Spatio-temporal distribution of Paralichthys olivaceus abundance and its relationship with environmental factors in the adjacent waters of Changshan Islands
-
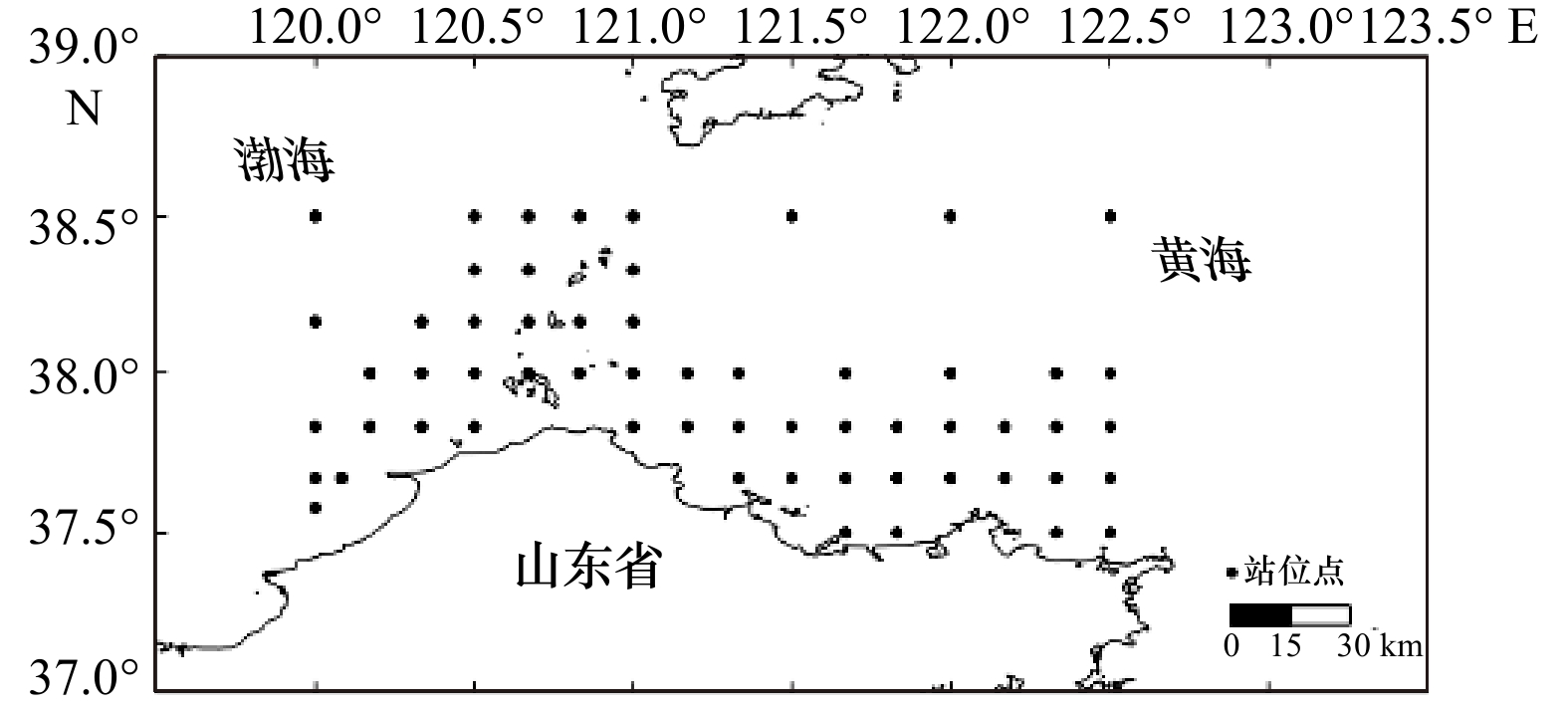
摘要: 本文根据2016−2017年在长山列岛邻近海域开展的渔业资源和环境季度调查数据,利用两阶段广义可加模型分析了该海域褐牙鲆资源丰度的时空分布及其与相关因子之间的关系。结果表明,长山列岛邻近海域褐牙鲆资源丰度具有明显的季节变化,春、秋季资源丰度高于冬、夏季;褐牙鲆春、秋季主要分布在120.5°~122.5°E水域,夏、冬季则向外海适宜水温水域移动;褐牙鲆出现概率主要受季节、底层盐度和底层水温的影响,在盐度31左右时出现概率较大;褐牙鲆相对资源量大小主要受底层盐度及水深影响,在水深33 m上下相对资源量较大。长山列岛邻近水域褐牙鲆资源丰度具有明显时空异质性,受到多重因素的共同影响。Abstract: According to the seasonal fishery resource survey data from 2016 to 2017 in the adjacent waters of Changshan Islands, two-stage generalized additive model is used to examine the spatio-temporal distribution of Paralichthys olivaceus abundance and its relationships with relevant factors. The results show that the abundance of P. olivaceus exhibites obvious seasonal variation, and the abundances in spring and autumn is higher than those in winter and summer. In spring and autumn, it mainly distributes in the waters of 120.5°−122.5°E; and in summer and winter, it moves to the waters with suitable water temperature. The occurrence probability of P. olivacvacus is mainly affected by season, bottom salinity and bottom temperature. The probability of occurrence is relatively high at the salinity of 31. The relative abundance of P. olivaceus are mainly affected by bottom salinity and depth, and the relative resources is higher at the depth of 33 m. The spatio-temporal heterogeneity of the abundance distribution of P. olivaceus is affected by multiple factors in the adjacent waters of Changshan Islands.
-
图 3 环境因子对长山列岛邻近海域褐牙鲆出现概率的影响(GAM1)
图中实线表示影响效应;虚线之间的区域表示影响效应的95%置信区间
Fig. 3 Effects of different environmental factors on occurrence probability of Paralichthys olivaceus in the adjacent waters of Changshan Islands (GAM1)
The solid lines in the figures represent the effect; the area between dotted lines represent the 95% confidence interval of the effect
图 4 环境因子对长山列岛邻近海域褐牙鲆相对资源量分布的影响 (GAM2)
图中实线表示影响效应;虚线之间的区域表示影响效应的95%置信区间
Fig. 4 Effects of different environmental factors on relative abundance of Paralichthys olivaceus in the adjacent waters of Changshan Islands (GAM2)
The solid lines in the figures represent the effect; the dotted lines represent the 95% confidence interval of the effect
表 1 褐牙鲆资源时空分布影响因子的两阶段 广义可加模型筛选过程
Tab. 1 Forward-selection procedure of two-stage generalized additive model for affecting factors on spatio-temporal distribution of resource abundance for Paralichthys olivaceus
GAM1 GAM2 影响因子 AIC 影响因子 AIC 季节 207.68 季节 165.12 底质 224.44 底质 173.90 水深 220.16 水深 170.71 底层盐度 221.03 底层盐度 161.18 底层水温 223.26 底层水温 173.42 六丝钝尾虾虎鱼 225.24 六丝钝尾虾虎鱼 179.52 鳀 230.09 鳀 179.05 口虾蛄 233.62 口虾蛄 176.13 季节+底质 203.58 底层盐度+季节 163.61 季节+水深 198.31 底层盐度+底质 162.68 季节+底层盐度 196.11 底层盐度+水深 160.64 季节+底层水温 197.90 底层盐度+底层水温 167.54 季节+六丝钝尾虾虎鱼 208.69 底层盐度+六丝钝尾虾虎鱼 166.33 季节+鳀 213.75 底层盐度+鳀 168.11 季节+口虾蛄 213.99 底层盐度+口虾蛄 165.52 季节+底层盐度+底质 200.32 底层盐度+水深+季节 161.25 季节+底层盐度+水深 198.68 底层盐度+水深+底质 161.64 季节+底层盐度+底层水温 191.81 底层盐度+水深+底层水温 165.28 季节+底层盐度+六丝钝尾
虾虎鱼198.18 底层盐度+水深+六丝钝尾
虾虎鱼167.00 季节+底层盐度+鳀 202.86 底层盐度+水深+鳀 164.20 季节+底层盐度+口虾蛄 201.49 底层盐度+水深+口虾蛄 164.58 季节+底层盐度+底层
水温+底质196.43 季节+底层盐度+底层
水温+水深193.71 季节+底层盐度+底层
水温+六丝钝尾虾虎鱼194.47 季节+底层盐度+底层
水温+鳀197.57 季节+底层盐度+底层
水温+口虾蛄196.18 表 2 模型拟合结果及各因子重要性分析
Tab. 2 Results from models fitting and analysis of important factors
模型 加入的因子 累计偏差解释率/% 贡献率/% AIC GAM1 季节 11.40 11.40 207.68 底层盐度 22.09 10.69 196.11 底层水温 25.54 3.45 191.81 GAM2 底层盐度 36.88 36.88 161.18 水深 48.02 11.14 160.64 -
[1] 成庆泰, 周才武. 山东鱼类志[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 1997.Cheng Qingtai, Zhou Caiwu. The Fishes of Shandong Province[M]. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 1997. [2] 李明德, 张洪杰. 渤海鱼类生物学[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1991.Li Mingde, Zhang Hongjie. Biology of Fishes in Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 1991. [3] 张秀梅, 朱杰, 高天翔, 等. 褐牙鲆(Paralichthys olivaceus)受精卵及仔稚鱼生理生态学研究进展[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 2001, 31(4): 495−500.Zhang Xiumei, Zhu Jie, Gao Tianxiang, et al. Advances in physiological and ecological studies on eggs, larvae and juveniles of Paralichthys olivaceus[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of Qingdao, 2001, 31(4): 495−500. [4] 陈大刚. 黄渤海渔业生态学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1991.Chen Dagang. Fishery Ecology of Bohai and Yellow Seas[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1991. [5] 单秀娟, 金显仕, 李忠义, 等. 渤海鱼类群落结构及其主要增殖放流鱼类的资源量变化[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2012, 33(6): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2012.06.001Shan Xiujuan, Jin Xianshi, Li Zhongyi, et al. Fish community structure and stock dynamics of main releasing fish species in the Bohai Sea[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2012, 33(6): 1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7075.2012.06.001 [6] Guisan A, Edwards T C Jr, Hastie T. Generalized linear and generalized additive models in studies of species distributions: setting the scene[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2/3): 89−100. [7] Bellido J M, Pierce G J, Wang J. Modelling intra-annual variation in abundance of squid Loligo forbesi in Scottish waters using generalised additive models[J]. Fisheries Research, 2001, 52(1/2): 23−39. [8] 马金, 黄金玲, 陈锦辉, 等. 基于GAM的长江口鱼类资源时空分布及影响因素[J]. 水产学报, 2020, 44(6): 936−946.Ma Jin, Huang Jinling, Chen Jinhui, et al. Analysis of spatiotemporal fish density distribution and its influential factors based on generalized additive model (GAM) in the Huanghe River Estuary[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2020, 44(6): 936−946. [9] 武胜男, 陈新军, 刘祝楠. 基于GAM的西北太平洋日本鲭资源丰度预测模型建立[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(8): 36−42.Wu Shengnan, Chen Xinjun, Liu Zhu’nan. Establishment of forecasting model of the abundance index for chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus) in the northwest Pacific Ocean based on GAM[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(8): 36−42. [10] Maunder M N, Punt A E. Standardizing catch and effort data: a review of recent approaches[J]. Fisheries Research, 2004, 70(2/3): 141−159. [11] Barry S C, Welsh A H. Generalized additive modelling and zero inflated count data[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2002, 157(2/3): 179−188. [12] 中国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12763.6−2007 海洋调查规范 第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration Committee. GB/T 12763.6−2007 Specifications for Oceanographic Survey-Part 6: Marine Biological Survey[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008. [13] 唐启升, 叶懋中. 山东近海渔业资源开发与保护[M]. 北京: 农业出版社, 1990.Tang Qisheng, Ye Maozhong. Development and Protection of Fishery Resources in Shandong Coastal Waters[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1990. [14] Kabacoff R I. R in Action: Data Analysis and Graphics with R[M]. Greenwich: Manning Publications, 2011: 1−474. [15] Rodrigues M, De La Riva J, Fotheringham S. Modeling the spatial variation of the explanatory factors of human-caused wildfires in Spain using geographically weighted logistic regression[J]. Applied Geography, 2014, 48: 52−63. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2014.01.011 [16] Akaike H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle[M]. New York: Springer, 1998: 199−213. [17] Hastie T J, Tibshirani R J. Generalized Additive Models[M]. London and New York: Chapman and Hall, 1990. [18] 中国科学院中国动物志编辑委员会. 中国动物志—硬骨鱼纲, 鲽形目[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995.Editorial Committee of Fauna Sinica, Academia Sinica. Fauna Sinica: Ostichthyes, Tleuronectiformes [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995. [19] 李明德. 中国经济鱼类生态学[M]. 2版. 天津: 天津科学技术出版社, 2012.Li Mingde. Ecology of Economic Fishes in China[M]. 2nd ed. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press, 2012. [20] 姜志强, 吴立新, 郝拉娣, 等. 海水养殖鱼类生物学及养殖[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 2005.Jiang Zhiqiang, Wu Lixin, Hao Ladi, et al. Biology and Culture of Marine Cultured Fish[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2005. [21] 殷名称. 鱼类生态学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1995.Yin Mingcheng. Fish Ecology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1995. [22] Spanopoulos-Hernández M, Martínez-Palacios C A, Vanegas-Pérez R C, et al. The combined effects of salinity and temperature on the oxygen consumption of juvenile shrimps Litopenaeus stylirostris (Stimpson, 1874)[J]. Aquaculture, 2005, 244(1/4): 127−138. [23] 刘立明. 海水鱼类繁殖发育生物学与健康养殖技术[M]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社, 2014.Liu Liming. Reproductive and Developmental Biology and Healthy Aquaculture Technology of Marine Fish[M]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China Press, 2014. [24] 龚政, 邰佳爱, 张东生. 陆源污染物对海州湾环境影响研究[J]. 河海大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 30(4): 5−8.Gong Zheng, Tai Jiaai, Zhang Dongsheng. Impacts of land pollution sources on Haizhou Bay environment[J]. Journal of Hohai University (Natural Sciences), 2002, 30(4): 5−8. [25] 李雪渡. 海水温度与渔场之间的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 1982, 4(1): 103−113.Li Xuedu. Studies on the correlation between the temperature of sea water and fishing grounds[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 1982, 4(1): 103−113. [26] 朱鑫华, 王云峰, 刘栋. 温度对褐牙鲆资源补充特征的生态效应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1999, 30(5): 477−485. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.05.003Zhu Xinhua, Wang Yunfeng, Liu Dong. Effects of temperature on the ecological patterns of resources recruitment of bastard halibut, Paralichthys olivaceus (T. ET S. )[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1999, 30(5): 477−485. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.1999.05.003 [27] Wood S N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R[M]. London: Chapman and Hall, 1990. [28] 刘逸文, 张崇良, 昝肖肖, 等. 山东南部近海秋季长蛇鲻相对资源量的分布及其影响因素[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(4): 45−53.Liu Yiwen, Zhang Chongliang, Zan Xiaoxiao, et al. Distribution of relative abundance of slender lizardfish and its influencing factors in southern coastal waters of Shandong during autumn[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2020, 50(4): 45−53. [29] 尹洁, 王晶, 张崇良, 等. 利用two-stage GAM研究海州湾及其邻近海域小黄鱼鱼卵的时空分布特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 2019, 26(6): 1164−1174.Yin Jie, Wang Jing, Zhang Chongliang, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of Larimichthys polyactis eggs in Haizhou Bay and adjacent regions based on twostage GAM[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2019, 26(6): 1164−1174. [30] Chang J H, Chen Y, Holland D, et al. Estimating spatial distribution of American lobster Homarus americanus using habitat variables[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2010, 420: 145−156. doi: 10.3354/meps08849 [31] Jensen O P, Seppelt R, Miller T J, et al. Winter distribution of blue crab Callinectes sapidus in Chesapeake Bay: application and cross-validation of a two-stage generalized additive model[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2005, 299: 239−255. doi: 10.3354/meps299239 -




 下载:
下载:



