GNSS-R sea level height estimation model based on the combination of VMD and WinLSP
-
摘要: 全球导航卫星系统反射(Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry,GNSS-R)技术是一种新兴的监测海平面高度变化的技术。本文依据GNSS-R技术中的信噪比分析法的原理,通过分析其分离趋势项和提取振荡频率的过程,建立了新的估测模型以提高反演精度。针对传统模型存在的信号分离不佳的问题,本文提出使用变分模态分解(Variational Mode Decomposition,VMD)算法替换传统的最小二乘拟合法(Least Squares Fitting, LSF)进行趋势项分量的分离。在此基础上,本文引入基于凯塞窗函数改进的LSP(Lomb-Scargle Periodogram)频谱分析法(记为WinLSP)来减弱因频谱泄露带来的反演误差。在瑞典翁萨拉的GTGU站和美国阿拉斯加州的SC02站开展的海平面高度反演实验结果表明,本文建立的估测模型相比于传统模型具有更高的反演精度。基于VMD+WinLSP估测模型得到的GTGU站反演结果的均方根误差(RMSE)、相关系数和反演点数分别为4.70 cm、0.98和5 647。与传统的LSF+LSP估测模型相比,反演精度和GNSS数据利用率分别提高了约29.7%和15.0%。SC02站的RMSE、相关系数和反演点数分别为14.34 cm、0.99和1 785,反演精度和GNSS数据利用率分别提高了约12.3%和9.4%。Abstract: Global navigation satellite system-reflectometry (GNSS-R) technology is an emerging technology for monitoring sea level changes. Based on the principle of the signal to noise ratio (SNR) analysis method in GNSS-R technology, this paper established a new sea level height estimation model to improve the accuracy by analyzing the process of separating the trend term and extracting the oscillation frequency. Aiming at the problem of poor signal separation in the traditional model, this paper proposed to use the variational mode decomposition (VMD) algorithm to replace the traditional least squares fitting (LSF) to separate the trend term components. On this basis, this paper combined Lomb-Scargle Periodogram (LSP) spectral analysis method and Kaiser window function (referred to as WinLSP) to reduce the inversion error caused by spectral leakage. The results of sea level inversion experiments carried out at GTGU Station in Onsala, Sweden and SC02 Station in Alaska, USA show that the estimation model established in this paper has higher inversion accuracy than traditional model. The root mean square error (RMSE), correlation coefficient and number of inversion points of the inversion results of GTGU Station based on the VMD+WinLSP estimation model are 4.70 cm, 0.98 and 5 647, respectively. The inversion accuracy and GNSS data utilization are increased by about 29.7% and 15.0%, respectively; The RMSE, correlation coefficient, and inversion points of SC02 Station are14.34 cm, 0.99 and 1 785, respectively, and the inversion accuracy and GNSS data utilization are increased by about 12.3 % and 9.4%.
-
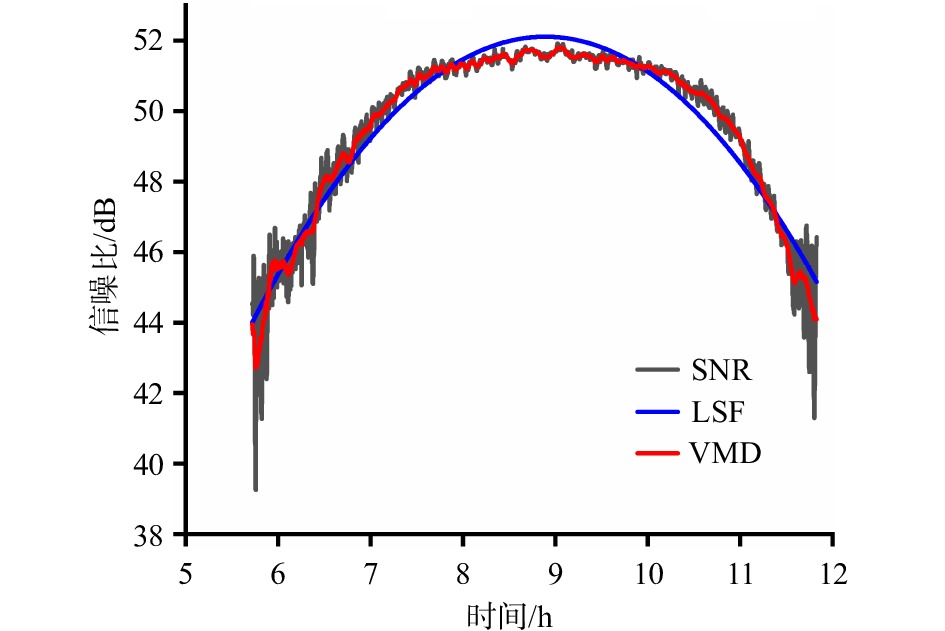
图 4 趋势项拟合效果对比
黑色曲线表示原始的信噪比(SNR)数据,蓝、红色曲线分别表示通过最小二乘拟合法(LSF)和变分模态分解算法(VMD)拟合得到的趋势项
Fig. 4 Comparison of the trend term fitting effect
The black curve represents the original signal to noise ratio (SNR) data, and the blue and red curves represent the trend terms fitted by the least squares fitting (LSF) method and the variational mode decomposition (VMD) algorithm, respectively
表 1 基于变分模态分解(VMD)算法的不同仰角范围的海平面高度反演结果
Tab. 1 Inversion results of sea level height in different elevation angle ranges based on variational mode decomposition (VMD)
仰角范围 RMSE/cm 相关系数 反演点数 5°~15° 5.01 0.98 2 852 5°~25° 5.18 0.98 4 545 5°~30° 5.50 0.98 5 268 表 2 基于最小二乘拟合+频谱分析(LSF+LSP)、经验模态分解+频谱分析(EMD+LSP)和变分模态分解+频谱分析(VMD+LSP)的GTGU站海平面高度反演结果的精度对比
Tab. 2 Accuracy comparison of sea level height inversion results of GTGU Station based on least squares fitting+lomb-scargle periodogram (LSF+LSP), empirical mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram (EMD+LSP) and variational mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram (VMD+LSP)
方法 RMSE/cm 相关系数 反演点数 LSF+LSP 6.69 0.96 4 909 EMD+LSP 5.58 0.97 4 641 VMD+LSP 5.50 0.98 5 268 表 3 基于最小二乘拟合+加窗的频谱分析(LSF+WinLSP)、经验模态分解+加窗的频谱分析(EMD+WinLSP)和变分模态分解+加窗的频谱分析(VMD+WinLSP)的GTGU站海平面高度反演结果的精度对比
Tab. 3 Accuracy comparison of sea level height inversion results of GTGU Station based on least squares fitting+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (LSF+WinLSP), empirical mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (EMD+WinLSP) and variational mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (VMD+WinLSP)
方法 RMSE/cm 相关系数 反演点数 LSF+WinLSP 5.50 0.97 5 439 EMD+WinLSP 5.51 0.97 5 450 VMD+WinLSP 4.70 0.98 5 647 表 4 基于最小二乘拟合+频谱分析(LSF+LSP)、经验模态分解+频谱分析(EMD+LSP)和变分模态分解+频谱分析(VMD+LSP)的SC02站海平面高度反演结果的精度对比
Tab. 4 Accuracy comparison of sea level height inversion results of SC02 Station based on least squares fitting+lomb-scargle periodogram (LSF+LSP), empirical mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram (EMD+LSP) and variational mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram (VMD+LSP)
方法 RMSE/cm 相关系数 反演点数 LSF+LSP 16.36 0.99 1 632 EMD+LSP 15.83 0.99 1 641 VMD+LSP 14.46 0.99 1 723 表 5 基于最小二乘拟合+加窗的频谱分析(LSF+WinLSP)、经验模态分解+加窗的频谱分析(EMD+WinLSP)和变分模态分解+加窗的频谱分析(VMD+WinLSP)的SC02站海平面高度反演结果的精度对比
Tab. 5 Accuracy comparison of sea level height inversion results of SC02 Station based on least squares fitting+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (LSF+WinLSP), empirical mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (EMD+WinLSP) and variational mode decomposition+lomb-scargle periodogram with window (VMD+WinLSP)
方法 RMSE/cm 相关系数 反演点数 LSF+WinLSP 15.45 0.99 1 696 EMD+WinLSP 15.44 0.99 1 725 VMD+WinLSP 14.34 0.99 1 785 -
[1] Bindoff N L, Willebrand J, Artale V, et al. Observations: oceanic climate change and sea level[M]//Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, et al. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007: 385−433. [2] Martín-Neira M, Caparrini M, Font-Rossello J, et al. The PARIS concept: an experimental demonstration of sea surface altimetry using GPS reflected signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 142−150. doi: 10.1109/36.898676 [3] Yoshihara T, Saito S, Fujii N, et al. A study on detection of sea level variation using GPS signal reflected by sea surface[C]//Proceedings of the 2006 National Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation. Monterey: ION, 2006: 217−223. [4] 张勇, 符养, 李烨, 等. 一种新型星载GNSS-R系统的地面验证实验[J]. 海洋测绘, 2013, 33(1): 18−21, 25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2013.01.006Zhang Yong, Fu Yang, Li Ye, et al. A ground experiment to demonstrate a new satellite-based GNSS-R system[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2013, 33(1): 18−21, 25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2013.01.006 [5] Zhang Yun, Tian Luman, Meng Wanting, et al. Feasibility of code-level altimetry using coastal BeiDou reflection (BeiDou-R) setups[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 4130−4140. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2446684 [6] Treuhaft R N, Lowe S T, Zuffada C, et al. 2-cm GPS altimetry over Crater Lake[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(23): 4343−4346. doi: 10.1029/2001GL013815 [7] 姚彦鑫, 杨东凯, 张其善. 利用GNSS反射信号载波测量湖面高度变化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 35(9): 1072−1075. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2009.09.002Yao Yanxin, Yang Dongkai, Zhang Qishan. Lake height variation measurement utilizing GNSS reflected signal carrier phase[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009, 35(9): 1072−1075. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2009.09.002 [8] Löfgren J S, Haas R, Johansson J M. Monitoring coastal sea level using reflected GNSS signals[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2011, 47(2): 213−220. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2010.08.015 [9] Zhang Yun, Li Binbin, Tian Luman, et al. Phase altimetry using reflected signals from BeiDou GEO satellites[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(10): 1410−1414. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2578361 [10] Hu Yuan, Yuan Xintai, Liu Wei, et al. GNSS-IR model of sea level height estimation combining variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10405−10414. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3118398 [11] 胡媛, 袁鑫泰, 陈行杨, 等. 小波变换和改进Burg算法的GNSS-IR海面高度反演模型[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(1): 21−24, 53. doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.01.005Hu Yuan, Yuan Xintai, Chen Xingyang, et al. GNSS-IR model of sea level altimetry inversion combining wavelet transform with improved burg algorithm[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(1): 21−24, 53. doi: 10.14075/j.jgg.2022.01.005 [12] Larson K M, Ray R D, Nievinski F G, et al. The accidental tide gauge: a GPS reflection case study from Kachemak Bay, Alaska[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(5): 1200−1204. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2236075 [13] Löfgren J S, Haas R, Scherneck H G. Sea level time series and ocean tide analysis from multipath signals at five GPS sites in different parts of the world[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2014, 80: 66−80. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2014.02.012 [14] York D. Least squares fitting of a straight line with correlated errors[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1968, 5: 320−324. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(68)80059-7 [15] Lomb N R. Least-squares frequency analysis of unequally spaced data[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 1976, 39(2): 447−462. doi: 10.1007/BF00648343 [16] 胡广书. 数字信号处理: 理论、算法与实现[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2003.Hu Gangshu. Digital Signal Processing: Theory, Algorithm and Implementatio[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2003. [17] Nievinski F G, Larson K M. Inverse modeling of GPS multipath for snow depth estimation—Part II: Application and validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6564−6573. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2297688 [18] Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531−544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [19] Huang N E, Shen Zheng, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903−995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [20] 张慧娟, 李冬. 相关系数判决的EMD在振动数据趋势项提取中的应用[J]. 舰船电子工程, 2018, 38(5): 159−163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.05.038Zhang Huijuan, Li Dong. Application of EMD of correlation coefficient judgment in the extraction of vibration data trend[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2018, 38(5): 159−163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2018.05.038 [21] 胡媛, 袁鑫泰, 刘卫, 等. 基于VMD-MA的GNSS-MR雪深监测方法[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1−12[2022−06−01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=BJHK20220323001&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=OizuDw5HNuMENFcfLu3840zfDU9p8qGXT15-9q9hf8ZmWIDAORcjqPsmh9G8awJe. DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0777Hu Yuan, Yuan Xintai, Liu Wei, et al. GNSS-MR snow depth monitoring method based on variational mode decomposition and moving average[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1−12[2022−06−01]. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=BJHK20220323001&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=OizuDw5HNuMENFcfLu3840zfDU9p8qGXT15-9q9hf8ZmWIDAORcjqPsmh9G8awJe. DOI: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0777 [22] 杨婧, 程乃平, 倪淑燕. Welch算法在弱信号检测中的性能分析[J]. 计算机仿真, 2020, 37(5): 235−240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.05.047Yang Jing, Cheng Naiping, Ni Shuyan. Performance analysis of welch algorithm in weak signal detection[J]. Computer Simulation, 2020, 37(5): 235−240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2020.05.047 [23] Lin Yuanpei, Vaidyanathan P P. A Kaiser window approach for the design of prototype filters of cosine modulated filterbanks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 1998, 5(6): 132−134. doi: 10.1109/97.681427 [24] Arya R, Jaiswal S. Design of low pass FIR Filters using Kaiser window function with variable parameter Beta (β)[J]. International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Research, 2015, 3: 220−224. [25] Geremia-Nievinski F, Hobiger T, Haas R, et al. SNR-based GNSS reflectometry for coastal sea-level altimetry: results from the first IAG inter-comparison campaign[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(8): 1−15. doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01387-3 -




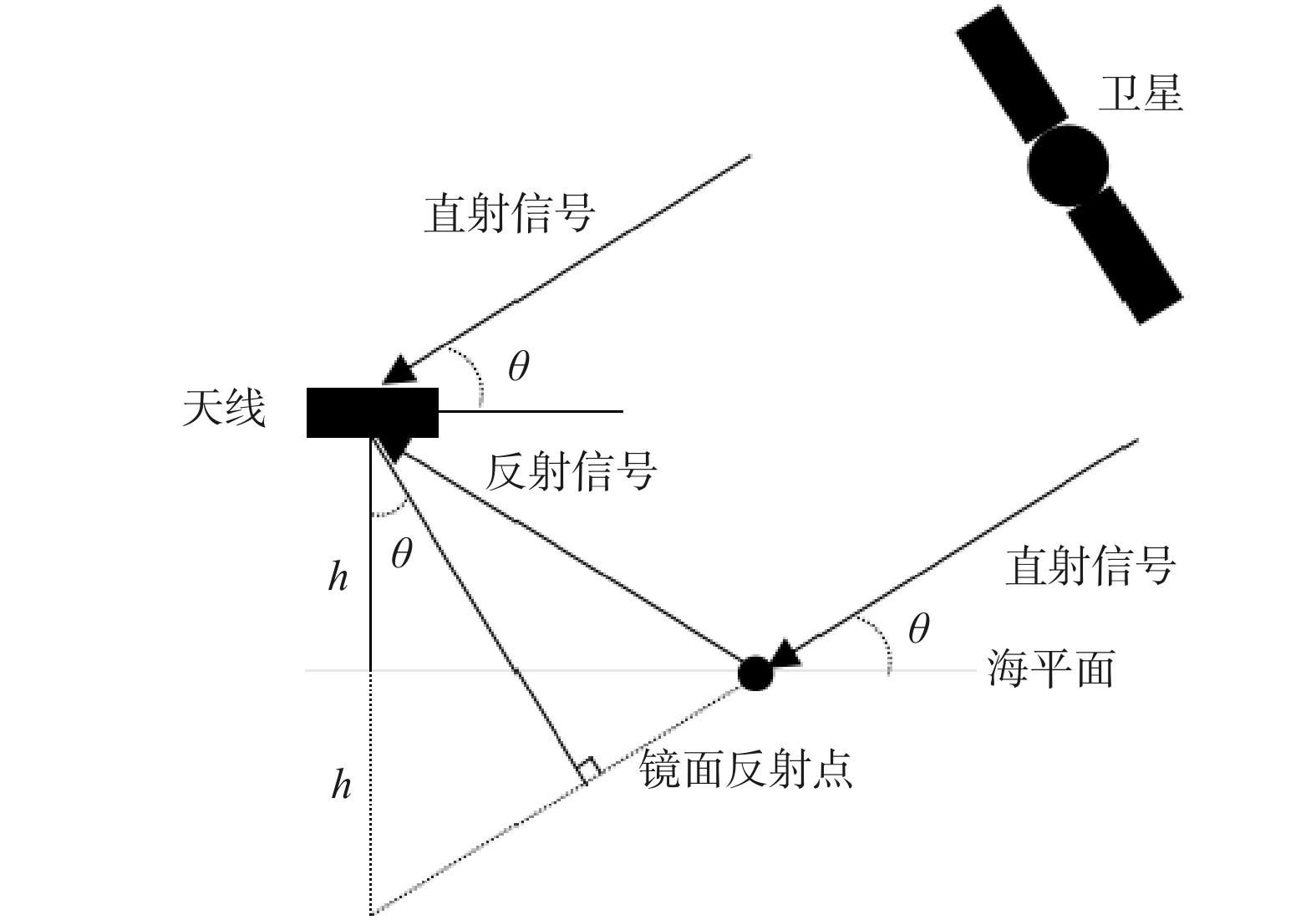
 下载:
下载: