Optimization of the Bohai Sea ice thickness retrieval algorithm based on MODIS data
-
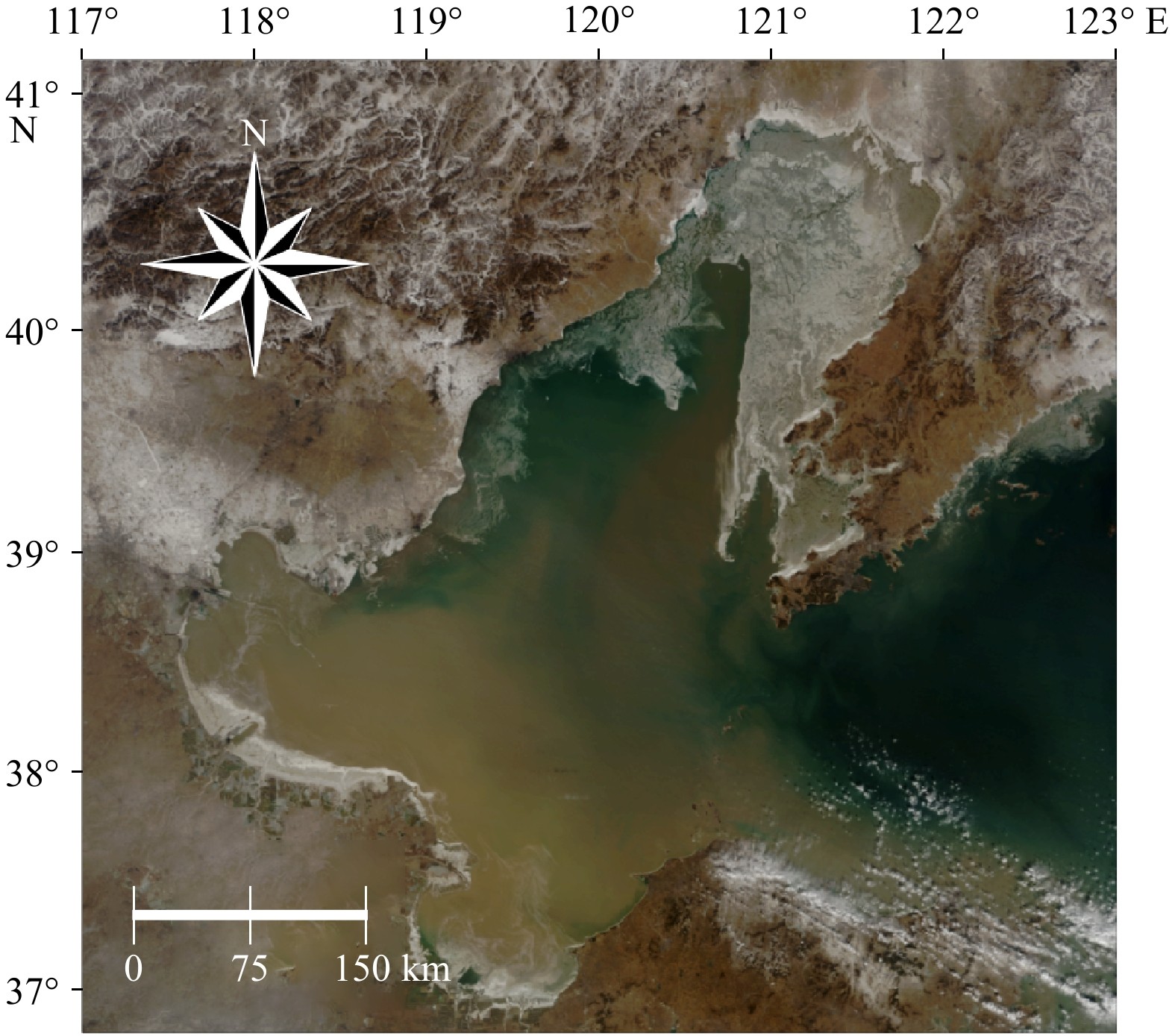
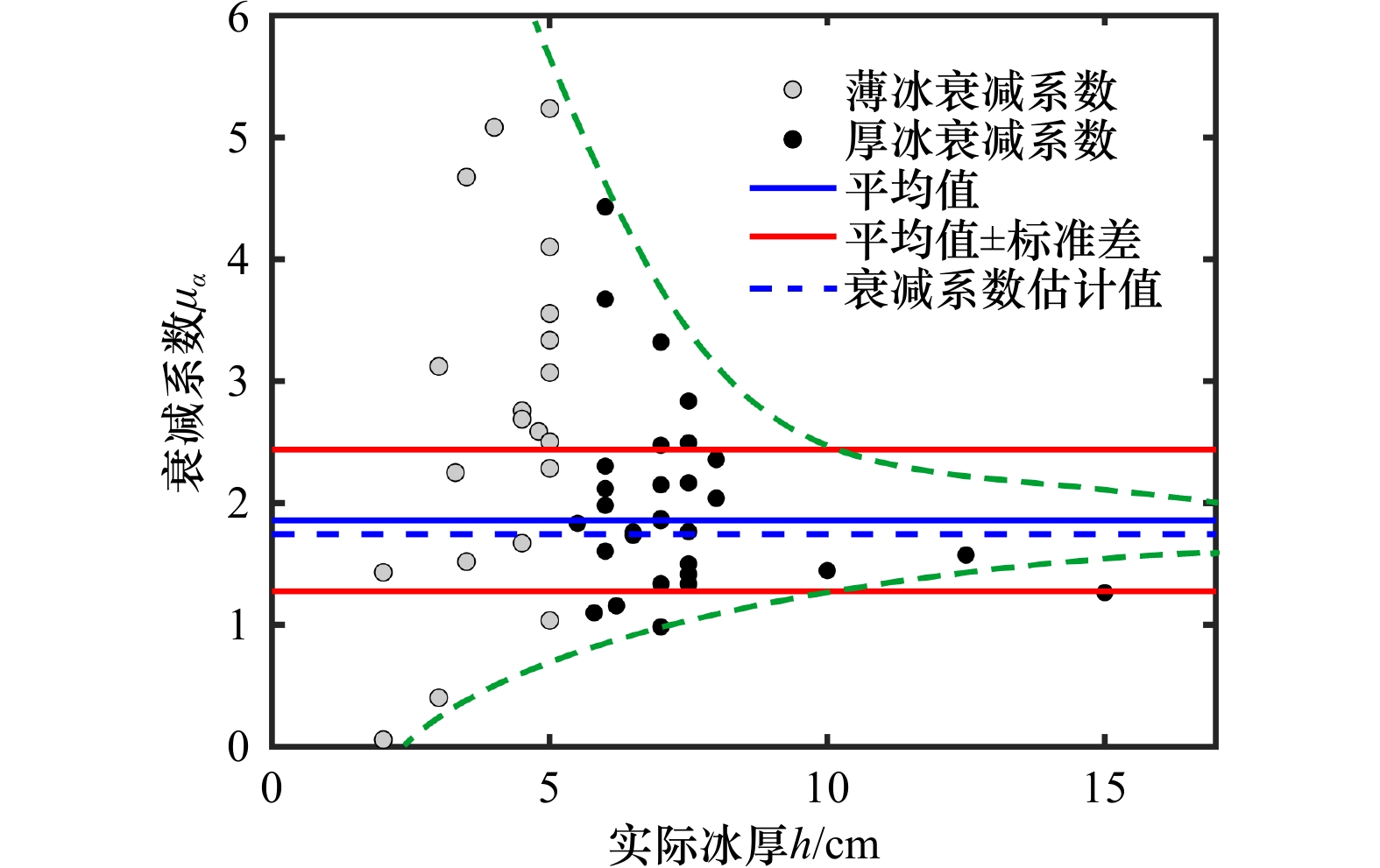
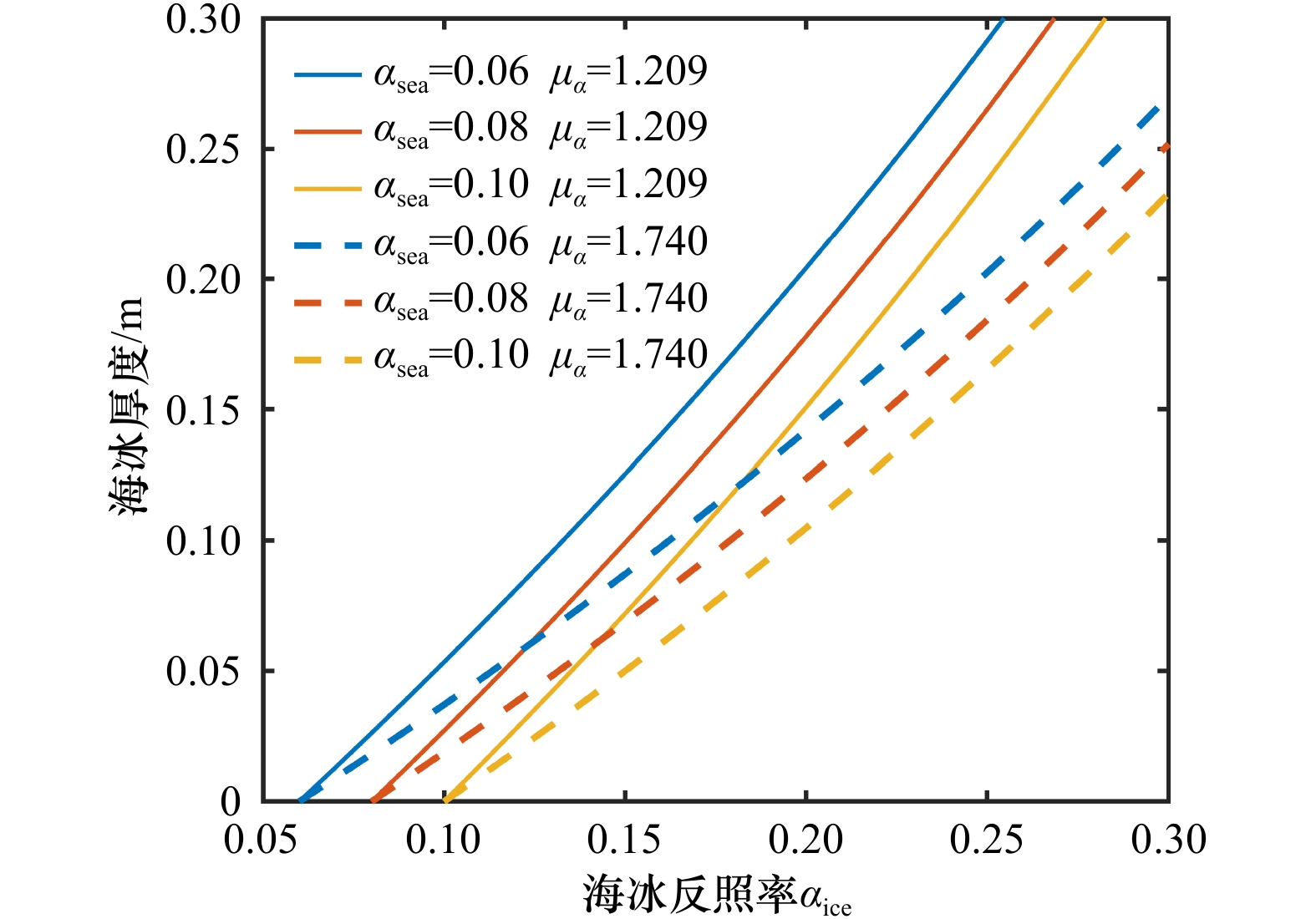
摘要: 海冰厚度是监测与研究渤海海冰的重要参数。为了获取更加可靠的渤海海冰厚度数据,本研究基于MODIS数据对海冰厚度反演中的冰水分离环节和冰厚计算方法都进行了改进。对于冰水分离环节,本文在Canny边缘检测算子提取海冰基础上,加入了二值化处理、阈值判别等步骤,实现了较高精度的渤海海冰范围自动化提取。通过试验确定了海冰厚度与反照率指数关系模型中的参数,包括海冰衰减系数和海水反照率参数,使其更加符合渤海海区的物理特征。将改进后算法的海冰厚度反演结果与渤海海上石油平台实测数据进行比较,并分析了误差来源。结果表明,经过对算法的改进,海冰厚度与反照率指数关系模型的反演结果与实测数据之间的平均绝对误差由7.05 cm缩小到2.74 cm,相关系数由0.434提高到0.485。Abstract: Sea ice thickness is a crucial parameter for monitoring and studying sea ice in the Bohai Sea. Aiming to get more reliable data conveniently, we improved the ice thickness retrieval algorithm based of MODIS data, including the ice separation process and ice thickness calculation method. In terms of ice-water separation process, some steps like binary processing, threshold discrimination were added based on sea ice extracting with Canny edge detector, which successfully realized the automatic high-precision extraction of sea ice range in the Bohai Sea. Meanwhile, through experiments, we optimize the parameters of the exponential model between sea ice thickness and albedo, including sea ice attenuation coefficient and sea water albedo parameters, to make it more consistent with the physical characteristics of the Bohai Sea area. The sea ice thickness retrieval results of the improved algorithm are compared with the measured data of the Bohai offshore oil platform, and the error reasons are analyzed. The results show that the average absolute error decreases from 7.05 cm to 2.74 cm, and the correlation coefficient increases from 0.434 to 0.485.
-
Key words:
- sea ice thickness /
- Bohai Sea /
- retrieval algorithm /
- MODIS /
- ice-water separation
-
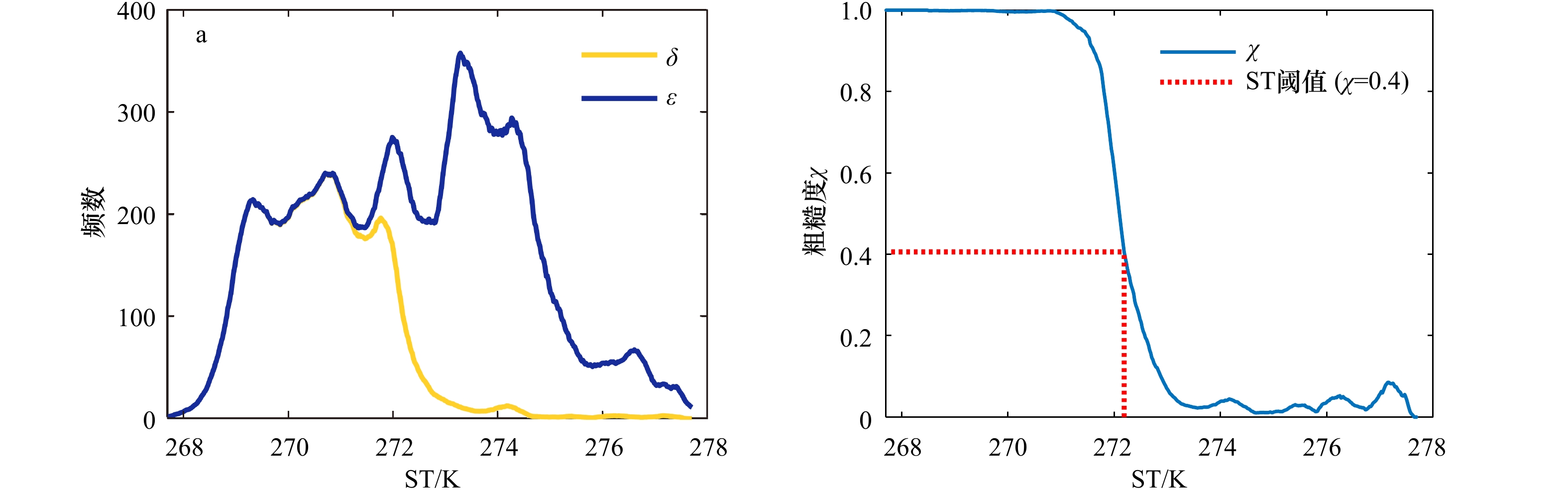
图 2 渤海海冰厚度反演算法流程
图中红色字部分为本文针对Canny算子提取海冰裂缝[32]新加入的步骤,蓝色字部分为针对海冰厚度指数关系模型[17]参数设置的改进
Fig. 2 Flow chart of Bohai Sea ice thickness retrieval algorithm
The red character part in the figure is the new step of the Canny operator to extract sea ice cracks[32], and the blue character part is the improvement of the parameter setting of the sea ice thickness exponential model[17]
表 1 MODIS部分波段光谱范围
Tab. 1 Spectral range of MODIS partial bands
波段 光谱范围/nm 分辨率/m 1 620~670 250(重采样为1 000) 2 841~876 250(重采样为1 000) 3 459~479 500(重采样为1 000) 4 545~565 500(重采样为1 000) 5 1 230~1 250 500(重采样为1 000) 6 1 628~1 652 500(重采样为1 000) 7 2 105~2 135 500(重采样为1 000) 31 11.770~12.270 1 000 32 13.185~13.485 1 000 表 2 海冰厚度测试数据集实测数据与反演结果
Tab. 2 Measured data of test data sets and retrieval results of Bohai Sea sea ice thickness
日期 站位 最大实测
厚度/cm平均实测
厚度/cm改进前算法厚
度(T0)/cm改进后算法厚
度(T1)/cm仅改变海水反照
率厚度(T2)/cm仅改变衰减系
数厚度(T3)/cmYuan等[26] 算
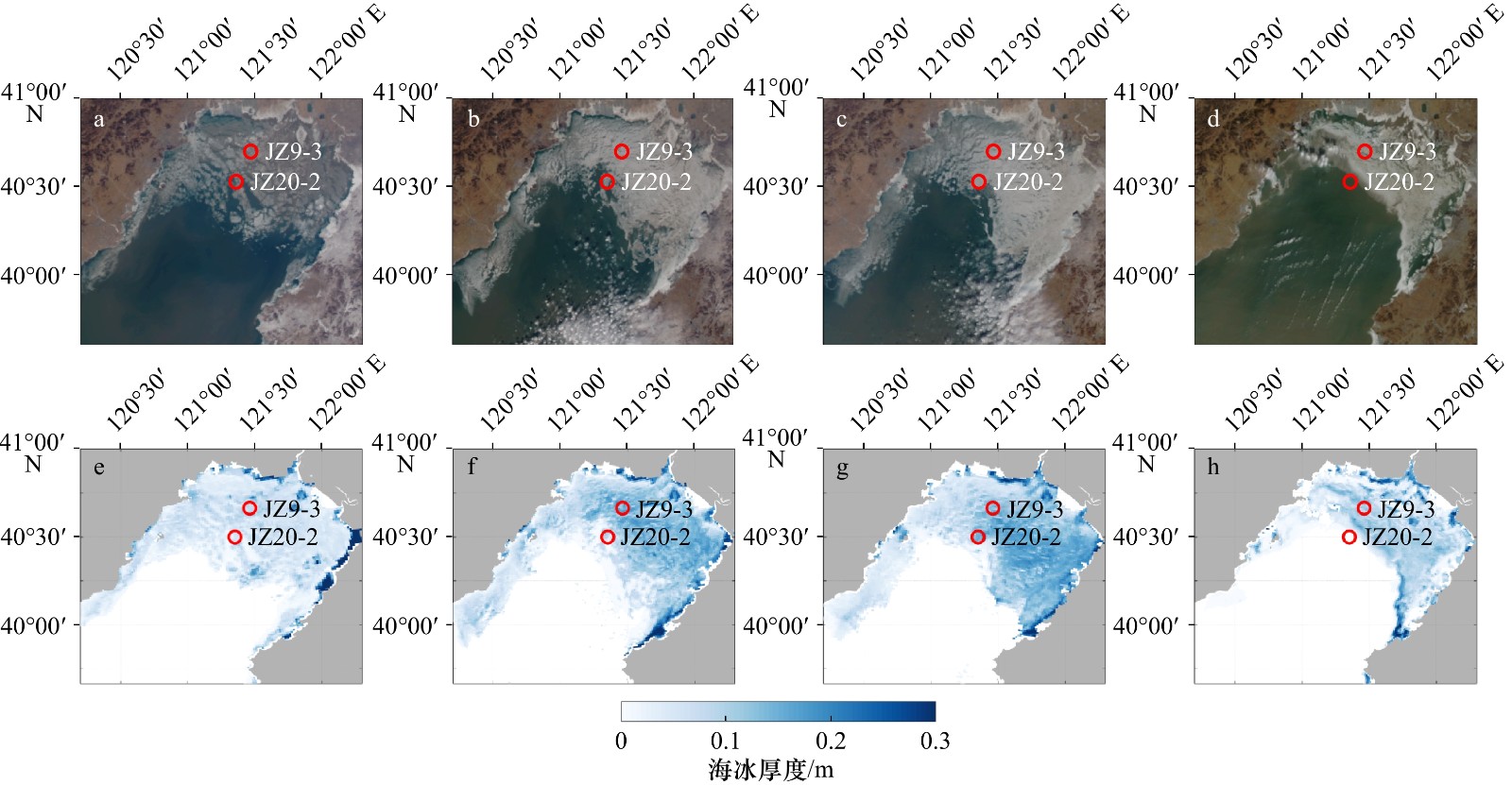
法厚度/cm2009年12月19日* JZ9-3 5 3.5 11.42 5.6 8.06 7.93 8.95 2010年1月6日* JZ9-3 8 6 16.6 9.49 13.66 11.54 12.7 2010年1月11日* JZ20-2 5 3 14.24 5.88 8.47 9.9 9.28 2010年1月24日* JZ9-3 15 12.5 13.6 6.39 9.2 9.45 7.99 2010年2月5日* JZ9-3 20 14 24.76 14.16 20.37 17.2 15.65 2010年2月16日* JZ20-2 8 6 11.38 5.59 8.05 7.9 11.61 2010年2月16日* JZ9-3 6 4 4.04 0.52 0.74 2.81 2.49 2010年1月29日* JZ20-2 4 3 5.92 2.66 3.83 4.11 3.37 2010年2月12日* JZ9-3 8 6 10.9 5.77 8.3 7.57 9.85 2013年1月26日* JZ20-2 8 5.5 12.23 6.74 9.71 8.5 11.21 2013年2月2日* JX1-1 10 7.5 10.65 6.85 9.85 7.4 10.87 2013年2月2日* JZ25-1S 30 22.5 17.09 11.29 16.25 11.87 14.81 2013年12月28日* JZ20-2 4 2 1.71 0.82 1.18 1.19 1.45 2014年1月12日 JZ20-2 4 3.5 17.84 10.78 15.52 12.4 13.8 2014年1月18日 JZ9-3 10 4.5 10.94 5.57 8.02 7.6 10 2014年2月11日 JZ20-2 8 4 12.37 6.84 9.84 8.59 11.61 2016年1月7日 JZ9-3 12 6 9.22 3.97 5.72 6.41 6.85 2016年1月8日 JZ9-3 13 8 10.44 4.5 6.48 7.25 7.25 2016年1月9日 JZ20-2 19 7.2 10.14 6.08 8.75 7.05 10.45 2016年1月12日 JZ20-2 13 5.8 10.29 5.21 7.5 7.15 8.64 2016年1月13日 JZ20-2 13 5.5 12.46 4.6 6.62 8.66 8.01 2016年1月18日 JZ20-2 10 5 20.56 12.09 17.41 14.28 14.42 2020年12月31日 JZ9-3 14 7 12.68 7.99 11.49 8.81 13.41 2021年1月1日 JZ9-3 12 6.5 17.29 8.95 12.89 12.01 14.83 2021年1月7日 JZ20-2 14 7 14.01 9.1 13.1 9.74 14.35 2021年1月8日 JZ9-3 14 8 22.02 13.62 19.6 15.3 17.68 2021年1月10日 JZ20-2 12 6 19.59 9.82 14.13 13.61 14.65 2021年1月13日 JZ9-3 10 7 18.63 10.69 15.39 12.95 15.35 2021年1月17日 JZ9-3 14 9 15.59 7.99 11.5 10.83 13.78 平均实测厚度误差 平均误差 6.66 0.49 3.66 2.57 4.13 平均绝对误差 7.05 2.74 4.72 3.72 5.17 均方根误差 8.25 3.75 5.8 4.73 5.94 相关系数 0.434 0.485 0.485 0.434 0.417 最大实测厚度
误差平均误差 2.37 −3.81 0.63 1.72 0.16 平均绝对误差 4.73 4.67 4.04 3.87 3.96 均方根误差 6.02 6.09 5.23 5.25 4.99 相关系数 0.435 0.480 0.480 0.435 0.459 注:T0为算法改进前的冰厚反演结果;T1为算法改进后的冰厚反演结果;T2为仅改进海水反照率的冰厚反演结果;T3为仅改进衰减系数的冰厚反演结果。日期后标注*的数据来源于参考文献[24, 35]。 -
[1] 白珊, 刘钦政, 吴辉碇, 等. 渤海、北黄海海冰与气候变化的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 2001, 23(5): 33−41.Bai Shan, Liu Qinzheng, Wu Huiding, et al. Relation of ice conditions with climate change in the Bohai Sea and the northern Huanghai Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2001, 23(5): 33−41. [2] Gong Daoyi, Wang Shaowu, Zhu Jinhong. East Asian winter monsoon and Arctic Oscillation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(10): 2073−2076. [3] 唐茂宁, 洪洁莉, 刘煜, 等. 气候因子对渤海冰情影响的统计分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2015, 34(2): 152−157. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.02.005Tang Maoning, Hong Jieli, Liu Yu, et al. Statistical analysis of climatic factors impacting on the Bohai Sea ice[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2015, 34(2): 152−157. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.02.005 [4] 药蕾, 苏洁. 渤海海冰与西伯利亚高压之间的关系及与北大西洋涛动之间的可能联系[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(6): 1−12. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20170128Yao Lei, Su Jie. Relationships between Bohai Sea ice and Siberian high and possible connections between Bohai Sea ice and north Atlantic Oscillation[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2018, 48(6): 1−12. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20170128 [5] 耿淑琴, 王旭. 2001−2002年冬季黄渤海天气气候特征及对渤海海冰的影响[J]. 海洋预报, 2002, 19(4): 38−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.04.006Geng Shuqin, Wang Xu. Features of weather and climate in winter of 2001−2002 and its effect on sea ice in Bohai[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2002, 19(4): 38−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2002.04.006 [6] 顾卫, 史培军, 刘杨, 等. 渤海和黄海北部地区负积温资源的时空分布特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2002, 17(2): 168−173. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2002.02.007Gu Wei, Shi Peijun, Liu Yang, et al. The characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of negative accumulated temperature in Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2002, 17(2): 168−173. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3037.2002.02.007 [7] 李彦青, 苏洁, 汪洋, 等. 渤海海冰外缘线候平均离岸距离的变化及其关键影响因子[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(7): 7−16. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2013.07.002Li Yanqing, Su Jie, Wang Yang, et al. Variability of the pentadly average distance between the sea ice edge and the coast in the Bohai Sea and its key impact factors[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2013, 43(7): 7−16. doi: 10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.2013.07.002 [8] 刘煜, 吴辉碇. 第1讲: 渤、黄海的海冰[J]. 海洋预报, 2017, 34(3): 94−101. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.03.012Liu Yu, Wu Huiding. Sea ice in the Bohai Sea and the northern Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2017, 34(3): 94−101. doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2017.03.012 [9] 邓树奇. 渤海海冰灾害及其预防概况[J]. 灾害学, 1986(1): 80.Den Shuqi. Sea ice disaster and its prevention in Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 1986(1): 80. [10] 国家海洋局. 2010年中国海洋灾害公报[EB/OL]. (2011−04−26) [2022−05−06]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2010nzghyzhgb/.State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin of China Marine Disaster 2010[EB/OL]. (2011−04−26) [2022−05−06]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2010nzghyzhgb/. [11] 国家海洋局. 2013年中国海洋灾害公报[EB/OL]. (2014−03−24) [2022−05−06]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2013nzghyzhgb/.State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin of China Marine Disaster 2013[EB/OL]. (2014−03−24) [2022−05−06]. http://www.nmdis.org.cn/hygb/zghyzhgb/2013nzghyzhgb/. [12] 郑新江, 邱康睦, 陆风. 定量计算渤海海冰参数的遥感方法[J]. 应用气象学报, 1998, 9(3): 312−316.Zheng Xinjiang, Qiu Kangmu, Lu Feng. Quantitative calculation of sea ice over the Bohai Sea using NOAA/AVHRR imagery[J]. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1998, 9(3): 312−316. [13] 罗亚威, 张蕴斐, 孙从容, 等. “海洋1号”卫星在海冰监测和预报中的应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2005, 27(1): 7−18.Luo Yawei, Zhang Yunfei, Sun Congrong, et al. Application of the “HY-1” satellite to sea ice monitoring and forecasting[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2005, 27(1): 7−18. [14] 吴龙涛, 吴辉碇, 孙兰涛, 等. MODIS渤海海冰遥感资料反演[J]. 中国海洋大学学报 (自然科学版), 2006, 36(2): 173−179.Wu Longtao, Wu Huiding, Sun Lantao, et al. Retrieval of sea ice in the Bohai Sea from MODIS data[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2006, 36(2): 173−179. [15] 刘志强, 苏洁, 时晓旭, 等. 渤海AVHRR多通道海冰密集度反演算法试验研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(11): 74−84.Liu Zhiqiang, Su Jie, Shi Xiaoxu, et al. Study on the multi-band retrieval algorithm for the Bohai Sea ice concentration using AVHRR data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(11): 74−84. [16] Zhou Ye, Fan Zhaopeng. Study on Bohai sea ice based on MODIS data[J]. E3S Web of Conferences, 2018, 53: 03038. [17] Grenfell T C. A radiative transfer model for sea ice with vertical structure variations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1991, 96(C9): 16991−17001. [18] 谢锋, 顾卫, 袁艺, 等. 辽东湾海冰资源量的遥感估算方法研究[J]. 资源科学, 2003, 25(3): 17−23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2003.03.003Xie Feng, Gu Wei, Yuan Yi, et al. Estimation of sea ice resources in Liaodong Gulf using remote sensing[J]. Resources Science, 2003, 25(3): 17−23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2003.03.003 [19] Yuan Shuai, Gu Wei, Xu Yingjun, et al. The estimate of sea ice resources quantity in the Bohai Sea based on NOAA/AVHRR data[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2012, 31(1): 33−40. doi: 10.1007/s13131-012-0173-4 [20] Su Hua, Wang Yunpeng. Using MODIS data to estimate sea ice thickness in the Bohai Sea (China) in the 2009−2010 winter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C10): C10018. [21] Liu Wensong, Sheng Hui, Zhang Xi. Sea ice thickness estimation in the Bohai Sea using geostationary ocean color imager data[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(7): 105−112. [22] Xu Zhantang, Yang Yuezhong, Wang Guifen, et al. Optical properties of sea ice in Liaodong Bay, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117(C3): C03007. [23] 陈树果. 黄渤海水体光学性质变化及其影响机制[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2015.Chen Shuguo. Variations and influencing mechanisms in the optical properties of the waters in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2015. [24] Zeng Tao, Shi Lijian, Marko M, et al. Sea ice thickness analyses for the Bohai Sea using MODIS thermal infrared imagery[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(7): 96−104. [25] Ning Li, Xie Feng, Gu Wei, et al. Using remote sensing to estimate sea ice thickness in the Bohai Sea, China based on ice type[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2009, 30(17): 4539−4552. [26] Yuan Shuai, Gu Wei, Liu Chengyu, et al. Towards a semi-empirical model of the sea ice thickness based on hyperspectral remote sensing in the Bohai Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2017, 36(1): 80−89. doi: 10.1007/s13131-017-0996-0 [27] Yuan Shuai, Liu Chengyu, Liu Xueqin. Practical model of sea ice thickness of Bohai Sea based on MODIS data[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2018, 28(5): 863−872. [28] 吴奎桥, 徐莹, 郝轶萌. MODIS数据在海冰遥感中的应用[J]. 海洋预报, 2005, 22(S1): 44−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2005.z1.007Wu Kuiqiao, Xu Ying, Hao Yimeng. Application in sea ice remote sensing of MODIS data[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2005, 22(S1): 44−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0239.2005.z1.007 [29] Su Hua, Wang Yunpeng, Xiao Jie, et al. Improving MODIS sea ice detectability using gray level co-occurrence matrix texture analysis method: a case study in the Bohai Sea[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 85: 13−20. [30] Zhang Na, Wu Yongshen, Zhang Qinghe. Detection of sea ice in sediment laden water using MODIS in the Bohai Sea: a CART decision tree method[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(6): 1661−1674. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1015658 [31] Su Hua, Wang Yunpeng, Xiao Jie, et al. Classification of MODIS images combining surface temperature and texture features using the support vector machine method for estimation of the extent of sea ice in the frozen Bohai Bay, China[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(10): 2734−2750. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2015.1041619 [32] Li Yawen, Yang Daiqin. Extraction of Bohai Sea ice from MODIS data based on multi-constraint endmembers and linear spectral unmixing[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020, 41(14): 5525−5548. [33] Canny J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, PAMI-8(6): 679−698. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.1986.4767851 [34] 刘荣高, 刘洋, 刘纪远. MODIS科学数据处理研究进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 2009, 19(2): 141−147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.003Liu Ronggao, Liu Yang, Liu Jiyuan. Research progress of MODIS scientific data processing[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2009, 19(2): 141−147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.02.003 [35] Karvonen J, Shi Lijian, Cheng Bin, et al. Bohai Sea ice parameter estimation based on thermodynamic ice model and earth observation data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(3): 234. [36] 李微, 方圣辉, 佃袁勇, 等. 基于光谱分析的MODIS云检测算法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2005, 30(5): 435−438, 443.Li Wei, Fang Shenghui, Dian Yuanyong, et al. Cloud detection in MODIS data based on spectrum analysis[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2005, 30(5): 435−438, 443. [37] 马开玉, 丁裕国, 屠其璞, 等. 气候统计原理与方法[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1993.Ma Kaiyu, Ding Yuguo, Tu Qipu, et al. Principles and Methods of Climate Statistics[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1993. [38] 许向阳, 宋恩民, 金良海. Otsu准则的阈值性质分析[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(12): 2716−2719. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.020Xu Xiangyang, Song Enmin, Jin Lianghai. Characteristic analysis of threshold based on Otsu criterion[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(12): 2716−2719. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.12.020 [39] 郭衍游, 焦明连. 利用MODIS数据反演渤海海冰分布[J]. 淮海工学院学报(自然科学版), 2010, 19(1): 84−87.Guo Yanyou, Jiao Minglian. Using MODIS data to retrieve distribution of sea ice in Bohai Sea[J]. Journal of Huaihai Institute of Technology (Natural Sciences Edition), 2010, 19(1): 84−87. [40] 刘良明, 周军元. MODIS数据的海洋表面温度反演[J]. 地理空间信息, 2006, 4(2): 7−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2006.02.003Liu Liangming, Zhou Junyuan. Using MODIS imagery to map sea surface temperature[J]. Geospatial Information, 2006, 4(2): 7−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4623.2006.02.003 [41] 赵进平, 任敬萍. 从航空数字影像提取北极海冰形态参数的方法研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2000, 21(4): 271−278. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20000406Zhao Jinping, Ren Jingping. Study on the method to analyze parameters of Arctic sea ice from airborne digital imagery[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2000, 21(4): 271−278. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20000406 [42] Allison I, Brandt R E, Warren S G. East Antarctic sea ice: albedo, thickness distribution, and snow cover[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1993, 98(C7): 12417−12429. [43] Liang Shunlin. Narrowband to broadband conversions of land surface albedo I: Algorithms[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2001, 76(2): 213−238. [44] 王维波, 苏洁. 基于形态学的海冰外缘线自动提取[J]. 遥感学报, 2015, 19(6): 983−997.Wang Weibo, Su Jie. Sea ice edge automatic retrieval based on morphology[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2015, 19(6): 983−997. [45] Kemp K K. Encyclopedia of Geographic Information Science[M]. Los Angeles: SAGE Publications, 2008: 146−147. [46] 丁德文. 工程海冰学概论[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1999.Ding Dewen. Introduction to Engineering Sea Ice Science[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1999. -




 下载:
下载: