The morphological and molecular phylogenetic studies of a new record Gymnothorax species in the coastal waters of China: Gymnothorax mucifer
-
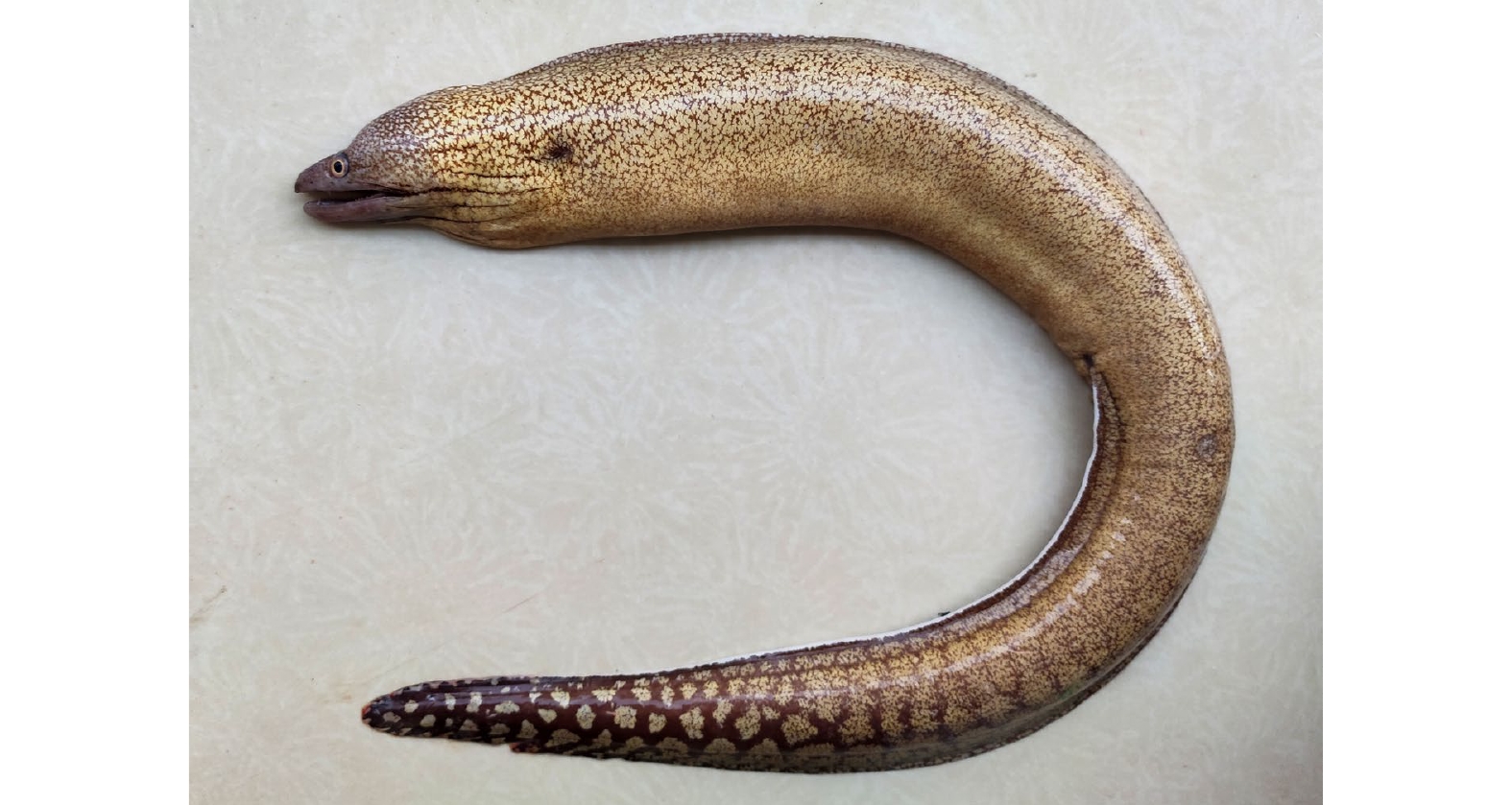
摘要: 本研究于2020−2021年在福建省厦门市近海水产市场采集到4尾黏裸胸鳝样品,为中国大陆近海新记录种。此前,该物种仅在澳大利亚、夏威夷等地有分布记录,并被认为是蠕纹裸胸鳝同种异名。本研究对采集的黏裸胸鳝进行详细形态特征分析,结合DNA条形码COI基因进行分子鉴定及系统进化关系分析。黏裸胸鳝的主要鉴别特征:体为黄棕色,头部前端淡紫色,身体布满细长、稀疏、弥散的树枝状不规则棕色斑纹,斑纹颜色靠近尾部加深加粗,形成网格状;臀鳍边缘白色,近尾部变为一列连续白色斑点;全长为体长的1.01倍,为头长的8.00~8.39倍;上颌齿每侧8~10个,下颌齿每侧14~20个,中央齿细长,均为单行;总椎骨数为117~139,平均椎骨式为6-47-130。基于COI基因分析,黏裸胸鳝与蠕纹裸胸鳝的遗传距离为0.074,大于Herbert设定的2%(0.020)作为区分不同物种最小遗传距离,表明两者应为不同的物种。形态上,两种裸胸鳝也存在差异特征,如黏裸胸鳝的斑纹较细长、稀疏、不明显,头部前端偏淡紫色,臀鳍白色边缘近尾部断裂成系列连续白色斑点;蠕纹裸胸鳝的斑纹粗大明显、颜色较深,头部前端黄白色,臀鳍白色边缘连续至尾尖。研究结果可为我国裸胸鳝属鱼类的系统分类及物种名录的修订提供分类基础。Abstract: In this study, four samples of Gymnothorax mucifer were collected from the fishery market of Xiamen City, Fujian Province during the year 2020 to 2021, which were newly recorded in the coastal waters of China. Previously, the species had only been recorded in Australia and Hawaii, and was considered to be a synonym of Gymnothorax kidako. Detailed morphological characteristics of four G. mucifer species were analyzed, and the molecular identifications as well as phylogenetic constructions were also carried out basing on DNA barcode COI gene in this study. The main distinguishing characteristics of G. mucifer were as follow: the colour of the body was yellowish brown, the front of the head was slightly purple, the whole body was covered with slender, sparse, irregular branch-liked brown marking and the markings became darker and thicker near the tail, forming clear net-liked patterns; the margin on the anal fin was white, and became serial pale blotches on posterior part of the tail; total length was 1.01 times of standard length and 8.00−8.39 times of head length; the maxillary teeth were 8−10 and dentary teeth were 14−20 on each side, both teeth were uniserial; the median inter maxillary teeth were slender and uniserial; the total vertebrae were 117−139 and mean vertebral formula was 6-47-130. Basing on the COI gene analysis, the genetic distance between G. mucifer and G. kidako was 0.074, which was greater than the value 2% (0.020) suggested by Herbert as minimum genetic distance value to distinguishing different species, revealing that the two species might be two independent species. Morphologically, G. mucifer could also be distinguished from G. kidako by certain external characteristic: the body markings of G. mucifer were slender, sparse and inconspicuous, the front of the head was slightly purple, and the white margin of the anal fin broke into series of pale blotches on posterior part of the tail; the markings of G. kidako were obvious and thick with darker colour, the front of the head was yellow-white, the white margin on the anal fin continuous to the tip of the tail. The results of the study provided a taxonomic basis for the systematic classification and the species list revision of the Gymnothorax fish in our country.
-
Key words:
- Gymnothorax mucifer /
- new record species /
- morphological characters /
- DNA barcoding
-
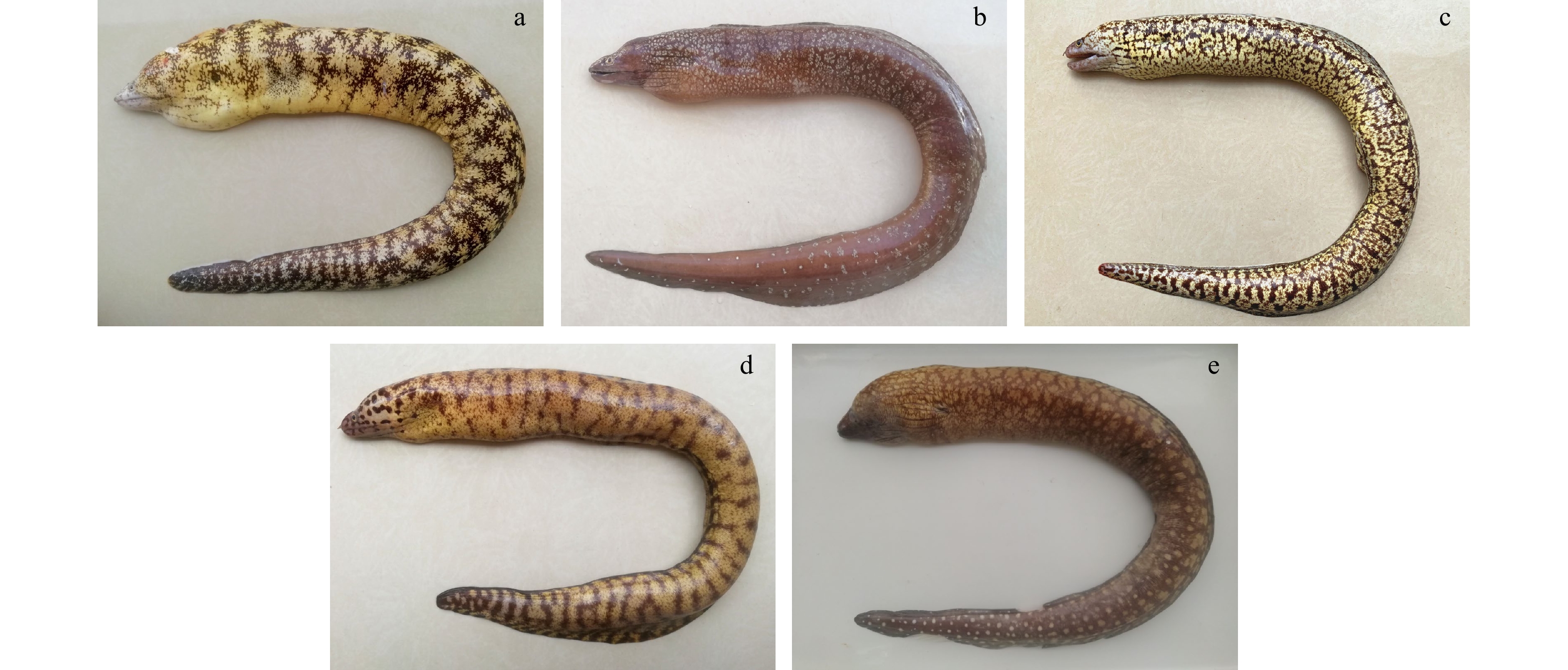
图 2 对比种类
a. 蠕纹裸胸鳝(福建厦门);b. 雪花斑裸胸鳝(广东深圳);c. 云纹裸胸鳝(广东汕头);d. 埃玛氏裸胸鳝(福建漳州);e. 白斑裸胸鳝(福建厦门)
Fig. 2 Comparison species
a. Gymnothorax kidado (Temminck & Schlegel, 1846) (Xiamen City, Fujian Province); b. Gymnothorax niphostigmus (Chen, Shao & Chen, 1996) (Shenzhen City, Guangdong Province); c. Gymnothorax chilospilus (Bleeker, 1864) (Shantou City, Guangdong Province); d. Gymnothorax emmae (Prokofiev, 2010) (Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province); e. Gymnothorax prionodon (Ogilby, 1895) (Xiamen City, Fujian Province)
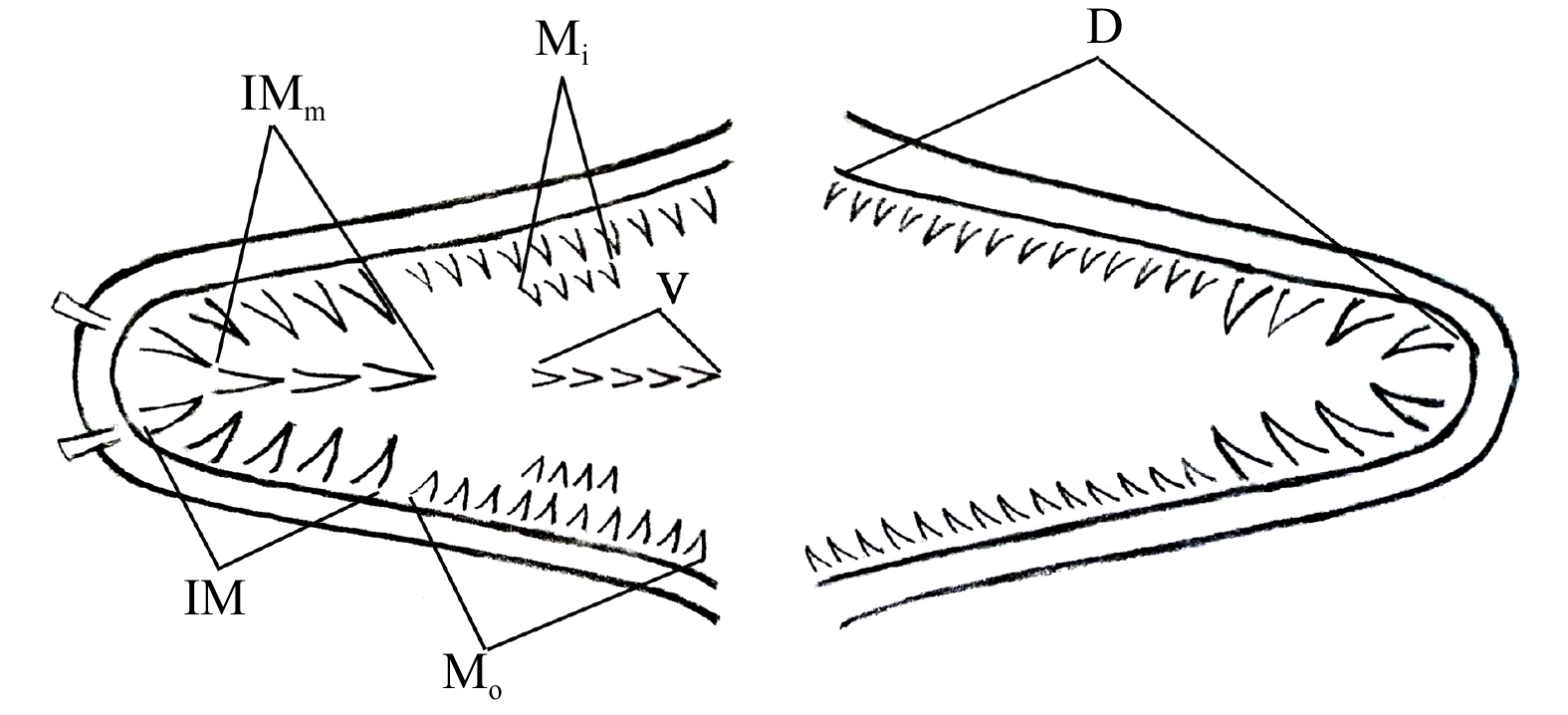
图 3 黏裸胸鳝外部可量性状示意图
AL. 全长;AK. 体长;OP. 体高;AG. 头长;MN. 头高;AC. 吻长;AE. 上颌长;BE. 下颌长;CD. 眼径;DG. 眼后头长;AF. 背鳍前距;AJ. 臀鳍前距;FK. 背鳍基长;JK. 臀鳍基长;AH. 肛前体长;IK. 肛后体长;眼间距以实际测量数据为准,未在图中标注
Fig. 3 Schematic diagram of external measurable traits of Gymnothorax mucifer
AL. Total length; AK. body length; OP. body depth; AG. head length; MN. head depth; AC. snout length; AE. upper jaw length; BE. lower jaw length; CD. eye diameter; DG. postorbital length; AF. predorsal length; AJ. preanal length; FK. base of the dorsal fin; JK. base of the anal fin; AH. distance from anus to snout; IK. distance from anus to cuadal tip; the interorbital width is subject to the actual measurement data and is not marked in the figure
表 1 本研究分析的裸胸鳝COI基因序列信息
Tab. 1 Information of the COI sequences of Gymnothorax species cited in this study
物种名 样品来源 样品编号 黏裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax mucifer福建厦门 GMFJXM1−GMFJXM4 GenBank MH400951−MH400958 GenBank HM422395 雪花斑裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax niphostigmus广东深圳 GDSZ GenBank MF774814−MF774816 蠕纹裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax kidako福建厦门 FJXM GenBank MH400959−MH400960 GenBank MF774817 白斑裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax prionodon福建厦门 FJXM GenBank KU885609 GenBank MF774818 埃玛氏裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax emmae福建漳州 FJZZ 广东深圳 GDSZ GenBank MK777089 云纹裸胸鳝
Gymnothorax chilospilus广东汕头 GDST1,GDST2 GenBank JQ431797 GenBank KU942754 GenBank JQ431795 GenBank MK658499 GenBank MK657751 GenBank KU942753 斑马裸海鳝
Gymnomuraena zebra海南三亚 HNSY1,HNSY2 表 2 黏裸胸鳝形态性状测量数据
Tab. 2 Morphometric measurement information of Gymnothorax mucifer
测量性状 本研究 模式
标本[35]
n=1文献[29]
Gymnothorax
mucifer
n=18FJXM1
n=1FJXM2
n=1FJXM3
n=1FJXM4
n=1全长/mm 537 617 515 600 715+ 246~666 体长/mm 534 610 512 596 − − 体高/mm 42 56 45 56 − 22~50 头长/mm 64 74 62 75 − 33~76 头高/mm 39 46 43 42 − − 吻长/mm 13 12 12 14 − − 上颌长/mm 35 34 34 40 − 17~40 下颌长/mm 38 40 37 45 − 18~42 眼径/mm 6 7 5 7 − 4~6 眼间距/mm 6 11 6 9 − 4~8 眼后头长/mm 44 56 46 53 − − 背鳍前距/mm 57 58 48 55 − 25~55 臀鳍前距/mm 255 286 245 285 − − 背鳍基长/mm 479 552 459 550 − − 臀鳍基长/mm 277 319 263 343 − − 肛前体长/mm 243 275 234 270 − 117~277 肛后体长/mm 286 332 275 325 − − 背鳍鳍
条数408 400 367 293 − − 臀鳍鳍
条数286 283 213 263 − − 背前脊椎
骨数7 8 4 6 5 4~6 肛门前
脊椎骨数56 43 43 44 53 51~55 总脊椎
骨数139 126 117 137 123+ 130~138 前颌齿1 6 6~8 4 5 6 5~7 中央齿1 3 3 2 4 3 2~3 犁骨齿1 6 9 3 6 10 5~14 上颌齿
外侧18~10 10 10 10 15~16 11~18 内侧1 4 4 0 0 − 1~4 下颌齿1 17~20 14~15 20 14~15 23~24 21~27 注:1仅表示牙齿单侧数据;“−”表示无数据;“+”表示原本存在但缺失的数据,数据较715 mm和123大。 表 3 黏裸胸鳝与相关近缘裸胸鳝形态特征比较
Tab. 3 Comparion analysis of morphological characteristics among Gymnothorax mucifer and related Gymnothorax species
黏裸胸鳝 蠕纹裸胸鳝 雪花斑裸胸鳝 埃玛氏裸胸鳝 云纹裸胸鳝 白斑裸胸鳝 身体颜色 黄棕色 黄色或棕色 红棕色 黄色或黄褐色 黄褐色至黑褐色 红褐色 身体斑纹 密布细小、稀疏的树
枝状不规则褐色横纹环绕较明显粗大的
树枝状褐色横纹身体密布雪花
状白色斑块分布许多曲折的
斜向或横向棕纹无明显横带,斑纹呈深
棕色斑块状或树枝状密布较大、模糊不规则白斑 头部斑纹 吻偏紫色,其后黄棕色,
眼后布密集细小网纹黄色,眼后分布
树枝状斑纹红棕色,无斑纹
或稀疏细小白纹黄棕色,具褐色
圆形或弧形斑纹淡黄色,吻部偏白,眼
后有不规则褐色斑纹红褐色,眼后有
不规则斑纹臀鳍边缘 白色,不延续至尾端 白色,延续至尾端 白色,延续至尾端 褐色 白色 红褐色,有白色斑点 分布范围 太平洋:中国、新喀
里多尼亚、夏威夷等印度−西太平洋:
中国、日本、印度等西北太平洋:中国、
越南、日本等越南 印度−太平洋:中国、
印度、澳大利亚等西太平洋:中国、日本、澳大利亚等 表 4 基于COI基因序列6种裸胸鳝的种内及种间遗传距离
Tab. 4 Intra-specific and inter-specific genetic distance among 6 Gymnothorax species for COI sequences
种名 黏裸胸鳝 雪花斑裸胸鳝 蠕纹裸胸鳝 白斑裸胸鳝 埃玛氏裸胸鳝 云纹裸胸鳝 黏裸胸鳝 0.008 雪花斑裸胸鳝 0.051 0.006 蠕纹裸胸鳝 0.074 0.063 0.007 白斑裸胸鳝 0.095 0.093 0.086 0.019 埃玛氏裸胸鳝 0.110 0.106 0.087 0.111 0.007 云纹裸胸鳝 0.146 0.164 0.157 0.162 0.160 0.007 注:对角线数字表示种内遗传距离;对角线下表示种间遗传距离。 -
[1] Randall J E, Golani D. Review of the moray eels (Anguilliformes: Muraenidae) of the Red Sea[J]. Bulletin of Marine Science, 1995, 56(3): 849−880. [2] Froese R, Pauly D. FishBase. World wide web electronic publication[DB/OL]. [2021−01−15]. https://www.fishbase.org. [3] Smith D G, Bogorodsky S V, Mal A O, et al. Review of the moray eels (Anguilliformes: Muraenidae) of the Red Sea, with description of a new species[J]. Zootaxa, 2019, 4704(1): 1−87. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4704.1.1 [4] 成庆泰, 郑葆珊. 中国鱼类系统检索[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 104−108.Cheng Qingtai, Zheng Baoshan. Systematic Synopsis of Chinese Fishes[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1987: 104−108. [5] 孟庆闻, 苏锦祥, 缪学祖. 鱼类分类学[M]. 2版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1995: 139−141.Meng Qingwen, Su Jinxiang, Miao Xuezu. Systematics of Fishes[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press, 1995: 139−141. [6] 沈世杰. 台湾鱼类志[M]. 台北: 台湾大学动物学系, 1993: 98−108.Shen Shijie. Fishes of Taiwan[M]. Taipei, China: Department of Zoology, Taiwan University, 1993: 98−108. [7] 中国水产科学研究院南海水产研究所. 南海诸岛海域鱼类志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979: 43−55.South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences. The Fishes of the Islands in the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1979: 43−55. [8] 中国科学院动物研究所, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 上海水产学院. 南海鱼类志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1962: 184−194.Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Fisheries University. The Fishes of the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1962: 184−194. [9] 《福建鱼类志》编写组. 福建鱼类志[M]. 福州: 福建科学技术出版社, 1984: 220−225.Fishes of Fujian Province Editorial Subcommittee. The Fishes of Fujian Province[M]. Fuzhou: Fujian Science and Technology Press, 1984: 220−225. [10] 朱元鼎, 张春霖, 成庆泰. 东海鱼类志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1963: 160−162.Zhu Yuanding, Zhang Chunlin, Cheng Qingtai. The Fishes of the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1963: 160−162. [11] 张春光. 中国动物志: 硬骨鱼纲, 鳗鲡目, 背棘鱼目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 224−288.Zhang Chunguang. Fauna Sinica: Ostichthyes, Anguilliformes and Notacanthiforme[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 224−288. [12] 陈大刚, 张美昭. 中国海洋鱼类[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2016: 235−266.Chen Dagang, Zhang Meizhao. Marine Fishes of China (Volume 1)[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2016: 235−266. [13] 黄宗国. 中国海洋生物种类与分布[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2008: 751−752.Huang Zongguo. Marine Species and Their Distribution in China[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2008: 751−752. [14] 李明德. 鱼类分类学[M]. 2版. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2011: 77−78.Li Mingde. Fish Taxonomy[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2011: 77−78. [15] 刘瑞玉. 中国海洋生物名录[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 906−909.Liu Ruiyu. Checklist of Marine Biota of China Seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 906−909. [16] 祝茜. 中国海海洋鱼类种类名录[M]. 北京: 学苑出版社, 1998: 48−51.Zhu Qian. A List of Marine Fishes in China Seas[M]. Beijing: The Academic Press, 1998: 48−51. [17] 杜民, 尹绍武, 刘艳红, 等. 中国裸胸鳝属10种鱼类分子系统发育关系的16S rDNA分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2013, 37(6): 16−23.Du Min, Yin Shaowu, Liu Yanhong, et al. Analysis of the molecular phylogenetic relationships of 10 Gymnothorax species from China Seas based on 16S rDNA fragment sequences[J]. Marine Sciences, 2013, 37(6): 16−23. [18] 杜民, 齐兴柱, 尹绍武, 等. 基于Cyt b基因序列研究6种裸胸鳝属鱼类的进化关系[J]. 中国水产科学, 2009, 16(1): 23−30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2009.01.004Du Min, Qi Xingzhu, Yin Shaowu, et al. Phylogenetic relationships of 6 species in Gymnothorax based on sequences of cytochrome b gene[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2009, 16(1): 23−30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2009.01.004 [19] 黄飞, 王吉, 骆剑, 等. 匀斑裸胸鳝消化道的显微与超微结构分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2014, 21(6): 1109−1115.Huang Fei, Wang Ji, Luo Jian, et al. Microstructure and ultrastructure of the digestive tract of Gymnothorax reevesii[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2014, 21(6): 1109−1115. [20] 杜民, 尹绍武, 刘艳红, 等. 4种裸胸鳝的分子遗传多样性和亲缘关系的RAPD分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2013, 32(3): 321−327.Du Min, Yin Shaowu, Liu Yanhong, et al. RAPD analysis of molecular genetic diversity and genetic relationship of four Gymnothorax species[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2013, 32(3): 321−327. [21] Sumod K S, Mohapatra A, Sanjeevan V N, et al. A new species of white-spotted moray eel, Gymnothorax smithi (Muraenidae: Muraeninae) from deep waters of Arabian Sea, India[J]. Zootaxa, 2019, 4652(2): 359−366. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4652.2.8 [22] Mohapatra A, Smith D G, Ray D, et al. Gymnothorax pseudotile sp. nov. (Muraenidae: Muraeninae) from Bay of Bengal India[J]. Zootaxa, 2017, 4286(4): 586−592. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4286.4.11 [23] Mohapatra A, Smith D G, Mohanty S R, et al. Gymnothorax visakhaensis sp. nov., a new species of elongate unpatterned moray eel (Muraenidae: Muraeninae) from the Indian Coast[J]. Zootaxa, 2017, 4300(2): 279−286. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4300.2.9 [24] Loh K H, Shao K T, Ho H C, et al. A new species of moray eel (Anguilliformes: Muraenidae) from Taiwan, with comments on related elongate unpatterned species[J]. Zootaxa, 2015, 4060: 30−40. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4060.1.5 [25] Smith D G. Catalog of type specimens of recent fishes in the National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, 6: Anguilliformes, Saccopharyngiformes, and Notacanthiformes[J]. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology, 1994, 566: 1−50. [26] Böhlke E B, Randall J E. Gymnothorax megaspilus, a new species of moray eel (Anguilliformes: Muraenidae) from southern Oman and Somalia[J]. Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 1995, 472: 1−5. [27] Mundy B C. Checklist of the fishes of the Hawaiian Archipelago[J]. Bishop Museum Bulletin in Zoology, 2005, 6: 1−704. [28] Böhlke E B, Randall J E. A review of the moray eels (Angulliformes: Muraenidae) of the Hawaiian Islands, with descriptions of two new species[J]. Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 2000, 150: 203−278. [29] Huang W C, Chen Hongming, Liao Teyu. Revalidation of a moray eel, Gymnothorax mucifer Snyder, 1904 (Teleostei: Anguilliformes: Muraenidae), with a revised distribution[J]. Zootaxa, 2019, 4559(1): 151−165. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4559.1.6 [30] Ward R D, Zemlak T S, Innes B H, et al. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2005, 360(1462): 1847−1857. [31] Thompson J D, Higgins D G, Gibson T J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1994, 22(22): 4673−4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673 [32] Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2016, 33(7): 1870−1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 [33] Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(9): 1312−1313. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033 [34] Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Van Der Mark P, et al. Mrbayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space[J]. Systematic Biology, 2012, 61(3): 539−542. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/sys029 [35] Snyder J O. A catalogue of the shore fishes collected by the steamer Albatross about the Hawaiian Islands in 1902[J]. Bulletin of the United States Fish Commission, 1904, 22(1): 513−538. [36] Hebert P D N, Cywinska A, Ball S L, et al. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2003, 270(1512): 313−322. [37] Reece J S, Bowen B W, Smith D G, et al. Comparative phylogeography of four Indo-Pacific moray eel species (Muraenidae) reveals comparable ocean-wide genetic connectivity despite five-fold differences in available adult habitat[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2011, 437: 269−277. doi: 10.3354/meps09248 [38] Huang W C, Nguyen V Q, Liao Teyu. First record of the snowflake-patched moray Gymnothorax niphostigmus Chen, Shao, & Chen, 1996 (Anguilliformes; Muraenidae) in Vietnam and its validity confirmed by DNA barcoding[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 2018, 34(3): 687−690. doi: 10.1111/jai.13684 [39] 范蔓桦, 杨杰銮, 谢瑞琳, 等. 我国沿海裸胸鳝属鱼类DNA条形码及分子系统进化研究[J]. 仲恺农业工程学院学报, 2020, 33(2): 59−65.Fan Manhua, Yang Jieluan, Xie Ruilin, et al. DNA barcoding and molecular phylogenetic relationship of Gymnothorax species from China Sea[J]. Journal of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2020, 33(2): 59−65. -





 下载:
下载: