Effect of environmental factors on fish distribution based on GAM and GWR model : A case study of Sillago sihama in the Shandong coastal waters
-
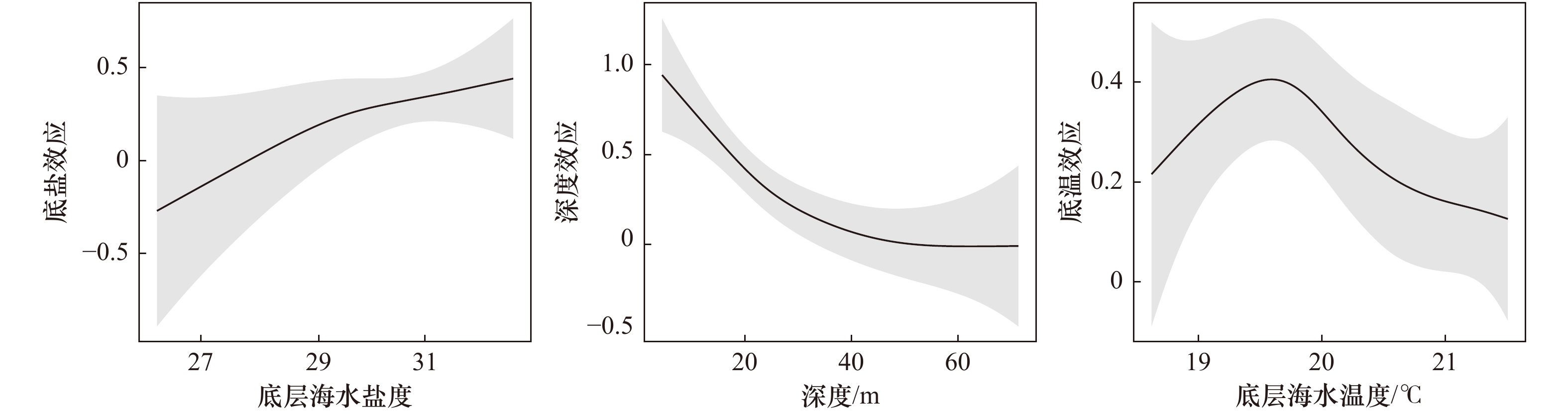
摘要: 多鳞鱚(Sillago sihama)是山东近海重要的渔业种类之一。本研究根据2016年秋季(10月)在山东近海开展渔业资源底拖网调查取得的数据,分析该海域多鳞鱚的空间分布特征,并运用广义可加模型(GAM)和地理加权回归(GWR)模型探究影响其分布的因素及其与环境因子的非线性和空间非平稳性关系。GAM拟合结果显示,影响秋季多鳞鱚分布的环境因子主要有水深、底层水温和底层盐度,水深的偏差解释率最大,为23.50%。GWR模型拟合结果显示,多鳞鱚分布与水深和底层水温之间存在空间非平稳性关系。水深与多鳞鱚相对资源量呈负相关关系,底层水温与多鳞鱚相对资源量呈正相关关系。赤池信息准则和决定系数(R2)指标对比结果显示,GWR模型的表现优于GAM,在渔业生态数据分析中表现出较好的发展潜力。本研究为今后开展渔业生物空间分布提供了一种新的方法。Abstract: Sillago sihama is an important fishery species in China and plays an important role in the marine ecosystem of the Yellow Sea. Species distribution models can be used to predict its distribution by establishing the relationships between its abundance and environmental factors. However, due to high mobility of the marine animals, the relationship between their distribution and environmental factors is often nonlinear and variable with spatial locations. Based on data collected from bottom trawl survey in the Shandong coastal waters in autumn of 2016, both generalized additive model (GAM) and geographically weighted regression (GWR) model were used to analyze nonlinear and spatial nonstationary relationships between distribution of the species and environmental factors, and results from the two models were compared. Results from the GAM indicated that the main environmental factors were depth, sea bottom temperature and salinity, and depth had the largest deviance explained (23.50%). GWR model results showed that there were spatial non-stationary relationships between distribution of the species and depth and sea bottom temperature. GWR model results indicated a negative correlation between depth and biomass of the species, and a positive correlation between sea bottom temperature and biomass of species. Regarding performance of the models, GWR model showed advantages over GAM in identifying influencing factors and predicting distribution, and GWR model was recommended for use in similar applications.
-
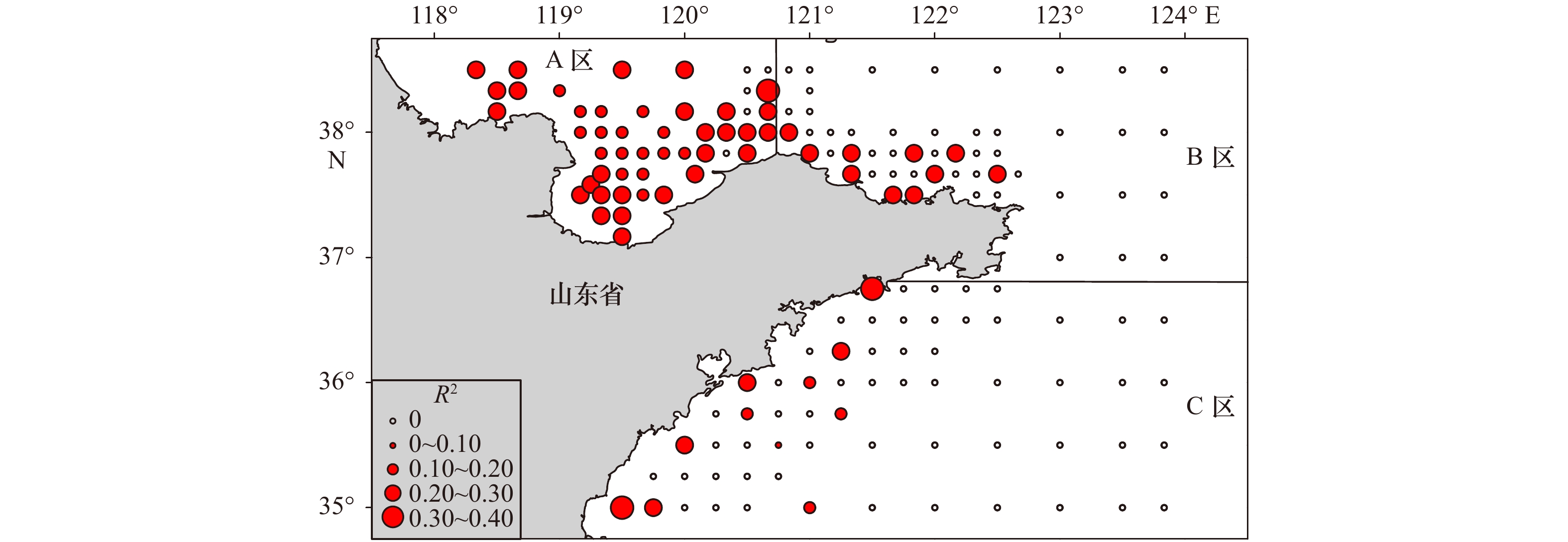
图 5 GWR模型中水深(a)、底层海水温度(b)局部回归系数值的空间分布
空心圆表示未捕获到多鳞鱚站位;蓝色实心圆表示与环境变量呈负相关关系;红色实心圆表示与环境变量呈正相关关系
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution of regression coefficient values for depth (a) and sea bottom temperature (b) in the GWR model
Small open circles indicate absence of Sillago sihama; blue filled circles indicate a negative correlation with the environmental variables; red filled circles indicate a positive correlation with the environmental variables
表 1 GAM变量筛选及影响因子的参数分析
Tab. 1 The variable screening process for GAM and parameters analysis
模型因子 AIC值 偏差解释率/% R2 Depth 177.058 23.50 0.222 SBS 201.342 11.00 0.096 SBT 199.252 13.10 0.113 Depth+SBS 170.596 28.70 0.264 Depth+SBT 169.368 29.80 0.272 Depth+SBT+SBS 168.113 31.87 0.285 表 2 多鳞鱚空间分布的环境影响因子的GWR模型筛选过程
Tab. 2 Forward-selection procedure of GWR model for environmental influencing factors on spatial distribution of Sillago sihama
模型 AIC值 R 2 带宽 Depth 126.478 0.446 0.099 SBS 139.011 0.387 0.154 SBT 135.911 0.405 0.104 Depth+SBS 130.291 0.426 0.167 Depth+SBT 126.296 0.449 0.113 SBS+ SBT 137.733 0.398 0.163 Depth+SBS+SBT 129.613 0.436 0.167 表 3 最优GWR模型局部参数估计汇总统计
Tab. 3 Summary statistics of the local parameter estimates for the optimal GWR model
变量 最小值 1/4分位数 中位数 3/4分位数 最大值 p 正相关/% 负相关/% 截距 −13.722 −3.901 1.265 1.814 7.805 <0.01 32.8 67.2 底层海水温度 −0.349 −0.066 −0.039 0.249 0.755 <0.01 68.8 31.2 水深 −0.028 −0.015 −0.009 −0.005 0.029 <0.01 23.4 76.6 -
[1] Qiu Bixun, Fang Shaobin, Ikhwanuddin M, et al. Genome survey and development of polymorphic microsatellite loci for Sillago sihama based on Illumina sequencing technology[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2020, 47(4): 3011−3017. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05348-z [2] Muchlis N, Prihatiningsih, Restiangsih Y H. Biological characteristics of silver sillago (Sillago sihama Forskål) in Bombana Water, South East Sulawesi[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 674: 012010. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/674/1/012010 [3] 王军, 林民君. 罗源湾多鳞鱚的食性[J]. 福建水产, 1993(2): 25−27, 33.Wang Jun, Lin Minjun. Feeding of Sillago sihama in Luoyuan Bay[J]. Fujian Fisheries, 1993(2): 25−27, 33. [4] Baset A, Liu Qun, Liao Baochao, et al. Growth and mortality of Sillago sihama (Forskål) from Karachi Coast, Pakistan[J]. Asian Journal of Research in Zoology, 2020, 3(1): 42−52. [5] 万瑞景. 多鳞鱚早期发育形态[J]. 海洋水产研究, 1996, 17(1): 35−41.Wan Ruijing. Morphology of early development of Sillago sihama (Forskål)[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 1996, 17(1): 35−41. [6] Lee C S, Hu F, Hirano R. Salinity tolerance of fertilized eggs and larval survival in the fish Sillago sihama[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1981, 4: 169−174. doi: 10.3354/meps004169 [7] 朱承之, 张云雷, 赛可, 等. 生物和非生物因子对秋季海州湾长蛇鲻栖息地适宜性的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(6): 44−51.Zhu Chengzhi, Zhang Yunlei, Sai ke, et al. Impacts of biotic and abiotic factors on the habitat suitability of Saurida elongata during autumn in the Haizhou Bay, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(6): 44−51. [8] 李迎冬, 张崇良, 纪毓鹏, 等. 山东半岛南部海域小黄鱼时空分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(4): 442−450.Li Yingdong, Zhang Chongliang, Ji Yupeng, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of Larimichthys polyactis in southern waters off the Shandong Peninsula and its relationship with environmental factors[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(4): 442−450. [9] 朱文斌, 朱海晨, 张亚洲, 等. 浙江沿岸日本鳀幼鱼数量分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(9): 1175−1183.Zhu Wenbin, Zhu Haichen, Zhang Yazhou, et al. Quantitative distribution of juvenile Engraulis japonicus and the relationship with environmental factors along the Zhejiang coast[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(9): 1175−1183. [10] Ciannelli L, Fauchald P, Chan K S, et al. Spatial fisheries ecology: recent progress and future prospects[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2008, 71(3/4): 223−236. [11] Liu Changdong, Wan Rong, Jiao Yan, et al. Exploring non-stationary and scale-dependent relationships between walleye (Sander vitreus) distribution and habitat variables in Lake Erie[J]. Marine and Freshwater Research, 2017, 68(2): 270−281. doi: 10.1071/MF15374 [12] 贾明秀, 黄六一, 褚建伟, 等. 基于GAM和GWR模型分析环境因子对南极磷虾资源分布的非线性和非静态性影响[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(8): 19−26.Jia Mingxiu, Huang Liuyi, Chu Jianwei, et al. Studies on the nonlinear and spatial nonstationary effects of environmental factors on the distribution of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba)[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2019, 49(8): 19−26. [13] 杨逍遥, 王建军, 李国栋, 等. 基于GWR模型的共享单车空间分布影响因素分析[J]. 交通运输研究, 2021, 7(1): 81−94.Yang Xiaoyao, Wang Jianjun, Li Guodong, et al. Factors impacting spatial distribution of bike sharing based on GWR model[J]. Transport Research, 2021, 7(1): 81−94. [14] 丁亚鹏, 张俊华, 刘玉寒, 等. 基于GWR模型的伊河流域土壤有机碳空间分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(12): 4876−4885.Ding Yapeng, Zhang Junhua, Li Yuhan, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in Yihe River Basin based on GWR model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(12): 4876−4885. [15] Windle M J S, Rose G A, Devillers R, et al. Exploring spatial non-stationarity of fisheries survey data using geographically weighted regression (GWR): an example from the Northwest Atlantic[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2010, 67(1): 145−154. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsp224 [16] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763.6−2007, 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 12763.6−2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: Marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008. [17] Wisz M S, Pottier J, Kissling W D, et al. The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: implications for species distribution modelling[J]. Biological Reviews, 2013, 88(1): 15−30. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00235.x [18] Kabacoff R I. R in Action: Data Analysis and Graphics with R[M]. 2nd ed. Shelter Island: Manning Publications Co. , 2015. [19] Guisan A, Edwards T C Jr, Hastie T. Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: setting the scene[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2/3): 89−100. [20] Wood S N. Generalized Additive Models: an Introduction with R[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017. [21] Gollini I, Lu Binbin, Charlton M, et al. GWmodel: an R package for exploring spatial heterogeneity using geographically weighted models[J]. Journal of Statistical Software, 2015, 63(17): 1−50. [22] Fotheringham A S, Brunsdon C, Charlton M. Geographically Weighted Regression: the Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, 2002. [23] Strawderman R L. Reviewed Work: Model Selection and Inference: A Practical Information-theoretic Approach[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2002: 181. [24] 杜涛, 黄洋. 多鳞鱚生物学特性及室内养殖试验[J]. 水产养殖, 2009, 30(3): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2009.03.001Du Tao, Huang Yang. Biological characteristics and indoor multiplication experiment of Sillago sihama Forskål[J]. Journal of Aquaculture, 2009, 30(3): 1−3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2091.2009.03.001 [25] 陈大刚. 黄渤海渔业生态学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. 1991.Cheng Dagang. Fishery Ecology in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea [M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press. 1991. [26] 史书杰. 渤海大型底栖动物生态学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014.Shi Shujie. The ecological study of macrobenthos in the Bohai Sea, China[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. [27] 李明坤, 徐宾铎, 薛莹, 等. 山东南部近海口虾蛄空间分布特征及其季节变化[J]. 水产学报, 2019, 43(8): 1749−1758.Li Mingkun, Xu Binduo, XueYing, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and seasonal variation of Oratosquilla oratoria in the southern coastal waters of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(8): 1749−1758. [28] 牟秀霞, 李明坤, 尹洁, 等. 山东半岛东南部海域星康吉鳗资源密度时空分布及其与环境因子之间关系[J]. 水产学报, 2019, 43(8): 1759−1767.Mu Xiuxia, Li Mingkun, Yin Jie, et al. Relationship between spatio-temporal distribution of Conger myriaster and the environment factors in the southeast waters of Shandong Peninsula[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(8): 1759−1767. [29] 薛泰强. 鱚科几种鱼类的形态学及遗传学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2010.Xue Taiqiang. Study on morphology and genetics of some Sillaginidae species[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2010. [30] 高彦洁. 莱州湾海域鱼卵仔稚鱼群落结构初步研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016.Gao Yanjie. Studies on community structure of ichthyoplankton in Laizhou Bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. [31] 周银环, 黄海立, 杜涛, 等. 多鳞鱚幼鱼盐度适应性研究[J]. 渔业研究, 2017, 39(1): 22−26.Zhou Yinhuan, Huang Haili, Du Tao, et al. Study on adaptability of juvenile of Sillago sihama to salinity[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2017, 39(1): 22−26. [32] 杨艳艳, 朱明明, 徐炳庆, 等. 山东半岛南部近岸海域鱼卵、仔稚鱼群落结构与环境因子相关性[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5): 995−1004.Yang Yanyan, Zhu Mingming, Xu Bingqing, et al. Community structure of ichthyoplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in coastal waters of southern Shandong Peninsula[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5): 995−1004. [33] 卢振彬, 陈骁, 杜建国. 闽南−台湾浅滩渔场多鳞鱚生长、死亡参数及种群动态[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2008, 29(5): 47−53.Lu Zhenbin, Chen Xiao, Du Jianguo. The population dynamics and parameter of growth and mortality of Sillago sihama in the Minnan-Taiwan fishing grounds[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2008, 29(5): 47−53. [34] 文斐. 黄东海春、夏季分粒级叶绿素α及初级生产力研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2012.Wen Fei. Study on the size fractionated chlorophyll a and primary productivty in spring and summer in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012. [35] 李进道. 莱州湾海洋渔业现状[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1994(3): 83−87.Li Jindao. Present situation of ocean fisheries in Laizhou Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1994(3): 83−87. [36] 于非, 张志欣, 刁新源, 等. 黄海冷水团演变过程及其与邻近水团关系的分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2006, 28(5): 26−34.Yu Fei, Zhang Zhixin, Diao Xinyuan, et al. Analysis of evolution of the Huanghai Sea cold water mass and its relationship with adjacent water masses[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2006, 28(5): 26−34. [37] Brunsdon C, Fotheringham A S, Charlton M E. Geographically weighted regression: a method for exploring spatial nonstationarity[J]. Geographical Analysis, 1996, 28(4): 281−298. [38] Cullen D W, Guida V. Use of geographically weighted regression to investigate spatial non-stationary environmental effects on the distributions of black sea bass (Centropristis striata) and scup (Stenotomus chrysops) in the Mid-Atlantic Bight, USA[J]. Fisheries Research, 2021, 234: 105795. doi: 10.1016/j.fishres.2020.105795 [39] 范巧, 郭爱君. 地理加权回归模型方法与研究新进展[J]. 数量经济研究, 2021, 12(2): 134−150.Fan Qiao, Guo Aijun. Research progress on geographical weighted regression models: a perspective of literature reviews[J]. The Journal of Quantitative Economics, 2021, 12(2): 134−150. -




 下载:
下载: