Estimation of coral reef area from multi-temporal and multi-spectral satellite images: A case study on Lingyang Reef, Xisha Islands
-
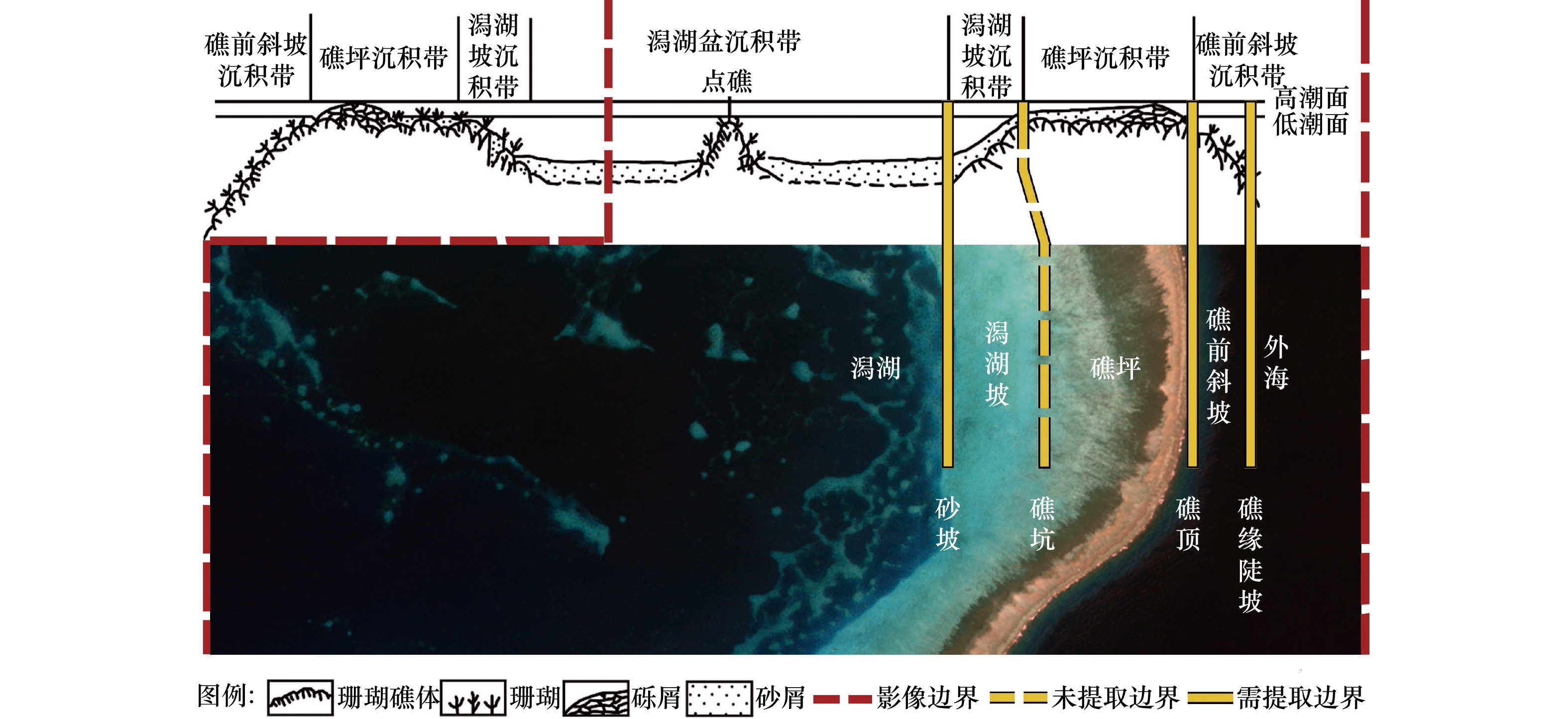
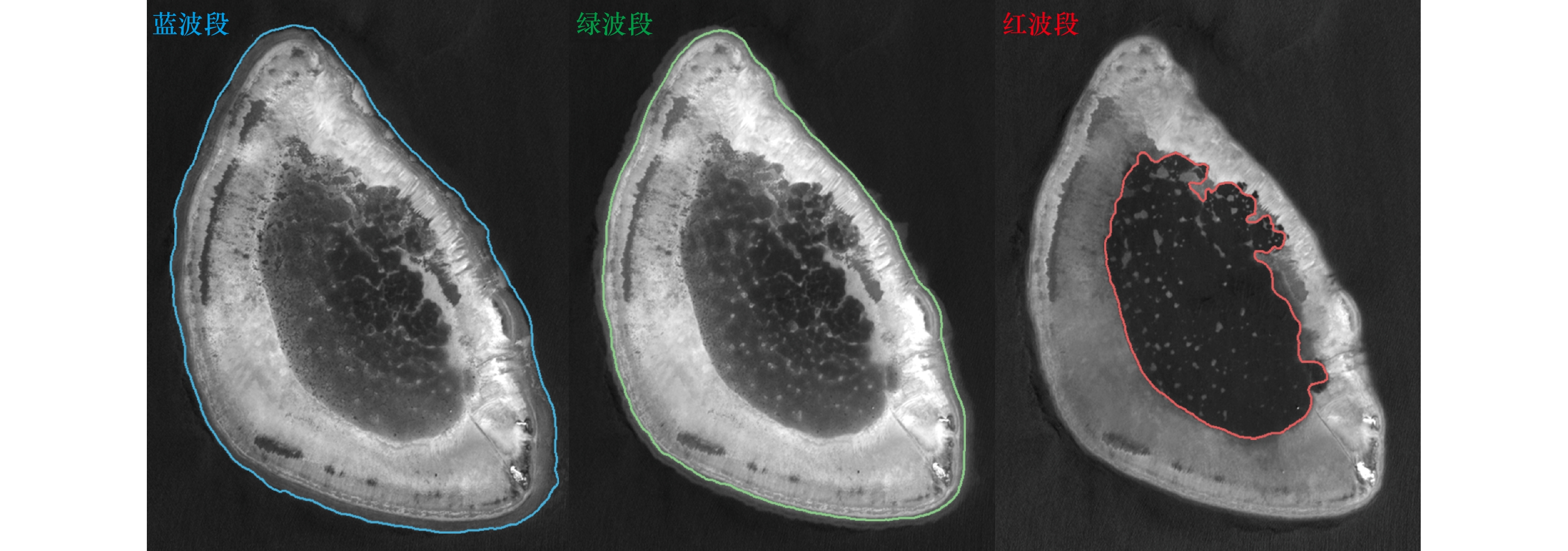
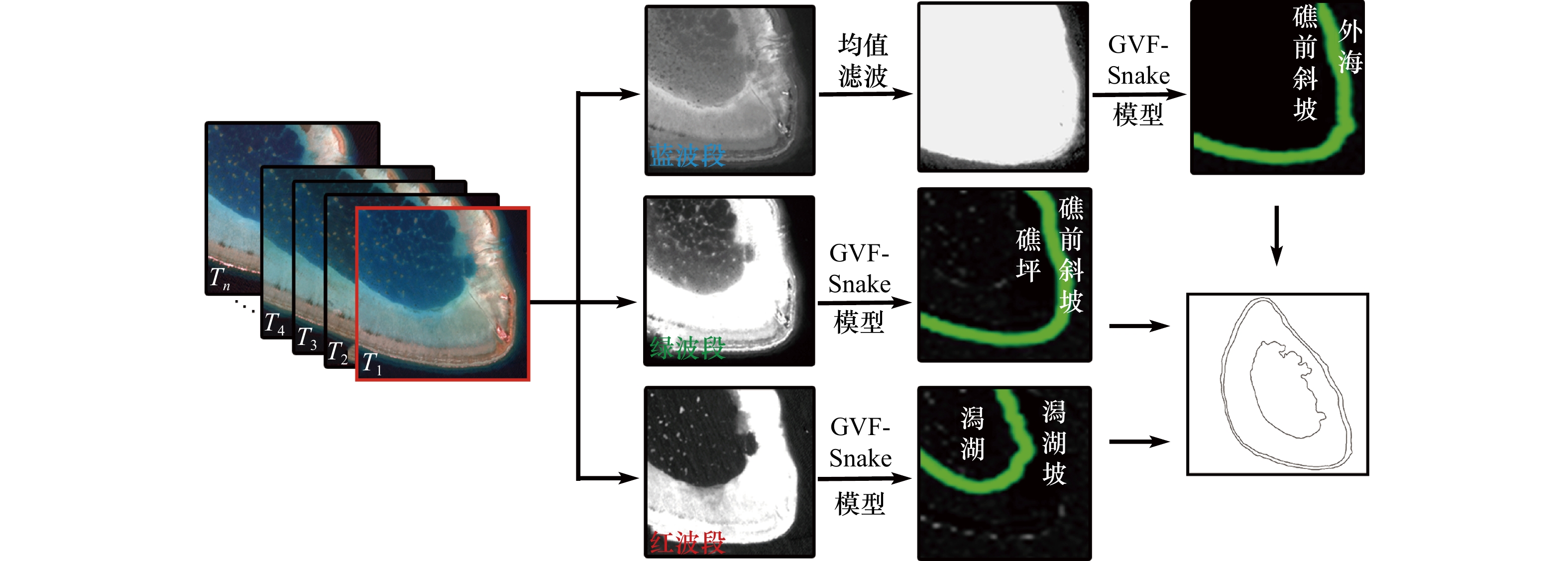
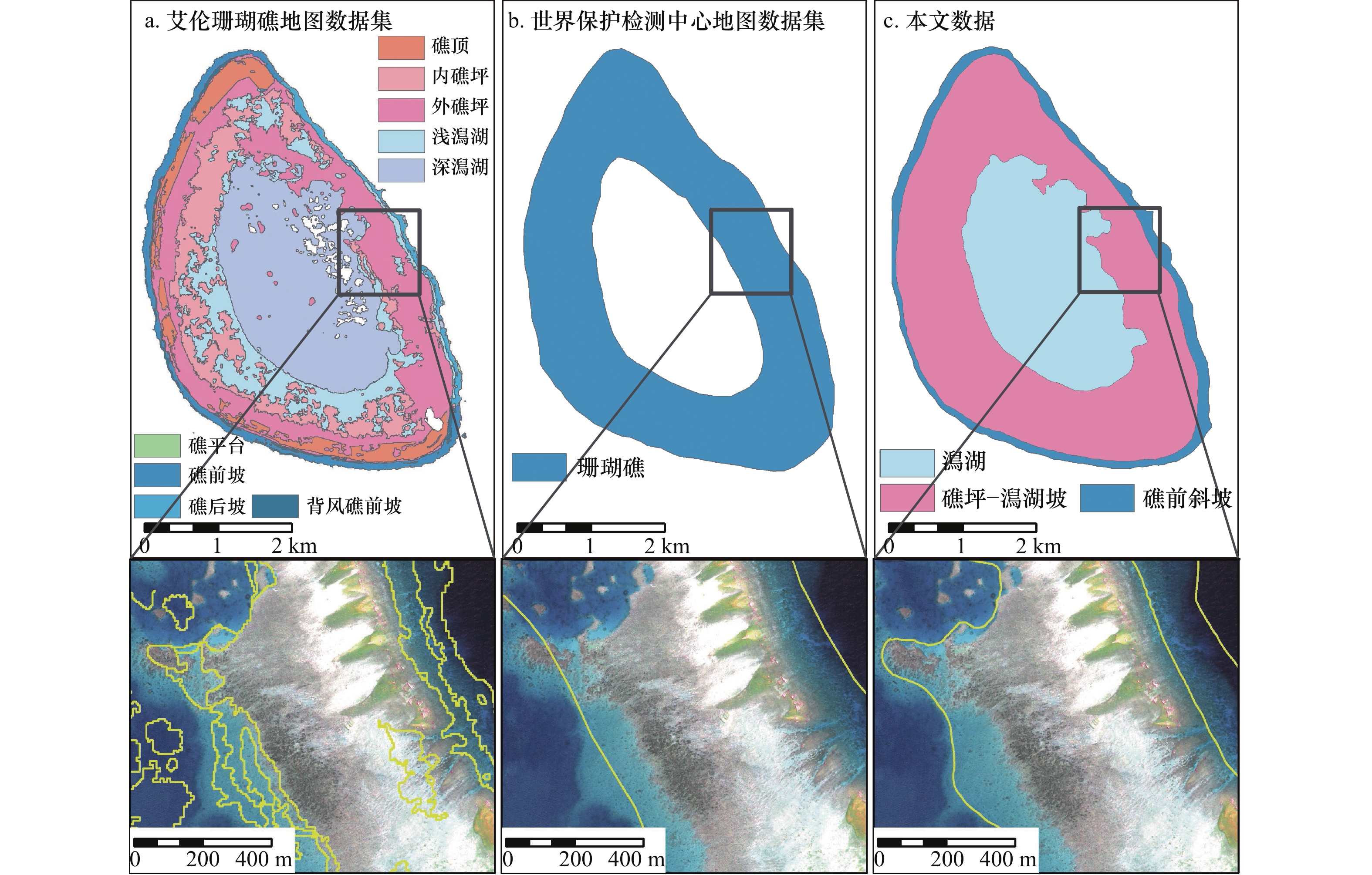
摘要: 准确计算珊瑚礁的面积是评估其资源、环境效应的基础,但我国迄今对南海珊瑚礁的面积估算仍缺乏共识,缺少可靠的估算方法是导致这一现象的重要原因。针对这一问题,本文以西沙群岛羚羊礁为例,提出了一种利用多时相多光谱遥感影像低成本半自动化估算珊瑚礁面积的方法。首先快速目视确定地貌带分界线的粗略位置,然后利用基于梯度向量场的主动轮廓线模型(Gradient Vector Flow-Snake, GVF-Snake)实现这些分界线位置的自动精化,最后将不同时相的瞬时分界线转换为面要素进行多时相的融合,从而得到珊瑚礁的面积。基于53景Sentinel-2 多光谱成像仪(MSI)影像的实验表明,羚羊礁的总面积为17.22 km2(Landsat 8 陆地成像仪(OLI)用于方法稳定性的验证,得到的羚羊礁面积为17.29 km2),其中礁前斜坡、礁坪−潟湖坡、潟湖的面积分别为1.76 km2、10.29 km2、5.17 km2。该数值与实测数据具有较好的一致性。具体地,该方法获得的地貌带分界点与实测水深所指示分界点的位置偏差能控制在0.2~4.9 m的范围内(不超过0.5个像素),珊瑚礁最外轮廓线与30 m等深线的位置偏差亦在1个像素大小内(5.7~9.5 m),而估算面积与高分辨率WorldView-2影像解译得到的面积差异为0.02%。同时,该方法获得的珊瑚礁边界线的完整度、正确度、提取质量精度能够由单时相平均的60%、64%和54%分别提高至84%、83%和72%。此外,该方法能够减小基于不同遥感数据源的珊瑚礁面积估算结果的差异,即6景以上的多时相Sentinel-2 MSI和Landsat 8 OLI影像提取的珊瑚礁面积标准差分别不超过0.01 km2和0.05 km2,仅相当于珊瑚礁总面积的0.2%和0.5%。总而言之,该方法能够用低成本的10 m分辨率Sentinel-2 MSI和30 m分辨率Landsat 8 OLI影像获得接近1.8 m分辨率WorldView-2影像的面积估算精度,且具有良好的稳定性和可靠性。Abstract: Estimating coral reef area accurately is fundamental for assessing the resource and environmental effects on coral reefs. However, there is little clear agreement on the areas of coral reefs until now. The main reason is that there is lack of a reliable method to estimate the areas of coral reefs. To address this problem, a low-cost semi-automatic method of coral reef area estimation by using multi-temporal and multi-spectral satellite images is proposed in this paper. The method contains extraction of instantaneous boundaries and fusion of the boundaries. Firstly, the boundaries of the coral reef geomorphologic zones are automatically delineated by using gradient vector flow-snake model (GVF-Snake) after roughly locating the positions of the geomorphic zone boundaries. Thereafter, the extracted multi-temporal geomorphic zone boundaries are converted to geomorphic zone areas and then fused to establish a reliable and accurate geomorphic zone. According to our experiments on the 53 images of Sentinel-2 MSI (the Landsat 8 OLI images are used to verify method stability, the area of Ling Yang Reef is 17.29 km2), the area of Ling Yang Reef is 17.22 km2, among which the areas of the front reef slope, the reef flat-lagoon slope, and the lagoon are 1.76 km2, 10.29 km2, and 5.17 km2, respectively. The results are consistent with in-field survey data. Specifically, the differences between the positions of the geomorphic zone boundaries extracted by using the proposed method and those determined by bathymetric data are in the range of 0.2−4.9 m (less than 0.5 pixel of Sentinel-2 MSI images). The differences between the outline of the coral reef and the 30 m isobath line is also within 1 pixel (5.7−9.5 m). The difference between the area extracted from multi-temporal images by using the proposed method and the area determined by using a high-resolution WorldView-2 image is 0.02%, i.e. Coral reef area calculated from multi-temporal Sentinel-2 MSI images by using our method is able to compete to high-resolution WorldView-2 image in accuracy. Furthermore, the complete, the correction, and the quality of the boundaries are improved from 60%, 64%, and 54% for single-image method to 84%, 83%, and 72% for our multi-temporal method, respectively. Besides, the proposed method can also reduce variations of the estimated coral reef area caused by using satellite images with different sensors. In other word, if more than 6 scenes of satellite images was utilized, the standard deviations of the estimated coral reef area are shown to be less than 0.01 km2 and 0.05 km2 respectively for Sentinel-2 MSI and Landsat 8 OLI images. They are only equivalent to 0.2% and 0.5% of the total coral reef area. In summary, the proposed method is accurate, reliable, and stable for coral reef area estimation.1) 底图来自自然资源部标准地图服务系统(http://hism.mnr.gov.cn/sjkf/bzdt/201902/t20190214_3124659.html),审图号为琼S(2020)038号。2) 精度评价示意图转绘自周亚男等[47]
-
图 1 研究区域①
Fig. 1 The study area
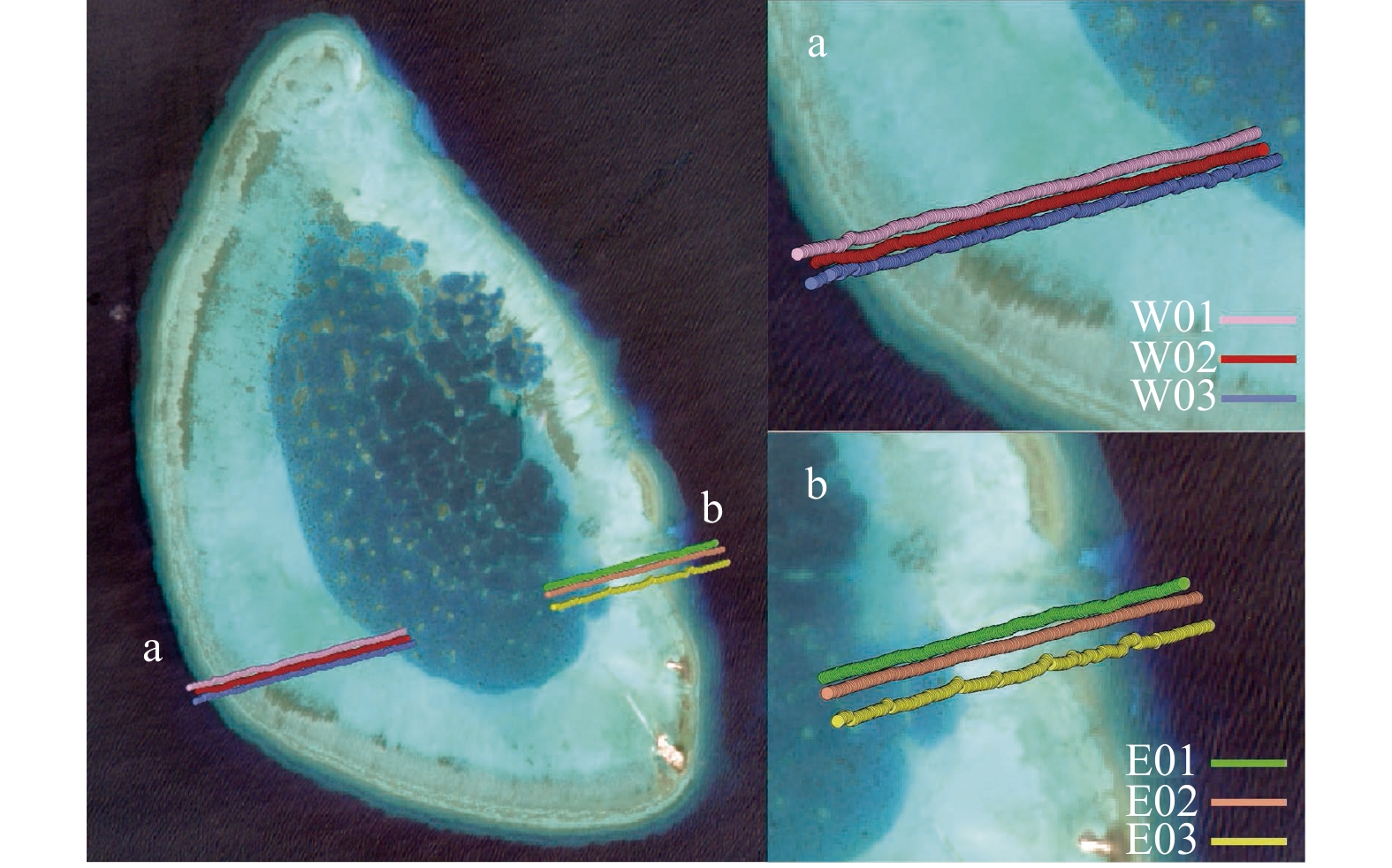
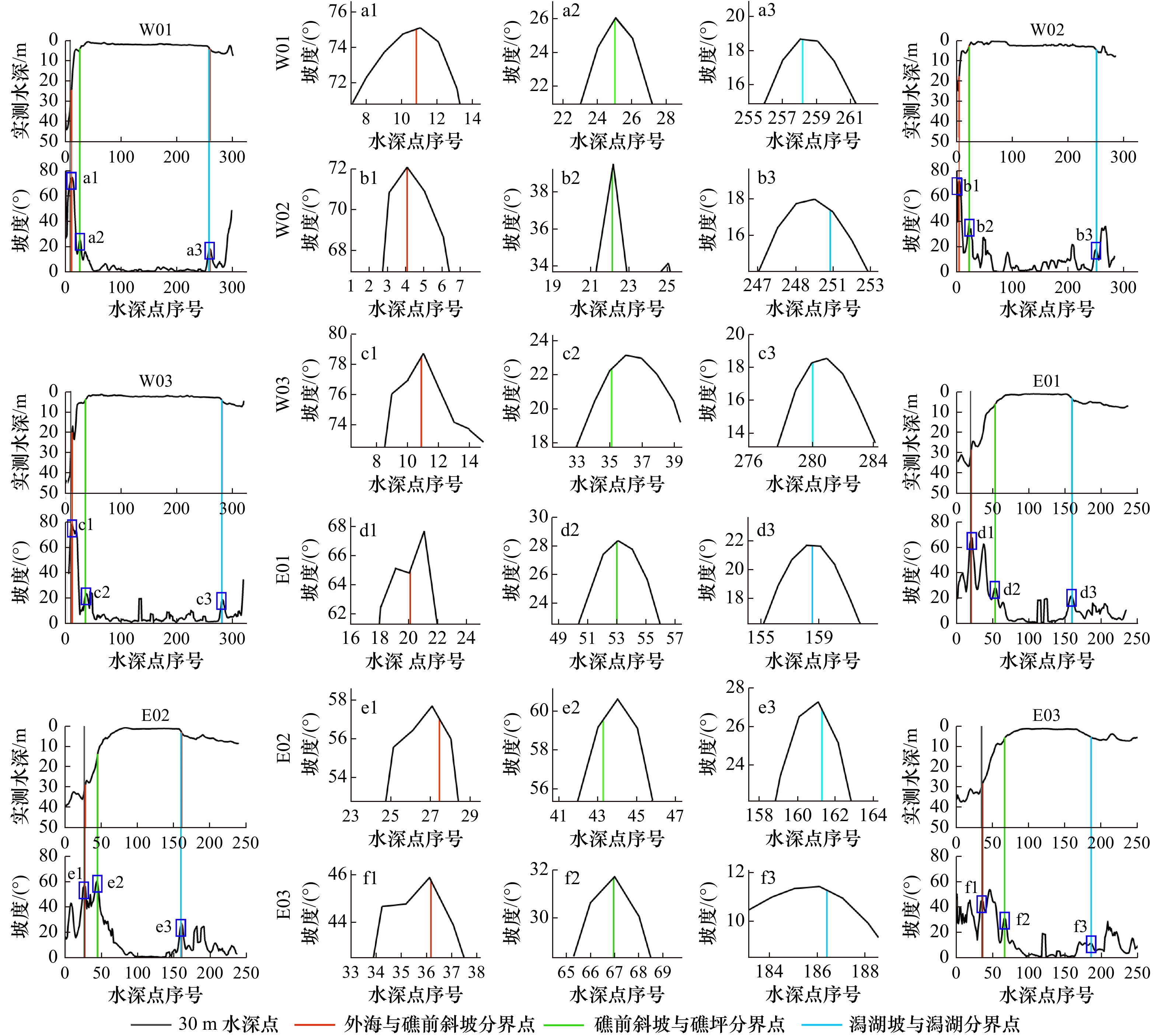
图 9 水深剖面与地貌分带的对比
a−f分别代表W01−W03和E01−E03 6条剖面;1~3分别代表外海与礁前斜坡分界线、礁前斜坡与礁坪分界线以及潟湖坡与潟湖分界线
Fig. 9 Comparison of water depth profile and geomorphic zonation
a−f represent six water-depth profiles W01−W03 and E01−E03 respectively; 1−3 represent the boundary between ocean and reef slope, reef slope and reef flat, and lagoon slope and lagoon respectively
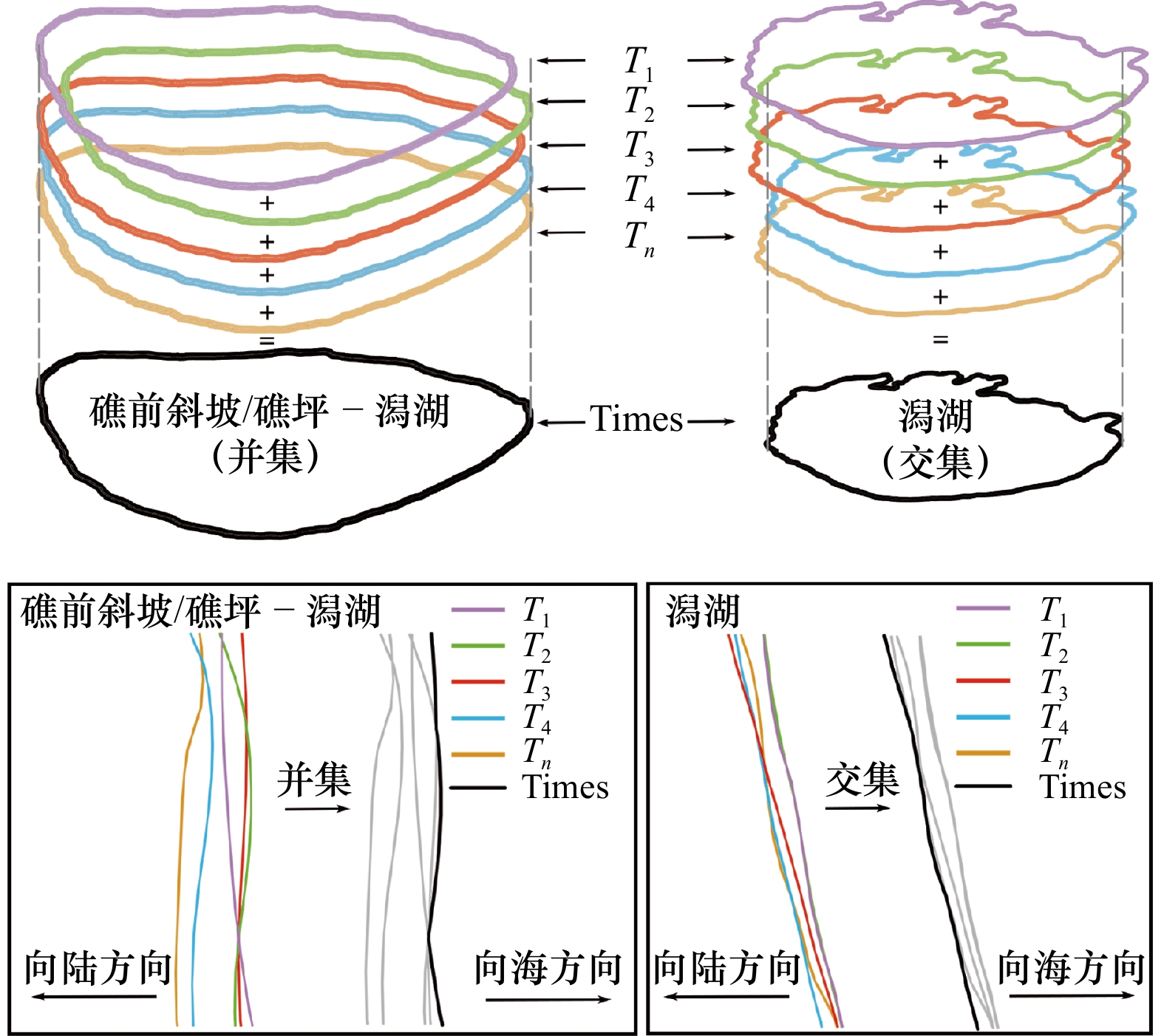
图 10 不同时相的提取面积与参考面积的差异
差异 = |(提取面积−参考面积)| / 参考面积,其中单时相的面积差异为随机挑选的8组单时相面积差异绝对值的平均值
Fig. 10 The difference between extraction area and reference area in different phases
Differences =|(extraction area−reference area)|/reference area, the difference when single phase of the area as randomly selected 8 groups of single phase area difference is the average of the absolute value
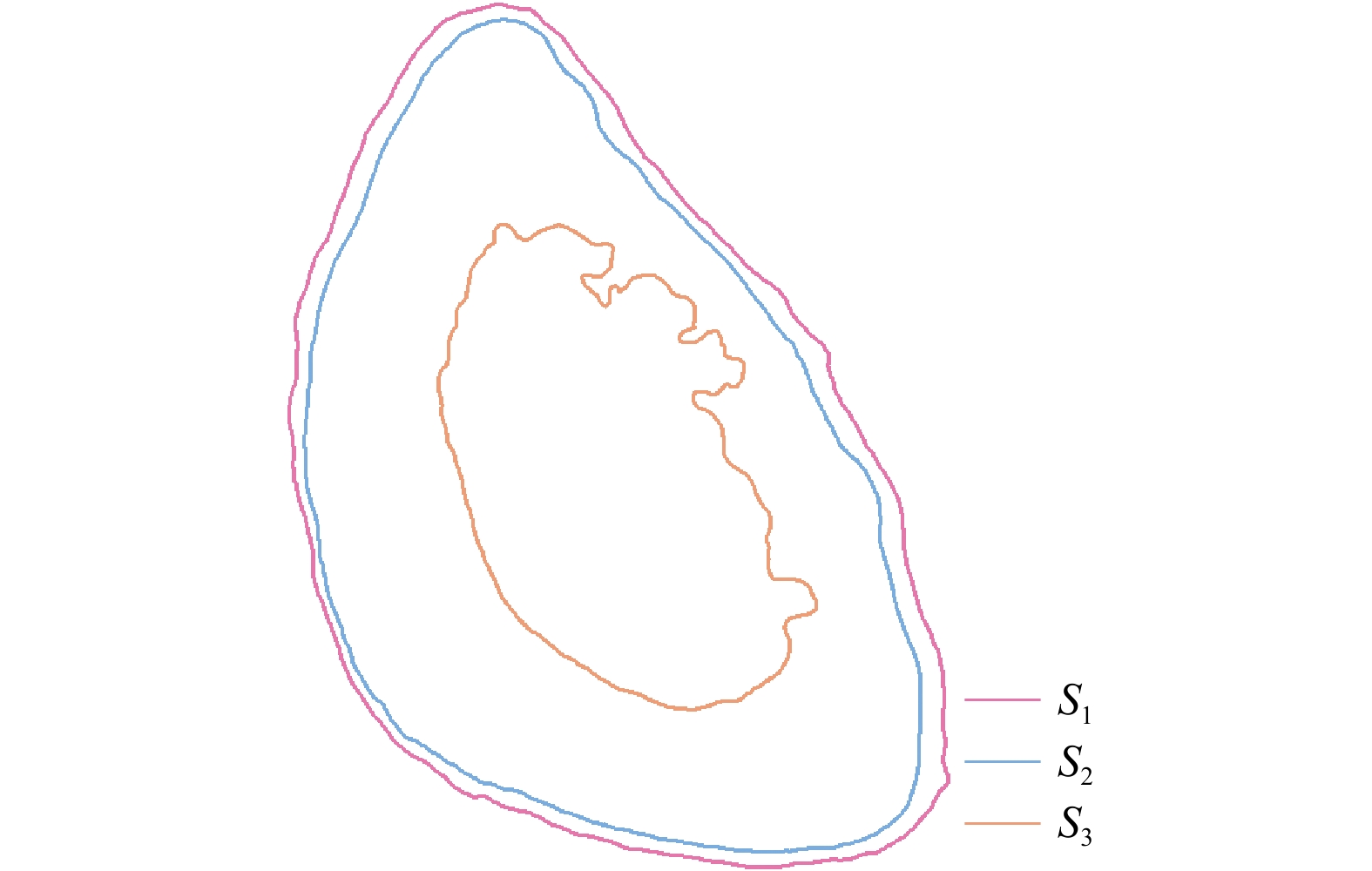
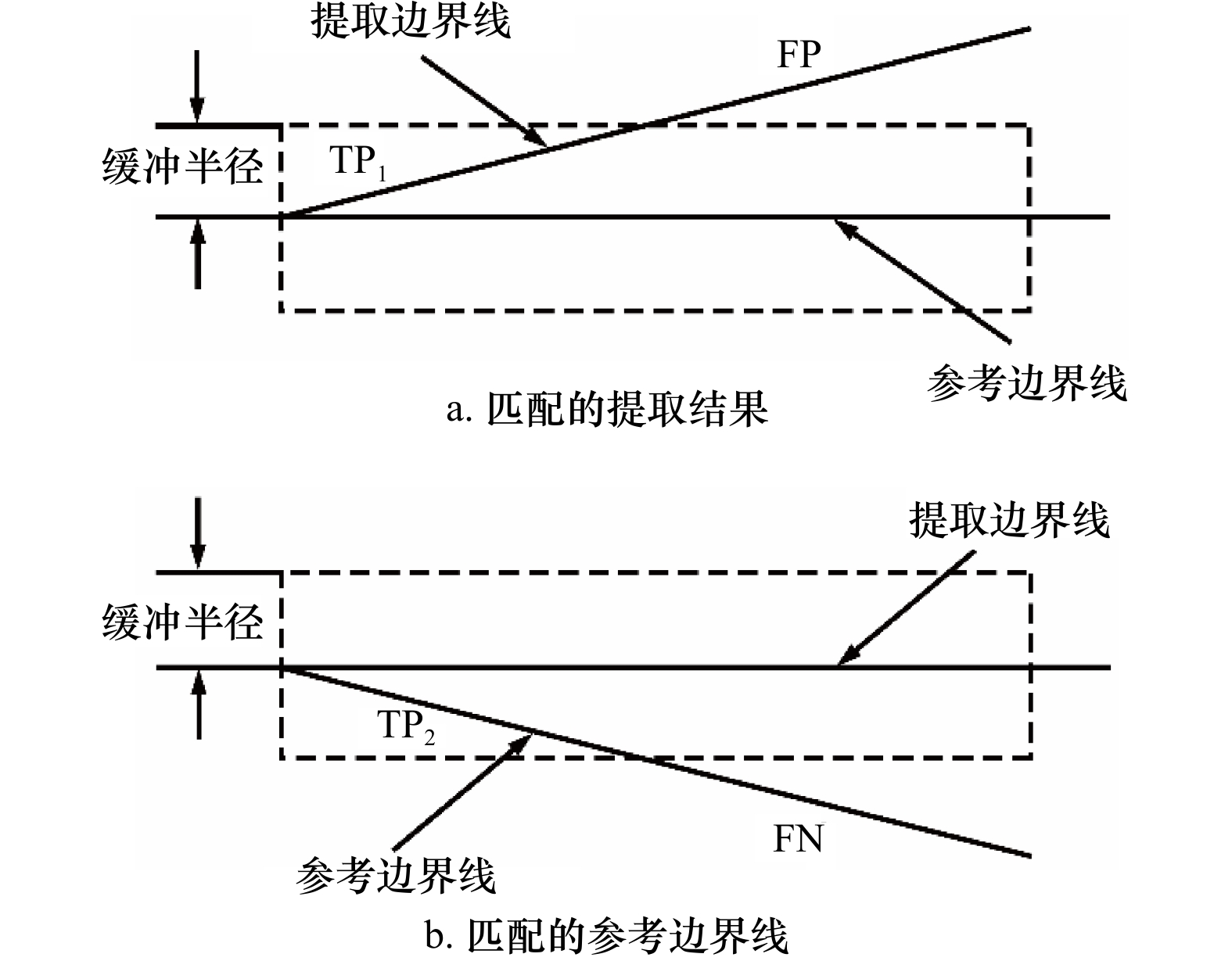
A1 精度评价示意图[②]
A1 Diagram of accuracy evaluation
表 1 提取地貌带分界点与实测剖面30 m水深点、坡度极值点的距离对比(单位:m)
Tab. 1 The distance between extracted boundary points of geomorphic zone with 30 m water depth points and measured slope extreme points is compared (unit: m)
实测数据类型 地貌带分界点 实测剖面 W01 W02 W03 E01 E02 E03 30 m水深点 外海与礁前斜坡 9.5 * 8.9 8.1 5.8 5.7 坡度极值点 外海与礁前斜坡 1.2 0.1 0.8 4.9 1.9 0.3 礁前斜坡与礁坪 0.2 0.2 4.8 0.7 3.8 0.2 潟湖坡与潟湖 0.5 4.2 4.8 2.3 1.1 1.2 注:*表示该实测剖面未包含30 m水深,故未有与提取地貌分界点的位置偏差数据。 A1 本文所用遥感影像信息列表
A1 List of satellite images used in this paper
序号 日期 时间(GMT) 传感器 Sentinel-2 1 2021年4月29日 02:55:39 MSI 2 2021年4月24日 02:55:41 MSI 3 2021年4月14日 02:55:41 MSI 4 2021年4月4日 02:55:41 MSI 5 2021年3月30日 02:55:39 MSI 6 2021年3月5日 02:56:11 MSI 7 2021年2月28日 02:56:49 MSI 8 2021年2月3日 02:59:31 MSI 9 2021年1月24日 03:00:21 MSI 10 2020年11月25日 03:00:31 MSI 11 2020年9月21日 02:55:49 MSI 12 2020年8月7日 02:55:51 MSI 13 2020年7月23日 02:55:49 MSI 14 2020年7月18日 02:55:51 MSI 15 2020年6月23日 02:55:49 MSI 16 2020年6月18日 02:55:51 MSI 17 2020年6月8日 02:55:51 MSI 18 2020年5月9日 02:55:51 MSI 19 2020年5月4日 02:55:39 MSI 20 2020年4月19日 02:55:51 MSI 21 2020年3月25日 02:55:39 MSI 22 2020年3月20日 02:55:41 MSI 23 2020年3月10日 02:55:41 MSI 24 2020年2月14日 02:58:19 MSI 25 2019年12月26日 03:01:29 MSI 26 2019年9月22日 02:55:41 MSI 27 2019年8月18日 02:55:49 MSI 28 2019年8月13日 02:55:51 MSI 29 2019年7月24日 02:55:51 MSI 30 2019年7月14日 02:55:51 MSI 31 2019年7月4日 02:55:51 MSI 32 2019年5月20日 02:55:59 MSI 33 2019年3月21日 02:55:49 MSI 34 2019年3月6日 02:56:01 MSI 35 2019年3月1日 02:56:39 MSI 36 2019年2月24日 02:57:11 MSI 37 2019年2月9日 02:58:59 MSI 38 2018年10月17日 02:57:11 MSI 39 2018年7月29日 02:55:51 MSI 40 2018年7月4日 02:55:49 MSI 41 2018年6月19日 02:55:41 MSI 42 2018年5月15日 02:55:39 MSI 43 2018年4月30日 02:55:51 MSI 44 2018年4月25日 02:55:49 MSI 45 2018年4月20日 02:55:51 MSI 46 2018年3月16日 02:55:39 MSI 47 2018年3月1日 02:56:31 MSI 48 2017年9月17日 02:55:39 MSI 49 2017年8月8日 02:55:39 MSI 50 2017年6月14日 02:55:41 MSI 51 2017年3月6日 02:55:51 MSI 52 2016年3月21日 02:56:02 MSI 53 2015年12月22日 03:01:32 MSI Landsat 8 1 2020年11月16日 02:54:08 OLI 2 2020年9月13日 02:54:04 OLI 3 2020年7月27日 02:53:46 OLI 4 2020年3月21日 02:53:39 OLI 5 2020年1月17日 02:54:00 OLI 6 2019年9月11日 02:54:05 OLI 7 2019年8月10日 02:53:57 OLI 8 2019年7月25日 02:53:50 OLI 9 2019年7月9日 02:53:46 OLI 10 2019年6月23日 02:53:42 OLI 11 2019年5月22日 02:53:29 OLI 12 2019年3月19日 02:53:30 OLI 13 2019年3月3日 02:53:30 OLI 14 2018年10月10日 02:53:39 OLI 15 2018年6月20日 02:52:47 OLI 16 2018年3月16日 02:53:24 OLI 17 2017年9月21日 02:54:00 OLI 18 2017年8月4日 02:53:49 OLI 19 2016年9月2日 02:54:02 OLI 20 2016年6月14日 02:53:32 OLI 21 2016年1月22日 02:53:55 OLI 22 2015年6月28日 02:53:12 OLI 23 2015年5月27日 02:52:54 OLI WolrdView-2 1 2014年10月9日 03:24:59 MUL -
[1] 余克服. 珊瑚礁科学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 578.Yu Kefu. Introduction to the Science of Coral Reefs[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018: 578. [2] 余克服, 张光学, 汪稔. 南海珊瑚礁: 从全球变化到油气勘探—第三届地球系统科学大会专题评述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2014, 29(11): 1287−1293. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1287Yu Kefu, Zhang Guangxue, Wang Ren. Studies on the coral reefs of the South China Sea: from global change to oil-gas exploration[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2014, 29(11): 1287−1293. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.11.1287 [3] Chen Xiaoyan, Yu Kefu, Huang Xueyong, et al. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition increases the possibility of macroalgal dominance on remote coral reefs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2019, 124(5): 1355−1369. doi: 10.1029/2019JG005074 [4] 刘嘉鎏. 南海珊瑚岛、礁对近40年气候变暖响应的遥感影像记录[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2020.Liu Jialiu. Response of coral reefs and islands in the South China Sea to climate warming in the past 40 years recorded by remote sensing images[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020. [5] McLeod E, Shaver E C, Beger M, et al. Using resilience assessments to inform the management and conservation of coral reef ecosystems[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 277: 111384. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111384 [6] 王丽荣, 余克服, 赵焕庭, 等. 南海珊瑚礁经济价值评估[J]. 热带地理, 2014, 34(1): 44−49.Wang Lirong, Yu Kefu, Zhao Huanting, et al. Economic valuation of the coral reefs in South China Sea[J]. Tropical Geography, 2014, 34(1): 44−49. [7] Courtney T A, Andersson A J. Evaluating measurements of coral reef net ecosystem calcification rates[J]. Coral Reefs, 2019, 38(5): 997−1006. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01828-2 [8] Liu Jialiu, Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu, et al. How lime-sand islands in the South China Sea have responded to global warming over the last 30 years: evidence from satellite remote sensing images[J]. Geomorphology, 2020, 371: 107423. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107423 [9] 黄荣永, 余克服, 王英辉, 等. 珊瑚礁遥感研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(6): 1091−1112.Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Progress of the study on coral reef remote sensing[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(6): 1091−1112. [10] Hughes T P, Huang Hui, Young M A L. The wicked problem of China’s disappearing coral reefs[J]. Conservation Biology, 2013, 27(2): 261−269. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01957.x [11] Spalding M D, Ravilious C R, Green E P. World Atlas of Coral Reefs[M]. Berkeley, California, USA: University of California Press, 2001: 436. [12] 赵焕庭. 华南海岸和南海诸岛地貌与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999: 528.Zhao Huanting. Geomorphology and Environment of South China Coast and South China Sea Islands[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999: 528. [13] Wang Pinxian, Li Qianyu. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and Sedimentology[M]. Dordrecht: Springer, 2009: 516. [14] 黄晖, 尤丰, 练健生, 等. 珠江口万山群岛海域造礁石珊瑚群落分布与保护[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(2): 189−197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.02.010Huang Hui, You Feng, Lian Jiansheng, et al. Status and conservation strategies of the scleractinian coral community in the Wanshan Islands at Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2012, 31(2): 189−197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2012.02.010 [15] 赵焕庭. 中国现代珊瑚礁研究[J]. 世界科技研究与发展, 1998(4): 98−105.Zhao Huanting. Researches of coral reef in modern China[J]. World Science and Technology Research and Development, 1998(4): 98−105. [16] UNEP-WCMC, World Fish Centre, WRI, et al. Global distribution of coral reefs[DB/OL]. [2021−06−09]. https://data.unep-wcmc.org/datasets/1 [17] Atlas A C. Imagery, maps and monitoring of the world's tropical coral reefs[DB/OL]. [2021−06−09]. https://integration.allencoralatlas.com/atlas/ [18] Dai C. Dongsha atoll in the South China Sea: past, present and future[C]//Islands of the World VIII International Conference “Changing Islands – Changing Worlds”. [S.l.: s.n.], 2004. [19] 曾昭璇. 南海环礁的若干地貌特征[J]. 海洋通报, 1984, 3(3): 40−45.Zeng Zhaoxuan. Geomorphological features of atolls in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1984, 3(3): 40−45. [20] 曾昭璇, 梁景芬, 丘世钧. 中国珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 广州: 广东人民出版社, 1997: 474.Zeng Zhaoxuan, Liang Jingfen, Qiu Shijun. The Physiognomy of Coral Reef in China[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong People’s Public House, 1997: 474. [21] 陈史坚. 南海诸岛地名资料汇编[M]. 广州: 广东省地图出版社, 1987.Chen Shijian. A Compilation of Geographical Names of Nanhai Zhudao[M]. Guangzhou: Guangdong Map Publishing House, 1987. [22] 钟晋梁. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁地貌研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.Zhong Jinliang. Geomorphology Research of Coral Reef of Nansha Islands[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [23] Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu, Wang Yinghui, et al. Bathymetry of the coral reefs of Weizhou Island based on multispectral satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(7): 750. doi: 10.3390/rs9070750 [24] Andréfouët S, Muller-Karger F E, Robinson J A, et al. Global assessment of modern coral reef extent and diversity for regional science and management applications: a view from space[C]//Proceedings of the 10th ICRS. Okinawa, Japan: Japanese Coral Reef Society, 2006: 1732−1745. [25] Purkis S J, Gleason A C R, Purkis C R, et al. High-resolution habitat and bathymetry maps for 65, 000 sq. km of Earth’s remotest coral reefs[J]. Coral Reefs, 2019, 38(3): 467−488. doi: 10.1007/s00338-019-01802-y [26] 朱海天, 冯倩, 梁超, 等. 基于随机森林的南沙岛礁分类方法研究[C]//“一带一路”战略与海洋科技创新——中国海洋学会2015年学术论文集. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.Zhu Haitian, Feng Qian, Liang Chao, et al. Study on classification method of Nansha Islands based on random forest[C]//“One Belt, One Road” Strategy and Marine Science and Technology Innovation—China Ocean Society 2015 Academic Papers. Beijing : China Ocean Press, 2015. [27] 李成鹏, 徐慧, 禹文清. 基于中等分辨率遥感影像的珊瑚礁信息提取[J]. 北京测绘, 2020, 34(2): 214−218.Li Chengpeng, Xu Hui, Yu Wenqing. Analysis of classification ability of island nearshore substrate based on medium resolution remote sensing image[J]. Beijing Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 34(2): 214−218. [28] 董娟, 任广波, 胡亚斌, 等. 基于高分辨率遥感的珊瑚礁地貌单元体系构建和分类方法——以8波段Worldview-2影像为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(4): 116−129.Dong Juan, Ren Guangbo, Hu Yabin, et al. Construction and classification of coral reef geomorphic unit system based on high-resolution remote sensing: using 8-band Worldview-2 image as an example[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 116−129. [29] 霍艳辉. 基于阈值分割的三亚珊瑚礁空间分布研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2020.Huo Yanhui. Research on spatial distribution of coral reefs in Sanya based on threshold segmentation method[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2020. [30] Dong Yanzhu, Liu Yongxue, Hu Chuanmin, et al. Coral reef geomorphology of the Spratly Islands: a simple method based on time-series of Landsat-8 multi-band inundation maps[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 157: 137−154. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.09.011 [31] 汪小勇, 李铜基, 周虹丽, 等. 中国近海海洋光学特性及其分布[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 44(1): 104−111.Wang Xiaoyong, Li Tongji, Zhou Hongli, et al. Discussion on ocean optics properties of Chinese offshore and its distribution characteristics[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2014, 44(1): 104−111. [32] 赵英时. 遥感应用分析原理与方法[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.Zhao Yingshi. Principle and Method of Remote Sensing Application Analysis[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. [33] Lucas M Q, Goodman J. Linking coral reef remote sensing and field ecology: it’s a matter of scale[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2015, 3(1): 1−20. [34] 唐军武, 田国良, 汪小勇, 等. 水体光谱测量与分析Ⅰ: 水面以上测量法[J]. 遥感学报, 2004, 8(1): 37−44. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20040106Tang Junwu, Tian Guoliang, Wang Xiaoyong, et al. The methods of water spectra measurement and analysis Ⅰ: above-water method[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2004, 8(1): 37−44. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20040106 [35] Hedley J D, Roelfsema C M, Phinn S R, et al. Environmental and sensor limitations in optical remote sensing of coral reefs: implications for monitoring and sensor design[J]. Remote Sensing, 2012, 4(1): 271−302. doi: 10.3390/rs4010271 [36] Mumby P J, Green E P, Edwards A J, et al. Coral reef habitat mapping: how much detail can remote sensing provide?[J]. Marine Biology, 1997, 130(2): 193−202. doi: 10.1007/s002270050238 [37] Hedley J D, Harborne A R, Mumby P J. Technical note: simple and robust removal of sun glint for mapping shallow-water benthos[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2005, 26(10): 2107−2112. doi: 10.1080/01431160500034086 [38] 张耀光, 刘锴, 刘桂春, 等. 中国海南省三沙市行政建制特点与海洋资源开发[J]. 地理科学, 2014, 34(8): 971−978.Zhang Yaoguang, Liu Kai, Liu Guichun, et al. The characteristics of administrative system of Sansha City in Hainan Province and the exploitation of its marine resources[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(8): 971−978. [39] Christensen V, Pauly D, He Xiaojia. Coral reef and other tropical fisheries[M]//Cochran J K, Bokuniewicz H J, Yager P L. Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences. 3rd ed. Oxford: Academic Press, 2019: 320−323. [40] 余克服, 赵焕庭, 朱袁智. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁区仙掌藻的现代沉积特征[J]. 沉积学报, 1998, 16(3): 20−24.Yu Kefu, Zhao Huanting, Zhu Yuanzhi. Modern sedimentary characteristic of halimeda on coral reefs of Nansha Islands[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1998, 16(3): 20−24. [41] Blanchon P. Geomorphic zonation[M]//Hopley D. Encyclopedia of Modern Coral Reefs: Structure, Form and Process. Dordrecht: Springer, 2011: 469−486. [42] 刘嘉鎏, 黄荣永, 余克服. 黄岩岛环礁地貌近40年变化的遥感分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(3): 775−790. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.15Liu Jialiu, Huang Rongyong, Yu Kefu. Analysis on the geomorphic changes of Huangyan Island based on satellite images over the Past 40 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(3): 775−790. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.15 [43] Xu Chenyang, Prince J L. Gradient vector flow: a new external force for snakes[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Juan : IEEE, 1997. [44] 周旻曦, 刘永学, 李满春, 等. 多目标珊瑚岛礁地貌遥感信息提取方法——以西沙永乐环礁为例[J]. 地理研究, 2015, 34(4): 677−690.Zhou Minxi, Liu Yongxue, Li Manchun, et al. Geomorphologic information extraction for multi-objective coral islands from remotely sensed imagery: a case study for Yongle Atoll, South China Sea[J]. Geographical Research, 2015, 34(4): 677−690. [45] Cheng Jierong, Foo S. Distraction in GVF-based segmentation[C]//2007 6th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing. Singapore: IEEE, 2007. [46] Himmelstoss E A, Henderson R E, Kratzmann M G, et al. Digital shoreline analysis system (DSAS) version 5.0 user guide[EB/OL]. [2021−11−01]. https://www.usgs.gov/publications/digital-shoreline-analysis-system-dsas-version-50-user-guide [47] 周亚男, 朱志文, 沈占锋, 等. 融合纹理特征和空间关系的TM影像海岸线自动提取[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 48(2): 273−279.Zhou Ya’nan, Zhu Zhiwen, Shen Zhanfeng, et al. Automatic extraction of coastline from tm image integrating texture and spatial relationship[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2012, 48(2): 273−279. [48] 乔学瑾, 王庆, 战超, 等. 基于多光谱数据的黄河三角洲岸线自动提取[J]. 海洋学报, 2016, 38(7): 59−71.Qiao Xuejin, Wang Qing, Zhan Chao, et al. Study on automatic extraction of coastline in the Yellow River Delta based on multi-spectral data[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2016, 38(7): 59−71. -





 下载:
下载: