A numerical simulation study on the response of tidal asymmetry to estuarine morphologies
-
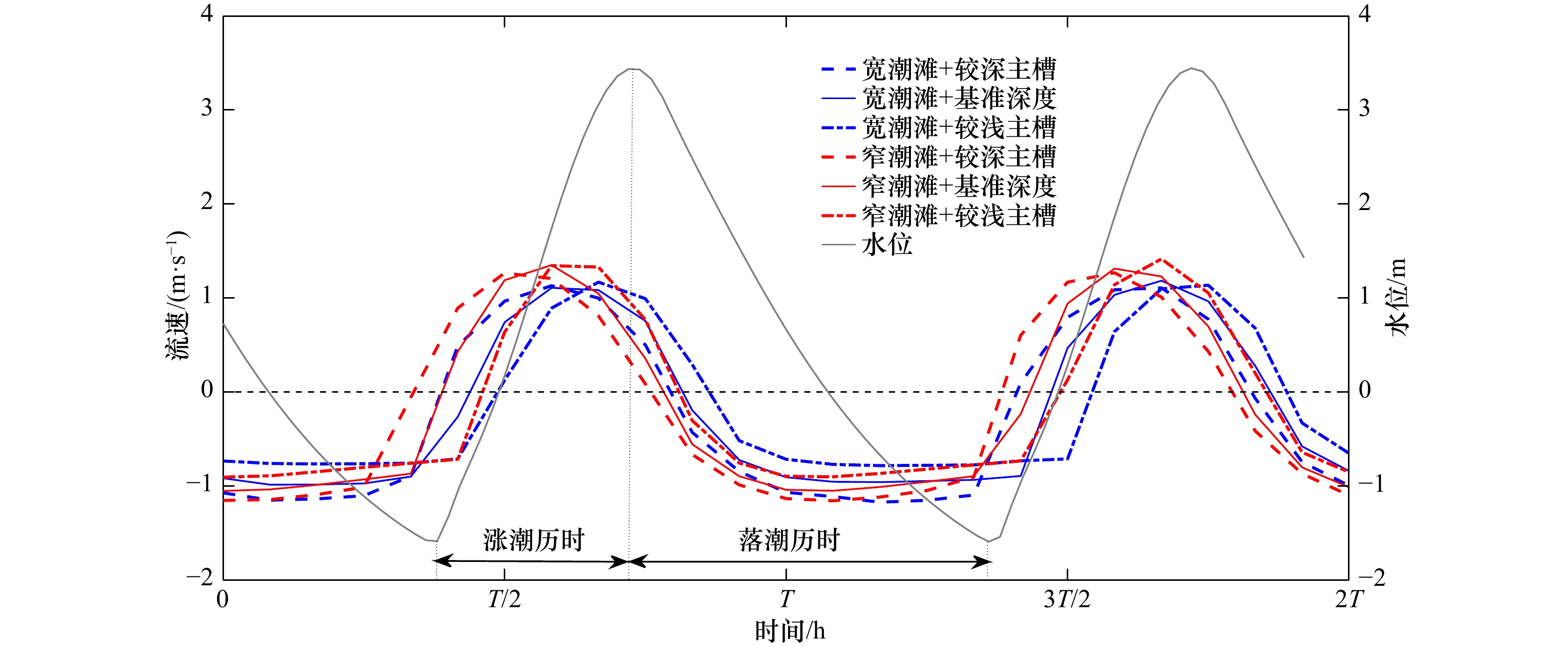
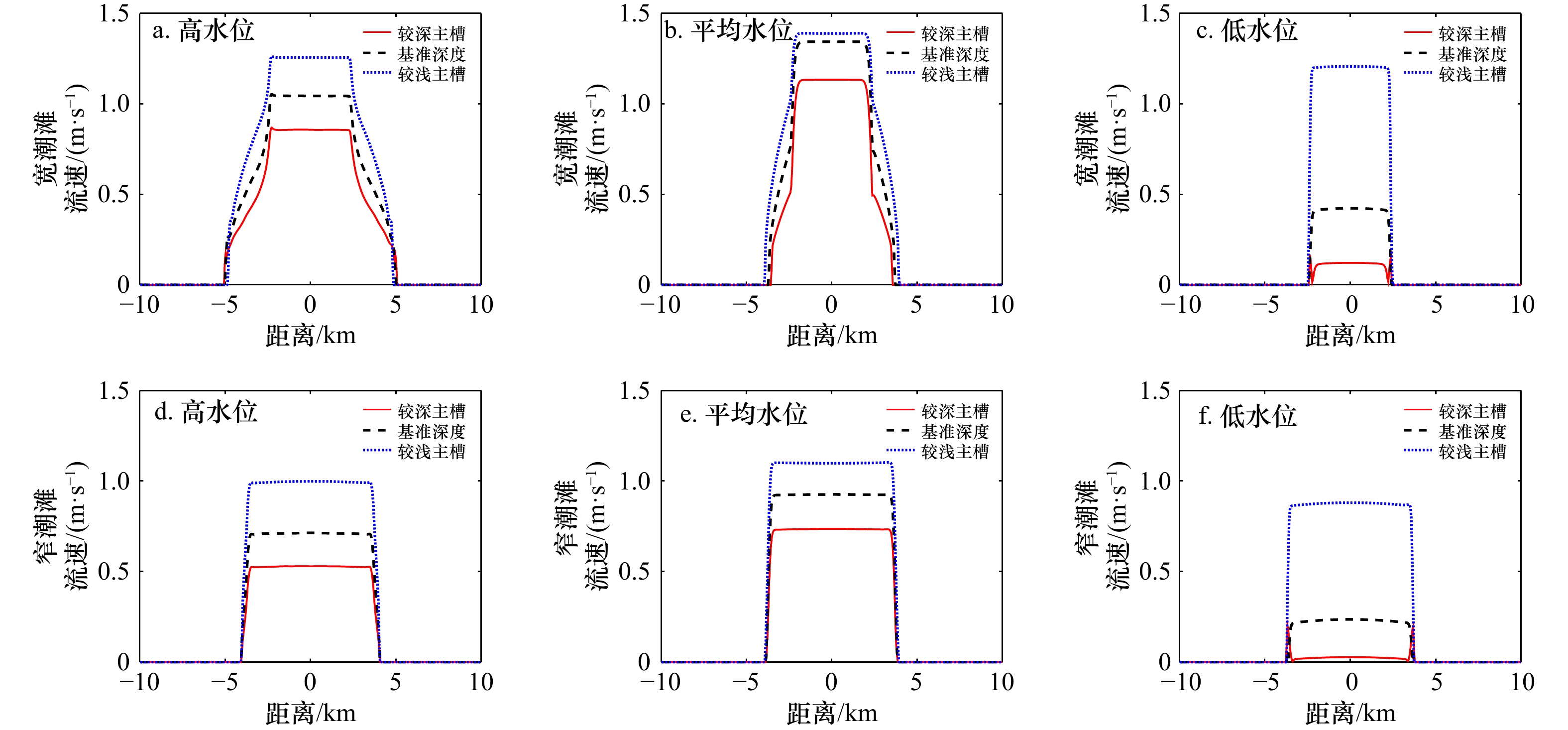
摘要: 河口地貌形态对潮汐不对称性的产生和发展有着至关重要的作用。本文根据英国Humber河口数据建立了概化模型,研究了在同一纳潮量情况下,主槽断面形态、平面形态和河口收缩率对河口潮汐不对称性的影响。结果表明,较深的主槽能使相位差峰值出现较晚且峰值更大,从而影响局部区域的涨潮流强弱,主槽越浅,最大落潮流速越小,落潮所需历时越长,河口更倾向于涨潮主导,窄潮滩倾向于涨潮主导型,宽潮滩倾向于落潮主导型;平面形态沿程收缩且长度较长的河口涨潮主导型最强,此外,河口宽度沿程缩窄会加大主槽的余流流速,减小潮滩的余流流速;随着河口平面收缩率的增强,主槽的余流流速减小,潮滩余流流速增大,潮滩更倾向于涨潮主导。本文进一步丰富了河口地形地貌变化对潮汐不对称性影响的认识,可为河口区工程建设和管理维护提供科学依据。Abstract: Estuarine morphologies play an important role on tidal asymmetry. A two-dimensional numerical model is established with the Humber Estuary, UK as a reference site. A series of simulations are designed to examine the effects of the estuary cross-section shape, planform and convergence on the development of tidal asymmetry, whilst maintaining the same tidal prism. Model results show that deeper channels result in the lag and enhancement of phase difference whilst shallower channels result in a decline in the maximum ebb-tide velocity and longer period of ebb tide, and the estuary tends to be flood-dominated; narrow tidal flat tends to favour ebb dominance while broad tidal flat tends to favour flood dominance. Flood dominance is strongest in the convergent and long estuary. In addition, narrowing the estuary width will enhance the residual flow velocity of the main channel but weaken the residual flow velocity of the tidal flat. With the increase in estuary convergence, the residual flow velocity of the main channel increases but decreases on the tidal flat, and strengthen the flood dominance of the tidal flat. This paper further improves the research on the influence of estuary landforms on tidal asymmetry, which has certain guiding significance for reclamation and coastal engineering.
-
表 1 潮汐不对称性类型
Tab. 1 The type of tidal asymmetry
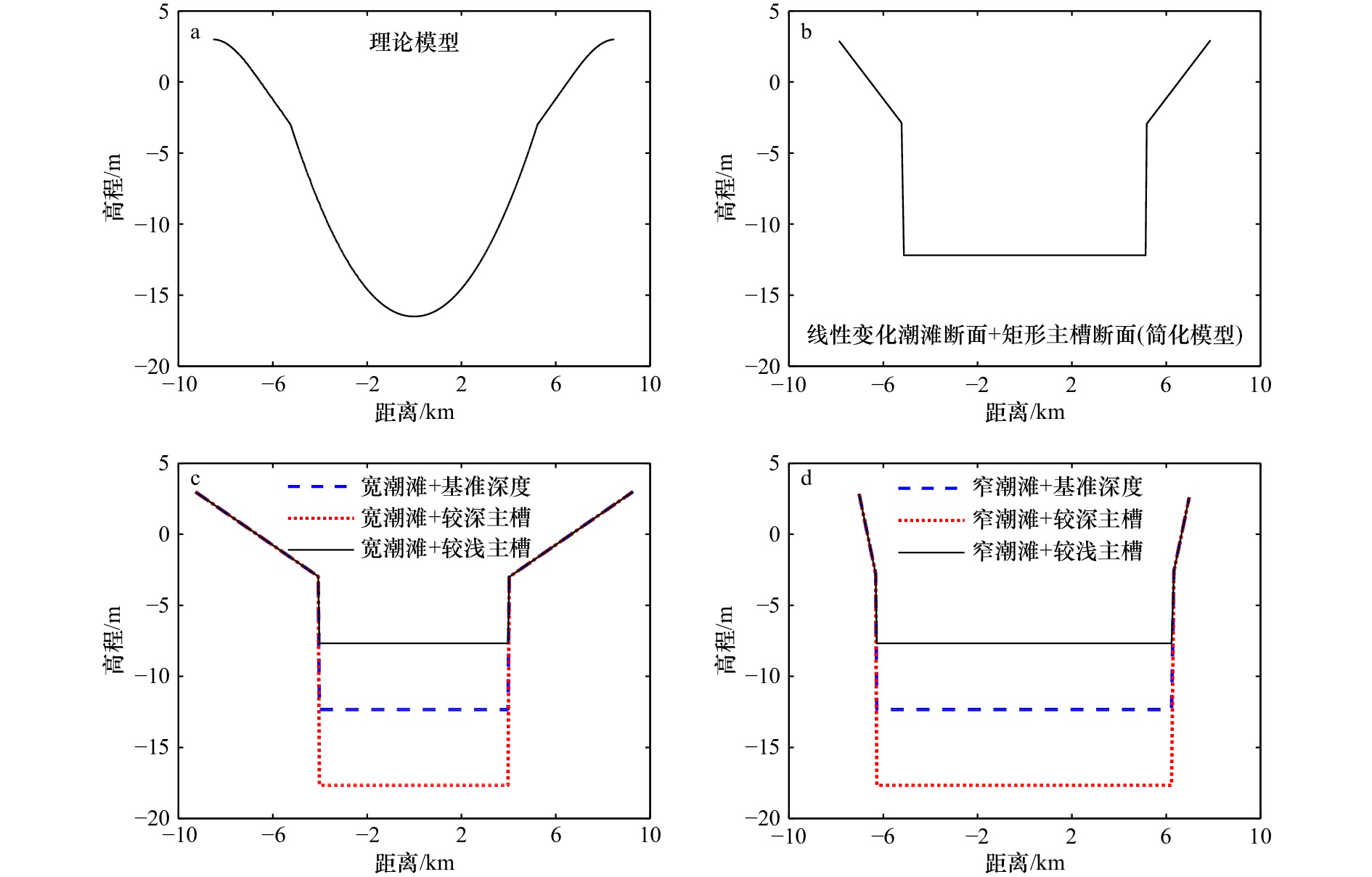
类型 垂直向 水平向 涨潮主导型 0°<$2\theta_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \theta_{{\rm{M}}_4}$<180° −90°<$2\phi_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \phi_{{\rm{M}}_4}$<90° 落潮主导型 180°(−180°)<$2\theta_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \theta_{{\rm{M}}_4}$<360°(0°) 90°<$2\phi_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \phi_{{\rm{M}}_4}$<270° 平衡状态 $2\theta_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \theta_{{\rm{M}}_4}$=0°或180° $2\phi_{{\rm{M}}_2} - \phi_{{\rm{M}}_4}$=90°或270° 表 2 不同断面形态模型汇总
Tab. 2 The summary of different cross sections
序号 名称 高水位时潮滩
宽度/km低水位时潮滩
宽度/km口门处主槽
深度/ma 理论模型 17 10.5 16.5 b 简化模型 16 10.5 12.3 c 宽潮滩+基准深度 18.5 8 12.3 宽潮滩+较深主槽 18.5 8 17.7 宽潮滩+较浅主槽 18.5 8 7.7 d 窄潮滩+基准深度 14 12.5 12.3 窄潮滩+较深主槽 14 12.5 17.7 窄潮滩+较浅主槽 14 12.5 7.7 表 3 不同平面形态模型汇总
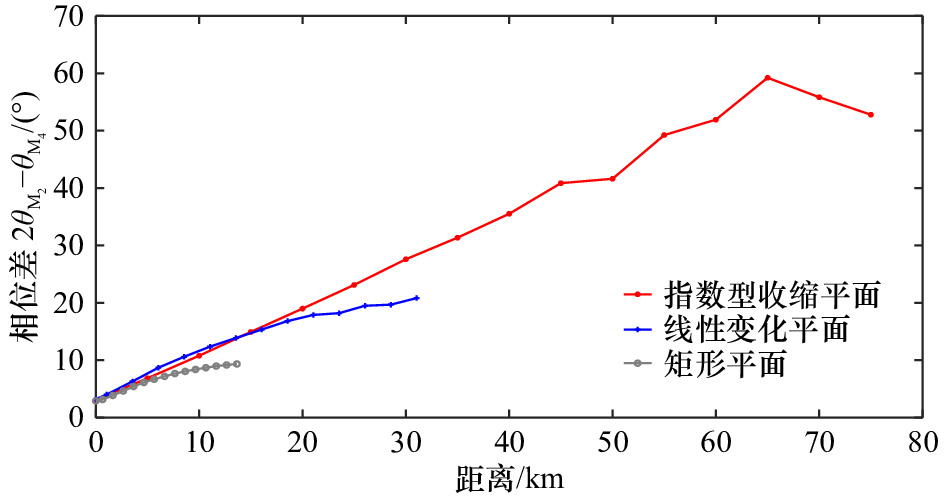
Tab. 3 The summary of different plan forms
序号 平面形态 长度/km 纳潮量/m3 收缩长度/km 备注 a 指数型收缩(强) 80 1.47×109 18.3 4种平面形态口门处的
断面保持相同b 线性变化 36 1.47×109 − c 矩形 18.6 1.47×109 − d 指数型收缩(弱) 80 − 60 注:− 代表不包含数据。 表 4 不同断面形态河口的沿程相位差均值
Tab. 4 The along-channel averaged relative tidal phases of estuaries with different cross sections
序号 断面形态 平均沿程相位差
$2{\theta }_{\mathrm{M}_2}-{\theta }_{\mathrm{M}_4}$/(°)潮滩宽度 主槽深度 a 基准宽度 基准深度 52.55 b 较宽 基准深度 50.10 c 较宽 较深 45.51 d 较宽 较浅 56.10 e 较窄 基准深度 58.76 f 较窄 较深 55.93 g 较窄 较浅 60.65 表 5 不同平面形态的沿程相位差均值
Tab. 5 The along-channel averaged relative tidal phases of estuaries with different plan forms
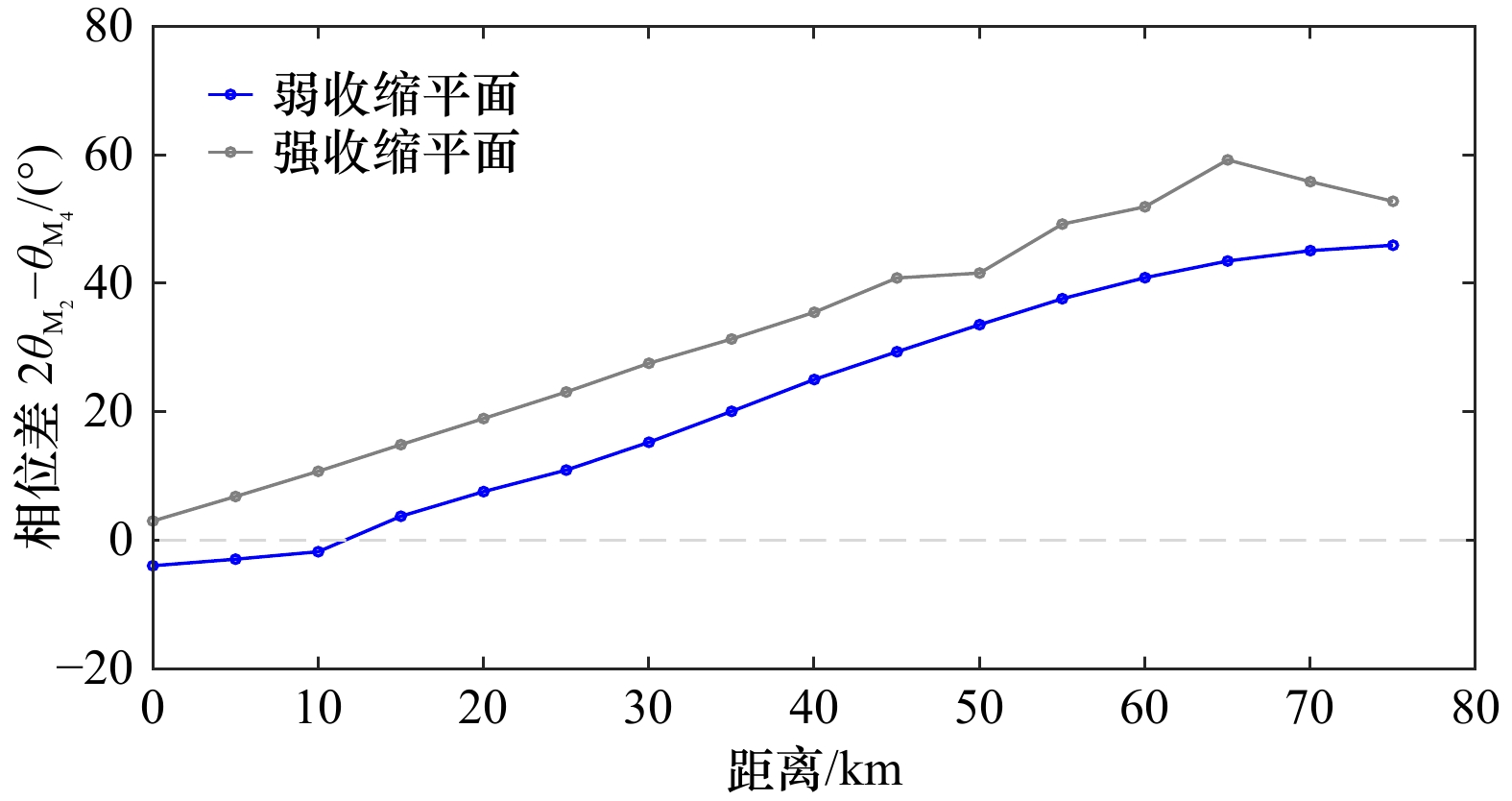
河口平面形态 平均沿程相位差$2{\theta }_{\mathrm{M}_2}-{\theta }_{\mathrm{M}_4}$/(°) 指数型收缩平面 32.73 线性变化平面 13.37 矩形平面 6.68 弱收缩平面(收缩长度60 km) 21.40 强收缩平面(收缩长度18.3 km) 32.73 -
[1] 王彪, 朱建荣, 李路. 长江河口涨落潮不对称性动力成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2011, 33(3): 19−27.Wang Biao, Zhu Jianrong, Li Lu. A study on the dynamics of the asymmetry between flood and ebb in the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2011, 33(3): 19−27. [2] 侯庆志, 陆永军, 王建, 等. 河口与海岸滩涂动力地貌过程研究进展[J]. 水科学进展, 2012, 23(2): 286−294.Hou Qingzhi, Lu Yongjun, Wang Jian, et al. Advances in morphodynamics of estuarine and coastal mudflats[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2012, 23(2): 286−294. [3] 乔立新, 张国安, 何青, 等. 长江分汊河口涨、落潮悬沙不对称特征及季节性差异[J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(3): 107−117.Qiao Lixin, Zhang Guoan, He Qing, et al. Tidal and seasonal asymmetry of suspended sediment concentration in branched channels of the Changjiang River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(3): 107−117. [4] Du Jiabi, Shen Jian, Zhang Yinglong, et al. Tidal response to sea-level rise in different types of estuaries: the importance of length, bathymetry, and geometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(1): 227−235. doi: 10.1002/2017GL075963 [5] Jewell S A, Walker D J, Fortunato A B. Tidal asymmetry in a coastal lagoon subject to a mixed tidal regime[J]. Geomorphology, 2012, 138(1): 171−180. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.08.032 [6] Aubrey D G, Speer P E. A study of non-linear tidal propagation in shallow inlet/estuarine systems Part I: Observations[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1985, 21(2): 185−205. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(85)90096-4 [7] 李谊纯. 潮流不对称与推移质泥沙长期净输运[J]. 泥沙研究, 2013(5): 21−26.Li Yichun. On relationship between tidal current asymmetry and long-term bed load net transport[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2013(5): 21−26. [8] 林国尧, 龚文平. 海南岛莺歌海近岸的潮汐不对称与潮致余流研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(7): 36−42.Lin Guoyao, Gong Wenping. Tidal asymmetry and tide-induced residual currents in the Yinggehai coast, Hainan Island[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(7): 36−42. [9] Latteux B. Techniques for long-term morphological simulation under tidal action[J]. Marine Geology, 1995, 126(1/4): 129−141. [10] 杨洋, 陈沈良, 徐丛亮. 黄河口滨海区冲淤演变与潮流不对称[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(6): 13−25.Yang Yang, Chen Shenliang, Qu Congliang. Morphodynamics and tidal flow asymmetry of the Huanghe River Estuary[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(6): 13−25. [11] Friedrichs C T, Aubrey D G. Non-linear tidal distortion in shallow well-mixed estuaries: a synthesis[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1988, 27(5): 521−545. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(88)90082-0 [12] Wang Zhengbing, Jeuken C, De Vriend H J. Tidal asymmetry and residual sediment transport in estuaries[R]. Delft: [s.n.], 1999. [13] 尹倩瑜, 龚政, 李欢, 等. 长江口北支河段潮汐不对称性分析[J]. 人民长江, 2013, 44(21): 81−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2013.21.021Yin Qianyu, Gong Zheng, Li Huan, et al. Analysis on tidal asymmetry in north branch of Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Yangtze River, 2013, 44(21): 81−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4179.2013.21.021 [14] 季荣耀, 陆永军, 詹小磊, 等. 伶仃洋茅洲河口动力地貌演变过程[J]. 水科学进展, 2019, 30(6): 781−788.Ji Rongyao, Lu Yongjun, Zhan Xiaolei, et al. Study on the morphodynamic evolution processes in the Maozhou Estuary of the Lingding Bay[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2019, 30(6): 781−788. [15] Zhou Zeng, Coco G, Townend I, et al. On the stability relationships between tidal asymmetry and morphologies of tidal basins and estuaries[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2018, 43(9): 1943−1959. doi: 10.1002/esp.4366 [16] Zhou Zeng, Coco G, Townend I, et al. Is “Morphodynamic Equilibrium” an oxymoron?[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 165: 257−267. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.12.002 [17] Gao Guandong, Wang Xiaohua, Bao Xianwen. Land reclamation and its impact on tidal dynamics in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 151: 285−294. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.07.017 [18] 方彤瑶, 李莉. 滩涂围垦对水动力环境的影响[C]//第十七届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集(上). 北京: 海洋出版社, 2015.Fang Tongyao, Li Li. Influence of tidal flat reclamation on hydrodynamic environment[C]//Proceedings of the 17th China Ocean (Shore) Engineering Symposium. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2015. [19] Gong Wenping, Schuttelaars H, Zhang Heng. Tidal asymmetry in a funnel-shaped estuary with mixed semidiurnal tides[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2016, 66(5): 637−658. doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0943-1 [20] 操进浪. 杭州湾海域岸线变化对其水动力过程影响的数值研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.Cao Jinlang. Numerical simulation on impacts of coastlinechanges on hydrodynamics in Hangzhou Bay[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018. [21] Pein J U, Stanev E V, Zhang Y J. The tidal asymmetries and residual flows in Ems Estuary[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 2014, 64(12): 1719−1741. doi: 10.1007/s10236-014-0772-z [22] 沈倩颖, 季小梅, 张蔚, 等. 河口挡潮闸对三角洲潮汐不对称时空变化的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(5): 1−9. doi: 10.11978/2020127Shen Qianying, Ji Xiaomei, Zhang Wei, et al. Impact of estuarine storm surge barriers on spatiotemporal variation of tidal asymmetry in a delta[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 1−9. doi: 10.11978/2020127 [23] Montaño-Ley Y, Peraza-Vizcarra R, Páez-Osuna F. The tidal hydrodynamics modeling of the Topolobampo coastal lagoon system and the implications for pollutant dispersion[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 147(1): 282−290. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.07.007 [24] 贾建军, 高抒, 薛允传. 山东荣成月湖潮汐汊道的时间−流速不对称特征[J]. 海洋学报, 2003, 25(3): 68−76.Jia Jianjun, Gao Shu, Xue Yunchuan. Patterns of time-velocity asymmetry at the Yuehu Inlet, Shandong Peninsula, China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2003, 25(3): 68−76. [25] 蔡伟章, 陈耕心, 丁锦仁. 象山港潮汐潮流特征及成因探讨[J]. 海洋通报, 1985, 4(3): 8−12.Cai Weizhang, Chen Gengxin, Ding Jinren. A discussion of the features of the tide and tidal current in the Xiangshan Harbour and their cause of formation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1985, 4(3): 8−12. [26] Van Der Spek A. Tidal asymmetry and long-term evolution of Holocene tidal basins in the Netherlands: simulation of palaeo-tides in the Schelde Estuary[J]. Marine Geology, 1997, 141(1/4): 71−90. [27] Fortunato A B, Oliveira A. Influence of intertidal flats on tidal asymmetry[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2005, 21(5): 1062−1067. [28] Le Hir P, Roberts W, Cazaillet O, et al. Characterization of intertidal flat hydrodynamics[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(12/13): 1433−1459. [29] Dyer K R. The typology of intertidal mudflats[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1998, 139(1): 11−24. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1998.139.01.02 [30] Friedrichs C T, Aubrey D G. Tidal propagation in strongly convergent channels[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1994, 99(C2): 3321−3336. doi: 10.1029/93JC03219 [31] Lanzoni S, Seminara G. On tide propagation in convergent estuaries[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1998, 103(C13): 30793−30812. doi: 10.1029/1998JC900015 [32] Ridderinkhof W, De Swart H E, Van Der Vegt M, et al. Geometry of tidal inlet systems: A key factor for the net sediment transport in tidal inlets[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2014, 119(10): 6988−7006. doi: 10.1002/2014JC010226 [33] Cao Shuyou, Knight D W. Entropy-based design approach of threshold alluvial channels[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1997, 35(4): 505−524. doi: 10.1080/00221689709498408 [34] Townend I. An exploration of equilibrium in Venice Lagoon using an idealised form model[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2010, 30(8): 984−999. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.10.012 [35] Townend I. The estimation of estuary dimensions using a simplified form model and the exogenous controls[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2012, 37(15): 1573−1583. doi: 10.1002/esp.3256 [36] Friedrichs C T, Aubrey D G. Equilibrium hyposometry of intertidal[J]. Mixing in Estuaries and Coastal Seas, 1996, 50: 405−429. [37] Friedrichs C T, Madsen O S. Nonlinear diffusion of the tidal signal in frictionally dominated embayments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1992, 97(C4): 5637−5650. doi: 10.1029/92JC00354 [38] 季小梅, 张永战, 朱大奎. 乐清湾近期海岸演变研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2006, 25(1): 44−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.01.007Ji Xiaomei, Zhang Yongzhan, Zhu Dakui. Study on marine environment and recent coastal evolution of Yueqing Bay, Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2006, 25(1): 44−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2006.01.007 [39] 陈红霞, 华锋, 刘娜, 等. 不同方式的纳潮量计算比较—以胶州湾 2006 年秋季小潮为例[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2009, 27(1): 11−15.Chen Hongxia, Hua Feng, Liu Na, et al. Comparison among different methods for tidal prism calculation —neap tide of Jiaozhou Bay in autumn 2006 as an expounded example[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2009, 27(1): 11−15. [40] 袁菲, 何用, 卢陈, 等. 多汊道潮汐通道狮子洋的纳潮量计算及演变分析[J]. 海岸工程, 2017, 36(4): 59−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2017.04.008Yuan Fei, He Yong, Lu Chen, et al. Calculation method and evolution analysis of the tidal prism of Shiziyang tidal channel[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2017, 36(4): 59−66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3682.2017.04.008 [41] Townend I, Zhou Zeng, Guo Leicheng, et al. A morphological investigation of marine transgression in estuaries[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2021, 46(3): 626−641. doi: 10.1002/esp.5050 [42] Davies A M, Jones J E. The influence of bottom and internal friction upon tidal currents: taylor’s problem in three dimensions[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 1995, 15(10): 1251−1285. doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(94)00076-Y [43] Kang J W, Jun K S. Flood and ebb dominance in estuaries in Korea[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2003, 56(1): 187−196. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7714(02)00156-7 [44] Wang Z B, Jeuken M C J L, Gerritsen H, et al. Morphology and asymmetry of the vertical tide in the Westerschelde Estuary[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2002, 22(17): 2599−2609. doi: 10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00134-6 [45] Speer P E, Aubrey D G. A study of non-linear tidal propagation in shallow inlet/estuarine systems Part II: Theory[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1985, 21(2): 207−224. doi: 10.1016/0272-7714(85)90097-6 [46] Boon III J D, Byrne R J. On basin hyposmetry and the morphodynamic response of coastal inlet systems[J]. Marine Geology, 1981, 40(1/2): 27−48. -




 下载:
下载: