Seasonal variations of the planktonic larvae community in the Huanghe River Estuary adjacent waters
-
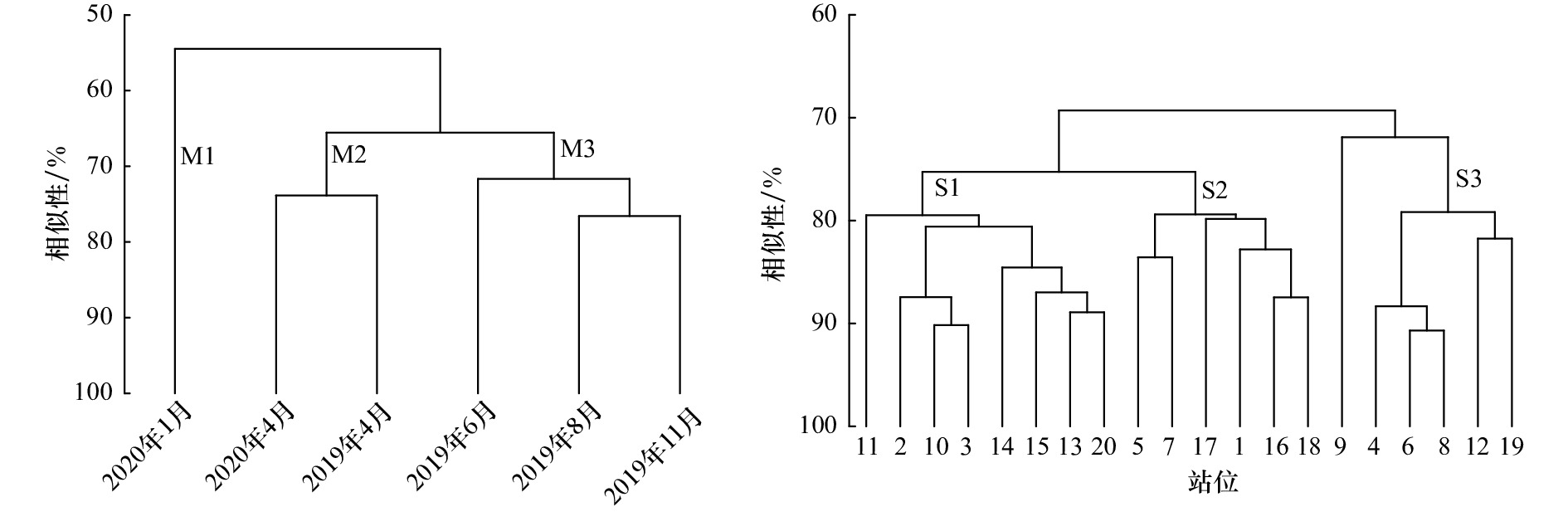
摘要: 基于2019−2020年4个季节的6个航次海上生态调查,研究黄河口邻近海域的浮游幼虫群落结构及其与环境因子的关系,旨在为海域生物多样性保护与重要生物资源养护提供科学基础。结果显示:在黄河口邻近海域,共鉴定出浮游幼虫16类,阶段性浮游幼虫是主要组成类群。浮游幼虫月均丰度以11月最高、1月最低。浮游幼虫香农−威纳多样性指数(H')夏季(6−8月)高和秋冬季(11月至翌年1月)低。双壳类幼虫和无节幼虫是海区各季节的优势种及浮游幼虫总丰度的主要贡献者,腹足类幼虫、多毛类幼虫以及耳状幼虫、桡足幼虫等是季节性出现的优势种。春−夏间优势种组成更替率高。相对高丰度浮游幼虫主要分布于黄河口入海口附近、小清河口及莱州湾中部。基于浮游幼虫类群丰度组成的聚类分析,可将调查月和站位各分为3个不同的聚类组。月聚类组分别为春季(4月)、夏秋季(6−11月)和冬季(1月),春季、冬季聚类组的代表类群是无节幼虫,夏秋季聚类组的代表类群是双壳幼虫。3个站位聚类组的组成站位的地理分布交错,代表类群都为双壳类幼虫和无节幼虫。多元方差(MANOVA)和相似性分析(ANOSIM)检验显示,海区内浮游幼虫的多样性指数、丰度、群聚结构等都表现为月间差异显著(p<0.05),站位间差异不显著(p>0.05)。生物−环境逐步多重回归分析表明,影响浮游幼虫群聚结构的最佳环境因子组合为水温和浮游动物丰度。Abstract: Planktonic larvae are the necessary stages during the growth and development of many fishery species, such as shellfish, benthic fish, polychaete in the Huanghe River Estuary adjacent waters. Seasonal studies on the planktonic larvae community were carried out for biodiversity and bio-resource protection researches in the region. The larvae samples were collected from the vertical hauling of a mesh size 0.160 mm plankton net onboarding of six cruises during April 2019, June 2019, and August 2019, November 2019, January and April 2020 in the sea. Of the 16 planktonic larvae identified, 87% groups were meroplankton. The community diversity index (H') showed higher in June and August than in November and January. For the study region, the dominant organisms of planktonic larvae were bivalve larvae, nauplii, gastropoda larvae, polychaeta larvae, copepodite larvae, auricularia larvae. But the composition of dominant species varied with seasons, with the highest seasonal turnover rate (67%) from April to June, only bivalve larvae and nauplii dominated the planktonic larvae community for all seasons. Total planktonic larvae abundance reached the highest in November, the lowest in January. The planktonic larvae had their high abundance mostly near the estuaries of the Huanghe River and the Xiaoqinghe River, and in the middle part of Laizhou Bay. By cluster analysis, three assemblages of communities were differentiated based on the family compositions and their abundance at each station of six surveyed months. The representative species for monthly cluster groups were nauplii for spring (April) and winter (January) groups, bivalve larvae for summer-autumn (June to November) group. The station cluster groups overlapped geographically with the same representative species (bivalve larvae and nauplii). From statistical analysis of MANOVA and ANOSIM, biodiversity index, abundance, similarity among cluster groups presented significantly different among measured months, but stations, suggesting a seasonal variation for planktonic larvae community. Bio-environment multiple regression analysis showed that the combination of water temperature and zooplankton abundance had the most effects on the planktonic larvae community.
-
Key words:
- planktonic larvae /
- community structure /
- Huanghe River Estuary
-
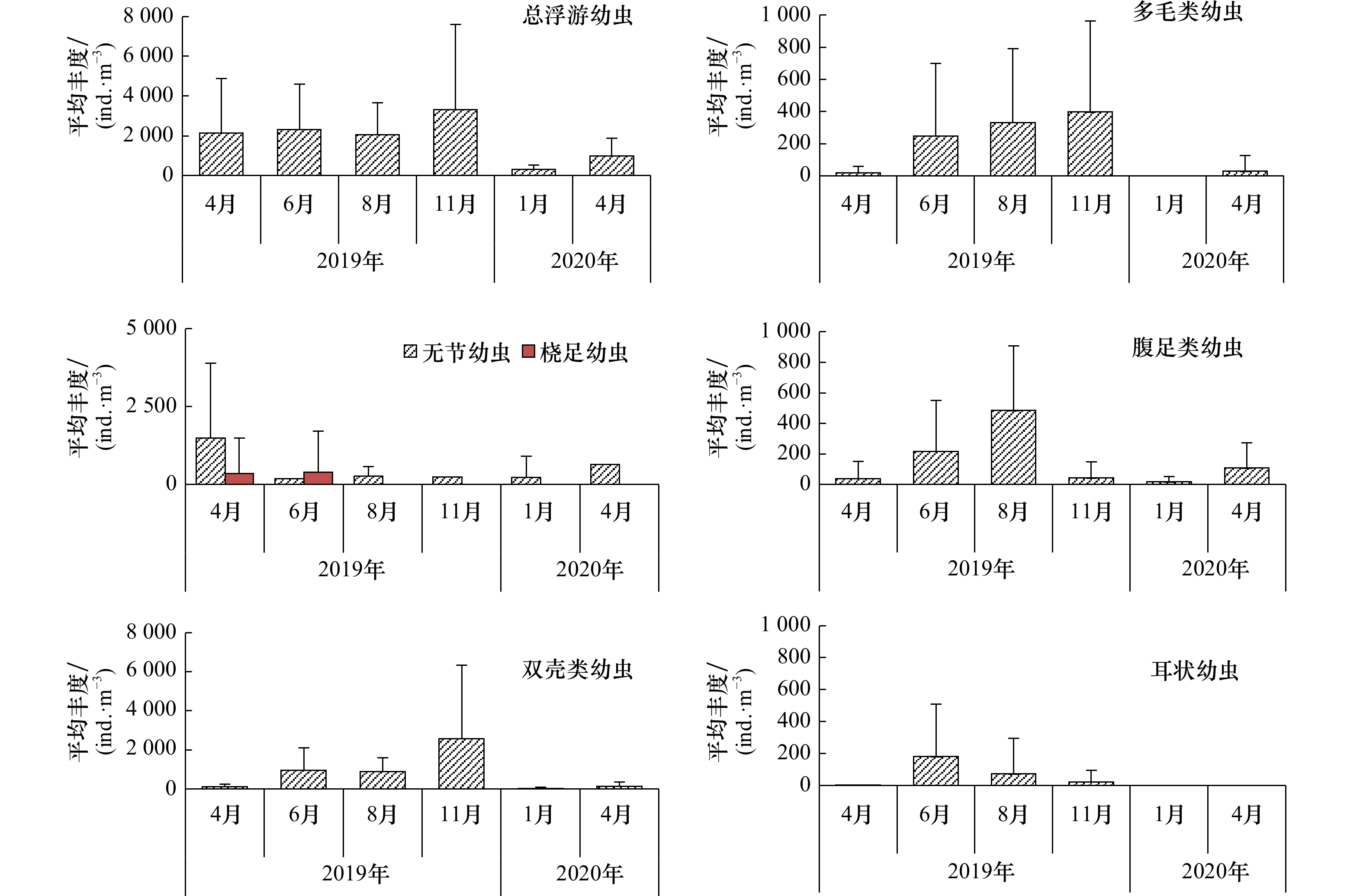
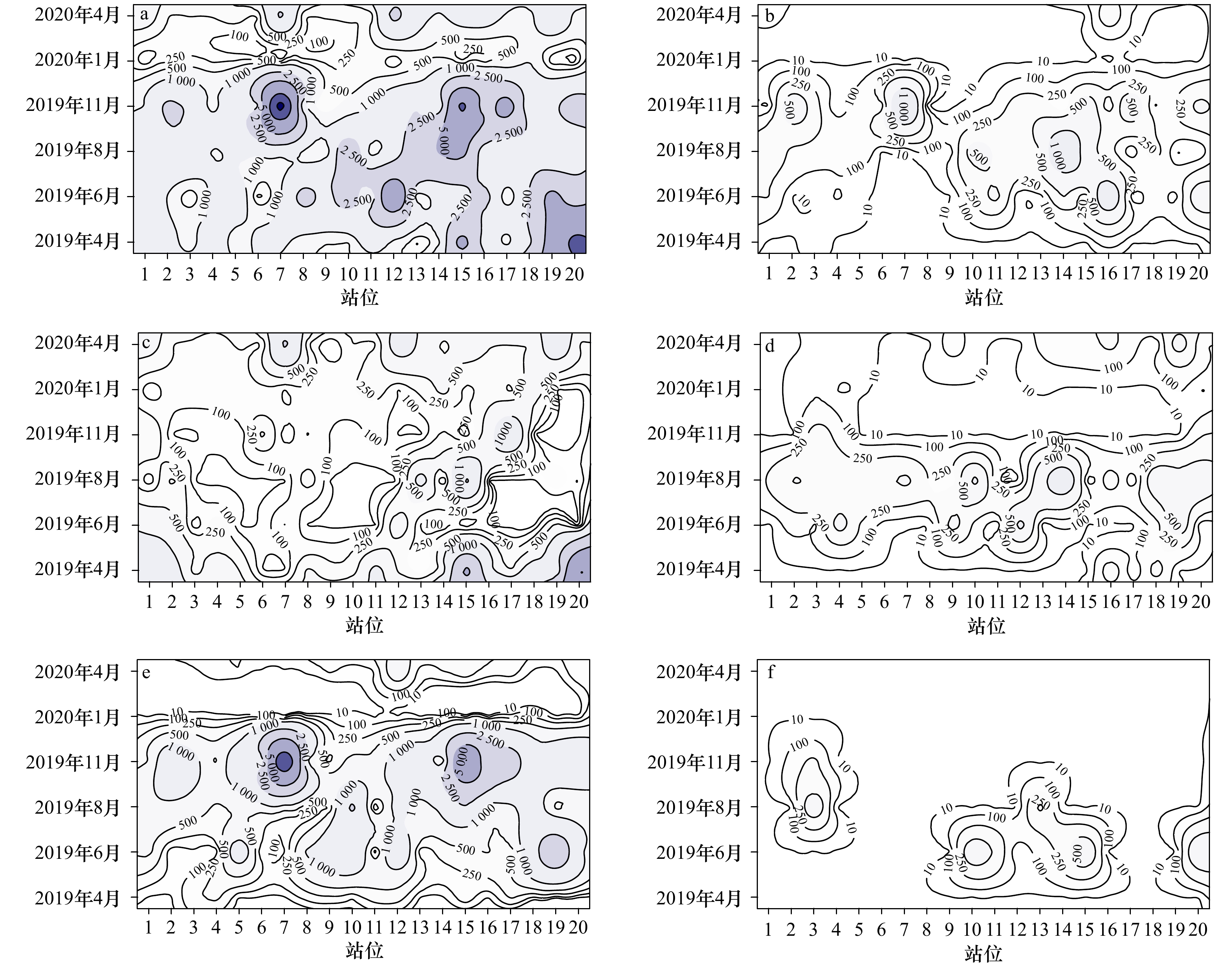
图 4 总浮游幼虫丰度(ind./m3)及主要类群丰度(ind./m3)的时空分布
a. 总浮游幼虫;b. 多毛类幼虫;c. 无节幼虫;d. 腹足类幼虫;e. 双壳类幼虫;f. 耳状幼虫
Fig. 4 Temporal-spatial abundance (ind./m3) distributions of total planktonic larva and major taxa
a. Total planktonic larvae; b. polychaeta larva; c. nauplii; d. gastropoda larva; e. bivalve larva; f. auricularia larva
表 1 黄河口邻近海域浮游幼虫及其优势种和优势度
Tab. 1 Dominant taxa and their dominance value of planktonic larvae in the Huanghe River Estuary adjacent waters
类别 2019年 2020年 4月 6月 8月 11月 1月 4月 环节动物门 多毛类幼虫 + 0.09 0.12 0.09 + 软体动物门 腹足类幼虫 + 0.06 0.18 + + 0.06 双壳类幼虫 0.02 0.36 0.40 0.77 0.05 0.09 头足类幼虫 + 节肢动物门甲壳类 无节幼虫 0.62 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.67 0.61 桡足幼虫 0.02 + 短尾类的蚤状幼虫 + + + + 短尾类的大眼幼虫 + 歪尾类的蚤状幼虫 + + 长尾类幼虫 + + + + + + 阿利玛幼虫 + + 帚虫动物门 辐轮幼虫 + + + + + 棘皮动物门 耳状幼虫 + 0.02 + + 长腕幼虫 0.02 + 脊索动物门 鱼卵 + + + + 仔鱼 + + + + 注:“+”表示出现,非优势种。 表 2 黄河口邻近海域浮游幼虫及环境因子多元方差分析统计信息
Tab. 2 Statistical information from MANOVA analysis of planktonic larvae and environmental factors in the Huanghe River Estuary adjacent waters
类别 站位间 月间 F p F p 总浮游幼虫 1.40 0.14 4.22 <0.01 多毛类幼虫 0.93 0.53 4.92 <0.01 腹足类幼虫 0.99 0.47 11.19 <0.01 双壳类幼虫 0.97 0.49 6.89 <0.01 无节幼虫 0.98 0.48 4.30 0.001 耳状幼虫 0.97 0.49 3.69 0.004 水温 1.21 0.26 692.11 <0.01 盐度 2.46 0.002 9.98 <0.01 pH 2 0.01 6 <0.01 Chl a浓度 1.25 0.23 11.00 <0.01 浮游动物 1.32 0.18 10.26 <0.01 浮游植物 1.34 0.17 2.80 0.02 底栖动物 1.03 0.43 1.11 0.36 表 3 环境因子及其最佳匹配组合与浮游幼虫群聚结构的 Weighted Spearman 等级相关系数
Tab. 3 Weighted Spearman rank correlation coefficient for environmental factors and their best combinations with the planktonic larvae assemblage structure
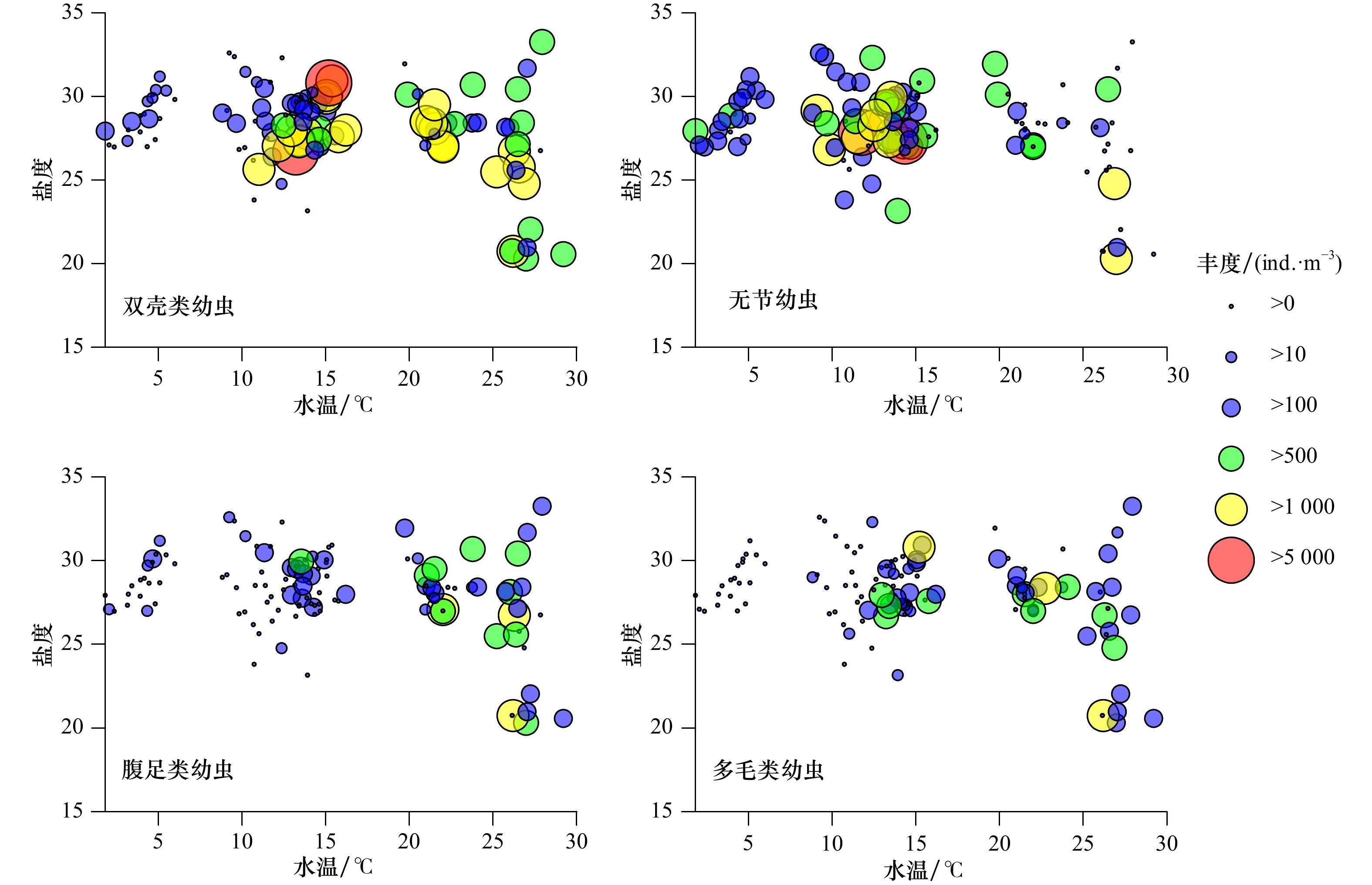
环境因子 相关系数 月间 站位间 水温 0.618 0.076 盐度 <0.001 0.100 pH <0.001 0.160 Chl a浓度 0.007 <0.001 月径流量 0.385 0.091 浮游动物 0.623 0.110 浮游植物 0.308 0.06 底栖动物 0.082 0.053 最佳组合 0.67*(水温,浮游动物) 0.169(pH,浮游动物) 注:*相关性达显著水平(p<0.05)。 -
[1] Richardson A J. In hot water: zooplankton and climate change[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 2008, 65(3): 279−295. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsn028 [2] Kirby R R, Beaugrand G, Lindley J A, et al. Climate effects and benthic–pelagic coupling in the North Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2007, 330: 31−38. doi: 10.3354/meps330031 [3] Kirby R R, Beaugrand G, Lindley J A. Climate-induced effects on the meroplankton and the benthic-pelagic ecology of the North Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2008, 53(5): 1805−1815. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.5.1805 [4] Patterson H M, Swearer S E. Long-distance dispersal and local retention of larvae as mechanisms of recruitment in an island population of a coral reef fish[J]. Austral Ecology, 2007, 32(2): 122−130. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.2006.01669.x [5] Turner J T, Levinsen H, Nielsen T G, et al. Zooplankton feeding ecology: grazing on phytoplankton and predation on protozoans by copepod and barnacle nauplii in Disko Bay, West Greenland[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2001, 221: 209−219. doi: 10.3354/meps221209 [6] de Almeida Fernandes L D, Quintanilha J, Monteiro-Ribas W, et al. Seasonal and interannual coupling between sea surface temperature, phytoplankton and meroplankton in the subtropical south-western Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2012, 34(3): 236−244. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fbr106 [7] Michelsen H K, Svensen C, Reigstad M, et al. Seasonal dynamics of meroplankton in a high-latitude fjord[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2017, 168: 17−30. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.12.001 [8] Williams R, Collins N R. Seasonal composition of meroplankton and holoplankton in the Bristol Channel[J]. Marine Biology, 1986, 92(1): 93−101. doi: 10.1007/BF00392751 [9] 郑重. 浮游幼虫生态研究——海洋浮游生物学的新动向之三[J]. 自然杂志, 1978, 1(8): 493−498.Zheng Zhong. Ecological research on planktonic larva—the third prospect on marine planktology[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 1978, 1(8): 493−498. [10] 蔡秉及. 大亚湾浮游幼虫的丰度[M]//国家海洋局第三海洋研究所. 大亚湾海洋生态文集(II). 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990: 232−236.Cai Bingji. The Planktonic Larva Abundance in Daya Bay[M]//Third Institute of Oceanography State Oceanic Administration. Collections of Papers on Marine Ecology in the Daya Bay (II). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990: 232−236. [11] 蔡国雄. 遮浪湾浮游幼虫主要类别的形态[J]. 热带海洋, 1992, 11(4): 96−101.Cai Guoxiong. Morphology of pelagic larvae from Zhelang Bay (South China Sea)[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1992, 11(4): 96−101. [12] 黄加祺, 白云彪. 闽南−台湾浅滩渔场浮游幼虫的分布[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 1994, 33(S1): 145−148.Huang Jiaqi, Bai Yunbiao. The distribution of pelagic larvae in Minnan-Taiwan Bank fishing ground[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 1994, 33(S1): 145−148. [13] 杨国锋, 汪文兰. 南海北部甲壳类浮游幼虫数量分布及其与海况的关系[J]. 生态科学, 1986, 5(1): 39−44.Yang Guofeng, Wang Wenlan. The quantitative distribution and variation of the planktonic crustacean larvae in the northern part of South China Sea and their relation to the sea condition[J]. Ecological Science, 1986, 5(1): 39−44. [14] 高琼珍, 李昌华. 珠江口一带浮游幼虫的初步报导[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 1962, 31(2): 60−63.Gao Qiongzhen, Li Changhua. Preliminary study on planktonic larvae in Pearl River Estuary[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1962, 31(2): 60−63. [15] 李开枝, 尹健强, 黄良民, 等. 珠江口浮游幼虫的生态研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2007, 26(6): 42−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.06.007Li Kaizhi, Yin Jianqiang, Huang Liangmin, et al. Ecological study on planktonic larvae in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 26(6): 42−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.06.007 [16] 王学锋, 李纯厚, 廖秀丽, 等. 北部湾浮游幼虫群落结构及其环境适应性分析[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2010, 19(4): 529−534.Wang Xuefeng, Li Chunhou, Liao Xiuli, et al. Community structure and environmental adaptation of the planktonic larvae in Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2010, 19(4): 529−534. [17] 刘镇盛. 长江口及其邻近海域浮游动物群落结构和多样性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2012.Liu Zhensheng. Community structure and biodiversity of zooplankton in the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012. [18] 马静, 陈洪举, 刘光兴. 2007年夏季黄河口及其邻近水域浮游动物的群落特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2012, 42(5): 74−80.Ma Jing, Chen Hongju, Liu Guangxing. Study on the zooplankton community structure in the Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent waters in summer, 2007[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2012, 42(5): 74−80. [19] 冷宇, 张继民, 刘霜, 等. 黄河口及邻近海域海洋生物物种多样性[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2013: 78−114.Leng Yu, Zhang Jimin, Liu Shuang, et al. Marine Biodiversity in the Yellow River Estuary and Adjacent Waters[M]. Qingdao: China Ocean University Press, 2013: 78−114. [20] 董志军, 杨青, 孙婷婷, 等. 黄河口邻近海域浮游动物群落时空变化特征[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(2): 659−667.Dong Zhijun, Yang Qing, Sun Tingting, et al. Spatial and seasonal variability of the zooplankton community in the Yellow River Estuary’s adjacent sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(2): 659−667. [21] 王文杰, 刘光兴. 2010年秋季黄河口及其邻近海域中小型浮游动物的群落特征[J]. 海洋科学, 2013, 37(11): 9−15.Wang Wenjie, Liu Guangxing. The characteristics of meso- and micro-zooplankton community in the Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent area in autumn, 2010[J]. Marine Sciences, 2013, 37(11): 9−15. [22] 田家怡, 李洪彦. 黄河口附近海域浮游动物的分布特征及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1985, 4(3): 32−41.Tian Jiayi, Li Hongyan. Distribution characteristics of zooplankton and its relationship with environmental factors in the waters near the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 1985, 4(3): 32−41. [23] Jin Xianshi, Shan Xiujuan, Li Xiansen, et al. Long-term changes in the fishery ecosystem structure of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2013, 56(3): 366−374. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4528-7 [24] 孙鹏飞, 单秀娟, 吴强, 等. 莱州湾及黄河口水域鱼类群落结构的季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(2): 367−376.Sun Pengfei, Shan Xiujuan, Wu Qiang, et al. Seasonal variations in fish community structure in the Laizhou Bay and the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(2): 367−376. [25] Song Yingfei, Zhang Longjun, Luo Xianxiang. Spatiotemporal distribution of fish eggs and larvae in the Huanghe (Yellow) River Estuary, China in 2005−2016[J]. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2019, 37(5): 1625−1637. doi: 10.1007/s00343-019-8167-0 [26] Ren Zhonghua, Li Fan, Wei Jiali, et al. Community characteristics of macrobenthos in the Huanghe (Yellow River) Estuary during water and sediment discharge regulation[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2016, 35(8): 74−81. doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0881-2 [27] 张士华, 刘艳芬, 左明, 等. 黄河口贝类资源与可持续利用[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2018.Zhang Shihua, Liu Yanfen, Zuo Ming, et al. Shellfish Resource and Its Sustainable Utilization in the Yellow River Estuary[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2018. [28] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763.6−2007, 海洋调查规范 第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008: 1-157.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. GB/T 12763.6−2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: Marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008: 1−157. [29] 郑重, 李少菁, 许振祖. 海洋浮游生物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1984.Zheng Zhong, Li Shaojing, Xu Zhenzu. Marine Planktology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1984. [30] Shannon C E, Weaver W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication[M]. Urbana IL: The University of Illinois Press, 1947: 125. [31] Clarke K R, Gorley R N, Somerfield P J, et al. Change in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation[M]. 3rd ed. Plymouth: PRIMER-E, 2014. [32] Shanks A L. Pelagic larval duration and dispersal distance revisited[J]. The Biological Bulletin, 2009, 216(3): 373−385. doi: 10.1086/BBLv216n3p373 [33] Pineda-Metz S E A, Montiel A. Seasonal dynamics of meroplankton in a sub-Antarctic fjord (Southern Patagonia, Chile)[J]. Polar Biology, 2021, 44(5): 875−886. doi: 10.1007/s00300-021-02823-6 [34] Chícharo L, Chícharo M A. Effects of environmental conditions on planktonic abundances, benthic recruitment and growth rates of the bivalve mollusc Ruditapes decussatus in a Portuguese coastal lagoon[J]. Fisheries Research, 2001, 53(3): 235−250. doi: 10.1016/S0165-7836(00)00290-3 [35] Ziadi B, Dhib A, Turki S, et al. Bivalve and barnacle larvae distribution driven by water temperature in a Mediterranean lagoon[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(9): 7002−7011. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3918-0 [36] Koettker A G, Lopes R M. Meroplankton spatial structure and variability on Abrolhos Bank and adjacent areas, with emphasis on brachyuran larvae[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 70: 97−108. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.10.004 [37] Meerhoff E, Tapia F J, Castro L R. Spatial structure of the meroplankton community along a Patagonian fjord—The role of changing freshwater inputs[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2014, 129: 125−135. doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2014.05.015 [38] MacTavish A L, Ladah L B, Lavín M F, et al. High frequency (hourly) variation in vertical distribution and abundance of meroplanktonic larvae in nearshore waters during strong internal tidal forcing[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2016, 117: 92−99. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2016.02.004 [39] Ershova E A, Descoteaux R, Wangensteen O S, et al. Diversity and distribution of meroplanktonic larvae in the Pacific Arctic and connectivity with adult benthic invertebrate communities[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2019, 6: 490. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2019.00490 [40] Brandner M M, Stübner E, Reed A J, et al. Seasonality of bivalve larvae within a high Arctic fjord[J]. Polar Biology, 2017, 40(2): 263−276. doi: 10.1007/s00300-016-1950-x [41] Descôteaux R, Ershova E, Wangensteen O S, et al. Meroplankton diversity, seasonality and life-history traits across the Barents Sea Polar Front revealed by high-throughput DNA barcoding[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021, 8: 677732. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.677732 -




 下载:
下载: