Holocene relative sea-level change of Fujian coast, southeastern China: Geological records and comparison with glacio-hydro isostatic adjustment modelling
-
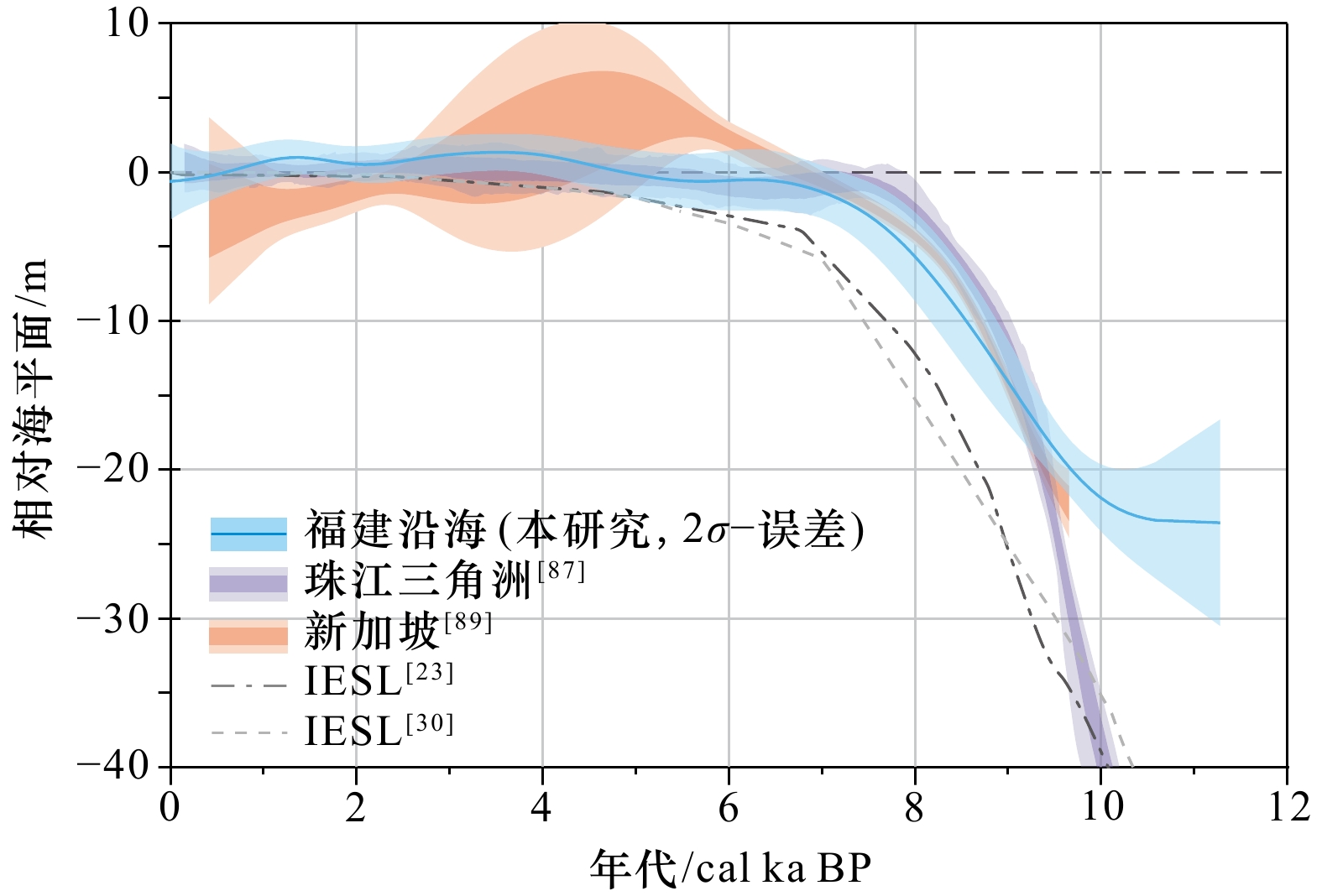
摘要: 重建高质量的全新世相对海平面变化曲线,可为海岸带人类社会科学预测及应对未来海平面上升风险提供重要的地质历史依据和长时间尺度的数据参考。目前已发表了多条福建海岸带全新世相对海平面变化曲线,然而已有曲线反映的相对海平面变化历史存在较大差异,甚至是矛盾结果。同时,相对海平面长期变化机制及影响因素也不明确。本研究收集、整理了福建沿海已发表的全新世相对海平面数据,对已有数据的年代、高程、指示意义等属性信息进行重新检查和校正,根据国际方法体系,建立了该区域一个标准化的全新世“相对海平面数据库”,共包括海平面数据183个。在此基础上,采用“变量误差–综合高斯(EIV-IGP)”统计学模型,提出了一条新的福建沿海全新世相对海平面变化曲线。并应用“冰川–水均衡调整”(GIA)理论,开展了相对海平面变化GIA模拟。最后,综合相对海平面变化地质记录及GIA模拟结果,得出以下结论:(1)福建沿海距今11.28~7.08 cal ka,相对海平面由(–23.55±6.94)m快速连续上升至(–1.51±1.80)m;距今7.08~4.08 cal ka,相对海平面由(–1.51±1.80)m缓慢上升至约(1.09±1.38)m;距今3.48 cal ka前后,相对海平面高于现代海平面约(1.35±1.23)m;此后,波动下降并逐渐接近现代位置;(2)“冰川–水均衡调整”作用是福建全新世相对海平面变化的主要长期作用机制;距今11.28~7.00 cal ka,相对海平面变化主要受冰盖融水控制;距今7.00 cal ka以来,“水均衡调整”作用逐渐占据主导;(3)福建沿海中–晚全新世(距今6.75~0.16 cal ka)期间,存在高于现今海面位置的“高海平面”现象;不同于传统构造运动主导观点,研究认为GIA引起的“陆地掀斜”和“海洋虹吸”作用,可能是该区域“高海平面”现象产生的主要原因;(4)福建沿海全新世相对海平面变化,存在一定程度的空间差异。不同岸段之间的沉积物压实、差异性构造运动和潮差变化等非GIA因素,可能是这一现象产生的重要原因。Abstract: Reconstruction of high-quality Holocene relative sea levels (RSL) based on geological records can provide important past analogue and long-term reference for coastal societies to make better prediction and preparation for future sea-level rise. In the last decades, several Holocene RSL curves have already been published from Fujian coast, southeastern China. However, obvious differences and even contradictory results existed in these early-stage researches. At the same time, the mechanism and factors which control the long-term RSL change in this area are also unclear. In this study, new and published RSL data have been compiled from Fujian coast. Attribute information including location, age, elevation and indicative meaning of each data point has been re-examined and corrected. After that, a standardized Holocene relative sea level database which includes a total number of 183 data were established. On this basis, a new regional Holocene RSL curve was proposed by using the errors in variable-integrated gaussian process (EIV-IGP) statistical model. Finally, theoretical RSL change was predicted through solving the sea level equation (SLE). Combining the RSL geological records and GIA simulation results, conclusions are drawn as follow: (1) New Holocene RSL history of Fujian coast was reconstructed. 11.28–7.08 cal ka before present, RSL rose from (–23.55±6.94) m to (–1.51±1.80) m continuously; 7.08–4.08 cal ka before present, RSL rose slowly from (–1.51±1.80) m to (1.09 ±1.38) m; around 3.48 cal ka before present, RSL was about (1.35±1.23) m higher than modern sea level. Since then, the RSL has declined close to the modern position gradually. (2) In the Early Holocene (11.28–7.00 cal ka before present), the RSL change was mainly controlled by the meltwater from continental ice-sheet; and since 7.00 cal ka before present, hydro-isostatic process dominated the regional RSL change. (3) Holocene sea level highstand existed during 6.75–0.16 cal ka before present on Fujian coast. The highstand of sea level could be attributed to continental levering and ocean syphoning processes caused by GIA rather than tectonic movement. (4) Holocene RSL change showed spatial variability on the Fujian coast. Non-GIA factors including the compaction of unconsolidated strata, differential tectonic movements and tidal range changes, supposed to be related to this phenomenon.
-
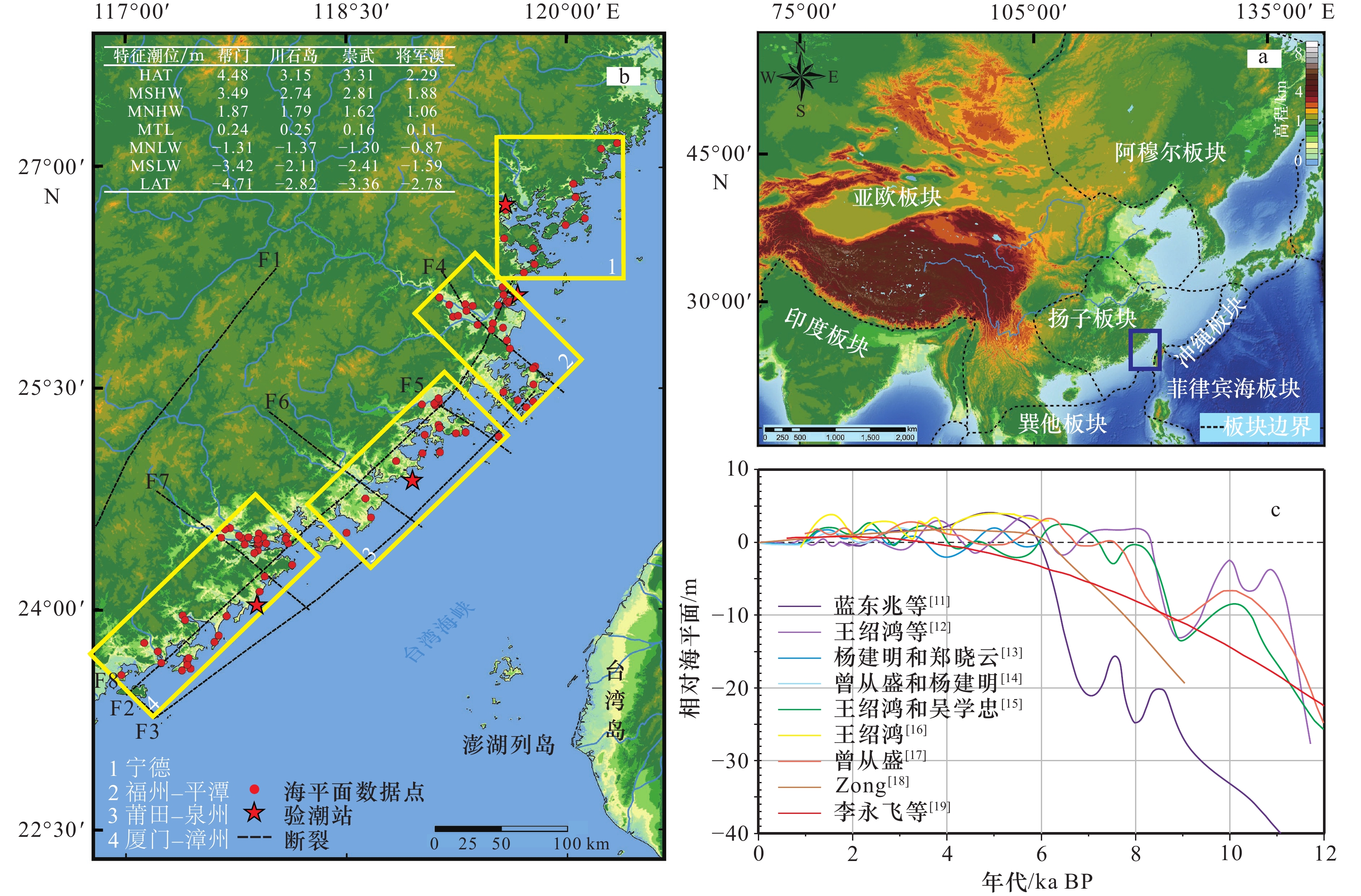
图 1 研究区概况
a. 东亚板块边界分布;b. 福建海岸带全新世相对海平面数据空间分布及分区;c. 福建沿海已发表的全新世相对海平面变化曲线
Fig. 1 Map of the study area
a. Locations of East Asia and the plate boundary;b. distribution of Holocene relative sea-level data along the Fujian coast and sub-zone;c. published Holocene relative sea-level curves from Fujian coast
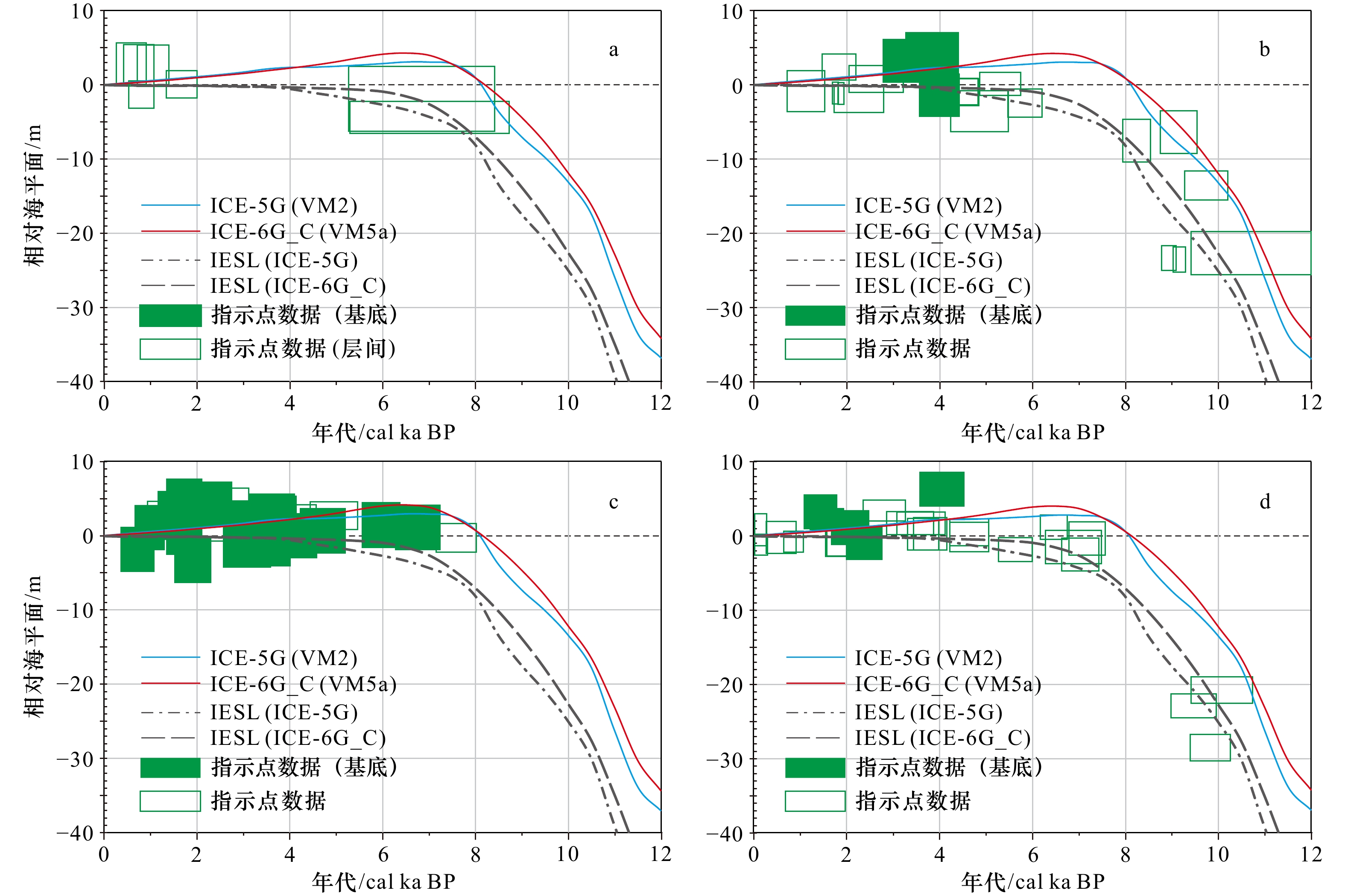
图 5 福建沿海全新世相对海平面指示点数据与“冰川− 水均衡调整”模拟结果(理论RSL曲线、IESL曲线)对比
a. 宁德;b. 福州− 平潭;c. 莆田− 泉州;d. 厦门− 漳州
Fig. 5 Comparison of sea level index point (SLIP) with relative sea level (RSL) curve and ice melt equivalent sea-level (IESL) curve at each subzone of Fujian coast
a. Ningde; b. Fuzhou-Pingtan; c. Putian-Quanzhou;d. Xiamen-Zhangzhou
表 1 福建海岸带全新世相对海平面标志物及其指示意义
Tab. 1 Indicative meaning of Holocene sea level indicators on Fujian coast
数据类型 海平面标志物 指示意义 参考水位 指示范围 海平面指
示点数据海滩岩(海滩型) (HAT+MLW)/2 HAT−MLW 贝壳堤(底部) (MSHW+MNHW)/2 MSHW−MNHW 牡蛎礁 (MTL+MSLW)/2 MTL−MSLW 埋藏红树林 (MSHW+MSLW)/2 MSHW−MSLW 盐沼泥炭 (HAT+MNHW)/2 HAT−MNHW 潮滩淤泥 (MSHW+MSLW)/2 MSHW-MSLW 潮间带沉积(上部) (MSHW+MTL)/2 MSHW−MTL 潮间带沉积(下部) (MTL+MSLW)/2 MTL−MSLW 陆地约束
数据海滩岩(沙堤型) MTL >MTL 贝壳堤 MTL >MTL 淡水泥炭 MTL >MTL 河湖相沉积 MTL >MTL 埋藏古树 MTL >MTL 海洋约束
数据海相贝壳、牡蛎壳
(原位)MTL <MTL 河口砂坝 MTL <MTL 河口湾沉积 MTL <MTL 潮下带淤泥 MTL <MTL 浅海相及海相沉积 MTL <MTL -
[1] Nicholls R J, Cazenave A. Sea-level rise and its impact on coastal zones[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5985): 1517−1520. doi: 10.1126/science.1185782 [2] Almut A, Humberto B, Tim B, et al. Summary for Policymakers[M]. In: Climate Change and Land, Geneva, Swizerland: IPCC, 2019. [3] Bamber J L, Oppenheimer M, Kopp R E, et al. Ice sheet contributions to future sea-level rise from structured expert judgment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(23): 11195−11200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817205116 [4] 福建省统计局. 2020福建统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020.Fujian Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Fujian Statistical Yearbook 2020[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020. [5] 自然资源部海洋预警监测司. 2020年中国海平面公报[R]. (2021–04–26) [2021–09–22]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202104/t20210426_2630186.htmlMarine Early Warning and Monitoring Division, Ministry of Natural Resources. China sea level bulletin of 2020[R]. (2021–04–26) [2021–09–22]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202104/t20210426_2630186.html [6] Horton B P, Rahmstorf S, Engelhart S E, et al. Expert assessment of sea-level rise by AD 2100 and AD 2300[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 84: 1−6. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.11.002 [7] Barlow N L M, Shennan I, Long A J, et al. Salt marshes as late Holocene tide gauges[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2013, 106: 90−110. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.03.003 [8] 陈承惠, 黄宝林, 王明亮. 闽南沿海全新世地质年代学研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 1982, 1(2): 64−73.Chen Chenghui, Huang Baolin, Wang Mingliang. Studies of Holocene geochronology in the coastal regions of southern Fujian[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1982, 1(2): 64−73. [9] 余兆康, 巫锡良. 福建沿海全新世地壳垂直运动速率[J]. 地震地质, 1989, 11(3): 27−33.Yu Zhaokang, Wu Xiliang. Rates of Holocene vertical movements of fault blocks along the coast of Fujian Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1989, 11(3): 27−33. [10] 曾从盛. 福建沿海全新世海平面变化[J]. 台湾海峡, 1991, 10(1): 77−84.Zeng Congsheng. Sea level variation along Fujian coast in Holocene[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1991, 10(1): 77−84. [11] 蓝东兆, 于永芬, 陈承惠, 等. 福州盆地晚更新世海侵及全新世海面波动的初步研究[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1986, 6(3): 103−111.Lan Dongzhao, Yu Yongfen, Chen Chenghui, et al. Preliminary study on Late Pleistocene transgression and Holocene sea-level fluctuation in Fuzhou Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1986, 6(3): 103−111. [12] 王绍鸿, 杨建明, 孙亨伦, 等. 闽江下游及邻近地区冰后期海平面变动[J]. 海洋学报, 1990, 12(1): 64−74.Wang Shaohong, Yang Jianming, Sun Henglun, et al. Postal glacial sea level change in the lower reach of Minjiang River and adjacent area[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1990, 12(1): 64−74. [13] 杨建明, 郑晓云. 福建沿岸6000年来的海平面波动[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1990, 10(4): 67−75.Yang Jianming, Zheng Xiaoyun. Sea-level fluctuations during the past 6000 years along the coast of Fujian[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1990, 10(4): 67−75. [14] 曾从盛, 杨建明. 福建古牡蛎礁与海面、海岸线变动[J]. 热带海洋, 1991, 10(4): 22−28.Zeng Congsheng, Yang Jianming. Paleo-oyster reefs and the changes of sea level and shoreline in Fujian Province[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 1991, 10(4): 22−28. [15] 王绍鸿, 吴学忠. 福建沿海全新世高温期的气候与海面变化[J]. 台湾海峡, 1992, 11(4): 345−352.Wang Shaohong, Wu Xuezhong. Climate and sea level changes during Holocene high temperature period along Fujian coast[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1992, 11(4): 345−352. [16] 王绍鸿. 福建全新世海滩岩及其地质意义[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 11(4): 106−112.Wang Shaohong. Holocene beachrocks and its geological implications in the area of Fujian coast[J]. Journal of Fujian Teachers University (Natural Science), 1995, 11(4): 106−112. [17] 曾从盛. 闽东北沿海晚第四纪海侵与海面变动[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 13(4): 94−101.Zeng Congsheng. Transgressions and sea level changes along the northeast coast of Fujian during the late Quaternary[J]. Journal of Fujian Teachers University (Natural Science), 1997, 13(4): 94−101. [18] Zong Yongqiang. Mid-Holocene sea-level highstand along the southeast coast of China[J]. Quaternary International, 2004, 117(1): 55−67. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(03)00116-2 [19] 李永飞, 徐柳园, 许斌. 福建沿海40 000年以来的海面变化[J]. 内江师范学院学报, 2016, 31(6): 46−55, 61.Li Yongfei, Xu Liuyuan, Xu Bin. Changes of sea-level in Fujian coast during the past 40 000 years[J]. Journal of Neijiang Normal University, 2016, 31(6): 46−55, 61. [20] 马明明, 刘秀铭, 周国华, 等. 福建沿海地区晚第四纪海侵研究进展及存在的问题[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报, 2016, 11(3): 9−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.03.002Ma Mingming, Liu Xiuming, Zhou Guohua, et al. A review of late Quaternary transgression studies and some basic questions in Fujian coastal area[J]. Journal of Subtropical Resources and Environment, 2016, 11(3): 9−19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2016.03.002 [21] Shennan I, Long A J, Horton B P. Handbook of Sea-Level Research[M]. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015. [22] Peltier W R. On eustatic sea level history: last glacial maximum to Holocene[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(1/3): 377−396. [23] Lambeck K, Rouby H, Purcell A, et al. Sea level and global ice volumes from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(43): 15296−15303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411762111 [24] 汪汉胜, Wu P, 许厚泽. 冰川均衡调整(GIA)的研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(6): 1958−1967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.06.005Wang Hansheng, Wu P, Xu Houze. A review of research in glacial isostatic adjustment[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2009, 24(6): 1958−1967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2009.06.005 [25] Clark J A, Farrell W E, Peltier W R. Global changes in postglacial sea level: a numerical calculation[J]. Quaternary Research, 1978, 9(3): 265−287. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(78)90033-9 [26] Milne G A. Glacial isostatic adjustment[M]//Shennan I, Long A J, Horton B P. Handbook of Sea-Level Research. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015: 419−437. [27] Pirazzoli P A. World Atlas of Holocene Sea-Level Changes[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1991: 1−280. [28] Lambeck K, Chappell J. Sea level change through the last glacial cycle[J]. Science, 2001, 292(5517): 679−686. doi: 10.1126/science.1059549 [29] Khan N S, Ashe E, Shaw T A, et al. Holocene relative sea-level changes from near-, intermediate-, and far-field locations[J]. Current Climate Change Reports, 2015, 1(4): 247−262. doi: 10.1007/s40641-015-0029-z [30] Bradley S L, Milne G A, Horton B P, et al. Modelling sea level data from China and Malay-Thailand to estimate Holocene ice-volume equivalent sea level change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 137: 54−68. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.002 [31] Mitrovica J X, Milne G A. On the origin of late Holocene sea-level highstands within equatorial ocean basins[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21(20/22): 2179−2190. [32] 汪汉胜, 贾路路, Wu P, 等. 末次冰期冰盖消融对东亚历史相对海平面的影响及意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(4): 1144−1153. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.010Wang Hansheng, Jia Lulu, Wu P, et al. Effects of last-deglaciation on the historical relative sea levels of East Asia seas and the implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(4): 1144−1153. doi: 10.6038/j.issn.0001-5733.2012.04.010 [33] 孙奕映, Wu P, 黄光庆, 等. 广东全新世海平面重建与冰川均衡调整模型结果的比较[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2): 281−290. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.04Sun Yiying, Wu P, Huang Guangqing, et al. Holocene sea-level reconstruction for Guangdong coast and a comparison with GIA model outputs[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 281−290. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.04 [34] Wang Fu, Zong Yongqiang, Mauz B, et al. Holocene sea-level change on the central coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Earth Surface Dynamics, 2020, 8(3): 679−693. doi: 10.5194/esurf-8-679-2020 [35] Xiong Haixian, Zong Yongqiang, Li Tanghua, et al. Coastal GIA processes revealed by the early to middle Holocene sea-level history of east China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 233: 106249. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106249 [36] Wang Zhanghua, Zhan Qing, Long Haiyan, et al. Early to mid-Holocene rapid sea-level rise and coastal response on the southern Yangtze Delta plain, China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2013, 28(7): 659−672. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2662 [37] Liu Yan, Sun Qianli, Fan Daidu, et al. Early to Middle Holocene sea level fluctuation, coastal progradation and the Neolithic occupation in the Yaojiang Valley of southern Hangzhou Bay, eastern China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 189: 91−104. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.04.010 [38] Hijma M P, Engelhart S E, Törnqvist T E, et al. A protocol for a geological sea-level database[M]//Shennan I, Long A J, Horton B P. Handbook of Sea-Level Research. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2015: 536−553. [39] Khan N S, Horton B P, Engelhart S, et al. Inception of a global atlas of sea levels since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2019, 220: 359−371. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.07.016 [40] 福建师范大学地理系《福建自然地理》编写组. 福建自然地理[M]. 福州: 福建人民出版社, 1987.Editorial Group of Fujian Physical Geography in Department of Geography, Fujian Normal University. Fujian Physical Geography[M]. Fuzhou: Fujian People’s Publishing House, 1987. [41] 潘国轩. 福建沿海全新世地层划分与海面变化[J]. 台湾海峡, 1984, 3(2): 166−178.Pan Guoxuan. Holocene stratigraphical divisions and sea level changes in coastal Fujian[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1984, 3(2): 166−178. [42] 福建省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查领导小组办公室. 福建省海岸带和海涂资源综合调查报告[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1990.Leading Group of Integrated Investigation on Fujian Coastal Zone and Tidal Flat Resources. Report on the integrated investigation on Fujian coastal zone and tidal flat resources[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1990. [43] 江甘兴. 福建海区的潮汐和潮流[J]. 台湾海峡, 1992, 11(2): 89−94.Jiang Ganxing. Tides and tidal currents in Fujian waters[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1992, 11(2): 89−94. [44] 郑文振, 陈福年, 陈新忠. 台湾海峡的潮汐和潮流[J]. 台湾海峡, 1982, 1(2): 1−4.Zheng Wenzhen, Chen Funian, Chen Xinzhong. Tides and tidal currents in the Taiwan Strait[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1982, 1(2): 1−4. [45] 张路, 曲国胜, 陈建强. 福建东南沿海第四纪盆地构造沉降[J]. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29(3): 633−643. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.03.024Zhang Lu, Qu Guosheng, Chen Jianqiang. Tectonic subside of Quaternary basins in coastal area of Southeast Fujian Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29(3): 633−643. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2009.03.024 [46] Pedoja K, Shen J W, Kershaw S, et al. Coastal Quaternary morphologies on the northern coast of the South China Sea, China, and their implications for current tectonic models: a review and preliminary study[J]. Marine Geology, 2008, 255(3/4): 103−117. [47] 张路, 曲国胜, 朱金芳, 等. 福建沿海盆地第四纪构造运动模式与动力学环境[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(3): 275−288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.03.004Zhang Lu, Qu Guosheng, Zhu Jinfang, et al. Model of Quaternary tectonic movement and dynamic setting of basins along the coast of Fujian, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(3): 275−288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.03.004 [48] Rolett B V, Zheng Zhuo, Yue Yuanfu. Holocene sea-level change and the emergence of Neolithic seafaring in the Fuzhou Basin (Fujian, China)[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2011, 30(7/8): 788−797. [49] 陈慧娴, 骆美美, 王建华, 等. 福建九龙江河口第四纪沉积物特征及沉积环境演变[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(2): 263−273. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.02.024Chen Huixian, Luo Meimei, Wang Jianhua, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and depositional environmental evolution of the Quaternary in Jiulongjiang Estuary, Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(2): 263−273. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.02.024 [50] 马明明, 葛伟亚, 李春海, 等. 福建霞浦钻孔沉积物记录的约7 800 a B. P. 以来海平面波动的磁学响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(5): 1307−1318. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.05.24Ma Mingming, Ge Weiya, Li Chunhai, et al. Magnetic responses to sea-level fluctuations since about 7 800 a B. P. recorded by core sediments at Xiapu, Fujian[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(5): 1307−1318. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2016.05.24 [51] Ge Weiya, Li Chunhai, Xing Huaixue, et al. Examining the chronology of transgressions since the late Pleistocene in the Fujian coast, southeastern China[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 527: 34−43. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.11.034 [52] 何梅, 刘庚余, 周国华, 等. 福州盆地钻孔沉积物记录的MIS3以来海侵−海退过程[J]. 地球环境学报, 2021, 12(1): 44−56.He Mei, Liu Gengyu, Zhou Guohua, et al. Transgression-regression process recorded by borehole sediments in Fuzhou Basin since MIS3[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2021, 12(1): 44−56. [53] 中国人民解放军海军海道测量局. 潮汐表. 2022. 东海海区[M]. 天津: 中国航海图书出版社, 2021.China Navy Nydrographic office. Tidal Tables. 2022. East China Sea[M]. Tianjin: China Navigation Publications Press, 2021. [54] 许家琨, 林有财. 福建沿岸当地平均海面的高程研究与应用[J]. 海洋测绘, 2007, 27(1): 34−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2007.01.009Xu Jiakun, Lin Youcai. The research and application of the height of Fujian coastwise local mean sea level[J]. Hydrographic Surveying and Charting, 2007, 27(1): 34−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3044.2007.01.009 [55] van de Plassche, O. Sea-level Research: a Manual for the Collection and Evaluation of Data[M]. Norwich: Geo Books, 1986. [56] Shennan I, Horton B. Holocene land-and sea-level changes in Great Britain[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2002, 17(5/6): 511−526. [57] Engelhart S E, Horton B P. Holocene sea level database for the Atlantic coast of the United States[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 54: 12−25. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.09.013 [58] Khan N S, Ashe E, Horton B P, et al. Drivers of Holocene sea-level change in the Caribbean[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 155: 13−36. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.08.032 [59] Xue Chunting. Historical changes in the Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Marine Geology, 1993, 113(3/4): 321−330. [60] 王宏, 陈永胜, 田立柱, 等. 渤海湾全新世贝壳堤与牡蛎礁: 古气候与海面变化[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(9): 1405−1411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.009Wang Hong, Chen Yongsheng, Tian Lizhu, et al. Holocene cheniers and oyster reefs in Bohai Bay: palaeoclimate and sea level changes[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(9): 1405−1411. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.009 [61] 耿秀山, 傅命佐, 徐孝诗, 等. 现代牡蛎礁发育与生态特征及古环境意义[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1991(8): 867−875.Geng Xiushan, Fu Mingzuo, Xu Xiaoshi, et al. Growth and ecological characteristics of modern oyster reef and implications for palaeoenvironment[J]. Science in China (Series B), 1991(8): 867−875. [62] 俞鸣同. 海滨盐沼泥炭在海平面研究中的作用[J]. 海洋科学, 1991, 15(4): 22−24.Yu Mingtong. The function of coastal saltmarsh peat in the sea level study[J]. Marine Sciences, 1991, 15(4): 22−24. [63] 王绍鸿. 海平面标志物识别的一些问题[J]. 台湾海峡, 1989, 8(4): 329−337.Wang Shaohong. Some problem on recognition of sea level indicators[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1989, 8(4): 329−337. [64] Törnqvist T E, Rosenheim B E, Hu Ping, et al. Radiocarbon dating and calibration[M]//Shennan I, Long A J, Horton B P. Handbook of Sea-Level Research. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell, 2015: 349−360. [65] Reimer P J, Austin W E N, Bard E, et al. The IntCal20 northern hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0−55 cal kBP)[J]. Radiocarbon, 2020, 62(4): 725−757. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2020.41 [66] Heaton T J, Köhler P, Butzin M, et al. Marine20—the marine radiocarbon age calibration curve (0−55,000 cal BP)[J]. Radiocarbon, 2020, 62(4): 779−820. doi: 10.1017/RDC.2020.68 [67] Yoneda M, Uno H, Shibata Y, et al. Radiocarbon marine reservoir ages in the western Pacific estimated by pre-bomb molluscan shells[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2007, 259(1): 432−437. doi: 10.1016/j.nimb.2007.01.184 [68] Hirabayashi S, Yokoyama Y, Suzuki A, et al. Short-term fluctuations in regional radiocarbon reservoir age recorded in coral skeletons from the Ryukyu Islands in the north-western Pacific[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2017, 32(1): 1−6. doi: 10.1002/jqs.2923 [69] 王绍鸿. 建立海平面变化曲线的若干问题[J]. 台湾海峡, 1990, 9(4): 301−308.Wang Shaohong. Some problems in sea level curve establishment[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1990, 9(4): 301−308. [70] Brain M J. Past, present and future perspectives of sediment compaction as a driver of relative sea level and coastal change[J]. Current Climate Change Reports, 2016, 2(3): 75−85. doi: 10.1007/s40641-016-0038-6 [71] Horton B P, Shennan I. Compaction of Holocene strata and the implications for relative sealevel change on the east coast of England[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(12): 1083−1086. doi: 10.1130/G30042A.1 [72] Cahill N, Kemp A C, Horton B P, et al. Modeling sea-level change using errors-in-variables integrated Gaussian processes[J]. The Annals of Applied Statistics, 2015, 9(2): 547−571. [73] Peltier W R. Global glacial isostasy and the surface of the ice-age Earth: the ICE-5G (VM2) model and GRACE[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2004, 32: 111−149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.082503.144359 [74] Peltier W R, Argus D F, Drummond R. Space geodesy constrains ice age terminal deglaciation: the global ICE-6G_C (VM5a) model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2015, 120(1): 450−487. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011176 [75] Dziewonski A M, Anderson D L. Preliminary reference Earth model[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1981, 25(4): 297−356. doi: 10.1016/0031-9201(81)90046-7 [76] Farrell W E, Clark J A. On postglacial sea level[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1976, 46(3): 647−667. [77] Mitrovica J X, Milne G A. On post-glacial sea level: I. General theory[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2003, 154(2): 253−267. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01942.x [78] Mitrovica J X, Wahr J, Matsuyama I, et al. The rotational stability of an ice-age earth[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 161(2): 491−506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246X.2005.02609.x [79] Mitrovica J X, Wahr J. Ice age earth rotation[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2011, 39: 577−616. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-040610-133404 [80] Spada G, Melini D. SELEN4 (SELEN version 4.0): a Fortran program for solving the gravitationally and topographically self-consistent sea-level equation in glacial isostatic adjustment modeling[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019, 12(12): 5055−5075. doi: 10.5194/gmd-12-5055-2019 [81] 施雅风, 赵希涛. 中国气候与海面变化及其趋势和影响2: 中国海面变化[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 1996.Shi Yafeng, Zhao Xitao. Climate and Sea-Level Change and Its Trends and Impacts in China 2: Sea-Level Change in China[M]. Ji’nan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 1996. [82] 薛春汀. 对我国沿海全新世海面变化研究的讨论[J]. 海洋学报, 2002, 24(4): 58−67.Xue Chunting. Holocene sea-level change along China coast[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2002, 24(4): 58−67. [83] 郑洪波, 周友胜, 杨青, 等. 中国东部滨海平原新石器遗址的时空分布格局——海平面变化控制下的地貌演化与人地关系[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2018, 61(2): 123−133. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9121-yZheng Hongbo, Zhou Yousheng, Yang Qing, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of Neolithic sites in coastal China: sea level changes, geomorphic evolution and human adaption[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(2): 123−133. doi: 10.1007/s11430-017-9121-y [84] Carlson A E, LeGrande A N, Oppo D W, et al. Rapid early Holocene deglaciation of the Laurentide ice sheet[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(9): 620−624. doi: 10.1038/ngeo285 [85] Ullman D J, Carlson A E, Hostetler S W, et al. Final Laurentide ice-sheet deglaciation and Holocene climate-sea level change[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 152: 49−59. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.09.014 [86] Lambeck K, Nakada M. Late Pleistocene and Holocene sea-level change along the Australian coast[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1990, 89(1/2): 143−176. [87] Xiong Haixian, Zong Yongqiang, Qian Peng, et al. Holocene sea-level history of the northern coast of South China Sea[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2018, 194: 12−26. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.06.022 [88] Bird M I, Austin W E N, Wurster C M, et al. Punctuated eustatic sea-level rise in the early mid-Holocene[J]. Geology, 2010, 38(9): 803−806. doi: 10.1130/G31066.1 [89] Chua S, Switzer A D, Li Tanghua, et al. A new Holocene sea-level record for Singapore[J]. The Holocene, 2021, 31(9): 1376−1390. doi: 10.1177/09596836211019096 [90] Lewis S E, Sloss C R, Murray-Wallace C V, et al. Post-glacial sea-level changes around the Australian margin: a review[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2013, 74: 115−138. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.09.006 [91] Horton B P, Gibbard P L, Mine G M, et al. Holocene sea levels and palaeoenvironments, Malay-Thai Peninsula, Southeast Asia[J]. The Holocene, 2005, 15(8): 1199−1213. doi: 10.1191/0959683605hl891rp [92] Tanabe S, Saito Y, Vu Q L, et al. Holocene evolution of the Song Hong (Red River) Delta system, northern Vietnam[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 187(1/2): 29−61. [93] 刘文会, 余克服, 王瑞, 等. 涠洲岛北港海滩岩的铀系年代及其海平面指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(3): 764−774. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.14Liu Wenhui, Yu Kefu, Wang Rui, et al. Uranium-series ages of Beigang beachrock at Weizhou Island and their significance in recording sea level variations[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(3): 764−774. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2020.03.14 [94] 时小军, 余克服, 陈特固, 等. 中−晚全新世高海平面的琼海珊瑚礁记录[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2008, 28(5): 1−9.Shi Xiaojun, Yu Kefu, Chen Tegu, et al. Mid-to late-Holocene sea level highstands: evidence from fringing coral reefs at Qionghai, Hainan Island[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2008, 28(5): 1−9. [95] Yu Kefu, Zhao Jinxin, Done T, et al. Microatoll record for large century-scale sea-level fluctuations in the mid-Holocene[J]. Quaternary Research, 2009, 71(3): 354−360. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2009.02.003 [96] Davis A M, Aitchison J C, Flood P G, et al. Late Holocene higher sea-level indicators from the South China coast[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 171(1/4): 1−5. [97] Chen Y G, Liu T K. Sea level changes in the last several thousand years, Penghu Islands, Taiwan Strait[J]. Quaternary Research, 1996, 45(3): 254−262. doi: 10.1006/qres.1996.0026 [98] Mitrovica J X, Peltier W R. On postglacial geoid subsidence over the equatorial oceans[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B12): 20053−20071. doi: 10.1029/91JB01284 [99] 杨怀仁, 谢志仁. 中国东部近20, 000年来的气候波动与海面升降运动[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1984, 15(1): 1−13.Yang Huairen, Xie Zhiren. Sea-level changes along the east coast of China over the last 20, 000 years[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1984, 15(1): 1−13. [100] 谢志仁, 袁林旺, 闾国年, 等. 海面−地面系统变化: 重建·监测·预估[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.Xie Zhiren, Yuan Linwang, Lü Guonian, et al. Sea Level and Land Surface System Changes: Reconstruction, Monitor and Projection[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012. [101] 李建芬, 商志文, 王福, 等. 渤海湾西岸全新世海面变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2): 243−264. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.01Li Jianfen, Shang Zhiwen, Wang Fu, et al. Holocene sea level change on the west coast of the Bohai Bay[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 243−264. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.01 [102] Li Jianfen, Shang Zhiwen, Wang Fu, et al. Holocene sea level trend on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China: reanalysis and standardization[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2021, 40(7): 198−248. doi: 10.1007/s13131-021-1730-5 [103] 战庆, 王张华. 利用盐沼泥炭重建长江三角洲北部全新世中期海平面[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(4): 548−556. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.04.045Zhan Qing, Wang Zhanghua. Mid-Holocene sea-level of northern Yangtze River Delta reconstructed by salt marsh peat[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(4): 548−556. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.04.045 [104] 王绍鸿, 杨建明, 曾从盛, 等. 福建沿海晚更新世以来的海平面变化[J]. 台湾海峡, 1994, 13(2): 166−175.Wang Shaohong, Yang Jianming, Zeng Congsheng, et al. Sea level changes since Late Pleistocene along Fujian coast[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1994, 13(2): 166−175. [105] Uehara K, Saito Y, Hori K. Paleotidal regime in the Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary, the East China Sea, and the Yellow Sea at 6 ka and 10 ka estimated from a numerical model[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 183(1/4): 179−192. [106] Wang Shuo, Ge Jianzhong, Kilbourne K H, et al. Numerical simulation of mid-Holocene tidal regime and storm-tide inundation in the south Yangtze coastal plain, East China[J]. Marine Geology, 2020, 423: 106134. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106134 [107] Shang Zhiwen, Wang Fu, Li Jianfen, et al. New residence times of the Holocene reworked shells on the west coast of Bohai Bay, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 115: 492−506. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.10.008 -
 附件:福建全新世相对海平面数据库(V1.0).xlsx
附件:福建全新世相对海平面数据库(V1.0).xlsx

-




 下载:
下载: