Study on fish species diversity in the East China Sea in summer based on environmental DNA technology
-
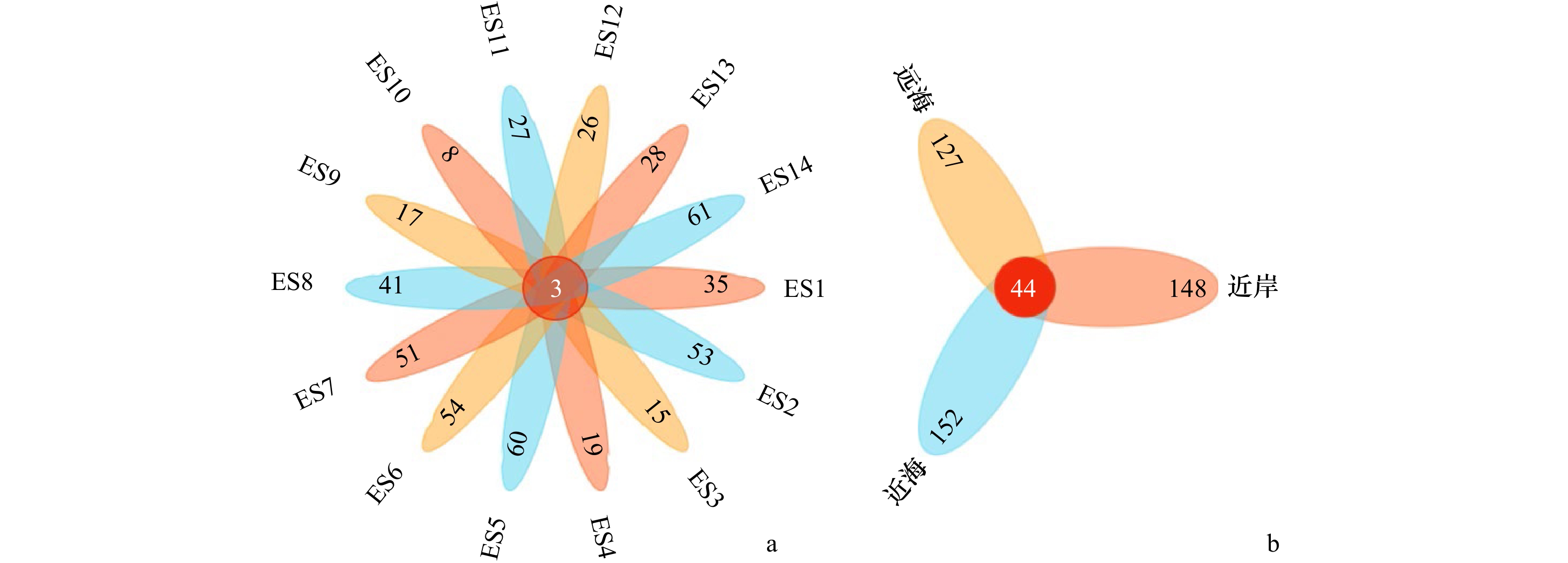
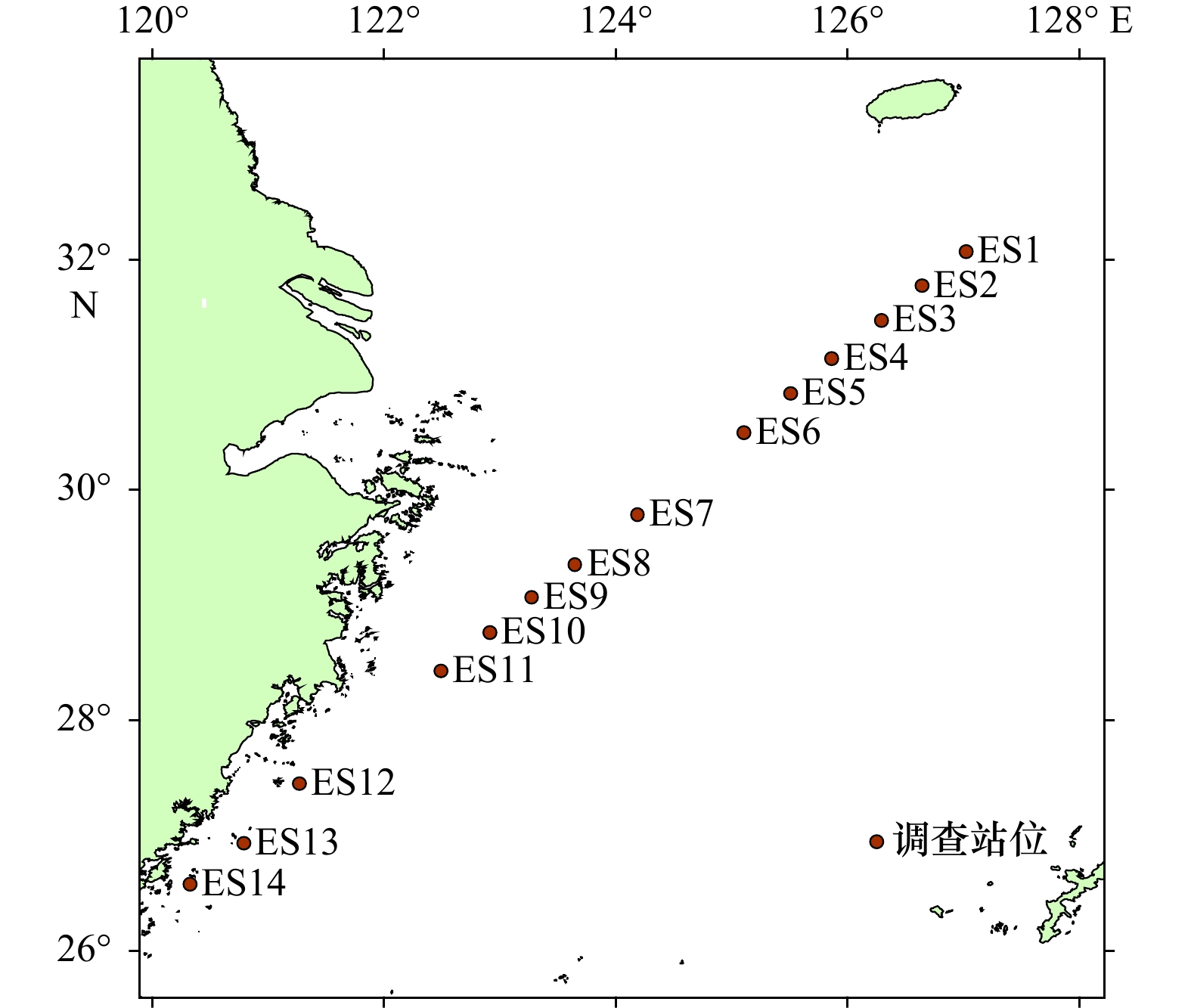
摘要: 为了解东海海域主要鱼类群落的种类组成,监测和保护其多样性,本研究利用环境DNA技术对东海鱼类进行物种多样性分析。通过海水样本的采集,环境DNA提取、扩增和高通量测序分析,从东海14个站点的环境DNA样本中共检测出2纲,23目,29科,42属,44种海水鱼类,大部分种类在东海传统渔业资源调查中均有出现。其中,相对丰度较高的物种为赤鼻棱鳀(Thryssa kammalensis)、蓝点马鲛(Scomberomorus niphonius)、日本鲐(Scomber japonicus)、小黄鱼(Larimichthys polyactis)和鲻(Mugil cephalus)。站点间α多样性差异较大,总体上呈现近海站点生物多样性高,远海站点生物丰度高的特点。研究结果表明,环境DNA技术可以作为传统渔业资源调查的补充,也可以对东海海域鱼类物种多样性及空间分布进行快速检测。Abstract: To understand the species composition of the dominant fish species communities in the East China Sea and to monitor and protect their diversity, environmental DNA technology to analyze the species diversity of fish in the East China Sea was used in this study. Through the collection of seawater samples, eDNA extraction, amplification and high-throughput sequencing analysis, a total of 44 species of marine fishes in 2 classes, 23 orders, 29 families and 42 genera were detected, and most of the species were found in the traditional fishery resources survey in the East China Sea. Among them, the species with high relative abundance were red nose anchovy (Thryssa kammalensis), blue-spotted horse mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius), Japanese mackerel (Scomber japonicus), small yellowtail (Larimichthys polyactis) and mullet (Mugil cephalus). The alpha diversity among stations was significant difference, and generally showed high biodiversity at coastal stations and high biological abundance at offshore stations. The results suggested that environmental DNA technology could quickly explore the diversity and spatial distribution of fish species in the East China Sea, as an effective supplementary to traditional fisheries resource monitoring.
-
Key words:
- environmental DNA /
- East China Sea /
- biodiversity /
- fish
-
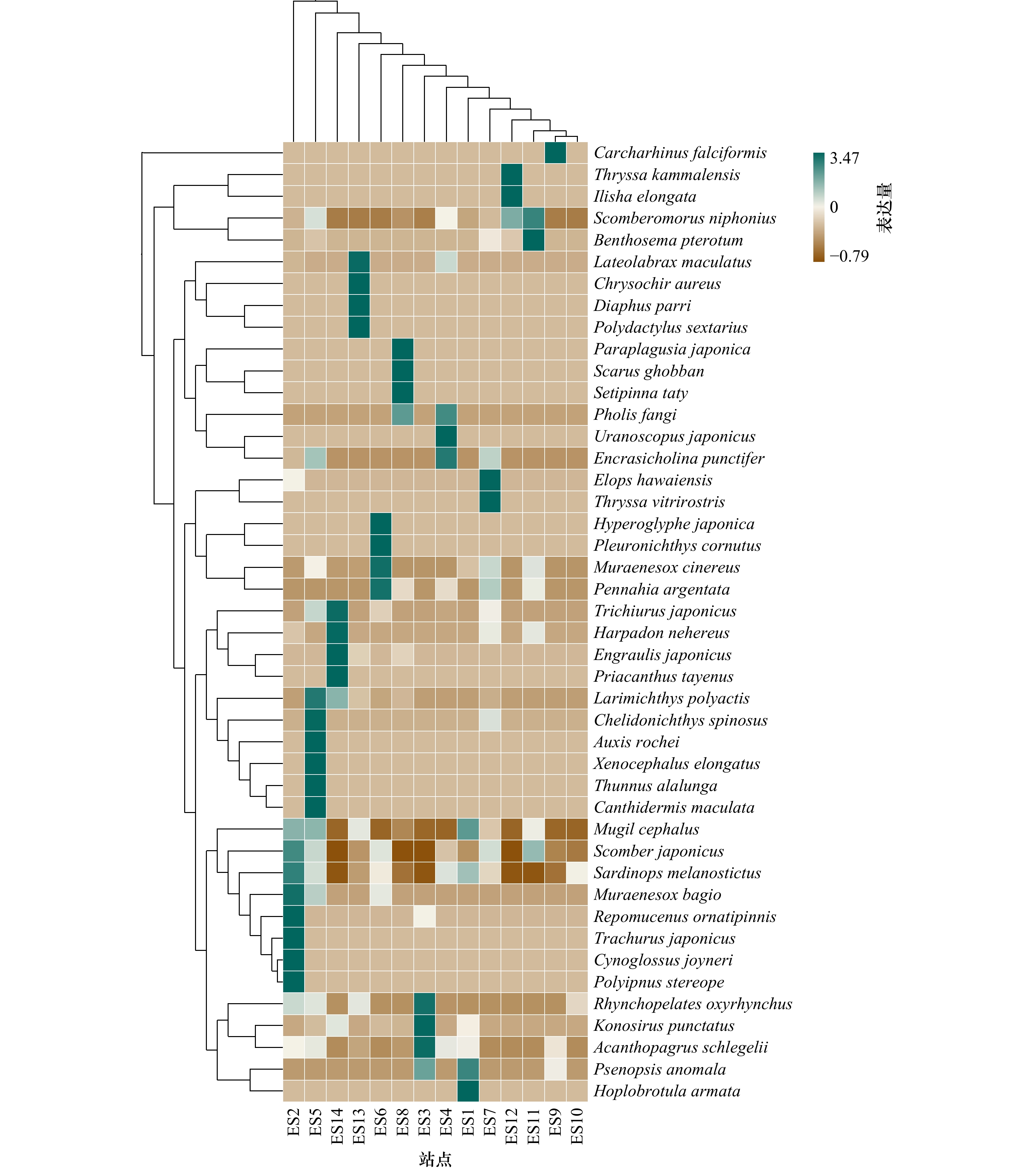
图 7 环境DNA检出的东海鱼类物种组成热图
样本按照物种组成数据的欧式距离进行UPGMA聚类,并根据聚类结果排列;物种按照其组成数据的Pearson相关性系数矩阵进行UPGMA聚类,并根据聚类结果排列;不同色标代表不同物种在不同样本中的表达量,色标数值通过物种丰度数据取Z值获得,由绿到棕表示对应样本中该种丰度逐渐降低
Fig. 7 Heat map of fish species composition in the East China Sea detected by eDNA
Samples are clustered by UPGMA according to the euclidean distance of species composition data, and arranged according to the clustering results; UPGMA clustering is carried out according to Pearson correlation coefficient matrix of species composition data, and arranged according to the clustering results; different color codes represent the expression of different species in different samples, and the value of color codes is obtained by taking Z value of species abundance data, and from green to brown, the abundance in corresponding samples gradually decreases
表 1 各站点的序列量(eDNA)结果
Tab. 1 Sequence quantity (eDNA) results of each station
样本
编号输入 拼接 过滤 去除嵌合体 去除稀有个体 ES1 49 783 44 714 44 391 42 432 42 408 ES2 46 901 41 393 40 861 38 840 38 805 ES3 40 025 32 226 31 836 28 594 28 582 ES4 51 372 46 714 46 342 44 584 44 577 ES5 48 368 42 888 42 569 38 711 38 693 ES6 40 211 36 323 36 045 35 215 35 191 ES7 45 536 37 148 36 896 33 504 33 477 ES8 42 894 38 350 37 916 36 222 36 206 ES9 39 905 35 718 35 365 33 794 33 779 ES10 36 894 34 166 33 866 33 029 33 025 ES11 47 798 42 483 42 025 40 463 40 452 ES12 48 212 44 930 44 405 42 827 42 818 ES13 57 782 52 829 52 126 50 612 50 594 ES14 61 182 52 154 51 314 48 608 48 582 注:表中第二列为原始数据中能同时匹配到正向和反向引物的序列量;第三列为拼接后的序列量;第四列为去除低质量序列后的数据量;第五列为聚类后去除嵌合体后序列量,即为高质量序列量;第六列为去除singleton OTUs(在所有样本中绝对丰度为1的OTU)后的序列量。 表 2 东海环境DNA检出的鱼类物种
Tab. 2 Fish species detected by eDNA in the East China Sea
目 科 属 种 Anguilliformes Muraenesocidae Muraenesox 褐海鳗 Muraenesox bagio 海鳗 Muraenesox cinereus Aulopiformes Synodontidae Harpadon 龙头鱼 Harpadon nehereus Carangaria Polynemidae Polydactylus 黑斑多指马鲅 Polydactylus sextarius Carangiformes Carangidae Trachurus 日本竹筴鱼 Trachurus japonicus Centrarchiformes Terapontidae Rhynchopelates 尖突吻䱨 Rhynchopelates oxyrhynchus Clupeiformes Clupeidae Konosirus 斑鰶 Konosirus punctatus Sardinops 远东拟沙丁鱼 Sardinops melanostictus Engraulidae Encrasicholina 银灰半棱鳀 Encrasicholina punctifer Engraulis 日本鳀 Engraulis japonicus Setipinna 太的黄鲫 Setipinna taty Thryssa 赤鼻棱鳀Thryssa kammalensis 黄吻棱鳀 Thryssa vitrirostris Pristigasteridae Ilisha 鳓 Ilisha elongata Elopiformes Elopidae Elops 夏威夷海鲢 Elops hawaiensis Eupercaria Sciaenidae Chrysochir 尖头黄鳍牙鱛 Chrysochir aureus Larimichthys 小黄鱼 Larimichthys polyactis Pennahia 银姑鱼 Pennahia argentata Labriformes Labridae Scarus 青点鹦嘴鱼 Scarus ghobban Mugiliformes Mugilidae Mugil 鲻 Mugil cephalus Myctophiformes Myctophidae Benthosema 七星底灯鱼 Benthosema pterotum Diaphus 帕尔眶灯鱼 Diaphus parri Ophidiiformes Ophidiidae Hoplobrotula 棘鼬鳚 Hoplobrotula armata Pempheriformes Lateolabracidae Lateolabrax 中国花鲈 Lateolabrax maculatus Perciformes Pholidae Pholis 方氏锦鳚 Pholis fangi Triglidae Chelidonichthys 棘绿鳍鱼 Chelidonichthys spinosus Pleuronectiformes Cynoglossidae Cynoglossus 焦氏舌鳎 Cynoglossus joyneri Paraplagusia 日本须鳎 Paraplagusia japonica Pleuronectidae Pleuronichthys 木叶鲽 Pleuronichthys cornutus Priacanthiformes Priacanthidae Polydactylus 长尾大眼鲷 Priacanthus tayenus Scombriformes Centrolophidae Hyperoglyphe 日本栉鲳 Hyperoglyphe japonica Psenopsis 刺鲳 Psenopsis anomala Scombridae Auxis 双鳍舵鲣 Auxis rochei Scomber 日本鲐 Scomber japonicus Scomberomorus 蓝点马鲛 Scomberomorus niphonius Thunnus 长鳍金枪鱼 Thunnus alalunga Trichiuridae Trichiurus 日本带鱼 Trichiurus japonicus Spariformes Sparidae Acanthopagrus 黑棘鲷 Acanthopagrus schlegelii Stomiiformes Sternoptychidae Polyipnus 闪电烛光鱼 Polyipnus stereope Syngnathiformes Callionymidae Repomucenus 饰鳍斜棘鴨 Repomucenus ornatipinnis Tetraodontiformes Balistidae Canthidermis 疣鳞鲀 Canthidermis maculata Uranoscopiformes Uranoscopidae Uranoscopus 日本 Uranoscopus japonicus Xenocephalus 青 Xenocephalus elongatus Carcharhiniformes Carcharhinidae Carcharhinus 镰状真鲨 Carcharhinus falciformis 表 3 东海鱼类物种相对丰度的α多样性指数
Tab. 3 Alpha diversity index of relative abundance of fish species in the East China Sea
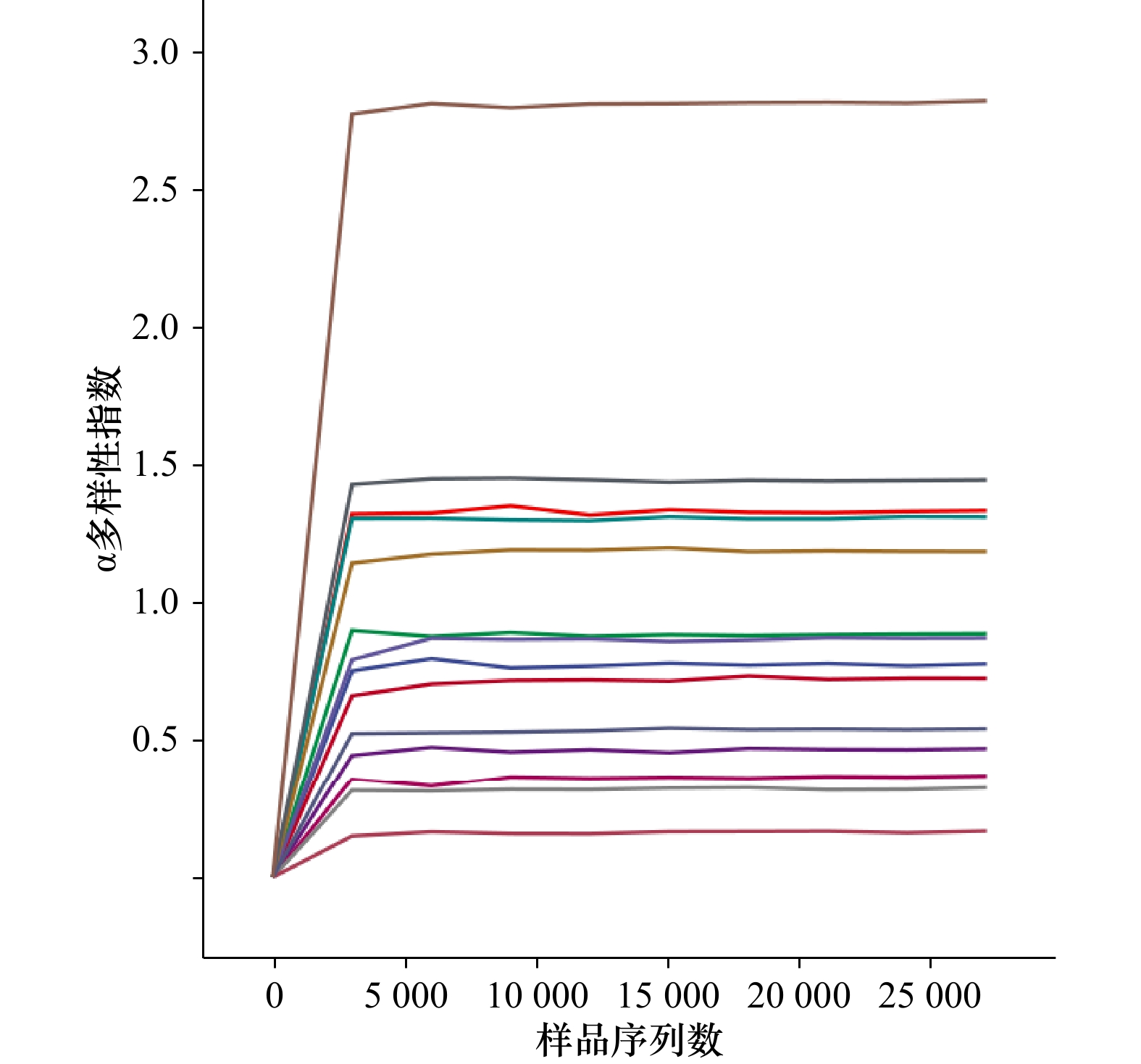
样本编号 α多样性指数 Chao1
指数Observed
species指数Pielou
均匀度指数Shannon
多样性指数Simpson
多样性指数ES1 136.067 110.9 0.114 603 0.778 447 0.146 170 ES2 141.298 118.8 0.194 134 1.338 000 0.279 125 ES3 66.306 52.5 0.155 547 0.888 807 0.210 343 ES4 87.058 70.4 0.076 428 0.469 034 0.087 745 ES5 180.581 158.0 0.179 919 1.313 980 0.260 339 ES6 146.008 131.1 0.103 214 0.726 042 0.137 918 ES7 179.801 156.1 0.120 015 0.874 447 0.159 080 ES8 123.483 104.2 0.055 219 0.370 140 0.060 713 ES9 96.789 73.4 0.052 500 0.325 372 0.055 633 ES10 52.628 41.3 0.031 302 0.168 019 0.028 676 ES11 128.553 113.0 0.174 276 1.188 490 0.266 132 ES12 76.652 65.1 0.240 004 1.445 680 0.358 558 ES13 97.967 84.7 0.085 121 0.545 044 0.099 298 ES14 155.352 140.8 0.396 211 2.827 730 0.644 819 -
[1] Edlinger A, Saghaï A, Herzog C, et al. Towards a multidimensional view of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning in a changing world[J]. New Phytologist, 2020, 228(3): 820−822. doi: 10.1111/nph.16881 [2] Noor N M, Das S K. Effects of elevated carbon dioxide on marine ecosystem and associated fishes[J]. Thalassas: An International Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 35(2): 421−429. doi: 10.1007/s41208-019-00161-3 [3] Worm B, Barbier E B, Beaumont N, et al. Impacts of biodiversity loss on ocean ecosystem services[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5800): 787−790. doi: 10.1126/science.1132294 [4] 李圣法, 程家骅, 严利平. 东海大陆架鱼类群落的空间结构[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(11): 4377−4386. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.001Li Shengfa, Cheng Jiahua, Yan Liping. Spatial structures of fish communities on the continental shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(11): 4377−4386. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.11.001 [5] Liu J Y. Status of marine biodiversity of the China Seas[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e50719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050719 [6] Takayanagi K, Nishiuchi K, Yokouchi K, et al. A possible collaboration with China on marine ecosystem research in the East China Sea[J]. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly: JARQ, 2006, 40(1): 59−64. doi: 10.6090/jarq.40.59 [7] 林龙山, 程家骅, 李惠玉. 东海底拖网渔业资源现状[J]. 现代渔业信息, 2006, 21(9): 13−15.Lin Longshan, Cheng Jiahua, Li Huiyu. Recent status of bottom trawl fishery resources in the East China Sea[J]. Modern Fisheries Information, 2006, 21(9): 13−15. [8] 刘勇, 程家骅. 东海及黄海南部渔业资源水文环境类群划分及其相关特征的初步分析[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(4): 796−810.Liu Yong, Cheng Jiahua. Preliminary analysis on the division of fishery resources based on hydrological environment factors in the East China Sea and south of the Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(4): 796−810. [9] 戴芳群, 朱玲, 陈云龙. 黄、东海渔业资源群落结构变化研究[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2020, 41(1): 1−10.Dai Fangqun, Zhu Ling, Chen Yunlong. Variations of fishery resource structure in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2020, 41(1): 1−10. [10] 高天翔, 陈治, 王晓艳. 近海鱼类多样性调查新方法—环境DNA分析技术[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 37(1): 1−7.Gao Tianxiang, Chen Zhi, Wang Xiaoyan. Environmental DNA, a new method for fish diversity investigation in the coastal waters[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 37(1): 1−7. [11] 张辉, 线薇薇. 环境DNA技术在生态保护和监测中的应用[J]. 海洋科学, 2020, 44(7): 96−102. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200119002Zhang Hui, Xian Weiwei. Application of environmental DNA technology in ecological conservation and monitoring[J]. Marine Science, 2020, 44(7): 96−102. doi: 10.11759/hykx20200119002 [12] 吴昀晟, 唐永凯, 李建林, 等. 环境DNA在长江江豚监测中的应用[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(1): 124−132. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18133Wu Yunsheng, Tang Yongkai, Li Jianlin, et al. The application of environmental DNA in the monitoring of the Yangtze finless porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides asaeorientalis[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(1): 124−132. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1118.2019.18133 [13] Lear G, Dickie I, Banks J, et al. Methods for the extraction, storage, amplification and sequencing of DNA from environmental samples[J]. New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 2018, 42(1): 10. [14] 单秀娟, 李苗, 王伟继. 环境DNA(eDNA)技术在水生生态系统中的应用研究进展[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2018, 39(3): 23−29.Shan Xiujuan, Li Miao, Wang Weiji. Application of environmental DNA technology in aquatic ecosystem[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2018, 39(3): 23−29. [15] Sigsgaard E E, Nielsen I B, Carl H, et al. Seawater environmental DNA reflects seasonality of a coastal fish community[J]. Marine Biology, 2017, 164(6): 128. doi: 10.1007/s00227-017-3147-4 [16] Fraija-Fernández N, Bouquieaux M C, Rey A, et al. Marine water environmental DNA metabarcoding provides a comprehensive fish diversity assessment and reveals spatial patterns in a large oceanic area[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2020, 10(14): 7560−7584. doi: 10.1002/ece3.6482 [17] 凌建忠, 姜亚洲, 孙鹏, 等. 环境DNA技术在象山港水域鱼类多样性调查中的应用与评估[J]. 中国水产科学, 2021, 28(2): 205−214.Ling Jianzhong, Jiang Yazhou, Sun Peng, et al. Application and evaluation of environmental DNA technology in fish diversity research in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2021, 28(2): 205−214. [18] 舒璐, 林佳艳, 徐源, 等. 基于环境DNA宏条形码的洱海鱼类多样性研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 2020, 44(5): 1080−1086. doi: 10.7541/2020.125Shu Lu, Lin Jiayan, Xu Yuan, et al. Investigating the fish diversity in Erhai Lake based on environmental DNA metabarcoding[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2020, 44(5): 1080−1086. doi: 10.7541/2020.125 [19] Wang Xiaoyan, Lu Guoqing, Zhao Linlin, et al. Assessment of fishery resources using environmental DNA: small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in East China Sea[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(12): e0244495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244495 [20] Miya M, Sato Y, Fukunaga T, et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2015, 2(7): 150088. doi: 10.1098/rsos.150088 [21] Bolyen E, Rideout J R, Dillon M R, et al. Author correction: reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(9): 1091. [22] Whittaker R H. Evolution and measurement of species diversity[J]. Taxon, 1972, 21(2/3): 213−251. [23] Chao Anne. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 1984, 11(4): 265−270. [24] Shannon C E. A mathematical theory of communication part I: discrete noiseless systems[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(3): 379−423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x [25] Shannon C E. A mathematical theory of communication part II: the discrete channel with noise[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 1948, 27(3): 623−656. [26] Simpson E H. Measurement of diversity[J]. Nature, 1949, 163(4148): 688. doi: 10.1038/163688a0 [27] Pielou E C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1966, 13: 131−144. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90013-0 [28] 赵淑江, 吕宝强, 李汝伟, 等. 物种灭绝背景下东海渔业资源衰退原因分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(11): 1628−1640.Zhao Shujiang, Lü Baoqiang, Li Ruwei, et al. A preliminary analysis of fishery resource exhaustion in the context of biodiversity decline[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 45(11): 1628−1640. [29] Bergman P S, Schumer G, Blankenship S, et al. Detection of adult green sturgeon using environmental DNA analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0153500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153500 [30] Lugg W H, Griffiths J, Van Rooyen A R, et al. Optimal survey designs for environmental DNA sampling[J]. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 9(4): 1049−1059. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12951 [31] 刘勇, 李圣法, 陈学刚, 等. 东、黄海2000年冬季底层鱼类群落结构及其多样性[J]. 海洋科学, 2007, 31(10): 19−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.10.009Liu Yong, Li Shengfa, Chen Xuegang, et al. The structure and diversity of demersal fish communities in winter 2000 in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea[J]. Marine Science, 2007, 31(10): 19−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.10.009 [32] 宫亚运, 章群, 曹艳, 等. 基于线粒体COⅠ基因的中国近海棱鳀属鱼类DNA条形码[J]. 水产学报, 2016, 40(10): 1513−1520.Gong Yayun, Zhang Qun, Cao Yan, et al. DNA barcoding of Thryssa in coastal waters of China based on the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I sequence[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2016, 40(10): 1513−1520. [33] 马春艳, 马凌波, 倪勇, 等. 基于形态特征和线粒体16S rRNA基因序列探讨棱鳀属的系统进化[J]. 中国水产科学, 2010, 17(3): 471−477.Ma Chunyan, Ma Lingbo, Ni Yong, et al. Phylogenetic relationship of Thryssa inferred from morphologic characteristic and mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene sequences[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2010, 17(3): 471−477. [34] 程家骅, 张秋华, 李圣法, 等. 东黄海渔业资源利用[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2006.Cheng Jiahua, Zhang Qiuhua, Li Shengfa, et al. Fishery Resource Utilization in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2006. [35] 杜萍, 陈全震, 李尚鲁, 等. 东海带鱼资源变动及其栖息地驱动因子研究进展[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2020, 40(1): 126−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.01.017Du Ping, Chen Quanzhen, Li Shanglu, et al. Advances in the Trichiurus lepturus changes and habitat driving factors in the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2020, 40(1): 126−132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.01.017 [36] 杨青, 李宏俊, 李洪波, 等. 海洋生物多样性评价方法综述[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2013, 32(1): 157−160.Yang Qing, Li Hongjun, Li Hongbo, et al. Review on assessment methods of marine biodiversity[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(1): 157−160. [37] 赵梦迪. 利用环境DNA分析冬季中国东黄海水域的鱼类多样性[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2017.Zhao Mengdi. Analysis of the fish diversity of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea in winter using environmental DNA[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2017. [38] 周永东, 李圣法. 东海区主要经济种类三场一通道及保护区图集[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2018.Zhou Yongdong, Li Shengfa. Atlas of Spawning Grounds, Feeding Grounds, Overwintering Grounds, Migratory Channels and Protected Areas of the Main Economic Species in the East China Sea[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2018. [39] 李圣法, 程家骅, 李长松, 等. 东海中部鱼类群落多样性的季节变化[J]. 海洋渔业, 2005, 27(2): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.02.005Li Shengfa, Cheng Jiahua, Li Changsong, et al. Seasonal changes on fish community diversity in the middle part of the East China Sea[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2005, 27(2): 113−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2490.2005.02.005 -




 下载:
下载: