Bottom sediment transport in the western Laizhou Bay during strong wind events based on a tripod measurement
-
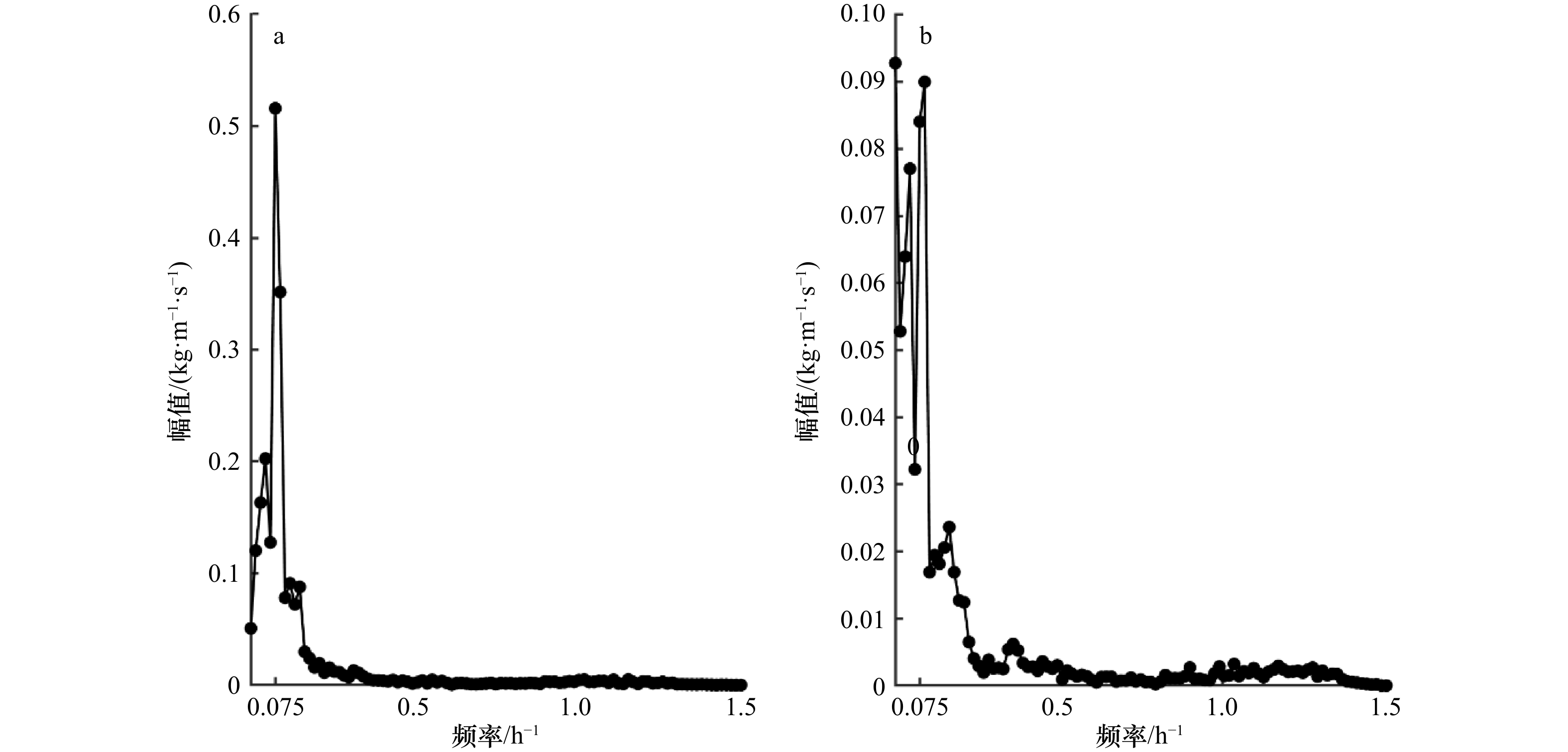
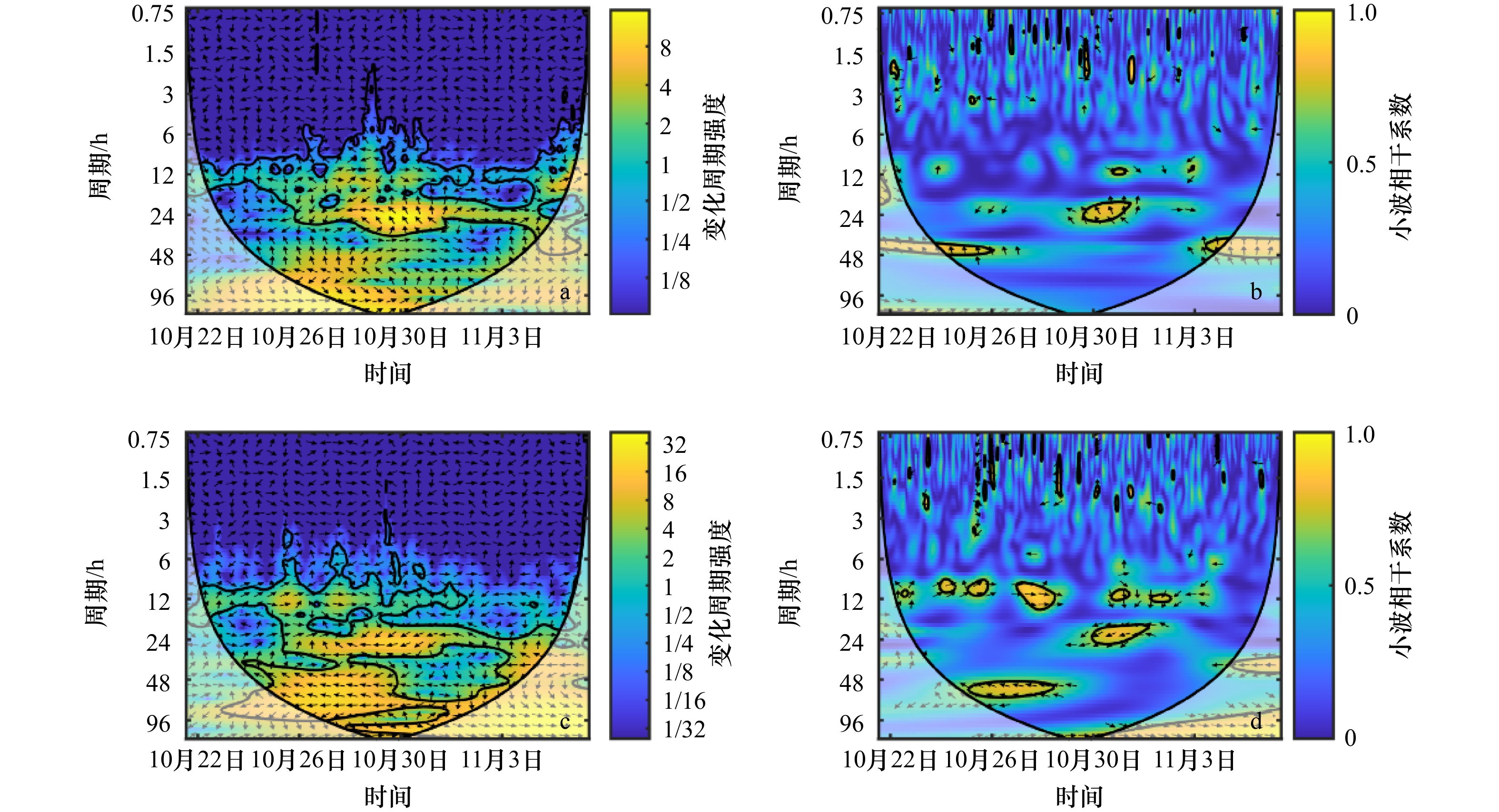
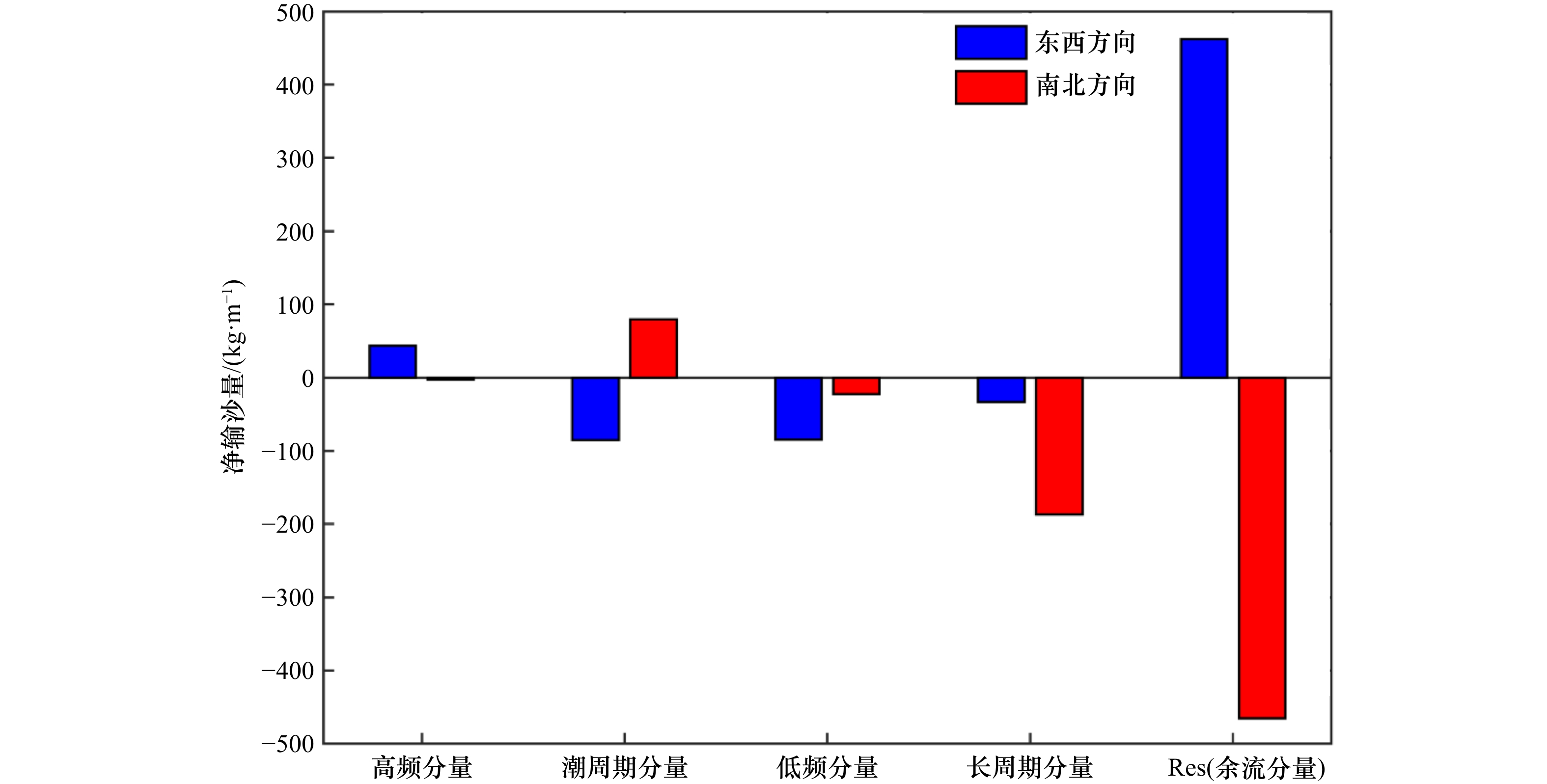
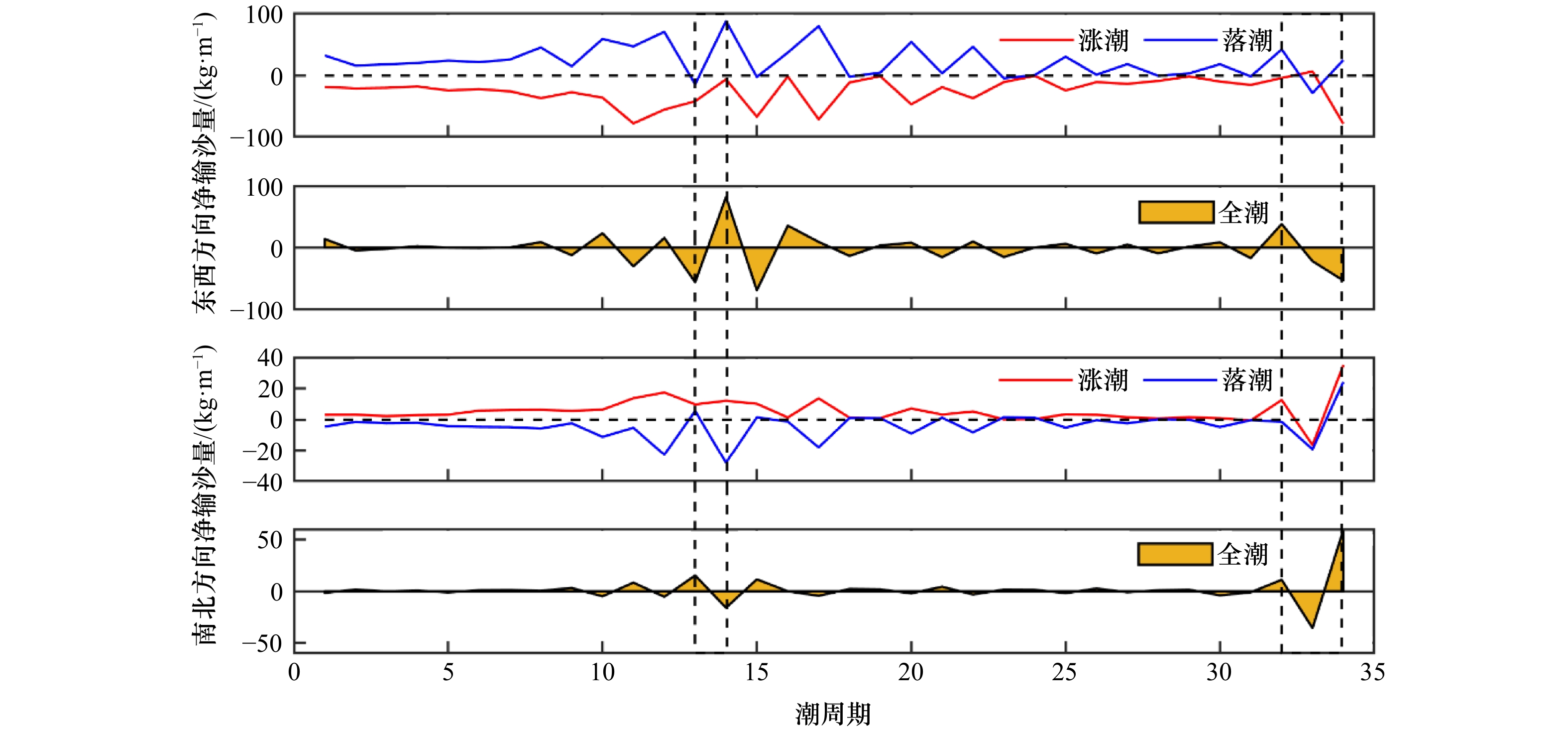
摘要: 基于2018年10月21日至11月6日莱州湾西岸连续站观测数据,本文利用集合经验模态分解、希尔伯特−黄变换和小波分析法对底层单宽输沙率的小尺度特征做分析,并针对观测期间出现的大风天气对泥沙输运的影响进行了探究。结果表明,单宽输沙率在观测时间段内具有高频、潮周期、低频以及长周期尺度变化特征,周期尺度从小到大。其中高频和潮周期分量方差贡献率及所含能量最高,对输沙率的影响最强。边际谱显示东西方向输沙率的显著周期为13.3 h,南北方向大于11 h的周期较为显著。观测期间底层净泥沙通量分别为东向305.77 kg/m、南向597.25 kg/m,余流分量贡献最大,低频和高频分量贡献最小。上强迫风场主要在风速衰减期通过湍流和波浪影响输沙速率的时频分布,使其低频变化显著增强的同时,产生1 h周期左右的高频波动。交叉小波分析显示,风速和单宽输沙率在低频波段上相干性较强,且单宽输沙率会滞后风速1/4至1/2个周期。另外,风浪会增强泥沙输运的涨落潮不对称性,进而增加潮周期分量上的泥沙净输运。Abstract: Based on a tripod measurement in the Laizhou Bay from October 21 to November 6, 2018, the unit-width bottom sediment transport rate and the effects of strong winds on bottom sediment transport are analyzed using the ensemble empirical mode decomposition, the Hilbert-Huang transform and the wavelet analysis method. The resuluts show thta the unit-width sediment transport rate can be divided into four intrinsic mode functions with increased periods including the high-frequency, tidal-period, low-frequency and long-period. The high-frequency and tidal-period components have the highest variance contribution rate and energy, indicating their greatest impact on sediment transport. The marginal spectrum shows a significant period of 13.3 h in the east-west direction, and a period larger than 11 h in the north-south direction. The net bottom sediment fluxes in the east-west and north-south directions are 305.77 kg/m and 597.25 kg/m, respectively; and the high-frequency and low-frequency component contribute least while the residual-current component contributes most. Winds work on the time-frequency distribution of the unit-width sediment transport rate mainly through the turbulence and waves during the wind decrease periods, which enhances the low-frequency domain significantly, and further induces the high-frequency fluctuations with periods about 1 h. The cross-wavelet analysis shows the winds and the unit-width sediment transport rate have a strong coherence on the low-frequency band; and the latter lags behind the former by 1/4 to 1/2 period. In addition, the wind-waves enhance the asymmetric sediment transport between flood and ebb tidal phase, which increases the net sediment flux of tidal period.
-
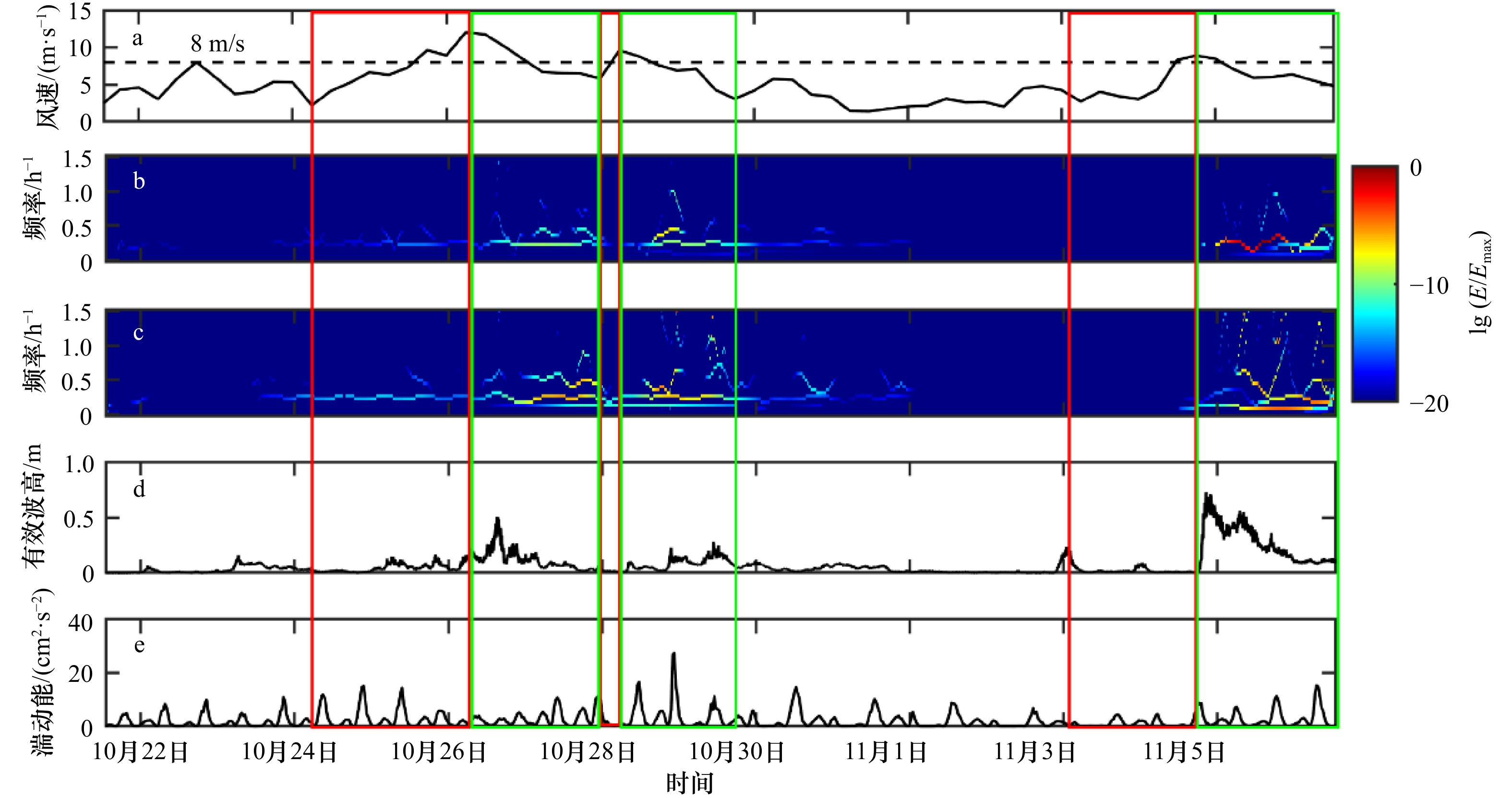
图 7 风速(a),东西方向(b)和南北方向(c)单宽输沙率的Hilbert谱,有效波高(d)和湍动能(e)随时间的变化
红色方框为风速增长期,绿色方框为风速衰减期
Fig. 7 Temporal variation of the wind speed (a), Hilbert spectrum of east-west (b) and north-south (c) unit-width sediment transport rate, significant wave height (d), and turbulent kinetic energy (e)
Red boxes indicate wind increase periods and green for wind decrease periods
表 1 测量仪器设置
Tab. 1 Settings of observation instruments
测量仪器 距海底距离/
cm采样周期/
min采样频率/
Hz测量参数 TD-WAVE 102 5 16 波高、波周期、水深 ADCP 向上 180 20 8 流速、流向、温度、压强 ADCP 向下 92 20 8 流速、流向、温度、压强 ADV 34 30 16 流速、流向 OBS1 102 20 8 浊度 OBS2 28 20 8 浊度 表 2 单宽输沙率EEMD分解各IMF分量平均周期和方差贡献率
Tab. 2 The period and variance contribution rate of each IMF of the EEMD decomposition on unit-width sediment transport rate
IMF分量 东西方向
平均周期/h东西方向
方差贡献率/%南北方向
平均周期/h南北方向
方差贡献率/%IMF1 1.04 1.52 0.98 7.19 IMF2 2.70 3.54 2.51 4.80 IMF3 6.99 56.30 5.96 12.34 IMF4 12.40 26.27 12.60 22.69 IMF5 24.80 6.33 23.29 14.52 IMF6 45.22 0.67 38.43 3.99 IMF7 109.81 1.12 109.81 1.32 IMF8 192.17 0.46 334.73 7.36 IMF9 384.33 0.08 380.61 2.66 Res / 3.70 / 23.11 -
[1] 胡日军. 舟山群岛海域泥沙运移及动力机制分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009.Hu Rijun. Sediment transport and dynamic mechanism in the Zhoushan Archipelago sea area[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2019. [2] 陈斌, 高飞, 刘健. 夏季浙江沿岸陆架区泥沙输运机制[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(3): 96−105.Chen Bin, Gao Fei, Liu Jian. Sediment transport mechanism in the Zhejiang inner continental shelf in summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(3): 96−105. [3] 庞重光, 于炜. 渤海表层悬浮泥沙的空间模态及其时间变化[J]. 水科学进展, 2013, 24(5): 722−727.Pang Chongguang, Yu Wei. Spatial modes of suspended sediment concentration in surface water in Bohai Sea and their temporal variations[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2013, 24(5): 722−727. [4] 王海龙, 韩树宗, 郭佩芳, 等. 潮流对黄河入海泥沙在渤海中输运的贡献[J]. 泥沙研究, 2011(1): 51−59.Wang Hailong, Han Shuzong, Guo Peifang, et al. Transportation of sediment from Yellow River in Bohai Sea due to tidal currents[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2011(1): 51−59. [5] 刘波, 胡日军, 袁晓东, 等. 龙口近岸海域潮流作用下悬浮泥沙时空分布特征及输运机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(4): 55−66.Liu Bo, Hu Rijun, Yuan Xiaodong, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution pattern and transport mechanism of suspended sediments in Longkou offshore under the action of tidal current[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(4): 55−66. [6] Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H, et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39−51. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.08.001 [7] Zhou Zhou, Bian Changwei, Wang Chenghao, et al. Quantitative assessment on multiple timescale features and dynamics of sea surface suspended sediment concentration using remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(11): 8739−8752. doi: 10.1002/2017JC013082 [8] Jiang Man, Pang Chongguang, Liu Zhiliang, et al. Sediment resuspension in winter in an exceptional low suspended sediment concentration area off Qinhuangdao in the Bohai Sea[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2020, 245: 106859. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106859 [9] Bi Naishuang, Yang Zuosheng, Wang Houjie, et al. Seasonal variation of suspended-sediment transport through the southern Bohai Strait[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2011, 93(3): 239−247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2011.03.007 [10] Wang Chenghao, Liu Zhiqiang, Harris C K, et al. The impact of winter storms on sediment transport through a narrow strait, Bohai, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2020, 125(6): e2020JC016069. [11] 李昶, 陈丽贵, 何造胜. 莱州湾小清河入海口水质变化及成因分析[J]. 环境与发展, 2020, 32(11): 118−119,121.Li Chang, Chen Ligui, He Zaosheng. Analysis of water quality change and causes of Xiaoqing River estuary in Laizhou Bay[J]. Environment and Development, 2020, 32(11): 118−119,121. [12] 王丽雪, 李雪艳, 王庆, 等. 莱州湾东部海岸剖面冲淤演变研究[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2020(6): 44−52.Wang Lixue, Li Xueyan, Wang Qing, et al. Study on profile evolution in the Eastern Coast of Laizhou Bay[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2020(6): 44−52. [13] Huang N E, Shen Zheng, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903−995. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1998.0193 [14] Wu Zhaohua, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1−41. doi: 10.1142/S1793536909000047 [15] 王俊杰, 拾兵, 卢仲翰. 黄河入海径流量周期变化与东亚夏季风的关系研究[J]. 海洋通报, 2020, 39(3): 316−324.Wang Junjie, Shi Bing, Lu Zhonghan. Study on the relationship between the periodic change of Yellow River runoff to Bohai Sea and East Asian Summer Monsoon[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2020, 39(3): 316−324. [16] 陈则煌, 张云峰, 谢菲, 等. EEMD在雷暴日趋势特征分析中的应用[J]. 热带地理, 2015, 35(4): 601−606.Chen Zehuang, Zhang Yunfeng, Xie Fei, et al. Applications of EEMD in the trends analysis of the thunderstorm days[J]. Tropical Geography, 2015, 35(4): 601−606. [17] Torrence C, Comfpo G P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1998, 79(1): 61−78. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1998)079<0061:APGTWA>2.0.CO;2 [18] 朱建荣, 薛元忠. 长江河口横沙小港泥沙浓度的观测及研究[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2001(3): 68−73.Zhu Jianrong, Xue Yuanzhong. Observation and study of suspended sediment concentration at Hengsha channel in the Changjiang estuary[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), 2001(3): 68−73. [19] 庞重光, 李坤, 于炜. 渤海表层悬沙的时空分布特征及其动力成因[J]. 海洋科学进展, 2014, 32(4): 450−458.Pang Chongguang, Li Kun, Yu Wei. Distribution characteristics, seasonal variability and dynamical mechanism of suspended sediment in the surface layer of the Bohai Sea[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 2014, 32(4): 450−458. [20] 崔廷伟, 张杰, 马毅, 等. 渤海悬浮物分布的遥感研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(5): 10−18.Cui Tingwei, Zhang Jie, Ma Yi, et al. The study on the distribution of suspended particulate matter in the Bohai Sea by remote sensing[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2009, 31(5): 10−18. -




 下载:
下载: