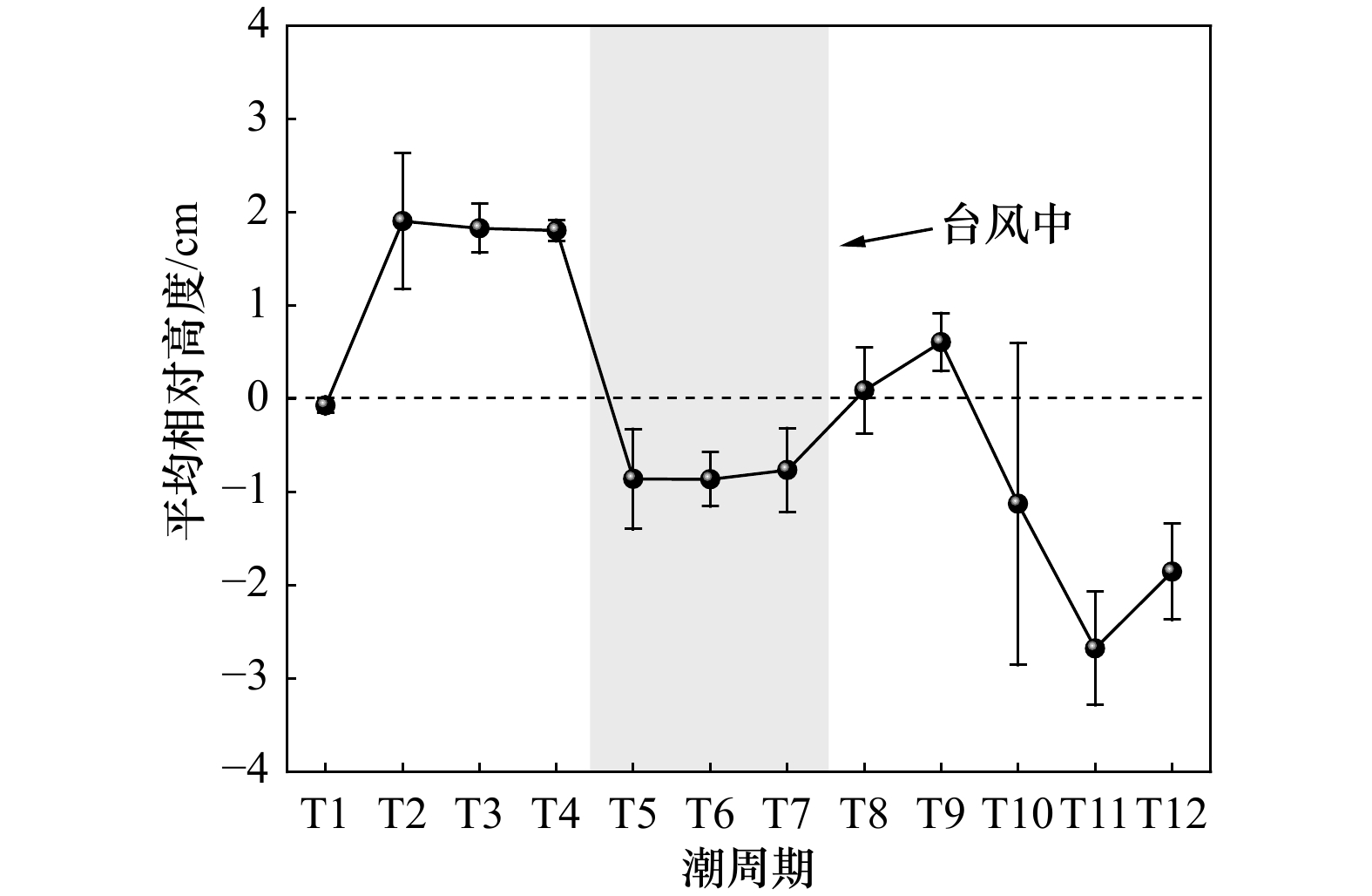
图 4 台风过程气象及近底层水动力和沉积变化
a. 风向风速、海平面气压、降水量图;b. T1−T12潮周期水动力观测点水深、流速和流向;c. 植被边缘观测点有效波高和波能;d. 悬沙浓度剖面变化过程。灰色区域为台风中
Fig. 4 Meteorological and near bottom hydrodynamic and sedimentary changes during typhoon
a. Wind direction, wind speed, sea level pressure and precipitation; b. water depth, velocity and direction at hydrodynamic observation points of T1−T12 tidal cycle; c. significant wave height and wave energy at observation points on the edge of vegetation; d. variation process of suspended sediment concentration profile. The gray area is in typhoon
-
[1] Chen Chen, Ma Yi, Ren Guangbo, et al. Aboveground biomass of salt-marsh vegetation in coastal wetlands: sample expansion of in situ hyperspectral and Sentinel-2 data using a generative adversarial network[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2022, 270: 112885. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112885 [2] Breithaupt J L, Hurst N, Steinmuller H E, et al. Comparing the biogeochemistry of storm surge sediments and pre-storm soils in coastal wetlands: hurricane Irma and the Florida everglades[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2020, 43(5): 1090−1103. doi: 10.1007/s12237-019-00607-0 [3] Crosby S C, Sax D F, Palmer M E, et al. Salt marsh persistence is threatened by predicted sea-level rise[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 181: 93−99. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.018 [4] 陈崇贤, 刘京一. 气候变化影响下国外沿海城市应对海平面上升的景观策略与启示[J]. 风景园林, 2020, 27(12): 32−37. doi: 10.14085/j.fjyl.2020.12.0032.06Chen Chongxian, Liu Jingyi. Landscape strategies and enlightenment of foreign coastal cities to cope with sea level rise under impact of climate change[J]. Landscape Architecture, 2020, 27(12): 32−37. doi: 10.14085/j.fjyl.2020.12.0032.06 [5] Razi M A M, Daud H Z B H, Mokhtar A, et al. Climate change, tsunami and biodiversity endangered at the South China Sea, past, current and prediction models for the future: a comprehensive study[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2022, 175: 113255. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113255 [6] IPCC Working Groupi. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis-conclusions[J]. Bulletin fur Angewandte Geologie, 2013, 18(2): 5−19. [7] Turner R E, Baustian J J, Swenson E M, et al. Wetland sedimentation from hurricanes Katrina and Rita[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5798): 449−452. doi: 10.1126/science.1129116 [8] Mo Yu, Kearney M S, Turner R E. The resilience of coastal marshes to hurricanes: the potential impact of excess nutrients[J]. Environment International, 2020, 138: 105409. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105409 [9] Douglas S H, Bernier J C, Smith K E L. Analysis of multi-decadal wetland changes, and cumulative impact of multiple storms 1984 to 2017[J]. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 2018, 26(6): 1121−1142. doi: 10.1007/s11273-018-9635-6 [10] Do K, Yoo J. Morphological response to storms in an embayed beach having limited sediment thickness[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 234: 106636. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106636 [11] Aung T T, Mochida Y, Than M M. Prediction of recovery pathways of cyclone-disturbed mangroves in the mega delta of Myanmar[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2013, 293: 103−113. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2012.12.034 [12] 王爱军, 叶翔, 李云海. 台风期间港湾海岸湿地侵蚀、淤积的环境动力学机制初探——以福建罗源湾为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(2): 315−324. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2013.02.010Wang Aijun, Ye Xiang, Li Yunhai. Environmental dynamic mechanisms for sediment erosion and accretion over embayment coastal wetland during typhoon event: a case study from Luoyuan Bay, Fujian China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(2): 315−324. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2013.02.010 [13] Yang Shilun, Friedrichs C T, Shi Zhong, et al. Morphological response of tidal marshes, flats and channels of the outer Yangtze River Mouth to a major storm[J]. Estuaries, 2003, 26(6): 1416−1425. doi: 10.1007/BF02803650 [14] Wu Mingxuan, Hu Yang, Wu Pengling, et al. Does soil pore water salinity or elevation influence vegetation spatial patterns along coasts? a case study of restored coastal wetlands in Nanhui, Shanghai[J]. Wetlands, 2020, 40(6): 2691−2700. doi: 10.1007/s13157-020-01366-6 [15] 陈沈良, 张国安, 谷国传. 长江口南汇边滩的演变及其沉积动力机制[J]. 上海地质, 2003, 4: 1−4.Chen Shenliang, Zhang Guoan, Gu Guochuan. Geomorphic evolution of Nanhui nearshore of the Yangtze Estuary and its sediment dynamic mechanism[J]. Shanghai Geology, 2003, 4: 1−4. [16] 赵建春, 李九发, 李占海, 等. 长江口南汇嘴潮滩短期冲淤演变及其动力机制研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(4): 103−111.Zhao Jianchun, Li Jiufa, Li Zhanhai, et al. Researches on characteristics and dynamic mechanism of short-term scouring and silting changes of the tidal flat on Nanhui Spit in the Changjiang Estuary in China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2009, 31(4): 103−111. [17] 丁平兴, 葛建忠. 长江口横沙浅滩及邻近海域灾害性天气分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 4: 72−78.Ding Pingxing, Ge Jianzhong. Analysis of disastrous weather in the Hengsha Shoal and adjacent waters of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2013, 4: 72−78. [18] 郜昂, 赵华云, 杨世伦, 等. 径流、潮流和风浪共同作用下近岸悬沙浓度变化的周期性探讨——以杭湾和长江口交汇处的南汇嘴为例[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2008, 26(1): 44−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2008.01.006Gao Ang, Zhao Huayun, Yang Shilun, et al. Seasonal and tidal variations in suspended sediment concentration under the influence of river runoff, tidal current and wind waves—taking the Nanhui headland, the joint area between Changjiang Estuary and Hangzhou Bay as an example[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2008, 26(1): 44−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2008.01.006 [19] Chen Dezhi, Li Mingliang, Zhang Yiyi, et al. Effects of diatoms on erosion and accretion processes in saltmarsh inferred from field observations of hydrodynamic and sedimentary processes[J]. Ecohydrology, 2020, 13(8): e2246. doi: 10.1002/eco.2246 [20] 马烨贝, 戴志军, 庞文鸿, 等. 崇明岛南侧盐沼潮滩消能状态研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2021, 39(5): 162−170. doi: 10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2021.05.017Ma Yebei, Dai Zhijun, Pang Wenhong, et al. Research on the wave energy dissipation over salt marsh tidal flat in the south of Chongming Island[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(5): 162−170. doi: 10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2021.05.017 [21] 周晓妍, 戴志军, 庞文鸿, 等. ASM-Ⅳ仪器在河口近底层悬沙浓度观测分析中的应用研究[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2020, 39(2): 221−228. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2020.02.009Zhou Xiaoyan, Dai Zhijun, Pang Wenhong, et al. Application study of ASM-IV instrument at the near-bed suspended sediment concentration measurement in estuary[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 221−228. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2020.02.009 [22] Chen Yining, Li Yan, Thompson C, et al. Differential sediment trapping abilities of mangrove and saltmarsh vegetation in a subtropical estuary[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 318: 270−282. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.018 [23] 魏晓, 汪亚平, 杨旸, 等. 浅海悬沙浓度观测方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(1): 161−170.Wei Xiao, Wang Yaping, Yang Yang, et al. Suspended sediment concentrations in shallow sea: comparative study of methods[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(1): 161−170. [24] 刘建华, 陈沈良, 杨世伦, 等. 长江口门附近海域潮周期内悬沙质量浓度变化及其动力机制探讨[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2014, 32(2): 188−199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.02.008Liu Jianhua, Chen Shenliang, Yang Shilun, et al. Study on the change of suspended sediment concentration during tidal cycle and its dynamic mechanism near the Changjiang Estuary[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2014, 32(2): 188−199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2014.02.008 [25] 张文祥, 杨世伦. OBS浊度标定与悬沙浓度误差分析[J]. 海洋技术, 2008, 27(4): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2008.04.002Zhang Wenxiang, Yang Shilun. Turbidity calibration of OBS and errors analysis of suspended sediment concentration[J]. Ocean Technology, 2008, 27(4): 5−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2029.2008.04.002 [26] Lemmin U, Lhermitte R, Nikora V I, et al. ADV measurements of turbulence: can we improve their interpretation?[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 1999, 125(9): 987−988. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1999)125:9(987) [27] 钟纯怿, 张俊波, 杨振昊, 等. 基于三维相空间法和稳健估算法的ADV流速数据后置处理效果研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(8): 152−159.Zhong Chunyi, Zhang Junbo, Yang Zhenhao, et al. Research on the detection effect of post-processing method of Acoustic Doppler Velocimetry data based on three-dimensional phase space thresholding method and robust estimation method[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(8): 152−159. [28] Fang Shubo, Jia Xiaobo, Qian Qingteng, et al. Reclamation history and development intensity determine soil and vegetation characteristics on developed coasts[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 586: 1263−1271. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.133 [29] Zhu Qin, van Prooijen B C, Maan D C, et al. The heterogeneity of mudflat erodibility[J]. Geomorphology, 2019, 345: 106834. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.106834 [30] 侯俊, 王超, 王沛芳, 等. 太湖表层沉积物粒度组成时空分布特征及分类命名[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(2): 114−119.Hou Jun, Wang Chao, Wang Peifang, et al. Temporal variability and spatial distribution of granulometric composition of surface sediments and classification in Taihu Lake[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2013, 41(2): 114−119. [31] 刘志杰, 公衍芬, 周松望, 等. 海洋沉积物粒度参数3种计算方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(3): 179−188.Liu Zhijie, Gong Yanfen, Zhou Songwang, et al. A comparative study on the grain-size parameters of marine sediments derived from three different computing methods[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2013, 35(3): 179−188. [32] 张锦明, 郭丽萍, 张小丹. 反距离加权插值算法中插值参数对DEM插值误差的影响[J]. 测绘科学技术学报, 2012, 29(1): 51−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2012.01.013Zhang Jinming, Guo Liping, Zhang Xiaodan. Effects of interpolation parameters in inverse distance weighted method on DEM accuracy[J]. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2012, 29(1): 51−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6338.2012.01.013 [33] 满卫东, 王宗明, 刘明月, 等. 1990−2013年东北地区耕地时空变化遥感分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 34(7): 1−10. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.07.001Man Weidong, Wang Zongming, Liu Mingyue, et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics analysis of cropland in Northeast China during 1990−2013 based on remote sensing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 34(7): 1−10. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2016.07.001 [34] 朱琴. 基于现场观测和数值模拟的淤泥质潮滩沉积动力过程研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2017.Zhu Qin. Sediment dynamics on intertidal mudflats: a study based on in situ measurements and numerical modelling[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2017. [35] 苗丽敏, 杨世伦, 朱琴, 等. 风暴过程中潮滩悬沙浓度和悬沙输运的变化及其动力机制——以长江三角洲南汇潮滩为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(5): 158−167.Miao Limin, Yang Shilun, Zhu Qin, et al. Variations of suspended sediment concentrations and transport in response to a storm and its dynamic mechanism—A study case of Nanhui tidal flat of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(5): 158−167. [36] Wang Teng, Liu Guangpeng, Gao Lei, et al. Biological and nutrient responses to a typhoon in the Yangtze Estuary and the adjacent sea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2016, 32(2): 323−332. [37] Wang Feifei, Yu Zhigang, Xu Bochao, et al. Nepartak typhoon influenced bottom sediments from the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent East China Sea-foraminiferal evidence[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2018, 19(4): 1049−1063. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007413 [38] 王浩斌, 杨世伦, 杨海飞. 台风对长江口表层悬沙浓度的影响[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2019(2): 195−208.Wang Haobin, Yang Shilun, Yang Haifei. A study of the surficial suspended sediment concentration in response to typhoons in the Yangtze Estuarys[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2019(2): 195−208. [39] 高抒, 贾建军, 于谦. 绿色海堤的沉积地貌与生态系统动力学原理: 研究综述[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 1−19. doi: 10.11978/YG2021002Gao Shu, Jia Jianjun, Yu Qian. Green sea dykes: an overview of their principles of sediment, geomorphology and ecosystem dynamics[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 1−19. doi: 10.11978/YG2021002 [40] Wang Xuming, Wang Weiqi, Tong Chuan. A review on impact of typhoons and hurricanes on coastal wetland ecosystems[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(1): 23−29. doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2015.12.006 [41] Héquette A, Hemdane Y, Anthony E J. Sediment transport under wave and current combined flows on a tide-dominated shoreface, northern coast of France[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 249(3/4): 226−242. [42] 王爱军, 叶翔, 陈坚. 台风作用下的港湾型潮滩沉积过程以2008年“凤凰”台风对福建省罗源湾的影响为例[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(6): 77−86.Wang Aijun, Ye Xiang, Chen Jian. Effects of typhoon on sedimentary processes of embayment tidal flat a case study from the “Fenghuang” typhoon in 2008[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2009, 31(6): 77−86. [43] Wang Xianye, Xie Weiming, Zhang D, et al. Wave and vegetation effects on flow and suspended sediment characteristics: a flume study[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2016, 182: 1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2016.09.009 [44] Yang Wankang, Feng Xingru, Yin Baoshu. The impact of coastal reclamation on tidal and storm surge level in Sanmen Bay, China[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019, 37(6): 1971−1982. doi: 10.1007/s00343-019-8247-1 [45] Leonardi N, Carnacina I, Donatelli C, et al. Dynamic interactions between coastal storms and salt marshes: a review[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 301: 62−107. [46] Lagomasino D, Fatoyinbo T, Castañeda-Moya E, et al. Storm surge and ponding explain mangrove dieback in Southwest Florida following Hurricane Irma[J]. Nature Communications 2021, 12(1): 4003. [47] Smith T J, Anderson G H, Balentine K, et al. Cumulative impacts of hurricanes on Florida mangrove ecosystems: sediment deposition, storm surges and vegetation[J]. Wetlands, 2009, 29(1): 24−34. doi: 10.1672/08-40.1 [48] Castagno K A, Tomiczek T, Shepard C C, et al. Resistance, resilience, and recovery of salt marshes in the Florida Panhandle following Hurricane Michael[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1): 20381. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99779-8 [49] 葛芳, 田波, 周云轩, 等. 海岸带典型盐沼植被消浪功能观测研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(8): 1784−1792.Ge Fang, Tian Bo, Zhou Yunxuan, et al. Analyzing the role of salt marshes on attenuating waves with Rb16-2050 mesearues in Changjiang Estuary[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(8): 1784−1792. [50] 谢泽昊, 史本伟, 田波, 等. 盐沼植被缓流能力观测研究——以崇明东滩海三棱藨草盐沼区为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(2): 571−581. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20200267Xie Zehao, Shi Benwei, Tian Bo, et al. Observation and study on flow attention capacity of saltmarsh: a case study of scirpus mariqueter in Chongming Dongtan[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(2): 571−581. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.20200267 [51] 陈雅慧, 袁琳, 曹浩冰, 等. 基于胁迫梯度假说和互惠理论的海三棱藨草种群恢复技术[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(12): 4233−4241.Chen Yahui, Yuan Lin, Cao Haobing, et al. The stress-gradient hypothesis and facilitation theory-based restoration technique for Scirpus mariqueter population[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(12): 4233−4241. [52] 陶燕东, 于克锋, 何培民, 等. 围垦后南汇东滩海三棱藨草的空间分布及其影响因子研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2017, 26(7): 1032−1041. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201707009Tao Yandong, Yu Kefeng, He Peimin, et al. Distribution of Scirpus mariqueter on Nanhui coasts after reclamation and the associated affecting factors[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2017, 26(7): 1032−1041. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201707009 [53] 张振伟, 刘贞文, 刘必劲. 风暴潮与盐沼相互作用研究进展[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2019, 36(7): 42−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.07.008Zhang Zhenwei, Liu Zhenwen, Liu Bijin. A review of dynamic interactions between coastal storms and salt marshes[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2019, 36(7): 42−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2019.07.008 [54] Gerbersdorf S U, Wieprecht S. Biostabilization of cohesive sediments: revisiting the role of abiotic conditions, physiology and diversity of microbes, polymeric secretion, and biofilm architecture[J]. Geobiology, 2015, 13(1): 68−97. doi: 10.1111/gbi.12115 -





 下载:
下载: